
Image Quality Assessment for Fake Biometric Detection
P. J. Suresh Babu
1
, K. Eswaramoorthy
1
, K. Sasikala
2
, P. Muthukumar
3
,
S. Sivamani
1
and T. Suresh Padmanabhan
1
1
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Saveetha Engineering College, Sriperumbadur, Chennai, Tamil
Nadu 602105, India
2
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Vels Institute of Science, Technology & Advanced Studies,
Chennai, Tamil Nadu – 600117, India
3
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Saveetha School of Engineering, Saveetha Institute of Medical and
Technical Sciences, Tamil Nadu - 602105, India
Keywords: Usefulness Expectations (UE), TV, Online Flow Experience (OFE), Internet Videos, Perceived Ease of Use
(PES), Perceived Behavioral Control (PBO).
Abstract: Detecting fake biometrics is crucial for ensuring the security and reliability of biometric authentication
systems. A recent paper proposes a method that extracts features from pre-processed images of the face and
fingerprint and compares them with those of a database image to obtain matching scores. The matching scores
then undergo a three-step process that includes normalization, generation of similarity scores, and fusion of
weighted scores. This ensures that the scores are on the same scale and comparable, allowing the system to
take advantage of the strengths of both biometric traits to increase accuracy and reduce false matches. The
weights for the scores obtained from the face and fingerprint traits are determined based on their individual
performance, and used to calculate a final score. The fusion of the face and fingerprint traits using a weighted
sum of scores technique has the potential to enhance the security of biometric authentication systems. The
proposed method ensures the correctness and dependability of the system by detecting fake biometrics and
preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information. Overall, this paper proposes an effective method to
improve the accuracy and reliability of biometric authentication systems by combining the strengths of two
biometric traits.
1 INTRODUCTION
Biometric authentication systems have become
increasingly popular in recent years due to their
ability to provide high levels of security and accuracy.
However, no single biometric trait is perfect and can
be affected by various factors, such as changes in
physical appearance or environmental conditions.
Therefore, combining multiple biometric traits can
improve the overall accuracy and robustness of the
system. The project aims to implement a biometric
authentication system that combines two biometric
traits, namely face and fingerprint, using a matching
score level architecture. The system extracts feature
from pre-processed images of the face and fingerprint
and compares them with those of a database image to
obtain matching scores. The individual scores
generated after matching are then passed through a
fusion module that consists of normalization,
generation of similarity scores, and fusion of
weighted scores. The fusion technique used in the
project is a weighted sum of scores technique, which
assigns weights to the individual scores based on their
relative importance. The final score obtained from the
fusion module is used to declare the person either
authenticated or unauthenticated. The proposed
system has the potential to improve the accuracy and
robustness of biometric authentication systems and
can be used in various applications such as access
control, secure transactions, and identity verification.
Image processing is a computer-based method of
modifying digital images using effective algorithms
to produce new images. The most popular software
for this is Adobe Photoshop, which is widely used for
processing digital photographs. Image processing is
used in various sectors, including face recognition,
medical imaging, and remote sensing. The process
involves taking a digital or analog image as input,
which is transformed into a physical picture using
Babu, P. J. S., Eswaramoorthy, K., Sasikala, K., Muthukumar, P., Sivamani, S. and Padmanabhan, T. S.
Image Quality Assessment for Fake Biometric Detection.
DOI: 10.5220/0013896500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
267-273
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
267

relevant technology. Digital photography saves
images as computer files, which are translated using
photography software to produce an actual image.
Image enhancement and correction are done using
specialized computer programs that use algorithms to
reduce signal distortion, clarify fuzzy photos, and
brighten dark images. While analog photography uses
chemicals to burn the picture onto film and requires
specialized training, digital photography is becoming
more popular due to its ease of use.
There are two categories of techniques in image
processing: analog and digital techniques. These can
process either using analog or visual techniques for
hard copies (e.g., printouts and photographs) as well.
These visual techniques are employed by image
analysts based on different principles of
interpretation. Image processing is not only limited to
a region that is analyzed but also the experience of the
analyst. Association is also an important technique in
image processing using visual methods. So what
analysts bring to image processing is the combination
of personal knowledge and collateral data. Digital
processing may be applied to processing of digital
images by computer. Because the raw data from the
imaging sensor on a satellite has shortcomings. In
order to overcome these imperfections and obtain the
original information, it must pass through several
processing stages. The three common stages that
should be addressed to handle every data type to be
used with digital methods are Pre-processing,
improvement and visualization and finally,
deconvolution. There are the five image processing
tasks. As follows:
• Visualization: Pay attention to intangible
objects.
• To improve the image, use image restoration
and sharpening.
• Search for the desired image using image
retrieval.
• Measures various things in a picture using a
pattern.
• Identify the things in a picture using image
recognition software.
Artificial Neural Networks and Representation
Learning are subsets of algorithms in the field of
deep learning (a subfield of machine learning) -
models and algorithms used to emulate human brain
and its natural processes. In computer vision, speech
recognition, natural language processing, audio
recognition, social network filtering, machine
translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical
image analysis, material inspection and board game
programs, where they have produced results
comparable to and in some cases superior to human
experts. Deep learning models are vaguely inspired
in information processing and communication
patterns in biological nervous system and "deep belief
networks" have been fed data that is representative of
a wide range of noises, such as the chatter of telegraph
operators. Deep learning brings a higher recognition
rate than ever. For safety-critical use cases like self-
driving cars, this is a must-have to make sure
consumer electronics are reliable enough for
customers to take for granted. As deep learning’s
capabilities have improved in recent years, it has
begun to surpass humans in some tasks, like
classifying objects in images. IQA can be used to
detect image manipulation by analyzing changes in
image quality metrics. For example, if an image has
been manipulated to change the facial features of the
person, IQA can detect the changes in the facial
features and alert the system about the possibility of
a fake biometric image. IQA can also be used to
assess the authenticity of an image. Biometric images
are typically captured using specialized cameras and
have specific quality characteristics. By comparing
the quality of an image against a database of genuine
biometric images, IQA can detect anomalies and raise
alarms if the image appears to be fake.
IQA can also be used to identify specific image
tampering techniques that are commonly used to
create fake biometric images. By analyzing image
quality metrics, IQA can identify the presence of
artifacts and inconsistencies that are characteristic of
particular tampering techniques. IQA can also be
used to enhance the accuracy of biometric
authentication systems by identifying poor quality
biometric images. By removing poor quality images
from the database, IQA can improve the accuracy of
biometric matching and reduce the likelihood of false
positives and false negatives.
The problem statement for image quality
assessment for fake biometric detection is to develop
a reliable and accurate system that can differentiate
between genuine and fake biometric images. This
system should be able to assess the quality of the
image, detect any alterations or tampering, and
identify whether the biometric data captured is from
a real or fake source. The system should be able to
handle various types of biometric data, such as facial
images, fingerprints, iris scans, and voiceprints. The
goal is to improve the accuracy and reliability of
biometric systems for security and identification
purposes by ensuring that only genuine biometric data
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
268

is used for verification and authentication.
2 RELATED WORKS
However, it's important to note that technology
evolves rapidly, and there may have been
advancements in this field since then. Here are some
existing methods used for fake biometric detection:
Spoofing Detection: Spoofing refers to the use of fake
or artificial biometric traits to deceive a biometric
system. Various techniques have been developed to
detect spoofing attacks, such as liveness detection.
Liveness detection aims to verify that the biometric
being presented is from a live person and not a replica
or forgery. It may involve analyzing factors like skin
texture, blood flow, and thermal properties, or even
requesting specific actions from the user to prove
their liveness.
Presentation Attack Detection (PAD): PAD
techniques are designed to detect presentation attacks,
where an attacker presents a fake or manipulated
biometric sample to the system. PAD methods can
include analyzing the characteristics of the presented
biometric data to identify anomalies or
inconsistencies that indicate potential attacks. These
methods often involve analyzing the image quality,
texture, and other features to distinguish between
genuine and fake biometric data.
Multimodal Biometrics: Combining multiple
biometric modalities, such as face, iris, fingerprint,
voice, or behavioral characteristics, can enhance the
overall security and accuracy of a biometric system.
By using multiple biometric traits simultaneously, it
becomes more difficult for an attacker to spoof or
fake all of them convincingly. Multimodal biometric
systems can provide better resilience against spoofing
attacks.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence:
Advanced machine learning algorithms, such as deep
learning, can be employed to train models that can
detect fake biometric data. These models can learn
patterns and features indicative of genuine or fake
biometric traits, allowing them to classify and
differentiate between them more accurately. By
continuously training the models with new data, they
can adapt and improve their detection capabilities
over time.
Database Comparison and Duplicate Detection:
Biometric systems often maintain databases of
enrolled biometric templates. By comparing newly
presented biometric samples against the existing
database, it becomes possible to detect potential
duplicates or inconsistencies that may indicate fake or
tampered data.
It's worth noting that the arms race between
attackers and system developers is ongoing, and new
spoofing techniques may emerge as technology
advances. Therefore, the field of fake biometric
detection continues to evolve, and researchers and
developers are constantly working to improve the
security and reliability of biometric systems.
2.1 Segmentation
The process of segmenting an image into various
areas or segments, each of which corresponds to a
different item or feature in the picture shown in figure
1 is known as "image quality analysis (IQA)".
Because it may be used to identify and isolate
particular areas of a picture that could include
irregularities or artifacts, segmentation can be helpful
in the identification of false biometrics. For instance,
segmentation may be used in a fingerprint
identification system to recognize and isolate certain
ridges or valleys in the fingerprint, which can be used
to detect modifications or fakes. In IQA,
segmentation is accomplished using a variety of
algorithms and methods, including thresholding,
clustering, and watershed segmentation. In order to
determine the borders between areas, these algorithms
examine the intensity or color gradients present
throughout the picture. After the picture has been
divided into segments, a number of metrics may be
generated for each segment to assess its authenticity
or quality. These metrics could include measurements
of form, size, homogeneity, contrast, and texture. As
a whole, segmentation are is a useful technique in
IQA for detecting false biometrics since it may assist
in separating paras of an image that might have
artifacts or anomalies, enabling more accurate and
consistent biometric authentication.
2.2 Feature Vector
A feature vector is a set of numerical values that
describe the characteristics or features of an image. In
image quality assessment (IQA) for fake biometric
detection, feature vectors are commonly used to
represent the biometric data in a way that is more
suitable for analysis and comparison. The process of
creating a feature vector typically involves extracting
relevant features or characteristics from the image,
such as texture, shape, and color, and quantifying
them as numerical values. The resulting feature
vector can then be used to compare the biometric data
with other samples and identify potential fakes or
Image Quality Assessment for Fake Biometric Detection
269

inconsistencies. There are several algorithms and
techniques used for feature extraction in IQA,
including wavelet transforms, principal component
analysis (PCA), and local binary patterns (LBP).
These algorithms work by analyzing different
aspects of the image, such as pixel values, edge
information, and texture patterns, to identify
relevant features. Once the feature vector has been
created, various metrics can be calculated to
determine the quality or authenticity of the biometric
data. These metrics may include measures of
similarity or distance between the feature vectors of
different samples, as well as measures of variability
and consistency within a single sample. Overall,
feature vectors are a valuable tool in IQA for fake
biometric detection, as they provide a way to
represent biometric data in a way that is suitable for
analysis and comparison, allowing for more accurate
and reliable biometric authentication.
Figure 1: Image Segmentation.
2.3 Limitations of the Existing System
This method is not very flexible because it is possible
to create duplicates of fingerprints or otherwise trick
the system. Currently, the system simply computes the
spatial domain, which is the order in which the data
are physically arranged. The spatial domain is merely
one type of data representation, and it may not be able
to offer a comprehensive picture of the data. The
paragraph recommends the application of the
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) technique to
enhance the biometric authentication system. By
spotting patterns and connections between variables,
PCA is a statistical approach used to simplify
complicated data sets. The system will be able to
calculate the co-variance and variance of the data and
locate more significant characteristics in the
biometric data by applying PCA. With the help of this
strategy, the system will be better able to identify and
authenticate people by giving a more accurate
depiction of the biometric data. Overall, the current
biometric authentication system has limitations and is
not very efficient, but a more advanced approach
using PCA can be used to improve the system's
accuracy and efficiency.
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
3.1 Theoretcal Structure
Biometric systems refer to systems that identify
individuals on the basis of some of their physical or
behavioral characteristics and are usually employed
for security or access control. It’s high time for
organizations and companies to develop a system that
will utilise the facial and fingerprint as two varied
biometrics to validate an individual. It takes a photo
of a person’s face followed by a photo of his/her
fingerprint. These two biometric data sets are then
compared to biometric reference data and data from
the same two different biometric tests to determine
whether the stored biometric data corresponds to a
stored human's body. Facial recognition technology
does this by using unique landmarks on the person’s
face, such as the distance between their eyes or the
shape of their nose, to produce a mathematical
representation of the face. Fingerprint recognition
technology works instead by taking the unique ridge
and valley pattern of a person's fingertip and creating
a list of the minutiae points in it. 2 the same system
we used Fundamentals of Image Processing By using
both facial and fingerprint recognition technology the
system can produce more accurate and reliable
method. The multi-modal biometric feature
minimizes the occurrence of false positives and false
negatives that are associated with reliance on only
one modality of biometric feature. This method may
allow for a more reliable and/or secure access control,
especially in high security environments where
identification is essential.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
270

3.2 System Implementation
Fundamentals of Image Processing
Figure 2: Fundamentals of Image Processing.
The Figure 2 shows Fundamentals of Image Processing.
3.2.1 Image Acquisition
Image acquisition is the acquisition of a digital image.
To do so requires an image sensor and the capability
to digitize the signal produced by the sensor. The
sensor could be a monochrome or color TV camera
that produces an entire image of the problem domain
every 1/30 sec. The image sensor could also be a line
scan camera that produces a single image line at a
time. In this case, the object moved past the line. For
example: Digital Camera, Mobile Camera in figure 3.
Figure 3: Digital Camera and Mobile Camera.
4 RESULTS AND EVALUATION
4.1 The Project Setup
Start by clearly defining the problem you want to
solve. In this case, the problem is detecting fake
biometrics, which could involve analyzing images to
assess their quality. Collect a dataset of images that
includes both real and fake biometrics. You could
use publicly available datasets or create your own.
Depending on the quality of the data, you may need
to preprocess the images to remove noise, blur, or
other artifacts that could affect image quality. Define
metrics for evaluating the quality of the images. For
example, you could use measures like sharpness,
contrast, or texture features to assess the quality of the
images. Choose a model to assess image quality. This
could include traditional image processing techniques
or more advanced machine learning algorithms. Train
the model using the dataset you have collected. You
may need to fine-tune the model to achieve the best
performance. Evaluate the model's performance on a
test set of images that it has not seen before. This will
give you an idea of how well the model can generalize
to new data. Once you are satisfied with the
performance of the model, integrate it into your
biometric detection system. Deploy the system and
monitor its performance in real-world scenarios.
Continuously collect feedback from users and update
the model to improve its performance over time.
4.2 Dataset Used in this Fake Biometric
Detection
The NIST Biometric Image Software (NBIS) provides
datasets of fingerprint, face, and iris images that are
suitable for training and testing biometric systems.
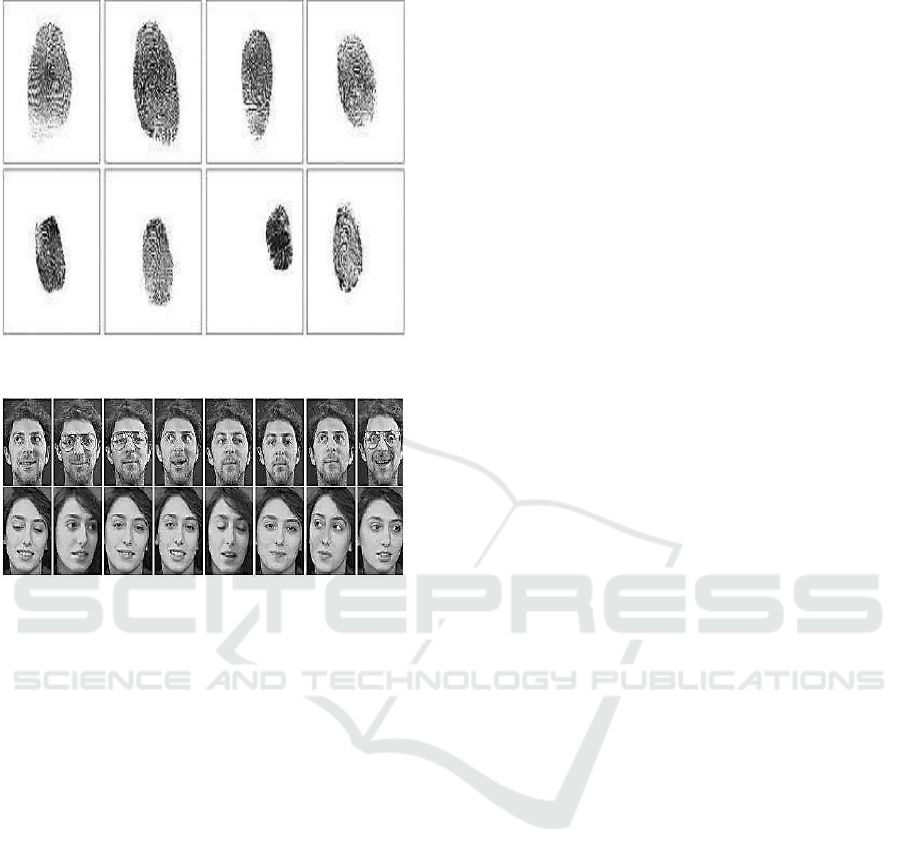
The Cross-Match dataset includes both genuine and
fake fingerprint images shown in Figure 4. It is widely
used in research on fake biometric detection. The 1:1
Verification Competition dataset from the
International Conference on Biometrics (ICB)
includes a large number of face images, including
both genuine and fake images. The Mobile Biometry
(MOBIO) dataset includes images of faces,
fingerprints, and voices, with both genuine and fake
samples. The Mobi Face dataset contains face images
captured in uncontrolled environments and includes
both genuine and fake images. The Replay-Attack
dataset includes both genuine and fake face images
captured under various conditions to simulate
different attack scenarios. The MSU Mobile Face
Spoofing Database includes both genuine and fake
face images in Figure 5, captured using high-quality
Image Quality Assessment for Fake Biometric Detection
271
cameras and mobile devices.
Figure 4: Fingerprint Dataset.
Figure 5: Face Dataset.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Fake biometric images can be generated using various
techniques, such as printing, replay, or synthetic
generation. These techniques can create images that
are similar enough to real biometric images to be
accepted by traditional biometric verification
techniques, making them difficult to detect. Image
quality assessment can help identify fake biometric
images by analyzing various image features such as
sharpness, contrast, and noise. By detecting anomalies
in these features, image quality assessment algorithms
can flag potentially fake images for further
investigation. For example, a fake biometric image
created using printing may exhibit different
characteristics than a real biometric image captured
using a biometric sensor. However, it is important to
note that image quality assessment is not foolproof
and can be bypassed by advanced attacks. Attackers
can try to mimic the image characteristics of real
biometric images, making them harder to detect.
Therefore, it is important to continuously improve and
update image quality assessment algorithms to stay
ahead of evolving attack techniques. Overall, image
quality assessment is a valuable tool in the fight
against fake biometrics and can help improve the
security and reliability of biometric systems. By
identifying and rejecting fake biometric images,
image quality assessment can help ensure that only
genuine users are granted access to protected
resources, improving the overall security posture of
the system. While current image quality assessment
algorithms can detect basic anomalies in image
features, there is room for improvement. Future work
could focus on developing more sophisticated
algorithms that can detect subtle differences between
real and fake biometric images. Machine learning
techniques, such as deep learning, have shown
promise in improving the accuracy of image quality
assessment. Future work could explore the use of
machine learning to enhance the performance of
image quality assessment algorithms. Image quality
assessment algorithms may perform differently
depending on factors such as the type of biometric
modality, lighting conditions, and the quality of the
biometric sensor. Future work could evaluate the
performance of image quality assessment algorithms
under a range of scenarios to identify areas for
improvement. Image quality assessment algorithms
typically rely on metrics such as sharpness, contrast,
and noise to identify anomalies in biometric images.
However, there may be other metrics that could be
useful in detecting fake biometric images. Future
work could focus on identifying and developing new
metrics that could be incorporated into image quality
assessment algorithms. As noted earlier, image
quality assessment is not foolproof and can be
bypassed by advanced attacks. Future work could
focus on developing complementary techniques for
fake biometric detection, such as liveness detection,
which can help detect attacks that bypass image
quality assessment.
REFERENCES
A. Peña, A. Morales, I. Serna, J. Fierrez, and A. Lapedriza,
"Facial expressions as a vulnerability in face
recognition," in 2021 IEEE International Conference on
Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 2988-2992, IEEE,
September 2021.
A. Brömme, C. Busch, N. Damer, A. Dantcheva, M.
Gomez-Barrero, K. Raja, C. Rathgeb, A. Sequeira, and
A. Uhl (Eds.), "Image quality assessment on identity
documents," in BIOSIG 2021, Lecture Notes in
Informatics (LNI), Gesellschaft für Informatik, Bonn,
2021.
A. George and S. Marcel, "On the effectiveness of vision
transformers for zero-shot face anti-spoofing," in 2021
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
272

IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics
(IJCB), pp. 1-8, IEEE, 2021.
J. Cui, P. Zhang, S. Li, L. Zheng, C. Bao, J. Xia, and X. Li,
"Multitask identity-aware image steganography via
minimax optimization," IEEE Transactions on Image
Processing, vol. 30, pp. 8567-8579, 2021.
M. Raif, A. E. Rharras, A. Chehri, and R. Saadane,
"Metamorphic testing for edge real-time face
recognition and intrusion detection solution," in 2022
IEEE 96th Vehicular Technology Conference
(VTC2022-Fall), pp. 1-5, IEEE, 2022.
P. Anthony, B. Ay, and G. Aydin, "A review of face anti-
spoofing methods for face recognition systems," in
2021 International Conference on Innovations in
Intelligent Systems and Applications (INISTA), pp. 1-
9, IEEE, 2021.
X. Zhu, H. Wang, H. Fei, Z. Lei, and S. Z. Li, "Face forgery
detection by 3D decomposition," in Proceedings of the
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, pp. 2929-2939, 2021.
Y. Wang, X. Song, T. Xu, Z. Feng, and X.-J. Wu, "From
RGB to depth: Domain transfer network for face anti-
spoofing," IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics
and Security, vol. 16, pp. 4280-4290, 2021.
Z. Li, H. Li, X. Luo, Y. Hu, K.-Y. Lam, and A. C. Kot,
"Asymmetric modality translation for face presentation
attack detection," IEEE Transactions on Multimedia,
vol. 25, pp. 62-76, 2021.
Z. Li, R. Cai, H. Li, K.-Y. Lam, Y. Hu, and A. C. Kot, "One-
class knowledge distillation for face presentation attack
detection," IEEE Transactions on Information
Forensics and Security, vol. 17, pp. 2137-2150, May
26, 2022.
Image Quality Assessment for Fake Biometric Detection
273
