
AI Powered Human Behaviour Detection and Monitoring
Saratha M., Aarthi B., Harshini M., Hemanth B. and Vishnu Priya C.
Department of Artificial Intelligence and Data Science, M Kumarasamy College of Engineering, Karur, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Face Recognition Technology, Haar Cascade Algorithm, Abnormal Activity, Gesture Movement.
Abstract: Examination malpractice refers to any intentional misconduct that violates examination regulations, aimed at
providing an unjustly favoured candidate. Essentially known as cheating, this unlawful activity involves
students attempting to achieve favourable grades through dishonest means. Such malpractice represents a
deviation from the established protocols governing the examination process. The prevalence of examination
malpractice has adversely affected students, as many have abandoned their studies, relying instead on the
deceptive practices they have come to depend on during assessments. Examination malpractice within the
Nigerian educational system has been extensively examined and recognized as a significant obstacle not only
for examination authorities but also for school organization, the broader educational framework,
governmental bodies, and society as a whole. The identification of impersonators in examination
environments is crucial for enhancing the examination management system, which can contribute to the
reduction of malpractices occurring in examination centres. A biometric approach presents an effective
strategy to combat examination malpractice through the detection of impersonators. Face Recognition
Technology is increasingly utilized across various applications, allowing for the identification of candidates
based on extracted facial features, which are processed using algorithms and other methodologies. To address
this issue, a robust solution that requires minimal manpower is essential. With the progress in deep learning
algorithms, resolving this challenge has become more feasible. This project aims to develop a framework for
facial recognition and to analyze students' behavioural patterns, employing HAAR cascade and Convolutional
Neural Network algorithms.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the field of imaging science, image process refers
to the manipulation of images through mathematical
operations, employ various forms of signal
processing. A single picture, a collection of pictures,
or video footage like still photos or video frames can
all be included in the input. A collection of traits and
parameters related to the original image or a changed
image are the possible outcomes of image processing.
Conventional signal-processing techniques are
typically used to treat images as two-dimensional
signals. Images can also be interpreted as three-
dimensional signals, with depth or time represented by
the third dimension. Although "image processing"
refers mostly to digital approaches, it also includes
optical and analog technologies. The broad
approaches that apply to all of these types are the main
topic of this discussion.
The process of producing images begins with
imaging. Instead of being taken from real-world
settings, as is frequently the case with animated films,
computer graphics visuals are painstakingly produced
using physical representations of things, surroundings,
and lighting. On the other hand, computer vision is
frequently seen as a sophisticated type of image
processing, in which devices or software attempt In
order to identify the physical elements of a single
image or a group of photos, like three-dimensional
magnetic resonance scans or films. The use of images
in modern science and technology has grown
considerably, especially as scientific visualization
which frequently entails intricate and extensive
experimental data becomes more and more relevant.
Examples include microarray data in genetic studies
and real-time multi-asset portfolio trading in finance.
Image analysis is the practice of using digital image
processing techniques to extract useful information
from images, mostly digital ones. Image analysis tasks
might
range from straightforward ones like barcode
312
M., S., B., A., M., H., B., H. and C., V. P.
AI Powered Human Behaviour Detection and Monitoring.
DOI: 10.5220/0013897200004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
312-317
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
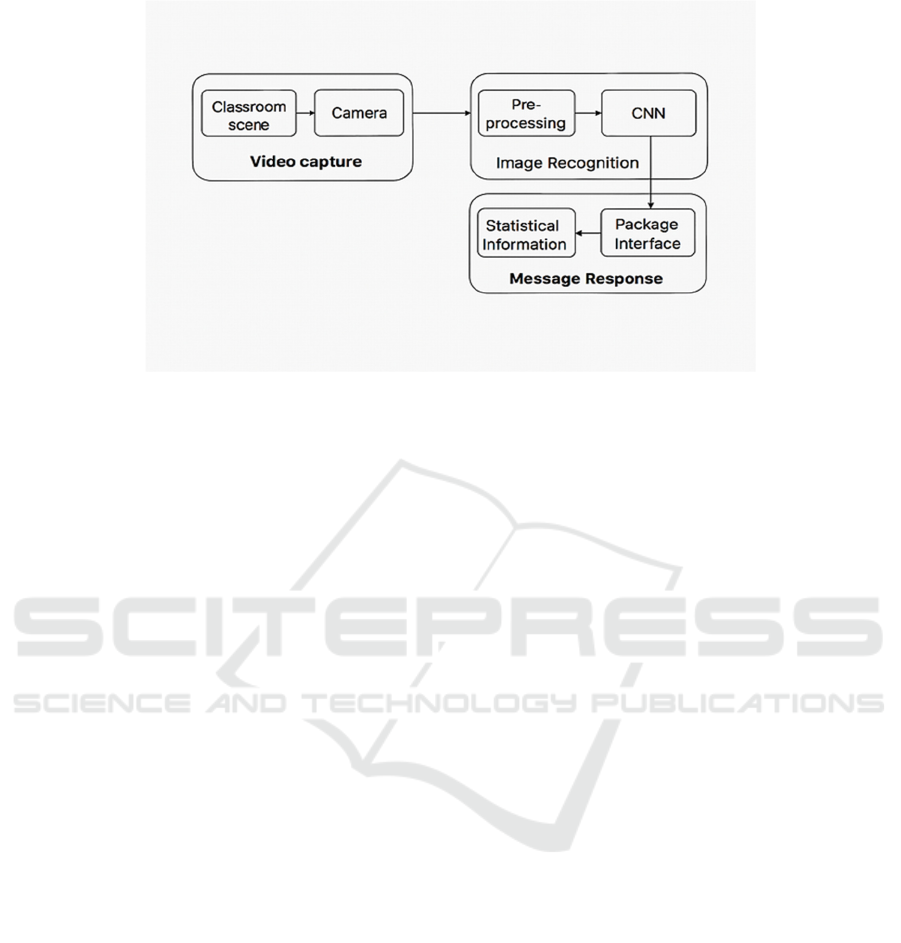
Figure 1: Abnormal Student Behaviour Process.
reading to more intricate ones like facial
identification. Figure 1 shows the abnormal student
behaviour process.
2 RELATED WORKS
Cerrahoğlu, Enes, et.al
2023.
Customized the Twitter
API to collect 168,274 English tweets. URLs,
hashtags, mentions, and emojis were filtered out from
the collected tweets. Subsequently, TextBlob Python
package was used to classify the Tweets as neutral,
negative, or positive. The classified tweets were
tested for classification accuracy using machine
learning algorithms such as Support Vector Machines,
Random Forest, Naive Bayes, Gradient Boosting, and
Logistic Regression. Logistic regression finally gave
the best classification accuracy of 94%. Finally, a web
interface was created to retrieve the last 50 tweets
from a user's profile and based on the sentiment for
each, it has an added emoji.
Krishna, P, et.al,
2024.
The study reports
predictions of conduct modification among SEN
children after treatments based on ABA using the
MMLA framework. ABA therapy is a specialized
education technique to solve the problem of
behavioral issues and promote positive conduct. Our
deep neural networks and machine learning models
accurately predict a 98% change in behavior for SEN
children with multimodal educational data, for
example, while the precision remains at 97%.
Moreover, we demonstrate that the inclusion of
environmental, psychological and mobility sensor
data can considerably enhance the predictive
performance of models when based on typical
educational data. Since DOT, the system has been
used to enhance intensive ABA therapies for over 500
SEN students in Singapore and Hong Kong via the
Integrated Intelligent Intervention Learning (3I
Learning) System.
Chan, Rosanna, et.al,
2023.
Suggested In older
adults, abnormal behaviour may indicate a medical
issue. Our unique unsupervised statistical idea drift
detection method employs random variable
autoencoders to estimate the parameters for a
statistical hypothesis test on anomalous days. The
Kullback-Leibler d function was the feature used.
Since 2020, our approach with the Integrated
Intelligent Intervention Learning (3I Learning)
system had improved intensive ABA therapy for more
than 500 SEN students in Singapore and Hong Kong.
The objective of ABA therapy, which is a form of
special education intervention, is to treat behavioural
problems and effect useful behavioural changes.
When we feed our deep neural networks and machine
learning models with multimodal educational data,
then we achieve around 98% accuracy and 97%
precision in predicting the behavior change on SEN
children. We further show that the statistical
performance of predictive algorithms using standards
educational data can be vastly increased by
environmental, psychological, and mobility sensor
data. Motion and power sensor maps of activity
probabilities come to play. We demonstrated broad
feasibility (minimum F1-Score of 91%) on an
artificial dataset comprising four concept drift
categories. Then we used our new technique to a real-
world dataset obtained from the residences of 20 (pre-
)frail older persons (average age 84.75 years). Our
AI Powered Human Behaviour Detection and Monitoring
313

technique was able to identify anomalous days when
a participant was suffering from a serious medical
condition.
Ryu, Riseul, et.al, 2023. Finding out how implicit
authentication can track students' behaviour without
interfering with their learning activities is the aim of
this investigation. To identify and explore context-
aware continuous implicit authentication systems'
architecture as well as possible future developments,
the essay performs a systematic and organized
evaluation of the body of existing literature. Future
requirements, according to the study, will involve the
following: 1) considering a range of appraisers to
cover all possible user encounters with online
learning environments, including those of students
who do not take online tests; 2) investigating template
modification to address the issue of biometric
template ageing; and 3) looking into evaluation
methods for context-aware implicit authentication
systems.
Hassan, Bassam, et.al, 2023. Discussed in the
study was about data that have been collected using
three standardized measures: The Coping Practices
Questionnaire, the Brief Resilience Scale, and the
Lockdown Fatigue Scale. Also, statistical analyses of
descriptive and inferential types were done using
SPSS. It is imperative for Iraqi university students to
build emotional resiliency, deal with hardship, and
recover from loss, for lockdown fatigue reached scary
proportions. Students tend to express great trouble
experiencing lockdown fatigue (average of about
33.48 out of 50), and the biggest concern is being able
to pull through difficult times and unpleasant
experiences. Mostly female, urban, and in the
sciences, were more likely to express "lockdown
lethargy" than men or other backgrounds.
Alafif,et al…,2023. Implemented the study
followed a simple structure: first a ten-question set,
then followed by a fifteen-question set. The survey
was created on Google Form and disseminated
through social media outlets such as WhatsApp and
Twitter. The data collected were compiled onto an
excel sheet to carry out statistical analysis. The
average number of students involved in this study was
21.45 ± 23.11. 72.3% of the female students were
involved. An estimated 30.2% of the students were
overweight or obese. While 32.2% got adequate sleep
and 67.8% were deprived of sleep, over 70% of
ordinary students fell asleep within 30 minutes after
going into bed. Altogether, 71.7% of students noted
that sleep was good, while 28.3% noted that it was
bad. BMI was further categorized, with underweight
students forming 17.7%, normal weight 52.1%,
overweight 20.6%, and obese 9.6%. The daily
consumption of fruits among the students is 6.4%,
while that of vegetables is 12.5%. Breakfast is taken
by only 8%. Lunch and dinner are consumed by
62.1% and 29.9%, respectively. To sum up, a
relationship was established in this study between the
development of obesity and sleep duration. Also,
some inroads were taken to establish a relationship
between duration of sleep and dietary patterns,
especially regarding the intake of fruits and
vegetables.
Gupta, Swadhaet al …,2023. Developed the
explore the effect size of MBPs in promoting
mindfulness and school adjustment, the current meta-
analysis controlled for the effects of study and
program features, including the program type, the role
of comparison groups, the educational level of
students engaged in MBPs, the qualification of
teachers, and prior mindfulness experience. It was for
MBPs conducted by external trainers with prior
mindfulness ability that there was a strong effect on
school adjustment, or mindfulness, where the view
about the outcomes differed for the mindfulness
approach and for the educational level of students.
After extensive searching through five databases, a
total of 46 studies with a randomised controlled
design with sampling on students from preschool
through undergraduate levels were found. On
average, a moderate effect of MBPs for mindfulness,
small to moderate for attention, and small for
academic performance, impulsiveness, and school
overall adjustment were seen. Overall, there were no
significant variations in student conduct, school
quality, or social skills. This meta-analysis provides
promising evidence of MBPs' effectiveness for
improving children's school adjustment outcomes in
educational settings besides their well-established
psychological benefits, especially when such studies
employ randomised controlled designs.
Kavitha, S., et al. 2023. Implemented the unique
approach proposed predicts student engagement in e-
learning by assessing 3 modalities, namely head
movement, blink count, and facial expression, based
on a live video survey of student behavior. This study
illustrates that the proposed multimodal approach
based on facial clues makes suitable predictions of
real-time student engagement. An experimental study
showed the proposed engagement detection
mechanism outperformed existing methods by an
accuracy of 92.58%. The proposed system is based on
the VGG-19 and ResNet-50 deep learning methods
for facial expression recognition, and eye-blinking
and head motions are based on a facial landmark
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
314

approach. The engagement index, which predicts
either the engagement or the disengagement of an
individual, is derived from the combination of results
across multiple modalities, for which algorithms are
proposed.
Mettleret et., al, (2023). proposed that we entreat
that we build up on previous discussions by way of
interrogating the assertions based on document
analysis and interviews with EdTech company
employees, we contend that automated interventions
contribute to arsenization. We trace its techno-
commercial logic by viewing learning situational
automations contributing to arsenization processes in
EdTech, if so, how do situations become concretised
through the production of digital objects and then
mechanised through specifically computational
interventions? Three processes of arsenization were
identified: Third place fetishism attacks other forms
of work and thus aims to shape student and employee
investment and student learning in a way that makes
the automation seem possible to be "acted" on by
EdTech and higher education stakeholders. First,
detaching digital objects from students and
employees enables the firms to take control of
automated learning interventions, and so forth.
Hansenet et., al, (2023). Described that based on
what is proposed, to absolutely measure a learner's
performance, attention, and emotionality in one fell
swoop, three data types are necessary: the actual score
from tests, that of attention scores, and facial
expressions of the learner. Applying such techniques
as Random Forest Algorithm for computing the test
score, Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) for
forecasting learners' time series-attention scores as
respective for the video lecture, and Convolutional
Neural Network (CNN) for the classification of the
facial expression pictures taken from online course
recordings into distinct emotions, electroencephalogr
aphy (EEG), facial expressions, and tests by machine
learning and deep learning models were the core of
the actual study. The test scores, the attentive scores,
and the general emotional state of the learner while
attending the online class form the anticipated
findings. According to study findings, there is a
positive correlation between attention scores and test
scores. While observing attention variability among
various films, the attention in the lecture video seems
greater than in the film entertainment. This tends to
imply that more happiness was felt while viewing the
entertainment video than the lecture video.
3 BACKGROUNDS OF THE
WORK
Students have recently adopted a variety of
examination misconduct methods. The most popular
tactic is impersonation, which can be hard to see,
particularly in a big class, and a plot by certain
professors or invigilators. The primary objective of
this project is to develop a biometric control
examination attendance record to prevent
impersonation during the test. Among the techniques
employed in biometrics are fingerprint, face
recognition, DNA, hand geometry, iris identification,
and retina. Numerous faces were recognised by the
facial recognition biometric technology used in this
study. The HAAR cascade algorithm model was used
to create the database of gathered photos, and deep
learning algorithms were used to start and improve
the database model, respectively. Skin segmentation
was used for face identification; candidates' faces
were searched for and verified, and face images were
processed and classified. The entire procedure was
developed in Testing of Python and the resultant
system showed that the recognition tests for
candidates/students used in the training and testing
stages were significantly accurate.
4 PROPOSED WORK
Education is not an exception to the gradual
digitization of all services and offerings brought
online by the advent of technology. The ubiquitous
availability of laptop computers and high-speed
internet has enabled a smooth transition to the online
environment. Learning Management Systems
(LMSs), which employ software to manage, report,
administer, and document content shared with
students, are a development and adaptation of
universities, schools, and other educational
institutions. A more balanced approach to information
transfer and simpler candidate grading are made
possible by this teaching and evaluation technique.
The purpose of online examinations is to ensure that
assessors can change their perspective from offline to
online processes. Features like simplicity, scalability,
wider reach, and customisation are driving the
internet industry's rapid growth. Current evaluation
techniques are becoming saturated and may soon
become outdated. Examiners can offer tests to remote
applicants using the internet or a company intranet
using online examination, also referred to as e-
AI Powered Human Behaviour Detection and Monitoring
315
examination. The majority of online assessments
feature response processing modules that enable
assessors to provide answers as soon as test takers
finish. In a lot less time, our fully automated approach
provides the findings while carefully evaluating the
examines. Furthermore, facial recognition technology
is being developed and used more and more for a
range of applications, including attendance and
security systems. Furthermore, because it deals with
managing a person's presence during an activity, an
attendance system is a recurring transaction. The
examination system is essential to the field of
education since student attendance helps ensure that
instruction and learning are adequately evaluated. In
this project, we will use the HAAR cascade technique
to detect faces using the Convolutional Neural
Network approach, which has a higher accuracy rate,
to identify them based on face feature points.
Additionally, give information regarding head
movements, gestures, and motions throughout the test
and warn of any unruly students. The suggested
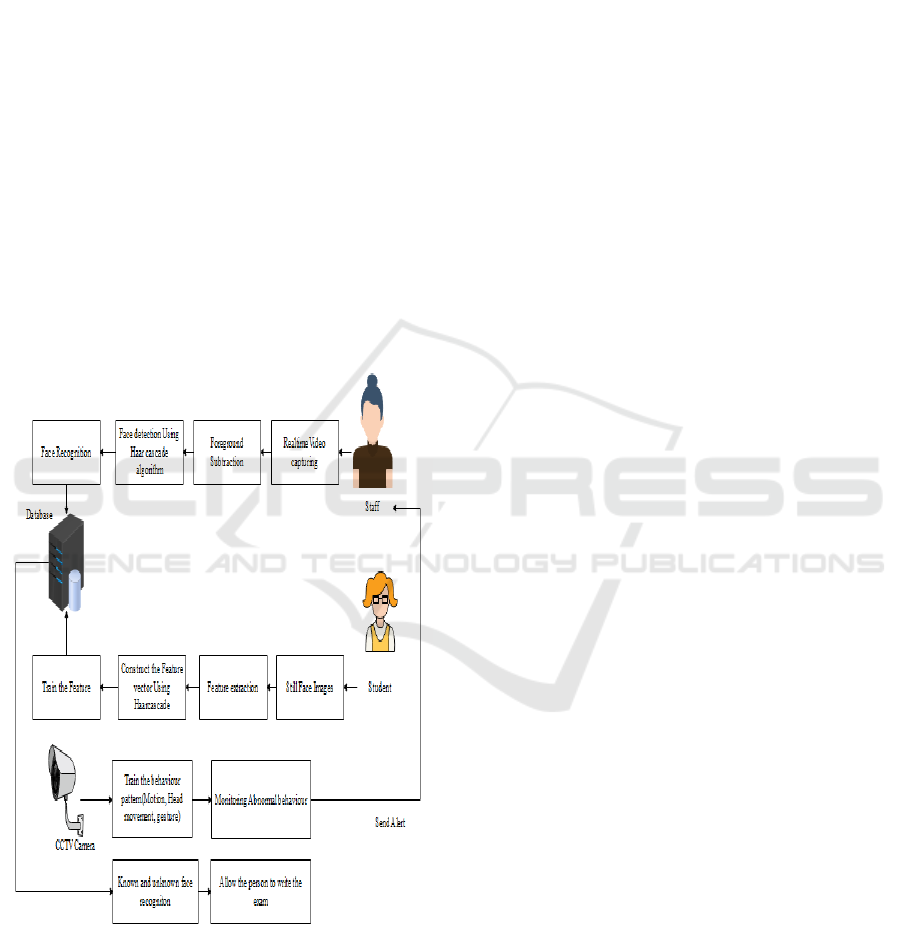
architecture is depicted in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Proposed Architecture.
4.1 Face Image Acquisition
In this module, administrators can train several faces.
Webcams or still photographs can be used to capture
faces. This picture displays the user's face in a straight
line, in regular lighting conditions, and without any
occlusion.
4.2 Features Extraction
This module retrieves and represents facial features
as feature vectors. The nose, eyes, and lips are
examples of facial features. A matrix is used to store
these values. In this process, cascade properties are
utilized. Features of digital images that help in object
recognition are called face-like traits. They were used
in the first real-time face identification and got their
name from their visual similarity to Haar wavelets. In
the past, it was computationally costly to calculate
features using just image intensities.
4.3 Register the Face
Converting many data sources into a single
coordinate system is known as face registration.
Features of the face are labelled. The process of
transforming many data sources into a single
coordinate system is known as face image
registration. Data may take into account several
photos, data from different sensors, times, depths, or
perspectives.
4.4 Classification of FCE
It is grown in popularity because of the vast range of
applications, which include diversion, smart cards,
information security, law social control and police
investigation. This module is referred to as the login
phase or testing phase. The input takes the form of
real-time video capture. The features are matched
using a deep learning technique. Video sequences'
temporal subject matter makes it possible to analyse
dynamic facial events and use them as biometric
symbols for person recognition.
4.5 Alert System
In this module, we can use neural network proficiency
to align the database still faces with the testing face.
The face image is classified as a recognised face if the
feature vectors match. Let the person write the test
after that. If the vectors of the properties don't match,
the faces are considered unknown. Set an alert for
unclear labelling. In addition, motion, object
detection, and gesture recognition are used to analyze
behaviour patterns.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
316
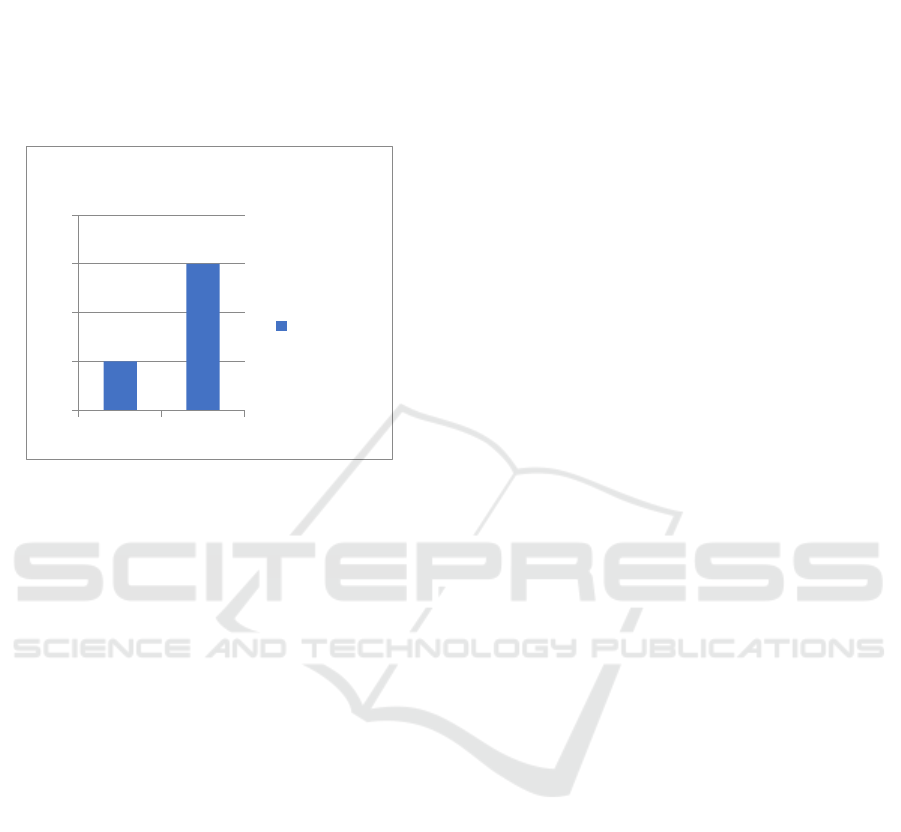
5 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
The false situation rate measures the likelihood of the
biometric insecurity system mistakenly rejecting a
malicious behaviour user’s activity (figure 3). A
system's FRR is commonly expressed as the ratio of
the number of erroneous rejections separate by the
number of determinations tries.
Figure 3: False Rejection Rate.
𝐹𝐴𝐿𝑆𝐸 𝑅𝐸𝐽𝐸𝐶𝑇 𝑅𝐴𝑇𝐸 = 𝐹𝑁 / (𝑇𝑃 +𝐹𝑁) (1)
Where FN =Genuine Scores Exceeding Threshold
TP+FN = All Genuine Scores
6 CONCLUSIONS
Candidate impersonation, often known as
malpractice, is a significant problem in the
examination system. Identity cards and hall passes are
frequently used in the examination process to identify
fraud. To identify, recognize, and categorize
applicants, the current exam system mainly uses
biometric technology and document image analysis
tools. The proposed methodology focuses on
image/video analysis, while fraud is typically found
through document image analysis. Face recognition
techniques can be used in the project. With increasing
research and integration, biometric face identification
is becoming more prevalent in facial image
applications. at order to discourage students from
mimicking during exams a practice that is prevalent
at many colleges this proposed effort used facial
recognition. This approach will be beneficial since it
will lessen the issue of student impersonation while
enhancing candidate identification and verification.
The staff will be able to monitor the student and
record their actions throughout the test.
REFERENCES
Alafif., Nora., and.Nawaf.W.. Alruwaili.. "Sleep.
Duration., body mass index,. & dietary behaviour
among .KSU. students.." Nut.rient.s 15.3 (2023): 510.
Cerrahoğlu, Enes, and Pınar Cihan. "Sentiment Analysis
and Emojification of Tweets." (2023).
Chan, Rosanna Yuen-Yan, Chun Man Victor Wong, and
Yen Na Yum. "Predicting Behavior Change in Students
with Special Education Needs Using Multimodal
Learning Analytics." IEEE Access 11 (2023): 63238-
63251.
Hansen, Morten, and Janja Komljenovic. "Automating
learning situations in EdTech: Techno-commercial
logic of assetisation." Postdigital Science and
Education 5.1 (2023): 100-116.
Hassan, Bassam Abdul Rasool, et al. "Exploring. The.
Level. Of. Lockdown. Fatigue & effect. Of. Personal.
Resilience. And. Coping. Behaviours. On. university.
Students. During. The. covid-19. Pandemic.: a cross-
sectional analysis from Iraq." Current
Psychology 42.17 (2023): 14851-14859...
Kavitha, S., et al. "Learning behaviour analysis of online
course learners using EEG and facial expression
data." Measurement: Sensors 25 (2023): 100669.
Krishna, P. Sandhya, et al. "2nd International Conference
on Integrated Circuits and Communication Systems
(ICICACS-2024) (60521).
Mettler, Jessica, et al. "Mindfulness-based programs and
school adjustment: A systematic review and meta-
analysis." Journal of school psychology 97 (2023): 43-
62.
Ryu, Riseul, et al. "A comprehensive survey of context-
aware continuous implicit authentication in online
learning environments." IEEE Access 11 (2023):
24561-24573.
Tekchandani. "A multimodal facial cues-based engagement
detection system in e-learning context using deep
learning approach." Multimedia Tools and
Applications 82.18 (2023): 28589-28615.
75
80
85
90
95
Existing Proposed
Accuracy
Accuracy
AI Powered Human Behaviour Detection and Monitoring
317
