
Smart Resource Optimization and Load Distribution in Cloud
Computing
E. Sai Koteswarao, G. Poorna Chandu and N. Kathirvel
Department of Information Technology, Vel Tech Rangarajan Dr. Sagunthala R&D Institute of Science and Technology,
Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Cloud Computing, Load Balancing, Resource Management, Task Scheduling, Virtual Machines (VMs),
Optimization Algorithms, Elastic Computing, Task Distribution.
Abstract: Cloud computing is a concept that incorporates virtualization, distributed computing, networking, software,
and web services. A cloud infrastructure consists of various components such as clients, data centers, and
distributed servers. Key advantages include fault tolerance, high availability, scalability, flexibility, reduced
user overhead, and cost-efficiency, along with on-demand services. At the core of these benefits is the design
of an efficient load balancing algorithm. The load could refer to CPU usage, memory, delay, or network load.
Load balancing is the process of distributing computational tasks among multiple nodes in a distributed system
to maximize resource utilization and minimize response times. It prevents some nodes from being overloaded
while others remain idle, ensuring an even workload distribution. The objective is to allow all processors or
nodes to handle approximately the same amount of work at any given time. Load balancing techniques are
broadly classified into three categories: sender-initiated, receiver-initiated, and hybrid methods that combine
both approaches. The goal is to develop an efficient load balancing algorithm that optimizes performance
factors such as latency and throughput, adapting to different cloud environments and application
requirements.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cloud computing has evolved into a reliable and
flexible model for delivering computing resources
and services online. As organizations increasingly
shift to cloud-based platforms to handle large-scale
workloads, efficient resource management has
become a crucial requirement. A key challenge in
cloud computing is task scheduling and load
balancing. Load balancing plays a vital role in
distributing workloads effectively across multiple
resources, preventing system congestion, and
improving overall performance. These strategies help
maintain system stability by ensuring an even
distribution of tasks, minimizing bottlenecks, and
maximizing resource utilization. On the other hand,
task scheduling is responsible for assigning
computing jobs to available resources in a way that
reduces delays, improves efficiency, and maintains an
equitable distribution of workloads.
This project focuses on designing and
implementing an effective load balancing algorithm
to optimize task scheduling in cloud computing
environments. By incorporating advanced scheduling
techniques and intelligent load distribution strategies,
the goal is to improve resource allocation, reduce
processing delays, and prevent both system overload
and resource underutilization. These enhancements
will contribute to better scalability, reliability, and
fault tolerance, making cloud infrastructures more
adaptable to changing workloads. This research aims
to support the development of efficient cloud systems
capable of handling large-scale, resource- intensive
applications in real-time.
Developing an effective load balancing algorithm
for cloud task scheduling is essential for optimizing
resource utilization, enhancing system performance,
and supporting scalability. These algorithms
efficiently allocate tasks across available resources,
reducing latency, preventing system overload, and
improving reliability. This project aims to advance
cloud computing by introducing solutions for
handling dynamic workloads and optimizing resource
distribution. The proposed methods help create cost-
effective, high-performance cloud infrastructures
capable of meeting growing user demands while
maintaining system stability and responsiveness.
Koteswarao, E. S., Chandu, G. P. and Kathirvel, N.
Smart Resource Optimization and Load Distribution in Cloud Computing.
DOI: 10.5220/0013893400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
143-148
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
143

2 RELATED WORKS
A dynamic load balancing algorithm functions
without relying on prior knowledge of job execution
or the overall system state. Instead, it makes real-time
decisions based on the system’s current workload. In
a distributed environment, all nodes participate in
executing the load balancing algorithm, ensuring that
workload distribution is a shared responsibility. The
coordination between nodes to achieve balanced
resource utilization can follow different approaches:
•
Cooperative
•
Non-cooperative.
In a cooperative approach, the nodes collaborate
towards a common goal, such as improving the
overall response time. In contrast, a non-cooperative
approach involves each node working independently
towards a goal that benefits only its local tasks, like
enhancing the response time of a specific task.
Dynamic load balancing algorithms with a
distributed nature often generate more messages than
non-distributed ones, as each node in the system
interacts with all other nodes. The advantage of this
approach is that even if some nodes fail, the load-
balancing process continues with minimal impact on
overall system performance. In non-distributed
systems, the load balancing task is handled by either
a single node or a group of nodes. Dynamic load
balancing algorithms in non- distributed systems can
be categorized into two types:
•
Centralized
•
Semi-distributed.
In a centralized system, load balancing is
controlled by a single node, referred to as the
central node. This node is responsible for
distributing workloads across the entire system, while
other nodes communicate only with it. In a semi-
distributed system, nodes are divided into clusters,
where each cluster follows a centralized load
balancing approach. A designated central node,
chosen through an election process, manages load
balancing within its cluster. The system-wide load
balancing is then coordinated by these central nodes.
Compared to other approaches, centralized dynamic
load balancing requires fewer messages for decision-
making, as only the central node handles
communication.
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
Cloud computing has transformed modern
technology
by providing flexible, scalable, and on-
demand computing resources. However, efficient
resource optimization and load distribution remain
critical challenges. Researchers have explored
various approaches to address these issues, including
machine learning-based optimization, heuristic
algorithms, and predictive models.
Aggarwal et al. developed a hybrid cloud
scheduling model that dynamically adjusts
scheduling priorities based on real-time cloud
conditions. Their study emphasized the importance of
adaptive scheduling techniques for improving load
balancing efficiency and minimizing processing
delays.
Brighten et al. developed a distributed P2P load
balancing model to improve performance in
decentralized cloud systems. Their research
demonstrated how decentralized scheduling
mechanisms enhance scalability and fault tolerance,
making them ideal for large-scale distributed
applications.
Chien et al. introduced a performance-driven load
balancing algorithm that improves response time by
evaluating service request completions. Their
research demonstrated how intelligent workload
distribution enhances system performance, making
cloud environments more reliable and scalable.
Lau et al. integrated fog computing into load
balancing to reduce latency and improve the Quality
of Service (QoS) for IoT applications. Their model
effectively distributes computational tasks between
edge and cloud devices, significantly reducing
response time and network congestion.
Shrivastava et al. proposed a GA-PSO hybrid
algorithm, combining Genetic Algorithms and
Particle Swarm Optimization to achieve better task
scheduling. Their research highlighted how hybrid
optimization techniques enhance adaptability and
efficiency in dynamic cloud environments.
Zhao et al. proposed a Bayesian clustering-
based model that optimizes task allocation, reducing
unnecessary computations and enhancing resource
utilization. Their approach integrates probability-
based selection with an intelligent clustering
mechanism, ensuring efficient task scheduling in
dynamic environments.
Smart resource optimization and load balancing in
cloud computing involve a multi-faceted approach,
incorporating heuristic algorithms, AI-driven
strategies, fog computing, energy-efficient models,
and blockchain security. Future research is expected
to focus on integrating these methods to develop
more adaptive and intelligent cloud resource
management systems.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
144

4 EXISTING SYSTEM
Round Robin: In this algorithm, tasks are distributed
among all processors, ensuring an even workload.
Each task is assigned to a processor in a round-robin
manner. The order of task allocation is maintained
locally, independent of assignments handled by
remote processors. Although processors have
identical capacities, variations in job execution times
can impact performance. At times, certain nodes may
experience heavy loads while others remain idle,
leading to imbalance. Round Robin algorithm is
frequently used in web servers where http requests are
of a like nature and scattered likewise.
• MIN-MIN load balance Algorithm: In this
approach, a list of tasks is maintained, and the
minimum completion time is calculated for all
available nodes. The task with the shortest
execution time is assigned to the most suitable
machine, making this method known as the
Min-Min load balancing algorithm. The task
queue and machine runtime are updated
accordingly. This algorithm performs efficiently
when there is a high number of short-duration
tasks.
• MIN-MAX Load balancing algorithm: A load-
balancing-based two-level task scheduling
method is analyzed to address users’ dynamic
requirements while op- timizing resource
utilization. Allocating tasks to virtual ma-
chines and mapping them to host resources
improves response times and enhances overall
system performance.
• Randomized: A randomized algorithm follows a
static approach, where a process is assigned to a
specific node n based on a predefined
probability p. In this algorithm, the task
allocation order for each processor remains
independent of assignments from remote
processors. It works effectively when tasks have
similar workloads. However, challenges arise
when computational complexities vary. Unlike
deterministic methods, randomized algorithms
follow a non-fixed approach, leading to efficient
execution. In contrast, the Round Robin
algorithm can intro- duce overhead due to the
management of the process queue.
5 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed system aims to enhance resource
utilization and load distribution in cloud computing
by incorporating intelligent scheduling, adaptive load
balancing, and energy- efficient strategies. It is
designed to optimize resource usage, reduce response
time, and improve Quality of Service (QoS) while
minimizing overall energy consumption.
5.1 Butterfly-Particle Swarm
Optimization
The Butterfly-Particle Swarm Optimization (BF-
PSO) Algorithm is a hybrid optimization technique
that combines butterfly foraging behavior with
Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) for efficient task
scheduling. Inspired by how butterflies use sensory
signals to locate food, the algorithm integrates local
and global search strategies to enhance solution
discovery. Butterflies move based on a local best (L-
best) value, learning from their own experience, and
a global best (G- best) value, influenced by the best
solution found in the population. Their positions are
updated using PSO equations, balancing exploration
and exploitation. The fitness function evaluates
solutions based on make span minimization, load
balancing, and resource utilization. BF-PSO
dynamically adapts to changing workloads, making it
highly efficient for cloud computing and distributed
systems. Its adaptive movement strategy prevents
premature convergence and enhances search
efficiency. Compared to traditional methods, it
achieves faster convergence and better task
distribution. By leveraging nature- inspired
principles, BF-PSO optimizes scheduling for updated
performance and reduced execution time.
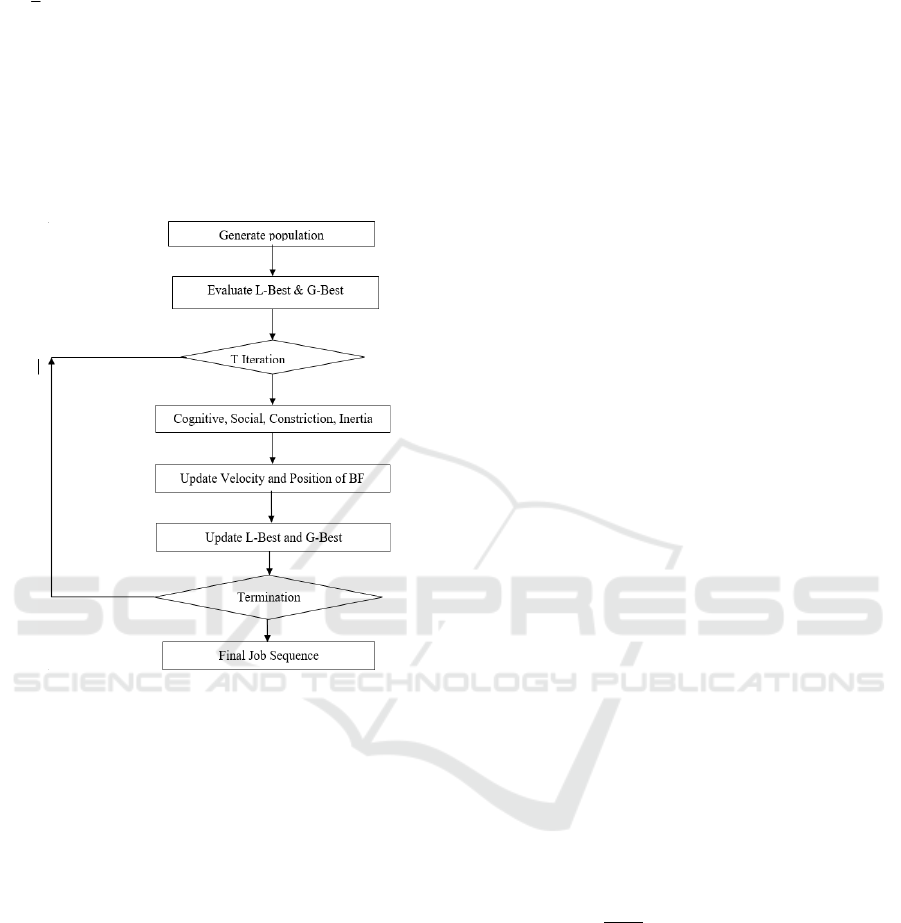
Figure 1
shows the block diagram of BF-PSO algorithm.
Velocity update equation in PSO is:
𝑉
ω𝑉
𝐶
𝑟
𝐿
𝑋
𝐶
𝑟
𝐺
𝑋
(1)
Where:
•
𝑉
is velocity of butterfly
i
at iteration
t
.
•
𝑋
is the position of butterfly
i
at iteration
t
.
•
w is the inertia weight, controlling the
influence of
previous velocity.
•
C
1
, C
2
are acceleration coefficients for local and
global learning.
•
r
1
, r
2
are random values in the range [0, 1].
•
L
•
•
Best
i
is the best solution found by an
individual butterfly.
•
G
Smart Resource Optimization and Load Distribution in Cloud Computing
145
•
•
Best
is the best solution found in the entire
population.
Fitness Function for Load Balancing:
𝐹
𝑚𝑎𝑥𝑇𝑖,
𝑖
1,2,...,𝑛
(2)
•
T
i
is the execution time of job i.
•
The objective is to minimize F to achieve
efficient scheduling.
Figure 1: Block Diagram of BF-PSO Algorithm.
5.2 Random Forest Decision Trees
Random Forest is a machine learning technique that
constructs multiple decision trees and aggregates
their outputs to enhance prediction accuracy and
model stability. It utilizes bootstrap aggregating
(bagging), training each tree on random data subsets.
Furthermore, it selects a random set of features at
each split, minimizing tree correlation. A random
subset features is chosen at each split, reducing
correlation among the trees. For classification tasks,
Random Forest predicts the final output based on
majority voting, while for regression, it averages the
predictions of all trees. This approach helps prevent
overfitting and improves generalization on unseen
data. The algorithm performs well on large datasets,
handles missing values effectively, and is resistant to
noise. Additionally, it evaluates feature importance,
helping to identify the influence of variables on
predictions. With its high stability and accuracy,
Random Forest is extensively applied in fields such
as healthcare, finance, and image recognition.
5.3 Energy-Efficient Resource
Management
Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS)
techniques will be implemented to reduce power
consumption in cloud data centers. Virtual Machine
(VM) migration strategies will optimize energy usage
by consolidating low-utilization VMs and shutting
down idle servers.
5.4 Hybrid Load Balancing Model
A Hybrid Load Balancing Model is an approach used
in distributed and cloud computing to effectively
allocate workloads, it distributes workloads across
multiple servers or virtual machines to maximize
performance and resource efficiency. This approach
leverages the advantages of both static and dynamic
load balancing and strategies to achieve optimal
performance, minimize response time, and prevent
server overloading. In a hybrid model, static load
balancing is used for initial workload distribution
based on predefined rules, while dynamic load
balancing continuously monitors system performance
and reallocates tasks based on real-time conditions.
This approach improves resource utilization, ensures
fault tolerance, and adapts to workload fluctuations
effectively.
By combining various algorithms like Round
Robin, Least Connections, and AI-based techniques,
the hybrid model improves efficiency over
conventional methods. It is extensively applied in
cloud computing, web servers, and distributed
systems. And high-performance computing systems
to ensure seamless task execution and optimized
resource management.
Mathematical Representation of Hybrid Load
Balancing:
The load factor for each server is calculated as:
𝐿𝐹
(3)
where:
–
LF
i
is the Load Factor of server
i
.
–
C
i
represents the current workload (active
connec- tions or tasks).
–
W
i
is the newly assigned workload.
–
P
i
denotes the processing capacity of server i.
The server selection for task allocation is determined
by:
𝑆argmin 𝐿𝐹
(4)
This means the server with the lowest load factor
is selected for the next task.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
146
6 METHODOLOGY
6.1 Task Detection and Classification
The task detection module is responsible for
identifying incoming computational tasks and
categorizing them based on their resource
requirements. The classification process includes the
following steps:
CV2 (OpenCV) Module: Used for data
preprocessing, feature extraction, and visual
representation of incoming tasks.
TensorFlow Module: Utilizes deep learning models
for unique classification based on task complexity.
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Recurrent
Neural Network (RNN): Used to classify tasks
dynamically.
Centroid Concept in Deep Learning: Determines
task parameters such as CPU usage, memory
consumption, and execution time, assigning tasks to
suitable processing units Tasks are categorized
according to resource demands and execution
priority using a cascade classifier in OpenCV. This
classifier evaluates task features and assigns labels
based on predefined categories.
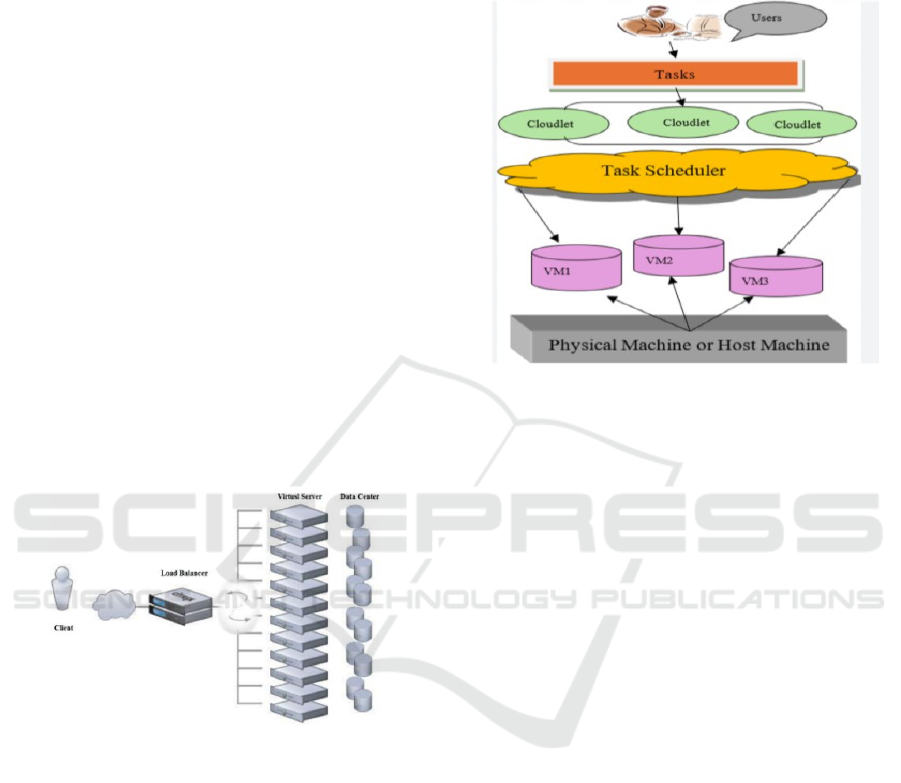
Figure 2: Load Balancer.
Figure 2 shows the picture visually represents the
load balancing process in cloud computing, where
tasks from multiple employees are efficiently
distributed across multiple cloud servers to optimize
performance.
6.2 Task Load Estimation
The
computational
load
of
each
task
is
estimated
by analyzing resource consumption (CPU, memory,
execution time, etc.). Figure 3 shows the task
scheduling in cloud computing. The process includes:
•
Creating a data table containing task profiles with
various execution demands.
•
Grouping tasks with similar execution times
under Category A, while tasks with varying CPU
and memory needs are further sub categorized.
•
Using a predictive machine learning model to
forecast future loads and optimize resource
distribution dynamically.
Figure 3: Task Scheduling in Cloud Computing.
6.3 Dynamic Task Scheduling and
Load Balancing
A combined scheduling method is utilized to
effectively allocate tasks across virtual machines
(VMs) and physical servers, ensuring balanced
workload distribution and optimal resource
utilization:
•
Reinforcement Learning-Based Scheduling:
Allocates tasks dynamically based on real-time
system load.
•
Priority-Based Scheduling: High-priority tasks
are executed first to minimize response time.
•
Weighted Least Connection Algorithm: Ensures
equal load distribution across processing nodes.
•
Auto-Scaling Mechanism: Dynamically allocates
or deallocates resources depending on workload
fluctuations.
7 FUTURE WORK
The current study introduces a machine learning-
based dynamic load balancing approach using neural
network training for job scheduling. However, there
are still opportunities for improvement. One major
area for future enhancement is the consideration of
process internal steps, which were not addressed in
this study. By analyzing and optimizing these steps,
we can further refine task allocation and improve
execution efficiency.
Smart Resource Optimization and Load Distribution in Cloud Computing
147

Another critical area for development is reducing
execution time. While incorporating machine
learning improves scheduling efficiency, it also
increases computational overhead. Future research
can focus on optimizing the learning process to
minimize execution delays while maintaining
accuracy. Additionally, exploring alternative
clustering approaches could enhance prediction
accuracy, as genetic algorithms are inherently
stochastic and may introduce variability in scheduling
results.
Additionally, Edge-Cloud Hybrid Load Balancing
could be further developed to improve real-time
processing capabilities, particularly for IoT and smart
applications. By leveraging AI- driven load
distribution between edge, fog, and cloud layers,
network congestion can be minimized, and
computational efficiency can be enhanced. This
approach would allow for better resource allocation
in latency-sensitive applications.
In conclusion, the future of Smart Resource
Optimization and Load Distribution in cloud lies in
convergence of quantum computing, federated
learning, edge-cloud collaboration, AI-driven
automation, blockchain security, and sustainable
computing practices. By advancing these
technologies, cloud computing can become more
intelligent, secure, and energy- efficient, meeting the
growing demands of modern applications.
8 CONCLUSIONS
The rapid growth of digital applications has
significantly increased the computational load on
cloud servers. Effective load balancing methods are
crucial for distributing workloads efficiently,
maximizing resource utilization, and minimizing
execution time. This study introduced a hybrid model
combining the BF-PSO algorithm with Random
Forest decision trees for dynamic job scheduling. By
incorporating the cognitive and social behaviors of
butterflies into the PSO framework, task allocation
was optimized, and execution efficiency was
enhanced.
Overall, this study highlights the effectiveness of
combining heuristic algorithms with machine
learning techniques for cloud-based job scheduling.
Future work can focus on integrating parallel
processing techniques, real-time adaptive scheduling,
and alternative deep learning models to further
optimize performance in large-scale distributed
computing environments.
REFERENCES
Chien, N. K., Son, N. H., Loc, H. D. (2020). ”Load
Balancing Algorithm Based on Estimating Finish Time
of Services in Cloud Computing,” ICACT, pp. 228-233.
Gao, R., Wu, J. (2021). ”Dynamic Load Balancing Strategy
for Cloud Computing with Ant Colony
Optimization,” Future Internet, doi:10.3390/fi70404
65.
Garg, S., Kumar, R., Chauhan, H. (2021). ”Efficient
Utilization of Virtual Machines in Cloud Computing
using Synchronized Throttled Load Balancing,” 1st
International Conference on Next Generation
Computing Technologies (NGCT-2021), pp. 77-80.
Kruekaew, B., Kimpan, W. (2023). ”Multi-objective Task
Scheduling Optimization for Load Balancing in Cloud
Computing Environment Using Hybrid Artificial Bee
Colony Algorithm with Reinforcement Learning,”
IEEE Access, 10:17803–17818.
Praditha, V. S., et al. (2023). ”A Systematic Review on
Round Robin as Task Scheduling Algorithms in Cloud
Computing,” Proceedings of the 6th International
Conference on Information and Communications
Technology (ICOIACT 2023), pp. 516–521.
Sharif, Z., Tang, L. J., Ayaz, M., Yahya, M., Pitafi, S.
(2023). ”Priority- Based Task Scheduling and Resource
Allocation in Edge Computing for Health Monitoring
System,” Journal of King Saud University - Computer
and Information Sciences, 35(2):544–559.
Yakhchi, S., Ghafari, S., Yakhchi, M., Fazeli, M.,
Patooghy, A. (2022). ”ICA-MMT: A Load Balancing
Method in Cloud Computing Environment,” IEEE
Transactions on Cloud Computing.
Yu, L., Chen, L., Cai, Z., Shen, H., Liang, Y., Pan, Y.
(2021). ”Stochastic Load Balancing for Virtual
Resource Management in Datacenters,” IEEE
Transactions on Cloud Computing.
Zhao, J., Yang, K., Wei, X., Ding, Y., Hu, L., Xu, G.
(2020). ”A Heuristic Clustering-Based Task
Deployment Approach for Load Balancing Using
Bayes Theorem in Cloud Environment,” IEEE
Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems.
Zhou X et al (2022) Intelligent small object detection for
digital twin in smart manufacturing with industrial
cyber-physical systems. IEEE Trans Ind Inform
18(2):1377–1386.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
148
