
Object Detection for Sign Language Recognition Using YOLOv8
Nagarani N, Abinandhan S, Elangovan C and Pranesh Raja V. K.
Electronics and Communication Engineering, Velammal College of Engineering and Technology, Madurai - 625009,
Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Hand Gesture Recognition (HGR), YOLOv8 Architecture (YOLOv8), Sign Language (SL), Real-Time
Detection (RTD), Communication Barriers (CB), Hearing-Impaired People (HIP), Anchor-Free Predictions
(AFP).
Abstract: Most people find difficulty in social communication with hearing-impaired people because they have less
understanding of sign language. The hand gesture recognition technology translates the meanings of hand
motions by detecting fundamental body signals which emerge through hand signals. The systems deliver
necessary connectivity between educational institutions together with public service departments that operate
within working environments. The YOLOv8 architecture creates an accurate system for hand gesture
identification of English letters and numbers. YOLOv8, the latest version of the YOLO (You Only Look Once)
series, combines real-time object identification with excellent computational efficiency and precision. The
model structure includes three advanced segments that extract features from the backbone segment, then
aggregates information through the neck before performing exact localization and classification in the
detection head. The CSP (Cross Stage Partial) network backbone structure of the model minimizes operational
costs without compromising its high feature performance capability. The implementation of PANet (Path
Aggregation Network) in the neck segment establishes a superior method for feature movement until results
are achieved. The detection head uses anchor-free predictions to achieve both high speed and accuracy in its
output generation. The detection head provides precise results quickly because it employs anchor-free
prediction systems. The detection head achieves rapid and accurate results by making predictions that do not
depend on anchor points. Real-time hand movement detection functions as the core concept enabling this
technology to perform effectively when users need it for social communication. Through its YOLOv8
technology, the system addresses communication barriers that enable hearing-challenged people to experience
ordinary group conversations with public audiences without any obstacles.
1
INTRODUCTION
Most individuals fail to communicate effectively with
hard-of-hearing people because they lack knowledge
of sign language. Sign language recognition systems
concentrate on recognizing major hand motions to
interpret their messaging content. Mohammad
areeb, St al, 2022 Sign language recognition systems
function to fill communication gaps that occur during
school sessions, workplace interactions, and public
service occasions. The presented research develops a
hand gesture recognition system using YOLOv5
which achieves precise identification of English
letters and numbers. YOLOv5 stands out for its ideal
performance-quality ratio through a segmentable
system structure which includes backbone and neck
parts alongside detection head elements. The
backbone module uses CSP (Cross Stage Partial)
networks to perform efficient feature extraction, then
the neck section utilizes PANet (Path Aggregation
Network) for better feature aggregation. Anchor-
based detection methods enable the detection head to
predict bounding boxes as well as classifications. The
design enables time-sensitive hand gesture detection
which makes it useful for daily applications.
YOLOv5 operates with several drawbacks because it
creates difficulties when recognizing small objects
and generates slow inference times under selected
conditions along with its dependence on anchor-
based detection that raises processing complexity.
The current performance constraints can be overcome
by adopting YOLOv8 as the newest version of
YOLO. YOLOv8 provides valuable improvements
through anchor-free detection capabilities that
decrease complexity and boost detection speed. A
246
Nagarani, N., Abinandhan, S., Elangovan, C. and K., P. R. V.
Object Detection for Sign Language Recognition Using YOLOv8.
DOI: 10.5220/0013896100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
246-252
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

new backbone and neck architecture of this model
enables better aggregation of features, thus improving
detection accuracy for small objects. The simplified
architectural structure of YOLOv8 makes the system
more effective in handling system resource
limitations. Future models will enhance hand gesture
detection systems with YOLOv8 technology
developments, processing data more rapidly and
precisely, and to generate more trustworthy real-time
communication that supports inclusiveness in daily
activities.
2
RELATED WORKS
Escalera, et al., 2016 This deep learning-based system
helps hearing impaired people in emergency
situations. The authors demonstrate awareness of
communication obstacles experienced by this
community during critical situations requiring
essential speech-based warnings. A system has been
created to translate Indian Sign Language (ISL) into
spoken language or text for real-time emergency
responder communications.
C.-Y. Wang, Et al 2022, The proposed method
demonstrates a promising ability to fill
communication gaps for emergency situations
involving hearing-impaired people, yet involves
several constraints. The system performance suffers
because of unpredictable lighting conditions and
surrounding background objects as well as changes in
signing speed and manner. The system restricts its
detection capability to both regional sign language
variations and the need to identify new signs unless
trained. Any emergency deployment of this system
demands rigorous evaluation of system delays
together with reliability protocols which will protect
user privacy boundaries. The successful execution of
this project depends on building a system with
maximum security protocols along with universal
accessibility. Emergency communication safety for
hearing-impaired individuals shows significant
improvement through this work where the authors
overcome key challenges. Prolonged research
activities and developmental work must continue to
improve the system implementation for practical
deployment.
Aditi Deshpande, et al., 2023 The research
advancement and challenges into multimodal gesture
recognition try to decode human body movements
through audio and video, yet also use depth
information to understand gestures effectively.
Single-modality systems have proven insufficient, so
the paper argues for multimodal approaches.
Although there are still significant challenges to
overcome. Complex methods for effective data fusion
generate crucial elements because they need
approaches to deal with different types of data and
resolution levels.
There must be exact temporal alignment between
different modalities, although achieving this
synchronization remains challenging due to
mismatch variations. The analysis of multimodal data
requires advanced algorithms together with
appropriate hardware resources because this process
demands significant computational strength. Strong
resistance against noise, variations in lighting and
changes in viewpoint stands as a critical requirement.
The analysis of how individual modalities contribute
to final recognition results is needed to enhance
system quality and find bugs.
The paper emphasizes the need for advanced
evaluation techniques combined with wide-ranging
datasets to develop the study field. The paper
demonstrates how deep learning methods can combat
some recognition issues by performing automatic
representation learning and feature extraction.
Multimodal gesture recognition technology
encounters various challenges, although it brings
major opportunities to human-computer interaction
along with applications in robotic systems and
healthcare management.
K Amrutha, et al., 2021 A Sign Language
recognition system operates with a Convolutional
Neural Network (CNN) architecture for its
functioning. Real-time interaction between hearing-
impaired persons and everyone else is the goal of this
system, which works to close communication
breakdowns. The system chooses a monocular
camera to record video footage that enables sign
detection and classification of ten different ASL signs
through processing. Through its CNN architecture,
this system effectively finds essential features present
in video frames that include hand positions and both
positions and movements. The training and
validation process of the model operates on ASL sign
datasets, which delivers an accuracy rate of 98.53%
during training and 98.84% during validation. The
research focuses on the use of various datasets and
evaluation metrics found in the field and emphasizes
that robustness depends on training systems with
diverse large datasets. The authors show how deep
learning advancements, especially convolutional
neural networks (CNNs) boost hand gesture
recognition accuracy through their automatic
processing of raw image data features.
The evaluation emphasizes crucial barriers which
researchers face during present studies. The main
Object Detection for Sign Language Recognition Using YOLOv8
247

disadvantage is that the system depends on high-
quality cameras and consistent lighting, since poor
quality cameras combined with unstable lighting
limits the ability of the system to recognize gestures
effectively. Alongside the complexity limitation is
another problem regarding the high computational
demands of advanced techniques like deep learning
models that reduce their usability on smartphones and
other embedded systems because of their limited
processing resources.
Real-time recognition systems face operational
challenges when assessing hand movements because
they must handle complex hand dynamics, which
appear in backgrounds with cluttered images. The
review shows that system robustness becomes
challenging because camera images lose both hand
sections and fingers due to occlusion. The paper lays
out developmental barriers in system design for
building universal recognition algorithms, which
handle varying hand sizes and shapes from different
users, while programmers need to refine the
algorithms to achieve cross-user generalization. Hand
gesture recognition systems with computer vision
find many uses in different domains, however these
recognized system weaknesses need strategies to
develop usable robust systems.
3
METHODOLOGY
This system detects helmets in visual content through
the implementation of YOLOv8 object detection
model. The system follows a three-step process for its
operations.
3.1 Preprocessing
The YOLOv8 model receives its image or video data
where it undergoes preparation before analysis. The
preprocessing operations need data size manipulation
to specific formats and standardized color channel
refinements.
3.2 Feature Extraction Module
The system detects helmets in visual content through
its implementation of YOLOv8 object detection
model.
3.3 Helmet Detection
YOLOv8 model uses image or video data to initiate
preprocessing operations that optimize data before
analysis. During preprocessing operations, the two
primary actions include data size standardization for
standardized formats and color channel normalization
processes.
3.4 Preprocessing
Md Tanzil Shahriar, Huyue Li et al, 2020 Model
accuracy depends entirely on image preprocessing to
achieve successful implementation of different
scenarios.
3.4.1 Random Resizing and Cropping
The selected random part of the image receives
dimension adjustment until it matches the target
dimensions of 640x640 pixels. The model operates
efficiently with diverse hand gesture sizes and
positions due to training on varied data which
improves its operational performance. The
methodology prevents the model from creating
dependencies with specific image dimensions
because it enables sign letter and number recognition
across multiple situations.
3.4.2 Random Flipping
The system chooses segments from images before it
can perform a resize operation to reach one million
equilateral pixels. The training procedure enables the
model to excel at multitasking through an expansion
of various hand gesture dimensions by enhancing data
variety in training examples. Image dimension
dependencies are prevented by this method which
enables the models to detect sign letters and numbers
across different contexts.
3.5 Feature Extraction Module
Chien-Yao., et al. 2019 CSPDarknet50 design forms
the basic component of YOLOv8 by which the model
extracts feature from input images. Convolutional
Layers: Multiple filters within layers process input
images until the features get divided into textures and
patterns and edge detection occurs. Image features
evolve from simpler to advanced levels through
successive layers which creates detailed information
about the input. Pooling Layers: The image
processing maintains essential information as it
reduces the spatial dimensions of the feature maps.
The reduction helps stop overfitting while helping to
control computational complexity in the framework.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
248

3.6 Activation Functions
The integration of activation functions into deep
learning models allows these neural networks to
detect complex patterns through their ability to
introduce non-linear behavior, and ReLU and Leaky
ReLU are known for efficient training.
3.7 C2f Module
The C2f module improves feature map definitions
together with detection precision through integrating
different scale features.
3.8 Feature Pyramid Network (FPN)
Tsung-Yi Lin, et al., 2017 The FPN element serves as
a vital component which produces an integration of
features from higher resolution layers by adding them
to matching features from lower resolution layers.
Higher-level upsampled features join corresponding
lower-level features to produce better feature maps
which combine semantic data with spatial details. The
detection ability of small and large objects by the
model improves through the FPN through utilizing
data analysis.
3.9 Object Detection
Rejin Varghese., et al, 2024 The analytical process in
the last stage uses refined feature maps for detecting
and classifying objects. Bounding Boxes: The model
predicts all possible image objects present before the
final analysis stage. Each bounding box contains an
assigned confidence score to represent the likelihood
of including an object. The model calculates
probability estimates for every bounding box to
indicate the exact object type.
3.9.1 Bounding Box Prediction
YOLO predicts bounding boxes directly from images.
The bounding box is defined by four parameters: (bx,
by, bw, by), which represent the center coordinates
(bx, by), height (bh), and width (bw) of the bounding
box.
3.9.2 Bounding Box Parameters
For each cell in the grid, YOLOv8 predicts:
Center coordinates: bx, by
Width and height: bw, bh
The parameters are typically normalized relative to
the grid cell and the anchor box dimensions.
3.9.3 Objectness Score
YOLO also predicts an objectness score of Po, which
shows the probability that an object exists within a
predicted bounding box.
3.9.4 Class Probability
YOLO predicts the conditional class probabilities P
(Ci | Object) for each class “I” given that the object
exists in the bounding box.
3.9.5 Loss Function
This in YOLOv8 is a combination of multiple losses:
confidence loss, localization loss, and classification
loss.
3.9.6 Localization Loss
By quantifying the discrepancy between predicted
and actual bounding box coordinates, the localization
loss—typically a composite of Mean Squared Error
(MSE) for the box's center and a dimensional loss for
its width and height—guides object detection models
toward precise object localization.
𝐿
=
∑∑
1
𝑥
−𝑥
+
𝑦
−𝑦
+
𝑤
−
𝑤
+
ℎ
−
ℎ
(1)
3.9.7 Confidence Loss
This measures the error in the objectness score
prediction.
𝐿
=
∑∑
1
𝐶−𝐶
+𝜆
1
𝐶−𝐶
(2)
3.9.8 Classification Loss
The classification loss measures the error in the
predicted class probabilities.
𝐿
=
∑∑
1
𝑝
𝑐
log𝑝̂
𝑐
(3)
3.9.9 Total Loss
The total loss function is a weighted sum of the
localization, confidence, and classification losses.
ℒ𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙=𝜆
ℒ𝑙𝑜𝑐+ ℒ
+𝜆
ℒ𝑐𝑙𝑠 (4)
Object Detection for Sign Language Recognition Using YOLOv8
249
3.9.10 Non-Maximum Suppression
After gaining the predictions, YOLOv8 applies NMS
to remove redundant bounding boxes. NMS selects
the bounding boxes based on their objective score and
eliminates boxes with high overlap (Intersection over
Union, IoU) with selected boxes.
𝐼𝑜𝑈=
(5)
Only boxes with IoU less than a threshold are kept.
4
RESULTS
The results of the sign letter and number detection
project using YOLOv8 provide key insights into the
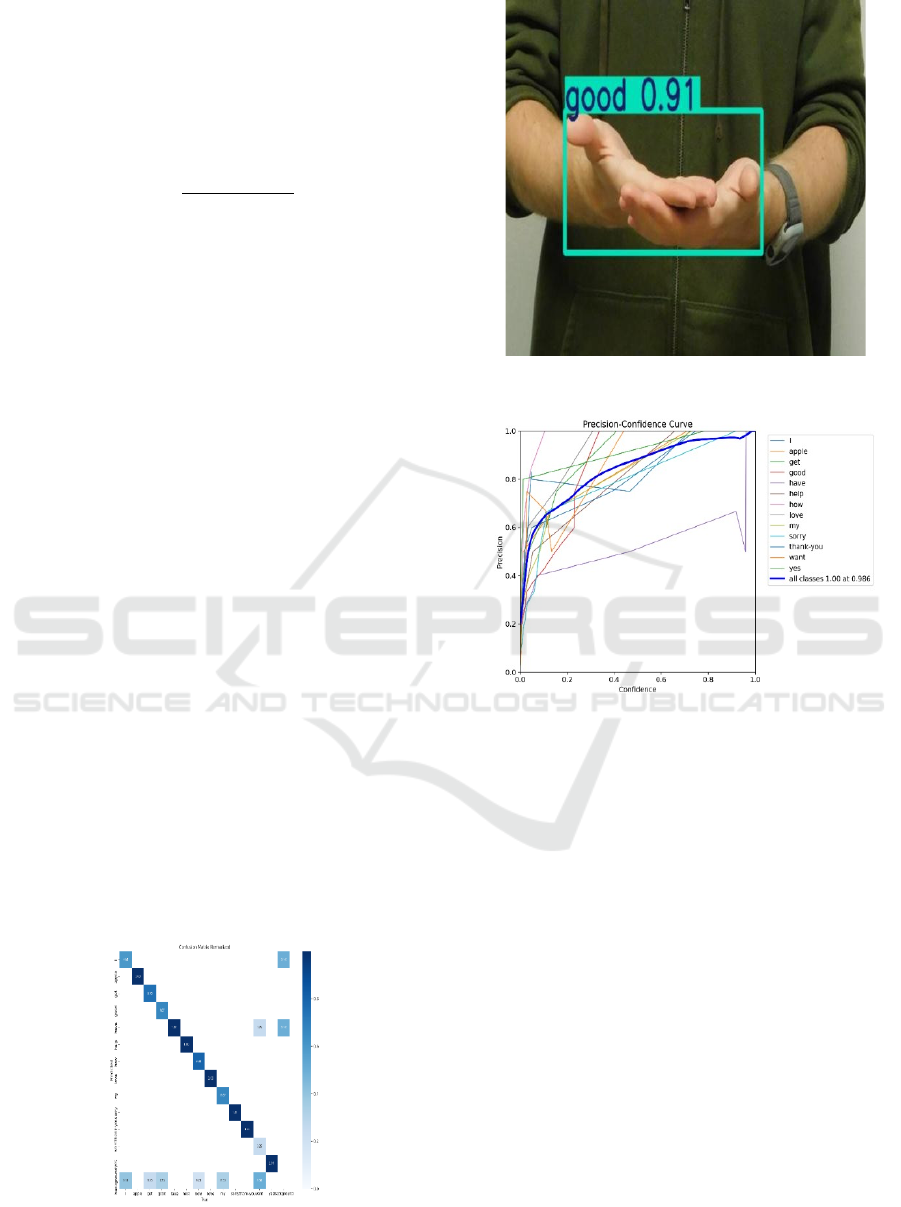
model's performance over five epochs. Figure 1
shows the Confusion Matrix. Each epoch's metrics
are meticulously recorded, showcasing the model's
progression in learning and generalizing. Training
Losses: Throughout the training process, all loss
components exhibited a consistent decline. for
example, the box loss dropped from 11647 in the first
epoch to 06593 by the fifth epoch. The classification
loss dropped significantly from 5.9412 to 1.2634,
indicating the model's growing capability to
correctly classify sign letters and numbers. The
distribution focal loss also improved, decreasing
from 1.7905 to 1.2985, reflecting enhanced precision
in bounding box localization. Figure 2 shows the
Example output. Validation Losses: The validation
losses show a similar trend, reinforcing that the
model
generalizes well to new data: The box loss
declined
from 1.1231 to 0.6244 over the epochs. The
validation
data yielded classification loss results of
3.4576 as
the starting value while the process ended
with a
value of 0.7643 and distribution focal loss
results
showed the same pattern with an initial value
of
2.0050
before reaching 1.4617. Figure 3 shows the
Figure 1: Confusion Matrix.
Figure 2: Example output.
Figure 3: Precision - Confidence Curve for words.
Precision – Confidence Curve for words. According
to precision and recall metrics the model showed
enhanced capabilities to identify genuine positives.
The model began with low precision that reached
0.9254 through five epochs while demonstrating
better accuracy for sign gesture detection. The model
achieved improved performance during the recall
increase ranging from 0.4311 to 0.8130 because it
better identified authentic motions. Mean Average
Precision (mAP): The mAP50 metric indicates better
detection precision because it showed an increase
from 0.3342 to 0.9885 thus demonstrating improved
accuracy at 50% threshold levels. Figure 4 shows the
F1 – Confidence Curve for Letters. The model
achieved better detection precision according to
mAP50 because it increased its scores from 0.3342
to
0.9885 when using a 50% Intersection over Union
(IoU) threshold. The mAP50-95 values progressed
from 0.2275 until reaching 0.8570 while
demonstrating steadiness over different IoU
thresholds. Interpretation: The YOLOv8 model
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
250
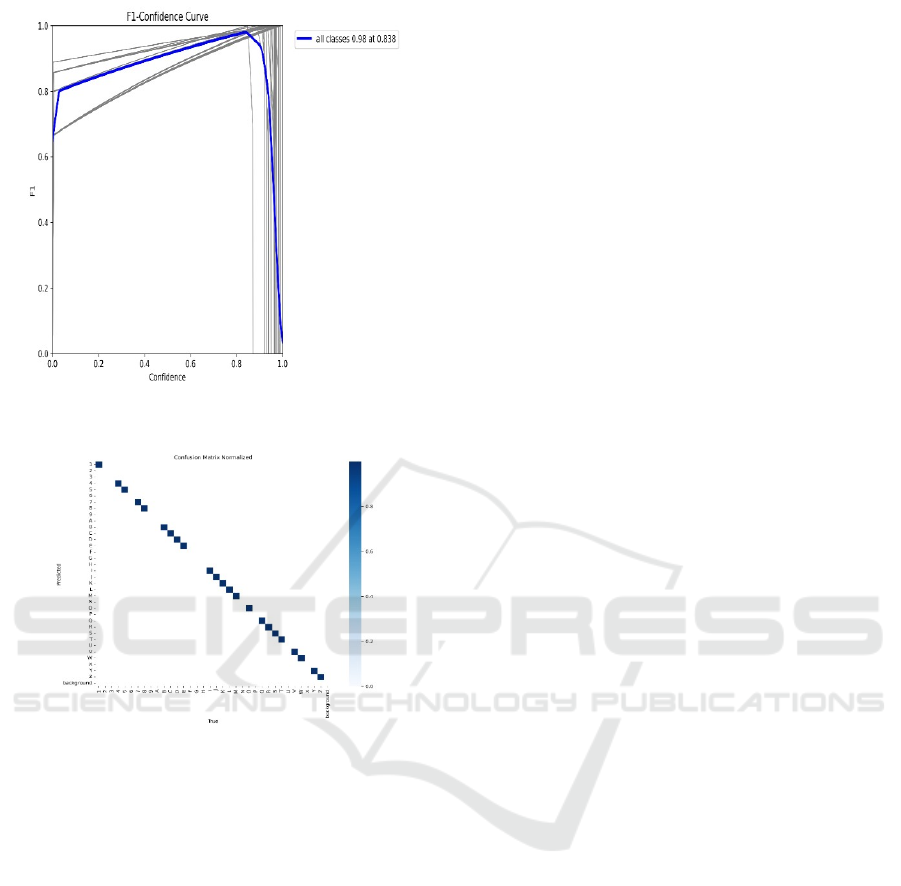
Figure 4: F1- Confidence Curve for Letters.
Figure 5: Confusion Matrix Normalized for Letters and
Numbers.
proves highly effective when recognizing sign letters
and numbers. The model demonstrates readiness for
real-time sign detection because its training and
validation losses decreased steadily while precision
and recall scores together with mAP scores
increased. YOLOv8 demonstrates capabilities to
develop an exact real-time system that allows
hearing-impaired people to overcome daily
communicational obstacles. Figure 5 shows the
Confusion Matrix Normalized for Letters and
Numbers.
5
CONCLUSIONS
A YOLOv8-based system for sign letter and number
detection showcased valuable understanding about
modern object detection strategies that enhance
communication abilities through implementation and
development. The application of YOLOv8
technology for sign letters detection and number
identification produced critical findings about
present-day detection procedures to improve
communication speed. The accomplishment of this
project involved creating a solid viable model which
precisely detected English letter and number gestures
in real time resulting in positive results. Throughout
the training YOLOv8 achieved notable progress in all
important performance metrics. Throughout training
both the training loss and validation loss numbers
continuously decreased which confirmed that the
model achieved good results on new data. As the
system shows improved ability in gesture localization
and classification accuracy, the focal loss values for
classification, box, and distribution decrease during
training. The model demonstrated better ability to
detect genuine positive results through Precision and
Recall metrics which improved steadily across every
epoch. The detection system demonstrates accurate
performance through its maintained mAP50 and
mAP50-95 scores which validate its ability to identify
objects at distinct intersection over union threshold
rates.
Malaga added image modifications that included
size changes and cutting and flipping methods to
improve training data collection results for gesture
recognition in varied dimensions and spatial layouts.
These procedures made the system ready to work
effectively across various real-world situations. The
impressive outcomes from the model do exist but
organizational challenges still persist. Further system
enhancement will come from addressing the
capability to handle occluded movements along with
fast hand actions and reduced lighting situations. The
problems of insufficient data diversity could be
solved in future updates by using advanced data
augmentation methods. The system creates
substantial opportunities to enhance various
communication access points. This system achieves
real-time sign letter and number recognition which
enables hearing-impaired individuals to improve their
communication effectiveness with nonsign language
speakers. The system shows potential uses in both
educational facilities and assistive technologies in
combination with automated systems which need
gesture recognition capabilities. The YOLOv8-based
detection system demonstrates strong efficiency and
accuracy for recognizing sign letters and numbers.
This technology retains the opportunity to generate an
inclusive society through enhanced communication
and mutual understanding among various
communities following additional operational
improvements.
Object Detection for Sign Language Recognition Using YOLOv8
251

REFERENCES
Aditi Deshpande, Ansh Shriwas, Vaishnavi Deshmukh,
Shubhangi Kale, Sign Language Recognition System
using CNN. (Jan 2023)
Ashok K. Sahoo, Gouri Sankar Mishra, Kiran Kumar
Ravulakollu, Sign Language Recognition: State of the
Art. (Feb 2014)
C.-Y. Wang, A. Bochkovskiy, and H.-Y. Mark Liao.
YOLOv7: Trainablebag-of-freebies sets new state-of-
the-art for real-time object detectors. (Feb 2022)
Chien-Yao Wang, Hong-Yuan Mark Liao, I-Hau Yeh, Yueh-
Hua Wu, Ping-Yang Chen, Jun-Wei Hsieh,CSPNet: A
New Backbone that can Enhance Learning Capability
of CNN. (Nov 2019)
Escalera, Athitsos, Guyon Challenges in multimodal
gesture recognition. (Feb. 2016)
Harshita Khubchandani, Karthick T, Sign Language
Recognition. (May 2023)
K Amrutha, P Prabu, ML Based Sign Language
Recognition System. (Feb 2021)
Md Tanzil Shahriar,Huyue Li,A Study of Image Pre-
processing for Faster Object Recognition. (Oct 2020)
Mohammad areeb, mohammad nadeem, faisal anwer.
Helping hearing-impaired in emergency situations: A
deep learning-based approach (Jan. 2022)
Rejin Varghese, Sambath M, YOLOv8: A Novel Object
Detection Algorithm with Enhanced Performance and
Robustness. (May 2024)
Sanjukta Sen, Shreya Narang, P. Gouthaman, Real-Time
Sign Language Recognition System. (Jan 2023)
Nirmala M, Sign Language Recognition Using Deep
Learning. (Dec 2022)
Shinde, Sign Language Recognition System using Machine
Learning. (oct 2023)
Tsung-Yi Lin, Piotr Dollár, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He,
Bharath Hariharan, Serge Belongie,Feature Pyramid
Networks for Object Detection. (Apr 2017)
Wanbo Li, Hang Pu, Ruijuan Wang, Sign Language
Recognition Based on Computer Vision. (Jun 2021)
Sakshi Bele, Anish Shinde, Kushal Sharma, Ashwini
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
252
