Text Production with Deep Learning Approaches in Natural
Language Processing
M. Sharmila Devi, V. Lakshmi Chaitanya, V. Samatha, V. Naga Lavanya,
V. Srividya and M. Rehana
Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Santhiram Engineering College, Nandyal 518501, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), Generative Pre‑Trained
Transformer (GPT), Bi Directional Encoder Representative for Transformer (BERT), Long‑Short Term
Memory (LSTM), Natural Language Processing (NLP).
Abstract: The majority of NLP applications revolve around text generation. It can be used, for instance, to generate
dialogue turns from dialogue moves, to express the content of knowledge bases, or to generate natural English
sentences from complex linguistic representations such as Abstract Meaning Representations or dependency
trees in data-driven systems. It uses Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), namely LSTMs and GRUs, for long-
range dependency capture and sequential data processing, enabling applications like text summarization and
machine translation. Examples of transformer models that demonstrate their many uses, from question
answering to code creation and creative writing, are GPT and BERT. Furthermore, additional relevant deep
learning techniques like hybrid models and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are briefly discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
The branch of artificial intelligence that gives
machines the ability to understand, read, and
deduce
meaning from human languages is known
as natural language processing, or NLP. The
translation of language structure and norms into
models that can understand breakdown and extract
significant facts from text is a combination of
computer science and linguistics as a topic of
study. NLP gives computers the ability to read and
understand human language using techniques like
machine learning for text analysis and
interpretation, allowing them to interact with
people in a natural way. NLP allows computers to
read, understand, and respond to human language,
which is more complex and subtler than
machine language and more natural to use when
interacting with technology
Lyu, Y., Adnan, A. B.
M., & Zhang, L. (2024)
. This helps to bridge the gap
between human and machine comprehension.
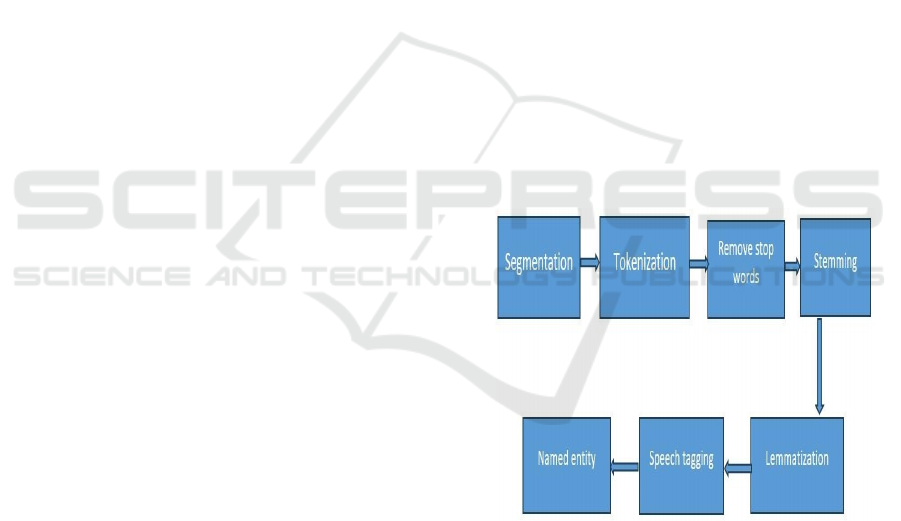
The figure 1 defines how NLP works to produce
the human understandable text which follows from
segmentation to the lemmatization by analyzing
each pattern of input.
Figure 1: NLP Process.
The components of NLP are
• Text Generation
• Text Summarization
• Information Retrieval
• Text Classification
Text Generation: The process of creating text that is
both grammatically correct and contextually
appropriate is known as text generation. The process
of text synthesis involves mimicking the linguistic
products of humans. Data preparation, model training,
Devi, M. S., Chaitanya, V. L., Samatha, V., Lavanya, V. N., Srividya, V. and Rehana, M.
Text Production with Deep Learning Approaches in Natural Language Processing.
DOI: 10.5220/0013891400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 3, pages
55-62
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
55
text generation, and decoding strategies are all
included
Celikyilmaz, A., Clark, E., & Gao, J. (2020).
Text Summarization: By looking at the most
important words, sentences, and patterns, text
summarization condenses the text of lengthy
publications. The human effort required to read
lengthy papers is reduced by text summaries. There
are two kinds of text summarization.
• Summarization of extractive texts
• summarization of abstractive texts
Extractive Text Summarization: In order to create a
summary text that is equal to the input pattern and the
generated text or sentences that are included in the
input data, extractive text summarization involves
scanning through input data and analysing it to extract
important words, sentences, and phrases.
Abstractive Text Summarization: By reading and
analysing the input data in terms of important phrases
and paragraphs, abstractive text summarization
creates new text that may or may not be present in the
input data.
Information Retrieval: Information retrieval is the
process of recovering information from documents.
The repository manages the organization by storing,
retrieving, and analysing the information. It is crucial
to extract pertinent information from the massive
documents; we can retrieve the information by
searching for the information we need.
Text Classification: Text classification is the process
of dividing unstructured data into different categories
hear classifier is used to classify the input data
classifier focus on patterns of input data and divide the
input data based on different patterns text
classification is mainly used in business organizations
to define user data.
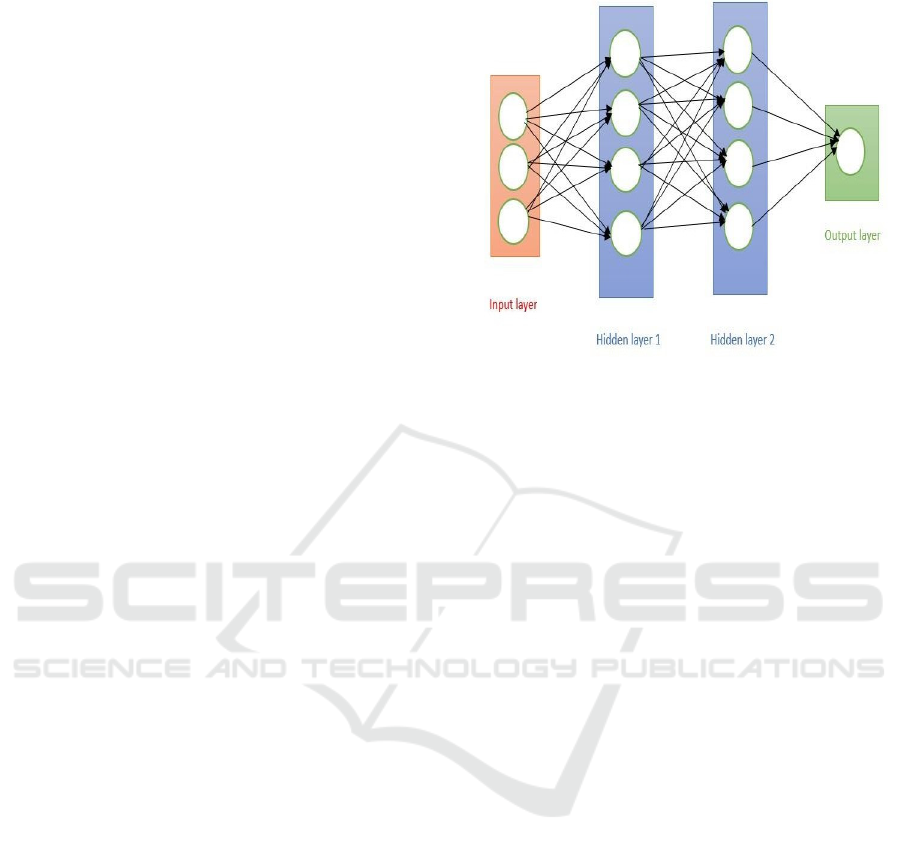
Deep Learning: Artificial neural networks are used
in deep learning, a subfield of machine learning, to
learn and predict from machines (
Mei et al., 2024).
Human-readable language is produced by deep
learning, which functions similarly to the human
brain. Three layers make to the deep learning process.
The input layer is where it first trains the input and
learns input patterns. The data being processed then
passes through a number of hidden layers that
transform the data into the desired output, which is
then accessible at the output layer. It uses a number
of strategies, including Generative Pre-trained
Transformers (GPT) like BERT (
Devlin, Jacob, et al.,
2019), GRU, and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN)
using LSTM Staudemeyer, R. C., & Morris, E. R. (2019).
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are another
method. Figure 2 provides a clear explanation of how
deep learning, which consists of three layers, operates
from input to output.
Figure 2: Deep Learning Process.
By analyzing four different components of natural
language processing we are going to focus on text
generation and text summarization.
2 TEXT GENERATION
Text generation uses artificial intelligence,
specifically deep learning algorithms, to produce
human-readable text. It is capable of producing entire
texts as well as sentences and paragraphs. Text
generation is important because it makes it possible
to share knowledge, interact with others, and
communicate ideas, facts, and thoughts clearly
Celikyilmaz, A., Clark, E., & Gao, J. (2020). Text
production is important in a variety of domains,
including customer service, content creation, and
natural language processing. In order to convert input
data into output text, text generation uses algorithms.
Training models on vast volumes of text data in
order to learn grammar, context, and patterns. Using
circumstances or training data, this model applies
learned information to produce new text.
These models use deep learning techniques,
specifically neural networks, to understand sentence
structure and generate content that is both coherent
and appropriate for its context. Clear communication,
knowledge sharing, social interactions, and
information exchange are the purposes of text
generation. One of the challenges of text
generation is maintaining coherence. The generated
text has a consistent style. Managing Context to
generate relevant text. Diverse outputs will help you
avoid using the same words over and over again
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
56

and provide a range of responses. Methods based on
deep learning perform well. We are using deep
learning algorithms since they are effective and we
need to overcome the obstacles.
2.1 Techniques
We use Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) for text
generation, including Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNN), Long Short-Term Memory
(LSTM)
Staudemeyer, R. C., & Morris, E. R. (2019).,
Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), Generative Pretrained
Transformer (GPT), and Bidirectional Encoder
Representations from Transformers (BERT). In order
to prevent grammatical errors in text production and
data management, we are using RNNs like LSTM in
this context. It will process and forecast the next word
or character in sequence mode, allowing the model to
learn lengthy documents and produce logical phrases.
Large datasets will be processed by this model, which
takes a word sequence as input and uses patterns it has
learnt to predict the next word. The model then uses
the training data to create new text.
It indicates that LSTMs
Staudemeyer, R. C., &
Morris, E. R. (2019). can effectively recognize the
connections between words in a phrase, which will
result in the creation of more grammatically sound
and coherent text. It also offers flexibility, as it can
generate various text kinds by training on various
datasets. It will analyse text sequences of varying
lengths, which is crucial for natural language
processing (NLP) activities when sentences have
varying word lengths. It will do this by mapping
complex linguistic patterns and the main advantage
over other approaches is that it will store data in word
sequences, making it possible to produce text, and it
will have more memory capacity to keep each node's
outputs for a longer period of time in order to
efficiently produce the following node's result. The
overall objective of BERT's bidirectional pretraining
methodology is to record contextual information from
left to right. It is mostly used to produce more logical
and contextually relevant content. It may also be used
to generate missing words in context and forecast
masked words within sentences. CNN will use filters
to extract features from text data in order to detect
complex features in the data. The main objective is to
identify patterns and extract features from a sentence
of text so that it can be used to create new text. It
learns to recognize word relationships and structures
to create text that is coherent and appropriate for the
context. This includes writing in different styles,
summarizing, creating creative content, and even
creating specific types of text, like poems.
• On the other hand, deep learning produces output
that is permanently improved as compared to
machine learning.
• Improved Efficiency and Scalability, which saves
time and effort when producing large amounts of
text.
• While it may not be feasible for humans to
produce greater creativity, artificial intelligence
will be able to produce new and innovative
material.
• Language accessibility will also offer translation
services, generating and translating text.
• It will also offer automatic feature extraction,
which means that it will automatically extract
features such as human names, location, and key
elements from any sentence or paragraph.
• Consistency and Accuracy, it means it will
maintains text style and grammar, minimizing
errors and ensures high quality output without
repetition.
2.2 Text Summarization
Text summarization is the process of summarizing the
large data and large documents in the short and
understandable form by taking the key information
and important words from the documents and produce
the summary is called text summarization. Text
summarization is a crucial in NLP by using the deep
learning techniques text summarization produce both
quality and efficient text .text summarization reduce
the human difficulty by producing the meaningful and
relevant text from the large data or from the large
documents. Text summarization categorized into two
components.
• Summarization of Extractive Texts
• Summarization of Abstractive Texts
Figure 3 provides the clear process about the
summarization of text from providing input to
produce the summarized output.
Text Production with Deep Learning Approaches in Natural Language Processing
57
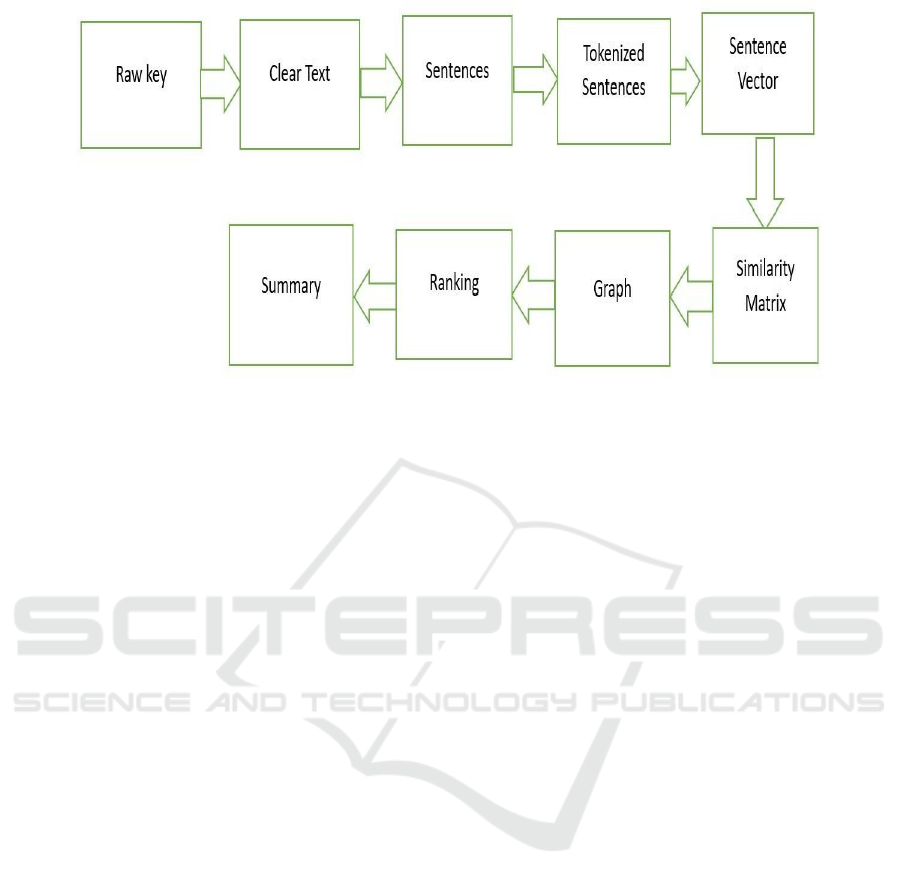
Figure 3: Summarization of Text Process.
3 EXTRACTIVE
SUMMARIZATIONS
Extractive Text Summarization involves that it reads
from input data and analyses by finding important
words, sentences, phrases from the original text and
produce the summarized text same like input pattern
and produced text or sentences which are present in
input data. In extractive summarization it identifies
the key phrases, sentences or select the words based
on importance, frequency or relevance of text.
Abstractive summarization: Abstractive Text
Summarization involves that it reads and analyses the
input data based on important text and sentences or
paragraphs from original text and generate new
sentences or text with new words or sentences which
may or may not be in input data.it requires a more
understanding of text and generate coherent and
contextually meaning full text.
Deep learning techniques for text summarization:
We can summarize the text by using deep learning
techniques models to learn complex patterns and
generate quality summaries
Techniques: BERT, Attention Mechanism for
focusing on input, improve quality, relevance of
output, RNN, CNN.
GPT methodology Transformers' bidirectional
encoder representations (BERT) are used to generate
text learning from complex input. Sentence phrasing
using convolutional neural networks (CNN).
Recurrent neural network (RNN) with LSTM
Staudemeyer, R. C., & Morris, E. R. (2019). (Long Short-
Term Memory), GRU (Gated Recurrent Unit) for
sequential data and feature extraction. In the
sequence-to-sequence model, attention is used to
focus on input and produce pertinent information
from the input data mechanism. It uses both encoders
and decoders to analyses input data and produce
summaries. Input data is processed by encoder and
generates the summary by decoder. Sequence-to-
sequence models use recurrent neural networks
(RNN) with long short-term memory (LSTM)
networks.
We can produce high-quality summaries that are
logical, contextually meaningful, and produce
language that is human-like with the aid of deep
learning for text summarizing. The text can be
summarized by deep learning without the need for
manually created features and rules. Deep learning is
scalable across multiple languages and disciplines and
can handle vast amounts of data needing a large
amount of labelled data to produce understandable
text. Rare words might cause problems for deep
learning when it comes to text summarization,
making the summary inaccurate.
Extractive Text Summarization: Extractive text
summarization is a technique where it learns and
analyses from the input data and takes important
sentences and phrases to create a summary instead of
generating new sentences it selects important context
from original data.
Techniques: To extract the summary (
Zhong et al.,
2020)
from the given text we are going to use deep
learning techniques like RNN techniques like Long
Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
Staudemeyer, R. C., &
Morris, E. R. (2019).
and Gated recurrent unit (GRU)
for sequential data means it process the data based on
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
58
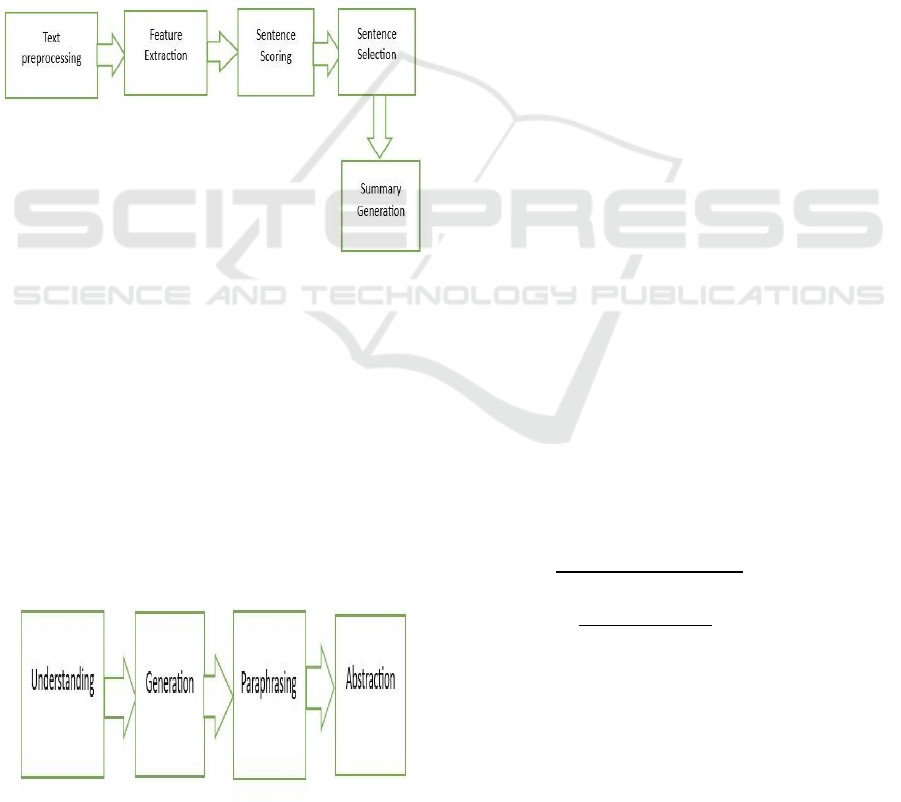
continuity from training the next word patterns.
Figure 4 involves analyzing the input and
removing the nuisance data, unwanted data from the
given text called text processing. Then based on
retrieved data it extracts the features like repeated
words, sentence positioning from them it collects the
data called features extraction. From retrieved
sentences it involves in sentence scoring like sorting
the sentences based on importance and continuity
called sentence scoring.
Based on sentences scoring techniques select the
sentences importance called sentence selection and
then from all sentences it generates the summary by
using a methodology called BERT (
Devlin, Jacob, et
al.2019)
. Bert make sure to select the correct important
sentences from the given text to generate the
summary (
Zhong et al., 2020).
Figure 4: Process of Extractive Summarization.
Abstractive Text Summarization: Abstractive text
summarization is a technique which involves in
understanding the text from input data and generate
new sentences (
Lin, H. and Ng, V., 2019) instead of just
copying the sentences from the given content. It
processes the data just like humans and produce the
summary while keeping the main idea intact.
Techniques: Abstractive text summarization uses the
deep learning techniques like Generative pretrained
transformer (GPT) like Bidirectional encoder and
representative transformer (BERT) for sentence level
representation and learn the information from
complex data.
Figure 5: Process of Abstractive Summarization.
Figure 5 involves Process of abstractive
summarization includes understanding of in Input
text based on patterns and divide the text into tokens
and Generating the text into sentences which are
efficient and grammatically correct and paraphrasing
the text (
Lin, H. and Ng, V., 2019) which means
Reducing the summary by generating the new text by
learning and analysing the input text and abstract the
summary with respect to context.
4 PERFORMANCE METRICS
Perplexity: One of the most crucial measures in
natural language processing for evaluating a language
model's quality is perplexity, which also serves as a
reliable gauge of the model's coherence and fluency.
It gauges how accurately a probability model
forecasts a sample. The ability of a language model to
anticipate the following word or character based on
the context of the preceding words or Characters is
measured by perplexity. The reduced perplexity
indicates that the model is quite confident in its
predictions and does a good job of predicting the
sequence.
Probability distribution: When a language model
generates text, it assigns probabilities to each possible
word that could come next, based on the current
context.
4.1 Calculating Perplexity
• Log-likelihood: The model calculates the log-
probability of each word in the sequence based
on the words that came before it.
• Averaging: The log-probabilities average is
calculated.
• Exponentiation: The negative average log-
probability is multiplied to determine the
perplexity score.
𝑅𝑒𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑙 =
similar tokens
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑜𝑘𝑒𝑛 𝑖𝑛 𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔
(1)
Precision =
(2)
Based on these probabilities, the model would
calculate a perplexity score. A lower perplexity would
indicate that the model is more confident in predicting
“mat” as the most likely next word.
Confusion matrix: As it provides a detailed
explanation of how well a model can classify
different classes and highlights areas where the model
Text Production with Deep Learning Approaches in Natural Language Processing
59
may be making mistakes between different types of
data, the confusion matrix is a popular performance
metric to evaluate the efficacy of deep learning
techniques, particularly for classification problems.
By comparing the values predicted by a model with
the actual values given a data set, a confusion matrix
helps assess how well categorization algorithms
perform in machine learning. The results of classifier
algorithms can be visually represented using a
confusion matrix, also known as an error matrix. A
confusion matrix may reveal that a model repeatedly
confuses cats and dogs in image recognition
applications, providing information on the model's
advantages and disadvantages rather than just its
overall accuracy.
Visual Representation: The matrix makes it easy to
understand how well the model performs for different
classes and displays the true positive (TP), true
negative (TN), false positive (FP), and false negative
(FN) classifications.
Detailed Analysis: While overall accuracy is a
common metric, a confusion matrix allows you to see
how well the model performs on specific classes,
which can be crucial when dealing with imbalanced
datasets.
Identify Misclassifications: By looking at the off-
diagonal elements of the matrix, you can pinpoint
which classes are most often confused with each
other, helping to guide model improvement
strategies.
4.2 Process of Confusion Matrix
• Generate the Matrix: After training your deep
learning model, use a function within your
machine learning library (like scikit-learn) to
calculate the confusion matrix on your test data.
• Interpret the Values: Analyse the diagonal
elements (correct predictions) and off- diagonal
elements (incorrect predictions) to understand
where the model is performing well and where it is
struggling.
• Calculate Derived Metrics: To further
understand the model's performance for each class,
calculate other important metrics including
precision, recall, and F1-score based on the
confusion matrix data.
5 RESULTS & DISCUSSIONS
To assess the potential of text generation and
summarization, there is a necessity for clear
evaluation metrices. For this we are using
performance metrics like perplexity for text
summarization, confusion matrix for text generation.
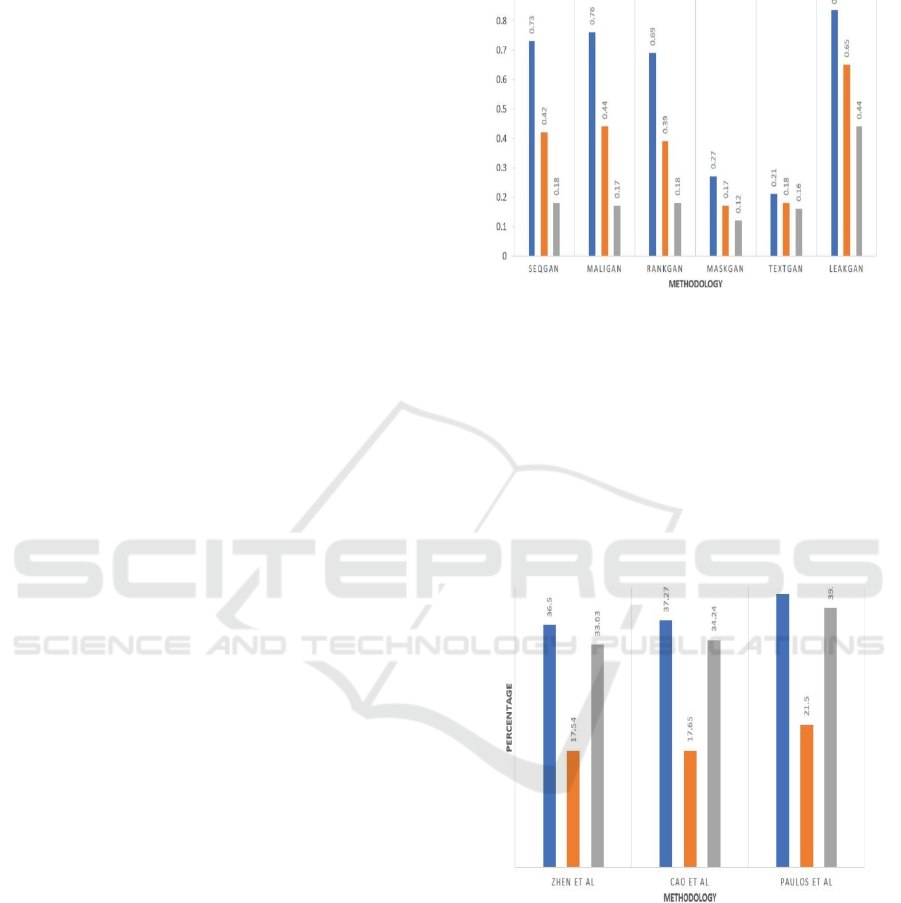
Figure 6: Confusion Matrix Score for Text Generation.
By using confusion matrix, it is observed that there is
efficient production of text by depicting the scoring of
sentences, patterns, phrasing, analysing the words,
grammatically correct context by al this confusion
matrix create a matrix in the form of rows and
columns and find the similarity by comparing the
rows and columns and remove the similarity, errors.
It compares from one row to one column and last row
to last column. By analysing figure 6 we can able to
determine the percentage.
Figure 7: Perplexity Score for Extractive Text
Summarization.
Perplexity performance metric used for the text
summarization where it detects the summary patterns
from first sentence to last sentence by analysing each
word, each letter, important sentences, new phrases.
It goes for the analysing whole input summary and
reduce the no of lines based on above mentioned
areas. From figure 7,8 it concludes the percentage of
extractive and abstractive text summarization.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
60
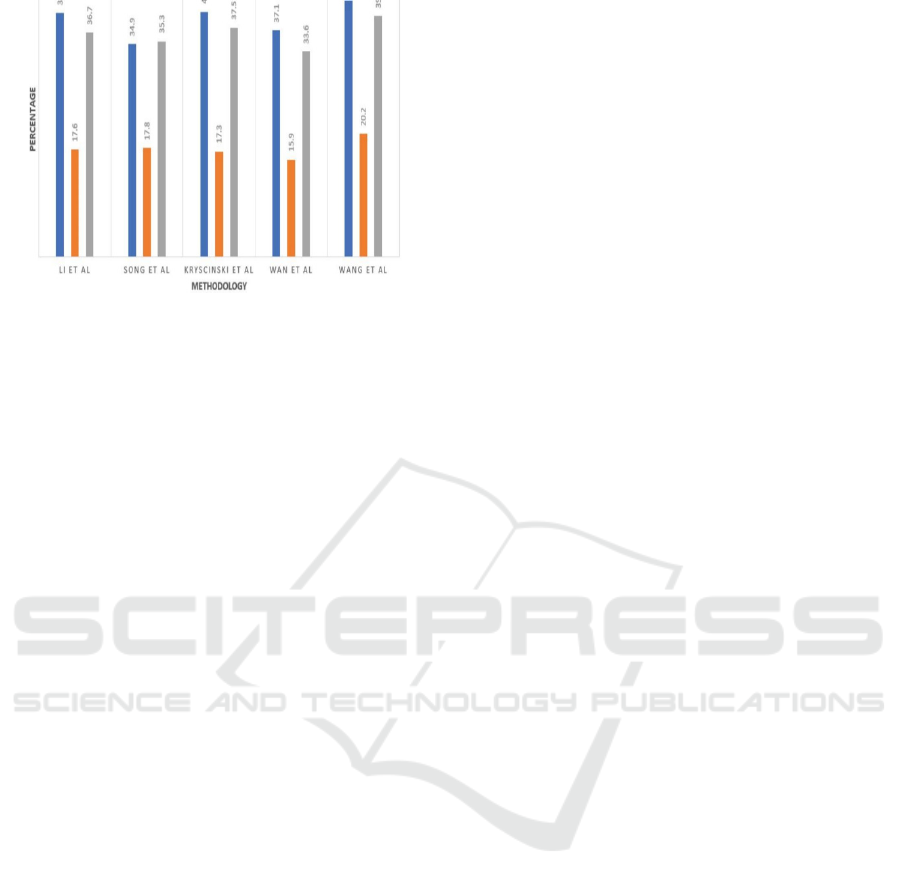
Figure 8: Perplexity Score for Abstractive Text
Summarization.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Deep learning provides a platform to work with large
and complex data. Dl techniques like LSTM, GRU in
RNN, and BERT in GPT for producing the efficient
text and for text summarization. DL provides wide
range of opportunities for researchers to learn and
evaluate more about text generation and
summarization. For better extraction of text
summarization uses the dl techniques like CNN,
RNN. The goal is not only to produce the human
understandable text but also efficient and
grammatically correct text. For text summarization
goal is to minimize the summary based on context and
importance. For evaluating the performance uses the
perplexity, confusion matrix. Perplexity check for
how efficient the sentences are generating based on
grammar, confusion matrix check for how efficiently
the sentences are generating based on patterns. The
common differences encountered in generation is
sometimes it gives less accurate text with errors in
grammar. For summarization it gives repetition of
sentences, lack of sentence accuracy.
7 FUTURE SCOPE
7.1 Automatic Text Summarization of
Superior Quality
Scope: Improving AI models to efficiently condense
massive text datasets while retaining crucial
information.
Solution: To guarantee greater accuracy and
relevance, use hybrid deep learning models (CNN +
RNN + Attention Mechanism) for abstractive and
extractive summarization.
7.2 Enhanced Information Retrieval and
Classification
Scope: Creating more efficient AI systems to retrieve
and classify information from vast data stores.
Solution: Leverage deep learning methods like
CNNs for feature extraction and NLP methods such
as named entity recognition (NER) in order to
enhance search precision and classification accuracy.
REFERENCES
Celikyilmaz, A., Clark, E., & Gao, J. (2020). Evaluation of
text generation: A survey. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2006.14799.
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi, and G. Vijaya Bhaskar. "Apriori vs
Genetic algorithms for Identifying Frequent Item Sets."
International journal of Innovative Research
&Development 3.6 (2014): 249-254.
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi. "Machine Learning Based
Predictive Model for Data Fusion Based Intruder Alert
System." journal of algebraic statistics 13.2 (2022):
2477-2483
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi, et al. "Identification of traffic sign
boards and voice assistance system for driving." AIP
Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028. No. 1. AIP
Publishing, 2024
Devi, M. Sharmila, et al. "Extracting and Analyzing
Features in Natural Language Processing for Deep
Learning with English Language." Journal of Research
Publication and Reviews 4.4 (2023): 497-502.
Devlin, Jacob, et al. "Bert: Pre-training of deep
bidirectional transformers for language understanding."
Proceedings of the 2019 conference of the North
American chapter of the association for computational
linguistics: human language technologies, volume 1
(long and short papers). 2019.
Lin, H. and Ng, V., 2019, July. Abstractive summarization:
A survey of the state of the art. In Proceedings of the
AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (Vol. 33, No.
01, pp. 9815-9822).
Lyu, Y., Adnan, A. B. M., & Zhang, L. (2024). Influencing
factors on NLP technology integration in teaching: A
case study in Shanghai. Education and Information
Technologies, 1-34.
Mahammad, Farooq Sunar, Karthik Balasubramanian, and
T. Sudhakar Babu. "A comprehensive research on video
imaging techniques." All Open Access, Bronze (2019).
Mahammad, Farooq Sunar, and V. Madhu Viswanatham.
"Performance analysis of data compression algorithms
for heterogeneous architecture through parallel
approach." The Journal of Supercomputing 76.4
(2020): 2275-2288.
Mahammad, Farooq Sunar, et al. "Key distribution scheme
for preventing key reinstallation attack in wireless
Text Production with Deep Learning Approaches in Natural Language Processing
61

networks." AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028.
No.1. AIP Publishing, 2024.
Mei, T., Zi, Y., Cheng, X., Gao, Z., Wang, Q., & Yang, H.
(2024, August). Efficiency optimization of large-scale
language models based on deep learning in natural
language processing tasksIn 2024 IEEE 2nd
International Conference on Sensors, Electronics and
Computer Engineering (ICSECE) (pp. 1231-1237).
Paradesi Subba Rao,”Detecting malicious Twitter bots
using machine learning” AIP Conf. Proc. 3028, 020073
(2024),https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0212693
Paradesi SubbaRao,” Morphed Image Detection using
Structural Similarity Index Measure”M6 Volume 48
Issue 4 (December 2024) ,https://powertechjournal.co
m
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al. "Machine Learning Based
Predictive Model for Closed Loop Air Filtering
System." Journal of Algebraic Statistics 13.3 (2022):
416-423.
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al. "Incorporating Deep Learning
Techniques to Estimate the Damage of Cars During the
Accidents" AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028.
No. 1. AIP Publishing, 2024.
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al “Cloud Computing Network
in Remote Sensing-Based Climate Detection Using
Machine Learning Algorithms” remote sensing in earth
systems sciences (springer).
Staudemeyer, R. C., & Morris, E. R. (2019). Understanding
LSTM--a tutorial into long short-term memory
recurrent neural networks. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1909.09586.
Suman, Jami Venkata, et al. "Leveraging natural language
processing in conversational AI agents to improve
healthcare security." Conversational Artificial
Intelligence (2024): 699-711.
Sunar, Mahammad Farooq, and V. Madhu Viswanatham.
"A fast approach to encrypt and decrypt of video
streams for secure channel transmission." World
Review of Science, Technology and Sustainable
Development 14.1 (2018): 11-28.
Zhong, Ming, Pengfei Liu, Yiran Chen, Danqing Wang,
Xipeng Qiu, and Xuanjing Huang. "Extractive
summarization as text matching." arXiv preprint
arXiv:2004.08795 (2020).
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
62
