
Reversible Generative Steganography Leveraging Distribution
Preserving Encoding for Enhanced Data Security and Integrity
J. Uthayakumar
1
, S. Sreeraj
2
, C. Sandhiya
3
, Ram Ganesh G. H.
4
, T. Mohanraj
5
and R. Senthilkumar
1
1
Department of CSE, Hindusthan Institute of Technology, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
2
M.Tech CSE, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
3
Department of CSE, Nehru Institute of Engineering and Technology Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
4
Department of IT, Kamaraj College of Engineering and Technology, Virudhunagar, Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of CSE, Karpagam Academy of Higher Education, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Steganography with Reversibility, Model of Generative Action, Coding for Distribution‑Preserving, Data
Inconspicuousness, Recovery of Information without Loss, Protection of Stego‑Images.
Abstract: Distribution-Preserving encoding combined with reversible generative steganography has been a key
development in safe data embedding and retrieval. Achieving lossless recovery is difficult with traditional
stenographic approaches since they frequently compromise reversibility and data integrity. In this paper, a
novel framework that combines a distribution-preserving encoding technique with reversible generative
steganography is proposed. The suggested technique embeds cover images with hidden messages while
guaranteeing that the encoded data maintains its statistical characteristics. In order to ensure imperceptibility
and reversibility, our method uses a deep generative model to map the secret message into a latent space while
maintaining the data distribution. In order to recover the original secret message without distortion, a stego-
image is created and decoded using an inverse generative model. We perform extensive tests on benchmark
datasets to assess the efficacy of our system, proving full reversibility, improved embedding capability, and
security. Our methodology offers state-of-the-art performance, ensuring lossless information retrieval and
preserving high quality in cover images when compared to conventional methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since steganography has the ability to secretly inject
messages into digital content, it is crucial for secure
data transmission. Examples of traditional
steganographic techniques that often have limited
capacity, obvious distortions, and are susceptible to
steganalysis include transform-domain embedding
and Least Significant Bit (LSB) substitution.
Furthermore, after message extraction, the original
cover image cannot be totally restored because many
of these approaches are irreversible. Researchers
have looked into reversible steganography as a way
to get around these limitations because it allows for
the full recovery of the cover image and the hidden
message after decoding. The development of
reversible generative steganography, which uses
invertible deep networks like Glow-based models to
learn data distributions and embed secret messages
while preserving statistical properties, has been made
possible by recent advances in deep generative
models, specifically in the area of normalizing flows.
This ensures high security, reversibility, and
imperceptibility. Because distribution-preserving
encoding guarantees that stego-images stay visually
and statistically identical to natural images, detection
becomes much more difficult than with traditional
deep learning-based steganography, which may
introduce residual distortions or require auxiliary data
for extraction. The goal of research in reversible
generative steganography is to create an effective,
high-capacity, and lossless steganographic
framework that addresses important issues like
detectability, reversibility, and robustness.
The necessity for safe and untraceable
information hiding in digital communication is what's
driving this. Many conventional methods fail to
strike a compromise between embedding capacity
and imperceptibility, introduce artifacts that are
observable by contemporary steganalysis techniques,
Uthayakumar, J., Sreeraj, S., Sandhiya, C., H., R. G. G., Mohanraj, T. and Senthilkumar, R.
Reversible Generative Steganography Leveraging Distribution Preserving Encoding for Enhanced Data Security and Integrity.
DOI: 10.5220/0013889000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
723-730
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
723

and, following extraction, the original cover image is
not recovered.
Glow-based reversible generative models are the
subject of this study in order to overcome these
difficulties. Probabilistic encoding and decoding
techniques are used to accomplish high-fidelity,
lossless message recovery while maintaining the
cover image's natural distribution. A reversible
encoding-decoding framework that uses Glow-based
normalizing flows, lossless message recovery, a
distribution-preserving mapping technique that
improves security against steganalysis, high-capacity
embedding with imperceptibility, and an optimized
extraction pipeline for effective and reliable message
decoding using inverse generative transformations
are some of the study's main contributions.
Modification-based approaches, which involve
changing transform-domain coefficients or pixel
values to insert hidden information into an existing
cover image, are the mainstay of traditional
steganographic techniques. Ntivuguruzwa and
Ahmad (2023) state that although these techniques
provide a certain degree of protection, they often
create tiny distortions that are detectable by
sophisticated steganalysis tools, particularly at high
hiding capacities. The risk of message disclosure is
increased by these artifacts, which also undermine the
stego-image's imperceptibility. Furthermore, most
traditional steganographic methods are irreversible,
which means that once the hidden message has been
recovered, the original cover image cannot be fully
restored. This restricts their use in delicate
applications like forensic investigations and medical
imaging.
One potential solution to these problems is
generative steganography. (2020) and (2023) assert
that generative models create stego-images, which are
intrinsically secret, rather than altering an existing
cover image. This method improves security by
removing artifacts caused by alteration, which makes
detection much more challenging. Additionally,
generative stego-pictures are quite challenging for
ordinary AIGC detectors to distinguish from other
AI-generated images, despite the fact that methods
for identifying AI-generated content (AIGC) have
been developed to categorize artificial images (2023;
2022).
Current generative steganographic techniques
usually convert secret messages into image labels or
latent noise vectors before supplying them to
generative adversarial networks (GANs).
1.1 Lack of Distribution-Preserving
Encoding
Most GAN-based models encode secret messages in
a way that disrupts the natural statistical distribution
of the generated image. Using statistical analysis in
the feature domain, attackers can identify the
existence of concealed information since the latent
vectors used to create stego-images are different from
those used for regular images (2021; 2021; 2022).
The discriminator's capacity to distinguish stego-
images from regular images is what makes these
techniques secure, although there isn't a solid
theoretical basis for complete security.
1.2 Irreversible Transformations
Perfectly reconstructing the original secret message is
challenging with GAN-based steganography since it
uses a one-way mapping from the latent space to the
image space. Because of this, message extraction is
prone to distortion, particularly when there is more
information packed in the image in high-capacity
circumstances. Because of this irreversibility,
message recovery is less reliable, which makes these
techniques inappropriate for applications that need to
retrieve data without loss.
Glow-based reversible generative steganography
employs advanced encoding and transformation
techniques to ensure secure, lossless information
hiding while maintaining the statistical properties of
cover images. The core algorithm relies on
distribution-preserving mapping, where secret
messages are mapped into a latent space following a
Gaussian distribution rather than being directly
embedded into the image. This ensures that the
encoded message remains indistinguishable from
natural data distributions, significantly enhancing
security against steganalysis. A Glow-based
generative model (a normalizing flow approach) is
utilized to learn an invertible transformation between
image space and latent space, allowing for reversible
image transformation without introducing distortions.
The use of reversible data embedding ensures that
both the message and the original cover image can be
recovered perfectly, overcoming the limitations of
traditional steganographic methods that often
introduce irreversible changes. Entropy encoding
optimizes data compression and embedding
efficiency, maximizing capacity while maintaining
imperceptibility. Furthermore, noise-aware encoding
adjusts the encoding process to account for variations
in image features, enhancing robustness against
detection. By leveraging an inverse mapping
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
724

function, the system ensures that message extraction
is lossless and highly accurate. The combination of
these techniques makes Glow-based generative
steganography a powerful approach for secure,
undetectable, and fully reversible data hiding.
2 RELATED WORKS
Generative Steganography:
As opposed to
traditional modification-based steganography,
which incorporates confidential data into an
existing cover image, generative steganography
generates stego-images from text using generative
models.covert communications. By eliminating
explicit pixel changes, this coverless technique
reduces statistical abnormalities that steganalysis
tools could take advantage of, hence enhancing
security. In order to safeguard digital forensics,
copyright, privacy, and secret communication,
generative steganography has been thoroughly
studied due to its strong anti-detectability. Early
methods of generative steganography used texture
creation to encode secret communications. Data
was incorporated into high-frequency texture
images in (2015), and words were transformed into
fingerprint-like holographic images (2018).
Attackers became suspicious, though, because
these methods created outputs that were visually
odd. Secret communications were encoded using
texture creation in early generative steganographic
techniques. Xu and colleagues (2015) integrated
data into high-frequency texture pictures, (2018)
converted words into holographic visuals that
resembled fingerprints. Attackers became
suspicious, though, because these methods created
outputs that were visually odd. Deep learning-
based generative models were introduced by
academics to increase realism. Techniques based
on GANs., (2014) gained popularity because they
made it possible to create stego-images that looked
realistic. A number of methods embedded secret
messages within significant visual structures using
semantic constraints: GAN-based picture synthesis
was constrained by messages encoded into anime
character attribute labels in (2020) (2017). Since
labels and attributes can only encode a limited
amount of information, these semantic-based
approaches have a low concealing capacity. Later
methods investigated direct message encoding into
GAN noise vectors to boost capacity: . (2018) and.
(2020) created stego-images with directly altered
noise vectors that included secret messages using
Deep Convolutional GANs (DCGANs) (2016). To
create images from message-encoded noise
vectors, (2020) used Wasserstein GAN with
gradient penalty (WGAN-GP) Normalizing flow-
based generative models, which offer invertible
and distribution-preserving transformations
between data and latent spaces, has been
investigated by researchers as a solution to these
problems. In contrast to GANs, normalizing flows
guarantee that each generated image has a
bijective, direct mapping to its associated secret
message, allowing for lossless message extraction.
With the help of normalizing flows like RealNVP
(2017) and Glow (2018), created images can
closely resemble real-world statistical distributions
since they achieve precise likelihood estimate. This
characteristic makes them especially well-suited
for distribution-preserving steganography, which
aims to produce stego-images that, even in feature
space, are identical to real images. Although
studies on normalizing flow-based steganography
are still in their infancy, some notable
developments include Secure picture concealment
and retrieval were made possible by Invertible
picture Encryption (2021), which used normalizing
flows for reversible image changes. The potential
of glow-based models in encoding secret messages
while maintaining picture distribution features was
demonstrated by flow-based steganography
(2022).
Reversible Generative Steganography Security
Definition Theoretically:
The first information-
theoretic security model for steganography was
created in 1998 and measured steganographic
security using relative entropy. The security of
reversible generative steganography with
distribution-preserving encoding is evaluated by
comparing the statistical differences between the
model's stego-images and natural images.
Let X S be a random variable representing the
stego-image space X S with a probability
distribution
(
) P S (X S), and X C be a
random variable representing the natural image
space X C with a probability distribution
(
)
P C (X C). The Jensen-Shannon divergence (JSD)
provides a more symmetric and stable metric for
evaluating the security of reversible generative
steganography than Kullback-Leibler divergence.
(1)
where M is the mixed distribution:
(2)
Reversible Generative Steganography Leveraging Distribution Preserving Encoding for Enhanced Data Security and Integrity
725

In contrast to conventional GAN-based generative
steganography, where non-distribution-preserving
transformations frequently cause the distributions P C
(X C) and P S (X S) to diverge, our Glow-based
normalizing flow model guarantees that the produced
stego-images adhere to the precise statistical
characteristics of natural images. Distribution-
preserving encoding results, which makes messages
harder for steganalyzers to detect while enabling
lossless message recovery via invertible
transformations.
Furthermore, the Wasserstein distance can be used to
measure how similar the two distributions are:
(3)
where Π (P C, P S) is the set of all conceivable joint
distributions with marginals
P C and
P S.
respectively. Compared to current generative
steganographic techniques, a shorter Wasserstein
distance indicates that the stego-pictures are
indistinguishable from genuine photos,
guaranteeing greater security and imperceptibility.
Reversible Generative Steganography via
Glow-Based Technology with Distribution-
Preserving Encoding:
Among flow-based
generative models that create a bijective mapping
between a simple-distributed latent space and a
complex-distributed image space, in creating
realistic, high-quality images while maintaining an
invertible transformation between the generated
images and the latent vectors, the Glow model
(2018) has proven to be incredibly effective.
Due to these characteristics, Glow-based
models are ideal for distribution-preserving
encoding in reversible generative steganography,
which guarantees lossless message retrieval and
improved security against steganalysis. In this
study, we use the Glow model to create stego-
pictures while maintaining the statistical
consistency between the produced and natural
images.
Latent Space Representation and Distribution-
Preserving Encoding:
With a straightforward,
effective, and computationally viable encoding
strategy, the Glow model uses a Gaussian prior to
approximate the latent space distribution,
efficiently capturing complicated dependencies in
data. Using a straightforward probability
distribution
(
) P Z (Z), which is commonly
represented as a spherical multivariate Gaussian
distribution, In the latent space, let Z be the random
variable. The variable in image space with the
complex probability distribution (
) P X (X) can
also be represented by the letter X.
It is possible to define the probability density
function P Z (Z) as a product of independent
components Z d, given that the dimension of Z is
equal to that of X:
(4)
A one-dimensional Gaussian distribution is
represented by (Z d).
A direct transformation between the image space and
latent space is established by training the Glow model
to learn an invertible function () f θ (X) in order to
produce a directive mapping:
(5)
where the encoding and decoding functions are
represented, respectively, by f θ and their inverse, g
θ.
Using a maximum log-likelihood estimation
technique, the Glow model is optimized given a
training dataset P data, which consists of picture
samples X normalized to (0,1)
(6)
By using the mapping functions () f θ (X) and
() g θ (Z), a pre-trained Glow model can be used
to bijectively translate the image space and latent
space. Thus, a reversible encoding method is enabled,
wherein secret messages are first transformed into
high-quality, realistic stego-images and then mapped
into a Gaussian space that guarantees distribution.
The proposed reversible generative steganographic
technique consists of two primary stages: secret
information extraction and secret information
embedding.
Structure of the Suggested Distribution-
Preserving Encoding Reversible Generative
Steganography: In the secret information
embedding step, a distribution-preserving mapping
technique is used to convert the secret message M into
a Gaussian-distributed latent vector z. Next, a stego-
image I is created using the Glow generative model
() G θ (z), which guarantees that the secret
information is embedded while preserving a natural
visual look. During secret information extraction, the
receiver can extract the latent vector ′ z ′ from the
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
726
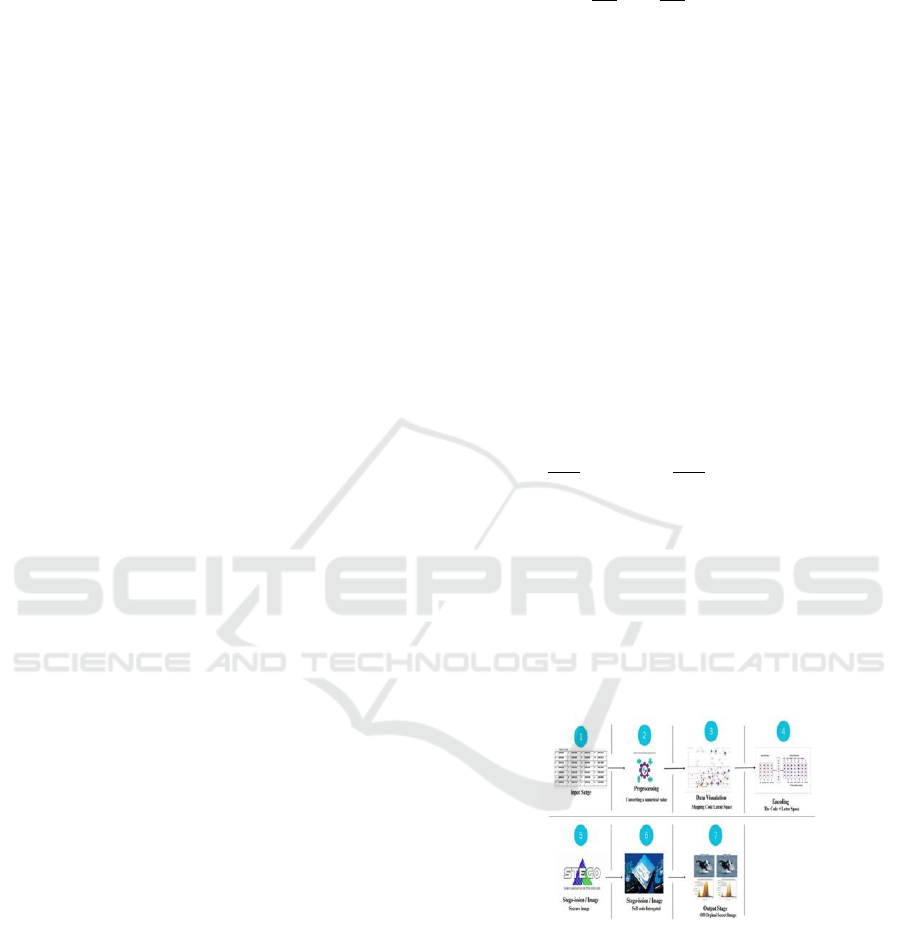
received stego-image I by using the inverse Glow
function − 1 ( ) G θ −1(z) since the Glow model
is invertible. The inverse distribution-preserving
mapping is used to recreate the secret message ′ M
′ from ′ z ′, allowing for lossless message retrieval
while maintaining security and reversibility.
Embedding Secret Information: The two primary
processes of the secret information embedding stage
are stego-image generation and message mapping.
This is accomplished by first mapping the secret
message to a latent vector using a distribution-
preserving encoding technique. In order to create the
stego-image while preserving statistical consistency
with naturally generated images, the Glow model is
then applied. According to the Glow model (in 2018),
an affine coupling layer, an invertible 1×11 \times
11×1 convolution, and an activation normalization
layer make up each stage of the normalizing flow. In
order to improve security and thwart steganalyzer
detection, the stego-image is made to statistically and
visually mimic real photos. This is done by making
sure that the underlying distribution is preserved
during the message encoding process, which keeps
the resulting stego-images distribution-consistent.
Message Mapping and Image Generation in
Reversible Generative Steganography with
Distribution Preservation Encoding: Since it
enables information to be inserted without a
designated cover image, secret message mapping is
crucial to reversible generative steganography. We
ensure statistical coherence with the original data
distribution by explicitly encoding the secret message
into a latent vector, in contrast to traditional
steganographic techniques. Algorithm 1 describes
how messages are mapped. The first secret message
can be represented by Mori, which is a l-bit bitstream
that must be hidden. The message is initially
encrypted using a secret key sequence k and a
cryptographically secure pseudo-random number
generator (CSPRNG) to increase security.
(7)
In what location is the XOR operator element-wise?
For mapping to be possible, M is split into N equal
segments (m₁, mᵢ, mₙ). M is a multiple of N in length,
which is ensured by using zero padding. The pre-
trained Glow model requires that the encrypted
message M be adjusted to meet the traditional
Gaussian distribution (z N (0,1)) due to its uniform
distribution (M U (0,1)). Put z = {z₁, zᵢ, zₙ} as the
latent vector and xᵢ as the decimal representation of
mᵢ. Here is how to make the switch from a uniform to
a Gaussian distribution:
(8)
where:
The term Rand (a, b) refers to a sampling function that
produces a random value within the range (a, b). The
CDF, or cumulative distribution function, is F (·) for
a Gaussian distribution and F⁻¹ (·) for its inverse.
Thus, the final transformation for creating the latent
vector z is:
A reversible Gaussian-distributed latent space is
mapped into message-embedded values to generate
the latent vector . Start by breaking the secret
message M into its component components
and converting each one to a decimal value x i.
The function Rand (, ) Rand(a,b) is used to sample a
uniform distribution and introduce a random
perturbation y to make sure that these values fall
inside a predetermined range. Values in the range (,)
(a,b) are obtained as a result.
(9)
By utilizing this distribution-preserving encoding,
the secret message is successfully incorporated
inside the latent space, ensuring that the resulting
stego-images preserve great perceptual and
statistical reliability.
Message Mapping and Image Generation in
Reversible Generative Steganography with
Distribution Preservation Encoding
Figure 1: A Demonstration of the Distribution-Preserving
Encoding Method of Reversible Generative
Steganography.
Mapping messages: Message mapping ensures that
hidden information is incorporated within a latent
vector while retaining a distribution-preserving
transformation in our reversible generative
steganography method. Here's how the mapping
function is defined:
Reversible Generative Steganography Leveraging Distribution Preserving Encoding for Enhanced Data Security and Integrity
727
Image generation:
Between the generated stego-
image and the latent space, the Glow model
produces a stable and objective transformation. This
makes reversible information embedding possible,
which enhances the accuracy of the secret message
extraction process after recovery. In summary,
distribution-preserving message mapping boosts
the imperceptibility of hidden information and
improves message extraction accuracy, while the
reversible alteration of the Glow model decreases
the likelihood of steg analysis detection.
3 DISTRIBUTION-
PRESERVING ENCODING
AND REVERSIBLE SECRET
INFORMATION
EXTRACTION IN
GENERATIVE
STEGANOGRAPHY
Reconstructing latent vectors: M = {m₁, ··, mᵢ, ··,
mₙ}, where N is the number of segments of the
encrypted secret message. Unlike conventional
steganographic techniques that modify existing
cover images, our methodology applies a Glow-
based generative model to create entirely new
stego-pictures. Figue 1 show the, a latent vector
with a Gaussian distribution is created from the
encoded secret message after the message mapping
process. Subsequently, this latent vector is
transformed into a corresponding stego-image by
the Glow model, facilitating secret communication.
Secret Message decoding : From z′, the recipient
decodes the message using the known length (l) of
the original secret message Mₒᵣᵢ. Since zero-padding
was used during the embedding process, the
following formula determines how many bits there
are in each segment δ:
(11)
(12)
Stego-images are statistically indistinguishable: To
avoid identification by attackers, created stego-
pictures must be statistically comparable to images
produced by ordinary generative models with no
information hiding. This is ensured by the mapping
between xi and zi. The conditional probability
distribution is defined as.
(13)
The inverse cumulative distribution function
(CDF) is denoted by F⁻¹(·), while the PDF of a normal
Gaussian distribution is denoted by f(zi). According
to the complete probability theorem, we determine
zi's probability distribution as
Table 1: Superior Accuracy Across Various Hiding Capabilities.
Input:
Secret message: M ori.
Secret key sequence: k.
The number of encoding segments is N.
Pre-trained normalizing flow model: G θ
Output
Output: Encoded latent representation: = {
1, …,
z={z 1,…,z N}
Steps:
To preprocess a message, convert the
characters , , , and to a binary sequence.
1. Split the binary sequence into N equal-length
segments: {1 , … , } {m 1,…,m N}.
2. Map Binary to Latent Space - Convert each
segment ( m i) to a decimal representation
( x i).
Normalize x iinside the desired latent
space.
3. Distribution-Preserving Encoding: - Sample
auxiliary noise (0,1) y i
N(0,1).Encode x iusing the invertible
sampling function ( , ) S(x i,y i),
ensuring z ikeeps the original distribution
parameters.
4. Use the Normalizing Flow Model to
transform z iusing the generative model
G θ, creating stego representation − 1 (
) G θ −1(z).
5. Output Encoded Representation: Store the
modified latent vector for reversible
retrieval.
6. End Algorithm
Accuracy in information extraction in reversible
generative steganography with distribution-
preserving encoding: To evaluate the proposed
method's information extraction accuracy (IEA)
across various hiding capacities, we compare it to
SWE, as shown in Table 1. Superior Accuracy Across
Various Hiding Capabilities The proposed technique
achieves a high IEA (≈1.0) across various hiding
capacities (0.1 to 4.0 bpp). Notably, it outperforms
SWE at various hiding capacities, particularly 0.5,
1.0, 2.0, and 4.0 bpp.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
728

Anti-Detectability Analysis in Reversible
Generative Steganography.: Two well-known
steganalysis models are used in our proposed
reversible generative steganographic technique to
assess its anti-detectability. This technique was first
described in 2012 and uses a set of high-dimensional
handcrafted attributes taken from photographs to
discover hidden information. This popular
steganalyzer examines residuals at the pixel level to
detect statistical irregularities caused by
steganography.
3 CONCLUSIONS
Recent developments in reversible generative
steganography with distribution-preserving encoding
are covered in this paper. These developments
address the shortcomings of conventional
modification-based and irreversible generative
stenographic techniques. The proposed approach
provides bijective transition between generated
stego-images and hidden messages using a Glow-
based normalizing flow model, enabling accurate
message extraction and high concealing capacity.
Unlike traditional steganography approaches, which
produce visible distortions, our method maps the
secret message into a Gaussian-distributed latent
space, resulting in stego-pictures that are statistically
indistinguishable from natural photos. Furthermore,
the Glow model's reversibility enables near-perfect
secret message recovery, even at large hiding
capacities. Furthermore, a comparison with existing
approaches such as SWE, S-UNIWORD, and UT-
6HPF-GAN demonstrates that these methods exhibit
detectability concerns and worse extraction accuracy
at larger embedding rates. Our technique, on the other
hand, retains strong security and resistance against
steganalysis tools like SRM and XuNet, particularly
when hiding capabilities reach 4.0 bpp. Finally, the
suggested distribution-preserving generative
steganographic approach represents a substantial step
forward in secure, reversible, and high-capacity
information concealment. These findings
demonstrate the possibility of normalizing flow-
based models in steganography, paving the path for
future research into more efficient and undetectable
steganographic frameworks.
REFERENCES
Cao, Y., Zhou, Z., Wu, Q., et al. (2020). Coverless
Information Hiding Based on the Generation of Anime
Characters. EURASIP Journal on Image and Video
Processing, 2020(1), 1–15.
Chen, K., Zhou, H., Zhao, H., et al. (2022). Distribution-
Preserving Steganography Based on Text-to-Speech
Generative Models. IEEE Transactions on Dependable
and Secure Computing, 19(5), 3343–3356.
Filler, T., Judas, J., Fridrich, J. J. (2011). Minimizing
Additive Distortion in Steganography Using
Syndrome-Trellis Codes. IEEE Transactions on
Information Forensics and Security, 6(3), 920–935.
Fridrich, J., Kodovsky, J. (2012). Rich Models for
Steganalysis of Digital Images. IEEE Transactions on
Information Forensics and Security, 7(3), 868–882.
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., et al. (2014).
Generative Adversarial Nets. In Advances in Neural
Information Processing Systems (NIPS), 2672–2680.
Holub, V., Fridrich, J., Denemark, T. (2014). Universal
Distortion Function for Steganography in an Arbitrary
Domain. EURASIP Journal on Image and Video
Processing, 2014(1), 1–13.
Jiang, W., Hu, D., Yu, C., et al. (2020). A New
Steganography without Embedding Based on
Adversarial Training. In Proceedings of the ACM
Turing Celebration Conference, 219–223.
Karras, T., Aila, T., Laine, S., et al. (2018). Progressive
Growing of GANs for Improved Quality, Stability, and
Variation. In International Conference on Learning
Representations (ICLR).
Kingma, D. P., Dhariwal, P. (2018). Glow: Generative
Flow with Invertible 1 × 1 Convolutions. In Advances
in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS),
10215–10224.
Li, J., Niu, K., Liao, L., et al. (2020). A Generative
Steganography Method Based on WGAN–GP. In
International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and
Security, 386–397.
Li, Q., Wang, X., Wang, X., et al. (2021). An Encrypted
Coverless Information Hiding Method Based on
Generative Models. Information Sciences, 553, 19–30.
Liu, M., Zhang, M., Liu, J., et al. (2017). Coverless
Information Hiding Based on Generative Adversarial
Networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.06951.
Liu, X., Ma, Z., Ma, J., et al. (2022). Image
Disentanglement Autoencoder for Steganography
without Embedding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition (CVPR), 2303–2312.
Luo, Y., Qin, J., Xiang, X., et al. (2020). Coverless Image
Steganography Based on Multi-Object Recognition.
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video
Technology, 31(7), 2779–2791.
Luo, Y., Qin, J., Xiang, X., et al. (2020). Coverless Image
Steganography Based on Image Segmentation.
Computers, Materials & Continua, 64(2), 1281–1295.
Pang, K. (2024). FreStega: A Plug-and-Play Method for
Boosting Imperceptibility and Capacity in Generative
Linguistic Steganography for Real-World Scenarios.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.19652.
Radford, A., Metz, L., Chintala, S. (2016). Unsupervised
Representation Learning with Deep Convolutional
Reversible Generative Steganography Leveraging Distribution Preserving Encoding for Enhanced Data Security and Integrity
729

Generative Adversarial Networks. In International
Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR).
Tang, W., Zhou, Z., Li, B., et al. (2024). Joint Cost Learning
and Payload Allocation with Image-Wise Attention for
Batch Steganography. IEEE Transactions on
Information Forensics and Security, 19, 2826–2839.
Wu, Y., Wang, J., Zhou, H., et al. (2023). A Resilient and
Accessible Distribution-Preserving Watermark for
Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.07710.
Xu, G., Wu, H., Shi, Y. Q. (2016). Structural Design of
Convolutional Neural Networks for Steganalysis. IEEE
Signal Processing Letters, 23(5), 708–712.
Yang, J., Ruan, D., Huang, J., et al. (2019). An Embedding
Cost Learning Framework Using GAN. IEEE
Transactions on Information Forensics and Security,
15, 839–851.
Yu, C., Hu, D., Zheng, S., et al. (2021). An Improved
Steganography without Embedding Based on Attention
GAN. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications,
14(3), 1446–1457.
Zhang, Z., Fu, G., Ni, R., et al. (2020). A Generative
Method for Steganography by Cover Synthesis with
Auxiliary Semantics. Tsinghua Science and
Technology, 25(4), 516–527.
Zhu, J., Chen, Z., Yang, L., et al. (2024). Plug-and-Hide:
Provable and Adjustable Diffusion Generative
Steganography. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.04878.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
730
