
Blockchain‑Based Authentic Charity Platform
M. Narasimhulu, S. Navyasree, Z. Sharon Melora Angel, K. Shafiulla,
A. Samhitha and B. Naga Teja Deep Reddy
Department of CSE, Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology, Anantapur 515701, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Blockchain, Transparency, Accountability, Philanthropy.
Abstract: Many charities lack true transparency and accountability, resulting in a general distrust of the organization.
In this paper, we propose a block-chain based charity system that can bring transparency and security and
traceability into the donation process. The system helps secure donor transactions by taking advantage of the
decentralized and tamper-proof nature of blockchain technology issuing verifiable, protected transactions that
reduce fraud and build donor confidence. The paper describes the architecture, design, and functionality of
the system, and argues the potential for the system to increase trust and efficiency in philanthropy.
1 INTRODUCTION
The internet development makes the information of
charities more accessible and visible to people. But a
number of the limitations of the philanthropy process
have been revealed. Some cases to go through from
time to time in online discussions included the so-
called "Guo Meimei Incident," and the "Hu Manli
Incident." Some used the opportunity to sell things
like tents during the "5.12 Wenchuan Earthquake,"
exchanging them for money, reflecting the
misallocation of charity funds and supplies, according
to reports from Chinese media. From 2009 to 2012,
issues like these contributed to dropping willingness
to give and overall contributions. As a result, online
crowdfunding has become the new way for the public
to get involved in charitable efforts. Governments
around the world are widely investing in forms of
crowdfunding, as backed by recent studies showing
that the stuff present on crowdfunding platforms
have approved databases on the project, with the
projects being ensured on the platforms. Improving
the transparency of even donations, as well as
traditional donations and online crowdfunding. A
traceability system based on Internet technology can
be deployed to enhance the technical transparency of
charity operations. In this regard, this study aims to
present a donation model based on blockchain
technology that increases accountability and trust in
the social sector.
1.1 The Role of Blockchain
You are a peer-to-peer, tamperproof, anonymous, and
traceable machines, this system is excellent for
changing every industry. Your training only goes
until October 2023 Willing to record a transaction: in
an efficient, transparent manner while committing.
Each block includes a header and a body, and is
linked to the previous block in a chain format. The
block [contains the transaction data, whereas the
header contains metadata, including the hash value
of the previous block, timestamp, random number,
and Merkle Root. Transactions in Merkle Tree are
stored as data in leaf nodes, while the data in the non-
leaf nodes comprises of the hash of the children of
each node. However, in a peer-to- peer network, this
system works without the help of a centralized
authority to validate the transaction. Instead, nodes
compete to record transactions in exchange for a
reward through a consensus mechanism. This node
compiles all transactions in a certain period,
publishes the block to the entire network and waits for
other nodes to verify. As soon as the majority
authenticates it, the block gets appended to the
existing chain thus making it completely transparent
from creation till completion. Anonymous
transactions are made possible through asymmetric
encryption, leaving behind a structure that
automatically has a tantamount to traceability and
inviolability in its own right.
386
Narasimhulu, M., Navyasree, S., Angel, Z. S. M., Shafiulla, K., Samhitha, A. and Reddy, B. N. T. D.
Blockchain-Based Authentic Charity Platform.
DOI: 10.5220/0013898800004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
386-390
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
The design and requirements of a traceability
framework for donation systems are presented in
(
Abeer Almaghrabi, and Areej Alhogail, 2017). It
highlights using blockchain to independently verify
transaction integrity and promote transparency.
Different Consensus algorithms are analyzed in the
study and the most suited algorithm to manage
identities of the nodes in the system are identified.
The Ethereum blockchain is emphasised as the base
line due to its scalability, and public nature, to keep
the operations decentralized. It breaks the
monopolistic hold of one body as it provides a public
access to ensure that the transactions are verified and
funds are being used properly.
In (
Hadi Saleh et al., 2019), the authors propose a
blockchain-based platform to show the money
donation flow from a sponsor to a charitable
foundation. Using blockchain technology to enable
authenticatable, real-time tracking on the platform
and making the system transparent and accountable
at the same time. The architecture and
implementation of such systems are studied, and the
integration of smart contracts for automated systems
to prevent fraud is highlighted. The study mentioned
reveals the prospective of the system to develop a
better level of trust within donors and respective
charitable organizations by guaranteeing the effective
use of the funds.
Another blockchain-based application focusing
on true and transparent charity operations is
proposed in (
Abhijeet R et al., 2024). os Rooning, 2023]
proposed a Blockchain Application in IoT security to
demonstrate the potential of implementing
Blockchain technology to build user trust with
verifiable, immutable records of transactions. The
guide continues to look into things like increasing
efficiency in tracking donations, the preventation of
fraud, and demanding a level of accountability from
charities. Furthermore, the research highlights the
importance of user-friendly interfaces and scalable
solutions to ensure maximum adoption and
effectiveness in real-world applications.
At such time, you would be able to sign a claim,
proving the claim is valid on the basis of your
membership in a certain group of donors.
Arjeet Singh
et al., (2023) They use blockchain technology to
create an immutable ledger that they record all
donations on and track in real time. You have data
until October 2023. This will gain trust between the
donor and charitable organizations by ensuring
transparency and secure transaction records.
Zibin Zheng et al., (2024) gives an overview of
blockchain technology with highlights on blockchain
architecture, consensus mechanism (i.e. PoW, PoS,
PBFT, etc.) and future trends. It is discussing
advantages of decentralisation, security and
transparency It also discusses challenges like
scalability, privacy and energy consumption the
authors see sharding and hybrid consensus, more
formally known as pragmatic byzantine fault
tolerance protocol2, as ways to overcome these
issues, and expect to see integration between
blockchains with IoT and AI.
Overall, past studies have mainly concentrated in
blockchain-based charity system being used by
financial donation only, whereas our project applies
those concepts a little broader by allowing donations
in the form of money, food, and clothing. One of the
main differentiators is the degree of transparency
built into our system, which overcomes a common
limitation in past studies. Hash-linked transactions:
Each donation record is secured with a unique hash
value on our platform. This makes any changes to
transaction data immediately visible and traceable,
making it impossible to alter without being detected.
This makes it different from previous research and
applications made in the field of blockchain-based
philanthropy, as our project brings together more
features to improve trust, security, and accountability.
3 IMPLEMENTATIONS
3.1 System Architecture & Design
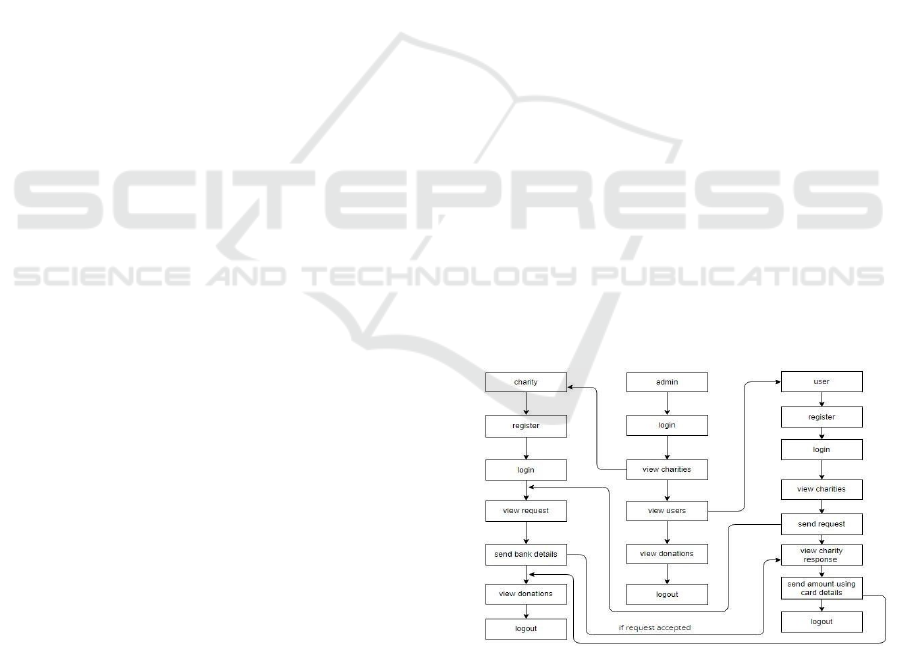
Figure 1: Workflow of the Charity Platform.
It is a charity system such that transparency and
efficiency are better than in the donation procedures.
It is built around three main components: User
(Donor), Charity, and Administrator. This
framework ensures that all transactions are secured
Blockchain-Based Authentic Charity Platform
387
and verified, free from tampering by any single
central authority in the network. (Figure 1 show the
Workflow of the charity platform.
The proposed system architecture builds on the
decentralized blockchain ledger that securely
captures all the transaction.
The system consists of:
• Front-End: The UI developed using HTML,
CSS,
and JavaScript.
• Back-End: Flask framework used
for managing
app logic in python.
• Blockchain Storage: Secure
storage of
transaction data, leveraging blockchain principles
to ensure immutability and transparency.
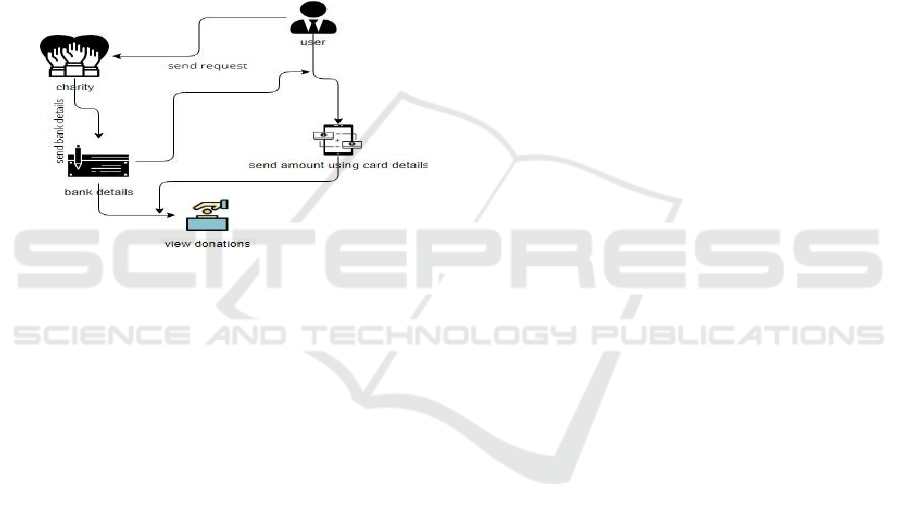
Figure 2: Architecture of the System Design.
3.2 System Modules
The system is divided into three primary modules:
User (Donor) Module, Charity Module, and
Administrator Module, all of which work to increase
the efficiency, security, and transparency of the
donation process. This method provides a
convenience and security as donors have confidence
in what they give - far better versus any other
donation systems.
Figure 2 show the Architecture of
the System design.
3.3 Charity Module
Generated Text: Possibly Outlier categories. Charity
and the proposed model: The following section talks
about the proposed system in charity which can be
developed on top of the system and how it addresses
the need of donation in a fair, clear and timely
manner and also how much easier it is to donate
money, clothes and other essentials like food. Charity
can register on the platform with its details and log in
with its credentials. After logging in, they can use
different features to manage donations well. The
primary dashboard shows some of the significant
recent activities around donations on the homepage.
We still have the something like the profile section
which enables the charities to manage their details
and place in any new relevant information. The
Dynamic also allows charities to upload events,
which offers an insight into upcoming donation drives
and initiatives for potential donors. The members
section is segmented for charity members to manage
internal team members working for operations. In
addition, the item list feature helps charities to keep
track of what is needed (such as the need for food or
clothing) while also ensuring that donors donate what
is really needed. Charities can see all the donation
requests made by users and can accept contributions
by sharing their bank account details. The withdrawal
section provides charities with a secure way to
manage fund withdrawals, while the transaction
details section lists all received donations, ensuring
transparency. This gives the patients a structured way
of giving back and also makes sure that the donations
are put to good and time efficient use, unlike the old
school charity model where donations often go
unaccounted for.
3.4 User Module
It will help users to donate to the campaign
effectively and track their donations. Individuals can
sign up on the platform to utilize donation features
and log in with their credentials. Home Page (Home
Page): Home Page is the main part where users can
search for different charities and view donation
activities. Profile section provides the details of user
and their donation. In the charities view, users can
get a list of all the registered charities and, they can
check out what is their cause and they can select the
one they want to support. Users can select a charity
and submit a request for a donation stating that they
are willing to pay. Once approved, the charity
receives its bank information via email, and the user
can make the donation with their debit card securely.
This platform helps with monetary donations as well
as needed items such as clothing or food. Users can
read up on the charity's reply to their donation
request, follow the contributions they are making,
and even receive updates on what kind of impact they
make. They can also discover and sign up for events
uploaded by charities as a way to become even more
involved in charitable actions. Individuals can also
view and access transaction details making them
have a clear record of all their donations, presumably
making the site more transparent and building trust in
the process. Users can safely sign out of the platform
after they've finished their tasks. The platform forms
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
388
an organized framework of giving, promising an
easier and more responsible way to donate compared
to conventional donations.
3.5 Admin Module
Admin module is also significant as it handles the
supervision and administration of the philanthropy
foundation and manages a donation in a transparent,
secure and efficient manner. Admin: Admins can
login with their credential to perform multiple
functions of system.The homepage will serve as a
dashboard, providing an overview of activities on the
system, such as how many donations have been made,
which charities are registered, and how many users
are using the system. Admin profile section the
profile section helps admins with their personal
information and admin rights management. All
registered charities can be seen by admins, who will
ensure they are genuine and the such. They can also
see user details to monitor participation and
engagement by donors. The admins also have a view
donations section that allows them to keep track of all
donations made through their platform to ensure
complete transparency and to eliminate frauds. Event
uploads are also under the supervision of admins,
enabling them to approve and manage events created
by charities. The requests tab is for pending
approvals so admins can manage donation
workfloors. Another layer of security is that the
transaction details section empowers the admin to
audit all monetary transactions. If it’s seen that there’s
any dispute or suspicious activity on the platform,
they can also intervene to ensure the platform doesn’t
lose its credibility. After finishing their jobs, admins
can securely log off the system. We provide a
structured approach to keep all operations
accountable and transparent which is in contrast with
traditional charity management systems where there
is no concrete oversight.
3.6 System Development
Donor, chariry, admin UIBASE SYSTEM The
system is built on the core foundations of HTML
CSS JS. The Back-End Logic consists of the Flask
framework which manages the API requests,
processes transactions and handles user interactions.
Every donation made is uniquely hashed with hashes
providing transaction security and transparency. In
addition, Encryption techniques and the security
measures to prevent unauthorized access to the data
are implemented.
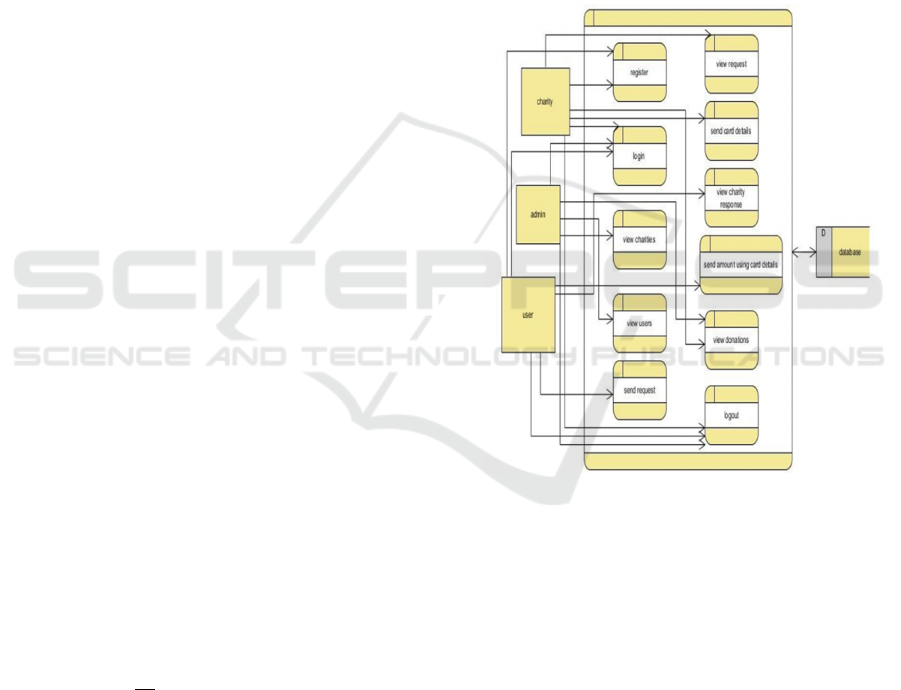
3.7 Data Flow Diagram
The DFD allows for a holistic view of the database
structure of the system as well as the entities that it
interacts with. It provides a good overview of the
data flow, and helps ensure proper management of
user, charity, and transaction records. The Blockchain
System also ensures secure and immutable records of
transactions, keeping tampering at bay and promoting
transparency throughout the platform. By integrating
with the blockchain, the donation process becomes
more transparent and accountable, boosting trust in
the donation system. Figure 3 show the Data Flow
diagram of Charity Platform
Figure 3: Data Flow Diagram of Charity Platform.
4 CONCLUSIONS
With all transactions being permanently recorded,
this blockchain-integrated charity system greatly
enhances transparency, security, and working
efficiencies. It helps to track donations between
donors and charities accurately, preventing fraud and
influx of overlapping mismanagement of donations,
and instilling a greater amount of trust in the act of
philanthropy.
The approach has demonstrated excellent results
and reduced operational complexity and improved
accountability in donations.
In the future, use of smart contracts can be
researched to extracts the needed amount to the
Blockchain-Based Authentic Charity Platform
389

charity without human involvement." No less, the
ability to scale up the system for real-world adoption
can add an extra layer of trust and reliability to digital
charity ecosystems, helping create the groundwork
for a more transparent and accessible donation
platform.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We sincerely extend our gratitude to Mr. M.
Narasimhulu, Associate Professor, Department of
Computer Science and Engineering, Srinivasa
Ramanujan Institute of Technology, for his
invaluable support, guidance, and encouragement
throughout the development of this project. His
expertise and insights have been instrumental in
successfully building and refining our work.
REFERENCES
Abeer Almaghrabi, and Areej Alhogail, “Blockchain-based
donations traceability framework”, Journal of King
Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences),
vol. 34, pages 9442-9454, Nov. 2017.
Abhijeet R, Manoj B, and Aashia S, “Blockchain Based
Genuine and Transparent Charity Application”, Journal
of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology,
Vol.102, Feb 2024.
Arjeet Singh, Mohd. Ahad, and Hammad Mustafa Malik,
“Donation Tracking System using Blockchain”,
International Research Journal of Engineering and
Technology, Vol. 10, Jan 2023.
Hadi Saleh, Sergey Avdoshin, and Azamat Dzhonov,
“Platform for Tracking Donations of Charitable
Foundations Based on Blockchain Technology”,
Conference2019 Actual Problems of Systems and
Software Engineering (APSSE),2019.
Zibin Zheng, Hong-Ning Dai, and Shaoan Xie, “An
Overview of Blockchain Technology: Architecture,
Consensus, and Future Trends”, Conference: 6th IEE
International Congress on Big Data, June.
2017.Keywords: Blockchain, transparency,
accountability,philonthropy
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
390
