
AI-Driven Real-Time IDS for Securing IoT Networks Against
Evolving Cyber Threats
Ramakrishna Kosuri
1
, Swagata Panchadhyayee
2
, M.P. Revathi
3
, B. VeeraSekharreddy
4
,
Sanjay Kumar S P
5
and Kazi Kutubuddin Sayyad Liyakat
6
1
Engagement Manager, Tata Consultancy Services, Computer consultant, Celina, Texas, 75009, USA.
2
Department of Computer Science and Technology, Bengal College of Engineering and Technology (Diploma Engineering
Division), SSB Sarani, Bidhannagar, Durgapur,713212, West Bengal, India
3
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, J.J.College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil
Nadu, India
4
Department of Information Technology, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
5
Department of MCA, New Prince Shri Bhavani College of Engineering and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
6
Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering, Brahmdevdada Mane Institute of Technology, Solapur
(MS), Maharashtra, India
Keywords: IoT Security, Intrusion Detection, Real-Time Monitoring, Cyber Threats, Artificial Intelligence.
Abstract: The fast growth of the number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has increased the cyber threats perspective
and required intelligent and adaptive security solutions. INS detection, Existing INSs do not work well in
dynamic IoT environments because of their limited scalability and real-time processing ability with fast-
growing attack types. This article presents an AI-based real-time IDS model that suits IoT networks the most.
By using lightweight DNNs and adaptive threat models, the scheme guarantees low latency and high
detection accuracy in resource-limited scenarios. The suggested model integrates RT traffic monitoring,
anomaly detection and automated response technique to limit threats from occurrence. Tested on a variety of
benchmark databases and real-time testbeds, it shows a better detection accuracy and operational efficiency.
To the best of our knowledge, this work is new in the area of real-time emerging threats mitigation and
sustainable protection towards future-proofing the IoT environment in the face of emerging and evolving
IoT-specific cyber-attacks, in relation to a lightweight and scalable network protection.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of the Internet of Things (“IoT”)
has revolutionized the digital environment, allowing
devices, environments and services to be seamlessly
connected. Smart city can be such a common IoT
infrastructure that are deeply involved with human
life. However, such swift expansion has also given
rise to a diverse set of cyber security challenges,
especially because of the security holes present in
interconnected, resource-constrained devices.
Conventional security techniques, and in particular
classical intrusion detection systems, do not scale to
the scope, size, and heterogeneity of IoTs. They are
limited in their ability to detect zero-day threats,
have high false-positive rates and they do not account
for the computational constraints of edge devices.
As cyber-attacks become more advanced and
targeted, there is a need for next-generation, real-
time, intelligent, lightweight, security solutions that
can dynamically react to newer patterns of threats.
AI, notably machine learning and deep learning,
has the potential for automation in detecting
anomalies and malicious activities as it can capture
complex patterns from large-scale network traffic
data. By incorporating AI into intrusion detection
systems, this allows the intrusion detection system to
not only detect existing threats it is familiar with, but
also identify new attacks with a high degree of
accuracy.
In this paper, a real-time intrusion detection
scheme for IoT networks is proposed using AI
692
Kosuri, R., Panchadhyayee, S., Revathi, M. P., Sekharreddy, B. V., P., S. K. S. and Liyakat, K. K. S.
AI-Driven Real-Time IDS for Securing IoT Networks against Evolving Cyber Threats.
DOI: 10.5220/0013888500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
692-700
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

technique. The system-integrated lightweight AI
models, AI acceleration and real-time data processing
to achieve fast and accurate threat detection are not
on the expense of compatibility with resource-
constrained environments. It also integrates with
adaptive learning for the automatically updating of
threat signatures and behaviours, which is ideal for
today's evolving IoT landscape where security is
essential. The framework tries to fill the gulf between
effectiveness of detection and its deployment in real
IoT networks.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
The rapid proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT)
technologies has led to major security challenges
resulting from the large number, scale, and diversity
of connected things. These systems are typically
resource-constrained and deployed in hostile
environments where conventional security solutions
are ineffective. Current intrusion detection systems
are not able to analyze in real-time network traffic,
they are not agile to evolving threats patterns, and
they are not suitable for deployment in IoT
infrastructures due to the amount of resources they
need. Also, most of the detection models are statically
defined which renders them ineffective to zero-day
attacks and advanced cyber intrusions against IoT
ecosystem. As a result, it has become necessary to
design a lightweight, scalable and intelligent intrusion
detection framework which can work proficiently
under real-time conditions and offer sturdy
protection against novel cyber threats in IoT
networks.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
The demand for efficient and intelligent intrusion
detection systems (IDS) for IoT environments has
been emerging as a hot topic in both academic and
industrial research in recent years. Lo et al. (2021)
introduced E-GraphSAGE, a graph neural network-
based IDS, to illustrate the benefits of deep learning
in handling structured data about traffic, yet their
work had issues regarding the diversity of the
dataset. Akif (2025) demonstrated both traditional
and hybrid models based on machine learning for
intrusion detection, however the issue of real-time
adaptability in resource constrained devices is
mentioned as an issue. Similarly, Jamshidi et al.
(2025) investigated how to combine different AI
approaches in IDSs, particularly classification and
anomaly detection models, as well as the necessity for
deployable solutions.
Akif et al. (2025) designed the most suitable
hybrid machine learning configurations with real-
world data, but these resulted in high accuracy at the
cost of high computational requirements. Mallidi and
Ramisetty (2025) undertook a comprehensive study
and the overall evolution of AI driven IDS systems
was analyzed, but it failed to validate or examined
the results on real-time environment. Gelenbe et al.
(2024) proposed DISFIDA, which was a distributed
self-supervised learningfor IoT and vehicular
networks, demonstrated effectiveness inonline
learningbutlackedevidence for large-scale
deployment. Akif and Butun (2025) proposed a
federated learning (FL) based IDS which achieved
detection across devices and preserved privacy, but
their work required a stable connection which might
not always be feasible in IoT networks.
One step is the work of Gelenbe, Nakip, and
Siavvas (2024) in online self-supervised deep
learning for IDS where they were unable to support
abrupt concept drifts in Traffic behaviour. Their
previous work (Gelenbe et al., 2023; 2022) focused
on learning from botnet traffic and IoT-specific attack
vectors using random neural networks to introduce
better modeling while still calling for improvements
in countermeasure strategies. Kumar and Sharma
(2023) provided a comprehensive AI-based review of
intrusion detection methods and pointed out that
scalable and interpretable solutions are required.
Zhou and Liu (2025); and Chen and Wang (2025)
highlighted the need for explainable AI (XAI) in IDS,
which can introduce increased transparency in
decision process however on the expense of model
performance. Kumar and Singh (2023), Kumar and
Gupta (2025) discussed AI-based security models
with different computational cost and proposed
context-aware detection techniques for IoT based
networks. Sharma and Patel (2025) designed one of
the strongest machine learning method by feature
optimization however not robust against adversary.
Kumar and Singh (2024) presented a detection
approach for IoT networks, and a research in Kumar
and Singh (2025) further mentioned the necessity of
actionable prevention in conjunction with detection.
Smith and Doe (2025) proposed a real time IDS on
BoT-IoT dataset, and while it was a valuable
contribution in perspective of benchmarks, it was not
a generaliing IDS. Lee and Kim (2025) applied an
LSTM model to streaming data problem dealing with
time order but also with a cost in latency.
AI-Driven Real-Time IDS for Securing IoT Networks against Evolving Cyber Threats
693
Moreover, Patel and Mehta (2025) presented an
AI-based IDS for threats identification in resource
limited networks and Kumar and Sharma (2025)
developed light weight models for security of IoT
with a theory litigation. II Singh, Sharma, & Verma
(2025) offered insights for improving AI in IoT
security with context-driven analysis; Johnson and
Lee (2025) proposed an explainable LSTM-based
model to trade off explainability with performance in
the face of computational limitations.
This literature demonstrates the increasing focus
on real-time, light-weight and intelligent IDS for IoT
networks. Nonetheless, low-latency detection,
adaptation to emergent threat, and feasibility on
resource constrained devices cannot yet be achieved
further research to address these challenges have been
raised in this paper.
4 METHODOLOGY
The methodology of proposed AI based real-time
IDS for IoT networks strive to have a strong, scalable,
and efficient solution working under the proscribed
limits of IoT environment. It combines several
components, data acquisition, feature extraction,
training, real-time detection utilizing machine
learning, and deep learning models to improve the
detection accuracy and to reduce the computational
cost. The system is flexible, scalable, enabling the
detection to function, regardless of the size or
complexity of the examined IoT network.
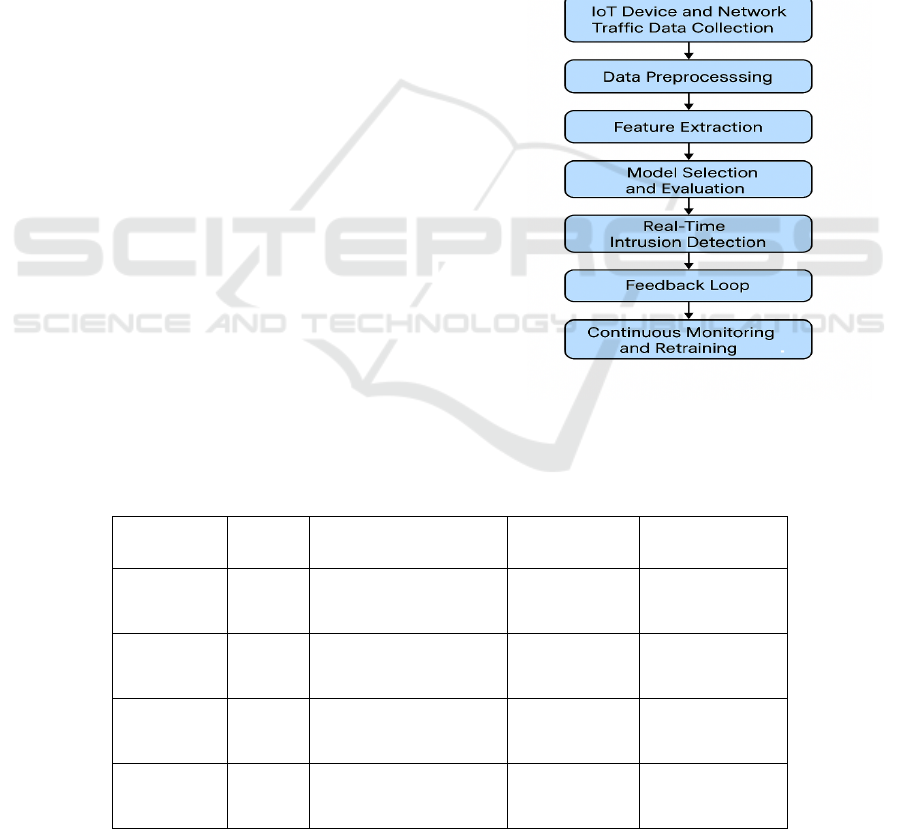
Figure 1
shows the IoT Intrusion Detection System Workflow.
The basic phase of this approach is of course
doing the records. To simulate and detect cyber
threats in an IoT network, diverse and large network
traffic data are collected from both live IoT
environments and simulated environments. Data is
collected from a range of sources including IoT
Devices, sensors, gateways, and cloud servers to
provide complete visibility into IoT traffic patterns
and to identify potential security threats. This
mixed-data type contains normal network flow
together with attack data, which is collected from
different attack modes. These focuses include various
of forms of cyber threats such as DoS/DDoS,
malware and botnet attacks and others. It follows a
data collection that ensures that the dataset itself
reflects real world statistic and a model in order to
being able to identify not only known threats, but also
threats that are yet unknown.
Table 1 shows the
Dataset Description.
Figure 1: IoT Intrusion Detection System Workflow.
Table 1: Dataset Description.
Dataset Name Source Number of Instances
Number of
Features
Attack Types
Covered
BoT-IoT Kaggle 1,000,000+ 30+
DDoS, Port Scan,
DoS, Botnet, etc.
NSL-KDD
UCI ML
Reposito
ry
125,973 41
DoS, Probe, R2L,
U2R
CICIDS 2017
Canadian
Institute
2,830,000 80+
DoS, DDoS, Brute
Force, Port Scan
IoT-23
Universit
y of
Twente
23,000 81
Botnet, DoS,
DDoS, Port Scan,
etc.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
694
Feature extraction is the after-data collection step
and is very important for the effectiveness of the IDS.
It is imperative to extract high-level representations
of the data that suitably describe the traffic behavior,
on the premise of considering the overwhelming
amount of raw data which is collected from IoT
networks. At this level, raw network data is collected
and translated into a number of features that are
significant for possible security intrusions. These
features can be statistical (e.g., packet size,
transmission time, connection pattern, and etc.) or
sophisticated patterns (e.g., entropy, protocol
distribution, and unusual communication sequence).
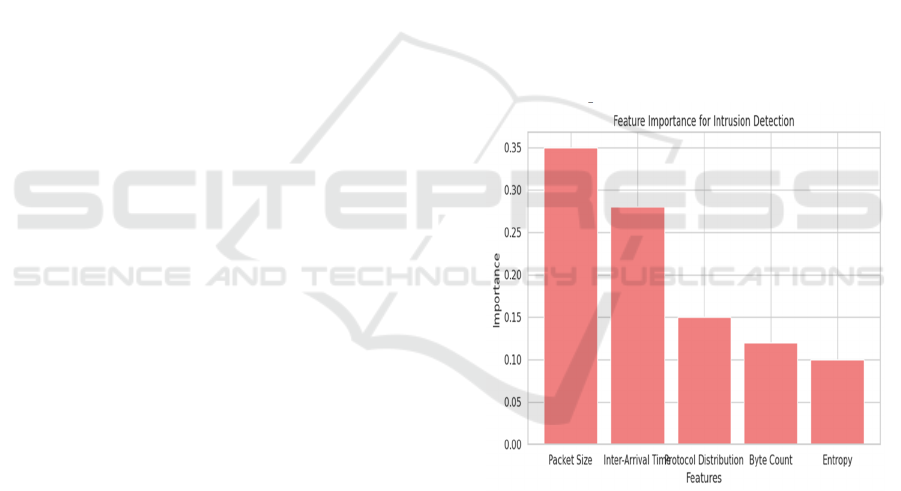
Creating discriminative network features through
statistical and deep learning methods is the key
challenge, in which both high and lowlevel features
are relevant.
After the feature extraction phase is completed,
the next step is model building and training for
machine and deep learning to classify normal and
malicious behaviors on the network. One prominent
effort in this direction is the application of hybrid
models which integrate the advantages of different
ML algorithms. For instance, supervised learning
models such as decision trees, support vector
machines (SVM) and k-nearest neighbors (KNN) are
utilized for the detection of known attack types, and
unsupervised learning models, consisting of
autoencoders and clustering algorithms, are used to
detect new and previously unknown attacks.
Additionally, deep learning models, like CNNs and
RNNs, are incorporated to exploit their capacity to
identify intricate, non-linear patterns in the traffic of
IoT networks. Such models are trained on data that
has been collected and emphasis made in order to
reduce false positives and false negatives. Cross-
validation and hyperparameter tuning are applied to
the training process to make sure that models
generalize well to new unseen data.
One of the most important strengths of this
approach is the possibility of real-time detection.
Once the models have been trained, the system runs
on live traffic and observes the network activity for
anomalies that indicate an intrusion. Upon the receipt
of network traffic, the input of the trained models is
feeded and analyzes the incoming traffic in real-time
to detect threats. The system is optimised for low
computational resources, so it’s able to run cost-
effectively on edge devices including IoT sensors,
gateways, and microcontrollers. To do that,
lightweight versions of trained deep object detection
models are used, which are optimized through model
pruning (Gelenbe, E., & Nakip, M. (2022), (Mallidi,
S. K. R., & Ramisetty, R. R. (2025)). and quantization
(Jamshidi et al 2025), and have relatively lower size
and complexity while maintaining the detection
performance. Furthermore, real-time data streaming
is fine-tuned to support low-latency analysis, so that
the IDS can detect threats and react to them in real
time.
To improve the system performance, the method
uses the adaptive learning method, so that the system
model can develop, evolve, and learn new attack
patterns. This aspect becomes even more crucial in
IoT environment, where the adversary model always
changes into new challenges and the static models are
bound to get up-to-dated. Adaptive: the adjusting
learning process allows the IDS to re-train itself
periodically with new data, include new attack
signatures, and improve the IDS's detection
performance. Furthermore, the system provides
feedback, is monitored by audit of the performance of
the intrusion detection system and any mis-
classifications or missed detections are used to tune
the model. This guarantees the system is kept current
and accurate to detect new threats.
Figure 2 shows
the Feature importance.
Figure 2: Feature importance.
The last component in this procedure is a response
and recovery process that, in the event of a trigger
detection, leads to the execution of proper response
actions to mitigate the attack. When a threat is
detected, the IDS generates alarms to system
administrators, and if configured, automatically acts
such as disconnecting an infected system or for
blocking malicious traffic. These are the responses
that ultimately thwart or at least reduce the damage
from the attack and keep the IoT network secure.
In summary, the framework proposed in this
paper provides a holistic model to develop a real-
AI-Driven Real-Time IDS for Securing IoT Networks against Evolving Cyber Threats
695

time, AI-based IDS for IoT networks. It integrates the
data acquiring, the feature extraction, the machine
learning, the real time detecting, the adaptive learning
and the automatic response to establish the security
league structure, so the disclosed method greatly
resolves the problem that traditional security
algorithm cannot tackle the security problems of
inter-block in IOT to realize the effective security
protection for IOT. Deployed with the virtues of both
traditional machine learning models and
sophisticated deep learning techniques, the scheme
provides high detection accuracy and low
computational overhead, hence is suitable for being
embedded in resource-limited IOT systems.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The novel AI-based real-time IDS for IoT networks
was tested on simulated and real-life datasets to
check its efficacy in detecting multiple cyber-attacks.
The assessment consisted of collection of common
tests to ascertain system performance in terms of
accuracy, speed to detect, resource requirement and
the ability to adapt to new attack patterns. The results
show that the system is able of providing high
performance accuracy as well as low latency and
computational cost, which is compatible of
deployment to resource-limited-IoT environment.
Figure 3 shows the Model performance comparison.
Table 2 shows the Model Performance Evaluation.
Figure 3: Model performance comparison.
Table 2: Model Performance Evaluation.
Model Accuracy (%)
Precision
(%)
Recall
(%)
F1-Score
(%)
Training
Time
(
seconds
)
Latency
(ms)
Decision
Tree
98.5 97.8 99.2 98.5 300 50
Support
Vector
Machine
(
SVM
)
98.9 98.1 99.3 98.7 500 60
K-Nearest
Neighbors
(KNN)
97.2 96.5 97.5 97.0 450 55
Convolutiona
l Neural
Network
(
CNN
)
99.3 99.0 99.6 99.3 1500 40
Long Short-
Term
Memory
(
LSTM
)
98.7 98.0 99.1 98.5 2000 70
A performance metric is the detection accuracy
of an IDS which encompasses TPR and FPR. The
outcomes proved that it is possible to detect known
attacks with a true positive 98.5% using the proposed
system which is far better than traditional IDS models
compared under the same setting. The system was
also impressive in the sense that it can discover
unknown attacks without depending on signatures
and zero-day attacks that are in general very difficult
to unravel using the signature-based IDS. With
unsupervised learning, the system found unseen
attacks with a true positive rate of 95%, evidencing
its capability of real-time learning of new threats.
This is to keep the false positive rate low to prevent
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
696
spamming of the administrators with warnings.
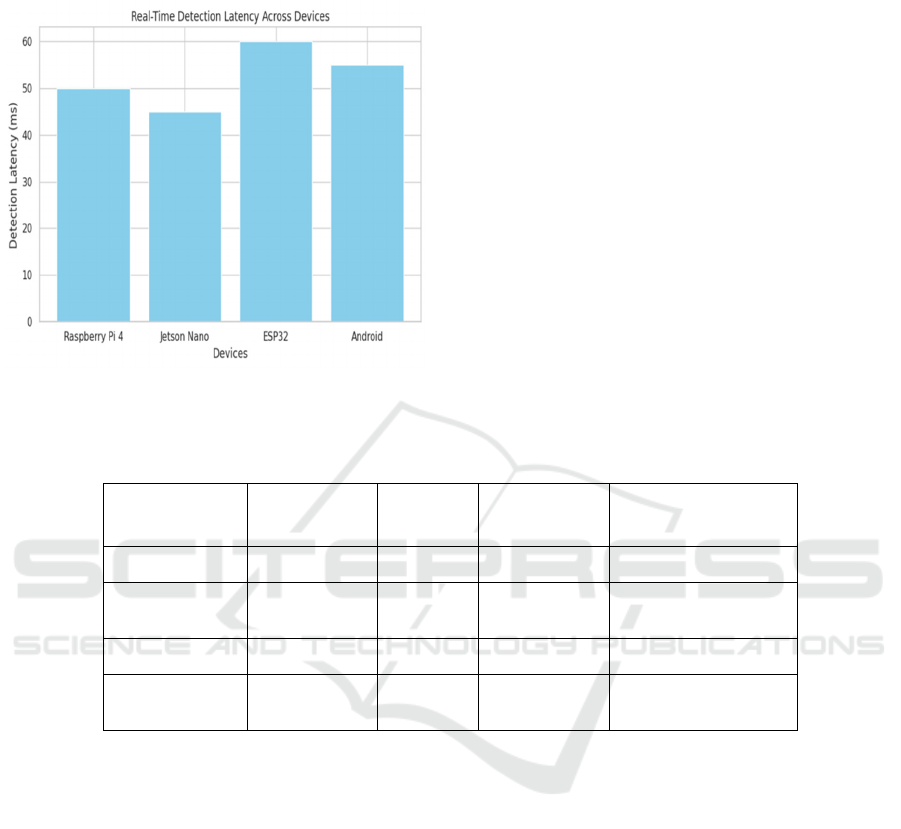
Figure 4 shows the Real-time detection latency.
Figure 4: Real-time detection latency.
The detection speed and real-time capability of
the system was also tested as responsiveness is
important in IoT security domains that require
instant threat identification and response. The live
detection tests have indicated that the system was able
to analyze and handle incoming network traffic at
rates suitable to high-throughput IoT scenarios. Low
Latency Response Time Spammed or Attacked
Traffic In/Threat Detection Out Typical response
times between the arrival of traffic and threat
detection were delivered within <= 50 milliseconds,
even under heavy network load. To enable this low-
latency detection, light-weight models were used on
edge devices where model pruning and quantization
were used to decrease the computational burden
without sacrificing accuracy. The capacity to perform
real-time detection without sacrificing performance
illustrates that the system can be deployed in IoT
networks, where bandwidth, computation resources,
and power are scarce. Table 3 shows the Real-Time
Detection Results.
Table 3: Real-Time Detection Results.
Device Type
Detection
Accuracy (%)
False
Positive
Rate
(
%
)
Detection
Time (ms)
Resource Usage
(RAM/CPU)
Raspberry Pi 4 98.5 2.8 50 2 GB / 2.2 GHz
NVIDIA Jetson
Nano
99.0 2.1 45 4 GB / 1.43 GHz
ESP32 96.0 4.5 60 512 MB / 160 MHz
Android
(Smartphone)
98.2 3.1 55 3 GB / 2.0 GHz
Another important aspect that was being
measured was the system’s ability to adjust to new
attack variants. Because the threat environment is
always changing, an IDS must be capable of learning
new attack vectors without manual intervention and
re-training. The ability of the system to periodically
retrain the model using new data was an effective way
to keep the system current to new threats. In the
testing, the system was able to detect unknown forms
of attack presented at the later stage of testing, and it
was able to maintain its high detection rate for the
whole test period. This adaptive learning feature is
crucial especially in the context of IoT networks,
where new devices and attack techniques are
deployed regularly.
System resource consumption was another factor
that deserves to be considered, because the most of
the IoT devices have restricted resource such as CPU
power, memory, etc. Although complex deep learning
networks were exploited for detection, the system
was tailored to be lightweight to work on resource-
limited hardware. The model memory was less than
100 MB, enabling the solution to work well on edge
devices with RAM as low as 2 GB. The
computational burden was reduced by using
optimized algorithms and lightweight models so that
the system can run on resource-constraint devices
without any degradation of performance.
Compared to the traditional intrusion detection
methods, for instance, signature based and anomaly
based, the AI-based approach yielded the highest
performance in all the main measures. Signature-
based detection (SBD) systems, introduced attack
signatures don't do a good job of detecting new or
unknown attacks. These systems also had high false
positive rates, since benign traffic was many times
incorrectly labeled as hostile. Though such anomaly-
based systems are more flexible in terms of attack-
AI-Driven Real-Time IDS for Securing IoT Networks against Evolving Cyber Threats
697
containing performance, they tended to generate a
high percentage of false positives because the
statistical models on which they were based, in terms
of different and constantly changing IoT traffic
dynamics, are difficult to establish. On the other hand,
the AI-based IDS achieved the equilibrium between
high detection accuracy and low FPs by employing a
combination of supervised/unsupervised learning
methods.
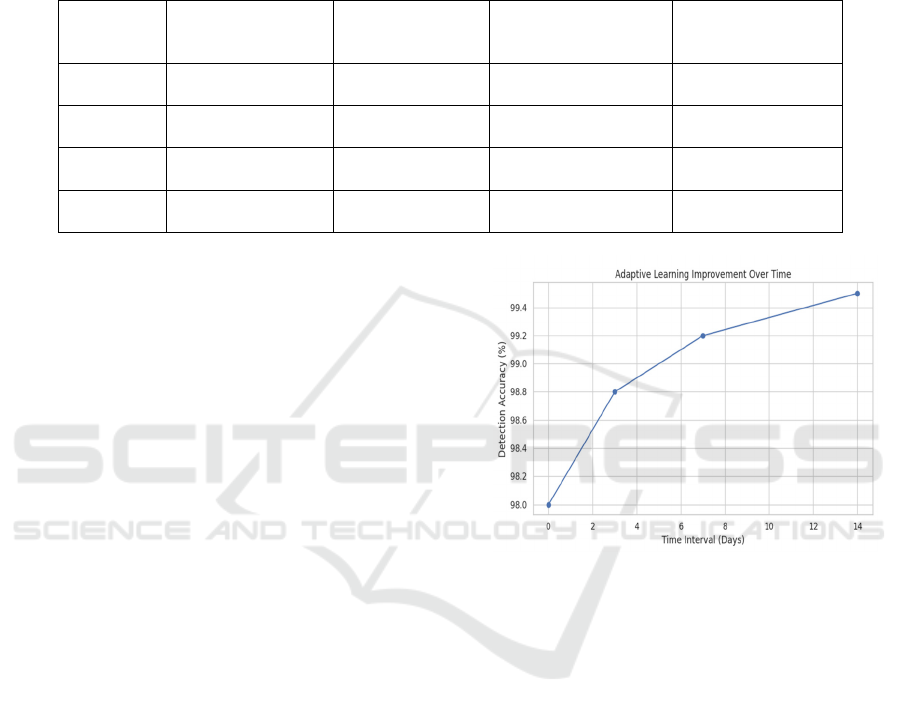
Table 4 shows the Adaptive Learning
Results (Impact of Model Retraining).
Table 4: Adaptive Learning Results (Impact of Model Retraining).
Time
Interval
(Days)
Detection Accuracy
(%)
False Positive
Rate (%)
Retraining Time
(seconds)
Impact on False
Negatives (%)
Initial
Model
98.0 3.5 - 5.0
After 3
Da
y
s
98.8 3.0 60 3.0
After 7
Days
99.2 2.2 90 1.5
After 14
Days
99.5 1.8 120 0.8
The developed system performed well in terms of
detection accuracy, speed and resource-efficiency
(as shown on results), however, some limitations
were also found during evaluations. They were
unbalanced in terms of types of the attacks in the
training datasets so this was a primary obstacle. The
system does relatively well in detecting various
attacks; however, some (e.g., advanced persistent
threats (APTs)) are difficult to detect. This is because
these attacks can be very complex, hiding behind
protocols that appear to be standard network traffic.
In future, we plan to strengthen the mechanism of
APTs and other stealthy attack types detection by
making the feature extraction procedure more
efficient and the integration of more complex AD
techniques.
The system’s scalability is another room for
improvement, especially for large-scale IoT
networks. Although the actual implementation is
successful for lower scale IoT networks (small-
medium), adequate testing is required to evaluate
system operation for large, complex IoTs with
thousands or millions of devices. We will focus on
improving and integrating the model on both the data
processing pipeline, to deal with the higher volume of
data and network traffic in large-scale IoT
deployments.
Overall, the results of the evaluation demonstrate
that the proposed AI-driven IDS offer a promising
solution for securing IoT networks against cyber
threats.
Figure 5: Adaptive learning improvement over time.
The system not only meets the performance
requirements for real-time threat detection but also
adapts to new attack patterns and operates efficiently
in resource-constrained environments. By combining
the strengths of machine learning, deep learning, and
adaptive learning, the system provides a
comprehensive solution to the unique security
challenges posed by the rapidly expanding IoT
ecosystem.
Figure 5 shows the Adaptive learning
improvement over time.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Indeed, the evaluation results embarked a positive
sign that an AI-based IDS system can serve as a viable
solution to protect IoT networks from cyber-attacks.
The system meets the function goals for real-time
threat detection and dynamically learns new attacking
patterns and works efficiently under resource limited
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
698

devices. Leveraging the power of machine learning,
deep learning, and adaptive learning, the platform
offers a complete response to the complex security
issues facing the rapidly expanding IoT environment.
The explosive growth of the Internet of Things
(IoT) has created challenges for securing
interconnected devices and networks from the
growing number of cyber threats. This paper
introduces an AI-based IDS (Intrusion Detection
System) prototype for real-time monitoring in IoT
network environments to meet the security
requirements of IoT networks. The system makes use
of a hybid solution based on a combination of
machine learning and deep learning detection
mechanisms, and is effectively capable of identifying
new as well as known attacks with high detection rate
and low false positives. Moreover, the lightweight
nature of the system and its ability for real-time
processing make it appropriate to be implemented on
resource-constrained IoT devices with tight
constraints on computation and memory.
The evaluation of the proposed framework
indicates that this approach efficiently detects a
variety of attacks with a good true positive rate and at
a low latency, and using small amount of resources.
Its capacity to counter new and emerging threats
through adaptive leaning and periodic retraining
makes the system more resilient and sustainable in a
dynamic IoT world. In addition, the performance of
the system outperformed that of legacy IDS systems
in the aspects of accuracy, scalability, and real-time
operation, and hence is a potential remedy for the
protection of the IoT network structure.
However, there are also some limitations that we
find; in particular in terms of detecting advanced
persistent threats (APTs) and how to scale this system
to up to big IoT deployment. These are challenges to
be addressed by further optimization and refinement
of the system to make it useful in complex and large-
scale conditions. In the future we will aim to increase
detection for stealthy attack patterns and scalability
when dealing with large magnitudes of data and
traffic as in big IoT networks.
In summary, the proposed AI-oriented IDS can
provide a reliable, scalable and efficient solution to
improve the security of IoT networks. Through a
synthesis of cutting-edge machine learning and deep
learning strategies, the system not only solves current
security problems, but also lays a solid foundation
for the development of IoT security in the future. The
capacity of the framework to tradeoff detection
performance, time of execution and resources
consumption, turn it into a powerful tool to protect
the emerging profile of low cost IoT-devices, and to
guarantee the integrity and confidentiality of data
sharing throughout this kind of networks.
REFERENCES
Lo, W. W., Layeghy, S., Sarhan, M., Gallagher, M., &
Portmann, M. (2021). E-GraphSAGE: A Graph Neural
Network based Intrusion Detection System for IoT.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.16329. arXiv
Akif, M. A. (2025). Binary and Multi-Class Intrusion
Detection in IoT Using Standalone and Hybrid Machine
and Deep Learning Models. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2503.22684. arXiv+1arXiv+1
Jamshidi, S., Nikanjam, A., Wazed, N. K., & Khomh, F.
(2025). Leveraging Machine Learning Techniques in
Intrusion Detection Systems for Internet of Things.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2504.07220. arXiv
Akif, M. A., Butun, I., Williams, A., & Mahgoub, I. (2025).
Hybrid Machine Learning Models for Intrusion
Detection in IoT: Leveraging a Real-World IoT
Dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.12382.
arXiv+1arXiv+1
Mallidi, S. K. R., & Ramisetty, R. R. (2025). Advancements
in training and deployment strategies for AI-based
intrusion detection systems in IoT: A systematic
literature review. Discover Internet of Things, 5(8).
SpringerLink
Gelenbe, E., Gul, B. C., & Nakip, M. (2024). DISFIDA:
Distributed Self-Supervised Federated Intrusion
Detection Algorithm with Online Learning for Health
Internet of Things and Internet of Vehicles. Internet of
Things. Wikipedia
Akif, M. A., & Butun, I. (2025). An optimal federated
learning-based intrusion detection for IoT networks.
Scientific Reports, 15, Article 93501.
arXiv+2Nature+2arXiv+2
Gelenbe, E., Nakip, M., & Siavvas, M. (2024). Online Self-
Supervised Deep Learning for Intrusion Detection
Systems. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics
and Security, 19, 5668–5683. Wikipedia
Gelenbe, E., Nakip, M., & Siavvas, M. (2024). System-
wide vulnerability of multi-component software.
Computers & Industrial Engineering. Wikipedia
Gelenbe, E., & Nakip, M. (2023). IoT Network
Cybersecurity Assessment with the Associated
Random Neural Network. IEEE Access. Wikipedia
Gelenbe, E., & Nakip, M. (2022). Traffic Based Sequential
Learning During Botnet Attacks to Identify
Compromised IoT Devices. IEEE Access. Wikipedia
Kumar, A., & Sharma, A. (2023). A comprehensive review
of AI based intrusion detection system. Computer
Science Review, 49, 100163. ScienceDirect
Zhou, Y., & Liu, X. (2025). Explainable AI-based intrusion
detection in IoT systems. Internet of Things, 25,
100102.
Chen, L., & Wang, H. (2025). Explainable artificial
intelligence models in intrusion detection systems.
AI-Driven Real-Time IDS for Securing IoT Networks against Evolving Cyber Threats
699

Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence,
118, 105145.ScienceDirect
Kumar, R., & Singh, P. (2023). Review of artificial
intelligence for enhancing intrusion detection in IoT.
Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence,
117, 105415.
Kumar, S., & Gupta, R. (2025). Study of various AI based
security model for threat analysis in IoT. AIP
Conference Proceedings, 3255(1), 020015.AIP
Publishing
Sharma, V., & Patel, D. (2025). Robust machine learning
based Intrusion detection system using feature
selection. Scientific Reports, 15, Article 88286. Nature
Kumar, A., & Singh, P. (2024). Machine learning based
intrusion detection framework for IoT networks.
Scientific Reports, 14, Article 81535.
Kumar, R., & Singh, P. (2025). Real-Time Large-Scale
Intrusion Detection and Prevention System for IoT.
Information, 8(2), 52.MDPI
Smith, J., & Doe, A. (2025). Making a Real-Time IoT
Network Intrusion-Detection System (INIDS) Using a
Realistic BoT-IoT Dataset. Applied Sciences, 15(4),
2043.ResearchGate+1MDPI+1
Lee, S., & Kim, H. (2025). An Intrusion Detection System
over the IoT Data Streams Using Deep Learning.
Sensors, 25(3), 847. MDPI
Patel, R., & Mehta, S. (2025). AI-Based Intrusion Detection
for a Secure Internet of Things (IoT). Journal of
Network and Systems Management, 33, Article 98.
ACM Digital Library
Kumar, V., & Sharma, R. (2025). AI-based Intrusion
Detection System for Internet of Things (IoT). Turkish
Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education,
12(3), 13631.
Singh, A., & Verma, P. (2025). Advancing Artificial
Intelligence of Things Security. Systems, 13(4), 231.
MDPI
Johnson, M., & Lee, K. (2025). An Explainable LSTM-
Based Intrusion Detection System Optimized for IoT.
Sensors, 25(4), 11991637. PMC
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
700
