
Real‑Time ECG Monitoring System Using AD8232 Sensor and
Arduino UNO for Biomedical Applications
B. A. V. N. Hasini
1
, Mekala Varun
2
, N. V. S. Sanjana
2
, Abburi Sai Keerthi
1
,
Sai Mani Deepika Somayajula
2
and Gayathri Ramaswamy
2
1
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Bengaluru‑560035,
Karnataka, India
2
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Bengaluru‑560035, Karnataka, India
Keywords: ECG Monitoring, AD8232 Sensor, Arduino UNO, Real‑Time Signal Processing, Biomedical Signal
Acquisition, Cardiovascular Health, Noise Filtering, Wearable Health Monitoring.
Abstract: The increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases necessitates the development of accessible and cost-
effective solutions for continuous electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring. This study presents a real-time ECG
monitoring system utilizing the AD8232 ECG sensor interfaced with an Arduino UNO microcontroller to
measure and analyze the electrical activity of the heart. The AD8232 sensor, equipped with integrated signal
conditioning capabilities, extracts, amplifies, and filters bio-potential signals while mitigating noise
interference, ensuring accurate ECG readings. The Arduino UNO serves as the primary processing unit,
facilitating data acquisition and transmission for real-time visualization. The ECG signal is displayed using a
serial plotter or the Processing IDE, enabling immediate observation and analysis. The hardware
implementation involves a structured integration of the AD8232 sensor with the Arduino UNO, accompanied
by a comprehensive circuit diagram for ease of replication. This system provides a reliable and cost-efficient
approach to real-time ECG monitoring, offering potential applications in remote healthcare and early cardiac
anomaly detection.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are accountable for
some of the major causes of death in the world and
are a main hindrance to public health. The covert
character of the diseases necessitates that they be
continuously monitored and diagnosed early to allow
timely intervention and improved patient outcomes.
As the prevalence of cardiac diseases increases, so
does the need for novel and lower-cost methods of
real-time monitoring of cardiac electrical activity.
Standard electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring
methods are largely limited to clinical settings, which
limits accessibility and results in a lag in detection of
potential abnormalities.
The Wireless ECG Monitoring System,
developed employing the AD8232 Sensor interfaced
with the Arduino UNO, meets this fundamental
requirement with the help of contemporary electronic
parts to provide an economical, convenient, and
accessible solution for live electrocardiogram
monitoring. The system attempts to balance
traditional healthcare practices and emerging
technological innovations, thereby ensuring
continuous monitoring accessible to various socio-
economic classes. This is congruent with the overall
objective of encouraging preventive healthcare
practices and combating the incidence of
cardiovascular diseases.
At the center of the system is the AD8232 ECG
sensor, a small and versatile chip that is capable of
capturing, amplifying, and filtering the heart
biopotential signals. The sensor is paired with the
Arduino UNO microcontroller, which amplifies and
sends the signals for graphical representation. The
ECG signals are visible in real time by the users on a
serial plotter or the Processing IDE, which provides
an easyto-use interface for heart activity analysis.
Furthermore, the wireless design of the system
greatly enhances its portability, making remote
monitoring feasible in many settings, from home
health care to community health care projects.
Hasini, B. A. V. N., Varun, M., Sanjana, N. V. S., Keerthi, A. S., Somayajula, S. M. D. and Ramaswamy, G.
Real-Time ECG Monitoring System Using AD8232 Sensor and Arduino UNO for Biomedical Applications.
DOI: 10.5220/0013892900004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
113-118
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
113

Aside from its technological innovation, the
system serves the interests of society since it enables
individuals to take an active role in the management
of their cardiovascular health. Continuous monitoring
that enables the identification of abnormalities early
on can greatly minimize the risks of heart diseases
and enable timely medical intervention. The cost-
effectiveness and reproducibility of the system make
its principle a suitable solution for mass application,
especially in developing regions. By integrating real-
time ECG monitoring with wireless communication,
this system is a paradigm shift in healthcare from
reactive treatment to proactive health maintenance.
Not only does it improve patient autonomy, but it
helps towards the larger vision of accessible and
preventive healthcare for everyone.
2 RELATED WORKS
Sangeethalakshmi K. et al. 2023 develop an IoT-
based realtime health monitoring system.
Methodology uses an ESP32, sensors, a mobile app,
and GSM for continuous monitoring. Results ensure
reliable patient management by healthcare
professionals. Future work includes advanced
sensors, better UI, and scalability.
Sadad et al. 2023 proposed an efficient ECG
image classification using a lightweight CNN with an
attention module and IoT. Results show high
accuracy with reduced computation, improving real-
time processing. Future work includes advanced
attention mechanisms and expanding the IoT
framework.
Xu et al. 2020 introduced a framework for ECG,
utilizing small, capable devices for sensing,
processing, and communicating. Integrates sensors
and embedding devices for secure data transmission.
Shows the feasibility of using IoT for secure and
efficient ECG monitoring. Future work could focus
on enhancing security measures and improving
scalability.
Yeh et al. 2021 integrated IoT-based ECG
monitoring with deep neural networks for remote
healthcare. Results showed improved accuracy and
efficiency in heart condition classification. Future
work aims to enhance robustness with diverse data
and advanced algorithms.
Hasan et al. 2020 introduced an ECG device using
Blynk app for heart disease diagnosis. It enables real-
time ECG data collection, transmission, and alerts for
abnormalities. Future work includes advanced ML for
predictive analytics and monitoring more vital signs.
Obaidur et al. 2022 developed ECG device for
rural healthcare in Bangladesh. It uses IoT sensors,
microcontrollers, and cloud computing for remote
heart monitoring. Future work includes adding health
parameters, improving security, and expanding
coverage.
Gawsalyan et al. 2022 introduced ANNet, real-
time detection in wearables of IOT. Using LSTM and
MLP, it ensures power-efficient processing of ECG
features. Future work aims to improve robustness to
artifacts and adaptability across demographics.
Morello et al. 2022 developed an IoT-based ECG
monitoring system for cardiac diagnosis in smart
cities. It demonstrated effective real-time detection of
cardiac issues. Future work includes improving
accuracy, scalability, and integrating machine
learning for better diagnostics.
O. Ankireddypalli et al. 2024 present a
piezoelectric-powered smart irrigation system for
urban sustainability. Footstep energy powers
irrigation based on real-time soil moisture data,
reducing water use by 30%. The system ensures
reliable automation, and future enhancements include
cloud integration and machine learning for efficiency.
Adithi et al. 2019 develop a low-cost robotic
mapping system using an ultrasonic sensor. The robot
scans a 180-degree area and plots real-time radar
maps. It efficiently detects motion via Bluetooth
control. Future work includes GPS tracking and
wireless communication.
M.Shyam et al. 2024 presented an health
monitoring system wearables. It collects and
transmits real-time vital signs securely. Results
confirm accurate monitoring. Future work focuses on
enhanced security and remote care.
Pradeep et al. 2017 propose an IoT-based
sustainable water management system for rural areas.
They analyze water scarcity issues in Gudipadu
Cheruvu and design an automated distribution and
storage system. The results demonstrate effective
regulation of water usage. Future improvements
include enhanced scalability and real-time
monitoring.
M.Tejaswi et al. 2023 discuss the implementation
of IoT-based precision agriculture for optimizing
farming operations. They use a NodeMCU, DHT11,
and soil moisture sensor to develop an automated
watering system. The results show improved water
management and increased crop yields. Future
enhancements include advanced AI-driven analytics
for better decision-making.
Ramaswamy et al. 2023 present a brain tumor
detection model using a modified Link-Net with SE-
ResNet152, achieving 99.2% accuracy. Future work
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
114
focuses on improving feature fusion and integrating
additional pre-trained models.
Ramaswamy et al. 2022 also propose an
Optimized Gradient Boosting model for Type-2
Diabetes Mellitus detection, achieving 94.5%
accuracy. Future improvements include additional
clinical features and advanced ensemble techniques.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Components Used
The implementation of the Wireless ECG Monitoring
System utilizes the following hardware components
(table 1):
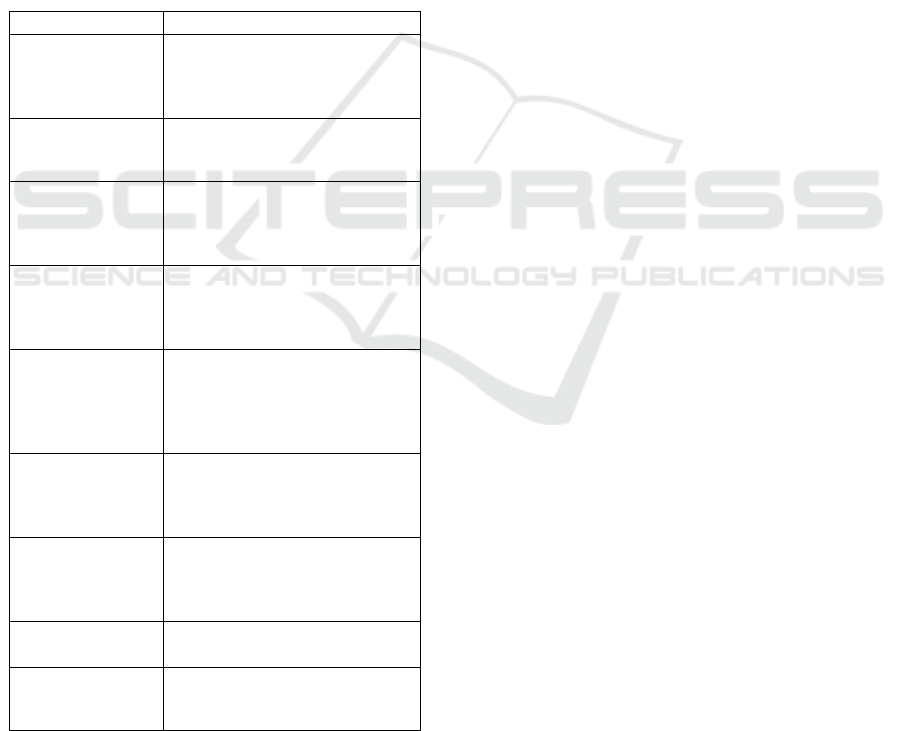
Table 1: Components Used.
Components Description
Arduino UNO A microcontroller board based
on ATmega328P, used for
reading sensor data and
p
rocessin
g
si
g
nals.
USB Power Cable Provides power supply to the
Arduino board from a computer
or ada
p
ter.
Pulse Sensor Optical sensor that detects
heartbeat by measuring blood
flow variations through green
li
g
ht absor
p
tion.
AD8232 Heart
Rate Monitor
An analog front-end module that
extracts, amplifies, and filters
ECG signals for accurate heart
activity monitoring.
LM35
Temperature
Sensor
A precision temperature sensor
that outputs a voltage
proportional to temperature in
°C, used for body temperature
measurement.
16×2 LCD
Display
A character-based display used
to show ECG readings, heart rate
(BPM), and temperature in real
time.
Connecting Wires Essential for establishing
connections between various
components and the Arduino
b
oard.
Potentiometer Used to adjust the contrast of the
LCD display for better visibility.
LED Provides visual indications, such
as power status or alerts for
abnormal ECG readings.
3.2 Software Used
The system employs the following software tools for
coding, visualization, and data processing:
• Arduino IDE 2.0.3 – Used for coding,
editing, and uploading the program onto the
Arduino microcontroller.
• Processing IDE – Employed for graphical
user interface (GUI) visualization of the
ECG signals.
3.3 Technical Aspects
• Pulse Sensor: The Pulse Sensor works by
emitting green light (550 nm) onto the user’s
finger and detecting the level of reflected
light using a photo sensor. Green light is
absorbed by oxygenated hemoglobin in
arterial blood, allowing pulse to be detected
by sensing changes. Illumination and photo
sensor levels persist while the system detects
heartbeat pulses precisely.
• LM35 Temperature Sensor: The LM35 is a
low-voltage, high-accuracy centigrade
temperature sensor produced by Texas
Instruments. It is a voltage-output
temperature sensor that is linearly
proportional to temperature in degrees
Celsius (°C). Specifically, this sensor does
away with the requirement for external
calibration, with ±0.5°C accuracy at room
temperature and ±1°Cover its full operating
range of -55°C to +155°C.
• Arduino UNO: The Arduino UNO is a
microcontroller board based on the
ATmega328P. It features:
• 14 digital input/output pins (6 can
be used as PWM outputs)
• 6 analog inputs
• 16 MHz ceramic resonator
• USB connection, power jack, ICSP
header, and reset button The board
is capable of operating via a USB
connection, an AC-to-DC adapter,
or a battery.
• AD8232 Heart Rate Monitor: The AD8232
sensor is a cost-effective solution that was
specifically intended to monitor cardiac
electrical activity. It is utilized to acquire
and amplify biopotential signals, thereby
producing an analog ECG output that is
employable for real-time monitoring.
• 16×2 LCD Display: A 16×2 LCD is capable
of showing 16 characters on one line and a
Real-Time ECG Monitoring System Using AD8232 Sensor and Arduino UNO for Biomedical Applications
115
total of two lines at its command. It shows
every character in a 5×7 pixel matrix and can
show 224 unique characters and symbols.
The LCD module has two registers:
• Command Register: Stores
commands and instructions given
to the LCD.
• Data Register: Holds the data
(characters) to be displayed.
The LCD facilitates on-screen visualization
of ECG data and other system parameters.
4 SYSTEM DESIGN
The design of the system of the ECG Graph
Monitoring project using the AD8232 ECG Sensor
and the Arduino platform involves the integration of
heterogeneous hardware components, such as the
Arduino UNO board and the AD8232 ECG Sensor,
and software code in order to monitor and present
ECG signals. The system design is divisible into three
main components: the hardware configuration, the
signal processing, and data presentation.
4.1 Hardware Setup
Hardware setup is done by plugging the AD8232
ECG Sensor into Arduino UNO board. AD8232
sensor detects electrical activity of the heart and
provides an analog signal. Pins of the sensor, such as:
These pins are connected to corresponding pins on the
Arduino for proper signal acquisition. Additionally,
the sensor pads are placed at specific body locations
(Right Arm, Left Arm, and Right Leg) to ensure
optimal signal detection. The connections are made
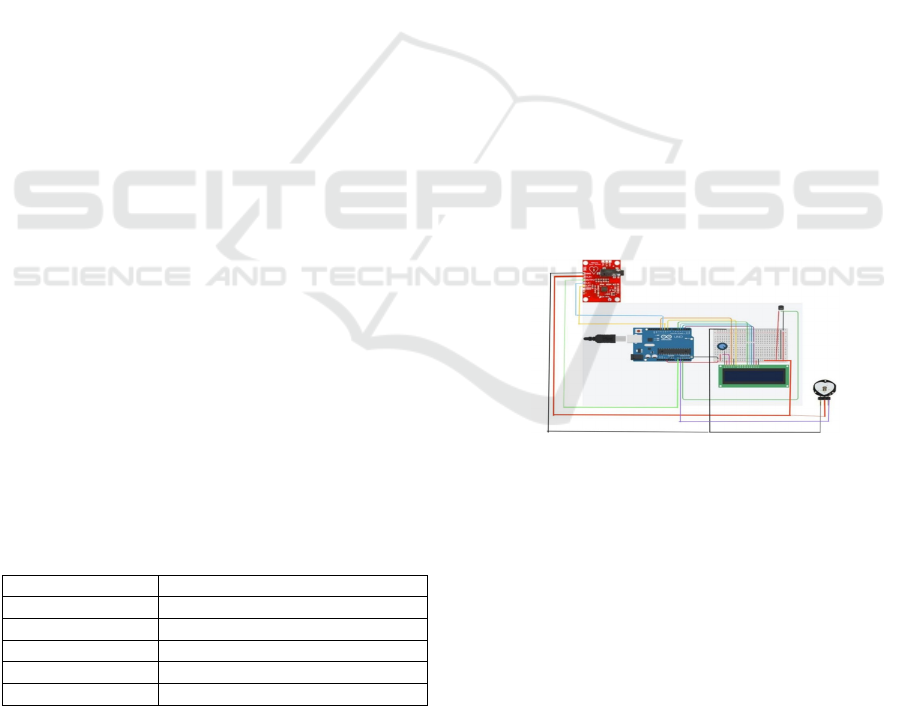
using a breadboard for ease of prototyping. Figure 2
shows the hardware setup. The Table 2 shows Pin
descriptions.
Table 2: Pin Descriptions.
Pin Name Description
GND Ground connection
3.3V Power su
pp
l
y
.
OUTPUT Analo
g
ECG si
g
nal out
p
ut.
LO- Lea
d
-off detection pin
LO+ Lea
d
-off detection pin.
4.2 Circuit Diagram
The connections between the AD8232 ECG Sensor,
Arduino UNO, and external components are shown in
the below diagram. The Arduino is programmed to
read the analog signal from the AD8232 sensor using
the analogRead() function. The obtained signal is
then processed to detect any lead-off condition,
indicated by the symbol”!”. If a lead-off condition is
detected, the system notifies the user by displaying a
blue line. Figure 1 shows the circuit diagram.
4.3 Signal Processing
If the incoming data is valid, the system processes the
analog signal to calculate the heart rate (BPM). This
is achieved by measuring the time interval between
successive peaks in the ECG waveform. The BPM
value is then sent to the connected computer for
further visualization.
4.4 Data Visualization
The processed data, including the ECG waveform and
BPM, is transmitted from the Arduino to a computer
using a serial connection. On the computer side, a
Processing sketch is employed to receive and
visualize the data in real time. The Processing sketch
performs the following tasks:
• Reads incoming data from the Arduino.
• Plots the ECG waveform dynamically using
the line() function.
• Displays the BPM periodically on the screen
Figure 1: Circuit Diagram.
5 RESULTS AND EVALUATION
ECG Graph Monitoring project with the AD8232
ECG Sensor and Arduino aims to create a cost-
effective system for monitoring and analyzing the
electrical activity of the heart. The AD8232 ECG
Sensor is employed to capture the heart’s electrical
signals, which are then processed and displayed using
an Arduino microcontroller. The project offers an
accessible solution for individuals to observe and
analyze their ECG signals at home, enabling early
detection of potential heart-related issues. The system
utilizes a simple circuit connection between the
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
116
AD8232 sensor and Arduino, making it user-friendly
for electronics enthusiasts and beginners. The real-
time ECG data is visualized on the Arduino’s serial
plotter or Processing IDE, providing a graphical
representation of the heart’s electrical activity.
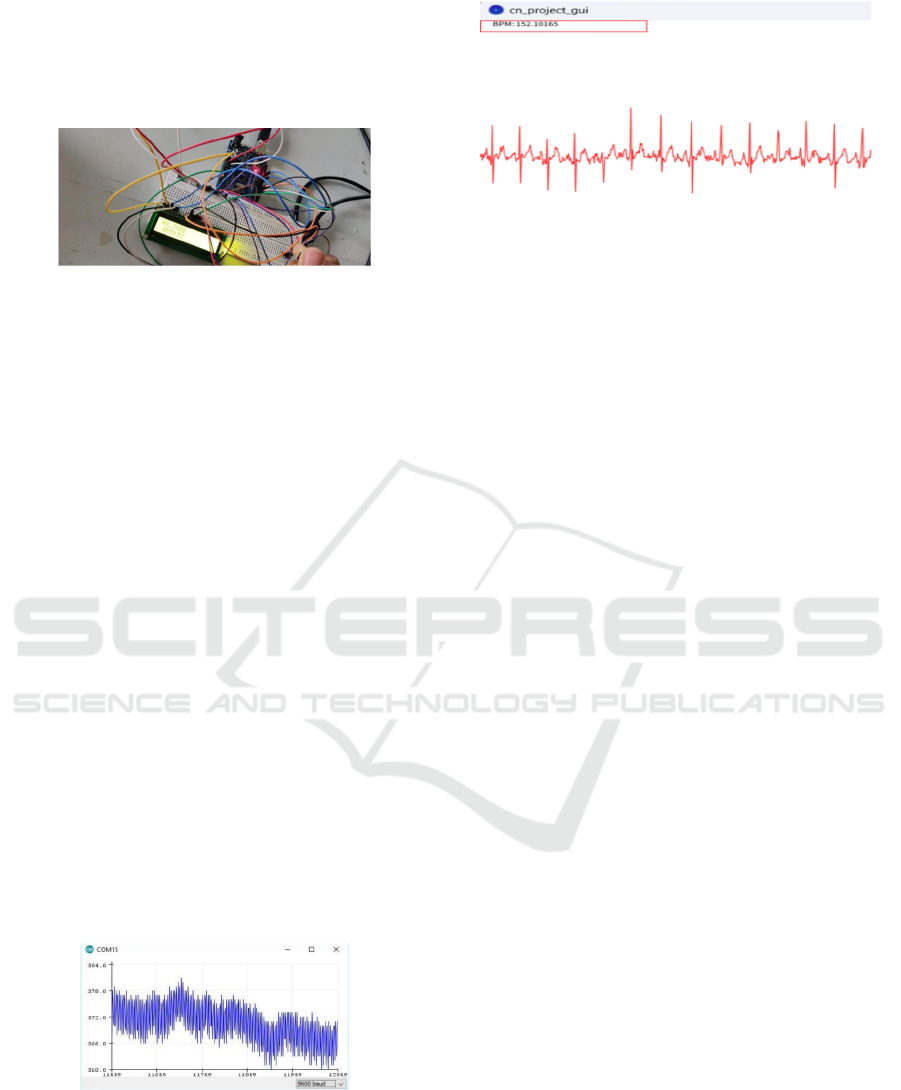
Figure 2: Hardware Setup of the ECG Monitoring System.
Inference: By implementing this project, individuals
can gain insights into their heart’s health and
potentially identify irregularities or abnormalities in
the ECG signal. The system’s affordability and
simplicity make it an accessible tool for personal
health monitoring. It serves as a valuable educational
project for learning about ECG signals, sensor
interfacing, and Arduino programming. While the
project provides a useful monitoring tool, it’s
important to note the disclaimer in the article,
emphasizing that the AD8232 module used is not a
medical device and is not intended for medical
diagnosis or treatment. Users should consult
healthcare professionals for accurate medical
assessments and diagnoses. Figure 3 shows the
inference result and figure 4 shows the graphical user
interface.
Circuit Diagram: The connections between the
AD8232 ECG Sensor, Arduino UNO, and external
components are shown in the below diagram. The
Arduino is programmed to read the analog signal
from the AD8232 sensor using the analogRead()
function. The obtained signal is then processed to
detect any lead-off condition, indicated by the
symbol”!”. If a lead-off condition is detected, the
system notifies the user by displaying a blue line.
Figure 3: Inference Results from the ECG Monitoring
System.
Figure 4: Graphical User Interface Displaying Real-Time
ECG Signals.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The AD8232 ECG Sensor and Arduino-based ECG
Graph Monitoring project is an inexpensive and
simple method of continuous monitoring of cardiac
health. With the use of minimum-cost hardware along
with open-source software, the system allows to
detect cardiac ailments in an early stage, thus helping
to stem the global problem caused by cardiovascular
diseases. Its application ranges from urban areas,
where it allows for regular monitoring, to rural areas
that do not have easy access to healthcare facilities,
and it can serve as a first-line diagnostic tool. The
open-source nature of the project encourages
innovation, which results in further advancement in
affordable healthcare technology.
In the future, wireless communication modules
like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi can facilitate real-time remote
monitoring with instant connectivity. In addition,
integration of machine learning algorithms for
autonomous ECG analysis can enhance predictive
diagnostics, providing valuable insights into potential
heart conditions. Integrations with healthcare experts
could also be utilized to validate and calibrate the
system for clinical use. With these enhancements, the
project has immense potential to evolve into an
advanced telehealth solution, facilitating proactive
cardiac care in home and clinical settings.
REFERENCES
D. Hasan and A. Ismaeel, “Designing ECG Monitoring
Healthcare System Based on Internet of Things Blynk
Application”, JASTT, vol.1, no. 3, pp. 106 - 111, Jul.
2020.
G. Xu,” IoT-Assisted ECG Monitoring Framework with
Secure Data Transmission for Health Care
Applications,” in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 74586-
74594, 2020.
Real-Time ECG Monitoring System Using AD8232 Sensor and Arduino UNO for Biomedical Applications
117

G. Ramasamy, T. Singh, and X. Yuan, "Multi-Modal
Semantic Segmentation Model using Encoder Based
Link-Net Architecture for BraTS 2020 Challenge,"
Procedia Computer Science, vol. 218, pp. 732-740,
2023. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2023.01.053.
G. Sivapalan, K. K. Nundy, S. Dev, B. Cardiff and D. John,
”ANNet: A Lightweight Neural Network for ECG
Anomaly Detection in IoT Edge Sensors,” in IEEE
Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, vol.
16, no. 1, pp. 24-35, Feb. 2022.
G. Ramasamy, P. B. Pati, T. Singh, and R. R. Nair, "A
Framework for the Prediction of Diabetes Mellitus
using Hyper-Parameter Tuned XGBoost Classifier,"
2022 13th International Conference on Computing
Communication and Networking Technologies
(ICCCNT), Kharagpur, India, 2022, pp. 1-5. doi:
10.1109/ICCCNT54827.2022.9984315.
O. Ankireddypalli, A. Mouhitha, S. Gujjula and T.
Somasundaram,” Piezoelectric Footstep Energy
Harvesting for Automated Garden Watering,” 2024
Second International Conference on Networks,
Multimedia and Information Technology (NMITCON),
Bengaluru, India, 2024.
Pradeep, Preeja Narendran, Sreekanth Vinodini Ramesh,
Maneesha. (2017). An Internet of Things (IoT) based
Sustainable Water Management.
10.1109/GHTC.2017.8239320.
R. H., R. Adithi, M. Vinodhini and J. M. Oli, ”2D Mapping
Robot using Ultrasonic Sensor and Processing IDE,”
2019 International Conference on Vision Towards
Emerging Trends in Communication and Networking
(ViTECoN), Vellore, India, 2019.
Rahman, M.O., Kashem, M.A., Nayan, A.A., Akter, M.,
Rabbi, F.,Ahmed, M. and Asaduzzaman, M., 2022.
Internet of things (IoT) based ECG system for rural
health care.
Rosario Morello, Filippo Ruffa, Ireneusz Jablonski, Laura
Fabbiano,Claudio De Capua, An IoT based ECG
system to diagnose cardiac pathologies for healthcare
applications in smart cities, Measurement,Volume 190,
2022.
S. Thangam, M. Tejaswi and V. Supritha,” Low Cost
Precision Farming and Remote Monitoring Using
Cloud”, 2023 14th International Conference on
Computing Communication and Networking
Technologies ICCCNT, 2023, 2023.
Sadad, T.; Safran, M.; Khan, I.; Alfarhood, S.; Khan, R.;
Ashraf, I. Efficient Classification of ECG Images Using
a Lightweight CNN with Attention Module and IoT.
Sensors 2023, 23, 7697.
Sangeethalakshmi K., Preethi Angel S., Preethi U., Pavithra
S., Shanmuga Priya V., Patient health monitoring
system using IoT, Materials Today: Proceedings,
Volume 80, Part 3, 2023, Pages 2228-2231, ISSN 2214-
7853,
T. S, N. D K, K. M. Shyam, M. C. K. Reddy and K. A. Sai,
”IoTBased Health Monitoring System for Forbidden
Patients,” 2024 10th International Conference on
Advanced Computing and Communication Systems
(ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 2024.
Yeh L-R, Chen W-C, Chan H-Y, Lu N-H, Wang C-Y, Twan
W-H, Du W-C, Huang Y-H, Hsu S-Y, Chen T-B.
Integrating ECG Monitoring and Classification via IoT
and Deep Neural Networks. Biosensors.2021
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
118
