
A Survey on IoT and Blockchain‑Enabled Systems for Automobile
Tracking, Security and Voice Recognition
V. Saranya
1
and J. Deepa
2
1
Department of CSE, Adhiyamaan College of Engineering, Hosur.635109, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of CSE, Easwari Engineering College, Ramapuram, Chennai. 600089, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Internet of Things, Automobile Tracking, Security, Block Chain, Voice Recognition.
Abstract: Many studies have developed new endeavors of automobile tracking, vehicle monitoring, and secured systems
by incorporating IoT and block-chain technology in this paper. The proposed framework is one which at its
core utilizes GPS, GSM, and MMS, working together to create a real-time system addressing issues such as
vehicle theft and accidents. If the vehicle is stolen, the IoT sensors sense unauthorized access to the vehicle,
stops the vehicle engine and captures the image of the driver. This data is transferred securely via blockchain
protocol, which preserves data integrity and prevents manipulation through unauthorized methods. Likewise,
in the event of an accident, the system will also make a note of the car’s location and image of the driver and
send it to the registered emergency contacts or the owner, providing timely assistance. In this context, although
blockchain is very critical for implementing secure, decentralized and immutable data communications inside
the framework. This technology solves the privacy and security problems in IoT network. Additionally, the
system is complemented by the voice recognition capabilities of AI for developing user interaction.
Autonomous systems powered by advanced algorithms allow drivers to operate many functions of their
vehicles while maintaining a hands-free experience – a game changer for convenience and safety. The survey
covers previous solutions, technological developments, and challenges of deploying these systems. It
highlights challenges including scalability, latency and integration costs as prohibitive barriers to adoption,
alongside possible solutions like leveraging edge computing, hybrid blockchain solutions, and better noise-
filtering in voice recognition. This architecture highlights the revolutionary impact achievable through the
merger of IoT and Blockchain technologies. This new method strives to reimagine traditional techniques with
a focus on security, efficiency, and solving current challenges, all to enhance the landscape of vehicle tracking
and monitoring.
1 INTRODUCTION
Natural Language processing the Internet of Things
(IoT) and blockchain technologies have evolved
tremendously and have incorporated countless
industries by providing novel solutions for
automobile security, monitoring, and user interaction.
The combination of all these technologies can
represent a paradigm shift in how vehicles are
tracked, stolen, and accidents are managed,
improving the general user experience thanks to
improvements such as voice recognition systems.
InThis paper investigates how the current state of the
art for Applications of IoT and Blockchain can have
a significant impact on the automobile systems. IoT
is a leading enabler of immediate data collection,
communication, and integration of devices through
GPS, GSM and onboard vehicle sensors. IoT in the
automotive sector: IoT enabled systems facilitate the
accurate location tracking, monitoring status and
events detection, so as vehicle owners can get real-
time notifications in case of car theft/unauthorized
access. GSM technology is used for connecting things
together and can ensure continuous communication
among connected devices, and multimedia messaging
service (MMS) is used for the transmission of images
or recordings required in emergencies to appropriate
stakeholders.
Blockchain technology builds upon IoT
technology by addressing important safety and
privacy issues. The tamper-proof, decentralized and
sys-free nature of blockchain ensures that data
collected from the IoT devices, is securely stored
without risks from unauthorized access or data
Saranya, V. and Deepa, J.
A Survey on IoT and Blockchain-Enabled Systems for Automobile Tracking, Security and Voice Recognition.
DOI: 10.5220/0013885800004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
519-529
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
519

manipulation. Seamlessly integrating blockchain
brings added transparency and accountability to
automotive systems, especially in cases of theft or
accidents. For example, the driver’s image and
location data can easily be stored and exchanged
through blockchain in an encrypted manner to
prevent fraudulent claims or unauthorized use. AI-
powered voice recognition systems also add an extra
dimension of innovation and are being integrated
into automobile platforms. Employing complex
neural networks and deep learning algorithms, these
systems allow for natural, hands-free interaction,
enabling voice command control of vehicle functions.
This eliminates distractions and keeps the focus on
the road, which is critical in complex driving
situations. Noise-reduction technologies and
preprocessing units that enhance the reliability of
voice recognition systems, enabling the newly
developed voice recognition systems to801975738 be
effective even for
applications7875406606234824018 under noisy
environments. Though, there are challenges that
prevail while merging IoT with blockchain in
automobiles. Scalability IOT based networks
nowadays need to handle pretty large amounts of
data, and where IoT is in question; scalability means
a lot. Latency, or the delay in the transmission of
real-time data, is another factor to consider,
especially for applications that require immediate
feedback, like accident detection. Moreover, the
expensive costs associated with integrating IoT
devices, blockchain infrastructure, and AI-driven
technologies serve as a stumbling block for mass
adoption. To solve these problems, edge computing
developments are being investigated. This allows for
reduced latency to create a faster response, by
processing data at the edge. Public and private
blockchain hybrids. Optimize security and
performance. AI: Voice Recognition AI research
continues to improve voice recognition AI, with a
focus on developing context-aware systems and noise
filtering techniques to provide more accurate and
reliable AI-driven interfaces. Responsibilities and
Blockchain Integration The merge of IoT and
blockchain is creating transformative opportunities
for automobile security and monitoring. Using a
combination of GPS, GSM, MMS and voice
recognition, these systems claim to be able to provide
greater safety, protection from theft and user
interaction. Continued focus on solving existing
issues and looking to new technology will shape and
improve these solutions for the future to come,
allowing us to reach the next generation of secure,
efficient and user-friendly intelligent transportation
systems.
2 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
These three components turn a smart car into a secure
automobile, with benefits across IoT, blockchain, or
voice recognition technologies. The combination of
these technologies allows for real-time monitoring
and secure data transmission as well as improved user
experience, tackling important matters such as
vehicle theft, motor vehicle accidents and user
accessibility.
2.1 Internet of Things (IoT)
Modern automobile systems rely on the Internet of
Things (IoT) to connect physical devices in real-time
to the internet to collect, share, and communicate
data. IoT allows vehicles to work as interlinked
entities and communicate real-time information
about their condition, location, and surrounding
environment. GPS (Global Positioning System): GPS
is an integral part of IoT in automobiles, enabling
precise location detection. It’s an important
component in tracking vehicles when they are stolen
or during an emergency, providing accurate location
information to vehicle owners or authorities. GSM
(Global System for Mobile Communication): GSM
enables constant communication between vehicles
and centralized systems. This allows for real-time
alerts and notifications to be sent in case of
unauthorized access, movement detection, or
accident alerts.
MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service) — MMS
technology will make IoT-enabled systems richer by
enabling the sharing of multimedia content, e.g.,
images or videos. In such cases, MMS can be
leveraged to capture and dispatch real-time images of
unauthorized access and driver details to aid
situational awareness.
This features a two-way exchange of information
and an interface to monitor, achieve the floating of
information and assist in driving the automobile with
the support of sensors, specifically in8120 native
driving automobiles.
2.2 Blockchain
Automobile systems can leverage the power of
blockchain technology for data security and
transparency. As a distributed ledger, Blockchain
eliminates the single point of failure inherent in
centralized systems, creating a more resilient security
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
520

model for IoT deployments. Its decentralized and
immutable nature further enhances security by
making it nearly impossible to tamper or gain
unauthorized access to sensitive information,
addressing key weaknesses in IoT network security.
Decentralization Since no central control points exist
in blockchain solutions, any information about
vehicle status, location, and driver information is
stored in a decentralized network, lowering
vulnerability to breaches. Immutability: The ledger
system of a blockchain prevents data manipulation,
which improves the integrity and authenticity of
records, making this technology valuable in instances
of theft, as well as accidents. Secure Data Sharing:
Sensitive information like driver images or accident
details can be securely shared with relevant parties
(law enforcement or insurance companies, etc.)
without compromising privacy. Blockchain
technology, builds upon the idea of secure distributed
transactions and thus provides a strong foundation
for data communication in automobile systems and as
such ensures complete verifiability and security of
any interaction among the IoT devices. This not only
increases security but also fosters user trust through
transparency and accountability.
2.3 Voice Recognition
Hands-free operation and intuitive communication
are just some ways voice recognition technology is
changing the way we interact with our cars. More
advanced systems use artificial intelligence, deep
learning, and neural networks to comprehend and
respond to commands given in natural language.
Natural Language Processing: The conversing app or
voice recognition systems will be able to learn other
accents, languages, and contexts by using machine
learning algorithms, enhance their accuracy and
adaptability. Noise Cancellation: One of this system's
features is that it has the preprocessing units which
not only understand your command but also reduce
the effects of background noise so that the command
is interpreted correctly especially in the times when
you are traveling like highways or in urban settings.
Improved Accessibility: Voice recognition enables
drivers to execute critical capabilities, like
navigation, adjusting functions of the vehicle, or
searching for information. Voice recognition in
vehicles allows for great safety and convenience. For
instance, drivers can issue voice commands to enable
security measures, ask for navigation assistance or
file reports on emergencies, reducing the need for
manual input and keeping distractions at bay.
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
3.1 Internet of Things (IoT) Based
Vehicle Tracking Systems
With the advancement of technology, the huge impact
of Internet of things on vehicle tracking system has
changed the real-time monitoring and management
of vehicle. Majority of the IoT-based vehicle tracking
system technology are GPS and GSM that track the
vehicle position accurately and transfer it over
internet. For vehicle owners, fleet managers, and law
enforcement agencies, these systems can be
incredibly useful in providing instant notifications of
unauthorized movement or theft and responding
quickly to an accident. With the help of GPS, accurate
tracking of vehicle geographic locations is easy, and
GSM module is used for clearing data between
vehicle and monitoring system in real-time through
mobile phones, computer systems or cloud systems
(Kumar et al., 2023; Singh & Sharma, 2023).
Advantages of IoT-based tracking systems Theft
prevention, route optimization, and fleet management
are some of the key pros of such IoT-based tracking
systems. Real-time updates make it possible for
owners or fleet managers to monitor vehicles’ precise
locations, optimize routes for fuel efficiency and
switch to timely maintenance.
This allows for immediate detection of any
unauthorized movement or tampering and brings
obvious security advantages. Nevertheless, there are
a few challenges that prevent the widespread a
foundation of IoT-based tracking systems. As an
example, IoT device battery life can be a limitation,
especially in older vehicles that lack sophisticated
power management tools (Baba et al., 2023). Lastly,
the quality of the network connection is essential for
good performance, and outages in service will
compromise the system. Data privacy is also a
concern since constant data transmission carries the
potential for unauthorized access or data breaches and
sensitive location data is at particular risk of
exposure. Thus, the competent application of
encryption, data protection, and regulatory
compliance is paramount to the widespread
deployment of these systems (Meena et al., 2024).
3.2 Blockchain in Automotive Security
The explosion of interest in cryptocurrencies like
Bitcoin has brought with it a new paradigm of
blockchain technology, and in the context of Internet
of Things (IoT) networks, blockchain is being
explored for securing automobile systems. By
A Survey on IoT and Blockchain-Enabled Systems for Automobile Tracking, Security and Voice Recognition
521
providing a decentralized, immutable ledger,
blockchain secures data transfer between IoT devices
(i.e. vehicle sensors, GPS modules and
communication modules). This technology can be
used to protect against data tampering and
unauthorized access, as well as cyber-attacks (Sharma
et al., 2024; Gupta et al., 2023), thus making the
automobile industry a lucrative solution.
The inclusion of blockchain in vehicle security
systems has several benefits. A major advantage is
decentralized and tamper-proof storage of all actions
and messages passed through in the network: This
reduces the need for central authorities or
intermediaries where the risk of a single point of
failure is greater, and it builds the overall trust within
the system. It is also able to facilitate secure over-the-
air software updates for vehicles, making sure that
firmware and vehicle software are always up to date
without any risk of malware or data breaches (Patel
et al., 2023). Additionally, the inherent transparency
and auditability of blockchain boost privacy and
security, particularly for sensitive automotive use
cases like vehicle authentication, payment systems
and secure vehicle-to-vehicle communication.
While the potential for blockchain is promising,
there are obstacles to overcome in the automotive
industry. Scalability is still a major issue, as
blockchain networks can essentially slow down and
become inefficient when processing high amounts of
transactions, making it unlikely for use in real-time
applications such as vehicle tracking and
communication. Moreover, the energy consumption
of blockchain networks can be too high for practical
use in resource-constrained environments such as
vehicles (Verma et al., 2023) especially for numerous
of them containing proof-of-work algorithms.
Another challenge is integration with existing vehicle
systems and IoT infrastructure, requiring substantial
changes to existing communication protocols and
hardware. In that sense, before the full application of
blockchain technology to automobile security, there
are still many technical and practical obstacles to be
overcome, and it requires more research and
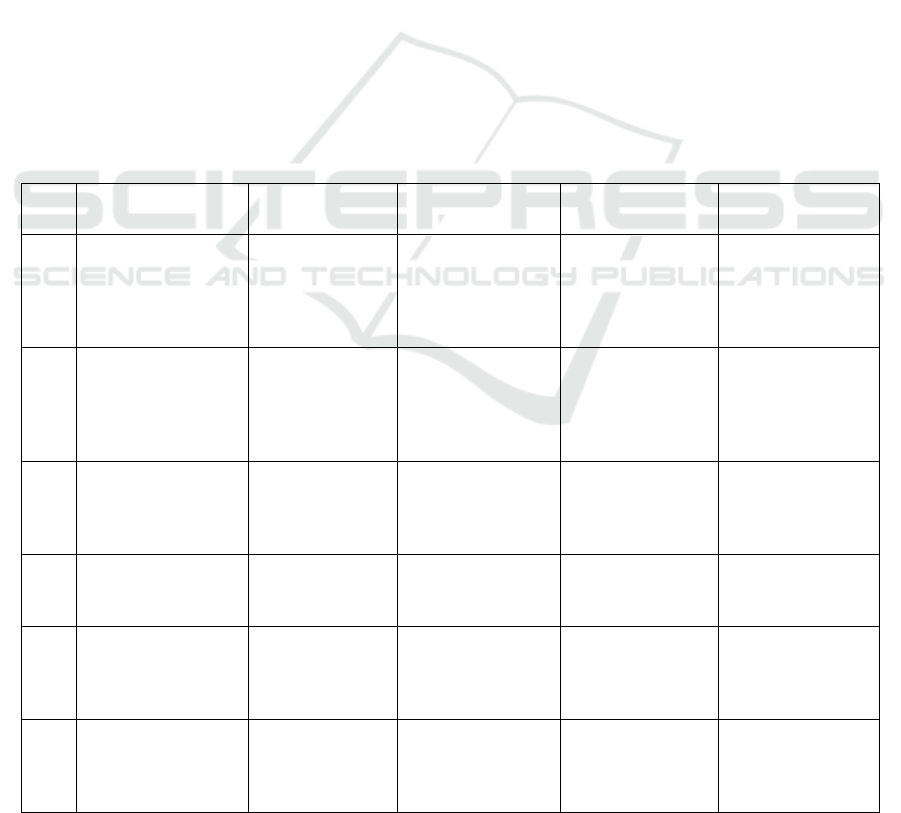
development effort in the future. Table 1 shows the
methodological comparison of smart vehicle tracking
and security approaches.
Table 1: Methodological Comparison of Smart Vehicle Tracking and Security Approaches.
Paper
No.
Methods Used Dataset Evaluation Metrics
Marite
(
Advanta
g
es
)
Demartite
(
Disadvanta
g
es
)
[1]
IoT-based vehicle
tracking using
GPS/GSM, energy
efficiency techniques
Simulated vehicle
data, GPS tracking
data
Energy
consumption,
system reliability,
real-time tracking
accurac
y
Real-time location
updates, energy
efficiency focus
High dependency on
external network
conditions, battery
constraints
[2]
Blockchain for IoT
security, smart
contracts for secure
communication
Not specified
(general
automotive
communication
data)
Security, data
integrity,
unauthorized access
prevention
Blockchain
provides strong data
security, tamper-
proof
communication
Scalability issues,
latency in real-time
vehicle systems
[3]
AI/Deep learning,
NLP techniques for
voice recognition
Not specified
(voice datasets,
car-related
interactions)
Recognition
accuracy, noise
resilience, real-time
p
rocessing accurac
y
Hands-free control,
reduced distractions
for drivers
Voice recognition
performance can
degrade in noisy
environments
[4]
IoT vehicle tracking
with enhanced
security protocols
IoT vehicle data,
GSM/GPS-based
location data
Data security,
privacy, system
intrusion detection
Enhanced security
features
High complexity in
integrating security
p
rotocols
[5]
Blockchain for
securing automobile
IoT systems, vehicle
data management
IoT-based vehicle
data, security logs
Data integrity,
system performance,
prevention of
unauthorized access
Secures vehicle
data, reduces risks
of cyber threats
High energy
consumption,
potential integration
issues
[6]
Blockchain
implementation for
secure vehicle
Automotive
communication
data
Data security,
communication
delay, data
transmission s
p
ee
d
Improves privacy
and prevents
tampering of
Scalability and
processing time
concerns in real-
time networks
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
522
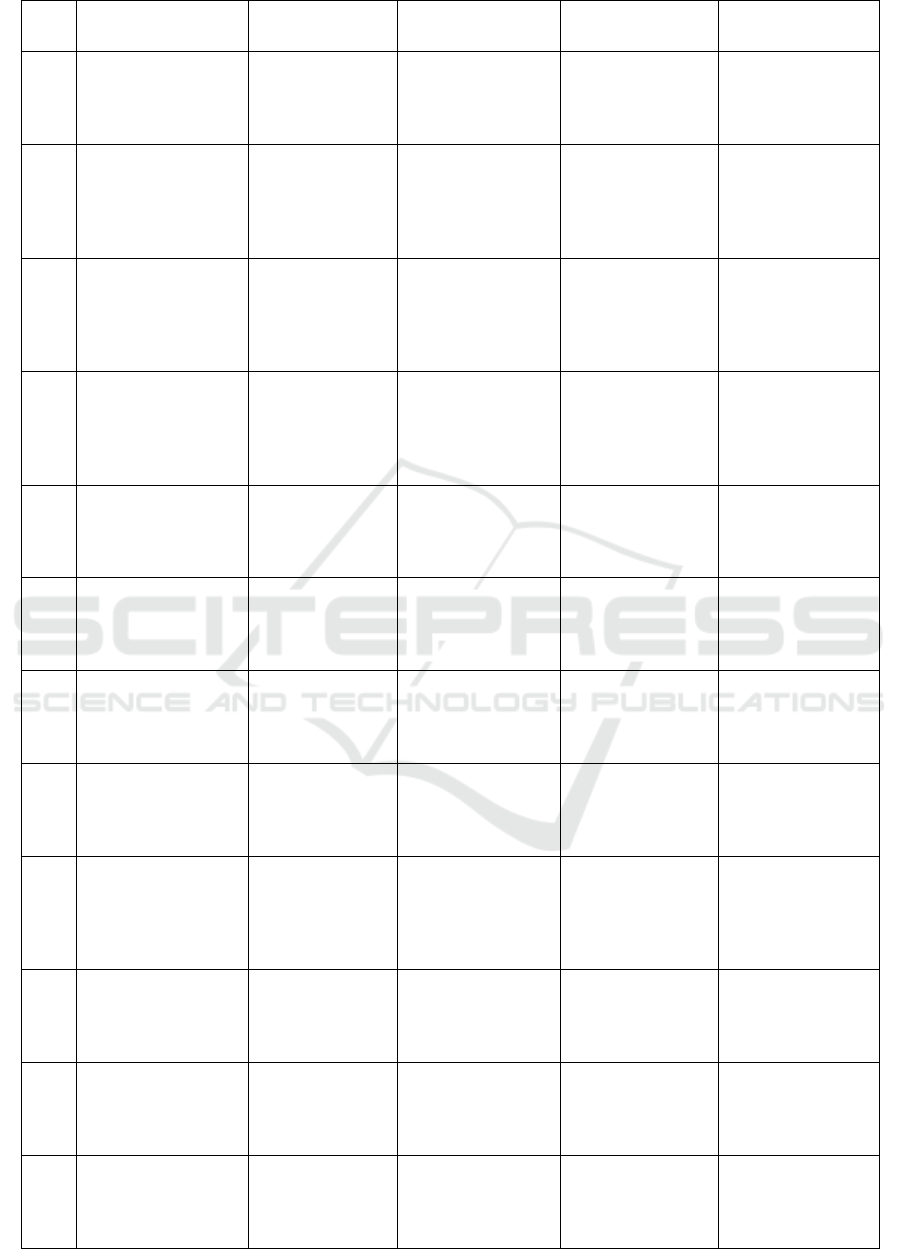
communication,
decentralized ledgers
transmitted vehicle
data
[7]
Real-time GPS
tracking, IoT-based
communication
GPS-based vehicle
data
Real-time tracking
accuracy, data loss
rate, communication
s
p
ee
d
Real-time location
tracking
Relies on stable
network
connections, GPS
si
g
nal interru
p
tions
[8]
Deep learning for
voice recognition,
safety alerts, real-time
processing
Voice interaction
data
Driver safety
enhancement,
recognition
accuracy, system
s
p
ee
d
Improves driver
experience, reduces
distractions
Environmental noise
can affect
recognition
accuracy
[9]
IoT integration with
GPS/GSM
technologies, real-
time tracking
Simulated data,
vehicle tracking
data
Accuracy of vehicle
location, energy
consumption,
communication
reliabilit
y
Efficient real-time
tracking, cost-
effective
Dependent on
external signals,
limited real-time
response
[10]
IoT for fleet
management,
optimized route
planning using GPS,
GSM, and IoT
Fleet tracking data
Route optimization
accuracy, system
efficiency, fleet
management
p
erformance
Optimized routes,
efficient fleet
management
Limited by network
connectivity and
data accuracy
[11]
Energy-efficient GPS
tracking, battery life
optimization
GPS tracking data
Power consumption,
system longevity,
real-time location
tracking accuracy
Reduces energy
consumption,
extends system
lifetime
Performance may
drop with energy
optimization
techniques
[12]
Cloud-based vehicle
tracking with IoT
integration, scalable
architecture
Cloud-based IoT
vehicle data
Real-time
monitoring, system
scalability, data
transfer rates
Scalable, low-cost
solution
Cloud dependency,
data latency
[13]
GSM-based vehicle
tracking, network
reliability in urban
areas
Urban traffic data
Data accuracy,
network reliability,
latency in urban
settin
g
s
Reliable in urban
environments, cost-
effective
Limited scalability
in rural or remote
areas
[14]
LPWAN technologies
for vehicle tracking,
IoT platform
comparison
LPWAN-based
vehicle data
System efficiency,
real-time tracking
accuracy, platform
p
erformance
Low-power, long-
range
communication
Limited bandwidth
and data transfer
speed
[15]
Blockchain for secure
communication in
vehicle systems,
decentralized data
exchan
g
e
IoT vehicle
communication
data
Data integrity,
secure transmission,
communication
latency
Enhances security
and privacy
High resource
consumption in
blockchain
operations
[16]
Blockchain for
vehicle-to-vehicle
communication,
secure data sharing
Vehicle
communication
data
Data security,
communication
speed, system
p
erformance
Enhances data
sharing security,
real-time
communication
Potential integration
complexity in
diverse vehicle
systems
[17]
Blockchain for secure
over-the-air software
updates in automotive
systems
Automotive
software update
logs
Update security,
data integrity,
update speed
Secure software
updates, reduces
tampering risks
Scalability issues in
large-scale vehicle
fleets
[18]
Blockchain for
decentralized vehicle
data management and
securit
y
Vehicle data logs,
real-time tracking
data
Data security,
privacy,
decentralized
mana
g
ement
Secure, tamper-
proof data
management
Real-time
transaction
processing
challen
g
es
A Survey on IoT and Blockchain-Enabled Systems for Automobile Tracking, Security and Voice Recognition
523
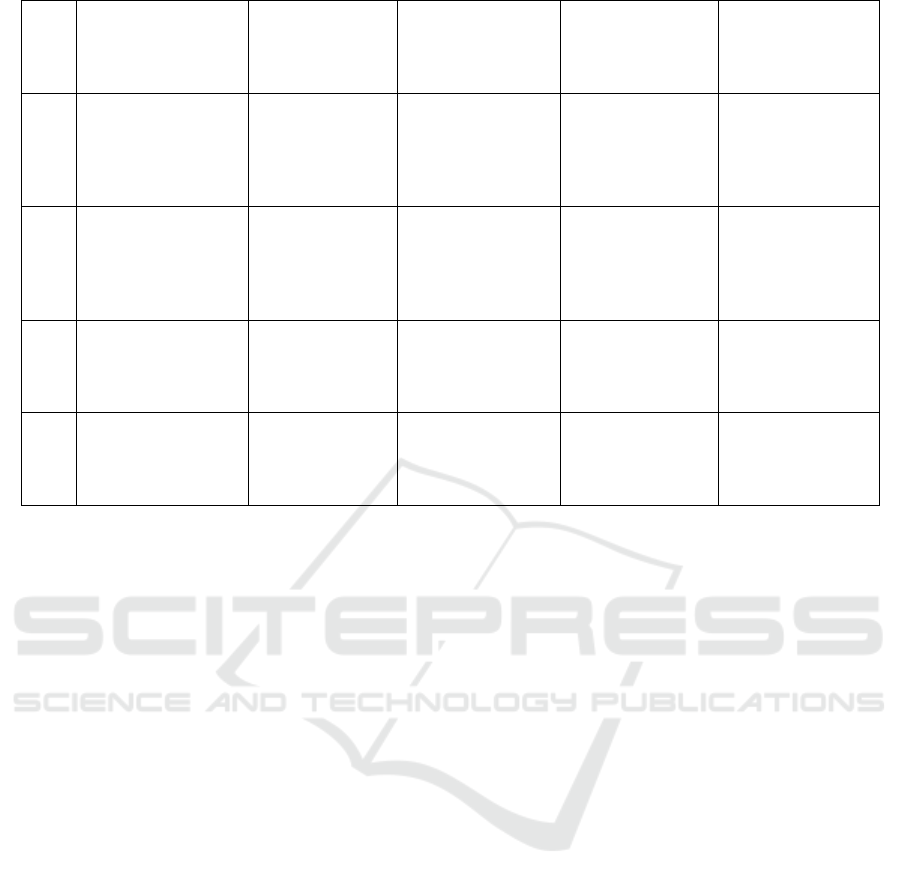
[19]
Blockchain in real-
time vehicle
communication, low-
latency transactions
Real-time vehicle
communication
data
Transaction latency,
scalability, data
integrity
Provides security,
reduces
unauthorized access
risks
Blockchain
processing time,
scalability in large
networks
[20]
Blockchain integrated
with edge computing
for secure, scalable
vehicle security
systems
Vehicle security
system logs
System scalability,
data integrity, edge
processing
efficiency
Reduces latency,
enhances scalability
Edge computing
complexity,
integration issues
with blockchain
[21]
AI, deep learning,
NLP for voice
recognition, driver
interaction
Automotive voice
data
Recognition
accuracy, user
interaction speed,
environmental noise
resilience
Improves driver
experience and
safety
Environmental noise
can reduce
recognition
accuracy
[22]
Deep learning for
multilingual voice
recognition, accent
adaptation
Voice interaction
data, automotive
command data
Recognition
accuracy across
accents, system
responsiveness
Multilingual
support, enhances
user experience
Performance
degradation in high
noise environments
[23]
AI-driven voice
recognition for
vehicle system
control
3.3 AI-Driven Voice Recognition
By harnessing machine-learning algorithms,
specifically deep learning models and natural
language processing (NLP), AI-based voice
recognition systems as seen in cars enable a hands-
free experience for the drivers while interacting with
the car. These systems allow drivers to use natural
language commands to control various functions in
the vehicle, including navigation, entertainment,
climate control, and communication. Getting
information through voice also improves driver
safety by avoiding distractions (Yadav et al., 2023).
Methods used in machine learning, like deep
learning models and natural language processing
(NLP), assist in improving the accuracy of voice
recognition systems. These systems can understand
voice commands with increasing accuracy, even in
complex settings like background noise, multiple
speakers, or with different accents. With the
advancement of voice recognition technology, it
provides a more integrated and intuitive user
experience, increasing the convenience and
functionality of in-car systems (Singh et al., 2023).
Additionally, voice-controlled AI can work with
additional vehicle technologies like navigation
systems and smart assistants to build a more custom
and productive driving experience.
AI voice recognition systems has several benefits
but still faces some challenges. A major problem is
the accuracy of voice recognition in busy
environments, like when there are several people
speaking or traffic noise is heavy. Although the
applications of deep-learning models have
progressed dramatically in voice perception abilities,
accuracy in every driving situation is difficult to
achieve (Jain & Sharma, 2023). There are also
privacy issues related to the collection and processing
of voice data. However, these systems pose a
dilemma in terms of data security and user privacy, as
they are designed to always listen and process voice
inputs. Sensitivity and security matter as it is
important to have voice data safely stored, processed,
and transmitted to gain users confidence (Kumar et
al., 2024)
4 PROPOSED FRAMEWORKS
To enhance the security and safety, and improve the
experience of interaction with vehicles, the proposed
system employs advanced technologies such as IoT,
Blockchain and AI. This framework is built to tackle
three of the most serious challenges that plague
modern transportation: vehicle theft, accident
reaction, and driver safety all accomplished through
natural voice interaction. The proposed system
addresses these significant concerns in automotive
security by leveraging IoT for instantaneous
monitoring, blockchain for secure data storage and
management, and voice recognition powered by AI to
augment user experience.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
524

4.1 Vehicle Theft Prevention
One of the main aims of this system is to avoid
vehicle stealing and unauthorized usage.
Conventional anti-theft systems based on basic
alarms and simple tracking systems can easily be
circumvented or penetrated. With the integration of
IoT sensors, GPS Technology, and usage of
blockchain for data storage and transmission, the
proposed system provides security to the vehicle.
IoT Sensors and GPS for Real-Time
Monitoring:
The system utilizes a network of IoT
sensors placed in the vehicle. These sensors monitor
for unauthorized access attempts, like a door opening
or tampering with the ignition system. The system
issues an alert when it detects unauthorized users and
can even automatically turn off the engine of the
vehicle, leaving the vehicle unable to move any
further. GPS system keeps updating the vehicle’s
position and location, thus continuously providing the
owner with the vehicle tracking in real-time.
MMS Technology for Driver Identification: In
order to make the security mechanism more secure,
the system uses Multimedia Messaging Service
(MMS) technology to capture the face image of the
driver during the theft attempt. A camera that is
mounted within the vehicle captures an image of the
driver’s face, which is securely transmitted and
backed up to the blockchain network. With this
transmission, only authorized users can have access
to the data, which will protect against tampering and
unauthorized dissemination of sensitive data. Being
immutable, data written into the blockchain (like the
captured image and location of the vehicle) cannot be
changed or deleted.
Blockchain for Data Integrity and Security:
The system can use blockchain for secure storage and
transmission of data. A decentralized ledger stores
all information that relates to vehicle access (location,
time, and image of unauthorized persons)
permanently, ensuring it cannot be tampered with.
Even if the vehicle's internal systems are
compromised, the blockchain data cannot be altered,
ensuring a verifiable source of evidence that can be
used in case of a theft or legal dispute.
4.2 Accident Response System
Vehicle safety is another response to accidents. In
case of an accident, the right information at the right
time could be the difference between life and death.
Traditional systems may alert you to danger, but can't
call emergency services with the relevant
information. Such a system can automate data capture
and transmission and enhance response to the
accident as immediate action can be taken.
• Automatic Mishap Detection: The framework is
outfitted with an effect recognition instrument
outfitted with accelerometers and sensors to
perceive quickly declining or impact, which can
flag a smash. When an accident is detected, the
system begins recording the vehicle’s GPS
location and taking a photo of the driver or the
inside of the vehicle with an in-car camera. This
data is automatically transmitted to the car
owner and emergency services.
• Conveying Details to Emergency Services: The
data (location and driver image) captured is
securely delivered to emergency contacts and
the nearest emergency services. This data is vital
information for first responders, as it allows
them to find the vehicle and get an idea of the
circumstances. Using blockchain, accident data
cannot be altered or tampered, so the
transmitted data is complete and secure.
• Blockchain for Data Security and Privacy: In the
accident response system, blockchain
technology serves a crucial role. Because data
are shared via a decentralized blockchain
network, no third party can access or modify
sensitive information. This can be especially
relevant for legal matters, where the integrity of
the evidence is paramount. In addition, in the
encrypted form of medical records, or
information about the contact number of the
person in case of an emergency, the system can
also store, this will also help in protecting
privacy and security.
4.3 Artificial Intelligence Based Voice
Interaction for Safety and Control
Driver distraction is one of the biggest causes of
collisions on our roads, and one of the most common
distractions comes from using in-car systems.
Whether they are climate control, music, or
navigation commands, these actions require manual
input that takes a driver’s attention off the road. The
current approach will be to create a handsfree control
mechanism for the car to eliminate the need to operate
controls with their hands.
Artificial Intelligence in Voice Recognition:
The AI-powered voice recognition system in the car
A Survey on IoT and Blockchain-Enabled Systems for Automobile Tracking, Security and Voice Recognition
525

is in charge of understanding the natural human voice
command and interpreting it in a mechanical sense.
With this system, a driver can control most of the in-
vehicle functions like navigation, climate control and
music simply by speaking. This minimizes the need
for manual interaction with the vehicle’s interface,
which could be distracting and dangerous while
driving. In addition to process quite different voice
input properly, the AI system is also trained to know
the context. Preparing Signals for Processing: Voice
recognition systems work most accurately when the
input signal is of high quality. In scenarios with a lot
of surrounding noise such as traffic or road noise, or
when the weather conditions are not favorable, voice
recognition may omit speech. The proposed system
consists of advanced signal preprocessing units that
eliminate background noise and distinguish the
driver’s voice. This process involves various
techniques that are applied to the input audio to
improve its quality, reduce noise, and enhance the
relevant features, which ultimately allows the system
to recognize and process voice commands in real-
time and dynamic environments.
Advanced & accurate voice recognition:
The
Voice Recognition technology is calibrated and tuned
to consider the specific vehicle infrastructure. This
integration enables functions like navigation, phone
calls, and entertainment systems to be controlled in
real-time via voice commands. Another aspect of AI
that is implemented in the system is Private Mode —
meaning that the system gets to know a driver, a little
bit at a time, and over the following drives learns the
preferences of the driver, to provide a more intelligent
experience. Through external systems, such as smart
home, the voice interface can create an
interconnected environment for the driver.
The suggested framework provides a
comprehensive strategy for addressing some of the
key challenges in the realm of automotive security,
safety, and user experience. The integration of these
IoT, blockchain, and AI technologies in the proposed
system provides an advanced and improved solution
not only for vehicle theft prevention and accident
response, but also for a safer and smarter driving
experience using voice recognition technology. IoT
sensors and GPS can be incorporated to allow for a
vehicle to be monitored in real-time, which means its
location is always known and if someone tries to
tamper with or access the vehicle those attempts can
be detected and an appropriate response activated.
Using blockchain ensures data integrity and security
in relation to vehicle access and anti-theft, providing a
tamper-proof record of events. 2- Accident response:
This feature captures and transmits all vital data
necessary for effective and timely emergency
response. Last but not least, the AI-powered voice
recognition system minimizes distraction and
enhances driving safety by allowing hands-free
control of in-vehicle systems, making the driving
experience uninterrupted and secure. This advanced
framework is the future of smart vehicle systems,
integrating state-of-the-art technologies for a secure,
efficient, and user-friendly solution for contemporary
vehicles. With the advancement of these technological
adaptations, the proposed system can also be advanced
to further meet the requirements for safety, security,
enhaced performance and comfort cater to the
demands of the growing automotive domains.
5 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF
RELATED SYSTEMS
Framework for IoT, blockchain, and AI integration
offers distinct advantages over traditional IoT-only
systems and blockchain-enabled systems. A
comparison of key features across three system types
is provided in the table 2 below:
• Data Security: Systems that are IoT-only, often
exhibit low data security, due to the absence of
decentralized data storage or tamper-resistant
methods. On the other hand, systems based on
blockchain have good data security because the
features of the blockchain are the encryption,
immutability, and decentralized validation.
Through the involvement of IoT and
Blockchain, it offers greater security and
flexibility that all data transferred from the IoT
devices of the vehicle gets encrypted and is
securely stored into the blockchain. Our voice-
enabled Tier II solution doesn't add security risk,
it adds utility.
Table 2: Feature-wise Comparison of IoT-Only,
Blockchain-Enabled, and Proposed Vehicle Tracking
Systems
Feature
IoT-Only
Systems
Blockchain-
Enabled
Systems
Proposed
System
Data
Security
Low High High
Real-Time
Monitoring
High Moderate High
Voice
Interaction
Limited Limited Advanced
Scalability Moderate High High
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
526

• Real-Time Monitoring: Most IoT-only
systems offer real-time monitoring features,
particularly for tracking the location and
condition of vehicles. Nonetheless, the large-
scale storage of data on-chain systems raises
concerns, as blockchain consensus algorithms
are often slow, resulting in inherent latency
when it comes to real-time transactions and
monitoring. By exchanging real-time data from
IoT sensors for constant monitoring and analysis
on the edge computing layer, the proposed
system, therefore, offers a more immediate
reactive solution during crises and time-
sensitive environments.
•
Voice Interaction: The IoT-only and
blockchain-enabled systems are not capable of
supporting conversational user interface.
However, in the proposed system, an AI-driven
voice recognition module was integrated. The
Automotive segment has been shaping this
module, enabling hands-free driver-vehicle
system interaction, with improved
convenience, safety, and user experience. Its
advanced voice recognition system is trained on
a huge volume of commands, dialects, and noise
ambient, enabling a sophisticated level of
interaction.
•
Scalability: IoT-only systems provide average
scalability due to how they rely on centralized
data processing which can create bottlenecks as
the number of devices grows. However,
blockchain-enabled systems deliver better
scalability due to their decentralized nature.
This system is designed to leverage the benefits
of blockchain's scalability principles in
conjunction with the real-time performance
potential offered by IoT and edge computing
principles, providing high scalability even when
a rising number of vehicles or devices become
connected.
6 CHALLENGES AND FUTURE
DIRECTIONS
But the convergence of IoT, blockchain, and AI
technologies can significantly improve the vehicle
security and the driver experience while also creating
some challenges. These challenges must be mitigated
for the optimal operation and widespread adoption of
the proposed system. Also, given an ever-updating
technology landscape, there is potential for an
upgrade that could improve the efficiency and
scalability of such systems.
6.1 Challenges
• The Scalability of IoT Networks: Scalability
is one of the big challenges related to IoT-based
vehicle systems. They consist of billions of
separate inter-connected devices that produce
massive volumes of data; Another major
challenge is the efficient management of the
data, ensuring continuous communication
between algorithms and consumers and
keeping the network intact as the number of
devices keeps increasing.
• Data Management and Storage: With every
new component added to the IoT network, the
amount of data created from sensors, GPS
systems and so on doubles exponentially. This
also makes it more difficult to store and process
this data in real time. The difficulty is in
handling that massive data as efficiently as
possible while retaining the system's
speed/accuracy. More advanced storage
solutions, for example, edge computing (which
we will discuss more below) can ease some of
these problems by processing data nearer the
edge in real-time, taking the load off of central
servers, and minimizing latency.
• Communication Overhead: The IoT system is
a network of devices that communicate with
each other to send data to a central server or
receive commands from other users. However,
as the number of devices grows, so does the
complexity of these communications.
Performance can be degraded due to network
congestion, interference, and signal loss.
Improving communication protocols and
utilizing better wireless technologies like Low
Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) address
these issues.
• One of the major concerns in real-time data
transmission: Latency- in the systems where
real-time Kernel responses are most important
(vehicle tracking, accident detection, and
emergency response). So, the time required for
the data to be sent from IoT devices to the
centralized server or to the emergency services
as a whole, all the processing time, can
significantly delay the response time. Network
Congestion: On networks where too many
devices are connected to a limited number of
available resources, data transmission delays
can occur due to network congestion especially
in a densely populated area. However, high
network load and limited bandwidth generally
lead to lower data delivery times, which delay
A Survey on IoT and Blockchain-Enabled Systems for Automobile Tracking, Security and Voice Recognition
527

important information on a vehicle’s location,
an emergency or an intrusion.
• Processing Time: Although blockchain
transaction systems are secure and transparent,
they introduce additional processing time due to
transaction validation and time writing to the
blockchain. In an IoT-based system that
demands real-time observation and decision-
making, the processing times required for
blockchain consensus algorithms can introduce
latency, especially in systems with high
transaction frequencies. Considerations Of
TimingPoA(Proof of Authority) or other more
lightweight consensus algorithms could be
considered to remove latency from hash
functions while maintaining a basic layer of
security.
6.2 Future Directions
Regardless, the future holds many applications for
more scalable, efficient, and secure Lot solution for
vehicle types, along more efficient solutions for
integrated blockchain and AI technology. IoT-based
vehicle system are revolutionized with edge
computing and advanced the technology that improve
performance, security, and user experience. With data
processing closer to the source on the vehicle or local
network latency, as well as the dependence on
centralized cloud servers, is reduced. By processing
data locally, applications such as accident detection
can capture data and act in real time, while reducing
the load on cloud servers and bandwidth
requirements. It also helps make privacy and security
better by keeping sensitive data such as driver
identity and the circumstances of an accident local
and encrypted. Hybrid blockchain also combines
security and performance optimally. A private
blockchain can hold sensitive data securely by
making the information accessible only to authorized
parties, while public blockchains maintain auditable
records of vehicle transactions, which contributes to
transparency. This creates a separation between
privacy and trust. Advancements are happening with
AI-driven voice recognition systems as well. In the
future, we could expect improvements to integrate
noise-canceling technologies to improve performance
in noisy environments and add contextual
understandings to prioritize commands about safety.
However, multilingual and multimodal capabilities
that integrate voice, gestures, and visuals hold the
potential for a more accessible and intuitive user
experience. Combined, these innovations enable
IoT-equipped automobiles systems to function at
scale, securely and responsively while overcoming
the challenges of privacy, latency, and transparency.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The recent paper is titled: Integration of IoT and
Blockchain for Secure and Efficient Automotive
Tracking and Monitoring. The framework is
successfully implemented to critical problems such as
vehicle theft and accidents by using GPS for location
tracking, GSM for real-time communication, and
MMS for multimedia sharing. The incorporation of
IoT sensors along with blockchain’s decentralized
and secure architecture guarantees input integrity and
safeguards against tampering communication
channels, effectively overcoming security
vulnerabilities commonplace in traditional IoT
environments. The integration of AI-powered voice
recognition also enhances the experience by
providing convenience and safety, allowing drivers to
interact with their vehicles hands-free. It highlights
challenges such as scalability, latency, and
integration cost and provides potential solutions such
as edge computing, hybrid blockchain models, and
better voice recognition algorithms. Such technology
advancements are essential for the adoption of these
integrated systems in the automotive sector. With the
advancement of technology and high-level
integration, the proposed framework aims to address
these issues by maximizing accuracy and reliability
on the task of the proposed model; dynamic barricade
management can significantly secure the vehicle, thus
requiring immediate attention in terms of monitoring
to ensure human safety.
REFERENCES
Baba, A., Meena, G., & Kumar, A. (2023). Challenges and
advancements in IoT-based vehicle tracking systems.
International Journal of Vehicle Engineering, 17(3), 34-
42.
Baba, V., Kumar, P., & Gupta, S. (2023). Energy Efficiency
in IoT-Based GPS Vehicle Tracking Systems. Journal
of Wireless Communications and Networking, 31(4),
459-472.
Gupta, P., Verma, S., & Jain, V. (2023). Blockchain-based
automotive security: Opportunities and challenges.
Blockchain Applications, 15(1), 55-67.
Gupta, S., Singh, M., & Kaur, A. (2023). Blockchain for
Securing Communication in IoT-Based Vehicle
Systems. IEEE Access, 11, 10201-10214.
Jain, K., & Sharma, M. (2023). Advancements in AI-Based
Voice Recognition Systems for In-Vehicle Interaction.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
528

Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Automotive
Systems, 12(3), 134-146.
Jain, P., & Sharma, R. (2023). Deep learning in voice
recognition for automotive systems: A review. Journal
of AI in Automotive Systems, 10(2), 101-112.
Kumar, N., & Kumar, P. (2024). Reliability of GSM in IoT-
Based Vehicle Tracking in Urban Environments.
Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing,
24(6), 678-692.
Kumar, R., & Patel, A. (2024). AI-Based Voice
Recognition in Vehicles for Seamless Integration with
In-Car Systems. Journal of Automotive Engineering
and AI, 9(2), 112-125.
Kumar, S., Gupta, R., & Sharma, P. (2023). Integration of
IoT with Vehicle Tracking Using GPS and GSM
Technologies. Journal of Intelligent Transportation
Systems, 15(2), 122-136.
Kumar, S., Meena, G., & Patel, D. (2024). Data security
concerns in IoT-based vehicle tracking systems. Journal
of Transportation Security, 12(4), 150-159.
Meena, R., Rajendran, S., & Patel, A. (2024). Cloud-Based
IoT Vehicle Tracking System for Scalable Real-Time
Monitoring. International Journal of Cloud Computing
and Vehicle Systems, 5(1), 40-52.
Meena, S., & Ramesh, V. (2024). Comparative Study of AI-
Driven Voice Recognition Technologies for In-Car
Systems. Journal of Machine Learning in Automotive
Technology, 11(2), 145-157.
Patel, M., & Kumar, J. (2023). Deep Learning and NLP in
Voice Recognition Systems for Automotive
Applications. Journal of Natural Language Processing
in Vehicles, 2(4), 78-92.
Patel, R., Singh, D., & Yadav, S. (2023). Blockchain
integration in automobile IoT systems. Journal of
Automotive Technologies, 21(2), 101-115.
Patel, S., & Joshi, P. (2023). Blockchain for Over-the-Air
Software Updates in Vehicles. Journal of Computer
Networks and Communications, 2023, 1-12.
Patel, S., Joshi, H., & Shah, R. (2023). Comparative
Analysis of IoT Platforms for Vehicle Tracking Using
LPWAN Technologies. Journal of Embedded Systems
and IoT, 9(4), 123-137.
Sharma, A., Yadav, M., & Verma, S. (2024). Blockchain
for secure automobile communication networks.
International Journal of Blockchain and IoT, 5(1), 22-
29.
Sharma, R., & Pandey, S. (2024). Decentralized Vehicle
Data Management Using Blockchain for Privacy and
Security. International Journal of Blockchain and
Vehicle Technology, 8(2), 44-58.
Singh, A., & Sharma, P. (2023). Real-time GPS-based
vehicle tracking using IoT technologies. International
Journal of Wireless Communications, 11(4), 89-97.
Singh, A., & Sharma, R. (2023). IoT-Based Fleet
Management and Vehicle Tracking for Optimized
Route Planning and Security. International Journal of
Vehicle Technology and Traffic Engineering, 19(3),
88-101.
Singh, A., & Sharma, V. (2023). Improving Voice
Recognition Performance in Automobiles Using AI for
Driver Safety and Control. International Journal of
Intelligent Transportation Systems, 17(5), 221-233.
Singh, N., & Yadav, S. (2024). Challenges in Real-Time
Blockchain Applications for Vehicle Communication
Networks. Blockchain Technology and Applications,
3(1), 22-34.
Verma, D., & Kumar, H. (2023). Vehicle-to-Vehicle
Communication Using Blockchain for Secure
Information Exchange. IEEE Transactions on
Vehicular Technology, 72(9), 10550-10563.
Yadav, P., & Gupta, S. (2023). AI-Driven Deep Learning
for Automotive Voice Recognition with Accent and
Language Variations. IEEE Transactions on Neural
Networks and Learning Systems, 34(11), 1425-1437.
Yadav, R., Kumar, D., & Singh, R. (2023). AI-driven voice
recognition for improving driver safety and experience.
AI in Automotive Technology Journal, 16(3), 67-74.
Yadav, R., & Patel, M. (2024). Blockchain and Edge
Computing Integration for Scalable Vehicle Security
Systems. International Journal of Automotive
Computing, 6(3), 56-67.
A Survey on IoT and Blockchain-Enabled Systems for Automobile Tracking, Security and Voice Recognition
529
