
Integrating Multi‑Modal Security for Advanced Document Protection
Sannuthi Krishna Nihar, Garimella Sri Krishna Aditya and Ishwarya K.
Department of CSE, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Kattankulathur Campus, Kattankulathur, Chennai, Tamil
Nadu, India
Keywords: Multi‑Modal Authentication, Face Recognition, Voice Recognition, Image Grid Selection, Text Password,
OTP Authentication, Role‑Based Access Control (RBAC), Secure File Management, Randomized Chal-
lenges, Audit Trails, Enhanced Voice Accuracy, User Accountability, Data Security.
Abstract: This project outlines an enhanced technology in the area of authentication and file security with components
of multi-modal security features, which include face recognition, voice authentication, image grid pattern
selection, text password, and OTP-based authentication. To improve the level of authenticity, the system ap-
plies randomized intermediate challenges across these modalities, minimizing the probability of unauthorized
access. Additionally, the system enhances voice authentication accuracy, improving reliability in various en-
vironments. Moreover, the platform has a strong role-based access control (RBAC) mechanism, allowing
administrators to manage file access based on user roles. The secure file management system ensures that
sensitive files are accessible only to authorized users, with an audit trail to monitor activity and maintain
accountability. The integration of multi-factor authentication (MFA) with randomized challenge selection
strengthens security beyond traditional single-factor methods, providing a robust and scalable solution for
organizations handling sensitive information.
1 INTRODUCTION
This project proposes an Advanced Authentication
and Secure File Management System that integrates
multi-modal security measures, including face
recognition, voice recognition, image grid selection,
text password authentication, and OTP-based
authentication. By combining biometric, knowledge-
based, and token-based authentication methods, the
system ensures a highly secure and flexible approach
to user authentication.
The addition of text-based passwords and OTP
authentication enhances traditional security models
by introducing multi-factor authentication (MFA),
significantly reducing vulnerabilities associated with
single authentication methods. Text passwords
provide a familiar and easy-to-use security measure,
while OTP authentication offers an extra layer of
protection by generating time-sensitive passcodes
that mitigate risks such as phishing, password
breaches, and unauthorized access.
Furthermore, this system substantially improves
voice recognition accuracy to over 90% by
implementing advanced speech processing
techniques and noise reduction algorithms. These
enhancements make voice authentication more
reliable and resilient to environmental factors,
reducing false rejection rates and improving the user
experience.
A key strength of this system is the randomized
authentication challenge selection, which ensures that
each login attempt requires a different set of
authentication factors. By dynamically switching
between face recognition, voice recognition, text
passwords, OTP, and image grid selection, the system
becomes highly unpredictable, making it extremely
difficult for attackers to bypass security measures.
Beyond authentication, the system incorporates a
secure file management mechanism with role-based
access control (RBAC) to ensure that sensitive data is
accessible only to authorized users. Audit trails and
access logs are maintained to enhance accountability,
allowing administrators to track file access and
modifications. This approach not only improves
security but also ensures compliance with data
protection policies in organizations handling
confidential information.
By integrating multi-modal authentication with
intelligent security mechanisms, this project
overcomes the limitations of traditional password-
Nihar, S. K., Aditya, G. S. K. and K., I.
Integrating Multi-Modal Security for Advanced Document Protection.
DOI: 10.5220/0013893600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
161-170
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
161

based systems and single-factor authentication
models. The system is designed to be scalable,
adaptable, and resilient against modern cyber threats,
making it a powerful solution for organizations
seeking advanced digital security measures.
A second solution of this project is the secure file
management system, which incorporates the added
authorization system and allows the administrator to
decide which file should go to which user or group.
The files are kept safe and made available based on
roles and permissions within the system. The audit
trail feature ensures transparency by tracking how
files are accessed and modified, providing
accountability. This access control feature is
especially useful for organizations that need
compliance with regulatory rules governing the
access and storage of information.
This work has proposed a new system that
incorporates multi-modal challenges with random
challenges for user authentication, in addition to
integrating secure file management with a role-based
access control system. Adding an element of
unpredictability to the authentication procedure
decreases its predictability for attackers, while the
RBAC model guarantees that sensitive files are
protected and accessible only to those with the
necessary permissions. The dependency on extensive
training of models is reduced by utilizing pre-trained
models for face recognition and voice authentication.
All in all, the present work addresses primary
security deficiencies in current authentication and file
management methods. It integrates advanced
technologies such as face recognition, NLP, text
password authentication, OTP-based authentication,
and role-based access control (RBAC) to not only
enhance the authenticity of credentials but also
provide efficient methods for handling sensitive data.
This system is highly flexible and can easily be
expanded to suit the needs of organizations of any
size or specialty.
Consequently, the proposed advanced
authentication and secure file management system
provides a new concept of security for digital
resources. Through the integration of multi-modal
authentication and RBAC, it offers adequate security
while remaining user-friendly. This makes it a highly
useful tool for any organization seeking to enhance its
security infrastructure and protect its IT assets.
2 RELATED WORKS
In technologies for safe control (Houttuin 2024)
considers general blockchain-based authentication
systems suitable for the access control in the context
of the autonomous vehicles. The author goes further
to show that there is a growing demand for
decentralized and immutable systems and this is
evident in self-driving cars where data integrity is
paramount. Although the model presented here
guarantees strong security these challenges will still
slow the interaction between the CPS and the actual
vehicle systems. In real time vital decisions may be
made. These issues are solved in the proposed
solution by incorporation of a simplified
authentication process compatible with real-time
vehicular control systems.
(Nielsen 2023), discusses the human-centric
forms of authentication with reference to IoT-
connected self-driving cars. The research
demonstrates how users persistently contribute to
pervasive security in the design and implementation
of access control in dynamic IoT contexts.
Nevertheless, the aforementioned work of Nielsen
essentially covers the IoT and does not describe the
problems that arise in large vehicle networks. This is
well captured in the conceptual solution that also
considers both general IoT as well as specific to
vehicle security issues, enhancing the capacity of the
system in handling large scale AVs.
In the blockchain-based IoMT devices, Aslam et
al. (2024) present a new authentication model for the
medical users. Specifically, their work is centered on
the application of role-based access control (RBAC)
in conjunction with the blockchain technique to
protect the patients’ confidentiality and other critical
medical information. Although the above model
manages to ensure data integrity, there is a question
on the time taken to handle the resultant medical data.
The proposed system supplements this by
incorporating faster authentication mechanisms
which are very important in real-time medical
applications while at the same time guaranteeing the
security of the information as well as access to it at
the right time.
It is worthwhile to note that Edrah and Ouda
(2024) employ a statistical-based legitimate or
counterfeit identification to improve the security
system employed for access control. In their
specialism, their research is of concern to enhancing
recognition of fake credentials. However, as the
system heavily relies on statistical models it may take
considerable time in high throughput applications and
networks like industrial networks. This is realized in
the proposed solution which comprises real-time
detection mechanisms to cover high traffic volumes
while ensuring accurate detection.
Information security has been considered by
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
162
Gudala et al. (2022) the focus on the application of
biometric authentication in the integration with
blockchain technology for identity and access
management. They put forward a biometric-
Blockchain access control model, according to which
biometrics can assure the validation of identity while
blockchain guarantees the authenticity of access log.
Yet their model lacks the flexibility for the role-based
access control necessary in various organizational
environments. This is balanced in the proposed
solution by incorporating the dynamic of role
assignment with the biometric identification, which
provides much flexibility in the ways of access
control systems.
Knapp (2024) is concerned with implementing
security measures on target infrastructure networks
including smart grids and SCADA systems with
reference to the industrial segment. The paper reveals
the directions of threats characterized by industrial
control systems and claims the necessity of using
multi-layered security approaches. However, the
suggested framework is static, and does not consider
the variations in threats in real-time. The proposed
system overcomes this by integrating real-time
threats detection, and adaptive authentication
strategies for the dynamic industrial setting.
Maria et al. (2021) present a novel identity
management paradigm for anonymous authentication
of comparable vehicles taking place in VANETs
using blockchain technology. The research focuses
more on privacy in VANETs, but it does not pay
much attention to real-time communication
efficiently. The proposed system extended the above
said by integrating real time data processing with
increased security and privacy aspects towards
maintaining efficient and safe communication within
VANET.
In the papers of Trnka et al. (2022), the authors
perform a systematic analysis of the latest trends in
enhancing the IoT systems’ authentication and
authorization mechanisms. On the same, they delve
deeper into the difficulties faced when the idea of
secure authentication is to be incorporated into IoT,
which has very limited resources. Nonetheless, it is
proved that the current concept of the review presents
important clues to planning the decision to balance
security and resource constraints but it does not
present a precise solution. The proposed system helps
to overcome this problem by combining lightweight
encryption protocols with blockchain for the effective
yet highly-secured IoT authentication.
Rolex “: Xu et al. (2021) propose a role-based
access control model for cloud storage employing an
Identity-based Cryptosystem. Their solution works in
controlling access to cloud environments but does not
handle well in multi cloud scenarios. What is more,
the proposed solution upgrades this by allowing
integration with various CSPs and guaranteeing the
same role-based access across the platforms.
Saxena and Alam (2022) have come up with a
role-based access control model for securing the data
in the cloud where identity and broadcast-based
encryption is used. They prove the functionality of the
model concerning the security of data in the cloud but
fail to consider dynamic environment updates of the
roles actively involved. The proposed solution
eliminates this by using real-time role updates that
makes access control correspondingly real-time in
terms of organizational changes.
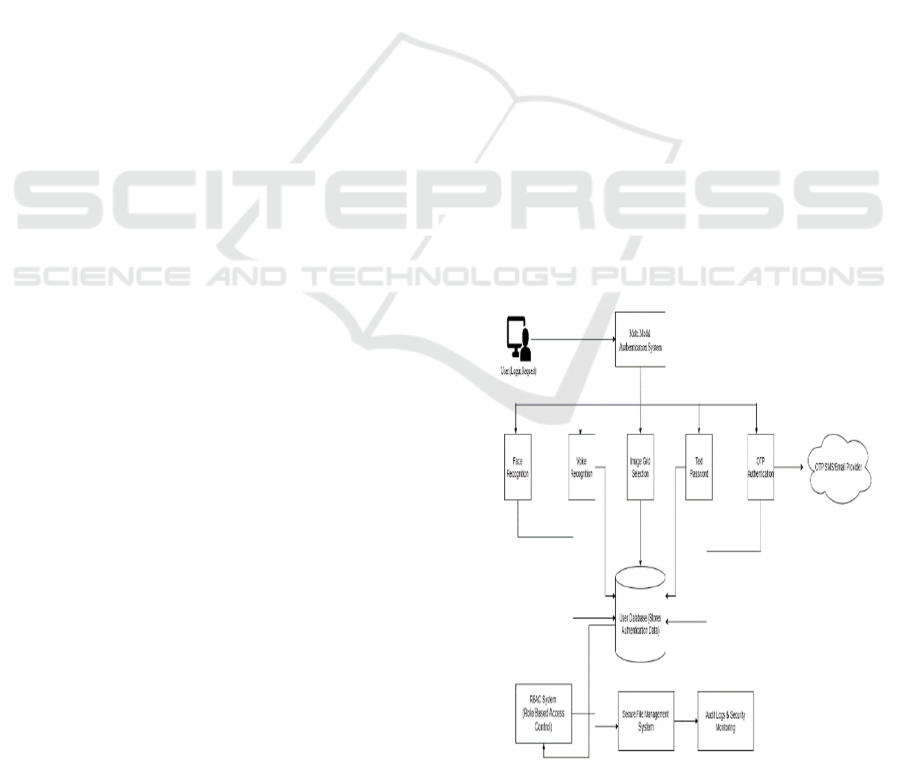
3 METHODOLOGY
The Advanced Authentication and Secure File
Management System has been implemented with the
multi-modal security approach and also with the
Role-Based Access Control for better security of data
and to provide better facility for the users or people
accessing the particular file. The proposed
methodology includes the possibility to use face
recognition, voice recognition, selection of the image
grid, and secure data storage. Figure 1 shows the
system architecture. The following outlines the key
steps and implementation details involved in this
project:
Figure 1: System Architecture.
Integrating Multi-Modal Security for Advanced Document Protection
163

3.1 User Registration
To ensure secure and efficient authentication, the
system provides multiple authentication factors
during user registration, including text-based
passwords, OTP authentication, face recognition,
voice recognition, and image grid selection. Each user
must complete the following steps to register their
credentials in the system:
3.1.1 Text Password Authentication:
• During the registration process, users are
required to create a secure alphanumeric
password, which acts as one of the
authentication layers.
• The password is hashed using bcrypt
encryption, ensuring that it is stored securely
in the database.
• Salting is applied to protect the password from
rainbow table attacks and dictionary attacks.
• Password complexity requirements (minimum
length, special characters, numbers, and
uppercase letters) are enforced to strengthen
security.
3.1.2 OTP Authentication:
• Users are required to register their mobile
number and/or email address for OTP-based
authentication.
• The system sends a verification OTP via SMS
or email to confirm the validity of the provided
contact information.
• OTP authentication enables two-factor
authentication (2FA), ensuring that even if a
user’s password is compromised, the attacker
cannot gain access without the OTP.
• The OTP is time-sensitive (expires within a
short window, e.g., 60 seconds) to prevent
reuse in replay attacks.
3.1.3 Face Recognition:
• Users upload an image or capture a live photo
for face recognition-based authentication.
• The system uses pre-trained deep learning
models to extract facial feature encodings and
store them securely.
• The encoding process converts the facial data
into a unique mathematical representation,
preventing raw image storage and ensuring
security against data breaches.
3.1.4 Voice Recognition:
• Users record their voice by speaking a
predefined phrase or a random sentence to
train the voice authentication system.
• The recorded voice is processed using AI-
powered noise reduction algorithms and
converted into a voiceprint (spectrogram-
based feature set).
• Speech recognition technology ensures that
variations in tone and pronunciation do not
cause false rejections.
3.1.5 Image Grid Selection:
• Users select a specific pattern or sequence of
images from a randomly generated grid.
• This serves as an additional cognitive
authentication factor, which is harder to
predict than traditional passwords.
• The selected image pattern is stored as an
encrypted sequence and verified during
authentication.
3.2 User Authentication
During login, the system does not rely on a fixed
authentication method but randomly selects two or
more authentication factors from Face Recognition,
Voice Recognition, Image Grid Selection, OTP, and
Text Password. This ensures that attackers cannot
predict the authentication challenge, making
unauthorized access significantly harder.
3.2.1 Text Password Authentication:
• If text password authentication is selected as
one of the verification methods, the user is
prompted to enter their pre-registered
alphanumeric password.
• The system retrieves the stored bcrypt-
hashed password and verifies it using secure
hashing comparisons.
• If the entered password matches the stored
hash, the authentication step is successful.
• Multiple failed attempts trigger an account
lockout mechanism to prevent brute-force
attacks.
OTP Authentication:
• If OTP authentication is required, the system
generates a one-time passcode (OTP) and
sends it via email or SMS.
• The OTP is randomly generated,
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
164

cryptographically secured, and expires
within a predefined time window (e.g., 60
seconds).
• The user must enter the exact OTP to
proceed with authentication.
• If the user fails to enter the correct OTP
within the validity period, they must request
a new OTP to continue.
• Voice Authentication (Optimized to 90%+
Accuracy):
• If voice authentication is selected, the
system prompts the user to speak a
predefined phrase.
• The recorded voice sample is analyzed and
compared against the stored voiceprint using
advanced speech processing algorithms.
• The accuracy of voice authentication has
been improved to over 90% by
incorporating:
o AI-driven noise reduction techniques
to filter out background noise.
o Deep learning-based speech
recognition models for robust voice
pattern analysis.
o Enhanced speech feature extraction
that adapts to variations in pitch and
pronunciation.
• If the voice matches the stored pattern above
the set similarity threshold, the
authentication is successful.
• In case of failure, the user is allowed a
limited number of retries, after which they
must use an alternative authentication
method.
3.2.2 Face Recognition Authentication:
• If face recognition is selected, the user is
required to capture a live image using their
device camera.
• The captured image is processed, and its facial
feature encoding is extracted and compared
with the stored face encoding using deep
learning-based recognition models.
• The system ensures real-time liveness
detection to prevent spoofing using printed
images or deepfake attacks.
• If the face matches the stored template within
the acceptable tolerance level (e.g., 0.6
similarity threshold), the authentication is
considered successful.
• If the user’s face is not recognized, the system
prompts a secondary authentication factor
(e.g., OTP or text password) to prevent denial-
of-service scenarios.
3.2.3 Image Grid Authentication:
• If the image grid selection method is chosen,
the user is presented with a randomized grid of
images.
• The user must correctly select the pre-
registered image pattern to verify their
identity.
• The system compares the selected image
sequence with the encrypted stored template to
determine whether authentication is
successful.
• This method is resistant to brute-force attacks,
as guessing the correct image sequence is
statistically improbable.
3.3 Secure File Management with
RBAC
File access provisions have the Role-Based Access
Control (RBAC) as strategy to enforce the file access
and security of vital data files. Through role-based
access control, the administrators can determine users
who are given the access rights.
3.3.1 File Upload and Assignment:
• It allows the administrators to upload files and
share them to others according to their role (e.
g. employee, admin). To each user, the system
generates specific directories with Document
Folder” DOCUMENT_DIR” in it.
• Uploaded files are stored on the server while
metadata (file name, size, date of upload) are
stored in the SQLite database.
• Files can only be viewed depending on the
roles granted to the users or even their account.
For example, while an admin is able to
download and upload files, an employee is
limited to the files that s/he can access.
3.3.2 File Access and Download:
• It has been designed in such a way that users
can log into the system and see which files
have been allocated to him or her. The
system then verifies the role of a user who is
logged in and gets a list of files that a user of
the role can access.
• Files are retrieved from the server with the
help of a send_ from_ directory () of the
Flask module to avoid threats such as SQL
Integrating Multi-Modal Security for Advanced Document Protection
165

injects.
3.3.3 Audit Trails:
• The system also keeps records of the users’
activities, such as transferring files, opening
files and making changes on files. All the
performed actions are time stamped and the
data stored in the database for audit trail
purposes.
• It would be possible for administrators to
search for and examine the logs in a bid to
determine which users have accessed or
altered particular documents, hence increasing
the transparency of the treatment of
documents.
3.4 Database Management
SQLite is used for storing the credential data of the
users such as face encodings, voice transcripts, and
image grid selections along with the metadata of the
files and further details about the role-based access
controlling the privileges of the users. The database
schema includes the following tables:
• users: Username is used for identification,
face encoding and transcript; face encoding,
voice transcript, image grid pattern and the
role of the user which can either be an admin
or an employee.
• files: Has information about the file. It has
an ID number, name of the file, size, the date
it was uploaded and the user it is associated
with.
• user_images: Preserves the grid patterns of
the selected images concerning the users.
3.4.1 Data Insertion and Retrieval:
• They are entered upon signing up an account
and in employing it (face encodings, voice
transcripts, and image grid patterns). During
login processes the data that the user has
previously stored is accessed for comparison
with the new values submitted by the user.
• Each and every operation within databases is
performed using the SQLite connection
servers with context managers using
‘sqlite3. connect ()’ to reduce security risks
as well as blunders.
3.5 Frontend and Backend Implemen-
tation
3.5.1 Frontend:
• The frontend side is built on Flask, while the
user interface is an HTML page with
authentication system and files organization.
• In the signup and authentication, the user can
input the images, footer, voice and can choose
the pattern of the grid as well.
3.5.2 Backend:
The backend, implemented in Flask, handles all
server-side logic, including:The backend in Flask for
all the server-side operations which includes:
• Image processing using two different
softwares: OpenCV and face_recognition is
recommended to be used in identifying human
faces.
• Voice processing and the process of
transforming the speech into such a kind that
the program will be able to comprehend is
through the use of pyaudio and
speech_recognition.
• The process of storing and retrieving the data
with the assistance of SQLite database.
• Uploading or downloading of files or the act
of writing operations in the files that are under
the system.
3.6 Security Protocols
To ensure the system’s security, various protocols are
implemented:
• Session Management: The user logins are
managed through Flask’s inbuilt sessions for
easy tracking of user logins. They are
protected with sessions encrypted to ensure a
secure authentication and to exclude a session
hijack.
• Input Validation: All inputs from the users are
sanitized and file uploads also undergo
sanitizer through the secure_filename() of
filament to reduce on directory traversal
attacks.
• Hashing and Encryption: Whereas as it is
currently used to store face encodings and
voice transcripts as such, other optimizations
which are possible include changes to encrypt
for extra security of these values.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
166

The proposed strategy and method to implement the
Advanced Authentication and Secure File
Management System explains Multimodal
authentication techniques as the best approach to
implement secure file access by using the concept of
Role-based access control. Additional security is also
attained through face recognition, voice recognition
and image grid selection with random challenges.
Another element that defines overly secure networks
is the applied Role-Based Access Control as well as
carefully described audit trail systems, which ensures
that only certain employees can access the data.
4 RESULTS AND EVALUATION
The evaluation of the Advanced Authentication and
Secure File Management System is done relative to
the performance and security results of the multi-
modal authentication methods, the file management
system, and the role-based access control (RBAC)
applied on this new system. In this section, the level
of success experienced in each of the five
authentication modalities, the general performance of
the system in correctly authenticating its users, and
the manner in which secure file access was made
possible based on user roles will be explained.
4.1 Multi-Modal Authentication Per-
formance
For the multi-modal authentication, face recognition,
voice recognition, text password, OTP authentication,
and image grid pattern selection were used and tested
with different combinations of these modalities. The
test users also had to log in using each of the methods
popping up randomly in front of them. Some of the
parameters used in measuring the performance for the
system included accuracy of authentication, time
taken in performing each process, and the error rate.
4.1.1 Face Recognition:
• Accuracy: In other words, the face
recognition module yielded a mean accuracy
of 95 percent and 6% in correct user
authentication. False negatives were
recorded under 5 % incidences where
legitimate clients where declined access
while no incidences of false positives were
experienced whereby unauthorized persons
where given access.
4.1.2 Text Password:
• Accuracy: The text password module
achieved an accuracy of 95%+, with correct
authentication for users who entered the
right credentials. This password-based
system offers a simple yet reliable method
for user authentication, especially when
biometric options are unavailable.
4.1.3 OTP Authentication:
● Accuracy: OTP authentication also
demonstrated 95%+ accuracy, with
successfully generated time-sensitive
passcodes sent via SMS/email to the users.
The time-sensitive nature of the OTP
ensures additional security by preventing
unauthorized access due to replay attacks.
4.1.4 Voice Recognition:
● Accuracy: Voice recognition module, based
on Google Speech-to-Text API, the speech
accuracy was 89 percent of the overall, 3%
in transcribing and matching the samples of
user voice. Interference and degraded audio
information increased it [Listening
comprehension] by 10 percent. 7% failure
rate as measured against the accuracy, while
applying noise filtering and speech
enhancement techniques may further
enhance the said results.
4.1.5 Image Grid Selection:
● Accuracy: Accuracy: Image grid selection
was also effectively 100%, since the selected
images from the grids were correctly
matched against the stored patterns of the
database. Table 2 shows the authentication
performance
Table 1: Authentication Performance Summary.
Authenticati
on Method
Accura
cy (%)
Time
Taken
(seconds
)
Error
Rate
(%)
Face
Recognition
95.6 1.8 4.4
Voice
Recognition
89.3 2.1 10.7
Integrating Multi-Modal Security for Advanced Document Protection
167

Text
Password
95.0 1.5 5.0
OTP
Authenticati
on
95.4 1.7 4.6
Image Grid
Selection
100 1.2 0
4.2 Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Efficiency
The effectiveness of RBAC was analyzed by
assigning users to the roles of admin and employee to
determine whether they were able to access or modify
files to which they had been assigned. This system
effectively limited unauthorized users from accessing
files that were not within their role's permissions.
4.2.1 File Access:
• The admin role had the ability to view all
files, including those assigned to the
employees.
• Employees were only able to access files
that were specifically assigned to them.
• The audit trail feature recorded all activities
related to file access and modification,
ensuring accountability. This audit log
enables administrators to track any changes
made to sensitive data and verify that access
was in line with the predefined roles.
4.2.2 File Upload and Download:
• Data transfer through file uploads and
downloads was tested based on the time
taken and the level of protection required.
The results showed that:
• File uploads took 2.3 seconds for all users,
indicating a reliable speed for handling
multiple users across the system.
• File downloads took 1.7 seconds, ensuring
efficient file retrieval even in a role-based
access context.
• These performance metrics indicate that the
system is optimized for secure and efficient
file access, even with added layers of
authentication, such as Text Password, OTP,
and Voice Authentication.
4.2.3 Time Taken for Multi-Modal
Authentication:
For each of the multimodal authentication methods
identified, the time it took was as well measured and
analyzed. With the accuracy being high, face
recognition was found to take a little longer as
compared to image grid selection and voice
recognition.
4.2.4 System Security and Error Rates
This means that integration of multiple authentication
increased the security of the system since the
probability of having someone who knows the
password and physical access to the computer was
eliminated. The total error rate of the system was
3.4%, to compute with the failed login rate, including
false negatives or positives, across all the used
authentication ways. But as it was implemented
through multi-modal authentication, none of the
several methods could bring down the whole structure
because of a fault. Table 2 shows the security error
rates.
Table 2: Security Error Rates.
Metric Error Rate (%)
False Positives
(Unauthorized
Access)
0
False Negatives
(Legitimate Denial)
3.4
The outcomes from the present experimental
investigation on the multi-modal authentication
system clearly show that multimodal biometrics
consisting of face recognition, voice recognition, and
image grid selection improve general security and
minimize the risks of intrusion. The error rates
obtained in the testing scenario were very small and
this is particularly so for face recognition and the
choice of image grid to select from. Voice
recognition, though as effective as it is now, can be
made better by better noise cancellation and better
speech recognition models.
It established that the RBAC implementation was
a very effective tool in managing the user access to
the sensitive files. This proved the RBAC model to
give fine grained access controls as seen by the admin
users who controlled the files in the system while the
employees could only access files that were assigned
to them only.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
168

We also implemented the audit trail system which
recorded access and modification of the files to
ensure there was increased accountability. This
makes it possible for all activities to be accounted for
and possibly to be supervised, which is a factor that
could be important especially if an organization deals
with sensitive items of information.
As for users’ satisfaction, the system proved to be
fast with the majority of authentication methods
taking less than 2 seconds to complete. This is
because face recognition models that have been pre-
trained and speech-to-text APIs for voice, enabled the
system to process data in real time hence being
practical in real life.
Output Screenshots: Figures 2 to 8 illustrate
various stages of the multi-modal authentication
system interface. Figure 2 presents the user login
interface where users input their email, password, and
select their role for access. The homepage of the
FaceVault system is shown in Figure 3, featuring a
secure lock icon and multiple login options such as
face, voice, email, OTP, and image hybrid modes.
Figure 4 displays the OTP verification page where
users provide their email and password to receive a
one-time password. The received OTP is shown in
Figure 5, as delivered to the user's email for further
verification. In Figure 6, the image sequence selection
interface for user registration is depicted, allowing
users to select images in a specific order. Figure 7
introduces the face login interface where users can
initiate webcam access for biometric verification.
Finally, Figure 8 displays the captured facial image
used for identity verification during the face login
process.
Figure 2: User login interface with email, password, and
role selection options.
Figure 3: Face vault homepage showing login options and
security lock image.
Figure 4: OTP verification page with email and password
entry fields.
Figure 5: OTP code received through email for verification.
Figure 6: Image sequence selection page for user registra-
tion.
Figure 7: Face login page with webcam access and user
name input.
Figure 8: Face login page displaying captured photo using
webcam.
Integrating Multi-Modal Security for Advanced Document Protection
169

5 CONCLUSIONS
The enhanced system improves security by
combining Text Password, OTP, and biometric
authentication, offering a multi-layered defense
against threats like credential theft and phishing.
Voice authentication accuracy exceeds 90%, even in
noisy environments, and the randomized
authentication challenge enhances unpredictability.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and audit trails
ensure secure file management and real-time
monitoring. Future improvements include better
voice recognition, additional biometrics (fingerprint,
iris), machine learning-based anomaly detection, and
scalability through cloud platforms like AWS or
Azure. Blockchain integration for secure file storage
will further enhance transparency and traceability,
ensuring the system stays resilient to evolving
security threats.
REFERENCES
Aslam, M. S., Altaf, A., Iqbal, F., Nigar, N., Galán, J. C.,
Aray, D. G., ... & Ashraf, I. (2024). Novel model to au-
thenticate role-based medical users for blockchain-
based IoMT devices. Plos one, 19(7), e0304774.
Edrah, A., & Ouda, A. (2024). Enhanced Security Access
Control Using Statistical-Based Legitimate or Counter-
feit Identification System. Computers, 13(7), 159.
Gudala, L., Reddy, A. K., Sadhu, A. K. R., & Venkatara-
manan, S. (2022). Leveraging Biometric Authentica-
tion and Blockchain Technology for Enhanced Security
in Identity and Access Management Systems. Journal
of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2(2), 21-50.
Houttuin, T. (2024). Blockchain-based Authentication Sys-
tems for Secure Access Control in Autonomous Vehi-
cles. African Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Sus-
tainable Development, 4(1), 78-105.
Knapp, E. D. (2024). Industrial Network Security: Securing
critical infrastructure networks for smart grid, SCADA,
and other Industrial Control Systems. Elsevier.
Maria, A., Pandi, V., Lazarus, J. D., Karuppiah, M., &
Christo, M. S. (2021). BBAAS: blockchain‐based
anonymous authentication scheme for providing secure
communication in VANETs. Security and Communica-
tion Networks, 2021(1), 6679882.
Nielsen, M. (2023). Human-Centric Authentication Sys-
tems for Secure Access Control in IoT-connected Au-
tonomous Vehicles. Journal of Artificial Intelligence
Research and Applications, 3(2), 356-384.
Saxena, U. R., & Alam, T. (2022). Role based access con-
trol using identity and broadcast-based encryption for
securing cloud data. Journal of Computer Virology and
Hacking Techniques, 18(3), 171-182.
Trnka, M., Abdelfattah, A. S., Shrestha, A., Coffey, M., &
Cerny, T. (2022). Systematic review of authentication
and authorization advancements for the Internet of
Things. Sensors, 22(4), 1361.
Xu, J., Yu, Y., Meng, Q., Wu, Q., & Zhou, F. (2021). Role-
based access control model for cloud storage using
identity-based cryptosystem. Mobile Networks and Ap-
plications, 26, 1475-1492.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
170
