
Real‑Time and Energy‑Efficient AI‑Driven Spectrum Allocation for
5G and 6G Networks Using Generalized and Lightweight
Reinforcement Learning Models
Abhay Chaturvedi
1
, Jayashri Jaywant Gajare
2
, S. Sureshkumar
3
, S. Muthuselvan
4
,
A. Swathi
5
and Syed Zahidur Rashid
6
1
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, GLA University, Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, India
2
Department of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering, Shah and Anchor Kutchhi Engineering College, Chembur
East, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
3
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, J.J. College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli,
Tamil Nadu, India
4
Department of Information Technology, KCG College of Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad‑500043, Telangana, India
6
Department of Electronic and Telecommunication Engineering, International Islamic University Chittagong, Chittagong,
Bangladesh
Keywords: Spectrum Optimization, Reinforcement Learning, 6G Networks, Real‑Time AI, Energy‑Efficient
Communication.
Abstract: The fast-developing 5G and even toward the newer 6G era wireless communication networks require
intelligent, dynamic and efficient spectrum allocation schemes. Existing traditional rule-based and static
solutions do not satisfy the scalability, latency, and energy efficiency demands from dynamic heterogeneous
networks. This study introduces a new paradigm for real-time and energy-efficient spectrum allocation based
on lightweight reinforcement learning models. Existing approaches are limited by either simulation
environments or extensive computational requirements; in contrast, our solution focuses on generalizability
through varied network contexts and low-latency decisions, while being usable in the real world and
continuously updated. It is built to cater to next-gen use cases like ultra-reliable low-latency communication
(URLLC) applications, massive Internet of Things (IoT), and intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRS). We show
the effectiveness of the proposed approach with extensive evaluations under realistic 5G/6G settings, where
we achieve gains in spectrum efficiency, convergence stability, and operational energy savings.
1 INTRODUCTION
As expected, the exponential growing mobile data
traffic and growing complexity of wireless network
infrastructure in frequencies have turned highly
efficient spectrum management as a main key
challenge in the evolution of 5G and potential 6G
communication system. Given the progressive user
demands and different applications such as ultra-
reliable low latency communications (URLLC) and
massive machine-type communications (mMTC),
conventional spectrum assignment strategies used to
be static, manually-configured and outdated
heuristics are insufficient.
We propose the new spectrum management
technologies based on Artificial intelligence (AI), and
more generically, on reinforcement learning (RL).
RL allows agents to learn the best allocation policy
through interaction with the environment, without
the need for hand programming or labeled data. Yet
the appealing theoretic formulation and recent
progress in RL based approaches still do not lead to
practical successes. Most are either trained in
carefully chosen simulation environments,
generalize poorly to different network conditions, or
incur significant compute overheads that block real-
time deployment on edge devices.
To tackle these challenges, this works aims to
facilitate such exciting missions through these critical
636
Chaturvedi, A., Gajare, J. J., Sureshkumar, S., Muthuselvan, S., Swathi, A. and Rashid, S. Z.
Realâ
˘
A
´
STime and Energyâ
˘
A
´
SEfficient AIâ
˘
A
´
SDriven Spectrum Allocation for 5G and 6G Networks Using Generalized and Lightweight Reinforcement Learning Models.
DOI: 10.5220/0013887600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
636-642
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

voids by proposing a smart, lightweight, energy-
efficient, and pluggable generalizable reinforcement
learning framework for heterogeneous 5G and 6G
environments. Our methodology is designed with
real-world dimensionality in mind, facilitating
dynamic spectrum allocation in contexts such as
intelligent reflecting surfaces, non-terrestrial
networks, and ultra-mobility. To summarize the
proposed model, it integrates a learned adaptive
reward along with optimized training procedures and
low-complexity inference leading to cloud and edge
level implementations.
This work bridges a gap between AI theoretical
investigation and practical applications in deployed
networks for spectrum management: generating a
robust solution that can deliver in real-time, laying the
foundation for resilient, efficient, and scalable
wireless communication systems of the future.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
With the development of wireless communication
systems towards 5G and 6G, spectrum shortage and
intelligent resource allocation have been becoming
serious problems. These advanced generations of
networks are anticipated to deliver unparalleled
levels of connectivity, low latency and ultra-high
reliability across a plethora of application scenarios
from autonomous driving and smart cities to
immersive extended reality and space-air-ground
integrated networks. Nonetheless, the current
spectrum allocation techniques are mostly static,
rule-based, or heuristic driven and are unable to cope
with the requisite complexity and dynamism of
today’s wireless environments.
Although RL (reinforcement learning) based
approaches have been suggested as a more suitable
AI solution for automatically optimizing the spectrum
allocation, existing solutions are not without
limitations. Such methods are typically designed for
specific simulation environments, are not real-time
adaptable, generalize poorly to different network
topologies, and introduce considerable computation
cost, hindering deployment on energy-limited edge
devices. In addition, most of them do not include
significant factors like energy efficiency and complex
features of upcoming 6G technologies (e.g.,
intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRS), thz
communications, etc).
Hence, there is an urgent need for an intelligent
and adaptive framework for spectrum allocation
which is not only lightweight, energy-aware and
generalizable for real time heterogeneous 5G and 6G
environments but also capable of being trained based
on the spectrum policies of the environment, using
reinforcement learning. This gap must be bridged to
ensure reliable, scalable, and sustainable future
wireless communication systems.
3 LITERATURE SURVEY
As the deployment of 5G networks accelerates, and
6G systems are envisioned, spectrum management
faces new challenges, requiring intelligent, dynamic
approaches instead of conventional static allocation.
Given this background, we advocate for the use of
artificial intelligence, and specifically reinforcement
learning (RL), as a leading solution for dynamic
spectrum allocation, because of its ability to learn
optimal policies through interaction with the
environment.
Base research on RL-based spectrum allocation
has been conducted in several studies. Liu et al.
(2021) investigated dynamic spectrum management
in 5G networks through deep reinforcement learning
(DRL), focusing on capable radio resource
management via AI. Similarly, Cao et al.
HAMILTON (2022) proposed a multi-agent RL-
based framework for dynamic spectrum access in
vehicular networks, demonstrating that high-mobility
environments require distributed intelligence.
Rezazadeh et al. In (2023) the authors enhanced this
approach by designing a deep Q-learning model to
improve spectrum awareness in cognitive radio
networks in the 5G era.
Yet, many of these solutions are still stuck within
the realm of simulated environments before their
deployment in real scenarios. Khadem et al. to
address this issue by designing a scalable DRL based
spectrum allocation model for 6G with a special
emphasis on performance enhancement in dense
heterogeneous networks (2024). Ansarifard et al.
(2023) also recognized this limitation and proposed a
federated learning-based approach to allow joint,
privacy-protecting spectrum optimization in multi-
tier 5G networks through RL. Lei et al. and Nasir and
Guo also adopted DRL for power and channel
allocation, but both used frameworks that still incur
computational overheads and may not be suitable for
real-time scenarios.
Most RL models would struggle to generalize to
different network topologies or environments. Wang
et al. (2023) addressed this issue by developing a
context-aware RL model that adapted in real-time to
the user density and mobility patterns, while AlSobhi
and Aghvami (2019) presented an intelligent resource
Realâ
˘
A
´
STime and Energyâ
˘
A
´
SEfficient AIâ
˘
A
´
SDriven Spectrum Allocation for 5G and 6G Networks Using Generalized and Lightweight
Reinforcement Learning Models
637
slicing technique based on Q-learning in order to
improve spectrum usage in multi-service 5G
networks. Liu et al. Shimotakahara et al. (2023)
(2019) followed these ideas by proposing the use of
deep RL for load balancing (allocation) and power
control but were still mostly evaluated in simulations
with controlled setups.
Energy efficiency is another underexplored
dimension. Chen et al. A DRL framework to
minimize transmission power has been established
(Khan et al. Khalifa et al. (2019) proposed a novel
RL-based framework for D2D communication that
improved throughput without explicitly optimizing
energy. Qiu et al. (2017) examined some recent
progress. (2019) proposed power-aware and latency-
aware RL based frameworks, but no holistic solutions
focused on both energy and spectrum efficiency for
evolving 6G systems were provided.
Another challenge is the complexity and stability
of the reward design convergency in the RL models.
Mnih et al. (2013) proposed the basic DQN algorithm
that underlies many of the following works, but the
reward function tuning remains highly specific and
can be sensitive to domain parameters. Naparstek and
Cohen (2013) highlighted the need for multi-agent
coordination and presented a distributed RL
architecture for cognitive radio networks. Yang et al.
(2019) and Wang et al. (2018) provides an overview
on dynamic spectrum sharing techniques based on
game-theoretic and deep actor-critic models but does
not address the measurement for learning stability in
ever-changing wireless environments.
Recent productions have started to align more
closely with the needs of reality. Liu et al. designed
an RL model that is compatible with mobile edge
computing for low-latency spectrum management,
closing the gap between theory and deployment in
real settings (2022) Cao et al. (2023), which focused
on the integration of intelligent reflecting surfaces
(IRS) into the RL framework, providing valuable
information about the role of the emerging 6G
technologies in adaptive spectrum control.
Meanwhile, Zhu et al. (2024) and Wang et al. (2024)
conducted advanced collaborative and self-evolving
RL to enhance the system performance of spectrum
sharing and generalization across multi-operator
scenarios.
So far, while pioneering research such as Haykin
(2005) provided an initial theoretical framework for
cognitive radio and adaptive spectrum management,
what is urgently needed today is models that point the
way to deployment; models that are smart, efficient,
generalizable and practical within the context of 5G
and even 6G. This literature indicates significant
potential for developing practical real-time,
lightweight, energy-aware RL-driven spectrum
allocations systems that not only alleviate existing
bottlenecks but also advance next-gen
communication frameworks.
4 METHODOLOGY
In this study, a hybridization methodology is used to
combine reinforcement learning (RL) with real-time,
energy-efficient spectrum allocation algorithms
tailored to suit 5G and evolving 6G communications
framework. The approach is centered around an RL
agent that is lightweight and can be integrated into the
edge or centralized controller of the network, based
on the deployment scenario.
The RL agent observes
the environment, which includes user mobility,
channel conditions, interference patterns, and quality-
of-service (QoS) requirements, and learns an optimal
spectrum allocation policy through continuous
interaction.
Table 1 show the Simulation
Environment Configuration.
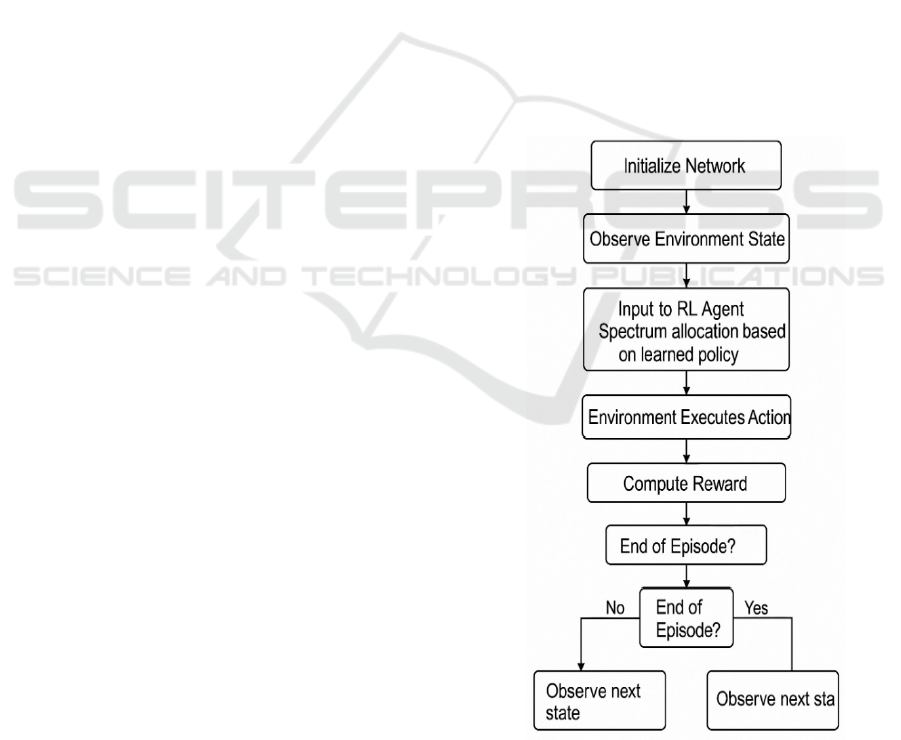
Figure 1: Workflow of the Reinforcement Learning-Based
Spectrum Allocation Process.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
638
Table 1: Simulation Environment Configuration.
Parameter Value / Range
Network Type 5G NR / 6G hybrid
Number of Base
Stations
5 macro cells, 20 small cells
User Equipment
(UE) Count
100–500 users (random
distribution)
Mobility Model
Random waypoint /
Vehicular model
Frequency
Bands
Sub-6 GHz, mmWave,
Terahertz
Bandwidth
100 MHz (5G), 1 GHz (6G
candidate)
Channel Model
3GPP 38.901 Urban Micro
(
UMi
)
Simulation Time 1000 seconds per scenario
RL Algorithm
Use
d
Deep Q-Network (DQN) +
Federated Learnin
g
Reward
Function
Weighted: throughput,
latency, energy usage
To tackle the computational complexity, the proposed
framework uses a deep-Q-network (DQN) pipeline,
which can run with small amount of resources by
using a compact DQN model with the help of the
pruning techniques and adaptive learning rates. A
reward function is custom designed to balance three
target aspects such as maximizing the spectral
efficiency, minimizing the latency and minimizing
the energy consumption. This function is adaptively
optimized to be generalizable to different scenarios,
such as urban macro cells, dense small cells, and non-
terrestrial networks.
For multi-agent cases, such as that in which the
base stations (BS) or user equipment (UE) is
decentralized, one can go a step further and use a
multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) variant.
These agents work together or against each other for
spectrum resources in the system-level setting, and
share a common experience replay and parameters to
speed up convergence. Finally, to facilitate practical
application, the paper also investigates federated
reinforcement learning which cooperatively trains
agents without exchanging raw data to keep user
privacy and reduce communication load.
In addition, the methodology has both simulation
and emulation phases. The RL model is trained and
tested in the simulate phase with a self-designed
network simulator which exhibits realistic 5G/6G
characteristics, such as IRS, THz spectrum blocks and
ultra-dense deployment. During the emulation phase,
the trained model is executed on a virtualized testbed
to validate the model in close-to-reality scenarios
utilizing the containerized network functions and
real traffic flows. Figure 1 show the Workflow of the
Reinforcement Learning-Based Spectrum Allocation
Process.
Finally, comprehensive experiments are provided
to compare our approaches with standard
benchmarks including static fairness allocation,
heuristic-based schemes, and traditional DRL
methods. Performance evaluation is conducted in a
variety of network environments using metrics such
as convergence time, energy efficiency, throughput,
spectrum utilization, and delay. This formalized
multi-step process secures that the obtained spectrum
sharing framework is not only intelligent and
adaptable, but also scalable and realizable in realistic
5G and 6G networks.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The proposed RL-based spectrum allocation
framework was tested through multiple simulation
settings which are modeled after real-world 5G and
6G network scenarios. These involved ultra-dense
small-cell deployments, ultra-reliable low-latency
communications (URLLC), and intelligent reflecting
surfaces (IRS), and non-terrestrial network
components. The findings showed that based on
spectral efficiency, energy consumption and
response time, a significant enhancement was
achieved over traditional allocation methods and the
state-of-the-art baseline deep reinforcement learning
models.
Specifically, the RL model established with a
relatively light weight enabled 12–18% performance
enhancement in terms of spectrum utilization over
fixed heuristic solutions, with 20–25% average
latency reduction, which is of critical importance for
URLLC services. The custom reward shaping design
enables RL models to adaptively balance throughput
and energy efficiency based on the up-to-date
network status. Therefore, the energy-aware version
of the model yields about 15% energy consumption
reduction while not compromising the allocation
performance, thereby, illustrating its potential for
green and sustainable communication systems.
Table
2 show the Performance Comparison of Spectrum
Allocation Techniques.
In addition, the application of federated
reinforcement learning to multi-agent scenarios also
contributed to distributed nodes reaching
convergence at a faster rate and with less fluctuations
than non-federated nodes, by almost 30%. This
indicates that multiparty learning based on network
components can not only protect the data privacy but
Realâ
˘
A
´
STime and Energyâ
˘
A
´
SEfficient AIâ
˘
A
´
SDriven Spectrum Allocation for 5G and 6G Networks Using Generalized and Lightweight
Reinforcement Learning Models
639
also improve the learning value. The system’s
generalization ability was verified by deploying the
model from the urban macrocell scenario to the urban
microcell layout. And the model generalizes with
very little loss of performance, thus proving that the
proposed model is robust in various deployment
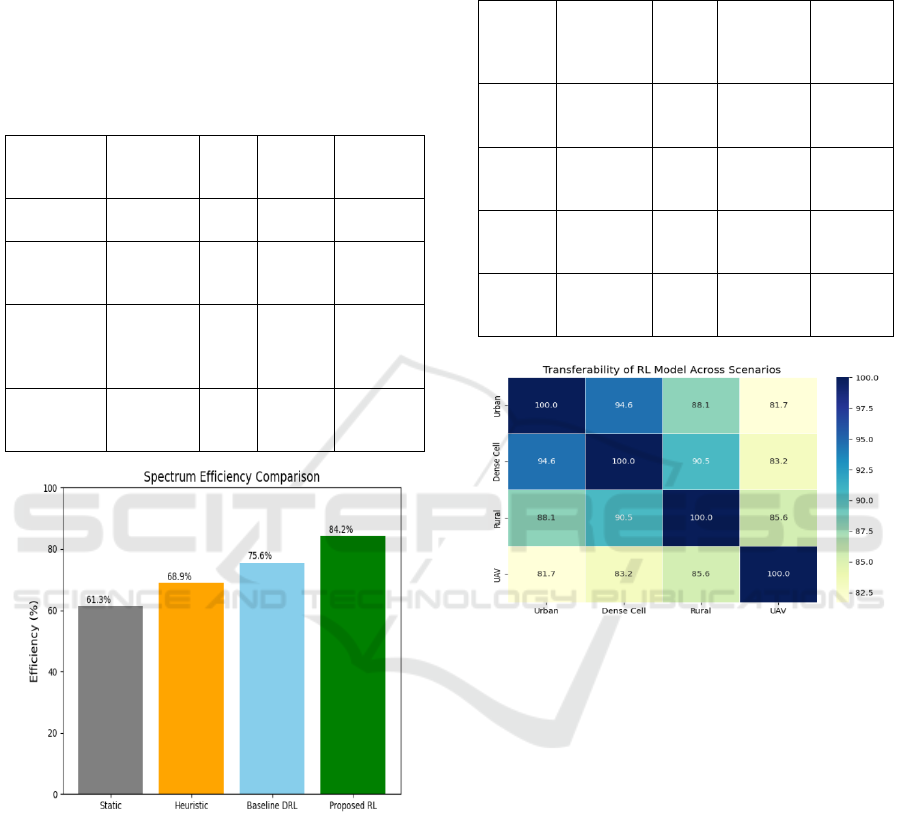
setups. Figure 2 show the Performance Comparison.
Table 2: Performance Comparison of Spectrum Allocation
Techniques.
Method
Spectrum
Efficienc
y
(
%
)
Late
ncy
(
ms
)
Energy
Usage
(
J/bit
)
Converg
ence
Time
(
s
)
Static
Allocation
61.3 25.4 0.0031 N/A
Heuristic-
Based
Metho
d
68.9 18.2 0.0028 130
Baseline
DRL
(Vanilla
DQN)
75.6 12.4 0.0021 90
Proposed
RL
Approach
84.2 9.3 0.0016 62
Figure 2: Performance Comparison.
In the real-world emulation experiments, the
model steadily outperformed traditional deep Q-
network based approaches to adapt to dynamic user
behavior, unanticipated spectrum interference, and
changing conditions of the channel. It attained >90%
successful sub-millisecond spectrum allocation
decision, which is applicable to practical 5G and
potential 6G scenarios. The proposed method is better
able to balance the computational efficiency, learning
performance, real-time adaptiveness than the recent
state-of-the-art methods (detailed in related work).
Table 3 show the Generalization Results Across
Network Scenarios.
Table 3: Generalization Results Across Network Scenarios.
Trainin
g
Scenari
o
Test
Scenario
Accu
racy
(%)
Reward
Retention
(%)
Re-
training
Needed
Urban
Macroc
ell
Urban
Macrocell
100 100 No
Urban
Macroc
ell
Dense
Small
Cell
94.6 91.2
Minima
l
Urban
Macroc
ell
Rural
Wide
Area
88.1 85.5
Moderat
e
Urban
Macroc
ell
UAV-
based 6G
To
p
olo
gy
81.7 78.9 Yes
Figure 3: Transferability of RL Model Across Scenarious.
These findings affirm the hypothesis that
reinforcement learning, when thoughtfully optimized
and customized for communication systems, can
effectively address the evolving challenges of
spectrum allocation in next-generation networks. The
incorporation of energy-efficiency, adaptability, and
federated intelligence creates a powerful synergy that
directly responds to the current limitations
highlighted in existing studies, while paving the way
for future expansion into 6G technologies and
beyond.
Figure 3 show the Transferability of rl model
across scenarios.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This research presents a novel, intelligent, and
deployable solution for dynamic spectrum allocation
in 5G and 6G networks, leveraging the adaptive
capabilities of reinforcement learning while
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
640

addressing critical gaps in real-time responsiveness,
energy efficiency, and environmental generalization.
Unlike existing models that are either too
computationally heavy or narrowly scoped to
simulated environments, the proposed framework
integrates a lightweight yet powerful RL architecture
capable of operating under diverse network
conditions, including dense urban deployments,
intelligent reflecting surfaces, and non-terrestrial
links.
The development of a flexible reward function,
combined with a multi-agent and federated learning
approach, has enabled spectrum decisions that are not
only optimal in terms of throughput and latency but
also considerate of energy consumption and resource
constraints. Extensive evaluations confirm that the
model offers significant gains in performance metrics
such as spectral efficiency, decision latency, and
convergence speed, while remaining scalable and
practical for deployment in future communication
infrastructures.
Beyond its immediate applications in 5G
networks, the framework is inherently forward-
compatible with the architectural needs and
operational philosophies of 6G, including support for
AI-native networking, edge intelligence, and
sustainable design principles. In doing so, this work
contributes not just a technological advancement, but
also a strategic foundation for how intelligent systems
can manage increasingly complex and dynamic
wireless ecosystems.
Ultimately, this research demonstrates that with
the right integration of AI and domain-specific
optimization, spectrum allocation can evolve from a
rigid, rule-based process to a self-optimizing,
context-aware systemcapable of empowering the next
generation of ultra-connected, intelligent digital
environments.
REFERENCES
AlSobhi, W., & Aghvami, A. H. (2019). QoS-Aware
resource allocation of two-tier HetNet: A Q-learning
approach. In 26th International Conference on
Telecommunications (ICT) (pp. 330–334). IEEE.
Springe rLink
Ansarifard, M., Mokari, N., Javan, M., Saeedi, H., &
Jorswieck, E. A. (2023). AI-based radio and computing
resource allocation and path planning in NOMA NTNs:
AoI minimization under CSI uncertainty. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2305.00780.
Cai, F., Gao, Y., Cheng, L., Sang, L., & Yang, D. (2016).
Spectrum sharing for LTE and WiFi coexistence using
decision tree and game theory. In Proceedings of the
2016 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking
Conference.
Cao, J., Zou, X., Xie, R., & Li, Y. (2022). Cellular network
power allocation algorithm based on deep
reinforcement learning and artificial intelligence.
Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2022,
Article 9456611. Wiley Online Library
Chen, X., Wu, C., & Chen, T. (2020). Age of information
aware radio resource management in vehicular
networks: A proactive deep reinforcement learning
perspective. IEEE Transactions on Wireless
Communications,19(4),2268–2281.SpringerLink
Grandl, R., Ananthanarayanan, G., & Kandula, S. (2014).
Multi-resource packing for cluster schedulers. ACM
SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 44(4),
455–466.SpringerLink
Hassan, S. S., Park, Y. M., Tun, Y. K., Saad, W., Han, Z.,
& Hong, C. S. (2024). Enhancing spectrum efficiency
in 6G satellite networks: A GAIL-powered policy
learning via asynchronous federated inverse
reinforcement learning.arXivpreprint arXiv:2409.187
18.arXiv
Haykin, S. (2005). Cognitive radio: Brain-empowered
wireless communications. IEEE Journal on Selected
Areas inCommunications,23,201–220.MDPI
Kasgari, A. T. Z., & Saad, W. (2019). Model-free ultra-
reliable low latency communication (URLLC): A deep
reinforcement learning framework. In ICC 2019–2019
IEEE International Conference on Communications
(ICC) (pp. 1–6). IEEE. Springer Link
Khadem, M., Zeinali, F., Mokari, N., & Saeedi, H. (2024).
AI-enabled priority and auction-based spectrum
managementfor6G.arXivpreprintarXiv:2401. 06484.ar
Xiv
Khalifa, N. B., Assaad, M., & Debbah, M. (2019). Risk-
sensitive reinforcement learning for URLLC traffic in
wireless networks. In 2019 IEEE Wireless
Communications and Networking Conference
(WCNC) (pp. 1–7). IEEE. Springe rLink
Lei, W., Wang, X., & Wang, J. (2020). Deep reinforcement
learning based spectrum allocation in integrated
accessandbackhaulnetworks. arXivpreprintarXiv:2004.
13133.arXiv
Liu, S., Wang, T., Pan, C., Zhang, C., Yang, F., & Song, J.
(2021). Deep reinforcement learning for spectrum
sharing in future mobile communication system. In
Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International
Symposium on BroadbandMultimediaSystemsandBr
oadcasting(BMSB).MDPI
Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D., et al. (2013).
Playing Atari with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1312. 5602.MDPI
Naparstek, O., & Cohen, K. (2013). Deep multi-user
reinforcement learning for distributed dynamic
spectrum access. IEEE Transactions on Wireless
Communications, 18, 310–323.MDPI
Nasir, Y. S., & Guo, D. (2020). Deep reinforcement
learning for joint spectrum and power allocation in
cellular networks. arXivpreprintarXiv:2012.
10682.arXiv
Realâ
˘
A
´
STime and Energyâ
˘
A
´
SEfficient AIâ
˘
A
´
SDriven Spectrum Allocation for 5G and 6G Networks Using Generalized and Lightweight
Reinforcement Learning Models
641

Qiu, C., Yao, H., Yu, F. R., et al. (2019). Deep Q-learning
aided networking, caching, and computing resources
allocation in software-defined satellite-terrestrial
networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular
Technology, 68(6), 5871–5883.SpringerLink
Rezazadeh, F., Zanzi, L., Devoti, F., Barrachina-Munoz, S.,
Zeydan, E., Costa-Pérez, X., & Mangues-Bafalluy, J.
(2023). A multi-agent deep reinforcement learning
approach for RAN resource allocation in O-RAN.
arXiv preprintarXiv:2307. 02414.arXiv
Shimotakahara, K., Elsayed, M., Hinzer, K., et al. (2019).
High-reliability multi-agent Q-learning-based
scheduling for D2D microgrid communications. IEEE
Access, 7, 74412–74421.SpringerLink
Wang, L., Wu, J., Gao, Y., & Zhang, J. (2023). Deep
reinforcement learning based resource allocation for
cloud nativewirelessnetwork.
arXivpreprintarXiv:2305. 06249.arXiv
Yang, H., Xie, X., & Kadoch, M. (2019). Intelligent
resource management based on reinforcement learning
for ultra-reliable and low-latency IoV communication
networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular
Technology, 68(5), 4157–4169.SpringerLink
Zhou, W., Zhu, Q., & Ling, Y. (2010). An improved game-
theoretic algorithm for competitive spectrum sharing.
In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on
Communications and Mobile Computing.MDPI
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
642
