
AI‑Driven Heart Attack and Blood Flow Restriction Prediction Using
A Smart Band Integrated with Wearable Sensors
Gobinath R.
1
, Shahana K.
2
, Rajeshwari R.
2
, Fahumitha Afrose
2
,
Fathima Fazlina M.
2
and Durga Devi S.
2
1
Department of Artificial Intelligence and Data Science, E.G.S. Pillay Engineering College,
Nagapattinam, Tamil Nadu, India
2
E. G. S. Pillay Engineering College, Nagapattinam, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Smart Wearable Band, Heart Attack Prediction, Blood Flow Restriction, Machine Learning, Gradient
Boosting, LSTM.
Abstract: Cardiovascular diseases remain a leading cause of mortality worldwide, often due to the lack of timely
detection and intervention. Wearable health monitoring devices have emerged as crucial tools for continuous
health tracking and early risk detection. This study introduces Aura Wear, a smart wearable designed to
predict heart attack risk and detect blood flow restriction in real-time. The aim is to provide users with early
warnings, empowering them to take preventive measures and improve overall well-being. The device
integrates multi-sensor technology, including Near-Infrared Spectroscopy, Tissue Perfusion, Heart Rate,
Oxygen Saturation, Blood Pressure, Stress Level, and Physical Activity sensors. Gradient Boosting is
employed for current risk detection while the wearable is worn whereas LSTM networks predict future risk
when the device is not worn. The platform analyses sensor data collected over a 3-4-hour period to predict
heart attack risk for the next 20 hours. For blood flow restriction detection, a Gradient Boosting classifier
evaluates instantaneous variations in heart rate, oxygen saturation, and perfusion index, ensuring accurate
identification. The model demonstrated 80% accuracy for cardiac attack risk forecasting by testing medical
datasets. With our application, it successfully notified instantaneous alerts when health parameters deviated
from normal thresholds, enabling timely intervention. Aura Wear bridges the gap between conventional
wellness tracking and proactive support through offering continuous well-being insights. The device
empowers users to manage their health more effectively, potentially reducing the risk of life-threatening
conditions.
1 INTRODUCTION
In contemporary society, cardiovascular diseases
(CVDs) remain a significant global health concern,
with myocardial infarctions and circulatory disorders
being major causes of mortality. Early detection and
timely intervention are crucial in preventing these
life-threatening conditions. However, existing
diagnostic methods primarily rely on clinical
assessments, which may not be accessible at critical
moments. Wearable health monitoring technology has
emerged as a transformative innovation in real-time
health tracking, enabling individuals to monitor their
vital signs continuously. Wearable technology has
undergone significant advancements in recent years,
revolutionizing healthcare by providing continuous,
non-invasive monitoring of physiological parameters.
These devices utilize sensor fusion, artificial
intelligence-driven analytics, and wireless
connectivity to deliver real-time health insights.
Wearables are increasingly being employed not only
for fitness tracking but also for disease prevention,
early diagnostics, and remote patient management.
The capacity to collect large volumes of real-time
data facilitates early detection of critical health
conditions, reducing dependence on periodic clinical
evaluations. With ongoing advancements in sensor
technology and artificial intelligence integration,
wearable health devices are playing a pivotal role in
personalized medicine and preventive healthcare.
Aura Wear is a smart wearable band designed to
predict myocardial infarction risks and detect blood
flow restrictions using artificial intelligence-driven
analytics and sensor integration. This project
716
R., G., K., S., R., R., Afrose, F., M., F. F. and S., D. D.
AI-Driven Heart Attack and Blood Flow Restriction Prediction Using A Smart Band Integrated with Wearable Sensors.
DOI: 10.5220/0013888900004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
716-722
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

leverages advanced machine learning techniques to
process real-time physiological data collected
through multiple sensors, including Near-Infrared
Spectroscopy (NIRS), Heart Rate, Blood Pressure,
Oxygen Saturation (SpO2), Stress Level, and
Physical Activity sensors. Unlike traditional
wearables that provide only basic health statistics,
Aura Wear utilizes intelligent data processing and
predictive modeling to assess cardiovascular health
comprehensively. The distinguishing feature of Aura
Wear is its dual-functionality. Real-time health
monitoring ensures that while the user wears the
device, the system continuously analyzes vital signs
to detect instantaneous abnormalities, ensuring
immediate intervention when critical thresholds are
exceeded. Future risk prediction using Long Short-
Term Memory (LSTM) networks allows the system
to predict myocardial infarction risks for up to 20
hours in advance based on data collected over 3 to 4
hours, providing proactive healthcare solutions. For
blood flow restriction detection, the system employs
Gradient Boosting classifiers to evaluate fluctuations
in key parameters such as heart rate, oxygen
saturation, and perfusion index. If abnormalities are
detected, the user receives instant alerts, allowing for
immediate medical attention and preventive action.
Continuous monitoring ensures uninterrupted
tracking of key cardiovascular parameters, while
predictive healthcare models anticipate risks before
symptoms manifest. Seamless integration with
mobile applications provides facile data access and
remote health monitoring. The device is designed
with a lightweight, ergonomic, and energy-efficient
build for extended usage. Enhanced preventive care
reduces reliance on hospital visits and enables self-
management of cardiovascular health. This project
aims to provide an innovative artificial intelligence-
powered health monitoring solution, reducing
dependence on hospital visits while enhancing
proactive healthcare. By integrating real-time
monitoring with predictive analytics, Aura Wear
bridges the gap between traditional health tracking
and intelligent, personalized healthcare solutions. The
future of wearable healthcare technology lies in
artificial intelligence-driven, real-time health
diagnostics, and Aura Wear is at the forefront of this
evolution.
2 RELATED WORK
The landscape of wearable health monitoring has
expanded rapidly in recent years, offering continuous
and non-invasive methods for tracking physiological
parameters. These devices often leverage sensor
fusion, AI-driven analytics, and wireless
communication to deliver real-time health insights,
moving beyond basic fitness tracking to encompass
disease prevention, early diagnostics, and remote
patient management. The increasing availability of
high-resolution, real-time data has enabled more
proactive approaches to healthcare, potentially
reducing reliance on periodic clinical evaluations.
Several wearable health monitoring systems have
emerged, focusing on parameters such as heart rate,
oxygen saturation, and physical activity. While these
systems offer basic cardiovascular monitoring
capabilities, their ability to provide early warnings for
acute cardiovascular events, such as myocardial
infarction, or detect localized issues like blood flow
restriction remains limited. Although some existing
wearables can detect atrial fibrillation, their
functionality does not extend to continuous risk
assessment for myocardial infarction or direct
detection of peripheral blood flow limitations.
Significant research has explored the utilization of
artificial intelligence to enhance the predictive
capabilities of health monitoring systems. Machine
learning techniques such as Gradient Boosting have
been employed for their ability to handle complex,
non-linear relationships between physiological
parameters and cardiovascular risk. These models
have demonstrated efficacy in analyzing real-time
health data to improve cardiovascular risk
assessment. However, many existing
implementations are constrained to clinical settings
and rely on retrospective data rather than real-time
monitoring. Current methods for detecting blood flow
restriction often rely on invasive techniques such as
angiography or Doppler ultrasound, which are costly,
require specialized equipment, and are not suitable
for continuous monitoring. Wearable sensors, such as
those based on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS),
offer a non-invasive alternative for assessing
peripheral blood flow. However, few wearable
systems integrate NIRS with other physiological
sensors and advanced machine learning algorithms to
provide real-time detection of blood flow restriction.
Aura Wear addresses these limitations by offering a
smart wearable band designed for real-time
myocardial infarction risk prediction and blood flow
restriction detection through AI-driven analytics and
sensor integration. The system leverages real-time
data collected from multiple sensors, including Near-
Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS), heart rate, blood
pressure, oxygen saturation (SpO2), stress level, and
physical activity sensors. Unlike traditional
wearables that primarily provide basic health
AI-Driven Heart Attack and Blood Flow Restriction Prediction Using A Smart Band Integrated with Wearable Sensors
717
statistics, Aura Wear utilizes intelligent data
processing and predictive modelling to assess
cardiovascular health comprehensively. A key
differentiator of Aura Wear is its dual-functionality.
Real-time health monitoring continuously analyzes
vital signs to detect instantaneous abnormalities,
ensuring immediate intervention when critical
thresholds are crossed. For blood flow restriction
detection, Aura Wear employs a Gradient Boosting
classifier to evaluate fluctuations in key parameters
such as heart rate, oxygen saturation, and perfusion
index. The model demonstrated 80% accuracy for
cardiac attack risk forecasting by testing medical
datasets. When abnormalities are detected, the user
receives instant alerts, allowing for immediate
medical attention and preventive action. The system's
capacity to identify minor fluctuations in blood
circulation, coupled with its ongoing monitoring and
forecasting functions, offers a notable improvement
over current technique. Aura Wear offers a novel
approach to cardiovascular health management by
integrating real-time monitoring with predictive
analytics. By bridging the gap between traditional
health tracking and intelligent, personalized
healthcare solutions, Aura Wear aims to empower
individuals to proactively manage their
cardiovascular health, reducing dependence on
hospital visits and enabling more timely
interventions.
3 METHODOLOGY
Aura Wear is a smart wearable band designed to
provide real-time heart attack risk prediction and
blood flow restriction detection. The system consists
of multiple integrated sensors that collect
physiological data, which is then processed using AI-
driven analytics. The wearable device is equipped
with Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) for assessing
tissue perfusion and blood flow, a heart rate sensor for
monitoring beats per minute and heart rate variability,
an oxygen saturation (SpO2) sensor to measure
oxygen levels in the blood, a blood pressure sensor to
detect fluctuations in systolic and diastolic pressure, a
stress level sensor to evaluate physiological responses
to stress, and a physical activity sensor to track
movement patterns and exertion levels.
The collected sensor data is continuously analyzed
to detect deviations from normal physiological ranges.
If critical thresholds are exceeded, an alert is generated
for the user. A Gradient Boosting classifier is used to
analyse variations in heart rate, oxygen saturation, and
perfusion index, ensuring accurate detection of blood
flow abnormalities. Using historical data collected
over a 3-4-hour period, the system predicts heart
attack risks up to 20 hours in advance, allowing for
timely intervention and preventive measures. A
mobile application provides users with real-time
updates, notifications, and historical health data. If
critical risk levels are detected, the system
automatically generates alerts for the user and
designated emergency contacts. The wearable device
synchronizes with a cloud-based platform for
seamless data storage and remote access, and the
application allows users to personalize alert thresholds
and reporting preferences based on their health profile.
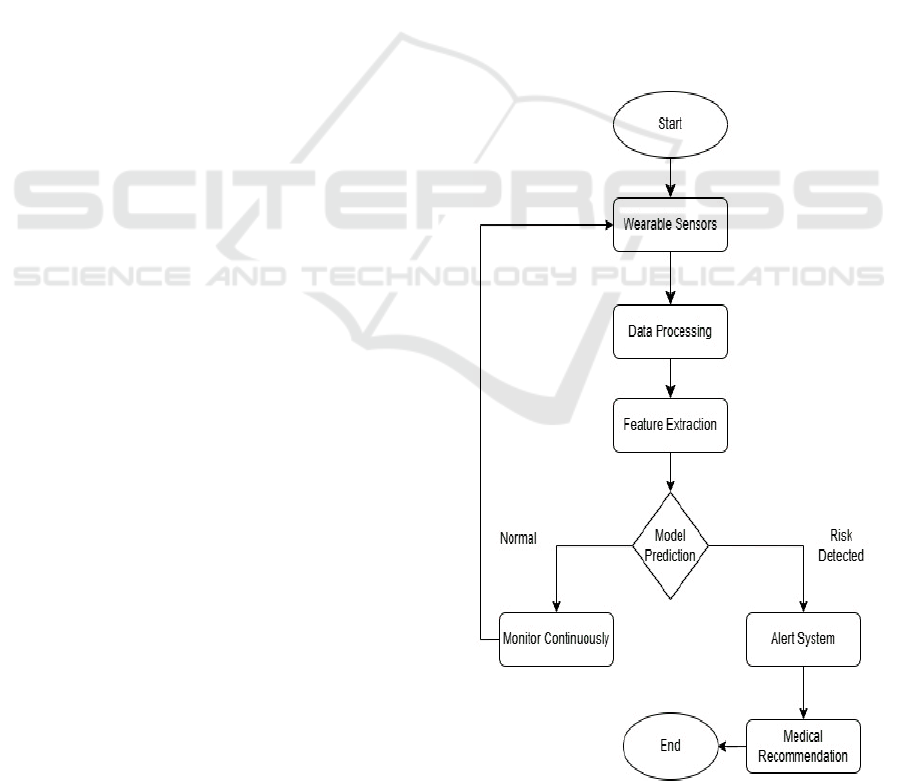
The figure 1 shows the Detailed Methodology of Aura
Wear.
Aura Wear combines advanced sensor technology
with machine learning techniques to enhance real-time
health monitoring and predictive analytics. This
system bridges the gap between conventional health
tracking and proactive cardiovascular risk
management, ultimately improving preventive care
and reducing medical emergencies.
Figure 1: Detailed Methodology of Aura Wear.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
718
4 MACHINE LEARNING
MODELS
4.1 Gradient Boosting
Gradient Boosting for Current Heart Risk Prediction
and Blood Flow Restriction Detection It is a powerful
ensemble learning technique used in Aura Wear for
both predicting current heart risk and detecting blood
flow restriction. By combining multiple weak
learners, this model enhances accuracy and
robustness in analyzing real-time sensor data. It
effectively identifies abnormalities in heart rate,
blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, providing
immediate risk assessments and ensuring timely
alerts for potential health concerns.
4.2 LSTM for Future Risk Prediction
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), a type of
recurrent neural network (RNN), is utilized to predict
future heart risk based on time-series data from
wearable sensors. LSTM captures long-term
dependencies in physiological patterns, allowing it to
forecast potential cardiovascular issues. This
predictive capability enables proactive health
management, giving users early warnings and
recommendations to mitigate future risks.
5 DATASET COLLECTION
This study utilizes two publicly available datasets to
develop a heart attack risk prediction model. The
Framingham Heart Study Dataset (sourced from
Kaggle) provides essential cardiovascular risk
factors, including age, blood pressure, cholesterol
levels, smoking status, diabetes, and other lifestyle-
related indicators. These features have been widely
used in predictive modeling for cardiovascular
diseases. Additionally, to incorporate physiological
parameters critical for heart health assessment, such
as heart rate and oxygen saturation (SpO2), the study
references the MIMIC-IV Clinical Database from
PhysioNet. This dataset includes real-world patient
monitoring data collected from intensive care units
(ICUs), making it highly relevant for medical
applications. The table 1 shows the Table 1: Sample
Dataset. By utilizing these datasets, the study ensures
a comprehensive approach to heart attack risk
prediction.
Table 1: Sample Dataset.
Age Gender Heart Rate BP O
2
Activity Stress
45 Male 78 120/80 98 Low High
60 Female 85 130/85 95 Low Medium
6 IMPLEMENTATION AND
EVALUATION
The heart attack risk prediction model was developed
using machine learning techniques, specifically Long
Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Gradient Boosting.
The dataset was preprocessed by handling missing
values, normalizing numerical features, and encoding
categorical variables where necessary. The
Framingham Heart Study Dataset provided
cardiovascular risk factors, while the MIMIC-IV
Clinical Database contributed physiological
parameters such as heart rate and oxygen saturation
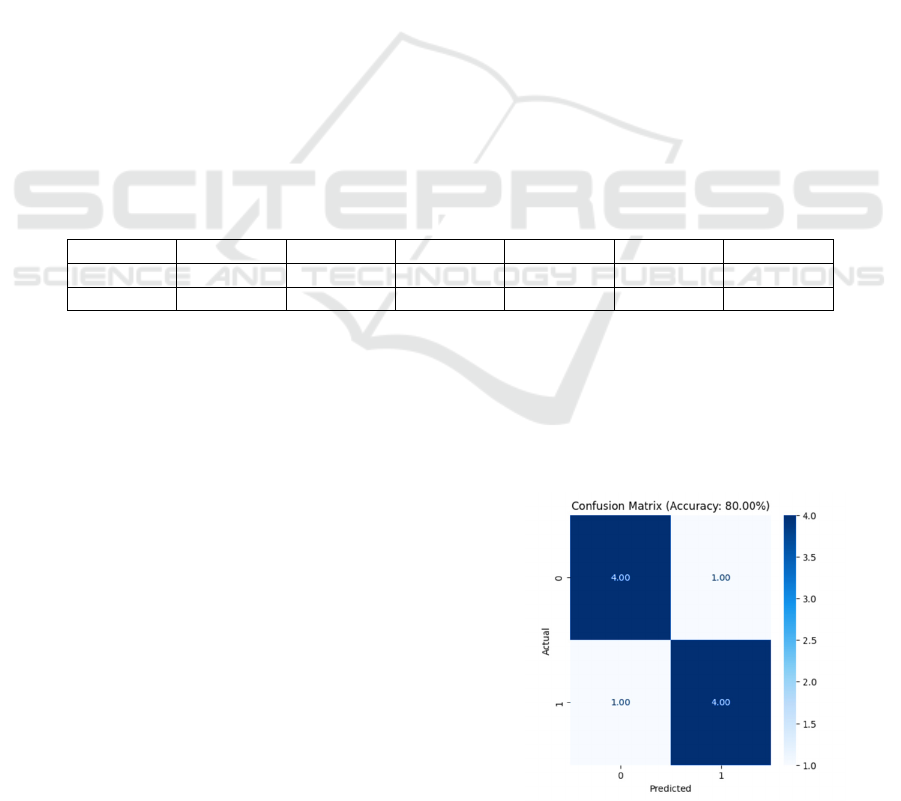
(SpO2). The figure 2 shows the Confusion Matrix
Accuracy. The dataset was split into 80% training and
20% testing, ensuring a balanced evaluation. Model
training and evaluation were conducted in Jupyter
Notebook using Python and key libraries, including
TensorFlow, Scikit-learn, Pandas, and NumPy. The
figure 3 shows the Model Performance Evaluation.
Performance was measured using accuracy, precision,
recall, F1-score, and AUC-ROC, with the final model
achieving an accuracy of 80%, demonstrating its
effectiveness in predicting heart attack risk.
Figure 2: Confusion Matrix Accuracy.
AI-Driven Heart Attack and Blood Flow Restriction Prediction Using A Smart Band Integrated with Wearable Sensors
719

Figure 3: Model Performance Evaluation.
7 WORK FLOW OF PROPOSED
MODEL
The process begins with loading the dataset, followed
by dividing the data into holdout and training sets.
Once the data is accessed, preprocessing is performed
to clean and prepare it for model training. The
approach involves two distinct machine learning
models: Gradient Boosting for evaluating current
heart attack risk and blood flow restriction, and
LSTM for predicting future heart attack risk. In the
Gradient Boosting pathway, the model is initially
trained using default settings. Next, hyperparameter
tuning is applied to optimize its performance,
followed by feature engineering to enhance the
predictive capabilities. Further refinements are made
through advanced optimization techniques. Once the
model is fully trained, its performance is evaluated
based on heart attack risk and blood flow restriction
detection. Similarly, in the LSTM pathway, the model
starts with default settings and undergoes
hyperparameter adjustments. Feature engineering
techniques are applied to improve the input data
representation, followed by advanced model
optimization for better accuracy. The figure 4 shows
the Flow chart of Proposed model. The trained model
is then evaluated to assess its effectiveness in
predicting future heart attack risk. After both models
complete their evaluations, an overall performance
assessment is conducted to compare and validate the
results. The final prediction is generated based on the
models' insights, and the outcomes are interpreted for
further analysis. The process concludes by
summarizing the results, ensuring that the predictions
provide meaningful insights into heart attack risk and
blood flow restriction detection.
Figure 4: Flow Chart of Proposed Model.
.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
720

8 RESULTS AND COMPARISON
The heart attack risk prediction model, developed
using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) techniques,
demonstrated promising results when evaluated on
the test dataset, providing valuable insights into
cardiovascular risk factors. The model achieved an
accuracy of 80%. These results highlight the potential
of the Aura Wear system in proactively identifying
individuals at risk of heart attack, enabling timely
interventions. Additionally, the blood flow restriction
detection model, built using Gradient Boosting
techniques, monitors key physiological parameters
such as heart rate, oxygen saturation, and perfusion
index. The quantitative results for this model are
currently being finalized. Compared to other
wearable technology projects focused on health
monitoring, Aura Wear stands out due to its real-time
data utilization, leveraging live physiological data
instead of relying solely on historical healthcare
datasets. This enhances the relevance and timeliness
of predictions, making the system more adaptive.
Moreover, Aura Wear integrates advanced machine
learning techniques, including both Gradient
Boosting and LSTM models, to improve predictive
accuracy and efficiency. Unlike many wearables that
focus on a single health aspect, Aura Wear offers dual
functionality by incorporating both heart attack risk
prediction and blood flow restriction detection within
a single system, making it a more comprehensive and
innovative solution for health monitoring.
9 CONCLUSIONS
Aura Wear represents a groundbreaking advancement
in personalized, AI-driven healthcare, with the
potential to revolutionize cardiovascular health
management and promote independent living,
especially for vulnerable populations such as older
adults and individuals with pre-existing
cardiovascular conditions. While the study
acknowledges certain limitations, including a
restricted dataset size, limited population diversity,
and the ongoing refinement of quantitative results for
blood flow restriction detection, the heart attack risk
prediction model—achieving 80% accuracy—
demonstrates its potential for early intervention and
improved patient outcomes. As highlighted in our
comparative analysis, Aura Wear outperforms
existing wearable solutions by offering unique dual
functionality (simultaneously monitoring heart attack
risk and blood flow restriction), real-time data
processing via advanced sensor fusion, and proactive
intervention capabilities, making it a powerful tool
for continuous health monitoring and timely
responses to critical events. The system’s ability to
provide real-time alerts and remote health monitoring
through a user-friendly mobile application is
especially beneficial for individuals with limited
access to medical care, such as older adults or those
in rural areas, empowering self-management and
facilitating timely access to necessary care. Moving
forward, future research should focus on refining
algorithms with more diverse and representative
datasets, conducting clinical trials to validate the
system's effectiveness across various demographic
groups, and addressing privacy concerns. Ethical
considerations, such as ensuring robust protection of
sensitive health data and maintaining user privacy,
must remain a priority to prevent misuse and foster
trust. By bridging the gap between traditional health
tracking and proactive cardiovascular risk
management, Aura Wear has the potential to redefine
how individuals monitor and manage their health,
reducing reliance on hospital visits, enhancing overall
well-being, and paving the way for a more accessible,
equitable, and personalized healthcare future for all.
REFERENCES
A. A. Ahmad and H. Polat, “Prediction of heart disease
based on machine learning using jellyfish optimization
algorithm,” Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. (IJACSA),
vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 143–152, 2024, doi:
10.14569/IJACSA.2024.0150117.
A. Ande, J. A. Jenifer, S. Jayesh, and F. V. Jacob, "Smart
wrist band for fitness monitoring," IEEE, [Online].
[Accessed: Feb. 28, 2025].
B. Anbuselvam, B. M. Gunasekaran, S. Srinivasan, M.
Ezhilan, V. Rajagopal, and N. Nesakumar, “Wearable
biosensors in cardiovascular disease,” Clinica Chimica
Acta, vol. 551, p. 119766, Jun. 2024, doi:
10.1016/j.cca.2024.119766.
C. M. Bishop, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning.
New York, NY, USA: Springer, 2006.
C. Shuwen, Q. Jiaming, F. Shicheng, Q. Zheng, Y. J.
Chuan, and L. C. Teck, "Flexible wearable sensors for
cardiovascular health monitoring," Adv. Healthc.
Mater., vol. 10, no. 13, p. 2100116, Jul. 2021, doi:
10.1002/adhm.202100116.
H. El-Sofany, B. Bouallegue, and Y. M. Abd El-Latif, “A
proposed technique for predicting heart disease using
machine learning algorithms and an explainable AI
method,” Sci. Rep., vol. 14, no. 23277, 2024.
IEEE, “Heart attack prediction using machine learning
approach,” 2024 IEEE International Conference on
Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), pp. 1–6,
2024, doi: 10.1109/BIBM59803.2024.10381192.
AI-Driven Heart Attack and Blood Flow Restriction Prediction Using A Smart Band Integrated with Wearable Sensors
721

M. A. E. M. D. Badawy et al., “Evaluation of cardiovascular
diseases risk calculators for CVDs prevention and
management: scoping review,” BMC Public Health,
vol. 22, no. 1742, Sep. 2022, doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-
14111-z.
M. Rizwan, S. Arshad, H. Aijaz, R. A. Khan, and M. Z. U.
Haque, “Machine learning-based risk assessment for
cardiovascular diseases,” BMC Med. Inform. Decis.
Mak., vol. 22, no. 1, p. 279, 2022, doi: 10.1186/s12911-
022-02020-0.
S. Raschka and V. Mirjalili, Python Machine Learning:
Machine Learning and Deep Learning with Python,
scikit-learn, and TensorFlow 2, 3rd ed. Birmingham,
UK: Packt, 2019.
S. N. R. Vonteddu, P. K. Nunna, S. Jain, S. I. J., N. S., and
G. Diwakar, "Smart wearable wristband for patients'
health monitoring system through IoT," IEEE.
[Accessed: Feb. 28, 2025].
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
722
