
Adaptive Machine Learning for Real‑Time Intrusion Detection in IoT
Ouku Bhulakshmi, Muddam Anusha, Ramisetty Somesh, Surasetty Badrinath,
Mangali Madhan Gopal and Pattan Thoufiq Khan
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Santhiram Engineering College, Nandyal 518501, Andhra Pradesh,
India
Keywords: Attack Process Analysis, Internet of Things (IoT) Malware, Machine Learning (ML) Algorithms, Network
Traffic Classification, Semantic‑Level Features.
Abstract: The Internet of Things (IoT) gadgets are extensively used throughout several domains, providing numerous
conveniences to individuals' lives. However, the extensive deployment of IoT devices has made maintaining
these systems against cyber-attacks a primary concern for researchers. IoT devices possess limited computing
capabilities and storage resources, leading to inadequate security defense mechanisms and heightened
vulnerability to malware and device assaults. Current IoT-focused intrusion detection solutions often merely
identify specific malicious attempts or require intricate models and substantial processing resources to achieve
elevated detection accuracy. In this study, we utilize three datasets: BoT-IoT, MedBIoT, and MQTT-IoT-IDS
2020. We implement various algorithms, including Decision Tree, Random Forest, KNN, XGBoost, DNN,
CNN, and advanced ensemble techniques such as Stacking Classifier (DT + RF with LightGBM) and CNN
+ LSTM. Our results demonstrate that the Stacking Classifier achieved the highest performance, with superior
accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score. The Stacking Classifier achieved a high accuracy of 100% in BoT-
IoT and MedBIoT, and 92.3% in MQTT-IoT-IDS 2020, effectively enhancing the robustness and accuracy
of IoT intrusion detection in resource-constrained environments. This method provides a lightweight and
efficient solution to improve security measures for IoT devices.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the network of
billions of devices worldwide that collect and share
data in real time. With the rapid evolution of
technology, the adoption of IoT is gaining
momentum, and more and more devices are
connecting daily. IoT has developed dramatically in
domains such as transportation, health care, industry
and smart city.
Azimjonov, J., & Kim, T. (2024). The
number of total IoT connections worldwide was 12.2
billion active endpoints in 2021, as reported by
Spring 2022. Amidst obstacles such as the COVID-
19 pandemic and a faltering supply chain, the IoT
market continued to develop with researchers
forecasting an 18% increase to 14.4 billion active
connections by 2022. Going forward, loosening
supply chain bottlenecks and an additional
acceleration of adoption may contribute to around
27bn connected IoT devices by 2025 (
Li et al., 2024).
Despite the benefits of the rapid spread of IoT
devices, it raises crucial privacy and security
concerns
Azimjonov, J., & Kim, T. (2024). Increasing
number of Internet of Things (IoT) deployments have
significantly resulted in risks that are associated with
data breaches and cybercrimes, which have
witnessed the loss of personal and corporate
information. In 2021, an Israeli cyber-security
company SAM disclosed more than 900 million IoT
attacks in that year (
Li et al., 2024). These are more
examples of the growing vulnerabilities of IoT
systems facing cyber threats.
IoT devices usually have constrained memory,
computation and communication resources, thus
complex and strong security protection is also hard
to be supported (
Fatima et al., 2024). Numerous
devices pass the un-encrypted network data amongst
devices over the wireless networks, thus attackers can
intercept, read, and analyze communications. Apart
from eavesdropping, attackers also create illicit
traffic to break IoT devices (
Tiwari et al., 2024). Such
654
Bhulakshmi, O., Anusha, M., Somesh, R., Badrinath, S., Gopal, M. M. and Khan, P. T.
Adaptive Machine Learning for Real-Time Intrusion Detection in IoT.
DOI: 10.5220/0013887900004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
654-662
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

malicious behavior may cause device to malfunction,
provide illegal access, or even turning into a zombie
by an adversary which uses the heterogeneity of the
IoT for large scale attack.
A prime example of IoT vulnerabilities was seen
in the 2016 Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS)
attack launched against Dyn, a major service
provider. The attack, facilitated by the Mirai botnet,
exploited weakly secured IoT devices, leading to
significant disruptions and outages across several
services
Otokwala, U., Petrovski, A., & Kalutarage, H.
(2024). Such incidents highlight the urgent need for
robust security measures to protect IoT networks. As
IoT continues to expand, addressing these
vulnerabilities remains a critical area of focus for
researchers and developers alike (
Almotairi, A et al.,
2024)
.
2 RELATED WORK
In their study, (Wardana et al., 2024) proposed a
lightweight, trust-managing, and privacy-preserving
collaborative intrusion detection system (IDS) for IoT
networks. Their system emphasizes collaboration
between nodes to improve detection efficiency while
preserving user privacy. By incorporating trust
management mechanisms, the proposed model
mitigates the impact of malicious nodes, ensuring
robust intrusion detection. The system achieves
lightweight performance through computationally
efficient algorithms and is particularly suited for
resource-constrained IoT environments. This work
contributes significantly to balancing security and
efficiency in distributed IoT networks.
Ramesh Kumar and Sudhakaran focused on
enhancing IoT network security by leveraging feature
selection techniques and the Light Gradient Boosting
Machine (LGBM). Their robust intrusion detection
system optimizes the computational overhead of
feature processing while maintaining high accuracy
in detecting intrusions. The authors utilized dataset
preprocessing methods and LGBM’s capability to
handle large-scale datasets effectively. The results
showed improved performance compared to
conventional machine learning techniques, making
the system a promising solution for securing IoT
networks.
Gowthami and Vigenesh introduced a lightweight
pyramidal U-Net architecture with a tri-level dual
inception-based framework for distributed intrusion
detection in IoT networks. This innovative
framework leverages the pyramidal U-Net’s
hierarchical feature extraction capabilities combined
with dual inception modules for efficient intrusion
detection. The authors emphasized the distributed
nature of their approach, allowing scalability and
adaptability to varying IoT network sizes. Their work
stands out for its advanced architecture, which
achieves superior detection rates with reduced
resource consumption.
Francis et al. proposed a hybrid intrusion
detection approach based on the Message Queuing
Telemetry Transport (MQTT) protocol for industrial
IoT. Their model addresses the unique vulnerabilities
of the MQTT protocol, which is widely used in IoT
communication. The hybrid approach combines
anomaly-based and signature-based detection
methods, ensuring comprehensive protection against
known and emerging threats. The authors validated
their approach using real-world MQTT datasets,
achieving high accuracy and low false-positive rates.
This work is particularly relevant for IoT applications
relying on MQTT.
Vyšniūnas et al. proposed a risk-based system-call
sequence grouping method for detecting malware
intrusions in IoT networks. Their approach analyzes
system call sequences to identify anomalous behavior
indicative of malware. By grouping system calls
based on risk levels, the model enhances the precision
of intrusion detection while reducing computational
complexity. The authors demonstrated the efficacy of
their method using real-world malware datasets,
showcasing its applicability to IoT environments
where traditional signature-based methods may fail.
Musthafa et al. developed a novel intrusion
detection system optimized for IoT by combining
balanced class distribution, feature selection, and
ensemble machine learning techniques. Recognizing
the challenges posed by imbalanced datasets, the
authors applied class balancing techniques to improve
detection accuracy for minority attack types.
Additionally, their feature selection approach reduces
computational overhead, and the ensemble machine
learning model achieves state-of-the-art performance.
This study offers valuable insights into handling data
imbalance in IoT intrusion detection.
Momand et al. introduced ABCNN-IDS, an
attention-based convolutional neural network
designed specifically for intrusion detection in IoT
networks. Their architecture integrates attention
mechanisms to focus on critical features, enhancing
detection accuracy and robustness. The authors
highlighted the model’s ability to handle diverse
attack types while maintaining computational
efficiency. Experimental results demonstrated the
superiority of ABCNN-IDS over traditional CNN-
Adaptive Machine Learning for Real-Time Intrusion Detection in IoT
655

based approaches, making it a promising solution for
advanced IoT security applications.
3 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The proposed system aims to develop a lightweight
and efficient intrusion detection method tailored for
Internet of Things (IoT) devices, addressing their
security vulnerabilities and limited computational
resources. We will implement various machine
learning algorithms, including Decision Tree
(
Almotairi et al., 2024), Random Forest (Wardana, A. A
et al., 2024)
, K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) Ramesh
Kumar, M., & Sudhakaran, P. (2024)
, XGBoost
Gowthami, D., & Vigenesh, M. (2024), Deep Neural
Network (DNN)
Francis, G. T., Souri, A., & İnanç, N.
(2024)
, and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
Vyšniūnas, T., Čeponis, D., Goranin, N., & Čenys, A.
(2024)
. Additionally, we will incorporate advanced
ensemble techniques such as Stacking Classifier,
which combines Decision Tree and Random Forest
with LightGBM, and a hybrid CNN + Long Short-
Term Memory (LSTM) model to enhance detection
accuracy and robustness. The system will utilize
datasets such as BoT-IoT (N. Koroniotis et al., 2019),
MedBIoT (
Guerra-Manzanares et al., 2020), and MQTT-
IoT-IDS 2020 (H. Hindy et al., 2020) for training and
evaluation. By combining multiple algorithms and
ensemble methods, the proposed system seeks to
provide a comprehensive solution for identifying and
mitigating malicious activities in IoT environments
while ensuring minimal resource consumption,
thereby improving overall security measures for IoT
devices.
This architecture in figure 1 aims to detect
intrusions in IoT networks. It starts with data
visualization and label encoding on the BoT-IoT (
N.
Koroniotis et al., 2019)
, MedBIoT (Guerra-Manzanares et
al., 2024)
and MQTT-IoT-IDS 2020 (H. Hindy et al.,
2021)
. dataset. Feature selection is then performed
followed by data processing. The processed data is
split into training and validation sets. Various
machine learning models, including Decision Tree
(
Almotairi et al., 2024) , Random Forest (Wardana, A. A
et al., 2024)
, KNN Ramesh Kumar, M., & Sudhakaran, P.
(2024), XGBoost Gowthami, D., & Vigenesh, M. (2024),
DNN Francis, G. T., Souri, A., & İnanç, N. (2024), CNN
Vyšniūnas, T., Čeponis, D., Goranin, N., & Čenys, A.
(2024).
, and a stacking classifier, are trained and
evaluated based on metrics like accuracy, precision,
recall, and F1-score.
Figure 1: Proposed Architecture.
3.1 Dataset Collection
In this analysis, three datasets are used, such as BoT-
IoT, MedBoTIoT, and MQTT-IoT-IDS 2020,
containing network traffic data with attack labels and
traffic behaviors, specifically for intrusion detection
in IoT environments.
3.1.1 BoT-IoT Dataset
Figure 2: BoT-IoT Dataset.
The dataset in figure 2 utilized is the BoT-IoT dataset
(N. Koroniotis et al., 2019), consisting of 1,000,000
entries and 46 features, capturing diverse network
traffic details. Key features include packet statistics,
byte rates, connection states, and protocol-specific
metrics. Attack labels are categorized as "DoS" with
subcategories TCP, UDP, and HTTP, with respective
counts of 615,800, 382,715, and 1,485. Non-essential
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
656
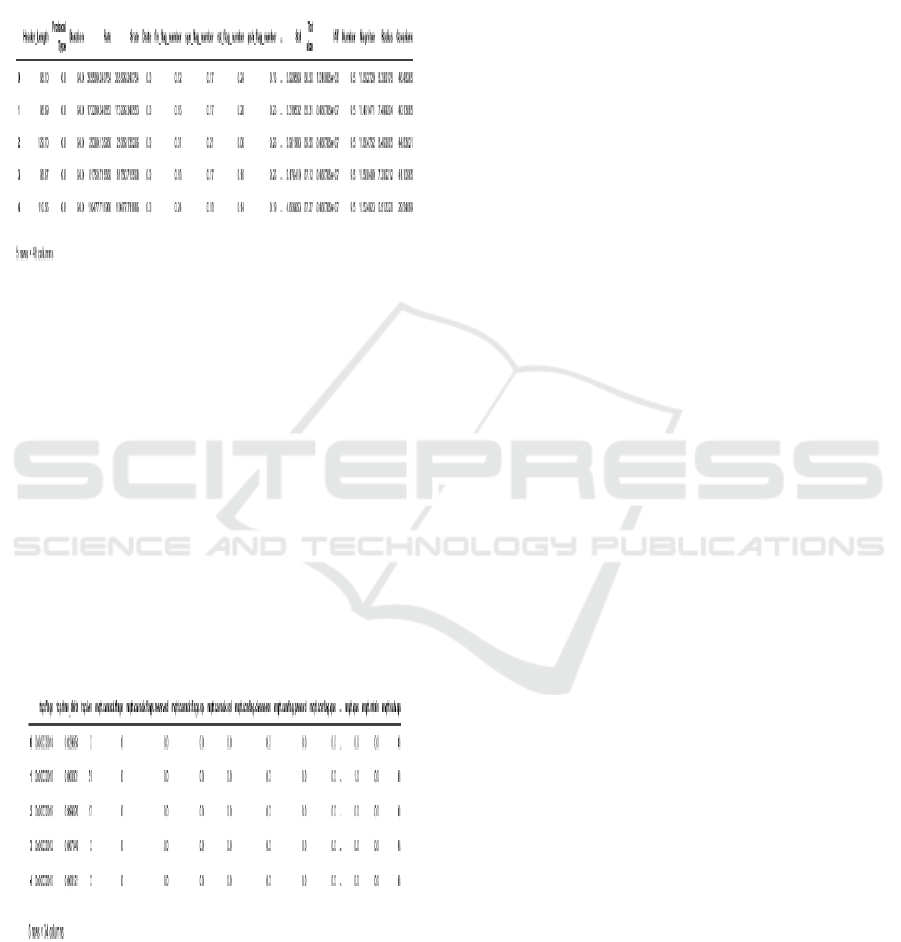
columns, including metadata and categorical attack
labels, were dropped to streamline the dataset for
analysis. Missing values were handled by dropping
rows with null entries, ensuring data consistency.
3.1.2 MedBIoT
Figure 3: MedBoT.
The dataset in figure 3, MedBoTIoT (Guerra-
Manzanares et al., 2020), comprises network traffic data
from multiple CSV files, including *MQTT-DDoS-
Connect Flood*, *MQTT-DoS-Connect Flood*,
*MQTT-Malformed Data*, and *Benign* traffic.
Each file represents specific traffic behavior, labeled
as "DDoS," "DoS," "Malformed," and "Benign,"
respectively, by adding a target column. These
datasets were combined using the `concat()` method
to create a unified dataset for analysis. The data is
tailored for intrusion detection in IoT networks,
focusing on distinguishing between malicious and
benign traffic patterns.
3.1.3 MQTT-IoT-IDS 2020
Figure 4: MQTT-IoT-IDS 2020.
The MQTT-IoT-IDS 2020 (H. Hindy et al., 2021).
dataset contains 99,290 entries of network traffic
data, focusing on MQTT-based IoT communication
(figure 4). It includes features such as message
lengths, quality of service, and connection flags,
providing insights into communication patterns. The
dataset categorizes traffic into six labels: legitimate,
DoS, brute force, malformed, slowite, and flood,
enabling comprehensive analysis of both normal and
malicious activities. It is structured with 28 columns,
excluding unnecessary fields, and serves as a resource
for intrusion detection and anomaly detection
research in IoT networks.
3.2 Pre-Processing
We used pre-processing steps like data cleaning, label
encoding, feature selection, and data visualization to
prepare the dataset for analysis, ensuring accuracy,
reducing complexity, and enhancing model
performance for predictions.
Data Processing: Data processing involves
preparing raw data for analysis by cleaning,
transforming, and organizing it to ensure accuracy
and reliability. This includes handling missing values,
removing irrelevant features, encoding categorical
variables into numerical formats, and scaling data for
uniformity. Feature selection techniques are applied
to identify the most important variables, reducing
complexity and improving model performance. Data
processing ensures the dataset is structured,
consistent, and optimized for machine learning
models, enabling effective pattern recognition,
prediction, and decision-making during analysis.
Data Visualization: The dataset's subcategory
distribution is visualized using a bar chart with a
vibrant color palette, providing a clear comparison of
data points across different classes. This highlights
the frequency of benign and malignant nodules for
better understanding of class imbalances.
Additionally, a heatmap is used to display the
correlation between features, offering a detailed view
of relationships within the dataset. The colorful
representation enhances the interpretability of feature
interactions, aiding in identifying significant
attributes relevant to the analysis and decision-
making process.
Label Encoding: Label encoding is applied to
transform categorical values into numerical ones,
ensuring the dataset is suitable for machine learning
algorithms. By converting subcategory labels into
numeric representations, the process simplifies the
data while retaining its meaningful structure. This
transformation assigns unique integers to each
category, allowing models to process and analyze the
data more effectively. Label encoding is particularly
useful for handling non-numeric columns, making
Adaptive Machine Learning for Real-Time Intrusion Detection in IoT
657

them compatible with computational methods while
preserving their inherent distinctions for accurate
analysis and prediction.
Feature Selection: Feature selection is performed to
identify and retain the most relevant variables that
significantly influence the target outcome, improving
model performance and reducing complexity. By
applying a percentile-based selection method, the
process evaluates the mutual information between
features and the target variable, ensuring only the top
25% of impactful features are retained. This approach
enhances the dataset by focusing on critical
predictors, eliminating irrelevant or redundant
variables, and enabling the model to achieve better
accuracy, efficiency, and interpretability in its
analysis and predictions.
3.3 Training and Testing
The dataset is divided into two parts: one for training
and another for testing, ensuring an effective
evaluation of the model's performance. The training
set, which comprises 80% of the data, is used to teach
the model by identifying patterns and relationships
between input features and the target variable. The
testing set, containing 20% of the data, evaluates how
well the trained model can generalize its predictions
on unseen data. This balanced split ensures accuracy
and reliability in assessing model performance.
3.4 Algorithms
A Decision Tree classifies incoming data as benign
or malicious by creating a series of rules based on
feature values. Its interpretability makes it effective
for identifying threats and understanding decision-
making processes in IoT environments (
Almotairi et
al., 2024).
Random Forest constructs multiple decision trees
and aggregates their predictions for classification. It
enhances accuracy, reduces overfitting, and handles
diverse IoT data, detecting complex attack patterns
with high performance and generalization capabilities
(
Wardana, A. A et al., 2024).
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) classifies data points
based on the majority class of their nearest neighbors.
It detects potential threats by comparing features of
incoming data with labeled examples, adapting well
to changes in data distribution in real-time
environments
Ramesh Kumar, M., & Sudhakaran, P.
(2024).
XGBoost is a gradient boosting algorithm that
improves speed and performance. It handles large
datasets and complex feature interactions,
minimizing loss functions and preventing overfitting,
ensuring robust and adaptive detection of evolving
cyber threats in IoT systems
Gowthami, D., & Vigenesh,
M. (2024).
Deep Neural Network (DNN) processes high-
dimensional data to learn complex patterns. It
enhances detection of sophisticated attacks,
improving accuracy in identifying malicious
activities by capturing intricate relationships between
features and handling diverse data types effectively
Francis, G. T., Souri, A., & İnanç, N. (2024).
Convolutional Neural Network (CNNs) analyze
structured grid data, such as images or signals. They
automatically extract relevant features, improving
anomaly detection and real-time threat identification,
making them highly effective for detecting attacks in
IoT environments through pattern recognition
Vyšniūnas, T., Čeponis, D., Goranin, N., & Čenys, A.
(2024).
Stacking Classifier (DT + RF with LightGBM):
The Stacking Classifier integrates Decision Trees,
Random Forest, and LightGBM to improve
prediction accuracy. By combining strengths from
each model, it reduces false positives and negatives,
creating a robust system for threat identification in
IoT devices.
4 RESULTS & DISCUSSION
Accuracy: The true accuracy of a test is the
proportion of the test to be able to correctly identify
patient and healthy subjects. When we want to
estimate the accuracy of a test, we need to compute
the ratio of true positive and true negative cases over
all tested cases. This can be expressed
mathematically as:
Accuracy
TPTN
TPFPTNFN
(1)
Precision: Precision measures the proportion of true
positives among the samples identified as positive.
Therefore, the precision formula is expressed as:
Precision
True Positive
True Positive False Positive
(2)
Recall: Recall is a machine learning metric that
calculates the model’s capability to find all relevant
objects of a class. It represents how successful the
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
658
classification was in predicting the positive class, in
relation to the actual positive instances.
Recall
TP
TP FN
(3)
F1-Score: F1 score is an ML evaluation metric which
gives an idea about how good your model is. It is a
combination of precision and recall for a model.
Accuracy measures how many times the model made
correct predictions over all predictions made.
𝐹1 𝑆𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒 2 ∗
X
∗ 100 (4)
In Table (1, 2 and 3) the Stacking Classifier
consistently achieved the highest accuracy,
outperforming all models across all datasets and
metrics.
Table 1: Performance Evaluation Table – BoT-IoT.
ML Model Accuracy Precision Recall F1_score
KNN 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000
DecisionTree 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000
RandomForest 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000
XGBoost 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000
Extension 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000
DNN 0.622 0.073 0.270 0.115
CNN 0.993 0.995 0.993 0.994
CNN+LSTM 0.616 1.000 0.616 0.762
Table 2: Performance Evaluation Table – MedBIoT.
ML Model Accuracy Precision Recall F1_score
KNN 0.991 0.994 0.991 0.992
DecisionTree 0.997 0.997 0.997 0.997
RandomForest 0.998 0.998 0.998 0.998
XGBoost 0.998 0.998 0.998 0.998
Extension 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000
DNN 0.504 0.198 0.445 0.274
CNN 0.975 0.992 0.975 0.983
CNN+LSTM 0.923 0.979 0.923 0.949
Table 3: Performance Evaluation Table – UNSW-NB15 – With SMOTEENN.
ML Model Accuracy Precision Recall F1_score
KNN 0.901 0.914 0.901 0.906
Decision Tree 0.907 0.922 0.907 0.912
Random Forest 0.907 0.922 0.907 0.913
XGBoost 0.908 0.925 0.908 0.914
Extension 0.923 0.934 0.923 0.926
DNN 0.393 0.002 0.043 0.004
CNN 0.793 0.895 0.793 0.821
CNN+LSTM 0.797 0.909 0.797 0.826
Adaptive Machine Learning for Real-Time Intrusion Detection in IoT
659
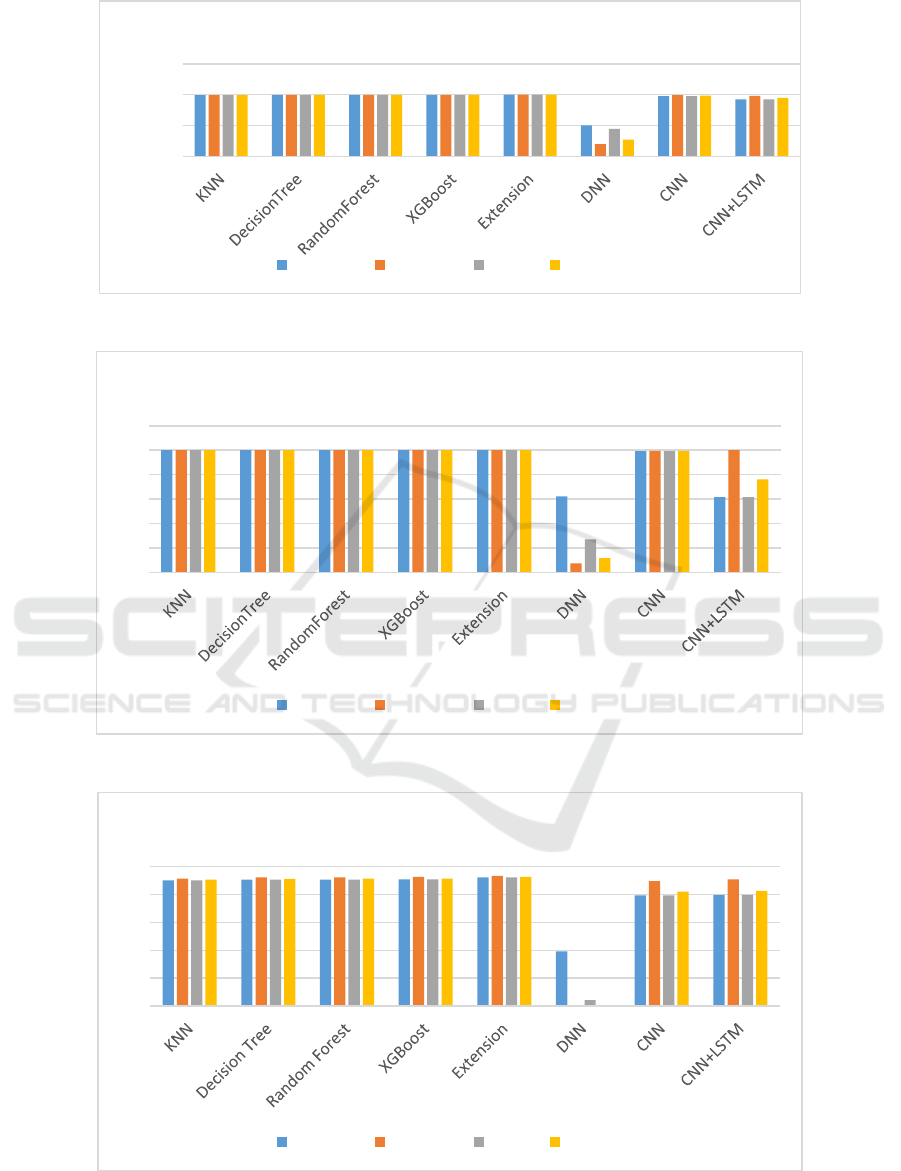
Figure 5: Comparison Graph – NSL-KDD – Without SMOTEENN.
Figure 6: Comparison Graph – BoT-IoT.
Figure 7: Comparison Graph – MQTT-IoT-IDS 2020.
0
0.5
1
1.5
Chart Title
Accuracy Precision Recall F1_score
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
Chart Title
Accuracy Precision Recall F1_score
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Comparison Graph
Accuracy Precision Recall F1_score
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
660

In figure (5, 6 & 7) accuracy is represented in light
blue, precision in orange, recall in grey and F1 Score
in yellow. The Graphs illustrate the Stacking
Classifier's superior performance across all metrics
and datasets, consistently achieving the highest
accuracy, demonstrating its robustness and
effectiveness in intrusion detection.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, this study highlights the critical
importance of robust and efficient intrusion detection
systems (IDS) for securing Internet of Things (IoT)
devices, which are increasingly vulnerable due to
their limited computational and storage resources.
The research explores a variety of machine learning
algorithms, including Decision Tree (
Almotairi et al.,
2024), Random Forest (Wardana, A. A et al., 2024),
KNN Ramesh Kumar, M., & Sudhakaran, P. (2024).,
XGBoost
Gowthami, D., & Vigenesh, M. (2024), DNN
Francis, G. T., Souri, A., & İnanç, N. (2024), CNN
Vyšniūnas, T., Čeponis, D., Goranin, N., & Čenys, A.
(2024).
, and advanced ensemble methods like
Stacking Classifier (DT + RF with LightGBM) and
CNN + LSTM, using datasets from BoT-IoT (
N.
Koroniotis et al., 2019), MedBIoT (Guerra-Manzanares et
al., 2020), and MQTT-IoT-IDS 2020 (H. Hindy et al.,
2021)
. The results reveal that the Stacking Classifier,
combining the strengths of multiple models,
outperforms individual classifiers, achieving
remarkable detection performance. It achieved 100%
accuracy on the BoT-IoT and MedBIoT datasets, and
92.3% accuracy on MQTT-IoT-IDS 2020. These
findings demonstrate that the Stacking Classifier
provides a highly effective, lightweight, and efficient
solution for IoT intrusion detection, significantly
enhancing security in resource-constrained
environments. This method addresses the challenges
posed by IoT devices' limitations while ensuring high
detection accuracy, thereby making a substantial
contribution to improving IoT security in practical
applications.
The future scope of this study includes exploring
more advanced ensemble techniques and hybrid
models to further enhance detection accuracy and
reduce computational overhead. Additionally, the
integration of real-time detection systems,
incorporating adaptive learning algorithms, can
improve the responsiveness to emerging threats.
Future research could also focus on incorporating
anomaly detection and federated learning to address
privacy concerns, enabling scalable and robust
security solutions for diverse IoT environments.
REFERENCES
A. Guerra-Manzanares, J. Medina-Galindo, H. Bahsi, and
S. Nõmm, “MedBIoT: generation of an IoT botnet
dataset in a medium-sized IoT network,” in Proc. 6th
Int. Conf. Inf. Syst. Security Privacy, 2020, pp. 207–
218.
Almotairi, A., Atawneh, S., Khashan, O. A., & Khafajah,
N. M. (2024). Enhancing intrusion detection in IoT
networks using machine learning-based feature
selection and ensemble models. Systems Science &
Control Engineering, 12(1), 2321381.
Azimjonov, J., & Kim, T. (2024). Designing accurate
lightweight intrusion detection systems for IoT
networks using fine-tuned linear SVM and feature
selectors. Computers & Security, 137, 103598.
Azimjonov, J., & Kim, T. (2024). Stochastic gradient
descent classifier-based lightweight intrusion detection
systems using the efficient feature subsets of datasets.
Expert Systems with Applications, 237, 121493.
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi, and G. Vijaya Bhaskar. "Apriori vs
Genetic algorithms for Identifying Frequent Item Sets."
International journal of Innovative Research &
Development 3.6 (2014): 249-254.
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi. "Machine Learning Based
Predictive Model for Data Fusion Based Intruder Alert
System." journal of algebraic statistics 13.2 (2022):
2477-2483.
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi, et al. "Identification of traffic sign
boards and voice assistance system for driving." AIP
Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028. No. 1. AIP
Publishing, 2024.
Devi, M. Sharmila, et al. "Machine Learning Based
Classification and Clustering Analysis of Efficiency of
Exercise against Covid-19 Infection." Journal of
Algebraic Statistics 13.3 (2022): 112-117.
Devi, M. Sharmila, et al. "Extracting and Analyzing
Features in Natural Language Processing for Deep
Learning with English Language." Journal of Research
Publication and Reviews 4.4 (2023): 497-502.
Fatima, M., Rehman, O., Ali, S., & Niazi, M. F. (2024).
ELIDS: Ensemble Feature Selection for Lightweight
IDS against DDoS Attacks in Resource-Constrained
IoT Environment. Future Generation Computer
Systems, 159, 172-187.
Francis, G. T., Souri, A., & İnanç, N. (2024). A hybrid
intrusion detection approach based on message queuing
telemetry transport (MQTT) protocol in industrial
internet of things. Transactions on Emerging
Telecommunications Technologies, 35(9), e5030.
Gowthami, D., & Vigenesh, M. (2024). Distributed and
Lightweight Intrusion Detection for IoT: A Lightweight
Pyramidal U-Net with Tri-Level Dual Inception-Based
Framework. In the Convergence of Self-Sustaining
Systems with AI and IoT (pp. 154-173). IGI Global.
H. Hindy, E. Bayne, M. Bures, R. Atkinson, C. Tachtatzis,
and X. Bellekens, “Machine learning based IoT
intrusion detection system: An MQTT case study
(MQTT-IoT-IDS2020 dataset),” in Proc. 12th Int.
Netw. Conf. Sel. Papers, 2021, pp. 73–84.
Adaptive Machine Learning for Real-Time Intrusion Detection in IoT
661

Li, J., Othman, M. S., Chen, H., & Yusuf, L. M. (2024).
Optimizing IoT intrusion detection system: feature
selection versus feature extraction in machine learning.
Journal of Big Data, 11(1), 36.
Li, J., Chen, H., Shahizan, M. O., & Yusuf, L. M. (2024).
Enhancing IoT Security: A Comparative Study of
Feature Reduction Techniques for Intrusion Detection
System. Intelligent Systems with Applications, 200407.
Mahammad, Farooq Sunar, Karthik Balasubramanian, and
T. Sudhakar Babu. "A comprehensive research on
video imaging techniques." All Open Access, Bronze
(2019).
Mahammad, Farooq Sunar, and V. Madhu Viswanatham.
"Performance analysis of data compression algorithms
for heterogeneous architecture through parallel
approach." The Journal of Supercomputing 76.4
(2020): 2275-2288.
Mahammad, Farooq Sunar, et al. "Key distribution scheme
for preventing key reinstallation attack in wireless
networks." AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028.
No. 1. AIP Publishing, 2024.
Mandalapu, Sharmila Devi, et al. "Rainfall prediction using
machine learning." AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol.
3028. No. 1. AIP Publishing, 2024.
Momand, A., Jan, S. U., & Ramzan, N. (2024). ABCNN-
IDS: attention-based convolutional neural network for
intrusion detection in IoT networks. Wireless Personal
Communications, 136(4), 1981-2003.
Mr.M.Amareswara Kumar, "Baby care warning system
based on IoT and GSM to prevent leaving a child in a
parked car" in International Conference on Emerging
Trends in Electronics and Communication Engineering
- 2023, API Proceedings July-2024.
Mr.M.Amareswara Kumar, Effective Feature Engineering
Technique For Heart Disease Prediction With Machine
Learning" in International Journal of Engineering &
Science Research, Volume 14, Issue 2, April-2024 with
ISSN 2277-2685.
Musthafa, M. B., Huda, S., Kodera, Y., Ali, M. A., Araki,
S., Mwaura, J., & Nogami, Y. (2024). Optimizing iot
intrusion detection using balanced class distribution,
feature selection, and ensemble machine learning
techniques. Sensors, 24(13), 4293.
N. Koroniotis, N. Moustafa, E. Sitnikova, and B. Turnbull,
“Towards the development of realistic botnet dataset in
the Internet of Things for network forensic analytics:
Bot-IoT dataset,” Future Gener. Comput. Syst., vol.
100, pp. 779–796, Nov. 2019. [Online]. Available:
https:// www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0
167739X18327687
Otokwala, U., Petrovski, A., & Kalutarage, H. (2024).
Optimized common features selection and deep-
autoencoder (OCFSDA) for lightweight intrusion
detection in Internet of things. International Journal of
Information Security, 1-23.
Paradesi Subba Rao, "Detecting malicious Twitter bots
using machine learning" AIP Conf. Proc. 3028, 020073
(2024), https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0212693.
Paradesi Subba Rao, "Morphed Image Detection using
Structural Similarity Index Measure"M6 Volume 48
Issue 4 (December 2024), https://powertechjournal.C
m.
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al. "Incorporating Deep Learning
Techniques to Estimate the Damage of Cars During the
Accidents" AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028.
No. 1. AIP Publishing, 2024.
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al "Cloud Computing Network
in Remote Sensing-Based Climate Detection.
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al. "Machine Learning Based
Predictive Model for Closed Loop Air.
Ramesh Kumar, M., & Sudhakaran, P. (2024). Securing IoT
networks: A robust intrusion detection system
leveraging feature selection and LGBM. Peer-to-Peer
Networking and Applications, 1-23.
Suman, Jami Venkata, et al. "Leveraging natural language
processing in conversational Al agents to improve
healthcare security." Conversational Artificial
Intelligence (2024): 699-711.
Sunar, Mahammad Farooq, and V. Madhu Viswanatham.
"A fast approach to encrypt and decrypt of video
streams for secure channel transmission." World
Review of Science, Technology and Sustainable
Development 14.1 (2018): 11-28.
Tiwari, R. S., Lakshmi, D., Das, T. K., Tripathy, A. K., &
Li, K. C. (2024). A lightweight optimized intrusion
detection system using machine learning for edge-
based IIoT security. Telecommunication Systems, 1-
20.
Vyšniūnas, T., Čeponis, D., Goranin, N., & Čenys, A.
(2024). Risk-Based System-Call Sequence Grouping
Method for Malware Intrusion Detection. Electronics,
13(1), 206.
Wardana, A. A., Kołaczek, G., & Sukarno, P. (2024).
Lightweight, Trust-Managing, and Privacy-Preserving
Collaborative Intrusion Detection for Internet of
Things. Applied Sciences, 14(10), 4109.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
662
