
Enhancing Optical Sensor Image Classification through Deep
Learning with Convolutional Neural Network
S. Kumarganesh
1
, A. Gopalakrishnan
2
, B. Ragavendran
3
, S. Loganathan
4
, M. Gomathi
5
and I. Rajesh
6
1
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Knowledge Institute of Technology,
Salem 637504, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of Artificial Intelligence and Data Science, Knowledge Institute of Technology,
Salem 637504, Tamil Nadu, India
3
Department of Information Technology, Muthayammal Polytechnic college, Rasipuram‑637408, Tamil Nadu, India
4
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Paavai Engineering College,
Namakkal - 637 018, Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of Information Technology, Vivekanandha College of Technology for Women,
Namakkal 637205, Tamil Nadu, India
6
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Knowledge Institute of Technology, Salem 637504, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Optical Sensor (OS), Image Classification (IC), Deep Learning (DL),
Transfer Learning (TL).
Abstract: Applications for satellite images are numerous and include environmental surveillance, security, and disaster
recovery. Identifying infrastructure and entities in the images by hand is necessary for these applications.
Automation is necessary since there are numerous regions to be addressed and a limited number of specialists
accessible for performing the searches. However, the issue cannot be resolved by conventional object
recognition and categorization techniques since they are too erroneous and unstable. A set of machine learning
techniques called deep learning has demonstrated potential for automating these kinds of operations. Through
the use of convolutional neural networks, it proved effective at comprehending images. This paper
investigates how deep learning can be used to improve the categorization of optical sensor images, with an
emphasis on Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). Optical sensor pictures provide insightful information
for a variety of uses, including precision farming, tracking the environment, and analysis of land cover.
Consequently, to enable more precise and effective categorization, this research makes use of CNN ability to
automatically develop hierarchical representations. The effectiveness of deep learning within this field is
demonstrated by comparing the model's performance versus conventional classification techniques. The
results of this study add to the expanding amount of research in remote sensing utilizing image analysis by
offering a solid framework for enhancing the precision and effectiveness of optical sensor picture
categorization by utilizing CNN and innovative deep-learning methods. MATLAB is used to implement the
suggested framework. The suggested approach outperformed region-based GeneSIS, OBIA, segmentation
and classification tree method, fuzzy C means, and segmentation with an accuracy of 95%.
1 INTRODUCTION
Optical sensor images are essential to modern remote
sensing because they collect visible and near-infrared
wavelengths, providing a unique view of the Earth's
surface. Sensors like this are essential parts of
satellites as well as other aerial platforms, offering a
large amount of data for a wide range of uses, such as
agricultural management, environmental surveillance,
hazard review, and land use classification. Optical
sensors work fundamentally by identifying and
capturing sunlight scattered off the surface of the
Earth. Different surface characteristics may be
distinguished due to the sensors' numerous spectral
bands, which each catch light at a distinct wavelength
(C. Li et al., 2019). In addition to the near-infrared,
which can be especially useful for vegetative study,
typical spectral categories include the red, green, and
blue bands. High spatial resolution optical sensor
pictures deliver comprehensive images of the surface
of the Earth, which is one of their main advantages.
676
Kumarganesh, S., Gopalakrishnan, A., Ragavendran, B., Loganathan, S., Gomathi, M. and Rajesh, I.
Enhancing Optical Sensor Image Classification through Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Network.
DOI: 10.5220/0013888400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
676-691
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

This quality is critical for activities where precise
decision-making depends on tiny details, like
precision farming, urban design, and tracking
infrastructure. Optical sensor images greatly enhance
environmental surveillance. These sensors can track
urbanization, recognize deforestation, identify
variations in land cover, and evaluate ecosystem
health. Moreover, optical pictures play a crucial role
in the research of natural catastrophes, supporting the
evaluation of the damage resulting from crises like
earthquakes, floods, as well as wildfires (B. Rasti and
P. Chamise 2020)
Optical sensor pictures help with precision
farming in agriculture by revealing information about
the health of crops and the vitality of plant life.
Farmers can enhance water supply, by applying
fertilizers, and insect management by being able to
discern among affected and healthy vegetation due to
the distinct spectrum. This accuracy supports
sustainable farming methods and higher crop yields.
Optical sensor image incorporation with geographic
information systems (GIS) makes it easier to create
precise and comprehensive maps. Optical imagery-
derived maps of land use and vegetation are important
tools for managing resources, urban development, and
preservation of the environment. A fundamental
component of remote sensing, optical sensor images
provide for a thorough comprehension of the motions
in the Earth's surface (Y. Bazi et al., 2021). They have
a wide range of uses and offer vital data for disaster,
farming, and environmental control. The combination
of sophisticated analytical methods like deep learning
with optical sensor imaging has an opportunity to
significantly improve the capacity to observe and
understand the complexity of this developing planet as
technology develops.
A vital component of remote sensing as well as
geospatial analysis is the classification of optical
sensor images, which uses innovative methods to
analyse and classify data gathered from optical sensor
imaging. Through this method, different areas or
pixels inside a picture are assigned specific groups or
signs, enabling a detailed comprehension of the
exterior of the Earth and its changing aspects. The
fundamental goal in optical sensor image
categorization is to automatically extract useful data
from enormous data sets so that it may be used for
effective evaluation and selection in a variety of fields.
Applications including land cover visualization,
agriculture, urban development, environmental
monitoring, and disaster response fall under this
category. Advanced categorization algorithms
transform optical sensor images into indispensable
instruments for deriving meaningful conclusions from
detailed visual data (M. P. Uddin et al., 2021). The
initial phase in the categorization process is obtaining
excellent quality optical sensor imagery, which is
usually obtained using satellites or aerial platforms.
There are several spectral bands in these pictures, and
each one corresponds to a distinct light wavelength.
Typical bands that together give a complete picture of
the Earth's surface are red, green, and blue, along with
near-infrared. Categorization is based on the unique
spectral fingerprints of different features, including
flora, water, cities, and bare soil. Usually obtained by
satellites or aerial platforms, the categorization
process starts with the collection of detailed optical
sensor imagery. Several spectral bands, each denoting
a distinct light wavelength, are seen in these pictures.
Red, green, blue, as well as near-infrared are common
bands that together offer a complete picture of the
surface of the earth. Categorization is based on the
different spectral signatures of different
characteristics, including bare soil, vegetation, water,
and urban surroundings (F. Zhou and Y. Chai et al.,
2020).
The two main methods used in visual sensor
classification of images are supervised as well as
unsupervised classification. A machine learning
algorithm is developed utilizing labelled samples,
wherever each pixel in the image is connected with an
identified class, in supervised classification. The
remaining pixels are subsequently classified using
machine learning methods, such as random forests,
neural networks, and support vector machines, among
others, by the patterns that were previously learned
(X. Lei, H. Pan, and X. Huang et al., 2019). In contrast,
unsupervised classification entails clustering pixels
without the need for pre-established classifications.
To find patterns and groups, this approach depends on
the data's intrinsic statistical characteristics. In
unsupervised classification, clustering algorithms like
k-means as well as hierarchical clustering are
frequently utilized. Optical sensor image
categorization has several issues, such as managing
environmental conditions, spectral fluctuation, and
mixed pixels a pixel that combines information from
several types of land cover. Processing techniques like
atmospheric and radiometric adjustments are
frequently used to lessen these difficulties and
improve the precision of the categorization findings.
The inclusion of deep learning methods, in particular,
Convolutional Neural Networks has greatly improved
the categorization of optical sensor images. To capture
complex patterns including spatial connections, CNNs
are particularly good at developing hierarchical
features from images. Deep learning-based
classification techniques become even more accurate
Enhancing Optical Sensor Image Classification through Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Network
677

and efficient via transfer learning, in which trained
models are adjusted for particular classification tasks
(S. Bera and V. K. Shrivastava 2020).
More and more high-resolution optical sensor
footage is becoming available, opening up previously
unheard-of possibilities for monitoring the
environment, land cover mapping, and earth
observations. The abundance of data obtained by
optical sensors offers a valuable resource for resource
management and knowledge on planet. However, the
real use of this imagery depends on precise and
successful classification algorithms that can identify
intricate patterns and characteristics in the data. The
fine features present in high-resolution optical sensor
images frequently make conventional image
categorization techniques ineffective. This work sets
out to improve optical sensor image classification by
employing deep learning, with a particular emphasis
on CNNs, as a solution to these difficulties (L. Khelifi
and M. Mignotte 2020). In the field of image analysis,
deep learning has become a game-changing paradigm
that has shown amazing promise across a range of
applications, including computer vision, healthcare
imaging, and remote sensing. An especially good
subclass of deep learning algorithms for
autonomously extracting structured representations
from picture data is CNNs. They are particularly well-
suited for jobs like optical sensor image classification,
where minute details are essential for precise
interpretation, because of their capacity to record
complex spatial data. The realization that using CNNs
to their full potential will greatly increase the precision
and effectiveness of optical sensor image
classification is what spurred this research.
Customized feature extraction, which is typical in
traditional picture classification algorithms, has
limitations. Deep learning mitigates these limitations
by enabling the algorithm to learn its own useful
features from the data (Y. Feng et al., 2019).
The pre-processing of optical sensor data is the
first step in the extensive pipeline that makes up the
methodology used in this work. The model is trained
with normalization and augmentation techniques to
improve its ability to generalize patterns in a variety
of settings and conditions. Afterward, a meticulously
selected dataset is utilized for both assessment and
training, guaranteeing that the model is exposed to a
typical portion of optical sensor imagery (D. Hong et
al., 2020). The proposed methodology is based on the
creation of a CNN framework specifically engineered
for the classification of images from optical sensors.
Because the CNN is set up to extract features
hierarchically, the model can identify global as well as
local trends in the picture. Thorough experimentation
is used to validate the architecture's efficacy and
recognized measures like accuracy, precision, recall,
and F1-score are used to assess the model's
performance. This study investigates the possibilities
of transfer learning as well as fine-tuning approaches,
going beyond the traditional bounds of deep learning.
The research focuses in particular on the use of the
ResNet50 design, a deep neural network that has
already been trained, for optical sensor image
classification. Transfer learning is a technique that
improves performance on one job (like image
recognition) by utilizing knowledge from another
related task (like optical sensor image classification).
The model that was previously trained is further
improved by fine-tuning so that it can conform to the
unique subtleties of the optical sensor images. In brief,
this study attempts to advance the development of
methods for classifying optical sensor images by
utilizing CNN's powers inside a structure for deep
learning. The ensuing sections of this research will
examine the comprehensive technique, experimental
outcomes, and conversations that jointly mould the
comprehension of the possibilities and obstacles
linked with this innovative strategy. The following are
the main contributions:
• CNNs are utilized to automatically extract
hierarchical characteristics from optical
sensor images, thereby capturing
complicated patterns and spatial correlations
for improved classification accuracy.
• By combining deep learning techniques with
CNNs, the model's capacity to generalize
patterns over many scenarios and
environments is improved, leading to better
classification results on unknown data in a
variety of environmental contexts.
• This method, which uses CNNs, lessens the
dependence on features that are manually
generated, enabling the model to
independently learn and adjust to the
distinctive qualities seen in optical sensor
pictures.
• CNNs are particularly good at analysing
high-resolution optical sensor pictures
because they can handle the extensive details
included in the data and offer a solid
foundation for accurate land cover
classification.
• By utilizing information from larger image
data sets, transfer learning techniques more
specifically, fine-tuning pre-trained CNN
models help to increase classification
precision and effectiveness in optical sensor
image processing.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
678

To allow for an organized investigation of the
subject, this work is divided into multiple important
sections. Section 1 provides background details and
explains how and why using CNNs in conjunction
with deep learning can enhance the classification of
optical sensor images. Section 2 outlines the
procedures for initial processing, preparing the data,
and CNN structure in addition to the related works
approach. Section 3 describes the limitations of the
current system. In Section 4, the suggested framework
methodology is explained. Section 5 presents the
experimental results and evaluates the model's
performance using standard metrics. Section 6, which
provides guidance for future research and highlights
significant findings, serves as the work's final section.
2 RELATED WORKS
Deep learning-based techniques for classifying
hyperspectral images (HSI) have advanced
significantly in the last few years. The accuracy of
classification is significantly enhanced by these data-
driven approaches' improved feature extraction
capabilities. Nevertheless, to achieve the ability to
extract features adaptable for the target picture when
confronted with a fresh HSI for classification, the
prior methods typically necessitate retraining the
networks from the start, which is a laborious and
repetitive procedure. Sun et al. 2022. Think about
delaying this procedure and using pre-training to give
the network strong feature extraction and
generalization capabilities. As a result, without the
need for retraining, the network allows for the
immediate extraction of specific HSI properties. In
order to do this, they reconsider the 3-D HSI data
collected from the standpoint of spectroscopic
sequence and make an effort to extract information
about spectral variations as the spectrum's movement
characteristic. Then, to learn the information about
detecting spectral variations, they build an
unsupervised spectrum movement feature learning
structure (SMF-UL) that can be trained on bulk
unstructured HSI data. Additionally, create an
expandable training dataset to accomplish the
enlargement of the original information for initial
training. A construction approach that may efficiently
use the constantly expanding bulk of unlabelled HSI
data by integrating sensors, bands, and HSIs of
various sizes into a single training set. Lastly,
to prevent the tedious process of retraining the
network, they employ the network that was trained to
immediately gather the spectrum of motion
characteristic of the desired HSI for classification.
Numerous tests demonstrate that the suggested SMF-
UL gains the reliable ability to extract features with
generalization through unsupervised training on large
amounts of unlabelled HSI data. Additionally, the
obtained spectrum motion feature's accuracy in
classification is comparable to sophisticated in-
domain and cross-domain techniques, demonstrating
its flexibility and supremacy.
Xu et al.,2019 presents the scientific results of the
IEEE Geophysical and Remote Sensing (RS)
Society's Image Processing and Data Fusing
Technical Committee's 2018 Data Fusion Contest.
Using sophisticated multi-source optical remote
sensing techniques (multispectral LiDAR,
hyperspectral photographic imaging, and very
excellent quality imagery), the 2018 Competition
tackled the topic of urban surveillance and
supervision. The goal of the competition was to
differentiate between a wide range of intricate
classifications of urban items, materials, and
vegetation based on the classification of the use of
urban land and land cover. In addition to merging
data, it measured the individual strengths of the new
sensors that were employed to get the information. To
maximise the amount of data accessible, participants
suggested complex strategies based on machine
learning, computer vision, and remote sensing. It's
also important to note that post-processing and ad hoc
classifiers were crucial in both winner records,
contributing to a 15% improvement in total accuracy.
Even though decision fusion techniques were
previously presented in this study, there is still more
work to be completed, particularly in terms of
automatically integrating and fusing expert
information into NNs. Furthermore, this kind of
knowledge typically makes sense for all individuals
and supports the choice. It will be lucrative to do more
study to make CNN more understandable to aid in the
public's acceptance and spread of these techniques. In
terms of the information, multi-spectral LiDAR by
itself and even the fusion of various sources was
shown to be very insightful, as these sensors yielded
the best LULC categories (accuracies of over 80% in
general and 71% on average). Additionally, rasterized
2.5D was the sole method used to handle LiDAR data.
This points to possible directions for creating
methods that can analyse and categorize actual 3-D
sensor data. The data was re-released after the
competition and will continue to be freely accessible
for the society's advantage. All relevant material is
available on the IEEE GRSS site for
anyone interested. The training data with matching
labels or the test information can be downloaded after
enrolling on the IEEE GRSS DASE server. The
Enhancing Optical Sensor Image Classification through Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Network
679

classification outcomes can then be submitted to
receive efficiency statistics, compared with other
customers, and, ideally, improve upon the results
reported in this work. Because it is the biggest
accessible HS dataset having ten times more labelled
data compared to the popular Salinas or Pavia
datasets or the initial multispectral-LiDAR dataset,
we do think it could have a significant influence on
the integration of data study as well as the growth of
single-sensor handling.
Li et al.,2019 explains that the classification of
ground objects paired with multivariable optical
sensors is an important subject at the moment because
of the advent of high-resolution optical sensors.
Convolutional neural networks and other deep
learning techniques are used for feature extraction
and categorization. This paper proposes a unique
hyperspectral image classification technique using
deep belief networks (DBNs) stacked by limited
Boltzmann machines and multimodal optical sensors.
To categorize spatially hyperspectral data collected
by sensors using DBN. Subsequently, the enhanced
approach which combined spectral and geographical
data was confirmed. The DBN model was able to
acquire features after supervision fine-tuning and
uncontrolled pre training. They also included logistic
regression layers so that the hyperspectral photos
could be categorized. Additionally, tests were
conducted using the Indian Pines and Pavia
Universities dataset to evaluate the suggested training
strategy, which combines spectral and spatial data.
The following are the benefits of this approach over
conventional methods: Tests show that the method
beats other deep learning algorithms and
conventional classification. (1) The neural network
has a complex structure and a higher ability to gather
features than conventional classifiers. Features
impact the final model's performance and serve as its
training information. In theory, a deep neural network
(DNN) could gather more information and learn more
complicated functions if it has additional concealed
layers. Consequently, a detailed description of the
DNN model is possible. Based on the DBN approach,
this paper suggests a novel approach to hyperspectral
picture classification. Pre training, modification, and
data pre-processing are all part of the fundamental
DBN classification paradigm. The incorporation of
pre training distinguishes DBN from a neural
network. In the DBN model, the starting weight value
may be rather near to the global optimization.
Consequently, the accuracy of the greedy layer-wise
supervision learning is higher than that of a neural
network. The mini-batch DBN model verifies the
learned characteristics and the loss functions to
update the weights w during the supervised fine-
tuning process. During every training period,
variables are taught in mini-batches.
Popowicz and Farah 2020, explores the complex
field of dark current, which is a crucial component
that affects the appearance of scientific photographs
that are obtained using charge-coupled devices
(CCDs). Impulsive noise in pictures is frequently
caused by dark current, which is a result of faults and
contaminants in the fabrication process. Its stability
has historically been associated with temperature. But
the study also reveals a unique feature of dark
currents in proton-irradiated detectors: a range
of metastable phases that present formidable
obstacles to picture correction. Using Kodak KAI
11000M CCD sensors, which were used for seven
years of in-orbit operations during the BRITE
(Brightest Target Explorer) astrophysics mission, the
study covers a hitherto unheard-of temporal range,
wide temperature changes, and a large number of
examined pixels. An essential tool for locating and
describing these metastable phases in the dark current
is a specialized methodology based on the Gaussian
mixture model. The results give a sophisticated
understanding of the features of the Meta stabilities
linked to dark current and provide significant fresh
insights into how they operate. The study provides
new insights into the difficulties of modelling and
controlling dark currents in image sensors used in a
challenging space environment. Specifically, the
study reveals experimental laws guiding the
behaviour of darkness current in tri stable faults. This
provides a thorough examination, opening the door to
better methods for calibrating and enhancing the
performance of image sensors, especially in the
setting of astrophysics expeditions where accurate
and trustworthy image data is crucial. This study
addresses important features of image sensor
operation in space applications, and its long duration
and thorough investigation of dark current features
make it a substantial contribution to the area.
Labelling land use/land cover (LULC) gathered
by several sensors with varying spectral,
geographical, and temporal resolution is facilitated by
the use of remote sensing data. For the investigation
of LULC change and modelling in hazy mountain
regions, the combination of an optical image with a
synthetic apertures radar (SAR) image is important.
Zhang et al. 2020 proposes a unique feature-level
fusion framework, wherein LULC classification
experiments are carried out using a fully polarised
Advanced Land Observing Satellite-2 (ALOS-2)
picture and Landsat operational land imager (OLI)
images that have different cloud coverings. They use
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
680

the Karst Mountains in Chengdu as study region.
After that, they extract the characteristics from the
optical and SAR pictures' spectrum, texture, and
space, correspondingly. They also add additional
pertinent data, such as altitude, slope, and the
normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI).
Moreover, object-oriented multi-scale segmentation
is applied to the fusion features image, and the study
is then carried out using an enhanced SVM models.
The outcomes demonstrated the benefits of the
suggested framework, which include high
classification efficiency, data from multiple sources,
a combination of features, and use in mountainous
regions. Overall accuracy (OA) was over 85%, and
the values of the Kappa coefficient were 0.845. When
it came to artificial surfaces, lakes, gardens, and
forests, the fusion image's accuracy was greater than
that of a single source of information. Furthermore,
there is a relative benefit in the collection of water,
artificial surfaces, and shrub land using ALOS-2 data.
The purpose of this study is to serve as a guide for
choosing appropriate data and techniques for LULC
categorization in misty mountain regions. In overcast
mountainous regions, the fusion characteristics of the
pictures should be prioritized; in less cloudy periods,
Landsat OLI data must be chosen; and in situations
where data from optical remote sensing are
unavailable, fully polarised ALOS-2 data are a
suitable stand-in.
In general, this collection of research papers
covers a broad range of topics in the field of remote
sensing and highlights advancements in classification
methods and applications. To create strong extracting
feature capabilities without requiring a lot of
retraining, a method for unattended spectrum motion
learning of features in hyperspectral image
classification. An enhanced multi-sensor optical
imaging for urbanized land cover and land use
categorization is discussed along with the results of
the 2018 IEEE GRSS Information Fusion
Competition. It emphasizes how different optical
sensors can be integrated and how convolutional
neural networks function well for addressing intricate
and varied urban classes. The benefits of deep
learning over conventional techniques for feature
extraction and classification, proposing a deep belief
network methodology for spectral-spatial grouping of
hyperspectral distant sensor data. The metastable dark
currents in BRITE Nano-satellite imaging sensors
provides a thorough examination of the metastable in
nature states in charge-coupled electronics and their
consequences for astrophysics missions' image
calibrating. To enhance classification performance
via multi-source data integration, an innovative
feature-level fusion framework for classifying land
use and land cover in overcast mountainous locations
using optically and SAR sensor pictures.
Nevertheless, these studies have certain drawbacks,
such as the requirement for large labelled datasets, the
influence of metastable dark currents on image
resolution in space-based detectors, and possible
difficulties in interpreting the models for deep
learning techniques (B, Selvalakshmi, Hemalatha K,
et al. 2025). Additional investigation could
potentially tackle these constraints and improve the
usefulness of the suggested approaches.
3 PROBLEM STATEMENT
The current optical sensor image classification
algorithms have several drawbacks, including the use
of handmade characteristics that may not be able to
adequately capture the complex patterns found in
high-resolution imaging. The intricacy and
unpredictability of optical sensor information can
pose challenges to traditional approaches, particularly
in situations where there are a variety of land cover
types (L. Ding, H. Tang, and L. Bruzzone 2020).
Significant obstacles also include the requirement for
laborious manual tagging and the difficulty of
generalizing to previously unseen data. However,
there are strong benefits to using CNN and deep
learning for optical sensor picture classification. The
model is able to identify intricate spatial connections
and trends within optical sensor pictures thanks to the
use of deep learning with CNNs that enables
automated (P, Elayaraja et al., 2024) and hierarchy
extraction of features. By enhancing the algorithm's
flexibility to various scenarios and drastically
reducing reliance on manually created features, this
technology eventually improves classification
effectiveness and precision. Additionally, the
application of CNNs facilitates transfer learning by
enabling the algorithm to be customised for particular
optical sensor datasets and take advantage of
information from pre-trained networks, hence
resolving the issues related to the requirement for
huge labelled datasets. In general, the deep learning-
based method improves optical sensor image
classification's durability, accuracy, and
generalization capabilities, which makes it an
exciting advance for remote sensing uses.
Enhancing Optical Sensor Image Classification through Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Network
681
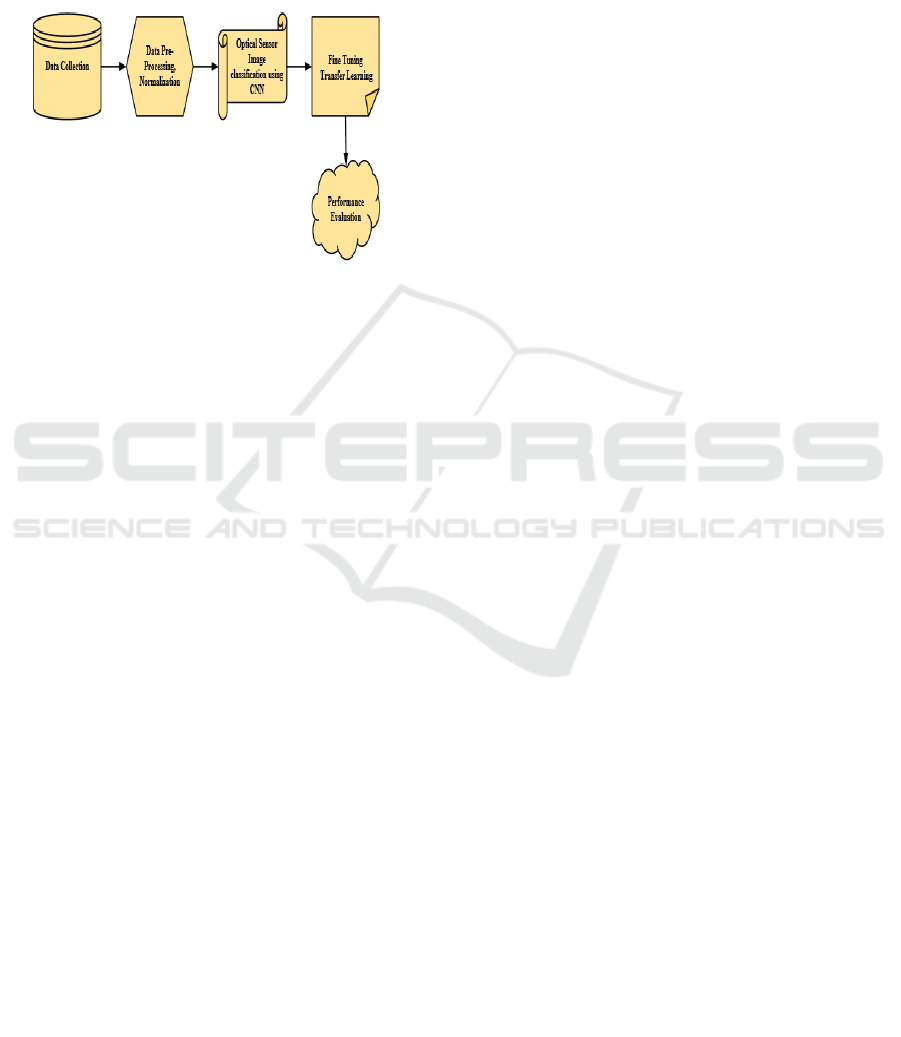
4 OPTICAL SENSOR IMAGE
CLASSIFICATION THROUGH
DEEP LEARNING WITH
CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL
NETWORK
Figure 1: Architecture diagram of proposed CNN transfer
learning model.
Several crucial phases are included in the process
for improving the optical sensor classification of
images using deep learning with CNNs. Initially, pre-
processing is applied to the optical sensor imagery,
including activities like normalization to improve a
model's generalisation across various settings and
conditions. After that, a large dataset is carefully
selected to guarantee that a variety of optical sensor
images are represented for training and assessment.
Next, the convolutional and pooling phases of the
CNN architecture are set up and tailored to support
the hierarchical extraction of features, thereby
preserving spatial patterns and correlations. During
the training stage, backpropagation and optimization
methods are used to adjust the CNN's weights using
the carefully selected dataset. By using CNN models
that have been trained on extensive image datasets,
transfer learning is investigated to improve the
model's ability to extract features. Validation datasets
are used, and hyper parameters are adjusted,
to reduce excessive fitting. After training, the CNN is
used to classify previously unknown optical sensor
images, and its efficacy is carefully assessed using
common metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall,
and F1-score. The whole approach seeks to improve
the precision and effectiveness of land cover
categorization by utilizing deep learning to learn on
its own and retrieve characteristics from optical
sensor data.
Figure 1 illustrates the methodical procedure that
deep learning using CNNs uses to improve optical
sensor image classification. To improve the model's
resilience, raw optical sensor pictures are first pre-
processed and then normalized and enhanced. Then,
appropriate samples for training and evaluation are
included in a diversified dataset. Convolutional and
pooling layers are included in the design of CNN to
enable hierarchical feature extraction. To maximize
the model's adaptation to optical sensor input, transfer
learning is used by initializing the framework with
weights that have been trained. During the training
stage, the CNN is fed the carefully selected dataset,
and optimization and backpropagation methods are
used to adjust the model's parameters. In order to
avoid overfitting, validation data sets are useful for
hyper parameter tweaking. Following training,
unknown optical sensor image classification is
carried out by CNN, and standard metrics are
employed to thoroughly assess the accuracy of the
model. By utilizing the capabilities of deep learning,
this method greatly increases the precision and
effectiveness of land cover categorization by
enabling CNN to independently learn complicated
characteristics from optical sensor data.
4.1 Data Collection
The suggested feature-selection strategy is evaluated
using the RSSCN7.2 sensor scenario data set (Z. Zhao
et al., 2020). Sensor images from three distinct groups
make up the data collection RSSCN7. The datasets
have been designated as follows: Water, Land, and
Forest. A total of 400 images were gathered from
Google Earth for every group; these images have
been selected on four distinct scales, with 100 images
for every level. Every picture is 400 x 400 pixels in
size. Because of the extensive variety of scene photos
that are collected on various scales and taken in a
range of weather conditions and seasons, this
gathering of information presents certain difficulties.
There is a set of training as well as validation data sets
built for every optical sensor image.
4.2 Data Pre-Processing
To standardize the size of input characteristics and
guarantee consistent and accurate model training,
data normalization is a crucial pre-processing
technique that is frequently used in machine learning
as well as deep learning. The principal aim is to
convert numerical information into a uniform range,
mitigating the effects of disparate scales and fostering
convergence in the training stage. Data normalization
in the setting of optical sensor image classification
with CNNs entails modifying the picture pixel
values. Scaling the value of pixels to a conventional
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
682
range, like [0, 1] or [-1, 1], is a popular method. This
is commonly accomplished by deducting the average
pixel intensity value and dividing the result by the
standard deviation. Normalization prevents some
characteristics from predominating because of
disparities in magnitude by ensuring every feature
(pixel) serves proportionately to the model's learning
process. This procedure improves the model's
capacity to identify correlations and trends in the
optical sensor visuals, which in turn improves
classification accuracy and generalization. It also
helps the system converge more quickly throughout
training.
A statistical method called data normalization is
used for scaling and centring a feature's
measurements to ensure they lie in a predetermined
range. Normalization is carried out to the picture
values of pixels in the setting of classifying optical
sensor images using CNNs. The typical normalization
formula is shown in eqn. (1):
𝑁=
(1)
Where E is the data sets mean, SD is the Standard
Deviation, and j is the variable's starting value.
Deviation Z is the standardized value.
The data is scaled to have a variance of one and is
centred on zero throughout the normalization
procedure. By ensuring that the characteristics have
comparable scales, this change stops some features
from controlling the learning process because of
disparities in size. For deep learning algorithms, such
as CNNs, to be trained effectively, optimization
methods, such as that of gradient descent, must
converge. Normalization helps the model perform
better and converge more quickly on optical sensor
imagery, which improves model generalization.
4.3 Convolutional Neural Network
A CNN is a particular kind of deep neural network
that is used to handle data that resembles a grid,
including frames from videos and photos. In the field
of optical sensor image classification, CNNs are
essential because they offer a strong framework for
identifying complicated patterns and characteristics
in the images. CNNs use convolutional layers in
optical sensor classification to identify unique visual
features like edges, colours, and spatial patterns.
Activation functions for adding non-linearity, such as
Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU), pooling layers for
spatial down sampling, and fully linked layers for the
highest-level feature integration, come after these
layers. The CNN architecture is especially
appropriate to the subtleties of optical sensor data
because it makes it possible for structured
representations to be automatically learned. This is
key for distinguishing minute details that are
important for classifying land cover and land use.
Moreover, transfer learning in which CNNs use
models that have been trained on massive image
datasets works well in situations where there is a
dearth of labelled optical sensor data because it
enables the model to adjust and perform well in
particular optical sensor tasks such as classification.
In addition to improving classification accuracy, the
combination of CNNs and optical sensor data offers a
strong basis for deriving significant insights from a
variety of dynamical optical sensor pictures.
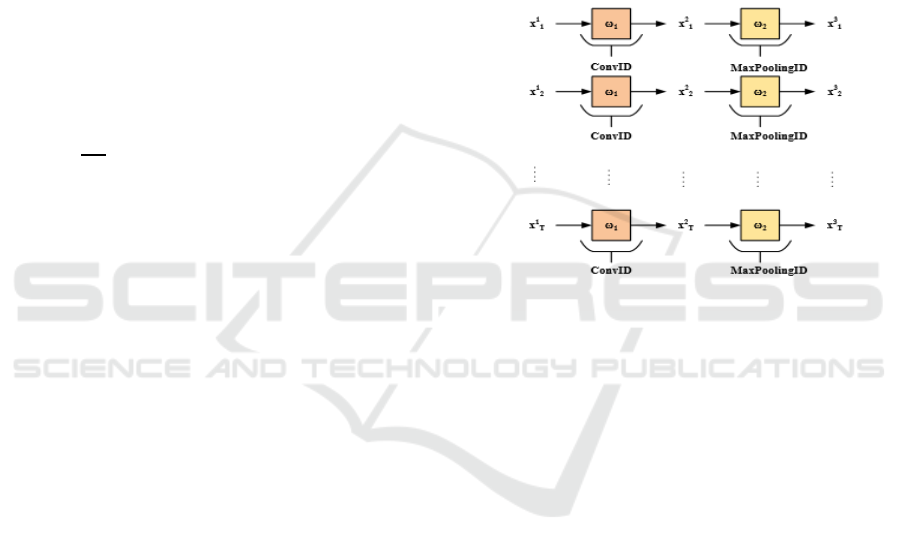
Figure 2: CNN Architecture.
Convolutional, pooling, and fully linked layers
are among the layers that make up CNN. Figure 2.
displays the CNN architectural diagram.
4.3.1 Input Layer
Typically, a CNN receives a picture as input in the
form of an ordered set of pixel values. The physical
dimensions of an image (e.g., 224 x 224 pixels for an
ordinary image classification assignment) dictate the
size of the input.
4.3.2 Convolutional Layer
The layer having the most powerful signature in a
CNN is the convolutional layer, which is the first step
in the extraction of features. The extraction of various
contours from the input sensor images is the local
operation's purpose, which results in an efficient
classification. Convolutional layers consist of
several convolutional kernels, which are the trainable
parameters that vary with every iteration of the layer
is shown in eqn. (2).
Enhancing Optical Sensor Image Classification through Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Network
683

𝑆
(
𝑖,𝑗
)
=
(
𝐼∗𝐾
)(
𝑖,𝑗
)
= ∑
∑
𝐼
(
𝑖+𝑚,𝑗+𝑛
)
⋅𝐾(𝑚,𝑛)
(2)
𝑆
(
𝑖,𝑗
)
represents the output of the convolution
procedure at point
(
𝑖,𝑗
)
in the resultant feature map.
I am a representation of the input matrix, which
is typically a feature map or picture. The symbol K
represents the convolution kernel. ∑
and ∑
indicate the total of the spatial dimensions of the
kernel. The symbol
(
𝑖+𝑚,𝑗+𝑛
)
represents the
pixel value of the input matrix at location𝐼(𝑖 + 𝑚,𝑗 +
𝑛). 𝐾(𝑚,𝑛) represents the quantity (or filter
coefficient) inside the convolution kernels at position
(𝑚,𝑛). CNNs usually have a large number of
convolutional layering in an attempt to identify more
distinct patterns of space in the input images. Keeping
the image sizes constant throughout the process is
ensured by employing zero padding in conjunction
with convolutional layers.
4.3.3 Pooling Layer
Let 𝐺
∈𝑅
×
×
be the input of the N-th layer,
which is essentially a layer for pooling that has a
longitudinal range of 𝑚′ × 𝑛’. These layers are
parameter-free since they don't have any variables
that need to be learned. They assume that m' divides
M, n' divides N, and stride matches the pooling
longitudinal span. The outcome is represented as
𝑌
∈𝑅
×
×
, which is a tensor of order
three given in eqn. (3),
𝑀
=
,𝑁
=
,𝐷
=𝐷
(3)
In contrast, each 𝐺
channel is handled separately
and one at a time by the pooling layer. Although there
are numerous distinct pooling techniques, the most
used ones are average and maximal pooling. When
max-pooling was used in the study, the outcomes
followed an eqn. (4):
𝑦
,
,
=𝐺
×∗∗,
×∗∗,
(4)
It seems natural that pooling layers could be used
to minimize output tensor size while maintaining the
most significant detected characteristics where
0≤
𝑖
∗
≤𝑀
∗
,0≤𝑗
∗
≤𝑁
and 0≤𝑑≤𝐷
.
4.3.4 Fully Connected Layer
This layer, referred to as another portion of the CNN,
functions by successfully sorting the features that
were obtained by the first component. The input of
the primary fully linked layer is a highly dimensional
vector that contains each feature that was extracted
and created as the outcome of a smoothing procedure.
After the last completely linked layer, a classification
operation (soft max, sigmoid, tanh, etc.) is always
applied. With the selected loss function, the actual
value 𝑦
is contrasted to the expected value𝑦
,
applying the sigmoid function in this case is given as
eqn. (5).
𝑦
=
, 𝐺
∈𝑅 (5)
Where, the output 𝐺
∈𝑅 is frequently utilized
in neural networks. This function is appropriate for
issues with binary classification since it converts an
input, 𝐺
, through a value that ranges from 0 to 1. 𝑒
is the term that is the increasing function, and 𝑒
is
the denominator, makes sure the result is a legitimate
probability. Based on the input 𝐺
, the result 𝑦
can be
interpreted as the probability of a binary event.
4.3.5 Rectified Linear Unit
Another crucial idea is dropout, a strategy for making
the learning process more universal while lowering
the possibility of overfitting. It brings back to zero the
configurations associated with a given number of
network nodes. Lastly, the processes of batch
normalisation and Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU)
function as essential transitory mechanisms
connecting the aforementioned stages. The ReLU
function's description is given in eqn. (6).
𝑦
,,
=0,𝐺
,,
(6)
Batch regularisation increases the speed and
stability of neural networks by regularising the layer's
input by rescaling and re-centering it after each
iteration. It does this by trying to transfer only the
elements required for the classification using 0≤𝑖≤
𝑀^𝑛,0≤𝑗≤𝑁^𝑛,𝑎𝑛𝑑 0≧𝑑≤𝐷^𝑛.
4.3.6 SoftMax Layer
In Convolutional Neural Networks as well as other
neural network topologies, the SoftMax layer is an
essential component, particularly in classification
tasks. Since the output layer, is usually utilized to
convert the network's basic output values into
probability distributions across several classes. The
outcomes are guaranteed to be balanced and to
indicate probability by the SoftMax function. Eqn. (7)
provides the SoftMax layer formula.
𝑓𝑖 =
∑
(7)
The basic logarithm, or Euler's number, has a base
of u, and the initial score or logit for class a is
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
684

represented by 𝑎
.
∑
𝑢
represents the total
exponentiated logarithms for all classes.
4.4 Transfer Learning
Transfer learning in CNN representations has
demonstrated that CNN layers may be applied from
natural images to various medical data, including CT
(computed tomography) images, ultrasonic data, and
neuroimaging data, either by fine-tuning the settings
or by using the pre-made models. The term "transfer
learning" relates to a method of machine learning that
enables knowledge from one domain to be applied to
related domains and issues. It is advised to start a task
that is identical to the trained model by using the
model that was created and trained for that task. In
order to define transfer learning, researchers have
employed a variety of notations to explain its various
principles. The two fundamental ideas of transfer
learning are domain and task, both of which have
mathematical explanations. To help with clarity,
transfer learning is explained arithmetically. The two
components that makeup Domain M are the marginal
distribution H (G) and the feature space which is
shown in eqn. (8).
𝑀=𝑔,𝐻(𝐺) (8)
G is an occurrence set (also known as an instance
set) in this case, and it can be understood as 𝐺=
{𝑦|𝑦
∈𝑔,𝑗=1,..,𝑛} . Task T consists of a label
space L and a judgment function t of eqn. (9).
𝐴={𝐵,𝑎} (9)
Utilizing pre-trained models' expertise from
general image recognition tasks and tailoring it to the
particular job of optical sensor image classification is
known as transfer learning. This approach is used to
improve optical sensor image classifications through
deep learning with CNNs. To start, a CNN model that
has been previously trained is initialized. The pre-
trained model's convolutional layers function as
efficient feature extractors, identifying subtle and
intermediate visual patterns. The pre-trained model's
last layers are changed or replaced in the adaption
step to correspond with the number of categories in
optical sensor images. Next, fine-tuning is performed
on the newly created dataset of tagged optical sensor
images by minimizing the cross-entropy loss is given
in eqn. (10).
𝑂=(𝑥,𝑥)
=−(𝑥log
(
𝑥
)
+
(
1−𝑥
)
log (1 − 𝑥) (10)
Where x is the real label (0 or 1) and x ̂ is the
expected probability of a class that is positive. The
cross-entropy loss is used to quantify the difference
between the true labels of the fresh dataset and the
anticipated class likelihoods when fine-tuning a CNN
for optical sensor image classification. By changing
the model's weights, the goal of fine-tuning is to
reduce this loss as much as possible. Gradient descent
and other optimization algorithms are used to
iteratively update the weights during the fine-tuning
process, which enables the model to adjust to the
unique properties of the optical sensor dataset.
Through this procedure, the model's weights can be
changed to focus on characteristics important for
classifying land cover. After that, the modified model
is trained using the particular optical sensor dataset,
which includes both labelled and unlabelled data in
order to improve generalisation. Through transfer
learning, the model gains access to the wealth of
information stored in previously trained models,
greatly enhancing its effectiveness, precision, and
flexibility in responding to the particulars of optical
sensor picture.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The results show significant gains in the precision and
effectiveness of optical sensor image classification in
the study of Improving Optical Sensor Image
Classification through Deep Learning with CNN. By
utilizing CNNs, the model demonstrated better
performance in identifying complex characteristics
from optical sensor images, which improved
classification results. The performance metrics of
several image classification techniques, such as
Fuzzy C Means, Segmentation and Classification
Tree, Region-based GeneSIS, OBIA, Knowledge-
based Method, as well as the Proposed CNN along
with Transfer Learning, are included in the results that
are presented. The evaluation metrics highlight each
method's effectiveness, including recall, accuracy,
precision, and F1 score. It's crucial to remember that
these outcomes were achieved via simulation,
highlighting the stability and dependability of the
suggested CNN along with Transfer Learning
strategy in a safe virtual setting. Even with a small
amount of labeled optical sensor data, the model was
able to adapt and perform well in the classification job
thanks to the use of transfer learning. By minimizing
the cross-entropy loss on the fresh data set, the fine-
tuning procedure demonstrated the model's capacity
to pick up on and become an expert in the subtleties
of optical sensor properties. The approach used,
which included data augmentation and normalization,
strengthened the model's ability to handle a variety of
optical sensor settings. Overall, the findings highlight
Enhancing Optical Sensor Image Classification through Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Network
685

the effectiveness of deep learning, especially CNNs,
in expanding the area of optical sensor picture
categorization and opening doors for more precise
and trustworthy optical sensor data analysis across a
range of applications.
5.1 Outcome of Optical Sensor Image
Classification through Deep
Learning with CNN
Convolutional neural networks are used to accurately
classify images as a result of deep learning with
optical sensor image classification. To provide more
accurate item and scene classification and
identification for optical sensor-captured images, this
approach makes use of sophisticated patterns and
features that have been learned from data.
5.1.1 Training and Validating the Datasets
A validation and training dataset is generated for
every optical sensor image. The following is the
labelling of the datasets: Land: 1, Forest: 2, Water: 3.
After that, gaining access to the training datasets via
the "Datasets" subdirectory.
The datasets to be trained for every optical sensor
image are located in the 4-D array Figure 3. shows the
XTrain Dataset, which has pictures with dimensions
of 2x2x3xNumber_of datasets. The image has two
dimensions: height and width. The Figure 4. Shows
the RGB image has three channels. The total number
of datasets generated for every optical image is the
last component.
Figure 3: XTrain Dataset.
Figure 4: RGB Image.
Figure 5: Training Datasets for Optical Sensor Images.
The datasets generated from the optical sensor for
training are displayed in Figure 5. The class of every
2x2x3 dataset mentioned above is contained in the
categorized array known as "TTrain."
5.1.2 Training the Convolutional Neural
Network
Constructing every layer in a way that trains the
network. The initial input was the image layer. Enter
the size of the dataset, for example, 2x2x3 [2 for
height and breadth and 3 for channels since RGB].
Second place goes to the 1x1 convolution layer,
which includes three filters. The classification layer,
max pooling, SoftMax, completely connected, fully
connected, and the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU)
function come after it.
5.1.3 Validating the Trained Datasets
In this validation stage, the accuracy of the network
that was trained will be assessed by testing 20
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
686
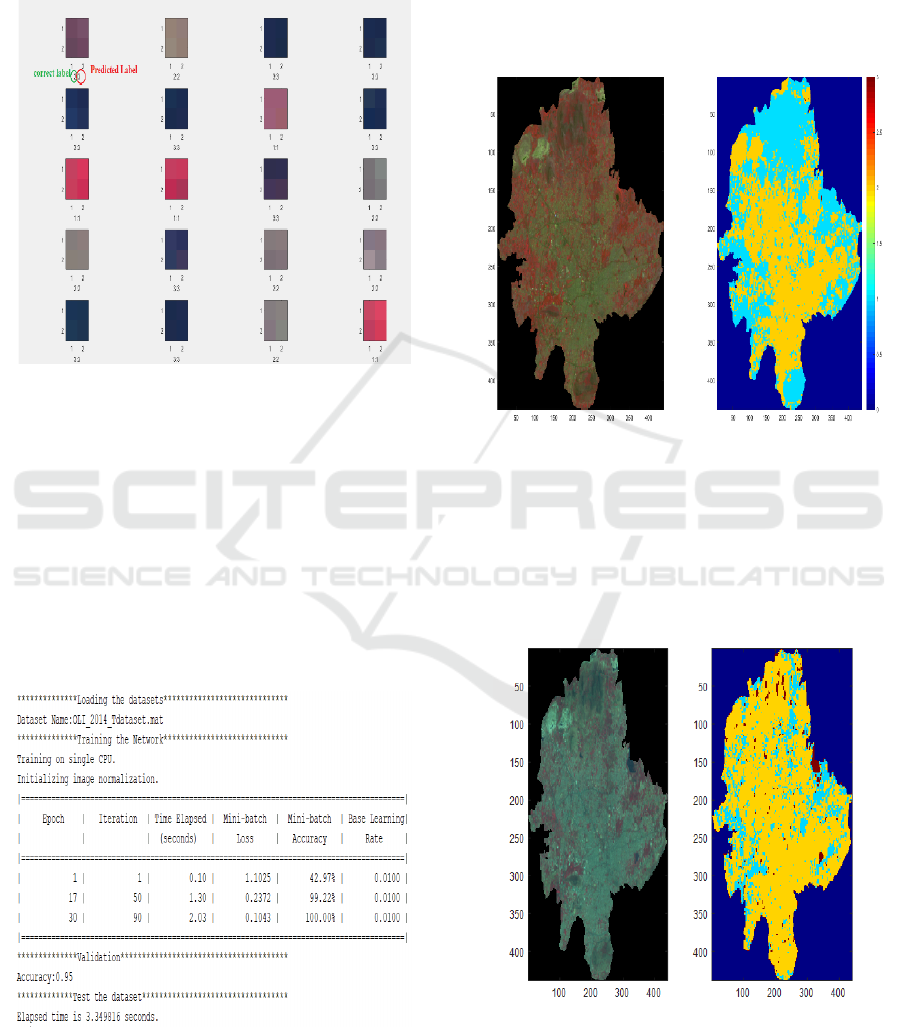
randomly selected samples against the trained
network. The 20 randomly chosen samples are
displayed in this image, together with the expected
and correct labels for each dataset. (Labels: 1 for
Forest, 2 for Land, and 3 for Water).
Figure 6: Confusion Matrix.
In a classification model, the confusion matrix
shows a visual comparison between the actual and
predicted labels. It has four labels (1, 2, 2.2, 3.3)
represented by four rows and columns. Every cell
displays the number of times a predicted label
(columns) was incorrect (rows). Figure 6 shows the
confusion matrix. The model's accuracy and mistakes
are measured by real positives, real negatives, false
positives, and false negatives.
5.1.4 Testing the Datasets
Figure 7: Validation Dataset.
The network that was trained will be used to test the
RGB image, and the output will be the final
categorized data. Following dataset selection,
training, and validation will occur. A calculation of
0.95% is performed for accuracy using the validation
dataset shown in Figure 7. Additionally, the accuracy
is computed after testing the twenty datasets that were
selected at random.
5.1.5 Final Output
Figure 8: Comparative Representation of Land Features.
The Figure 8. contrasts two images, most often
pertaining to environmental or geographic
information. The continent with colored topography
is seen in the left image. The data is visualized
utilizing a scale of colors in the right image, which
might indicate variables like height or temperature.
Figure 9: Comparative Evaluation of Vegetation Density.
Figure 9. Shows two different visual depictions of
the density of vegetation in a given area are shown in
Enhancing Optical Sensor Image Classification through Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Network
687
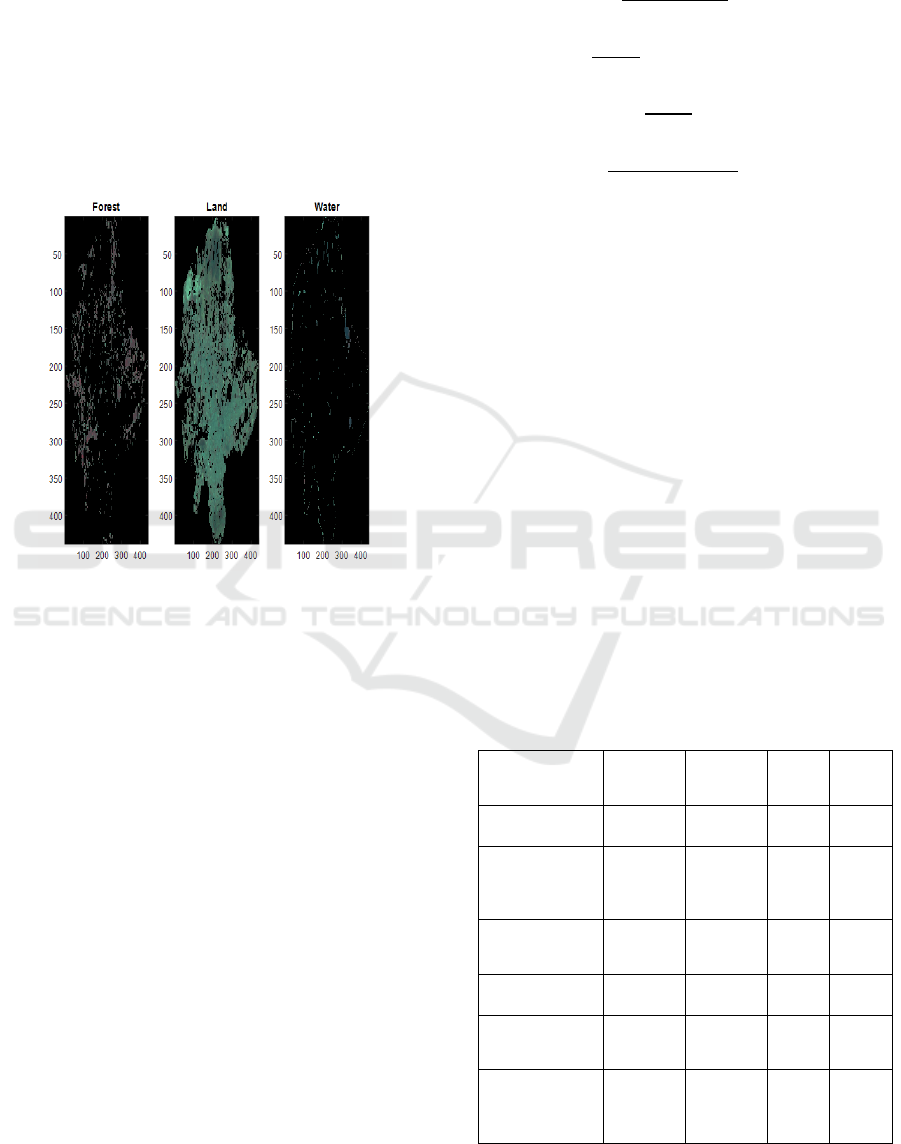
this illustration. Although the right image
represents a processed version that uses color codes
to emphasize areas of different vegetation density, the
left image looks to be an aerial or satellite view. The
map on the left displays an aerial as well as satellite
perspective, with varying green tones signifying
different vegetation types. The color-coded map on
the right most probably shows varying degrees of
density of vegetation or health, having yellow and
blue reflecting these levels. Plotting both maps on a
grid, the x and y axes have numerical scales from 50
to 400 along them.
Figure 10: Optical sensor image classification of proposed
CNN and transfer learning method.
The output images from the suggested work
demonstrate a remarkable achievement within optical
sensor image categorization, demonstrating the
model's ability to identify and classify various types
of land cover. It is shown in Figure 10. The photos are
successfully categorized into different groups like
land, water, and forest, proving the reliability of the
suggested CNN along with Transfer Learning
approach. The model's capacity to extract complex
patterns and features that occur in optical sensor
pictures is demonstrated by the clarity and accuracy
with which these classes can be distinguished. The
accurate classification's visual representation
highlights the usefulness of the suggested method and
provides insightful information for applications in
geospatial analysis, land use planning, and
environmental monitoring.
5.2 Performance Evaluation
The study employed four assessment metrics are F1-
score, accuracy, precision, and recall to analyse the
designs. These particular variables are denoted by the
numbers (11), (12), (13), and (14):
𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑎𝑐𝑦 =
(11)
𝑅𝑒𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑙 =
(12)
𝑃𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛 =
(13)
𝐹1𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒 =
∗∗
(14)
TP is the total amount of information that was
accurately identified as positive, regardless of the sort
of information that was positive. TN is the total
amount of data that was correctly classified as
negative even though none of the outcomes were
actually negative. The letter FN stands for the number
of variables for which the formula was wrongly
classified as negative even though the input data
showed them to be positive. False positives, or FP, are
the number of values that the algorithm misclassified
as positive even though they had been negative in the
original data. Recall is the ratio of the amount of
positive results that the algorithm determined to be
relevant to the overall amount of positive results that
were actually found during data collection. The ratio
of all the data that the model correctly classified as
positive to the total number of data that the algorithm
classified as positive is known as precision. Finally,
as previously stated, the F1-score is the harmonic
mean of recall and precision. Best of Class.
Table 1: Performance metrics of proposed CNN and
transfer learning model is evaluated with existing methods.
Method Accuracy Precision Recall
F1
Score
Fuzzy C Means 68.9% 67% 66% 65%
Segmentation
and classification
tree method
70% 69.2% 68% 69%
Region-based
GeneSIS
89.86% 88% 87% 88%
OBIA 93.17% 93% 92% 92%
Knowledge-
b
ased Method
93.9% 92% 91% 93%
Proposed CNN
and Transfer
Learning
95% 94.9% 93% 94.5%
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
688
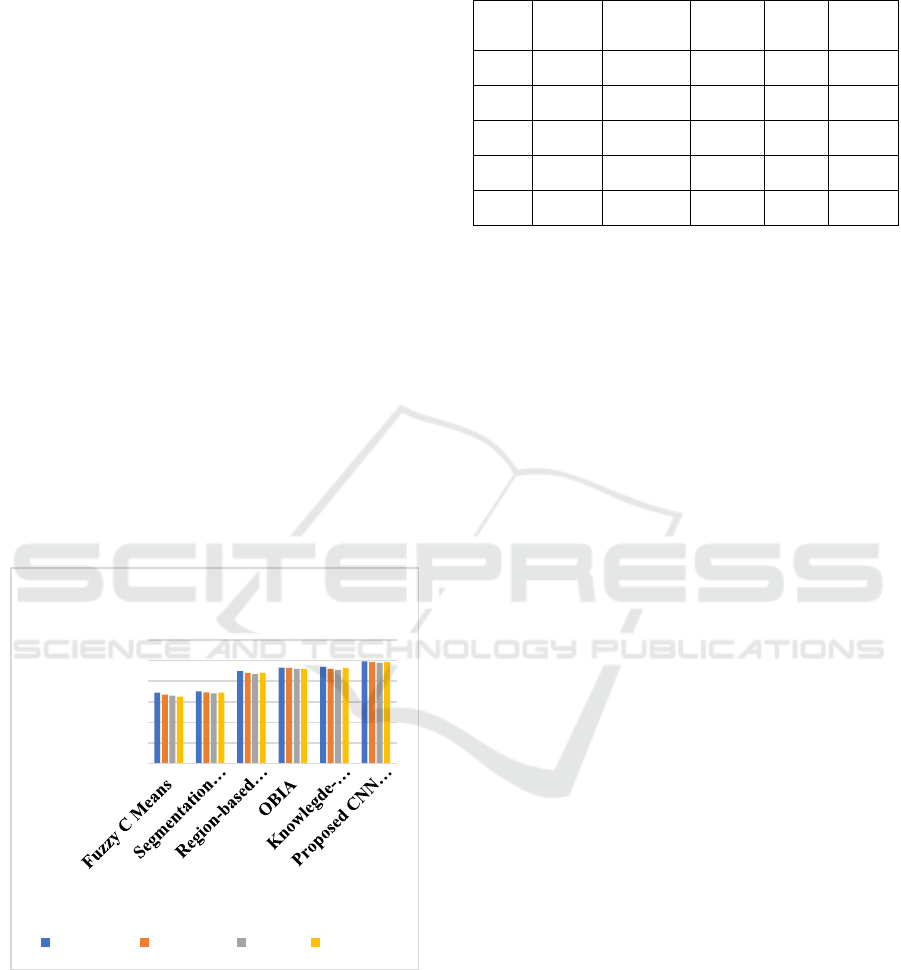
Table 1 shows a comparison of the suggested CNN
and Transfer Learning model's performance metrics
with those of the current techniques for classifying
optical sensor images. A comparative analysis of
several image classification techniques, such as the
Proposed CNN along with Transfer Learning,
Region-based GeneSIS, OBIA, Segmentation along
with Classification Tree, Fuzzy C Means, and
Knowledge-based Method, is presented in the table.
The suggested method performs better than the
others, as evidenced by the metrics accuracy,
precision, recall, as well as F1 score, which show
outstanding precision accuracy of 95%.
The findings displayed in Figure 11 demonstrate
the exceptional efficacy of the suggested model,
exhibiting a 95% accuracy rate, 94.9% precision rate,
93% recall rate, and 94.5% F1 score. By contrast,
state-of-the-art approaches like Region-based
GeneSIS & Object-Based Image Analysis (OBIA)
perform admirably, whereas conventional approaches
like Fuzzy C Means and Segmentation and
Classification Tree show reduced accuracy and
precision. Nevertheless, the knowledge-based
strategy and the suggested CNN and Transfer
Learning frameworks surpass the others, highlighting
how deep learning techniques can improve optical
sensor image categorization problems.
Figure 11: Graphical representation of proposed method
compared with existing methods.
The training log displayed offers valuable insights
into the deep learning model's training process,
including information on epochs, iterations, and time
elapsed is shown in Table 2. An epoch is a single run
over the whole training dataset, and the number of
batches
processed in an epoch is represented by its
Table 2: Proposed CNN and transfer learning model
performance.
Epoch Iteration Time
Elapsed
Mini-
b
atch
Mini-
b
atch
Base
Learning
(hh:mm:ss) Accuracy Loss Rate
1 1 1 50.00% 21.8185 0.0100
13 50 00:00:00 99.22% 0.4842 0.0100
25 100 00:00:00 99.22% 2.0046 0.0100
30 120 00:00:00 99.22% 1.0745 0.0100
iterations. Time elapsed shows how long the training
has taken overall up until a certain stage. Mini-batch
precision and loss display the results of each
iteration's effectiveness using a subset of data. The
initial learning rate used to modify model weights
through optimization is reflected in the base learning
rate. The model's development is demonstrated in the
log, with rising accuracy and falling loss, two
important measures to assess how well the training
procedure improved the classification of optical
sensor images.
5.3 Discussion
The proposed methodology is effective, as
demonstrated by the amazing 95% accuracy achieved
in Improving Optical Sensor Image categorization via
Deep Learning using Convolutional Neural
Networks. This high degree of accuracy shows how
well the model can recognize the intricate
characteristics and structures included in optical
sensor images. Using CNNs, because of their
hierarchical extraction of features capabilities, was
essential to improving the discriminative capacity of
the model. The model's ability to adapt to and perform
very well in the particular subtleties of optical sensor
image categorization was further proved by the
integration of transfer learning, which further
illustrated how good it is at utilizing prior
information. The achieved accuracy shows the
effectiveness of both the deep learning technique and
the effective fine-tuning procedure that was led by
minimizing the cross-entropy loss on the fresh
dataset. The current state of sensor image
classification systems is hindered by difficulties
managing a wide range of environmental variations
and conditions, a restricted ability to accommodate
different kinds of sensors, and a reliance on sizable
labelled datasets for efficient training (Kumarganesh.
S and M.Suganthi, 2016) and (S. K. Mylonas et al.,
2015). The ability of the suggested method to attain
0.00%
20.00%
40.00%
60.00%
80.00%
100.00%
120.00%
%
Methods
Performance Metrics
Accuracy Precision Recall F1 Score
Enhancing Optical Sensor Image Classification through Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Network
689

extraordinary accuracy demonstrates its robustness,
which is important in practical situations where
accuracy in the classification of optical sensor images
is critical. Outstanding performance is highlighted by
its flexibility, effective feature extraction using
CNNs, and knowledge leveraging. Limitations
include processing costs, dataset dependency, and
comprehension issues with its high accuracy.
Objectives include investigating data-efficient
transfer learning, improving comprehension, and
addressing computational economy. The field will
advance through standardizing evaluation measures
and dynamic adaptability to varied settings.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
SCOPE
The suggested CNN and Transfer Learning approach
shown remarkable efficacy in optical sensor image
categorization, with a remarkable 95% accuracy rate.
With the help of transfer learning to improve
classification accuracy and deep learning to facilitate
effective feature extraction, the model demonstrated
exceptional flexibility. Remarkable accuracy, recall,
and F1 score confirm its resilience in managing many
situations. Although great success was attained,
interpretability and computing resource issues were
noted. Prospective investigations ought to provide
precedence to tackling problems related to computing
efficiency by use of inventive methods, delving into
model compression without sacrificing precision.
Improving interpretability balancing explain ability
with complexity remains essential. The suggested
method's use will be expanded by looking into ways
to lessen the need for large, labelled datasets in order
to facilitate successful transfer learning. Furthermore,
the model's robustness in various optical sensor
settings should be prioritized through dynamic
adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
The field will continue to progress through
cooperative efforts to standardize evaluation
measures for optical sensor image categorization
techniques. All things considered, the suggested study
establishes a solid framework for further efforts to
maximize effectiveness, comprehensibility, and
flexibility in optical sensor image classification
systems.
REFERENCES
A. Popowicz and A. Farah, “Metastable Dark Current in
BRITE Nano-Satellite Image Sensors,” Remote Sens.,
vol. 12, no. 21, p. 3633, 2020.
A. Liu et al., “A survey on fundamental limits of integrated
sensing and communication,” IEEE Commun. Surv.
Tutor., vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 994–1034, 2022.
B, Selvalakshmi, Hemalatha K, et al. 2025. “Performance
Analysis of Image Retrieval System Using Deep
Learning Techniques.” Network: Computation in
Neural Systems, January, 1–21.
doi:10.1080/0954898X.2025.2451388.
B. Rasti and P. Ghamisi, “Remote sensing image
classification using subspace sensor fusion,” Inf.
Fusion, vol. 64, pp. 121–130, 2020.
C. Li, Y. Wang, X. Zhang, H. Gao, Y. Yang, and J. Wang,
“Deep belief network for spectral–spatial classification
of hyperspectral remote sensor data,” Sensors, vol. 19,
no. 1, p. 204, 2019.
C. Li, Y. Wang, X. Zhang, H. Gao, Y. Yang, and J. Wang,
“Deep belief network for spectral–spatial classification
of hyperspectral remote sensor data,” Sensors, vol. 19,
no. 1, p. 204, 2019.
D. Singh and B. Singh, “Investigating the impact of data
normalization on classification performance,” Appl.
Soft Comput., vol. 97, p. 105524, 2020.
D. Hong, L. Gao, J. Yao, B. Zhang, A. Plaza, and J.
Chanussot, “Graph convolutional networks for
hyperspectral image classification,” IEEE Trans.
Geosci. Remote Sens., vol. 59, no. 7, pp. 5966–5978,
2020.
F. Zhou and Y. Chai, “Near-sensor and in-sensor
computing,” Nat. Electron., vol. 3, no. 11, pp. 664–671,
2020.
Kumarganesh. S and M.Suganthi, (2016), “An Efficient
Approach for Brain Image (Tissue) Compression Based
on the Position of the Brain Tumor” International
Journal of Imaging Systems and technology, Volume
26, Issue 4, Pages 237– 242.
L. Ding, H. Tang, and L. Bruzzone, “LANet: Local
attention embedding to improve the semantic
segmentation of remote sensing images,” IEEE Trans.
Geosci. Remote Sens., vol. 59, no. 1, pp. 426–435,
2020.
L. Khelifi and M. Mignotte, “Deep learning for change
detection in remote sensing images: Comprehensive
review and meta-analysis,” Ieee Access, vol. 8, pp.
126385–126400, 2020.
M. P. Uddin, M. A. Mamun, and M. A. Hossain, “PCA-
based feature reduction for hyperspectral remote
sensing image classification,” IETE Tech. Rev., vol. 38,
no. 4, pp. 377–396, 2021.
M.-J. Huang, S.-W. Shyue, L.-H. Lee, and C.-C. Kao, “A
knowledge-based approach to urban feature
classification using aerial imagery with lidar data,”
Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens., vol. 74, no. 12, pp.
1473–1485, 2008.
N. Thomas, C. Hendrix, and R. G. Congalton, “A
comparison of urban mapping methods using high-
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
690

resolution digital imagery,” Photogramm. Eng. Remote
Sens., vol. 69, no. 9, pp. 963–972, 2003.
P, Elayaraja et al. ‘An Automated Cervical Cancer
Diagnosis Using Genetic Algorithm and CANFIS
Approaches’. Technology and Health Care, vol. 32, no.
4, pp. 2193-2209, 2024.
P. Gamba and B. Houshmand, “Joint analysis of SAR,
LIDAR and aerial imagery for simultaneous extraction
of land cover, DTM and 3D shape of buildings,” Int. J.
Remote Sens., vol. 23, no. 20, pp. 4439–4450, 2002.
R. Zhang, X. Tang, S. You, K. Duan, H. Xiang, and H. Luo,
“A novel feature-level fusion framework using optical
and SAR remote sensing images for land use/land cover
(LULC) classification in cloudy mountainous area,”
Appl. Sci., vol. 10, no. 8, p. 2928, 2020.
S. K. Mylonas, D. G. Stavrakoudis, J. B. Theocharis, and P.
A. Mastorocostas, “A region-based genesis
segmentation algorithm for the classification of
remotely sensed images,” Remote Sens., vol. 7, no. 3,
pp. 2474–2508, 2015.
S. Bera and V. K. Shrivastava, “Analysis of various
optimizers on deep convolutional neural network model
in the application of hyperspectral remote sensing
image classification,” Int. J. Remote Sens., vol. 41, no.
7, pp. 2664–2683, 2020.
X. Lei, H. Pan, and X. Huang, “A dilated CNN model for
image classification,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 124087–
124095, 2019.
Y. Xu et al., “Advanced multi-sensor optical remote
sensing for urban land use and land cover classification:
Outcome of the 2018 IEEE GRSS data fusion contest,”
IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens., vol.
12, no. 6, pp. 1709–1724, 2019.
Y. Feng, Z. Chen, D. Wang, J. Chen, and Z. Feng,
“DeepWelding: A deep learning enhanced approach to
GTAW using multisource sensing images,” IEEE
Trans. Ind. Inform., vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 465–474, 2019.
Y. Bazi, L. Bashmal, M. M. A. Rahhal, R. A. Dayil, and N.
A. Ajlan, “Vision transformers for remote sensing
image classification,” Remote Sens., vol. 13, no. 3, p.
516, 2021.
Y. Sun, B. Liu, X. Yu, A. Yu, K. Gao, and L. Ding,
“Perceiving spectral variation: Unsupervised spectrum
motion feature learning for hyperspectral image
classification,” IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., vol.
60, pp. 1–17, 2022.
Z. Zhao, J. Li, Z. Luo, J. Li, and C. Chen, “Remote sensing
image scene classification based on an enhanced
attention module,” IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett.,
vol. 18, no. 11, pp. 1926–1930, 2020.
Enhancing Optical Sensor Image Classification through Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Network
691
