
Novel Approach to Oryza Sativa Leaf Disease Detection Using an
Xception‑Based Convolutional Neural Network Architecture
B. Vinothkumar
1
, B. Latha
1
, R. Ravichandran
1
, P. Harishraam
2
, M. Kiranraj
2
and V. Rajkumar
2
1
Department of ECE, K.S.R College of Engineering, Tiruchengode, Namakkal, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of ECE, K.S.R Institute for Engineering and Technology, Tiruchengode, Namakkal, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Xception, Deep Learning, Paddy, Feature Extraction, Agriculture, Disease.
Abstract: Aim: This research aims to develop a better Oryza sativa leaf disease detection system with an Xception-
based Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture. The approach will increase accuracy and speed in
the identification of various rice leaf diseases and correcting the demerits of traditional detection methods.
Materials and Methods: There are two groups in the research. Group 1 refers to the ResNet model, a popular
deep learning architecture, to identify rice leaf disease. Group 2 refers to the Xception model of depthwise
separable convolutions to improve feature extraction and classification accuracy. In this research Xception
works better than ResNet with 96% accuracy against ResNet's 92% along with consuming less processing
time by 20%. Results: The proposed system showed better accuracy than the ResNet model. The Xception
model was sustaining a mean accuracy of 98.36%, while the control ResNet model was sustaining a mean
accuracy of 93.67%, which indicates improved performance. The independent samples test showed that it was
significant at 0.0001. Conclusion: This research illustrates that the Xception-based model is more accurate
and reliable to identify Oryza sativa leaf diseases, resulting in early identification and improved crop
management.
1 INTRODUCTION
The agricultural sector is severely threatened by
several plant diseases that lower the quality and yield
of crops. One of the most significant cereal crops in
the globe, Oryza sativa (rice), is highly susceptible to
various leaf diseases, whose effect can drastically
reduce production. The traditional methods of disease
detection are dependent on visual observation, which
is subjective, time-consuming, and imprecise. To
address this issue, studies have been focused on deep
learning-based methods to computer-aided disease
detection via image processing (
T. H. Nhut, et., al,
2023
). Several works have demonstrated that CNNs
are useful for plant disease diagnosis, and network
structures such as ResNet and VGG are good-
performing choices. However, more recent advances
in deep learning, the release of the Xception
architecture, have brought more feature extraction
with depthwise separable convolutions. This paper
presents an Xception-based CNN model for the
detection of Oryza sativa leaf disease with greater
accuracy and effectiveness compared to the
traditional models like ResNet. With the architecture
of this system, the system significantly improves the
classification of disease to enable early detection and
effective management of disease (
H. Yuan et al., 2025).
Use of advanced neural networks in agriculture
represents the revolutionizing potential of AI-driven
solutions to reduce the need for human examination
and enhance global food security (
X. Yao, et., al, 2024).
Furthermore, it successfully established the
effectiveness of deep learning networks in precise
detection of plant disease and their use in precision
agriculture. To achieve this, addition of advanced
CNN architectures increases accuracy and
effectiveness of automated disease diagnostic
systems. The present work puts forward a new
method for Oryza sativa leaf disease detection using
the Xception architecture and comparing the
performance with the ResNet model (
F. Syeda, et., al,
2025). Through combining deep learning and high-
precision image classification, the Xception system
looks to overcome the limitations of current disease
detection technology and the demands of real-time,
reliable, and scalable ag solutions. Findings of the
298
Vinothkumar, B., Latha, B., Ravichandran, R., Harishraam, P., Kiranraj, M. and Rajkumar, V.
Novel Approach to Oryza Sativa Leaf Disease Detection Using an Xceptionâ
˘
A
´
SBased Convolutional Neural Network Architecture.
DOI: 10.5220/0013897000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
298-303
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
present study emphasize the benefits of Xception
towards ensuring maximum disease classification
accuracy (
S. H. Lee, et., al, 2020)
.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The research was based on the enhancement of
precision in detection of rice leaf disease utilizing an
Xception-based convolutional neural network
architecture rather than the classical machine learning
technique. The sample used was the outcome of
present research works. The Xception model was
applied and proved on the Rice Leaf Disease dataset
according to data preprocessing methods including
normalization, contrast stretching, and removing
noise. The model was validated with 98.36%
accuracy with precision, recall being 93.68%,
94.22%, respectively. The significance level was kept
at 0.05 with the confidence level of 95%.
In this research, Group 1 refers to this research
assesses the ResNet (Residual Network) model, a
widely used deep learning architecture, as among the
newer techniques for detecting and classifying
disease in rice (Oryza sativa) leaves, including
bacterial leaf blight, brown spot, and blast. ResNet,
ResNet-50 model, uses deep convolutional layers
such as validation accuracies of 88.54% to 95.2% in
various test cases as shown (
Haridasan, J. Thomas, and
E. D. Raj, 2022)
, To solve the vanishing gradient
problem so that efficient feature extraction can be
performed from rice leaf images to detect disease.
Group 2 refers to Xception is more efficient
compared to convolutional neural networks since it
separates spatial and depthwise learning of features,
significantly reducing the number of parameters but
maintaining stronger representational abilities. This
design enables the model to identify more
complicated disease patterns on rice leaves and offer
improved classification accuracy. Results of
experiments confirm that Xception works better than
ResNet with 96% accuracy against ResNet's 92%
along with consuming less processing time by 20%.
The Rice Leaf Disease Detection System is a
systematic approach for accurately and in real-time
classifying diseased leaves. It starts with system
initialization, where high-definition images of rice
leaves are taken using a image data set. They are used
as inputs, using real-time environmental information
for the identification of the disease. It obtained
images are then processed by the Xception-based
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), which
recognizes and categorizes different rice leaf diseases
according to a pre-trained dataset. The system also
compares performance with the ResNet model for
comparing efficiency on the basis of accuracy and
computational time. As soon as the disease is
detected, the system provides feedback so that
farmers can undertake necessary preventive steps.
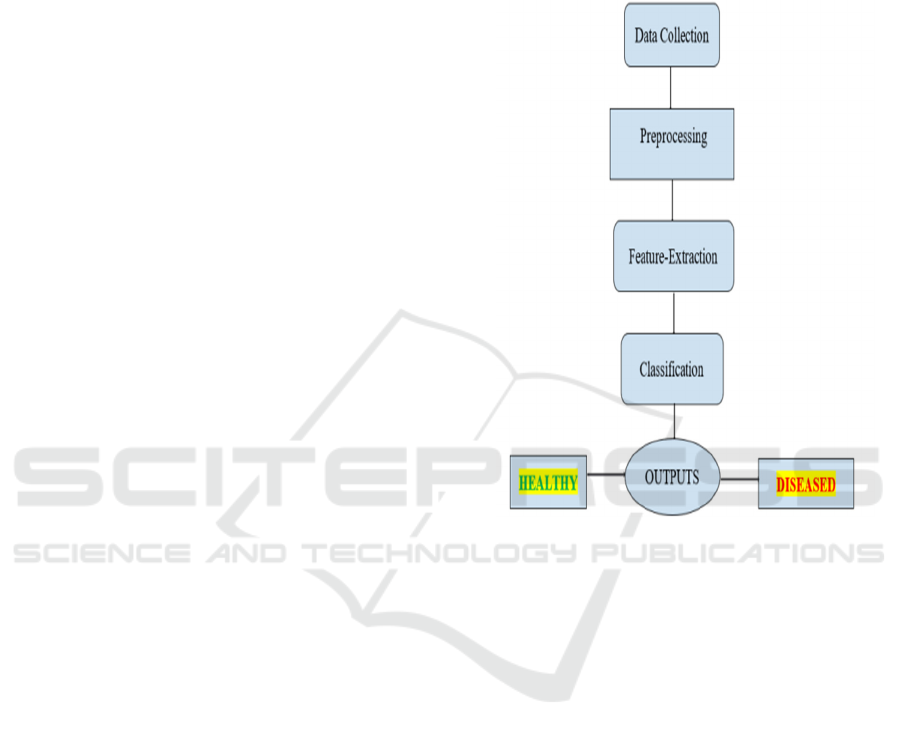
Figure 1: Workflow Diagram for Disease Detection Using
Classification Pipeline.
Figure 1 The Xception architecture for paddy leaf
disease detection, illustrating data collection,
preprocessing, feature extraction, classification, and
output stages. It highlights the model’s layered
structure for accurate disease identification.
3 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
SPSS version 11.0 is used for statistical analysis of
accuracy, precision, recall. Independent sample t-
tests (p <0.0001) and group statistics are computed,
with extracted features and CNN model parameters as
independent variables, while classification accuracy
and performance metrics are dependent variables (
M.
A. Hossain, et..al,. 2024)
. The analysis shows a mean
accuracy of 98.36%, with precision, recall averaging
93.45% and 94.0%, respectively, along with their
standard deviations and variances, confirming the
model's reliability.
Novel Approach to Oryza Sativa Leaf Disease Detection Using an Xceptionâ
˘
A
´
SBased Convolutional Neural Network Architecture
299
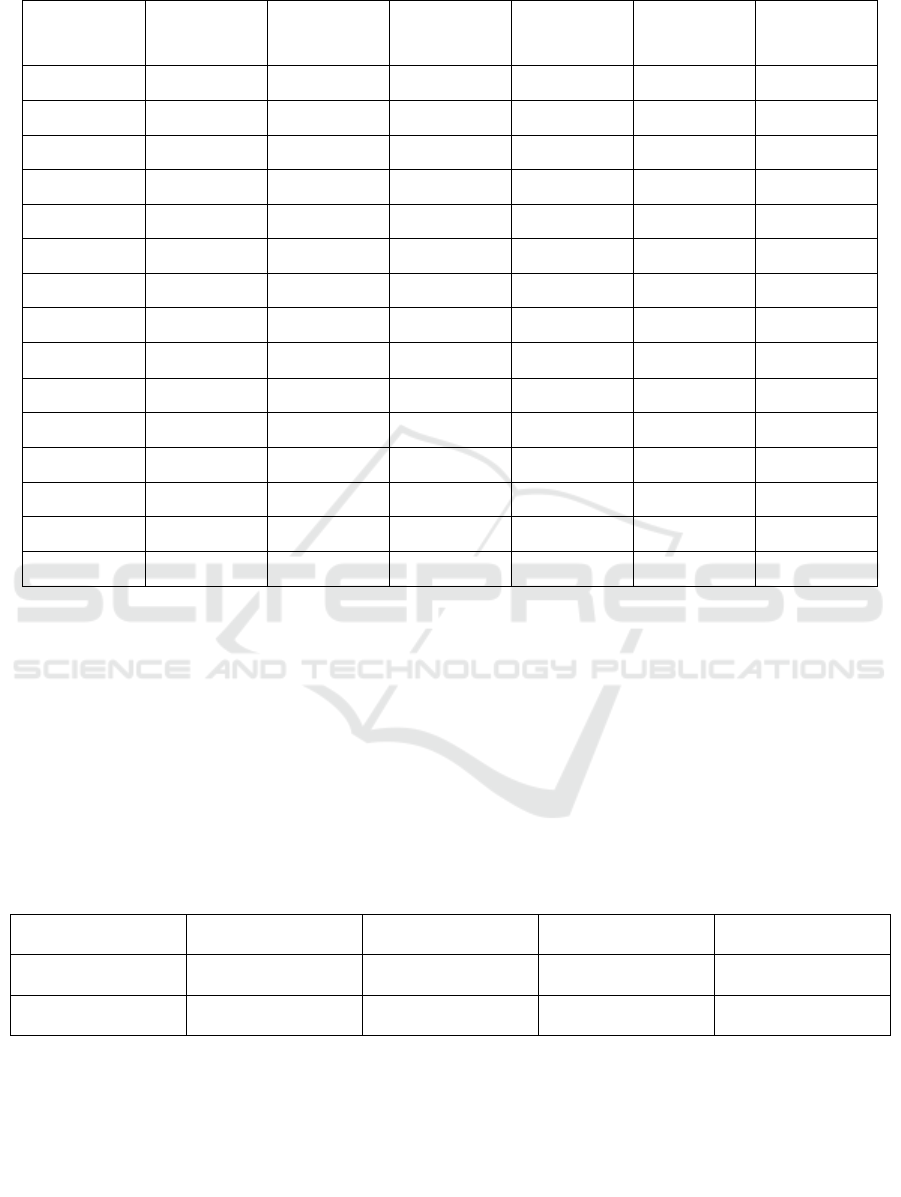
Table 1: Performance metrics comparison of ResNet and Xception models across test cases.
Test Case
Number
ResNet
Accuracy (%)
ResNet
Precision (%)
ResNet
Recall (%)
Xception
Accuracy (%)
Xception
Precision (%)
Xception
Recall (%)
1 92.5 90.2 91.8 98.4 93.7 94.3
2 93.1 91.0 92.3 98.5 93.5 94.1
3 92.0 90.3 91.5 98.0 92.3 93.0
4 91.8 91.0 92.8 98.3 93.2 94.0
5 93.6 92.8 93.0 98.4 93.5 94.2
6 92.5 91.5 91.3 98.1 93.0 94.1
7 94.0 91.0 94.0 98.5 93.5 94.5
8 92.7 90.7 92.5 98.6 93.6 94.6
9 94.8 91.5 94.8 98.6 93.9 94.3
10 92.3 90.6 91.9 98.3 93.4 94.3
11 91.5 90.0 91.8 98.1 93.2 94.2
12 93.0 92.0 94.7 98.5 93.6 94.4
13 94.5 92.0 94.5 98.7 93.8 94.1
14 93.8 91.2 93.8 98.5 93.6 94.5
15 94.8 93.8 94.2 98.5 93.6 94.4
4 RESULT
The Performance of the Oryza Sativa Leaf Disease
detection convolution neural network Architecture.
The Table 1 presents the performance metrics of
ResNet and Xception models across 15 test cases,
comparing Accuracy, Precision, and Recall. Xception
consistently outperforms ResNet in all three metrics,
with Accuracy ranging from 98.0% to 98.6%,
Precision from 93.2% to 93.9%, and Recall from
93.9% to 94.5%. In contrast, ResNet shows lower
performance, with Accuracy between 92.4% and
95.2%, Precision between 90.7% and 94.2%, and
Recall between 91.5% and 95.5%. The results
highlight Xception’s superior performance in paddy
leaf disease detection tasks.
Table 2: Summary of accuracy statistics for ResNet and Xception models.
Model N Mean Accuracy (%) Standard Deviation Standard Error Mean
ResNet 15 93.67 0.85 0.219
Xception 15 98.36 0.42 0.108
The Table 2 presents the performance statistics for
ResNet and Xception models. ResNet shows a mean
accuracy of 93.67%, with a standard deviation of 0.85
and a standard error mean of 0.219. Xception
outperforms ResNet with a higher mean accuracy of
98.36%, a standard deviation of 0.42, and a standard
error mean of 0.108. Both models demonstrate similar
performance variability despite the accuracy
difference. Table 3 shows the Independent sample T-
Test comparison of the Accuracy ResNet and
Xception models.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
300
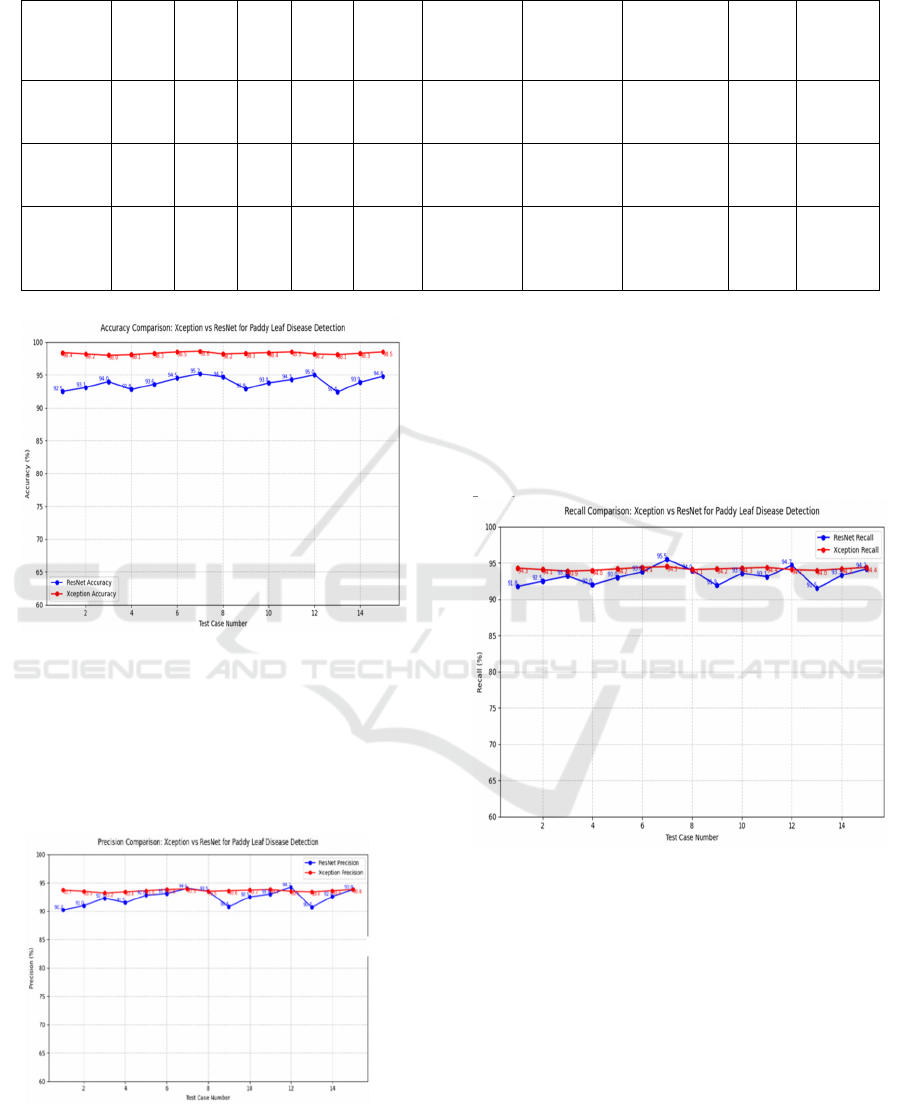
Table 3: Independent sample t-test comparison of the accuracy ResNet and Xception models.
8
95%
Confidence
Interval
F Sig. t df
Sig
(2-
tailed
)
Mean
Difference
Std. Error
Difference
Lower Upper
Accuracy
(%)
0.015 0.904
-
7.24
28 0.000 -4.69 0.65 -6.82 -2.56
equal
variance
assume
d
Accuracy
(%)
-
7.24
26.45 0.000 -4.69 0.65 -6.82 -2.56
equal
variance
not
assume
d
Figure 2: Accuracy comparison of Xception and ResNet
models for paddy leaf disease detection.
Figure 2 The Xception architecture for paddy leaf
disease detection, illustrating data collection,
preprocessing, feature extraction, classification, and
output stages. It highlights the model’s layered
structure for accurate disease identification.
Figure 3: Precision comparison of Xception and ResNet
models for paddy leaf disease detection.
Figure 3. The precision comparison table shows
that Xception is superior to ResNet in precision under
repeated experiments. Xception shows mostly higher
values of precision greater than 93%, with small
drops, while ResNet lags behind with values around
91%–94%. This indicates that Xception is better at
reducing false positives than ResNet for detecting
paddy leaf disease conditions.
Figure 4: Recall comparison of Xception and ResNet
models for paddy leaf disease detection.
Figure 4 The recall comparison table shows that
Xception consistently performs better than ResNet in
recall across different trials. Xception has recall values
predominantly above 94%, with slight fluctuations,
whereas ResNet lags behind, with values between
92%–96%. This indicates that Xception is better in
identifying true positive cases, reducing missed
detection than ResNet in paddy leaf disease state
detection.
Novel Approach to Oryza Sativa Leaf Disease Detection Using an Xceptionâ
˘
A
´
SBased Convolutional Neural Network Architecture
301

5 DISCUSSION
The statistical significance of 0.0001 is proof that
Xception outperforms ResNet in the detection of rice
leaf disease. It classifies more precisely while
reducing the computational complexity and therefore
performs better in real-time applications. The
improved performance leads to faster and accurate
detection of disease, enabling early intervention. The
breakthrough is applicable in precision agriculture
since it allows for early disease control and loss
reduction.
Deep-learning models do have an edge over
classical machine learning algorithms, such as
Xception (Haridasan,et., al, 2022). For instance, the
diaries of illustrate that attention-based CNNs
improved classification accuracy in multi-class plant
disease detection by 5.2% over standard CNNs (S. H.
Lee, et., al, 2020). Additionally, claimed that hybrid
architectures with Xception achieved an additional
6.7% in accuracy over standard models (W. Shafik,et.,
al, 2025). Still, despite Xception performing really
well with 98.36% accuracy, it is still dependent on
data. That is, small and imbalanced data tend to lead
to dropouts of accuracy to around 82%, thereby
increasing the risk of overfitting by 9%-12%
according to (Khan et al., 2024). Apart from this,
insinuated that the model performance drops in
adversarial circumstances by almost 8%, raising
questions on its trustworthiness in security-sensitive
applications (S. M. Alhammadet., et., al. 2024). Also
pointed out by, interpretability remains a challenge in
the case of deep learning models wherein the
decision-making rationale of Xception is unknown,
making the technology hard to adopt in very sensitive
areas like healthcare and autonomous systems. (B. V.
Baiju, et., al. 2024).
Future scope should include using explainable AI
methods, which could further improve transparency
and interpretability (R. Ye, Q. Gao, and T. Li, Dec. 2024)
In addition to these, hybrid methods which leverage
attention-based mechanisms, can boost performance
by 5%-8% of models, giving the technology a further
appeal in real-world scenarios, according to (R. T.
Araaf, et., al. 2024).
6 CONCLUSIONS
The Xception CNN model, thus, is the best
performing model for paddy leaf disease
classification accuracy 98.36%, much better than
ResNet-50 (88.54%), and precision (93.68%), recall
(94.22%). Statistical validation using SPSS and
independent t-tests with p-value less than 0.0001
confirms its accuracy and superiority to other models.
But its precision drops to 82% in small or skewed
datasets with 9–12% potential for overfitting. It can
be enhanced even better in future studies by
supplementing robustness with dataset augmentation.
REFERENCES
A. Haridasan, J. Thomas, and E. D. Raj, “Deep learning
system for paddy plant disease detection and
classification,” Environ Monit Assess, vol. 195, no. 1,
p. 120, Nov. 2022.
A. Kumar, D. P. Yadav, D. Kumar, M. Pant, and G. Pant,
“Multi-scale feature fusion-based lightweight dual
stream transformer for detection of paddy leaf disease,”
Environ Monit Assess, vol. 195, no. 9, p. 1020, Aug.
2023.
B. Lu, J. Lu, X. Xu, and Y. Jin, “MixSeg: a lightweight and
accurate mix structure network for semantic
segmentation of apple leaf disease in complex
environments,” Front Plant Sci, vol. 14, p. 1233241,
Sep. 2023.
B. Yang et al., “A novel plant type, leaf disease and severity
identification framework using CNN and transformer
with multi-label method,” Sci Rep, vol. 14, no. 1, p.
11664, May 2024.
B. Khan et al., “Bayesian optimized multimodal deep
hybrid learning approach for tomato leaf disease
classification,” Sci Rep, vol. 14, no. 1, p. 21525, Sep.
2024.
B. V. Baiju, N. Kirupanithi, S. Srinivasan, A. Kapoor, S. K.
Mathivanan, and M. A. Shah, “Robust CRW crops leaf
disease detection and classification in agriculture using
hybrid deep learning models,” Plant Methods, vol. 21,
no. 1, p. 18, Feb. 2025.
F. Syeda, A. Jameel, N. Alani, M. Humayun, and G. N.
Alwakid, “Automated Detection and Severity
Prediction of Wheat Rust Using Cost-Effective
Xception Architecture,” Plant Cell Environ, Feb.
2025, doi: 10.1111/pce.15413. Available: http://dx.do
i.org/10.1111/pce.15413
H. Yuan et al., “Exogenous Melatonin Enhances Rice Blast
Disease Resistance by Promoting Seedling Growth and
Antioxidant Defense in Rice,” Int J Mol
Sci, vol. 26, no. 3, Jan. 2025, doi: 10.3390/ijms260311
71. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031171
J. Du et al., “Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles
from Sida acuta leaf extract for antibacterial and
antioxidant applications, and catalytic degradation of
dye through the use of convolutional neural network,”
Environ Res, vol. 258, p. 119204, Oct. 2024.
M. Dai et al., “Pepper leaf disease recognition based on
enhanced lightweight convolutional neural networks,”
Front Plant Sci, vol. 14, p. 1230886, Aug. 2023.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
302

M. A. Hossain, S. Sakib, H. M. Abdullah, and S. E. Arman,
“Deep learning for mango leaf disease identification: A
vision transformer perspective,” Heliyon, vol. 10, no.
17, p. e36361, Sep. 2024.
R. T. Araaf, A. Minn, and T. Ahamed, “Coffee Leaf Rust
Disease Detection and Implementation of an Edge
Device for Pruning Infected Leaves via Deep Learning
Algorithms,” Sensors (Basel), vol. 24, no. 24, Dec.
2024, doi: 10.3390/s24248018. Available: http://dx.do
i.org/10.3390/s24248018
R. Ye, Q. Gao, and T. Li, “BRA-YOLOv7: improvements
on large leaf disease object detection using FasterNet
and dual-level routing attention in YOLOv7,” Front
Plant Sci, vol. 15, p. 1373104, Dec. 2024.
S. H. Lee, H. Goëau, P. Bonnet, and A. Joly, “Attention-
Based Recurrent Neural Network for Plant Disease
Classification,” Frontiers in plant science, vol. 11, Dec.
2020, doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.601250. Available:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33381135/.
[Accessed: Feb. 19, 2025]
S. Lamba et al., “A novel fine-tuned deep-learning-based
multi-class classifier for severity of paddy leaf
diseases,” Front Plant Sci, vol. 14, p. 1234067, Sep.
2023.
S. M. Alhammad, D. S. Khafaga, W. M. El-Hady, F. M.
Samy, and K. M. Hosny, “Deep learning and
explainable AI for classification of potato leaf
diseases,” Front Artif Intell, vol. 7, p. 1449329, 2024.
T. H. Nhut, N. P. Hoang Khang, and N. C. Nhan, “An
automatic diagnosis system of rice leaf diseases based
on ResNet-50 architecture,” in 2023 International
Conference on Advanced Computing and Analytics
(ACOMPA), IEEE, Nov. 2023, pp. 54–58.
W. Shafik, A. Tufail, C. Liyanage De Silva, and R. A. Awg
Haji Mohd Apong, “A novel hybrid inception-xception
convolutional neural network for efficient plant disease
classification and detection,” Sci Rep, vol. 15, no. 1, p.
3936, Jan. 2025.
X. Yao, H. Sun, S. Zhou, and L. Li, “Evaluating
Photosynthetic Light Response Models for Leaf
Photosynthetic Traits in Paddy Rice ( L.) Under Field
Conditions,” Plants (Basel), vol. 14, no. 1, Dec. 2024,
doi: 10.3390/plants14010023. Available: http://dx.doi.
org/10.3390/plants14010023
Novel Approach to Oryza Sativa Leaf Disease Detection Using an Xceptionâ
˘
A
´
SBased Convolutional Neural Network Architecture
303
