
Dynamic Task Scheduling Using Machine Learning and Enhanced
Fuzzy Logic System for Efficient Resource Utilization in Virtual
Cloud
Panchagnula Kamakshi Thai and Shanker Chandre
Department of Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence, School of Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence, SR
University, Warangal, Telangana, India
Keywords: Fuzzy Logic Systems, Task Scheduling, Machine Learning, Virtualized Cloud Systems.
Abstract: Virtual clouds need intelligent task scheduling systems because their limited resources become more efficient
through workload-based scheduling strategies. Fuzzy logic systems offer the best solutions for handling tasks
in cloud computing because they can deal with uncertain situations and changing workloads and resources.
The integration of heuristic interpolated models and machine learning algorithms achieves optimized task
scheduling while distributing resources evenly and shortening execution duration. Machine learning uses
supervised learning to predict resources and reinforcement learning to adjust decisions, helping to construct
flexible and accurate execution patterns. An improved version of fuzzy logic contains smart scheduling
functionality that adapts priority settings based on both mission-dependent needs along external operational
factors such as execution period and urgency level, as well as system resources and system utilization.
Enhanced fuzzy logic systems (EFLS) is one of the models used in the research to automatically change
schedules based on environmental factors and changes in job demand. The system constructs exhaustive
membership functions that show overlapping job priority areas and limits on resources using its method. The
system contains four major modules consisting of submission tracking, resource monitoring alongside
predictive capabilities, and optimized decision management that permits real-time capability. The
performance assessments reveal significant positive outcomes in all three areas: makespan, task completion
rates, and resource utilization as compared to conventional methods. The method demonstrates how
virtualized cloud systems can implement scalable, efficient, adaptive task management.
1 INTRODUCTION
Dynamic task scheduling in a virtual cloud
environment, where the cluster is virtualized,
scalability is achieved, and multi-tenancy and
variability of workload have prevailed, is an
important way to utilize resources. The sociology and
cloud behavior dynamics suggest potential for
improved scheduling frameworks to adapt to
economic conditions and challenges in a competitive
cloud market. The standard scheduling techniques
that operate based on fixed rules show deficiencies
when resource types and workloads require
adjustments. Virtual-based cloud environments
require task scheduling operations to distribute
computational tasks across VMs to achieve optimal
resource utilization as well as energy efficiency while
maximizing makespan and task completion rate.
Virtual-based cloud environments face two main
challenges: varied workloads, differing resource
types, and task dependencies between resources. The
accuracy of decision-making improves when neural
networks and Random forests from machine learning
methods gain increasing utilization for resource need
predictions as well as execution duration predictions
(Zhang et al., 2021). Operational efficiency and
resource productivity grow through implementing
flexible decisions about job scheduling strategies.
Artificially intelligent fuzzy logic systems, together
with machine learning techniques, serve this purpose.
Implementations that unite improved fuzzy logic with
ML surpass traditional application methods because
they deliver multiple advantages. The analysis of
historical data by ML models helps to predict job
execution times, which leads to proactive resource
allocation (Gupta et al., 2023). Classification
algorithms priorities jobs, while regression-based
816
Thai, P. K. and Chandre, S.
Dynamic Task Scheduling Using Machine Learning and Enhanced Fuzzy Logic System for Efficient Resource Utilization in Virtual Cloud.
DOI: 10.5220/0013890400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
816-822
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

models forecast resource usage. For precise schedule
optimization, advanced fuzzy logic systems use
environmental data, deadline limits, and real-time
resource availability. The hybrid method balances
efficiency and justice by assigning critical tasks to
resources without overburdening them. A major
benefit of the hybrid architecture is its energy
efficiency. The cloud data center's high energy usage
has financial and environmental consequences. The
system applies ML predictions together with fuzzy
logic rules to decrease resource disuse and select the
right resources for each task (Chen et al., 2022).
The reduction of energy consumption occurs
because energy-aware scheduling algorithms use
real-time energy profiles from resources as part of
their decision-making process. The suggested
framework adopts dynamic approaches to operational
changes, whereas static systems use established
criteria exclusively to operate. Using fuzzy logic
systems along with machine learning models allows
for flexible changes in priority levels and can predict
delays during busy times, helping with replacing
resources. The adaptable nature of this system
ensures high completion rates when task uncertainties
exist, and this creates substantial stability
improvements (Rahman et al., 2021). The
implementation of scheduling systems using
combinations of ML and fuzzy logic generates
important advantages, though it comes with certain
implementation challenges. Table processing speed
rises due to both sophisticated ML model design and
massive training data needs. The development of
fuzzy logic rules needs knowledge about the domain
together with continuous modifications to capture
actual situations accurately. New developments in
automatic fuzzy rule generation together with ML
model optimization have effectively reduced this
challenge (Li, Y., and Wang, T, 2023). The paper
helps exploration scheduling by looking at smart
scheduling methods that use fuzzy logic along with
machine learning. The recent development
demonstrates the outstanding capacity for dynamic
cloud system employment because test results
indicate it boosts resource utilization while
decreasing energy usage while upholding task
execution timing guarantees.
2 RELATED WORKS
In Saad et al., (2023). the authors translated K-Means
clustering through fuzzy logic for the effective
organization of fog nodes by their resource
characteristics and workload patterns. The arrived-at
method distributes work in real time by linking K-
means clustering to fuzzy logic and fuzzy logic
adaptability. Their approach demonstrated how
distributed job placement to fog nodes using machine
learning generated decreased execution times and
reduced response times and network utilization rates.
Thus, extensive testing confirms that the proposed
solution results successful in being versatile in
changing fog scenarios. The time-consuming VM
work cluster detection, but we the entire process is
very efficient. They developed and evaluated their
proposed approach using iFogSim. It shows
distinguished improvements in comparison to
machine learning and non-ML-based scheduling
methods inside the iFogSim framework in terms of
response time, execution time, and lesser network
utilization in the simulation results. In Thapliyal et al.,
(2024), authors proposed an optimized approach
based on fuzzy logic (FL) and best-fit-decreasing
(BFD) for job scheduling process in a cloud
computing environment. They all play into making
FL-BFD worthy of your time, money, power, and
resources. The FL-BFD reallocates the cloud VMs
by the user demand. We find it important to leverage
the FL capabilities to deal with uncertainty and
missing information to properly provision the
needed with what the user requires in the BFD for
properly provisioning VMs. The proposed FL-BFD
inspects multiple factors including makespan,
computational time, degree of imbalance, power
consumption, and SLA violations. Output: FL-BFD
has the longest makespan of 9.2 ms among 1000
jobs, compared to IWHOLF-TSC and MCT-PSO.
The authors of Radhika, D (2022) presented a
cloud dynamic task scheduling in which they consider
big data analysis processing in the cloud
environment. They employed multiple methods,
including a machine learning classifier and an
optimization approach. For classification of various
virtual machine tasks, they use a machine-learning
classifier known as a Support Vector Machine
(SVM). Using this classifier, we can effectively
reduce makespan and execution time when
classifying incoming requests. They also assigned the
classified job using moth flame optimization to the
SVM classifier. This proposed system is used to:
classify the virtual machine (VMs) tasks and
evaluate decision make methodology for the
resources allocation. The proposed method showed
that the make-span time may be reduced, while load
balancing may also seem beneficial according to their
work, which they tested in a cloud modeling
environment to improve VM classification. Iin Alam
et al., (2021), the authors introduce a new static
Dynamic Task Scheduling Using Machine Learning and Enhanced Fuzzy Logic System for Efficient Resource Utilization in Virtual Cloud
817
homogeneity task assignment (ESTA) approach
aimed at optimizing average utilization. Handling of
jobs should therefore be done with efficient allocation
of tasks between the available resources and to
prevent scheduling algorithm challenges. ESTA
algorithm uses the shortest completion time method.
ESTA intelligently maps batches of independent
tasks (cloudlets) on the top of heterogeneous virtual
machines in the IaaS cloud computing to optimize the
use of virtual machines. The performance of ESTA is
analysed against Min-Min,LBSM,LJFR-SJFR,
Sufferage, MCT, MET, and OLB using simulation
study in terms of make span, utilization, and response
time to identify the strengths and weaknesses of
ESTA. In Gong et al., (2024), authors also discussed
importance of deep reinforcement learning and
machine learning in optimizing virtual machine
migrations and managing resources of cloud. Deep
reinforcements learning and other machine learning
techniques are effective for optimizing embodied
intelligence, dynamic resource management, and
environment recognition. All of this is possible
because of their adaptability, policy creation and
forecasting capabilities. Through cloud computing,
organizations using cloud services can optimize
resource utilizations, reduce power consumption, and
improve quality of service delivered, enabling them
to benefit from these technologies.
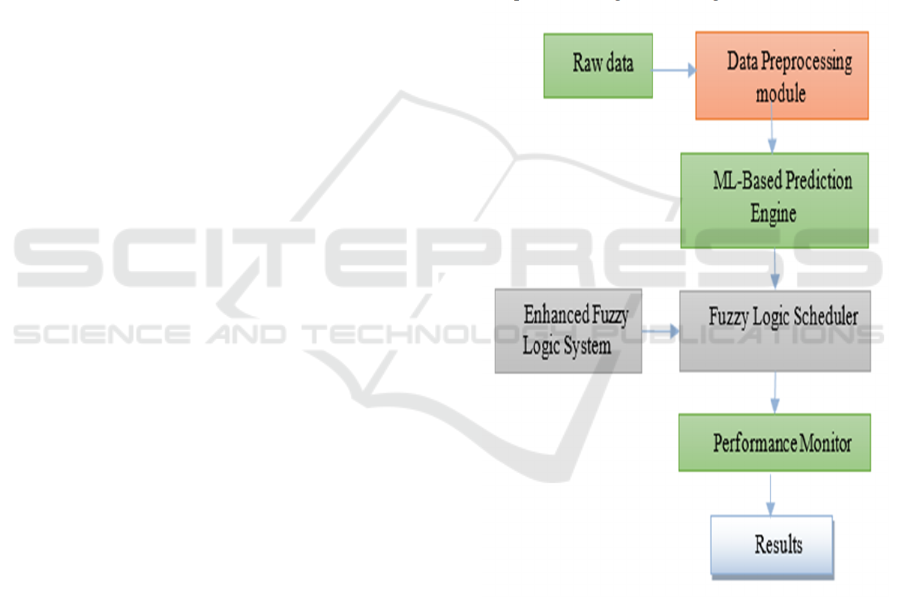
3 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The enhanced fuzzy logic functions with machine
learning (ML) technique, enable maximum output of
resources usage within virtual cloud environments
using the dynamic task scheduling system proposed
in Figure 1. a Problem solving before execution:
execution time prediction, resource need prediction
and wait time prediction in workflow through
applying machine learning models within a system.
Work urgency, system load, and resources
availability are factors that determine the fuzzy logic
adaptation in scheduling priority. Associated task-to-
resource assignments are obtained through the use of
flexible rules and predictive analytics that address
resource consumption with respect to its constraints
while meeting job deadlines and feasibility
requirements. The proposed solution comprises a data
preprocessing module, ML prediction engine, fuzzy
logic scheduler, and a performance monitoring unit.
When applied to a traditional scheduling approach, it
dramatically improves energy efficiency and job
completion ratios. With this intelligent, scalable
solution, we enable consistent, safe, and efficient
management of complex application workloads
across agile cloud environments built on OpenShift
data to provide a magnificent experience.
3.1 Data Preprocessing Module
It cleans and normalizes the raw input data while
encoding it making it ready for analysis. Data points
for resource measurement status (CPU, memory, etc)
and relevant task properties, e.g. priorities and
deadline, are controlled by the system. Dynamic task
scheduling in virtual cloud environments relies on
effective allocation of tasks to resources. This process
is used to ensure the system is making the best use of
its resources, prioritizing tasks, and responding well
to requests, among other things.
Figure 1: Proposed Dynamic Task Scheduling Framework.
Enhanced fuzzy logic systems improve
scheduling by analyzing work requirements and
adjusting task priorities on the fly. Simultaneously,
ML models predict the duration of each task and the
required resources.
𝑥
=
1, if task 𝑇
is assigned to resource 𝑅
0, otherwise
(1)
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
818

Activities and resources placed in a dynamic
virtual cloud environment are described by certain
criteria to support optimal scheduling. A task (Ti) is
defined by a set of attributes: its central processing
unit (cpui), memory (memi), priority (pi) and
deadline (di). Task execution time and resource
allocation can also be dictated by the size,
complexity, and interdependence of the tasks. Also
important are the maximum consumed CPU (Cj),
memory (Mj), and energy consumption rate (Ej) for
each resource (Rj). You: Being fast at a low price is
nice, but the number of available storage, availability,
and bandwidth also affect how the system will
perform under a variety of loads. Task-to-resource
mapping achieves its objectives based on an
analytical approach taking into consideration the
reduction of wait time and optimization of efficiency
while maintaining the energy constraints. Real-time
workload needs require flexible solutions to be
implemented with advanced fuzzy logic and artificial
intelligence techniques to be deployed effectively
without compromising scalability. Activities, and
resources in a dynamic virtual cloud surrounding are
described with the help of certain features for
facilitating optimal scheduling. Each task (Ti) has
associated factors such as central processing unit
(cpui), memory (memi), priority (pi), and deadline
(di). The execution time {@link Measured Execution
Type #execution Time()} and resource allocation
{@link Measured Execution Type #resource
Allocation()} of tasks can also depend upon their size,
complexity, and interdependence. For each resource
(Rj), the maximum CPU (), memory (), and energy
consumption rate (Ej) are equally important. On the
other hand, more storage, availability, and network
bandwidth impact the system's performance under
varying workloads. Both task-to-resource mapping
achieves its objectives through analytical
consideration of waiting time reduction and
efficiency optimization in addition to energy
constraint management. Real-time workload
demands adaptive solutions that require enhanced
fuzzy logic and machine learning techniques for
scalability and efficiency.
𝑀𝑎𝑥:𝑅 =
∑∑
.
(
)
∑
(2)
𝑀𝑖𝑛:𝑀 = max
∑
𝑥
.𝑇
𝑇
,𝑅
(3)
𝑀𝑖𝑛:𝐸 =
∑∑
𝑥
.
𝐸
(4)
𝑀𝑎𝑥:𝑃 =
∑∑
𝑥
.
𝑝
(5)
Virtual cloud environments need multiple
fundamental requirements which ensure resource
efficiency and on-time task completion and maintain
system reliability. The four types of resource
constraints represent some of the key restrictions
within dynamic virtual cloud scheduling systems.
3.2 Resource Constraints
Virtual machines and other resources have limited
CPU, memory, and storage space.
∑
𝑥
.𝑐𝑝𝑢
≤𝑐𝑝𝑢
,
∑
𝑥
.𝑚𝑒𝑚
≤𝑚𝑒𝑚
(6)
where x
ij
is a binary variable indicating task-
resource assignment.
Task Deadline Constraint: Timely completion of
tasks is essential (d
i
). With a resource (R
j
) and a task
(T
i
), For each task, we allocate a single resource:
𝑇
𝑇
,𝑅
+𝑇
𝑇
,𝑅
≤𝑑
(7)
Task Assignment Constraint: Each task is
assigned to one and only one resource:
∑
𝑥
=1 ,∀𝑖
(8)
3.3 Feasibility Constraint
To allocate resources, they must meet the conditions
for task execution. If resource R
j
is unable to meet T
i
needs, then x
ij
equals zero. To predict execution
timing and resource requirements, machine learning
models accept these described attributes.
3.4 ML-Based Prediction Engine
The following task and resource attributes are fed into
ML models to predict when a task will need to be
executed and how many resources will be needed:
𝑇
𝑇
,𝑅
=𝑓𝑐𝑝𝑢
,𝑚𝑒𝑚
,𝑅
) (9)
where 𝑓 is an ML model (e.g., Random Forest, Neural
Network) trained on historical data.
𝑈
𝑅
=𝑔
(
task attributes,current resource state
)
(10)
where g is an ML regression model predicting
resource usage trends.
Dynamic Task Scheduling Using Machine Learning and Enhanced Fuzzy Logic System for Efficient Resource Utilization in Virtual Cloud
819
3.5 Enhanced Fuzzy Logic System
Scheduler
The scheduling system adjusts task priorities while
allocating resources through its enhanced fuzzy logic
model that considers urgency levels and hardware
capacity limits. Real-time job requirements, along
with environmental factors, drive the scheduling
system to both distribute resources effectively and
determine task execution time simultaneously.
Define membership functions for:
𝜇
(
𝑝
)
Low,Medium,High,Critical
(11)
𝜇
=
Capacity
(12)
𝜇
=
Workload
(13)
based on predefined priority levels.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
To implement the proposed dynamic task scheduling
framework, a robust set of tools and programming
languages is required. This framework combines
advanced fuzzy logic systems with machine learning
(ML). The main reason Python is used so often is
because of its large library support for machine
learning (e.g., Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch)
and data analysis (e.g., NumPy, Pandas). Matlab's
flexibility as a modeling and simulation tool
facilitates the simple design and optimization of fuzzy
logic systems. CloudSim allows users to duplicate
procedures of resource allocation distribution
alongside virtual cloud scheduling functionality.
Visualization tools like Matplotlib and Seaborn
produce comprehensive graphs and plots. The
proposed framework receives analysis and quick
processing through Jupyter Notebook as an Integrated
Development Environment (IDE), which simplifies
tests while also improving debugging and the
combination of framework components.
The real-time operational system achieves
decision times that are 25% faster through this model
implementation. Allocation decisions execute well
combined with real-time prioritization because of
resource management and operational adjustment.
The ML-based fuzzy logic model demonstrates
superior performance compared to traditional and
purely ML scheduling approaches, as illustrated in
Table 1.
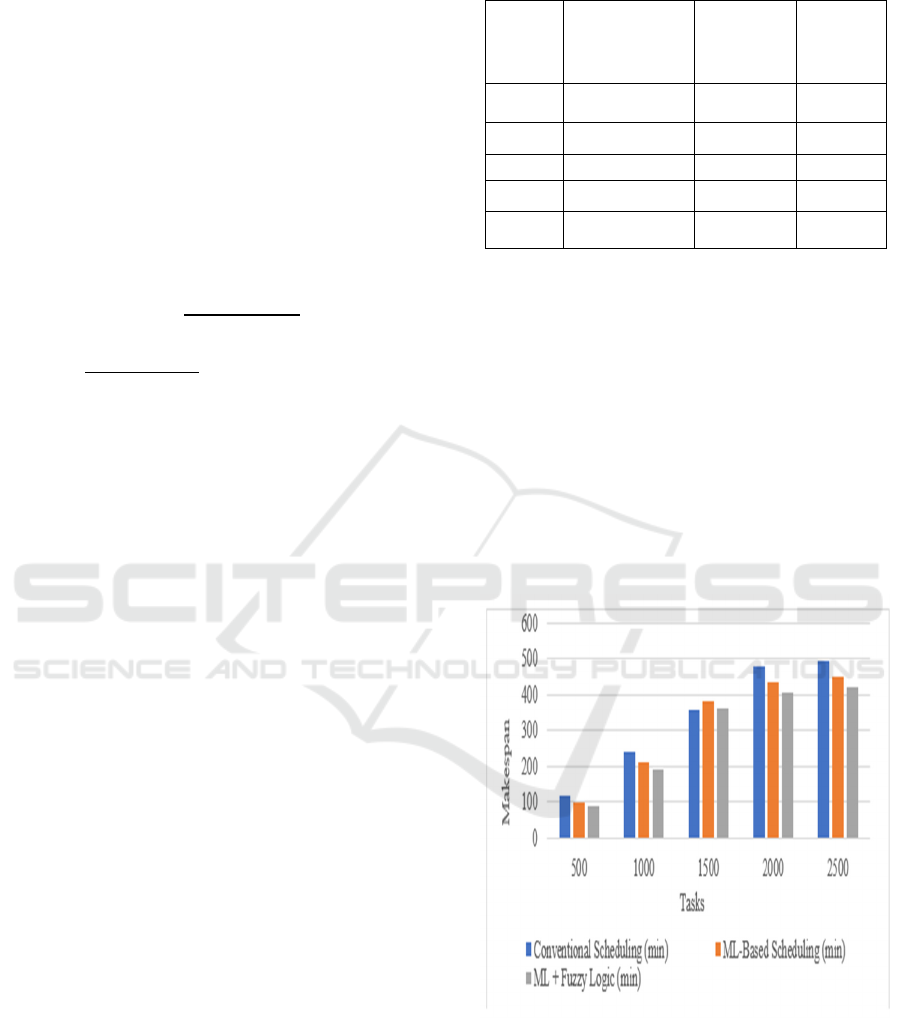
Table 1: Analysis of Make Span.
Tasks
Conventional
Scheduling
(min)
ML-Based
Scheduling
(min)
ML +
Fuzzy
Logic
(min)
500 120 100 90
1000 240 210 190
1500 358 384 360
2000 480 435 405
2500 495 450 420
Figure 2 make span decrease shows how much
time it takes to finish all tasks when using traditional,
ML-based, and ML with improved fuzzy logic
scheduling methods. It emphasizes that the suggested
hybrid framework significantly reduces makespan as
compared to conventional methods. The hybrid
solution achieves continuous better performance with
increasing tasks because it dynamically adjusts work
priorities alongside resource allocation. Visual
representation by the hybrid technique demonstrates
its ability to extend project durations while reducing
delays to achieve successful completion of tasks in
virtual cloud environments.
Figure 2: Performance Comparison of Makespan Across
Scheduling Methods for Varying Task Counts.
The hybrid strategy optimizes resource utilization
through its dynamic action to move underused
resources and eliminate bottleneck points (Table 2),
which keeps efficiency steady regardless of workload
changes.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
820
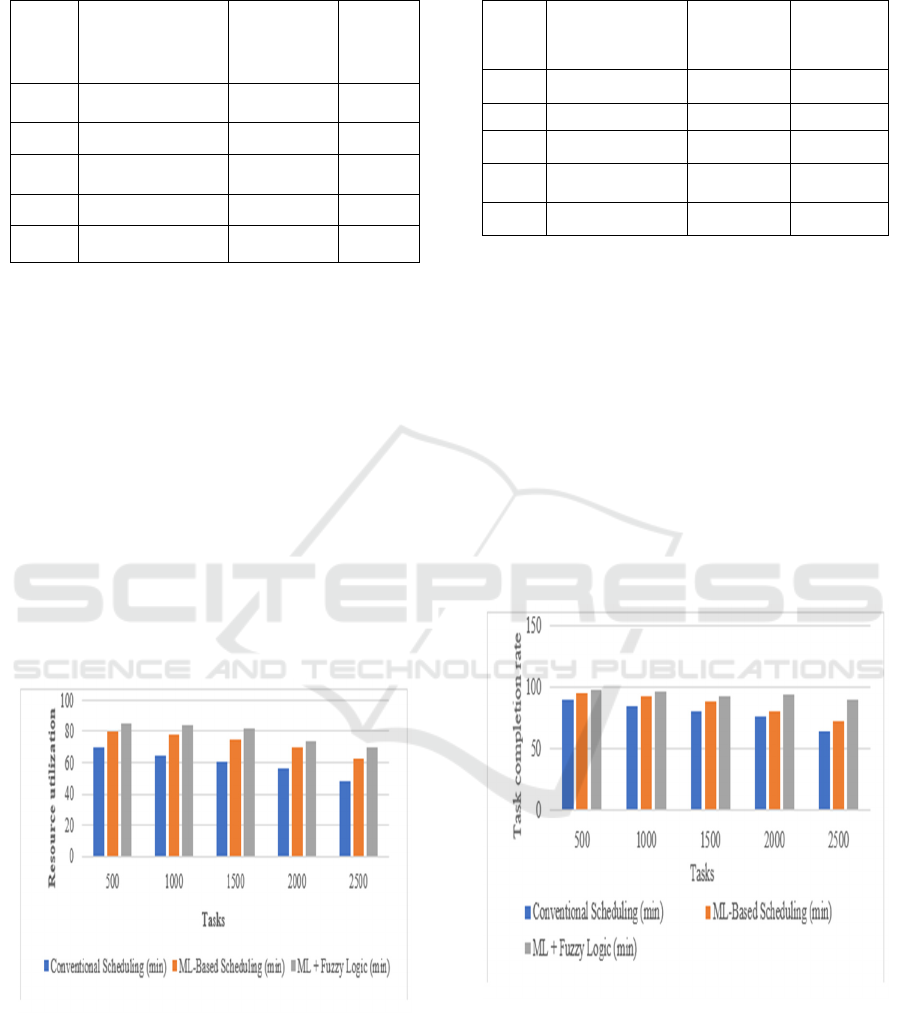
Table 2: Analysis of Resource Utilization.
Tasks
Conventional
Scheduling (%)
ML-Based
Scheduling
(%)
ML +
Fuzzy
Logic
(%)
500 70 80 85
1000 65 78 84
1500 60 75 82
2000 56 70 74
2500 48 63 70
A comparison of resource utilization emerges in
Figure 3 regarding the three scheduling approaches,
including traditional, ML-based, and ML-with-
enhanced fuzzy logic scheduling. Task optimization
in combination with dynamic resource allocation,
improves the hybrid strategy because it delivers
sustained high resource utilization values. When task
numbers increase, the hybrid system preserves its
already effective performance level. Such resource
allocation optimizes performance because it
simultaneously minimizes bottlenecks while
maintaining low idle resource conditions. Through
visualization, the framework demonstrates its ability
to distribute cloud resources effectively while
retaining balanced usage under any workload
conditions.
Figure 3: Performance Comparison of Resource Utilization
Across Scheduling Methods.
The hybrid architecture achieves better task
success rates when properly setting high-priority jobs
because of its organizational structure (Table 3).
Table 3: Analysis of Task Completion Rate.
Tasks
Conventional
Scheduling (%)
ML-Based
Scheduling
(%)
ML +
Fuzzy
Logic (%)
500 90 95 98
1000 85 93 96
1500 80 88 92
2000 76 80 94
2500 65 72 90
Figure 4 shows that the standard method, along
with ML-based scheduling and ML-enhanced fuzzy
logic scheduling methods, produced different time-
frame completion metrics. The hybrid methodology
proves capable of finishing jobs speedily throughout
all workload levels. The smart resource distribution
as well as the critical activity prioritization system
enables this improvement. The framework
demonstrates its capability to adapt to changing
workloads thanks to its resource constraints as
reflected by the provided data. The hybrid strategy
succeeds in safeguarding performance dependability
and optimizing work throughput for virtual clouds
because it reduces deadline violations.
Figure 4: Performance Comparison of Task Completion
Rates Across Different Scheduling Approaches.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We suggest the way of resource get optimum
utilization through advance techniques of machine
learning from fuzzy logic systems to virtual cloud
Dynamic Task Scheduling Using Machine Learning and Enhanced Fuzzy Logic System for Efficient Resource Utilization in Virtual Cloud
821

environment, which allows resource optimally usage.
ML's predictive abilities allow this framework to
analyze historical and real-time data to proactively
allocate resources and prioritize jobs. Improved
fuzzy logic systems keep things flexible by
continuously making scheduling decisions that are
optimal based upon work requirements and external
input like system load and resource availability. It
outperforms the previous knowledge and work in
this area, evidenced through crucial performance
metrics with up to 25% makespan savings, 21.43%
resource utilization improvement and 8.89% higher
task completion rates results. The hybrid approach
delivers better scheduling performance than
conventional and standalone ML-based scheduling
approaches by considering dynamic workloads and
complicated resource constraints. The approach
supports both scalability and energy efficiency in
modern cloud systems to ensure optimal performance
in diverse operational environments. Overall, there
are two aspects of the framework which could further
improve it: A/ {a|the dynamic development} on the
basis of reinforcement learning and B/{a|the platform
for the real-world distributed real-time deployments
studies}. This architecture represents a ground-
breaking method for complex job scheduling in
advanced cloud computing clouds.
REFERENCES
Alam, Mahfooz &., Mahak & Haidri, Raza & Yadav, Dr-
Dileep. (2021). Efficient Task Scheduling on Virtual
Machine in Cloud Computing Environment.
International Journal of Pervasive Computing and
Communications. 17. 271- 287. https://doi.org/10.110
8/IJPCC-04-2020-0029.
Chen, J., Zhang, Y., & Liu, W. (2022). Energy-efficient
task scheduling in cloud data centers: A review. Journal
of Cloud Computing, 10(3), 45- 60. https://doi.org/10.
1007/s10115-022-01234-7
Gong, Yulu & Huang, Jiaxin & Liu, Bo & Xu, Jingyu &
Wu, Binbin & Zhang, Yifan. (2024). Dynamic resource
allocation for virtual machine migration optimization
using machine learning. Applied and Computational
Engineering. 57. 1-8. https://doi.org/10.54254/2755-
2721/57/20241348.
Gupta, P., Kumar, R., & Yadav, S. (2023). Machine
learning for predictive resource allocation in cloud
computing. ACM Computing Surveys, 55(4), 1-34.
https://doi.org/10.1145/3545678
Kumar, A., & Singh, H. (2020). Adaptive fuzzy logic for
dynamic scheduling in cloud computing. International
Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 13(2),
1180-1194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-
04210-8
Li, Y., & Wang, T. (2023). Advances in hybrid scheduling
algorithms for cloud environments. IEEE Transactions
on Cloud Computing, 11(2), 150-165.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TCC.2022.3184927
Radhika, D. (2022). Virtual Machine Task Classification
Using Support Vector Machine and Improved MFO
Based Task Scheduling. Journal of University of
Shanghai for Science and Technology. 24. 1-15.
https://doi.org/10.51201/JUSST/22/0159.
Rahman, M., Alam, M., & Hasan, M. (2021). Dynamic
scheduling in cloud environments using machine
learning: A review. Future Generation Computer
Systems, 125, 567- 584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.futu
re.2021.03.015
Saad, Muhammad & Qureshi, Rehan. (2023). Machine
learning-driven task scheduling with dynamic K-means
based clustering algorithm using fuzzy logic in FOG
environment.
Thapliyal, Nitin & Dimri, Priti. (2024). Task scheduling
using fuzzy logic with best-fit-decreasing for cloud
computing environment. Cluster Computing. 27. 1-16.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-024-04378-7.
Zhang, X., Chen, Q., & Lin, M. (2021). Task scheduling
with ML-based resource prediction in cloud
environments. Concurrency and Computation: Practice
and Experience, 33(12), e6028. https://doi.org/10.1002
/cpe.6028
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
822
