
The Study of Communication Networks Using Vectors of an
Interconnection Network: A Review
Surya Prakash Pandey
1
, Rakesh Kumar Katare
1
and Charvi K.
2
1
Department of Computer Science, Awadhesh Pratap Singh University, Rewa, Madhya Pradesh, India
2
Velocis Systems Pvt. Ltd. A‑25, Sector‑67, Noida‑201301, Uttar Pradesh, India
Keywords: Interconnection Network, Vector Operation, Vector Symbolic Architecture (VSA), Vector Processing,
Perfect Difference Network (PDN), Hybrid Routing, q‑Learning.
Abstract: In this paper, we review the recent advances of the communication networks represented by the vector
networks and adaptive routing algorithms in relation to high performance computing (HPC) and edge
computing. You will look to see how these technologies improve computational efficiency, energy
optimization, and data transfer speeds; as well as challenges like scalability, congestion, and power
consumption. The interconnection nodes and edges of a vector operation and software-defined execution
models have become a significant solution to the rapid advances of a parallel cognitive computing and AI
workload. You will be looking at interconnection networks, one of the technologies What started ever since
mesh and torus topologies which had a huge effect on reliable and fast transfer of data, have evolved over the
time providing state of the art hierarchical and de Bruijn based networks which serve mainly with respect to
bandwidth efficiency and low latency. While all these improvements are very helpful, congestion, engineering
complexity and wiring limit scalability. Q-learning-based optimizations for routing algorithms, adaptive
routing, and hybrid adaptive routing have shown promise in improving some aspects of network performance,
such as reducing congestion and optimizing path selection. Here, we present a review of these innovations,
how they compare in effectiveness, and potential research avenues to optimize computing architectures for
next-generation HPC and edge applications. The adoption of these approaches is likely to not only overcome
existing performance and power limitations but also drive towards an ultimate transformation in the high-
speed computing system.
1 INTRODUCTION
Transformative computing paradigms have evolved
at a fast pace with the development of
communication networks (using vectors of
interconnection networks and routing algorithms)
during the last years. Heterogeneous processing with
more than one computing unit is popularly known as
High-performance computing (HPC) and edge
computing while the definition of a cross-device
process is known as an interconnection network in
vector operations (Kleyko et al., 2021).
Interconnection network topology design plays a
critical role in the performance and scalability of
parallel computer systems (Pandey et al. 2018), which
are determinative of latency and throughput. The
figure 1 illustrated Scalar vs. Vector Processing.
Newer topologies and analytical methods have been
investigated in recent years to overcome the
challenges of high-speed and reliable data transfer.
Also included are new trends in the area of network
topologies, such as Recursive Cube of Rings (RCR),
Star-Mobius Cube (SMQ), and Perfect Difference
Networks (PDN), analytical methods using vector
operations and logical operations on network
connectivity.
Figure 1: Scalar vs. Vector Processing.
530
Pandey, S. P., Katare, R. K. and K., C.
The Study of Communication Networks Using Vectors of an Interconnection Network: A Review.
DOI: 10.5220/0013886000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
530-537
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

Vector operations of an interconnection network
have attracted attention due to their capability of
making low-power AI computation and cognitive
processing, thereby being more suitable for nanoscale
AI (Cheikh et al., 2021). In fact, striking the right
balance between not just computing throughput but
also energy efficiency is still a major challenge,
especially in edge computing scenarios where power
is limiting the processing capacity.
Meanwhile, interconnection networks play a
critical role in scalable and high-speed data
transmission in HPC and manycore systems. Classic
topologies, like mesh and torus, have evolved to
hierarchical and de Bruijn-based architectures,
achieving increased bandwidth utilization and latency
reduction (Etzion, 2024). Although these solutions
improve scalability, challenges such as network
congestion, wiring complexity, and engineering
overheads remain (Lu & Lai, 2022). With the
expansion of computing systems, this has highlighted
the need for adaptive and intelligent routing
algorithms.
To overcome these challenges, hybrid routing
mechanisms that combine both static and adaptive
routes have been proposed by researchers. Several
AI methodologies, such as congestion control
mechanisms based on Q-learning or the concept of
Software Defined Networking (SDN), have shown
encouraging improvement regarding the path
selection and reduction of latency (Chen et al., 2020).
Nonetheless, optimizing these strategies for real-
time applications with reduced overheads remains an
open research direction. When evaluating cutting-
edge advances and highlighting critical hurdles, the
purpose of this study is to share perceptions about
future trajectories and research paths in this field of
high-speed computing architectures.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Vector Symbolic Architectures for
Nanoscale Hardware
Vector Symbolic Architectures (VSAs) have gained
attention as a computing paradigm suitable for
nanoscale hardware and for artificial intelligence
problems. Kleyko et al. the figure 2 illustrated the
Flowchart of Data Encoding and Transformation in VSAs
Use of VSAs: Rausendorff et al. (2021) elaborate on
the potential of VSAs in achieving operations in
superposition, necessary for nanoscale devices. VSAs
support AI-based cognitive operations and
combinatorial search problems via distributed
representations.
Figure 2: Flowchart of Data Encoding and Transformation
in VSAs.
Perhaps the most interesting VSA model,
Hyperdimensional Computing (HDC), where high-
dimensional binary or real-valued vectors are used
for parallel information processing, is discussed
herein. The possible applications of VSAs in low-
power, hardware-efficient designs enable them to
meet the future requirements of emerging AI
workloads running on nanoscale chips. This work
lays the groundwork for the integration of VSAs with
next-generation computing architectures including
cognitive computing and neuromorphic processing
(Kleyko et al, 2021).
2.2 Vector Coprocessors for
Multithreaded Edge-Computing
Cores
Processing units must be high-performance and
energy-efficient to handle computational workloads
on Edge. Cheikh et al. (2021) work on micro-
architectural enhancement of RISC-V-based
multithreaded edge-computing cores with
customized vector coprocessors. Klessydra-T is
introduced as a coprocessor that achieves better
energy efficiency in the training phase with low
hardware cost . Sentinel learns benefits from Sol and
improves power efficiency to stay versatiles during
training phase. We examine the strengths of highly
interleaved multithreading (IMT) with vector
coprocessing, introducing a general methodology for
leveraging this approach to accelerate edge
workloads. Key Takeaway l Klessydra-T achieves up
to 44× speedup over state-of-the-art in parallel
workloads, but suffers from execution stalls caused
by resource contention in some functional units.
Some key points include that vector processing can
be well integrated into edge computing cores to help
gain significant performance; however, optimizing
the architecture will help address potential
bottlenecks (Cheikh et al., 2021).
The Study of Communication Networks Using Vectors of an Interconnection Network: A Review
531

2.3 Interconnection Networks and
Their Optimization
Interconnect networks are widely used in high
performance computing (HPC) and parallel
processing. Etzion (2024) investigates various
network topologies specifically addressing their
computational efficiency in routing and
implementation of permutations. The paper
examines de Bruijn graphics and their involvement in
parallel computations, and indicates that network
layout optimization could boost data communication
efficacy. Lu and Lai (2022) are also concerned about
the interconnection networks in Top500
supercomputers and thus identify the main challenge
(scalability header) in exascale computing related to
their performance analysis also highlights power
consumption as a primary lifecycle issue.
Figure 3: Timeline of Interconnection Network
Architectures.
The figure 3 illustrated Timeline of
Interconnection Network Architectures. The results
showed that (1) although improving the overall
efficiency of the system, engineering complexity and
reliability of high-performance interconnection
networks was still an obstacle (Lu & Lai, 2022).
2.3.1 Recursive Cube of Rings (RCR)
Katare et al. (2020) proposed Recursive Cube of
Rings (RCR), a family of interconnection network
topologies. RCRs: Adding ring edges recursively.
Fixed degree, small diameter, wide bisection width /
symmetry / fault tolerance is some of the properties
of these topologies that are useful in building
scalable parallel machines. The design of the
interconnection network topology is critical for the
scalability of parallel computer systems (2023). The
paper also discusses the tradeoff between desirable
features like having a low diameter and a fixed degree
which are often at odds in previous works on
networks.
2.3.2 Star-Mobius Cube (SMQ)
Pattanayak et al. (n.d.) describe a novel
interconnection network topology, called Star-
Mobius Cube (SMQ). SMQ topology is a product
graph of star graph and Mobius cube. The authors
use multiple topological and performance metrics,
including diameter, cost, average distance, and
message traffic density to evaluate SMQ. Their
analysis shows that SMQ would be a viable
competitor to current networks, with better
performance. Moreover, the embedding and
broadcasting properties of the SMQ topology are
studied in this paper.
2.3.3 Perfect Difference Networks (PDN)
Katare et al. T. S. et al. (2021) Explore Structural
Relationships between Processors in Perfect
Difference Networks (PDN). PDNs are expressed as
a graphical model, with processors as the nodes and
links as the edges. The interconnection network
architecture is highly dependent on communication
complexity and data structures which is being
highlighted in the study. First, to address the
structural algebraic features of PDNs, a processor
matrix is created to investigate the structural
algebraic correlations of PDNs. EDT, an introduction
to logical operations (AND and XOR) on matrices to
study connectivity. Bhardwaj and Katare (2018)
analyze connection features of PDNs using AND and
XOR logical operators and showcase that the result of
these operators applied to the incidence, circuit and
path matrices conveys connection information.
Katare et al. (2019) also perform bitwise connection
analysis using the connectivity matrix and matrices
constructed from existing nodes on the PDN, where
the nodes are treated as vectors engaged in vector
operations.
These heterogeneous interconnection network
topologies have different characteristics offering
trade-offs. For example, the hypercube networks have
low diameter but a logarithmic increase in node
degree with respect to network size, limiting
scalability. Topologies such as RCR and SMQ
attempt to find a compromise between these different
requirements, by providing fixed degree nodes and
small diameters, making them more suitable for
large-scale parallel systems. Skills: Based on data up
to October 2023, analytical methods using processor
matrices and logical operations are developed for
network connectivity of which PDNs are one.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
532
2.4 Congestion-Aware Routing in
Network-on-Chip (NoC)
NoCs are now a fundamental architecture element in
digital circuits and SoCs, and thus efficient routing
algorithms are needed to prevent traffic congestion.
Ahmad et al. (2021) develop a congestion-aware
routing approach that minimizes latency and
maximizes throughput through data flow
manipulation via dynamic handling of network
congestion levels. The figure 4 illustrated the AI-
Driven Adaptive Routing Their approach enables
effective bandwidth utilization at the same time
provide high-speed communication between cores.
Figure 4: AI-Driven Adaptive Routing.
Despite the improvement in overall efficiency, the
emergence of network congestion and issues with
fault tolerance are common concerns for large-scale
NoC implementations. In a similar vein, Kaleem and
Isnin (2021) survey routing algorithms in NoCs, and
stress the importance of scalable and energy-efficient
designs. While their survey shows that improvements
in routing techniques will yield better performance, it
does highlight congestion and energy consumption
as botttlenecks (Kaleem & Isnin, 2021).
2.5 Cost-Effective High-Performance
Interconnection Networks
Rahman et al. (2020) proposed a hierarchical
interconnection network enables the so-called TFBN
for massively parallel computing (MPC) systems.
TFBN, which has better communication performance
in terms of diameter and arc connectivity compare
with traditional network topologies (torus, mesh and
TESH) are also shown in the study. This has the
essential advantage of TFBN that it is both cost-
effective and works extremely well, but it increases
wiring complexity, remaining a challenge for
applying it in large scales. However, TFBN can
maintain an optimal trade-off between cost and
efficiency for the next generation of parallel
computing systems (Rahman et al., 2020).
2.6 Vector-Deductive Memory-Based
Transactions for Fault Simulation
March 10, 2021: Fault simulation is an important
aspect of hardware reliability evaluation. Devadze et
al. (2022), propose an entirely new vector-deductive
memory-based transaction8 approach for fault-as-
address simulation. Using read-write memory
transactions to model faults without logic, their
technique allows deterministic vector-quantum
computing measurements. This method improves
automaticity for fault analyse but also decreases
computational load. The study, however, comments
that the quadratic complexity regarding register
operations is still a limitation of this method.
Likewise, Hahanova (2023) builds upon the concept
of vector-deductive, refining it to become a method
where a matrix of deductive vectors is created for
FPGA and ASIC circuits, increasing fault
propagation analysis efficiency. These studies are
important for the digital circuit fault modeling and
play an important role in the increasing of parallel
processes (Devadze et al., 2022; Hahanova, 2023).
2.7 Software-Defined Vector
Processing in Manycore Fabrics
A recent trend among modern computing
architectures is the use of software-defined
techniques to improve the performance of hardware.
Bedoukian et al. (2021) put forth a software-defined
vector processing model customised to manycore
execution plans, gaining a 1.7× efficiency
improvement over a traditional MIMD execution
environment.
Figure 5: System Architecture of Software-Defined
Execution.
Their study shows that tiled architectures can
switch dynamically between manycore and vector
execution modes, for another 22% energy reduction.
The figure 5 shows the System Architecture of
Software-Defined Execution. These studies highlight
the promise of software-defined processing to attain
The Study of Communication Networks Using Vectors of an Interconnection Network: A Review
533

a balance between performance and power savings in
high-performance computing systems (Bedoukian et
al, 2021)
2.8 Adaptive Routing in InfiniBand
Networks
InfiniBand (IB) is commonly used in HPC cluster
high-speed interconnection. Rocher-Gonzalez et al.
2022), proposed adaptive routing mechanisms to
improve traffic balance and networking efficiency.
The research recommends adaptive routing not only
reduces congestion and improves utilization at the
expense of more complex workload balancing, but
also introduces unfair flow distribution and
congestion spreading. Hybrid routing strategies that
combine static and adaptive techniques also show
promise in alleviating these limitations (Rocher-
Gonzalez et al. 2022).
Interconnection networks can be used enormously
well if efficient routing algorithms are developed.
For example, Katare et al. (2020) described a general
deadlock-free routing algorithm for RCR networks,
and Pattanayak et al. (n.d.) that present routing
algorithms for the SMQ topology.
2.9 Adaptive Routing in Silicon
Photonic Interconnects
Silicon photonic interconnects are emerging as a
promising technology for high-speed, low-power
data communication in interconnects on chip. Chen et
al. proposes adaptive routing algorithm, Dijkstra-Q
in (2020), which combines multiple-path-finding
Dijkstra’s algorithm and Q-learning to improve path
selection. Experimental results indicate that the
proposed method constantly achieves better
performance than random, traditional Dijkstra and
standalone Q-learning-based solutions in terms of
load balancing, congestion and insertion loss. The
initial latency in path setup remains an issue, and
continued optimizations for real-time
implementations need to be considered (Chen et al.,
2020).
3 INFERENCE FROM
LITERATURE
The surveyed approaches show that communication
networks leveraging an interconnection network
vector, vector processing architectures, which
significantly improve computation throughput in both
edge and high-performance computing paradigms. In
particular, VSAs facilitate concurrent cognitive
processes, while software-defined processing
improves energy efficiency. Yet, the intricate
balance between processing power and energy
efficiency in edge-based architectures presents a
challenge. Interconnection networks are typically
analyzed using mathematical and computational
techniques that capture their structural and
functional characteristics. Incidence, circuit, path
and processor matrices make a powerful way of
representing network topologies and analysing
connectivity. As shown by Bhardwaj & Katare
(2018), logical operations like AND and XOR
executed on these matrices can expose important
knowledge about the network function. Moreover,
representing the node connections as vectors and
performing vector operations, as demonstrated by
Katare et al. (2019), but enabling detailed
exploration of links and auto-configuration of the
network.
Interconnection network is a known bottleneck in
manycore and exascale systems. This transition from
classic torus and mesh topologies to hierarchical and
de Bruijn-based networks has resulted in better
acting bandwidth utilization and reduced latency. But
engineering complexity and wiring limits make large
scale implementations very difficult. Routing
algorithms that take congestion into account when
determining paths through switches (congestion-
aware routing) and routing algorithms augmented
with artificial intelligence (AI-enhanced routing) are
also crucial for high speeds to improve latency in
NoC and HPC interconnects, such as found in
InfiniBand2 and silicon photonic interconnects.
One of the notable trends in this context is the
adoption of hybrid routing and networking
architectures that integrate static and adaptive routing
mechanisms to facilitate optimal path selection.
While AI-based algorithms such as Q-learning and
Software-defined Processing techniques adequately
improve efficiency in handling congestion, they
incur overheads that should be minimized through
optimization techniques.
4 KEY TAKEAWAYS
The table 1 shows the Vector Processing
Enhancements in High-Performance and Edge
Computing. The table 2 shows the Table 2: Advances
in Interconnection Networks and Routing Strategies.
Table 3 shows the Hybrid Adaptive Routing andAI-
Based Optimization.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
534
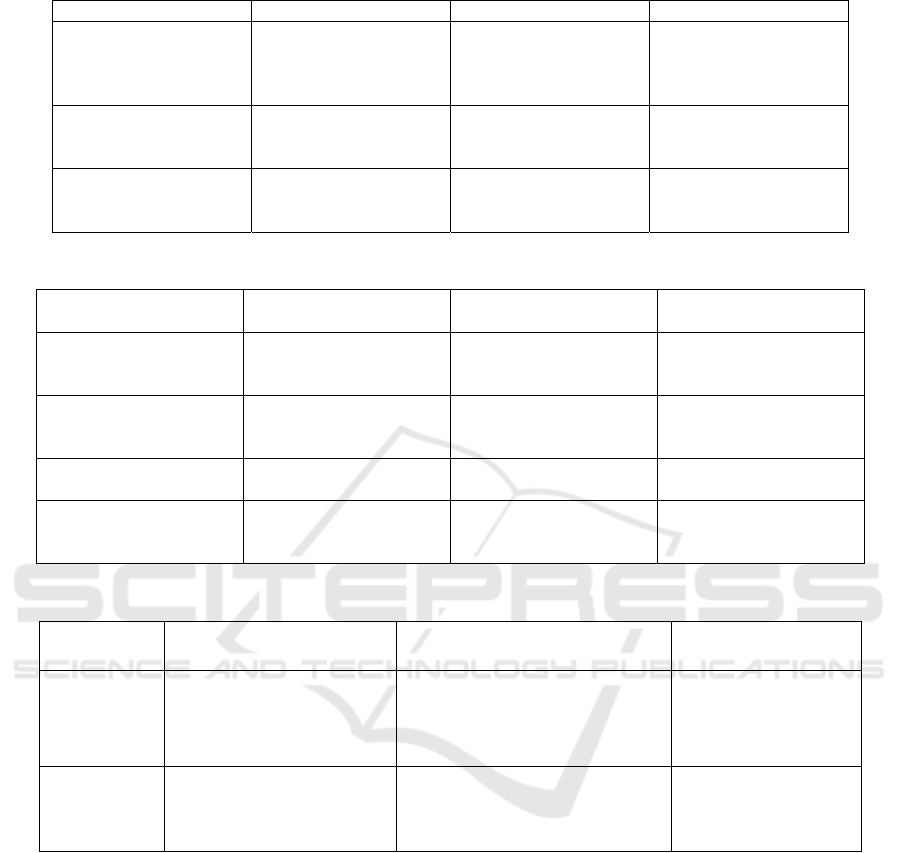
Table 1: Vector Processing Enhancements in High-Performance and Edge Computing.
Stud
y
Method/A
pp
roach Ke
y
Findin
g
s Challen
g
es
Kleyko et al. (2021)
Vector Symbolic
Architectures (VSAs)
for AI and nanoscale
computing
Improved parallel
cognitive processing
and low-power AI
computations
Limited scalability in
large-scale AI
applications
Cheikh et al. (2021)
RISC-V-based vector
coprocessor (Klessydra-
T)
44× speedup in parallel
workloads for edge
computing
Execution stalls due to
resource contention
Bedoukian et al. (2021)
Software-defined vector
processing in manycore
fabrics
1.7× execution
efficiency, 22% energy
savings
Balancing power and
performance remain a
challenge
Table 2: Advances in Interconnection Networks and Routing Strategies.
Study
Interconnection/Routing
Metho
d
Key Findings Challenges
Etzion (2024)
Optimized de Bruijn
graphs for HPC networks
Improved efficiency in
parallel computing
networks
Engineering complexity
Lu & Lai (2022)
Performance evaluation
of interconnects in
Top500 supercomputers
Scalability and power
remain major concerns in
exascale computing
Reliability issues in
large-scale deployments
Rocher-Gonzalez et al.
(
2022
)
Adaptive routing in
InfiniBand networks
Reduced congestion,
im
p
roved
p
ath utilization
Traffic unfairness and
con
g
estion s
p
readin
g
Ahmad et al. (2021)
Congestion-aware
routing in NoC
Increased throughput and
reduced latency
Fault tolerance in large-
scale NoC
implementations
Table 3: Hybrid Adaptive Routing and Ai-Based Optimization.
Study
Hybrid Routing/AI
Approach
Key Findings Challenges
Chen et al.
(2020)
Dijkstra-Q (Dijkstra’s
algorithm + Q-learning) for
silicon photonic
interconnects
Improved path selection and
congestion management
Initial latency in real-
time path setup
Rahman et al.
(2020)
TFBN hierarchical network
for parallel computing
Low diameter, high arc
connectivity, and cost-
effectiveness
Increased wiring
complexity
5 CONCLUSIONS
Results: Much work has been done both on the end of
the routing algorithm to ensure high-performance
edge computing, such as mapping high-performance
data from low-coherence topologies, and on the
opposite end of the interconnection networks to build
performant communication networks; all of this is
covered in the literature reviewed. The vector
symbolic platforms (VSAs) are a low-power solution
to the nanocomputer AI implementations, and
provide a distributed representation suitable for
cognitive and neuromorphic computing. Energy-
efficient operations in widely-used multithreaded
architectures occur via accelerated processing
through vector coprocessors and software-defined
computing, which help boost edge computing
performance. On the other hand, interconnect
networks have evolved along with adaptive routing
algorithms to ameliorate congestion and latency,
especially in NoC and HPC solutions.
Though these innovations help improve
scalability, efficiency, and processing speed, issues
remain with network congestion, energy
consumption, and computational complexity. With
data ingestion models indicating that the incoming i/o
The Study of Communication Networks Using Vectors of an Interconnection Network: A Review
535

is very large and continues to grow, new trends such
as hybrid adaptive routing techniques, AI-driven
optimizations and software-defined execution models
to overcome these limitations. According to the
literature, there is an increasing transition from
traditional fault tolerant computing loops to
intelligent and self-optimizing network architectures
using AI, laying the groundwork for manycore and
exascale systems of tomorrow.
In this review we have highlighted recent efforts
in bridging novel interconnection network topologies,
such as RCR and SMQ, and novel analytical
techniques based on vector operations and logical
matrices. These advances are part of the continuing
work to build effective, scalable, and resilient
computer architectures for HPC ages and edge
computing.
5.1 Final Thoughts
1 Vector Processing and Software-Defined
Architectures
• VSAs and software-defined processing offer
significant performance improvements in AI-
driven workloads and edge computing.
• Energy efficiency remains a major concern, and
further optimization is needed to balance power
consumption and computational throughput.
2 Interconnection Network Challenges in NoC and
HPC
• Scalability and congestion control remain
persistent challenges in network-on-chip (NoC)
and high-performance interconnects.
• Hybrid network architectures (e.g., de Bruijn-
based networks and TFBN) offer performance
improvements but introduce design complexity.
3 AI-Driven and Hybrid Routing Strategies
• AI-enhanced routing algorithms like Q-learning
and adaptive routing mechanisms provide better
congestion management.
• Hybrid routing techniques that blend static and
adaptive methods offer a promising direction for
optimized data flow in high-speed
interconnects.
6 FUTURE WORK
To minimize initial latency and overhead in real-time
applications, upcoming research must aim at
improving AI-based routing strategies. Lastly, new
energy-efficient architecturing techniques for vector
processing and interconnection networks would yield
better scalability options. The next generation of
high-performance computing architectures will be
characterized by hybrid execution models that
incorporate software-defined processing and AI-
guided decision-making. Additionally, examining
hybrid architectures and incorporating advanced
analytical models for predicting network
performance under varying conditions would allow
for a deeper understanding of optimal routing
practices.
REFERENCES
Ahmad, K., Sethi, M. A. J., Ullah, R., Ahmed, I., Ullah, A.,
Jan, N., & Karami, G. M. (2021). Congestion-Aware
Routing Algorithm for NoC Using Data Packets.
Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing,
2021, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8588646
Bedoukian, P., Adit, N., Peguero, E., & Sampson, A.
(2021). Software-Defined Vector Processing on
Manycore Fabrics. International Symposium on
Microarchitecture, 392–406. https://doi.o rg/10.1145
/3466752.3480099
Bhardwaj, M., & Katare, R. K. (2018). Study of
connectivity using AND and XOR logical operation on
Perfect Difference Network for Parallel and Distributed
Systems. International Journal of Electronics, Electrical
and Computational System, 7(3).
Cheikh, A., Sordillo, S., Mastrandrea, A., Menichelli, F.,
Scotti, G., & Olivieri, M. (2020). Klessydra-T:
Designing Vector Coprocessors for Multi-Threaded
Edge-Computing Cores. arXiv: Hardware
Architecture. https://doi.org/10.1109/MM.2021.30509
62
Cheikh, A., Sordillo, S., Mastrandrea, A., Menichelli, F.,
Scotti, G., & Olivieri, M. (2021). Klessydra-T:
Designing Vector Coprocessors for Multithreaded
Edge-Computing Cores. IEEE Micro, 41(2), 64–71.
https://doi.org/10.1109/MM.2021.3050962
Chen, Y., Li, H., & Liu, F. (2020). An Adaptive Routing
Algorithm Based on Multiple-Path-Finding Dijkstra’s
and Q-learning Algorithm in Silicon Photonic
Interconnects on Chip. International Conference on
Communication Technology, 117–120. https://doi.org/
10.1109/ICCT50939.2020.9295898
Devadze, D., Davitadze, Z., & Hahanova, A. (2022).
Vector-Deductive Memory-Based Transactions for
Fault-As-Address Simulation. International Conference
on Dependable Systems, Services and Technologies, 1–
6. https://doi.org/10.1 109/DESSER
T58054.2022.10018769
Etzion, T. (2024). Interconnection networks (pp. 405–457).
Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-44-
313517-0.00018-4
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
536

Ganaie, Gh., & Sheetlani, J. (2020). Study of Structural
Relationship of Interconnection Networks (pp. 379–
385). Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-
981-32-9690-9_39
Hahanov, V., Litvinova, E., Shevchenko, O. V.,
Chumachenko, S., Khakhanova, H., & Hahanov, I.
(2022). Vector Models for Modeling Logic Based on
XOR-Relations. 2022 IEEE 16th International
Conference on Advanced Trends in Radioelectronics,
Telecommunications and Computer Engineering
(TCSET), 823–828. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcset5563
2.2022.9766894
Hahanova, A. (2023). Vector-deductive Faults-as-Address
Simulation. International Journal of Computing, 328–
334. https://doi.org/10.47839/ijc.22.3.3227
Kaleem, M., & Isnin, I. F. B. (2021). A Survey on Network
on Chip Routing Algorithms Criteria (pp. 455–466).
Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-
15-6048-4_40
Katare, R. K., Premikar, S., Singh, N., Tiwari, S., & Katare,
C. K. (2019). Vector Operation on Nodes of Perfect
Difference Network Using Logical Operators.
International Journal of Advanced Research in
Computer Science, 10(6), 29-39. https://doi.org/10.26
483/ijarcs.v10i6.6485
Katare, R. K., Singh, M., Singh, N., Pandey, A., Katare, C.,
& Bharadwaj, M. (2020). Recursive Cube of Rings and
Their Implementation in Interconnection Networks.
International Journal of Advances in Engineering and
Management, 2(10), 463-467.
Katare, R. K., Singh, N., Pandey, A., & Katare, C. (2021).
Study of Communication Structural Relationship
between Processors of Parallel and Distributed System.
International Journal of Scientific Research in
Computer Science, Engineering and Information
Technology (IJSRCSEIT), 7(5), 21- 27. https://doi.or
g/10.32628/CSEIT21759
Kleyko, D., Davies, M., Frady, E. P., Kanerva, P., Kent, S.
J., Olshausen, B. A., Osipov, E., Rabaey, J. M.,
Rachkovskij, D. A., Rahimi, A., & Sommer, F. T.
(2021). Vector Symbolic Architectures as a Computing
Framework for Nanoscale Hardware. arXiv: Hardware
Architecture. http://export.arxiv.org/pdf/2106.05268
Liu, H., Wei, H., Puchinger, S., Wachter-Zeh, A., &
Schwartz, M. (2021). On the Gap Between Scalar and
Vector Solutions of Generalized Combination
Networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,
67(8), 5580–5591. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIT.2021
.3065364
Lu, P., & Lai, M. (2022). A Survey of High-Performance
Interconnection Networks in High-Performance
Computer Systems. Electronics, 11(9), 1369.
https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11091369
Lv, Y., Lin, C.-K., & Wang, G. (2021). An Exchanged 3-
Ary n-Cube Interconnection Network for Parallel
Computation. International Journal of Foundations of
Computer Science, 32(03), 235–252. https://doi.or
g/10 .1142/S0129054121500131
Pandey, Surya Prakash, Katare, Rakesh Kumar. (2018).
Application of Fixed-Point Algorithm in Parallel
Systems, International Journal of Computer Sciences
and Engineering, Vol.6, Issue 6, https://doi.org/10.26
438/ijcse/v6i6.714719
Pattanayak, D., Tripathy, D., & Tripathy, C. R. (2014).
Star-Mobius Cube: A New Interconnection Topology
for Large Scale Parallel Processing. International
Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational
and Applied Sciences (IJETCAS).
Rahman, M. M. H., Al-Naeem, M., Ali, M., & Sufian, A.
(2020). TFBN: A Cost-Effective High-Performance
Hierarchical Interconnection Network. Applied
Sciences, 10(22), 8252. https://doi.org/10.3390/APP1
0228252
Rocher-Gonzalez, J., Gran, E. G., Reinemo, S.-A., Skeie,
T., Escudero-Sahuquillo, J., García, P., & Quiles, F. J.
(2022). Adaptive Routing in InfiniBand Hardware.
2022 22nd IEEE International Symposium on Cluster,
Cloud and Internet Computing (CCGrid), 463–472.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ccgrid54584.2022.00056
Vazifedunn, S., Reza, A., & Reshadi, M. (2022). Low‐cost
regional‐based congestion‐aware routing algorithm for
2D mesh NoC. International Journal of
Communication Systems, 36(1). https://doi.org/10.10
02/dac.5360
Vector-Deductive Memory-Based Transactions for Fault-
As-Address Simulation. (2022).
https://doi.org/10.1109/dessert58054.2022.10018769
Vector-deductive Memory-based Transactions for Fault-as-
address Simulation. (2023). Èlektronnoe
Modelirovanie, 45(1), 3–26. https://doi.org/10 15407/
emodel.45.01.003
The Study of Communication Networks Using Vectors of an Interconnection Network: A Review
537
