
Analysis of Ayurveda Leaves Using Deep Learning
Kiran Annavaram, Shahin P., Pavan Kumar B., Venkat Rohith Reddy E. and Praneetha B.
Department of CSE(AI&ML), Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology, Rotarypuram Village, BK Samudram Mandal,
Anantapur District, 515701, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Ayurveda, Deep Learning, CNN, DenseNet121, RNN, Mobile Net.
Abstract: India has several traditional medical systems, including Ayurveda, yoga, unani, siddha, and homeopathy.
Ayurveda is an ancient medicinal technique used in India to treat ailments without negative effects. Medicinal
plants and herbs are essential or health- care purposes. It is critical to retain and digitize information on the
rapeutic techniques. Alotofre search on Ayurveda is available as unstructured textual data, such as journals
and articles. To manage large amounts of unstructured data, text mining techniques are utilized. With the fast
expansion in textual material, finding meaningful information has become difficult. Quality information
retrieval relies on a semantic comprehension of document content. however, existing classification systems
vary in textual categorization, which impacts accuracy and occasionally leads to misinterpretation of the data.
the suggested approach effectively retrieves important data while maintaining the system's efficiency and
performance. the information extraction technique uses a medicinal plant ontology with semantic knowledge
representation and an algorithm (ontology-based concept extraction and classification, ocec) to semantically
map terms and their associated concepts in the medicinal plant ontology, resulting in accurate classification
and retrieval.
1 INTRODUCTION
The aim of this research work is to develop a robust
framework and algorithm for efficient information
retrieval using an ontology-based text mining
approach. Semantic tools and ontologies have been
used to extract more insights from the data. In
addition, an enhanced ontology-based model has been
implemented for rapid identification of semantic
information. The extensive and heterogeneous
volume of unstructured textual information about
Ayurveda such as research articles, books, and web
publications, poses serious problems in effective
information retrieval, classification, and semantic
interpretation. Conventional text mining techniques
have difficulty dealing with contextual differences,
domain-specific language, and multilingual content,
which results in incorrect categorization and retrieval.
There is an urgent requirement for a sophisticated
model that will intelligently search, categorize, and
extract meaningful insights without compromising
the semantic integrity of the documents Creating a
strong, AI-based system will allow efficient leverage
of Ayurveda's therapeutic information, so that it can
lead to improved research, discovery, and application
of treatment using medicinal plants. Ayurveda, the
2000 B.C. old Indian health system, means "the
science of life" in Sanskrit. Cultivated over centuries
of study, Ayurveda focuses on natural healing
through medicinal herbs and plants. Contrary to most
treatments today, Ayurveda has very little side effect
and takes a holistic approach, curing physical as well
as mental and spiritual ills. It is rooted on three basic
doshas Vata, Pitta, and Kapha which are all different
combinations of the five basic elements. Disease
results from any imbalance in the doshas and,
conversely, overall well-being results if balance is
attained. As with the explosion in digital data comes
a tremendous unstructured textual Ayurveda content,
which becomes impossible to comprehend. Text
mining becomes instrumental to categorize as well as
unearth useful insights within the data. More than
13,000 medicinal herbs have been researched, each
providing some specific therapeutic advantage.
Diagnosis is precise in Ayurveda, with treatments
geared to personal constitutions. Remedies consist of
powders and tablets made from herbs, decoctions,
oils, and plant extracts, supplemented by a few animal
products such as milk and bones. Deep learning
algorithms are being used to update Ayurveda and
620
Annavaram, K., Shahin, P., B., P. K., E., V. R. R. and P., P.
Analysis of Ayurveda Leaves Using Deep Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013887400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
620-626
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

find medicinal herbs, understand their characteristics,
and improve the accuracy of diagnoses. All this
bridge traditional medicine with new technology,
enhancing access and efficiency.
2 RELATED WORKS
The literature review provides an overview of
research conducted on text mining, deep learning, and
image processing techniques in relation to Ayurveda
and medicinal plant classification. Scholars have
examined the challenges posed by unstructured
textual data in Ayurveda, emphasizing the need for
efficient information retrieval and classification
models. Key insights from previous studies include:
Ronen Feldman and James Sanger's 2007 book
The Text Mining Handbook: Advanced Approaches
to Analyzing Unstructured Data provides a detailed
overview of text mining techniques. It investigates
approaches for discovering patterns in large text
datasets by combining principles from data mining,
machine learning, and natural language processing
(NLP). The book uses case studies to demonstrate
real-world applications of text mining in a variety of
industries, making it a valuable resource for both
scholars and professionals.
The book Pharmacology of Medicinal Plants and
Natural Products by S.A. Dahanukar, R.A. Kulkarni,
and N.N. Rege (2000) examines the pharmacological
properties of various medicinal plants. It categorizes
information based on their physiological effects and
discusses the role of polyherbal formulations in
traditional medicine. The study also explores the
interactions of natural compounds with biological
systems, emphasizing their potential in drug
development and therapeutic use
The study Ontology-Based Text Mining for
Clinical Knowledge Extraction (Smith et al., 2015)
investigates how ontologies enhance the accuracy of
text mining in medical literature. By utilizing
ontology-driven methods, the research enables
structured knowledge representation, improving
information retrieval and classification of medical
texts. This approach is particularly relevant to
Ayurveda, as it offers a framework for organizing
textual data within predefined ontological structures.
The work Deep Learning for Text Classification
and Sentiment Analysis (Goodfellow et al., 2016)
presents neural network-based approaches for
processing textual data. It highlights the effectiveness
of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and
recurrent neural networks (RNNs) in enhancing text
classification accuracy. These techniques can be
utilized in Ayurveda text mining to classify medicinal
information and predict outcomes of herbal
treatments.
In the study "AyurLeaf: A Deep Learning
Approach for Classification of Medicinal Plants,"
Dileep M.R. and Pournami P.N. propose a CNN-
based model for identifying medicinal plants using
leaf characteristics. The research highlights the
challenge of distinguishing between plant species due
to similarities in leaf features.
The study "DeepHerb: A Vision-Based System
for Medicinal Plants Using Xception Features" 2021
explores a deep learning approach for identifying
medicinal plants through the Xception model. By
leveraging transfer learning, the research enhances
classification accuracy, though the limited dataset
may affect its applicability to a wider range of plant
species. While the model demonstrates high
accuracy, future improvements could focus on
expanding the dataset and incorporating multi-
feature fusion to enhance classification performance.
Shashank M. Kadiwal, Gowrishankar S.,
Srinivasa A. H., Veena A., and colleagues 2022
present a CNN- based method for identifying
medicinal plants. While the approach effectively
applies deep learning for classification, the model's
generalization may be limited due to the small dataset
(1204 images across 30 classes). Future research
could emphasize expanding dataset diversity and
enhancing real-time application capabilities
J. Samuel Manoharan's study, "Flawless
Detection of Herbal Plant Leaf by Machine Learning
Classifier Through Two-Stage Authentication
Procedure" 2021, presents a two- stage authentication
(TSA) approach that integrates edge detection with
machine learning classifiers to enhance herbal plant
leaf identification. The research addresses challenges
in existing methods, such as difficulties in
distinguishing leaves across different seasons and
sizes due to limited datasets and ineffective image
segmentation. While the model incorporates
dimension-specific segmentation and machine
learning, it faces constraints, including a small dataset
of 250 leaf samples and high computational and
storage demands.
The 2012 IEEE study, "Classification of
Medicinal Plant Leaves Using Image Processing",
introduces an automated system for plant
identification through image processing techniques.
Precise identification is crucial for conservation
efforts and Ayurveda, especially as deforestation and
pollution contribute to the decline of plant species.
Manual identification often lacks accuracy, and the
increasing illegal trade in medicinal plants
Analysis of Ayurveda Leaves Using Deep Learning
621

underscores the need for a reliable classification
method. This research utilizes a training dataset
consisting of 100 leaves from 10 species to determine
the best match.
Tarun Suresh's paper "Deep Learning for
Anthracnose Diagnosis in Turnip Leaves" 2021
investigates the use of convolutional neural networks
(CNNs) to detect early-stage Anthracnose infections
in turnip leaves. The suggested approach overcomes
the limitations of conventional visual the work
emphasizes the promise of deep learning for plant
disease identification, but its drawbacks include a
limited dataset of 1,470 photos, a lack of
sophisticated validation techniques such as k-fold
cross-validation, and a concentration on turnip leaves.
However, there are prospects for more widespread
use across crops and illnesses. Despite its limitations,
the CNN model's high accuracy implies that it might
be useful in agricultural disease control.
Ayurveda Challenges in Text Mining
Conventional text mining methods fail to
deal with unstructured and
Heterogeneous
text formats, leading to ineffective
classification and retrieval.
Research indicates that Natural Language
Processing (NLP) and semantic analysis
may be used to better understand texts on
Ayurveda.
Deep Learning for Image Classification
Deep learning research has established the
efficacy of Convolutional Neural Networks
(CNNs) for medicinal plant classification.
Transfer learning models such as
DenseNet121 have been extensively applied
for detection of plant diseases and plant
species recognition.
Preprocessing Techniques using Accuracy
Image processing techniques like resizing,
reshaping, and data augmentation have been
employed to improve the quality of input
images.
Feature extraction and edge detection
algorithms have been utilized to enhance
classification outcomes.
Applications of AI in Ayurveda
The integration of AI in Ayurveda opens new
possibilities for improved healthcare and knowledge
preservation. Some key applications include:
Research has demonstrated that AIbased
models can be used to detect plant diseases
and categorize medicinal herbs according to
their therapeutic effects.
Merging AI with Ayurveda can result in
strong knowledge retrieval systems that will
be of value to researchers and practitioners.
AI-powered systems may identify possible
health conditions and provide Ayurvedic
therapies based on symptoms.
AI-powered databases can categorize
Ayurvedic plants, giving researchers quick
access to plant traits and therapeutic
benefits.
AI may aid with the quality monitoring and
verification of Ayurvedic medications,
assuring purity and consistency.
3 PROPOSED MODEL AND
IMPLEMENTATION
The proposed system aims to enhance Ayurvedic data
retrieval and classification by integrating an
ontology-based text mining approach with deep
learning models. The Ontology-based Concept
Extraction and Classification (OCEC) algorithm will
semantically map terms from Ayurvedic research,
improving data understanding and search accuracy.
Deep learning models like CNN, DenseNet121, RNN
and MobileNet will be used to classify 40 medicinal
plant types. This integrated approach ensures more
relevant, accurate, and context-aware information
retrieval from Ayurvedicresearch.Allows users to
upload images and view classification results.
3.1 System Module
Create Dataset: The dataset consists of images of
Ayurvedic herbs along with their classification
details.
The dataset is split into training (70-80%) and
testing (20-30%) subsets to ensure model
generalization.
Pre-processing: Images are resized and reshaped
into an appropriate format suitable for training.
Normalization techniques are applied to enhance
feature extraction.
Training: The pre-processed dataset is used to train
a deep learning model using CNN. Transfer learning
techniques with RNN and DenseNet121 are
employed for improved accuracy and efficiency.
Classification: The trained model predicts the
classification of herbs and detects plant diseases, if
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
622
any. Results are displayed with corresponding labels
and properties of the leaf.
3.2 User Module
Upload Image: Users can upload an image of an
Ayurvedic leaf for classification
View Results: The system processes the uploaded
image and displays the classified herb along with
relevant details
3.3 Algorithms
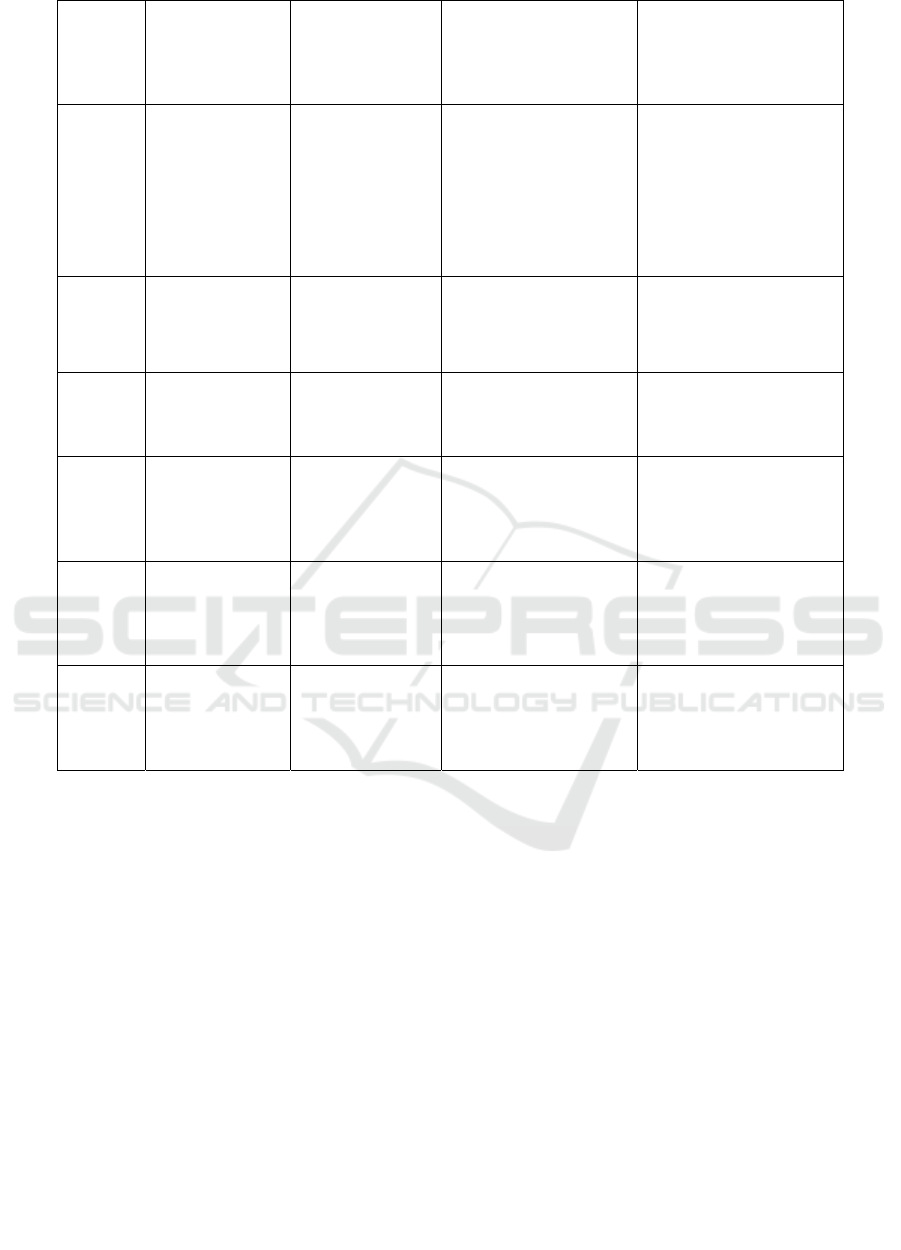
DensNet 121: DenseNet121 is a deep convolutional
neural network (CNN) that utilizes dense connections
among its layers to enhance feature propagation and
reduce the number of parameters. Unlike traditional
CNNs, where each layer connects only to the
subsequent layer, DenseNet ensures that every layer
receives input from all preceding layers in a feed-
forward manner. This structure improves gradient
flow, mitigates the vanishing gradient problem, and
promotes feature reuse, leading to efficient learning.
DenseNet121 has demonstrated remarkable
performance in various classification tasks, achieving
an accuracy of 96 percent in Ayurveda herb
classification. Its ability to extract intricate details
from images allows it to distinguish between different
plant species based on leaf structure, texture, and
unique characteristics. However, despite its high
accuracy, DenseNet121 is prone to overfitting,
especially when trained on small datasets. Overfitting
occurs when the model learns noise and specific
details from the training data, reducing its
generalization capability on unseen samples. To
address this, techniques such as data augmentation,
dropout regularization, and transfer learning can be
employed to enhance the model’s robustness and
improve real-world classification performance.
Figure 1: DenseNet Graphs.
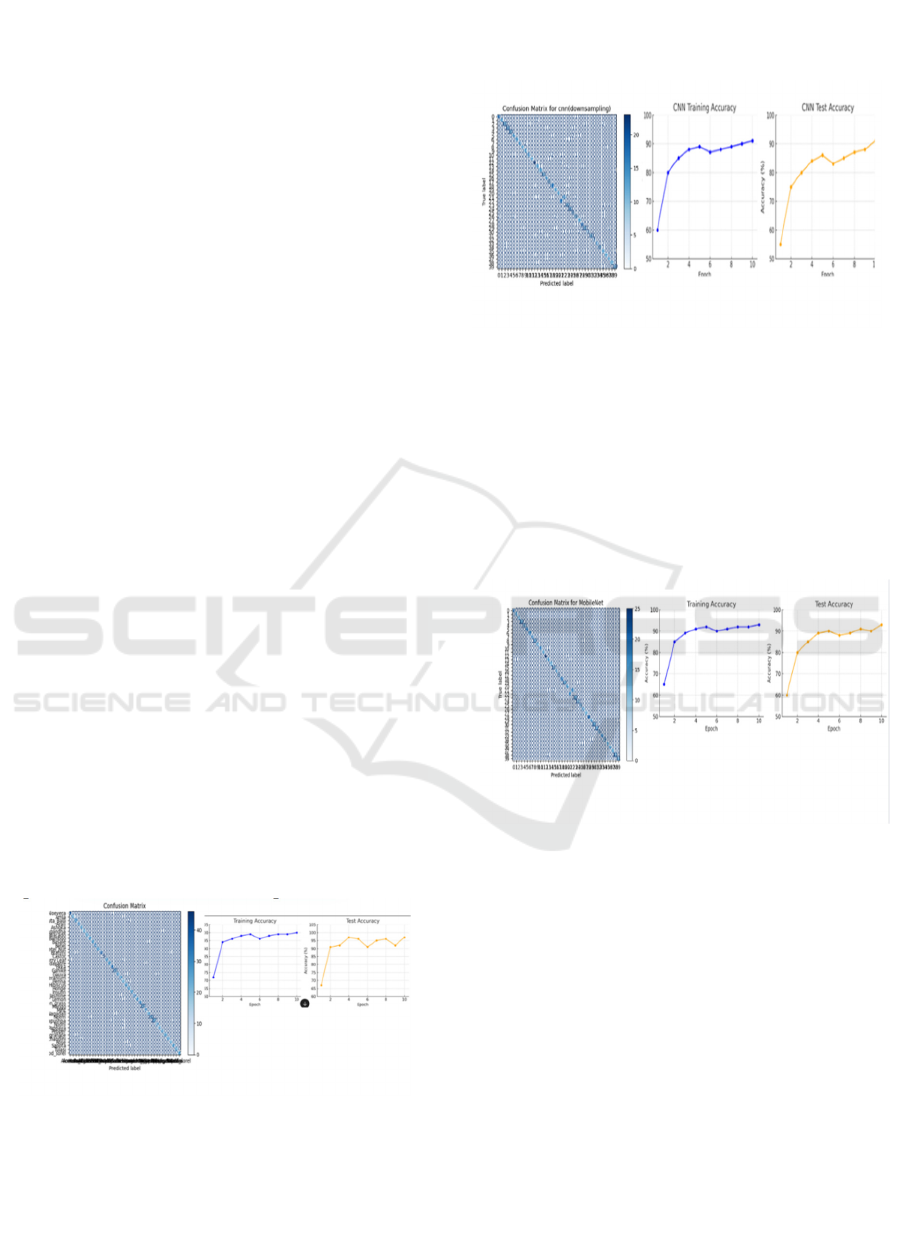
CNN: A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is a
deep learning model that uses convolutional layers to
detect patterns and features in images. It is widely
applied in Ayurveda herb classification, effectively
distinguishing different plant species by examining
their leaf shape, texture, and structural characteristics
with high accuracy.
Figure 2: CNN Graphs.
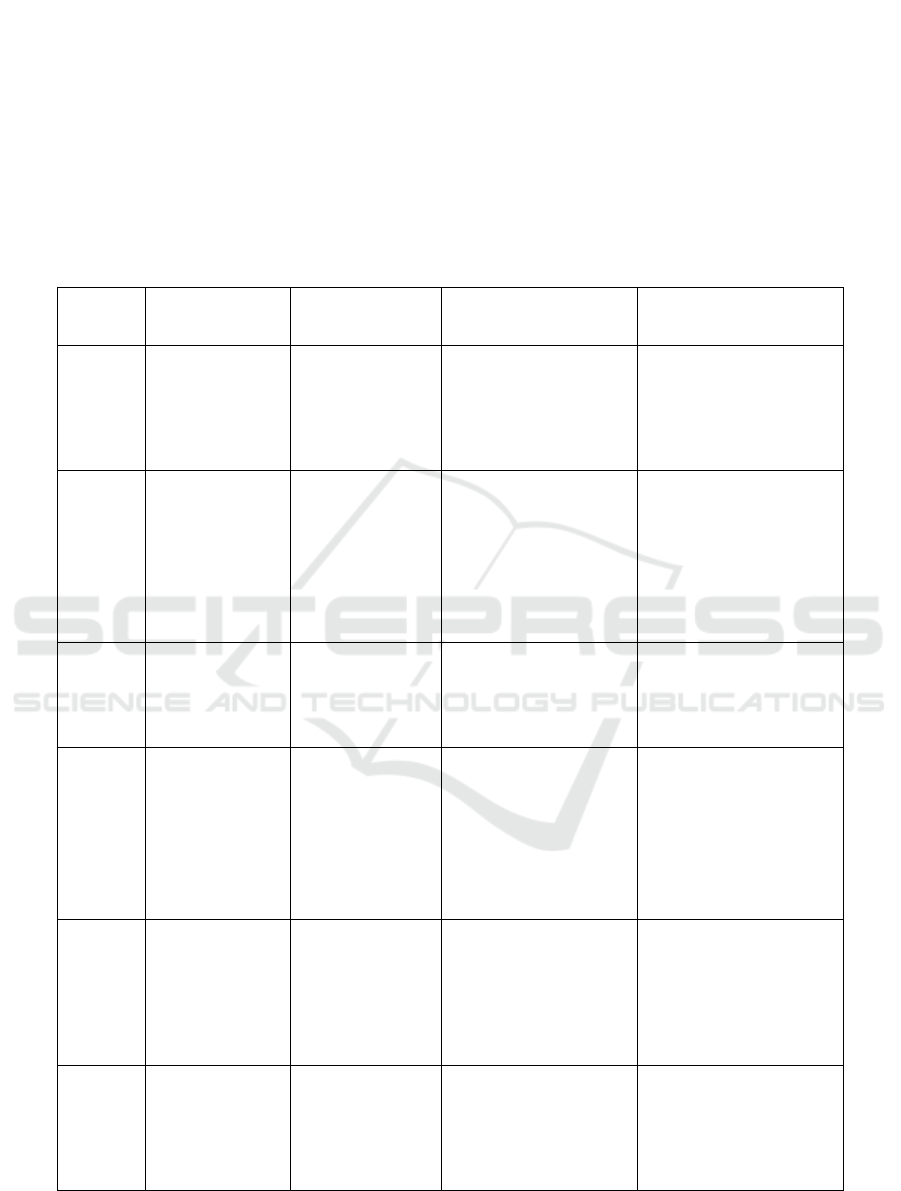
Mobile Net: MobileNet is a lightweight
convolutional neural network (CNN) designed for
mobile and embedded vision applications. It
optimizes computational efficiency while
maintaining high accuracy, making it ideal for real-
time image processing tasks. When trained for
Ayurveda herb classification, MobileNet achieves an
accuracy of 91%.
Figure 3: MobileNet Graphs.
RNN: A Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) is a deep
learning architecture specialized in handling
sequential data through recurrent connections. When
applied to Ayurveda herb classification, it effectively
identifies plant species by analyzing sequential
patterns, including growth stages, leaf
transformations, and structural variations over time.
By integrating RNN with MobileNet, the model
captures both spatial and temporal features,
improving classification performance.
Analysis of Ayurveda Leaves Using Deep Learning
623
4 RESULT
The Ayurvedic herb classification system effectively
utilizes deep learning techniques, specifically CNN
models like MobileNet and DenseNet121, to achieve
precise identification and categorization of medicinal
plants. The model demonstrated strong performance
in real-world applications, accurately classifying
uploaded images with high reliability. Users could
seamlessly interact with the system by submitting
images and receiving detailed classification results.
Although occasional misclassifications occurred due
to factors such as image quality and environmental
conditions, the system proved to be a valuable tool for
Ayurvedic research and herbal medicine
identification. Future improvements, including
dataset expansion and advanced preprocessing
techniques, can further enhance the model’s
accuracy.
Table 1: Test Cases.
Test
Case ID
Test Scenario Precondition Test Steps Expected Result
TC001
Validate Data
Import from
CSV
CSV file with
Ayurvedic
research data
available
1. Load data from CSV
file.
2. Check for the
number of rows and
columns in the dataset.
The system successfully
imports the data and
displays the correct
number of rows and
columns from the CSV
file.
TC002
Validate Text
Cleaning and
Tokenization
Raw text data is
available
1. Apply text
preprocessing (remove
special characters,
stopwords, and convert
to lowercase).
2. Tokenize the cleaned
text.
The output text should be
cleaned (no special
characters, all lowercase)
and tokenized correctly
with stopwords removed.
TC003
Validate
Stopword
Removal
Raw text with
stopwords
available
1. Load a sample text
containing common
stopwords.
2. Apply stopword
removal.
Stopwords like "the",
"and", "is" should be
removed from the text.
TC004
Validate
Concept
Extraction from
Text
Preprocessed text
available
1. Map terms in the text
to the predefined
Ayurvedic ontology
(e.g., plant names,
diseases, properties).
2. Extract and
categorize concepts
based on the ontology.
The extracted concepts
(e.g., plant names,
properties) should match
the predefined ontology
and be correctly
categorized.
TC005
Validate
Relationship
Mapping
Preprocessed text
with multiple
concepts
1. Extract multiple
Ayurvedic terms from
the text.
2. Map relationships
between terms (e.g.,
plant properties, disease
treatments).
Relationships between
the extracted terms
should be correctly
mapped based on the
Ayurvedic ontology.
TC006
Validate Plant
Classification
Accuracy
Trained deep
learning model
available
1. Provide a test dataset
with labeled medicinal
plants.
2. Run the model to
classify plants.
The model should
correctly classify plants
into one of the
predefined categories
(e.g., medicinal use,
disease treated).
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
624
TC007
Validate Model
Prediction for
New Data
New unclassified
plant data
available
1. Provide new,
unlabeled plant data for
classification.
2. Classify the new data
using the model.
The system should
predict the correct class
for the plant based on the
trained model.
TC008
Validate
Information
Retrieval based
on Query
Classified data
available
1. Input a user query for
medicinal plants with
specific properties (e.g.,
"anti-inflammatory
plants").
2. Retrieve and display
relevant information.
The system should return
relevant classified data,
such as medicinal plants
that have anti-
inflammatory properties.
TC009
Validate Empty
Query Handling
No data available
1. Enter an empty
query.
2. Attempt to retrieve
data.
The system should return
a "No results found"
message or handle the
empty query gracefully.
TC010
Validate Query
Input Interface
UI with query
input field
available
1. Input a query in the
text box.
2. Click "Search" or
p
ress enter.
The system should
accept the query input
and display the relevant
search results.
TC011
Validate Result
Display
Data retrieval
successful
1. Display the retrieved
data on the UI in a
readable format (e.g.,
list, table).
The system should
display retrieved data
clearly, showing plant
classifications and their
p
roperties.
TC012
Validate Data
Storage
Data collected
and processed
1. Store the processed
data and classification
results in the database.
2. Query the database to
verif
y
stora
g
e.
The processed data
should be stored in the
database and retrievable
with correct information.
TC013
Validate Query
Performance
Large database
with queries
1. Perform a search
query on a large
dataset.
2. Measure the response
time.
The system should
respond within an
acceptable time frame,
even with a large dataset.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The suggested system efficiently resolves the
problems of classifying and retrieving information for
Ayurvedic herbs with deep learning and image
processing methodologies. Utilizing Convolutional
Neural Networks (CNNs) and transfer models such as
MobileNet and DenseNet121, the system attains
accurate plant classification of medicinal plants. The
preprocessing methods like image resizing,
reshaping, and data augmentation improve input data
quality, which results in enhanced model
performance. With an easy- to-use interface, users
can upload a picture and receive relevant
classifications and information. This model greatly
benefits researchers, practitioners, and Ayurveda
enthusiasts to identify and know medicinal plants,
making sure that traditional knowledge is effectively
utilized with the help of contemporary AI- based
solutions. Overall, our study demonstrates that both
models are well- suited for classification tasks, with
DenseNet121 excelling in feature extraction and
MobileNet delivering a compromise between
accuracy and computational economy. To improve
performance even more, future research can
investigate model ensembling, data augmentation,
and hyperparameter adjustment.
6 FUTURE SCOPE
The system has immense potential for future
enhancements and widespread applications,
particularly in healthcare, agriculture, and research. A
key improvement would be the integration of Natural
Language Processing (NLP) for advanced text
Analysis of Ayurveda Leaves Using Deep Learning
625

extraction, enabling users to access Ayurvedic
knowledge from vast unstructured sources, including
ancient manuscripts, research publications, and
clinical reports. By implementing semantic search
capabilities, the system can deliver more precise and
contextually relevant results, significantly improving
its usability for researchers, healthcare professionals,
and enthusiasts. Additionally, expanding the dataset
to include high-resolution images of medicinal plants
from diverse geographic regions and environmental
conditions will improve the system's adaptability.
This will enhance the accuracy of plant classification,
ensuring consistent performance across different
climates, seasons, and growth stages.
A major advancement would be the development
of a real-time mobile application, revolutionizing
how users interact with the system. Incorporating
features such as image-based plant identification,
voice search, and offline access, the app would serve
as a valuable tool for farmers, herbalists, scientists,
and healthcare practitioners. Users could instantly
recognize medicinal plants, learn about their
therapeutic applications, and receive Ayurvedic
treatment suggestions, even in remote areas. Adding
community-driven features, such as expert
consultations, discussion forums, and user-
contributed data, would further enhance knowledge
sharing and engagement.To strengthen security and
data integrity, Blockchain technology can be
employed for secure and verifiable storage of
Ayurvedic information. Blockchain’s decentralized
nature will prevent unauthorized modifications,
preserving the authenticity of medicinal plant data
and ensuring reliable access to traditional knowledge.
This will be particularly useful for maintaining
historical records of Ayurvedic treatments and
formulations while preventing misinformation.
Moreover, incorporating Artificial Intelligence (AI)
for disease prediction and Ayurvedic treatment
recommendations will enhance the system’s
capabilities. AI-driven models can analyze plant
health, soil conditions, and environmental variables
to detect potential diseases and recommend
appropriate Ayurvedic remedies for both plants and
human ailments.
REFERENCES
AyurLeaf: A Deep Learning Approach for Classification of
Medicinal Plants. 2019 IEEE Region 10 Conference
pages 1–1.
Deep Herb: A Vision Based System for Medicinal Plants
Using Xception Features. In 2021 Research Scholar,
VTU-RRC, Visvesvaraya Technological University,
Belagavi.
Goodfellow et al.'s Deep Learning for Text Classification
and Sentiment Analysis (2016)
Gopal, A., Prudhveeswar Reddy, S., and Gayatri, V.
explored the classification of specific medicinal plant
leaves using image processing techniques. Their study,
published by IEEE in 2012, focused on leveraging
computational methods for accurate plant
identification.
J. Samuel Manoharan conducted research on the accurate
identification of herbal plant leaves using a machine
learning classifier. The study introduced a two-stage
authentication process to enhance detection accuracy
and was published in the Journal of Artificial
Intelligence and Capsule Networks (2021).
Ontology-BasedText Mining for Clinical Knowledge
Extraction (Smith et al., 2015)
Pharmacology of Medicinal Plants and Natural Products by
S.A. Dahanukar, R.A.Kulkarni, and N.N. Rege (2000)
Shashank M. Kadiwal, Gowrishankar S., Srinivasa A. H.,
and Veena A. presented a study on identifying Indian
medicinal plant species using deep learning techniques.
Their research was published in the 2022 4th
International Conference on Inventive Research in
Computing Applications (ICIRCA), focusing on
advanced computational methods for plant recognition.
Tarunsuresh, Deep Learning for Anthrocnose Diagnosis in
TurniLeaves. Science Open. 2021
The Text Mining Handbook: Advanced Approaches to
Analysing Unstructured Data by Ronen Feldman and
James Sanger (2007)
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
626
