
File Data Security Using Elliptic Curve Cryptography
K. Venkatesh, Swaroopa Bhupalam, Rohini Bheemanapalli,
Suvarchala Bhupalam and Yugandhar Kodigi
Department of CSE (Data Science), Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology Anantapur‑515001, Andhra Pradesh,
India
Keywords: Encryption, Data Security, Symmetric Encryption, Quantum Threats.
Abstract: By encrypting the data, private information can be sent through insecure channels without loss of it or
alterations by the other participants. Many algorithms are designed for users data security. AES is fast
symmetric encryption, ECC is efficient asymmetric encryption and Quantum ECC finds an accurate way to
thwart emerging quantum attacks. Due to quantum computing a safe, effective way to secure the files and
with the security of the data could be established.
1 INTRODUCTION
We care most about file data security in recent years.
Actually, Cloud offers numerous security
algorithms, flexibility and accessibility to the files’
data. Some sensitive information is transferred via
cloud/internet, but thus there can be cyberattacks.
Classical cryptographic algorithms, such as RSA,
AES, etc., are instrumental in securing data-in-
motion and data-at-rest.
However, RSA and AES are symmetric
algorithms which means it has to have same key for
encryption and for decryption. Just as an added bit of
information, yes symmetric key management is
helped by symmetric encryption algorithms like AES.
Goodman (R. Lu, X. Yuan, and X. Lin et al., 2021)
states that in cloud data, massive data are stored in
the distributed system. Of more interest to us is the
necessity of new cryptosystems that are secure, yet
still scalable. Furthermore, As ECC with Quantum
grows the possibility to break aged encryption
systems is real. The second bit, due to the fact that it
is able to be in all states at the same time, is the basis
for giving quantum computers a much higher
processing capacity than traditional ones. The use of
ECC with quantum gives strong security on data and
also the time of encryption and decryption is better
than both RSA and AES. We will describe how
encryption based on quantum computing offers a
great potential to fix these problems by introducing
better security protocols.
QKD is one of the protocols that securely transfers
the keys by utilizing the nature of qunatum. With
quantum encryption, any interference with quantum-
encrypted data can interfere with its transmission, and
thus signalling its transmission status is more easily
detected. Long-term security is guaranteed with the
quantum algorithms against these threats. There is a
brighter side of the use of data encryption through
quantum mechanism. Now-a-days, using cloud
providers data shall be stored in encrypted form.
Faster encryption methods could be conceivable from
quantum systems according to quantum mechanism
(Grover’s method for faster search and Shor’s method
for factoring large numbers) that would be more
power-efficient and resource-efficient compared to
traditional encryption techniques. These attributes are
particularly useful in cloud scenarios, where
computing resources are usually spread across several
centers and the network traffic is large (J. Shen, J.
Niu, J. Cao, and Y. Mei et al., 2020). Quantum
computing has also impacted applications ranging
from cloud environments to network protocols since
quantum computing also provides an opportunity to
revisit the entire architecture of data protection
systems (Chhabra and S. Arora et al., 2024). Rather
than a singular focus on application-level data at
rest/on the move encryption, Quantum cryptography
may drive a new holistic approach to security that
spans from continually and holistically protecting
data from processing to storage to transmission etc.
Furthermore, using ECC for quantum encryption
can detect new threats like cyber or AI-driven attacks
648
Venkatesh, K., Bhupalam, S., Bheemanapalli, R., Bhupalam, S. and Kodigi, Y.
File Data Security Using Elliptic Curve Cryptography.
DOI: 10.5220/0013887800004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
648-653
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

that can rapidly break an encryption algorithm. A
quantum encryption/AI protection system combo
could be the next generation of security measures
that are more responsive to dynamic threats as the
capabilities of AI also continue to advance. Quantum
computer-oriented encryption and ECC in cloud
environments 103 This may also standardize the
industry-wide usage of QSC. (X. Kong, J. Wang, and
Q. Ni et al., 2022)
As ever more sophisticated digital networks link
the world, quantum computing is needed to protect
sensitive information, and this research will help
bring this technology nearer to the mainstream
through cloud-based service. As quantum computing
evolves, this has already far-reaching consequences
for cybersecurity in the cloud, and now lays the
groundwork for the creation of secure, efficient data
protection mechanisms vital for preserving privacy
and trust in a digital world. ECC with quantum
mechanism designed for cloud environment remove
more secure principle even image encryption and
decryption take less time than traditional method. It
logs the file request information in the user data
logins. Additionally, presents the decrypted data to
the end users. It’s also one of the best benefits to the
other as who uses it can easily track their details. This
is the most empowering use for us.
1.1 Purpose of the Study
In particular, this study aims to develop quantum
computing-based ECC and to compare it with AES,
for overcoming the limitations of conventional
encryption technology, improving the efficiency of
encryption technology for large-scale data, and
establish an effective response system for changes in
cyber threats by supplementing the limitations of
traditional encryption technologies in terms of
scalability and computational efficiency. The
development of ECC with quantum and the
corresponding comparison with AES to mitigate the
limitations of classical cryptographic solutions in
terms of scalability and computational overhead,
enhance the performance of large data encryption,
and guarantee the resilience of cyber security against
new type of attacks will be an outcome of the
research.
1.2 Problem Statement
Conventional file-based encryption schemes in
(EB)DS are challenged by limited scalability,
computational efficiency issues, and non-quantum
resistance. AES has a high-speed encryption but
dedicate to the key management problem, while ECC
has a smaller key size with a strong security service.
But new quantum breakthroughs are challenging
traditional encryption systems. In this paper it has
proposed a hybrid Encryption of files replacing AES
with ECC (Quantum) with Quantum for files security.
The encryption and decryption times are compared,
and the graph-based performance analysis is provided
to maximize security and efficiency. The model
offers confidentiality, integrity, and quantum- safe
encryption to provide secure scalable cloud data
protection.
2 RELATED WORKS
Proposed method the quantum encryption scheme
that presented in (PristiQ 2024) has been designed of
the cloud data based on the multi-client universal
circuit for full-blind computationally secure query.
Using the proposed technique, the cryptographic
computation is outsourced to the key center by a large
number of customers who possess restricted quantum
capabilities, in order to contract with a trusted key
center for key generation and data encryption, and
then upload the encrypted data to a data center.
Fusing Grover’s search algorithm, the scheme
provides a searchable and query-able ciphertext, and
retains its quantum resistance. The authors also give
a detailed explicit example for searching on an
encrypted 2-qubit data and perform a full security
analysis which show that the scheme is secure against
external attack and internal attack.
Paper (M. S. Ali et al., 2021) explores various
paradigm of cloud computing, blockchain and
quantum computing, the symbiotic association
among cloud computing, blockchain and quantum
computing etc and alleviate the current constrains by
symbiotic solution. The framework protects data from
quantum attacks by applying lattice-based
cryptographic techniques and quantum-safe
cryptographic protocols, like QKD, to secure data
against quantum attacks. Enterprises are primarily
focusing on securing their data from the quantum
attacks and gain maximum advantage of overall
system efficiency, quantum key generation rate, and
encryption and decryption operations. It is useful
mostly in security for data in files also as to security
for quantum threats.
The paper titled "PristiQ: This preprint published
by arXiv in 2024 introduces "PristiQ" which
represents a Co-Design Framework devoted to
safeguarding quantum learning security in cloud
environments. The research presents "PristiQ" as a
File Data Security Using Elliptic Curve Cryptography
649

co-design framework which addresses data security
requirements for quantum machine learning (QML)
applications within quantum-as-a-service (QaaS)
systems. The authors include an encryption subcircuit
with additional safe qubits connected to a user-
specified security key since they are aware of the risks
of data leakage while utilizing cloud-based quantum
computers to run QML models. This approach
enhances data security by ensuring that the quantum
data remains encrypted during computation. The
study introduces an automated search system which
optimizes model execution on quantum data while it
remains encrypted. Experimental evidence
demonstrates PristiQ delivers secure quantum data
protection along with QML application performance
maintenance through system testing on IBM quantum
hardware and simulation models.
Article (V. S. Pendyala et al., 2021) shows the
necessity of safeguarding proprietary and sensitive
quantum code in cloud-based quantum computing
systems against hostile or unreliable actors is
discussed in this paper. In order to stop sensitive data
from leaking over the cloud, the authors suggest
"SPYCE," a system that obfuscates quantum code and
output.
Article (IBM 2024) IBM's article discusses the
emerging cybersecurity challenges posed by quantum
computing, particularly concerning data. IBM
advocates for the adoption of quantum-safe
cryptographic algorithms to mitigate these risks,
highlighting the importance of proactive measures to
secure data against future quantum attacks.
3 METHODOLOGY
The methodology introduces a quantum computing
algorithm to encrypt cloud data, enhancing security
and efficiency. This approach enables rapid
encryption and decryption processes, reducing
computational overhead compared to classical
methods. The system enhances scalability using
quantum key distribution for secure key management
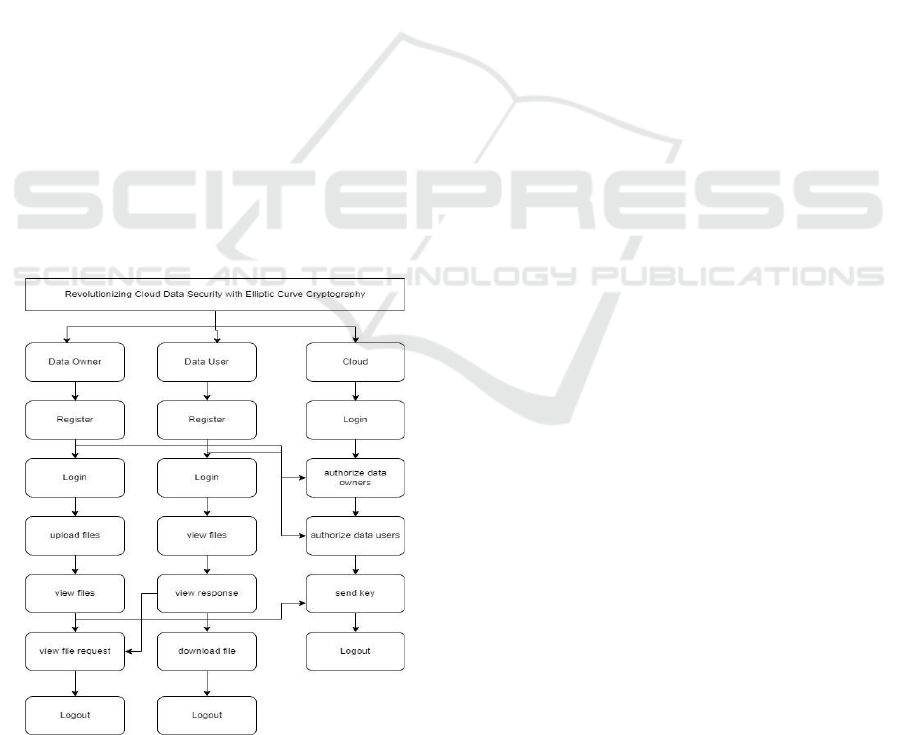
in cloud environments. Figure 1 shows the
File Data
Security with Elliptic Curve Cryptography flowchart.
3.1 Implementation Modules
In our Advancing files Data Protection with
Cryptographic Algorithms, we have performed the
implementation of certain modules.
3.1.1 Data Owner
Register: This option allows the data owner to sign
up on the website by providing his/her credentials.
Login: It enables the data owner to access the
website using the credentials after receiving
authorization from the cloud administrator.
Upload Files: This allows the data owner to upload
the files into the cloud and these uploaded files can be
viewed by the data user and can send file requests to
the owner to download the files.
View Files: It allows data user to view files that are
uploaded by the data owner in that website and can
also send the file request to the data owner.
View file Requests: It enables the data owner to see
requests from data users and decrypt files as needed.
3.1.2 Data User
Register: This option allows the data user to
create an account on the website by providing
his/her credentials.
Login: It enables the data owner to access the
website using the credentials after receiving
authorization from the cloud administrator.
View Files: It allows data user to view files that
are uploaded by the data owner in that website
and can also send the file request to the data
owner.
View Responses: It allows the data user to track
the status of the file request that was send to the
data owner.
Download Files: Once we get the acceptance of
file request from the data owner then the data
user can download the file and read it.
3.1.3 Cloud Administrator
Authorize Data Owners: It enables the
administrator to review and authorize or deauthorize
registered data owners.
Authorize Data Users: This permits the
administrator to review and authorize or deauthorize
registered data users.
Send Keys: The key was securely shared to the
registered data user for decrypting the data.
3.2 Architecture & Performance
3.2.1 Quantum-Based Encryption in ECC
Algorithm
As part of the encryption and decryption processes,
this quantum-based encryption method puts to use the
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
650
special capabilities of quantum computing in order to
produce cryptographic keys as well as carry out
encryption and decryption procedures.
3.2.2 Quantum Key Generation
The primary idea behind this algorithm is that it is
based on the use of quantum circuits to create a
random cryptographic key. There is a key operation
in quantum computing known as the Hadamard gate,
which is essentially a superposition of states for the
qubit, resulting in a more randomized outcome.
Putting the Hadamard gates behind the qubits, the
circuit measures their states after they have been
applied to the qubits There is an inherent randomness
in quantum systems that ensures the key is
unpredictable and very difficult for any adversary to
replicate without access to the quantum system itself
in order to obtain the key.
3.2.3 Advantages of Quantum Key
Generation in ECC
One of the key strengths of this algorithm lies in the
quantum-generated key. Traditional random number
generators (RNGs) rely on algorithms and can, in
theory, be predicted if an attacker has enough
computational power.
3.3 Text to Binary Conversion
Figure 1: Flow chart for File Data Security with Elliptic
Curve Cryptography.
The text_to_binary function converts the text to be
encrypted into a binary representation. Encrypting
and decrypting binary data is only possible with
XOR-based encryption and decryption.
def text_to_binary_v3(text):
return ' ‘. join (format (byte, '08b') for byte in
text.encode('utf-8'))
3.4 Encryption
The encrypt_text function in the algorithm converts a
bitwise XOR (exclusive OR) operation between the
binary representation of the text and the
quantum-generated key. XOR encryption is a simple
and effective method for changing the data. In this
case, the binary text is encrypted by iterating over
each bit and performing XOR with the corresponding
bit. If the key is shorter than the text, it wraps around
and repeats the key. Encrypted code is given below:
encrypted_data = ''.join(str(int(b) ^ int(k)) for b, k
in zip(binary_text, key)
This results in an encrypted binary string, which
is the ciphertext.
3.5 Decryption
The decrypt_text function is reverse mechanism of
encryption process by applying XOR operation again.
The decrypted is given below:
decrypted_binary = ''.join(str(int(b) ^ int(k)) for b, k
in zip(encrypted_data, quantum_key))
XOR is a symmetric operation, meaning that the
same key used for encryption can also decrypt the
data. The encrypted binary string is XORed with the
same key to recover the original binary text, which is
then converted back to the original text using the
binary_to_text function.
3.6 AES vs ECC-Quantum
File data security in cloud relies on encryption
algorithms to ensure data confidentiality, integrity,
and authentication. AES is widely used symmetric
encryption method is for speed and efficiency. Data
is encrypted using a single key that can be used for
both methods, making it ideal for fast processing of
data. However, AES requires complex key
management and is vulnerable to brute-force attacks
as computing power increases.
Unlike AES, ECC-Quantum ensures long-term
security by making cryptographic attacks infeasible
even with quantum advancements. This paper
compares AES and ECC-Quantum by analyzing their
encryption and decryption times and presenting a
File Data Security Using Elliptic Curve Cryptography
651

graph-based performance evaluation. While AES
remains efficient for short-term encryption, ECC-
Quantum provides a future-proof solution against
quantum threats. By integrating both techniques,
cloud security can achieve optimal performance and
resilience, balancing speed, scalability, and quantum
resistance in modern encryption systems.
4 RESULTS AND EVALUATION
The results for the files Data Protection with ECC of
Quantum mechanism:
Figure 2: Graph Performance for AES Algorithm.
In Figure 2, AES provides the fast and efficient
symmetric encryption but also faces some challenges
in key management and quantum vulnerabilities,
making it suitable for short-term security. As it also
includes a single key for encryption and decryption.
Figure 3: Graph Performance for ECC-Quantum
Algorithm.
In figure 3, ECC with Quantum Cryptography
provides the secure encryption, faster decryption, and
reduced computational overhead. As it uses two keys
for the encryption and decryption process.
5 CONCLUSIONS
File data security is used to address the emerging
threats, computational efficiency, and scalability
challenges. Traditional encryption methods like AES
and ECC provide strong security, but they face
limitations in key management and resistance to
quantum attacks. AES is widely used for fast and
efficient symmetric encryption, making it ideal for
real-time data processing but vulnerable to brute-
force attacks as computing power increases. On the
other hand, ECC offers the strong asymmetric
encryption with smaller key sizes, reducing
computational overhead while maintaining high
security. However, ECC alone is not sufficient to
quantum threats. To overcome those challenges, ECC
with Quantum Cryptography provides the quantum-
resistant techniques, along with long-term security
against advanced attacks. The combination of AES,
ECC, and ECC with Quantum optimizes the
encryption and decryption times, high security and
performance in cloud environments. Graph-based
analysis shows that while AES provides fast
encryption, ECC- Quantum helps in the future-proof
data protection with significantly improved
decryption efficiency. The study shows a hybrid
encryption model which shows the AES for speed,
ECC for security, and Quantum Cryptography for
quantum attacks provides the most efficient cloud
security framework. As quantum computing
advances, integrating quantum-resistant encryption
becomes essential for securing the cloud-based
applications and protecting sensitive data in the long
run.
REFERENCES
A. Chhabra and S. Arora “An Elliptic Curve Cryptography
Based Encryption Scheme for Securing the Cloud
Against Eavesdropping Attacks” by IEEE 3rd
International Conference on Collaboration and Internet
Computing, 2024
B. Liu and X. Li, "Towards Secure Cloud Storage: A
Survey of Cryptographic Techniques", in IEEE 3rd
International Conference on Computing,
Communications and Networking, 2020, pp. 305-310.
D. R. S. C. R. P. Kumar, "Cloud Data Security and Privacy
Using Multi-Level Encryption Mechanism", Journal of
Cloud Computing: Advances, Systems and
Applications, vol. 8, pp. 110-118, 2020.
Dong Pan; Gui-Lu Long; Liuguo Yin; Yu-Bo Sheng; Dong
Ruan; Soon Xin Ng; Jianhua Lu; Lajos Hanzo,” The
Evolution of Quantum Secure Direct Communication:
On the Road to the Qinternet” Vol. 26 ,202
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
652

G. Wang and Z. Zong, "A Secure Data Sharing and Privacy-
Preserving Scheme Based on Blockchain in Cloud
Computing", Journal of Cloud Computing: Advances,
Systems and Applications, vol. 8, pp. 79-94, 2021.
H. Zhang, C. Wang, and F. L. Lewis, "An Efficient and
Secure Data Sharing Scheme in Cloud Computing",
International Journal of Communication Systems, vol.
33, no. 3, pp. e4464, 2020.
IBM, "Quantum-safe cryptography: How it affects your
information in the cloud," IBM Think Blog, 2024.
J. Shen, J. Niu, J. Cao, and Y. Mei, "A Survey on Cloud
Security Issues and Techniques: Cryptographic and
Non- Cryptographic Approaches", IEEE Transactions
on Services Computing, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 434-451,
2020.
K. Khan and R. Qazi, "Data Security in Cloud Computing
Using Elliptic Curve Cryptography," International
Journal of Computing and Communication Networks,
vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 46-52, 2022.
Kyu-Seok Shim; Boseon Kim; Wonhyuk Lee “Research on
Quantum Key, Distribution Key and Post-Quantum
Cryptography Key Applied Protocols for Data Science
and Web Security” published in IEEE Access in 2024.
L. Wang, L. Xie, and L. Xu, "Privacy-Preserving Cloud
Data Access Control Based on Attribute-Based
Encryption", IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing,
vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 637-646, 2018.
M. - Q. Hong, P. - Y. Wang, and W. - B. Zhao,
"Homomorphic Encryption Plan In view of Elliptic
Bend Cryptography for Security Assurance of
Distributed computing", in IEEE second Global
Meeting on Huge Information Security on Cloud
(BigDataSecurity), Superior Execution and Brilliant
Figuring (HPSC), and Savvy Information and Security
(IDS), 2016, pp. 152-157.
M. Xu, D. Zhang, and X. Zhou, "A Lightweight Cloud Data
Encryption Scheme for Data Privacy Protection", IEEE
Access, vol. 8, pp. 151315-151325, 2020.
M. S. Ali, K. K. R. Choo, and S. H. Ahmed, "Blockchain-
Based Secure Data Storage and Access Control for
Cloud Applications", IEEE Transactions on Cloud
Computing, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 1215-1226, 2021.
M. S. Siddiqui, M. M. Rashid, and S. S. K. Iqbal, "Post-
Quantum Cryptography: Securing Cloud Data from
Quantum Threats", Future Generation Computer
Systems, vol. 122, pp. 76-88, 2021.
M. Albrecht, "Quantum-Resistant Cryptography in Cloud
Environments", in ACM International Conference on
Security and Privacy, 2021, pp. 211-220.
PristiQ "Towards an Original Protection Safeguarding
Circulated Multiparty Information Reevaluating Plan
for Distributed Computing with Quantum Key
Dispersion", 2024
R. Lee, S. L. Liu, and W. L. Yang, "Design and
Implementation of a Privacy-Preserving Cloud Storage
System", Journal of Cloud Computing: Advances,
Systems and Applications, vol. 10, pp. 45-58, 2021.
R. Lu, X. Yuan, and X. Lin, "Homomorphic Encryption for
Cloud Computing: An Overview", IEEE
Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 23, no. 4,
pp. 2381-2405, 2021.
T. K. Shanmugam, K. L. P. Nair, and R. S. G. Dinesh,
"Security and Privacy in Cloud Computing: A Survey",
International Journal of Advanced Computer Science
and Applications, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 404-409, 2017.
V. S. Pendyala, S. M. Arafath, and S. R. Kulkarni, "Elliptic
Curve Cryptography for Real-Time Data Encryption in
IoT and Cloud Computing", IEEE Internet of Things
Journal, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 3615-3623, 2021.
Wenjie Liu et al.,"Quantum Accessible Encryption for
Cloud Information In view of Full-Blind Quantum
Calculation" arXiv in 2023.
X. Kong, J. Wang, and Q. Ni, "Efficient Data Security and
Privacy-Preserving Scheme in Cloud Computing",
IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 24356-24367, 2022.
File Data Security Using Elliptic Curve Cryptography
653
