
Identifying Deceptive Reviews Using Machine Learning
Benson Mansingh, J. Sandeep, A. Basanth, M. Yagnesh and G. Asritha
Department of ACSE, VFSTR Deemed to be University, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Deceptive Reviews, Sentiment Analysis, Text Classification, Random Forest Classifier, Machine Learning.
Abstract: Deceptive Reviews System that utilizes Machine Learning, natural language processing (NLP), and sentiment
analysis to accurately distinguish between genuine and fraudulent reviews. The system enhances transparency
and reliability in e- commerce by identifying deceptive feedback. It incorporates TF- IDF vectorization to
extract key textual features. It supports informed purchasing decisions and helps businesses improve based
on genuine user reviews, addressing the challenges posed by fake reviews in the digital marketplace. This
solution plays a crucial role in maintaining the credibility and effectiveness of online review systems
credibility and effectiveness of online review systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Deceptive Reviews are a major challenge in today’s
digital age, particularly on e-commerce platforms
where people rely on feedback from other customers
before making purchases. Misleading reviews can
influence buying decisions and affect business
reputations. Positive deceptive Reviews can promote
low-quality products, while negative fake reviews can
harm the brands. Since Deceptive Reviews often
appear genuine, detecting them manually becomes
difficult. Using this automated technique to identify
and filter out deceptive Reviews is necessary to
maintain trust in online review systems. As more
users turn to online platforms for shopping,
identifying and eliminating deceptive Reviews has
become a critical task to protect consumers from
misinformation (
Mohawesh et al., 2021).
Several strategies, such as pattern analysis and
rule-based algorithms, have been put out in recent
years to identify fraudulent reviews. These models
can detect patterns that are not easily visible to
humans. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
techniques help convert text data into numerical
values, making it easier for models to identify
deceptive Reviews. Sentiment analysis is also useful
in identifying the emotional tone behind reviews,
which adds another layer of information for
improving model accuracy, by leveraging these
techniques, machine learning models can effectively
classify reviews as genuine or fake (
T. Sree and R.
Tripathi, 2023
). The deceptive Reviews System uses
machine learning (ML) and natural language
processing (NLP) approaches to detect bogus product
evaluations. Online reviews influence customer
purchasing decisions. Our system processes reviews
by performing text preprocessing, sentiment analysis
and classification using a random forest model. The
system offers both single review and bulk product
analysis, ensuring transparency and authenticity in
online shopping (
Abdulqader et al., 2022).
In this study, Random Forest classifier used to
distinguish between fake and real reviews .The
process involves cleaning and preparing the text data
by removing unnecessary words, applying
stemming, and converting the text into numerical
format using TF-IDF. The trained model is tested on
unseen data, and the results show that the random
forest classifier performs well in detecting deceptive
Reviews, offering a practical solution for maintaining
the authenticity of online plat- forms. By integrating
sentiment analysis with machine learning, this
approach not only enhances review classification but
also provides a deeper understanding of the emotional
patterns associated with fake and genuine reviews.
This solution plays a crucial role in maintaining the
credibility and effectiveness of online review
systems, fostering a trustworthy environment for
buyers and sellers in the e-commerce ecosystem
(
Chauhan et al., 2022).
1.1 Structure of the Paper
The article starts with an introduction that explains
Mansingh, B., Sandeep, J., Basanth, A., Yagnesh, M. and Asritha, G.
Identifying Deceptive Reviews Using Machine Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013890000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
789-794
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
789

why deceptive Reviews is significant and how
machine learning models can help. The objectives
section shows the list of research objectives. The
description of data set and models used in the study
are explained in the methodology section. The
performance of the different models are presented in
the result and interpretation section. Finally, The
conclusion, which and interpretation section. Finally,
the conclusion, which follows a references section
containing a list of all the sources consulted,
concludes the study and makes recommendations for
further research.
1.2 Objectives
• To examine the machine learning models used
for deceptive Reviews system.
• To assess how well the machine learning
models, detect misleading reviews.
• To train and test a machine learning model to
identify fake and genuine reviews.
• To evaluate the model’s performance using
accuracy, precision, recall, and confusion
matrix.
2 RELATED WORKS
Several machine learning (ML) and deep learning
(DL) techniques have been used in recent advances in
fraudulent reviews, greatly increasing the precision
and effectiveness of detecting false information in
online reviews.
In order to improve the accuracy of deceptive
review identification across various platforms, a
number of researches have investigated sophisticated
machine learning and deep learning techniques. Sree
and Tripathi (2023) utilized Evidential Classifiers to
improve classification accuracy by leveraging
probabilistic reasoning in identifying deceptive
reviews. Similarly, Abdulqader et al. (2022)
developed a Unified Detection Model that integrates
deception theories with behavioral science to analyze
online review patterns, enhancing the detection of
fraudulent content. Chauhan et al. (2022) provided a
comprehensive review of techniques for detecting
fake images and videos, which can be extended to
identifying manipulated reviews through neural
networks and GAN-based models. Catelli et al.
(2023) proposed a method leveraging BERT and
ELECTRA for sentiment analysis to detect deceptive
reviews in datasets related to Italian cultural heritage,
demonstrating the effectiveness of deep learning
models in distinguishing deceptive content. Liu et al.
(2021) explored a multidimensional representation
approach with fine-grained aspect analysis to identify
deceptive reviews by modeling semantic
relationships and contextual information.
Furthermore, Tufail et al. (2022) investigated the
impact of fake reviews on e-commerce platforms
during and after the COVID-19 pandemic and
introduced SKL-based models using K-Nearest
Neighbor (KNN) and Support Vector Machine
(SVM) to classify reviews as genuine or deceptive
(
Pandit, Anala 2018). Deep learning models, especially
convolutional neural networks (CNNs), have proven
to be effective in establishing robust classification
baselines by capturing subtle patterns in review data
(
Rathore et al., 2023). These models demonstrate
superior performance in analyzing contextual
information, sentiment polarity, and behavioral
patterns that distinguish genuine reviews from fake
ones.
3 METHODOLOGY
In this study focuses on deceptive Reviews by first
pre-processing the text data through steps like
removing punctuation, converting to lowercase,
eliminating stop words, and ap- plying stemming.
The dataset is split into training, validation, and
testing subsets, where the model undergoes training,
fine- tuning, and performance evaluation,
respectively. This process involves preprocessing the
textual data by removing irrelevant terms, applying
stemming techniques, and converting the text into
numerical form using TF-IDF. The figure 1 shows the
Flow of the work. The model’s performance is
assessed through evaluation metrics such as accuracy,
precision, recall, F1-score, and ROC-AUC.
Furthermore, a confusion matrix is employed to
analyze and understand the nature of prediction
errors. The models are then tested on unseen data to
ensure they generalize well to new inputs. This
methodology allows us to identify the most effective
model for accurately detecting fake reviews.
3.1 Stemming
In deceptive Reviews, writers may use different
forms of words, such as” buying”,” bought”, and”
buys”, which all con- vey similar meaning. Stemming
normalizes these variations to a single root word like”
buy”, reducing the vocabulary size, and improving
model efficiency. This process helps the model
generalize better by focusing on the core meaning of
the text. In deceptive review detection, stemming
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
790
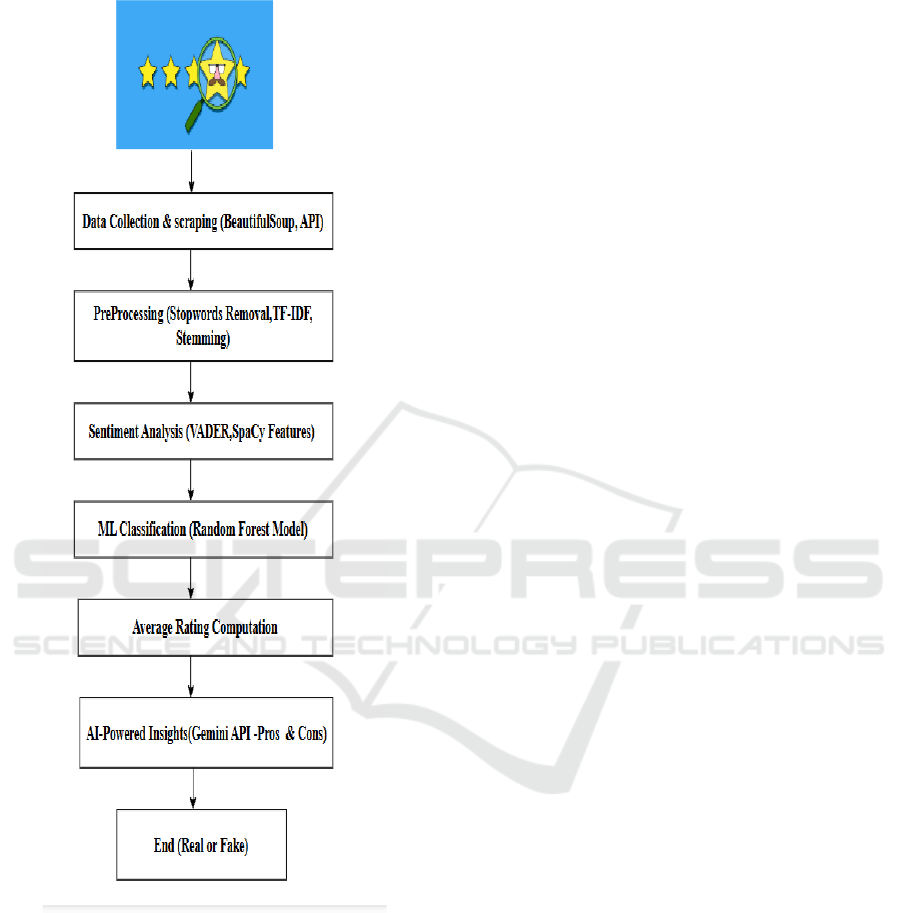
simplifies textual data, making it easier for the model
to identify patterns and classify reviews accurately.
Figure 1: Flow of the Work.
3.2 Stop Words Removal
Stop words removal is an important pre-processing
step in a deceptive Reviews system where
common words like” the”,” is”, and “and” in” are
eliminated since they do not contribute meaningful
information. These words often appear frequently but
provide little value in distinguishing between genuine
and fake reviews. Removing them reduces noise and
allows the model to focus on more significant terms,
improving efficiency and reducing complexity. In
fake review detection, eliminating stop words ensures
that only relevant words are analyzed, helping the
model detect patterns more effectively and classify
reviews with better accuracy.
3.3 Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment Analysis is a technique used in deceptive
Reviews systems to analyze the emotional tone or
opinion expressed in a text. It helps categorize reviews
as positive, negative or neutral based on the sentiment
conveyed. By identifying these pat- terns, sentiment
analysis can detect that may indicate deceptive
behavior. The VADER model from the NLTK is
widely used for sentiment analysis, as it is effective
in capturing sentiment intensity and is optimized for
short text, such as reviews. In deceptive review
detection, sentiment analysis serves as an additional
layer of evaluation, enhancing the model’s ability
to
identify suspicious patterns and improve
classification ac- curacy.
3.4 TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse
Document Frequency)
TF-IDF is an effective technique for extracting
features from text, often applied in identifying fake or
deceptive reviews. It converts textual content into
numerical formats that can be efficiently processed by
machine learning algorithms. The figure 2 shows the
TF-IDF. Term Frequency (TF) quantifies the
occurrence of a word within a given document, while
Inverse Document Frequency (IDF) adjusts its
significance by down-weighting terms that frequently
appear across numerous documents, thereby
emphasizing rarer yet more informative words. In
the realm of fake review identification, TF-IDF
plays a crucial role by highlighting distinctive terms
that differentiate authentic reviews from fraudulent
ones, assigning greater importance to unique and
contextually relevant words. This transformation
reduces noise caused by frequently used words and
improves the model’s ability to detect patterns. By
applying TF-IDF, the system enhances the
effectiveness of classifiers by providing a more
accurate representation of the textual data.
Identifying Deceptive Reviews Using Machine Learning
791
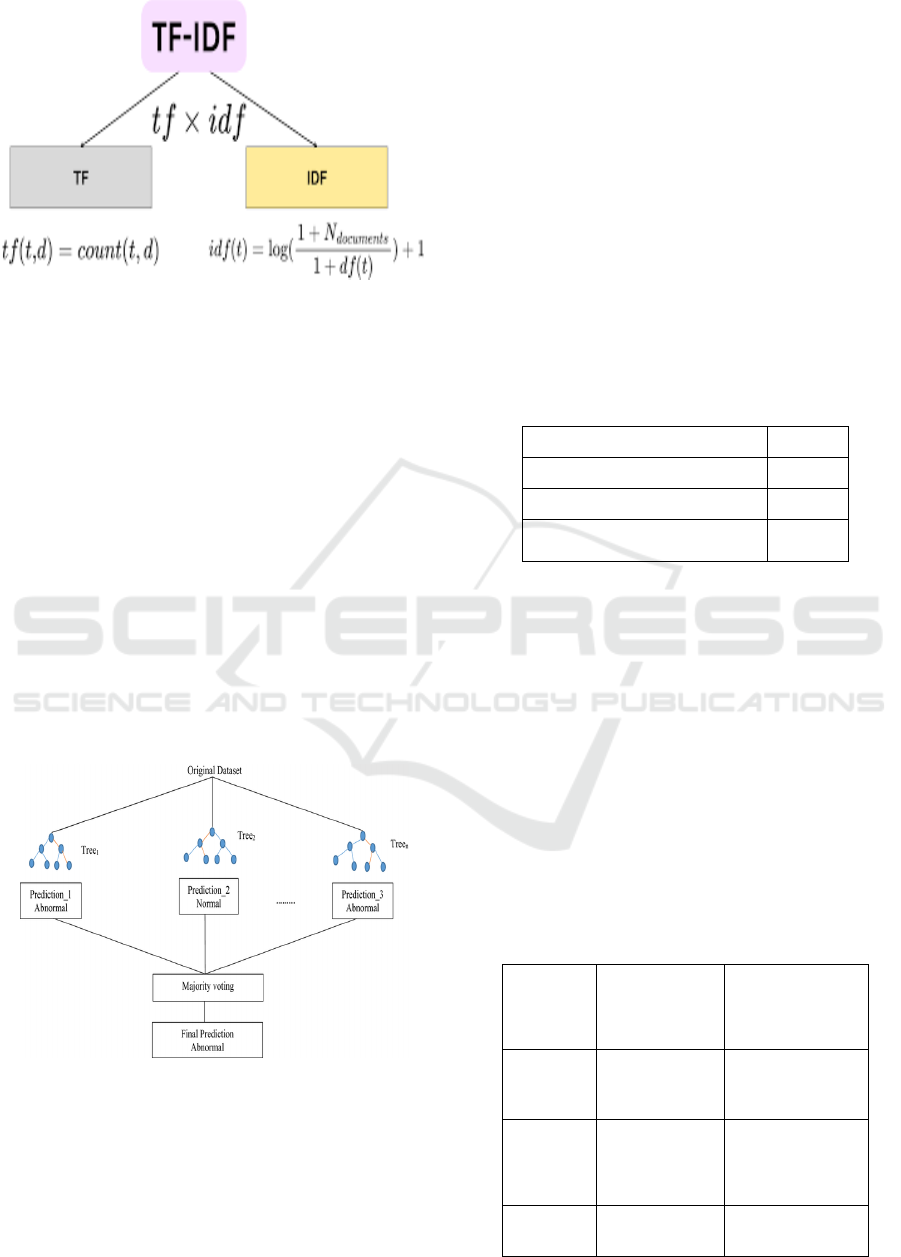
Figure 2: TF-IDF.
3.5 Random Forest Model
Random Forest is a powerful machine learning
algorithm commonly used in deceptive Reviews due
to its effectiveness in handling large datasets and
reducing overfitting. It is an ensemble method that
constructs multiple decision trees and combine their
predictions to generate a more accurate result. The
figure 3 shows the Random Forest Model. In fake
review detection, Random Forest processes features
extracted from text, such as word frequencies and
sentiment scores, to classify reviews as either
genuine or fake. Each tree in the forest makes an
independent prediction, and the final decision is
determined through majority voting, improving
model reliability, it is well-suited for identifying
patterns in fake reviews, leading to better accuracy
and performance in unseen data.
Figure 3: Random forest model.
4 RESULTS AND
INTERPRETATION
Several models were used to determine whether a
review is fake or not, and many machine learning
models are put into practice once the data has been
preprocessed.
4.1 Dataset Description
The” Deceptive Reviews Dataset” consists of 40,000
product reviews, evenly split into 20,000 genuine
reviews and 20,000 deceptive reviews. Authentic
reviews are composed by real users, expressing their
actual experiences, whereas fake reviews are
artificially generated to mimic genuine customer
feedback. This dataset is structured to help develop
and evaluate machine learning models for fake review
detection, offering opportunities for feature analysis,
sentence analysis and classification tasks.
Table 1: Summary of the fake reviews dataset.
Dataset Description Details
Total Number of Reviews 40,000
Number of Real Reviews (OR) 20,000
Number of Deceptive Reviews
(CG)
20,000
Table 1 displays the distribution of the Fake review
dataset. The dataset consists of 40,000 overalls, split
into two categories: Real and Deceptive. Specifically,
20,000 are Real reviews and remaining 20,000 are
deceptive reviews.
Table 2 presents the Deceptive Reviews Dataset
where it is partitioned into training, validation, and
testing sets. The Training Set comprises 28,000
reviews (14,000 genuine and 14,000 deceptive). The
Validation Set includes 6,000 reviews (3,000
authentic and 3,000 deceptive), while the Testing Set
also consists of 6,000 reviews (3,000 real and 3,000
fake), used to evaluate the model’s effectiveness on
unseen data.
Table 2: Dataset split for fake review detection.
Dataset Split
Number of
Reviews
Real+Deceptive
Review
Training Set 28,000 14,000 + 14,000
Validation
Set
6,000 3,000 + 3,000
Testing Set 6,000 3,000 + 3,000
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
792
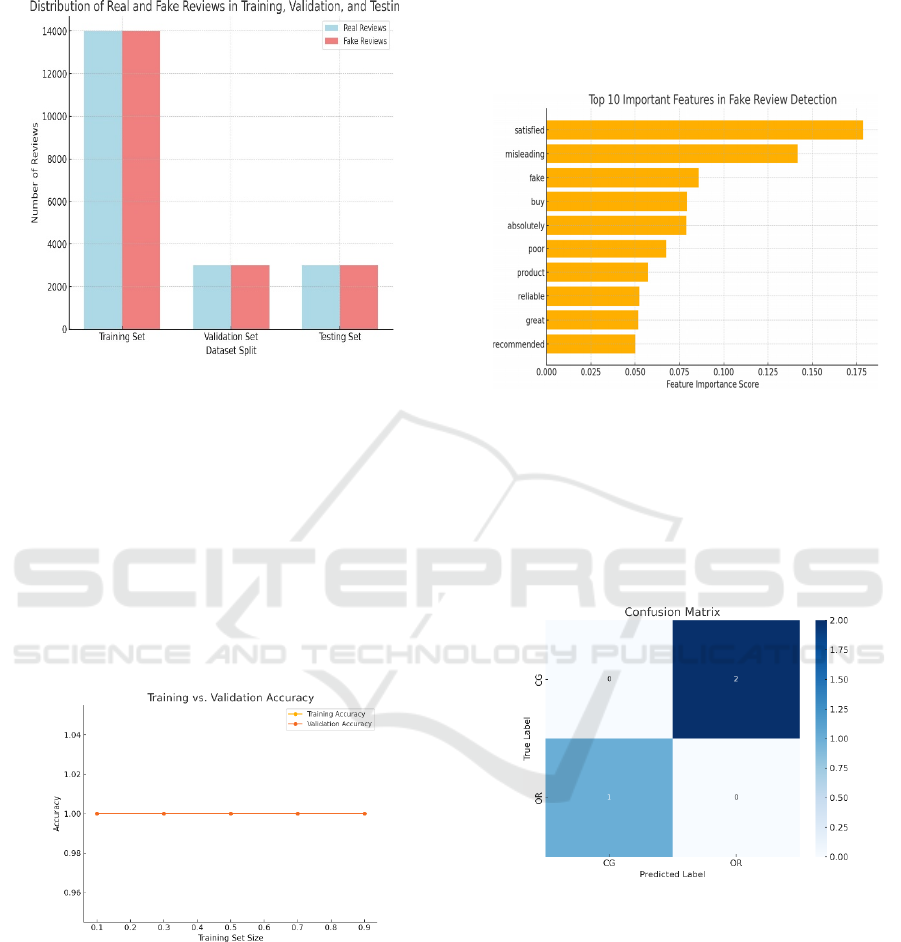
4.2 Data Split Based on Reviews Graph
Figure 4: Data split based on reviews.
The graph shows the distribution of real (OR) and
deceptive (CG) reviews across the dataset splits. The
figure 4 shows the Data Split based on reviews. The
Training Set has 28,000 reviews (14,000 real and
14,000 deceptive), while the Validation Set and
Testing Set each contain 6,000 reviews (3,000 real
and 3,000 deceptive). This balanced split ensures the
model is trained and evaluated effectively.
4.3 Training vs Validation Accuracy
Graph
Figure 5: Training vs validation accuracy graph.
The graph compares Training Accuracy and
Validation Accuracy at different training set sizes. As
the training size increases from 10% to 90%, the
model’s performance improves, with both accuracies
converging closely. The figure 5 shows the Training vs
validation Accuracy Graph. This indicates that the model
generalizes well, with minimal overfitting or
underfitting.
4.4 Feature Extraction for Reviews
Graph
The Feature Importance graph highlights the top 10
features contributing the most to the classification of
deceptive and real reviews.
Figure 6: Feature extraction for reviews graph.
The figure 6 shows the Feature Extraction for Reviews
Graph. These features are identified using the Random
Forest model, where higher scores indicate stronger
influence on the model’s decision-making.
4.5 Confusion Matrix
Figure 7: Confusion matrix.
The Confusion Matrix serves as a graphical
representation of the model’s classification
performance by contrasting predicted outputs with
actual labels. The figure 7 shows the Confusion
Matrix. It displays the number of correctly and
incorrectly classified instances for both real (OR) and
fake (CG) reviews, enabling a detailed assessment of
classification accuracy and helping to detect potential
misclassification errors.
Identifying Deceptive Reviews Using Machine Learning
793

5 CONCLUSIONS
The Deceptive Review Detection System efficiently
detects fraudulent reviews by utilizing Natural
Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning
(ML) methods. Through a combination of text
preprocessing, sentiment analysis, and a robust
random classifier, the system achieves high
accuracy in between genuine and fake reviews. The
integration of a user-friendly streamlit interface
allows seamless analysis of both individual and bulk
reviews, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
By promoting transparency and trust in online
platforms, this system helps safeguard consumers
from deceptive reviews, ultimately contributing to a
more reliable and secure e-commerce environment.
REFERENCES
Abhijeet A Rathore, Gayatri L Bhadane , Ankita D Jadhav
, Kishor H Dhale, Jayshree D Muley, 2023, Deceptive
Reviews Detection Using NLP Model and Neural
Network Model, international journal of engineering
research technology (ijert) Volume 12, Issue 05 (May
2023)
H. Tufail, M. U. Ashraf, K. Alsubhi and H. M. Aljahdali,”
The Effect of Deceptive Reviews on e-Commerce
During and After Covid-19 Pandemic: SKL-Based
Fake Reviews Detection,” in IEEE Access, vol. 10,
pp. 25555-25564, 2022, doi:
10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3152806.
M. Liu, Y. Shang, Q. Yue and J. Zhou,” Detecting Decep-
tive Reviews Using Multidimensional Representations
With Fine-Grained Aspects Plan,” in IEEE Access, vol.
9, pp. 3765-3773, 2021, doi: 10.1109/AC-
CESS.2020.3047947.
M. Abdulqader, A. Namoun and Y. Alsaawy,” Deceptive
Online Re- views: A Unified Detection Model Using
Deception Theories,” in IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp.
128622-128655, 2022, doi: 10.1109/AC-
CESS.2022.3227631.
Pandit, Anala. “Deceptive Review Detection Using Clas-
sification.” International Journal of Computer Appli-
cations, Foundation of Computer Science, 2018.
R. Mohawesh, M. Hasan, and E. Damiani,” Deceptive
Reviews Detection: A Survey,” IEEE Access, vol. 9,
pp. 65771-65802, 2021, doi:
10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3075573.
R. Chauhan, R. Popli and I. Kansal,” A Comprehensive
Review on De- ceptive Images/Videos Detection
Techniques,” 2022 10th International Conference on
Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization
(Trends and Future Directions) (ICRITO), Noida,
India, 2022, pp. 1- 6, doi:
10.1109/ICRITO56286.2022.9964871
R. Catelli et al.,”A New Italian Cultural Heritage Data Set:
Detecting Deceptive Reviews with BERT and
ELECTRA Leveraging the Sentiment,” in IEEE Ac-
cess, vol. 11, pp. 52214-52225, 2023, doi:
10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3277490.
R. Catelli et al.,” A New Italian Cultural Heritage Data Set:
Detecting Deceptive Reviews With BERT and
ELECTRA Leveraging the Sentiment,” in IEEE Ac-
cess, vol. 11, pp. 52214-52225, 2023, doi:
10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3277490.
T. Sree and R. Tripathi,” Deceptive Review Detection
using Evidential Classifier,” 2023 Second International
Conference on Advances in Computational Intelligence
and Communication (ICACIC), Puducherry, India
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
794
