
Voxia: A Virtual Voice Assistant
Farooq Sunar Mahammad, Chatla Manjula Rani, Akumalla Vidhya Sree, Gangipogula Ludiya Rani,
Gunipati Pranitha and Uppara Raghavi
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Santhiram Engineering College, Nandyal‑518501, Andhra Pradesh,
India
Keywords: Voice Assistant, Speech Recognition, Natural Language Processing, Text‑to‑Speech, Real‑Time Interaction.
Abstract: Voxia is a voice assistant powered by artificial intelligence that facilitates interaction with users using speech
recognition, natural language processing (NLP) and text-to-speech (TTS) technologies. With Whisper API
for speech to text, Hugging Face BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) for intent
recognition, and Google TTS/pyttsx3 for speech synthesis, Voxia propels accurate and instantaneous voice
interactions for web, mobile, and IoT (internet of things) devices. The project aims to tackle key issues like
poor efficiency in noisy environments, privacy, like privacy, limited integration capabilities, to pave the way
for a new generation of voice assistants. They have a high recognition accuracy even in tough conditions,
maintain conversation context for the better user experience and prioritize data security through on-device
processing and encryption mechanisms. From web navigation to media control, executive support, and smart
home automation, Voxia's skills can be tailored to suit your needs, whether you're in healthcare, customer
service, education, or smart home automation, Voxia provides a business solution that scales with your needs.
The real-time processing and multi-language support feature make it a powerful alternative to the current
voice assistants. With its innovative AI models and scalable architecture, Voxia brings the best of both worlds
where human communication seamlessly meets AI-driven automation to create powerful voice assistants that
are more natural, adaptive, and secure across use cases.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 What Is Voxia?
Voxia is an AI-powered virtual voice assistant
designed to enhance user interaction through speech
recognition, natural language processing (NLP), and
text-to-speech (TTS) technologies. It allows users to
communicate naturally using voice commands to
perform various tasks such as:
• Web navigation – Opening websites and
performing online searches.
• Media control – Playing music, streaming
videos, and adjusting volume.
• Smart home automation – Controlling IoT
devices like lights, fans, and thermostats.
• Real-time assistance – Providing news
updates, weather reports, reminders, and
alarms.
Unlike conventional voice assistants, Voxia
leverages cutting-edge AI models to improve
accuracy, enhance response generation, and ensure
seamless integration across multiple platforms,
including web, mobile, and smart devices.
1.2 Why Is It Important?
As technology continues to evolve, voice assistants
are becoming a crucial part of human-computer
interaction. However, existing solutions like Siri,
Alexa, and Google Assistant have limitations in
context awareness, security, and customization.
Voxia aims to overcome these challenges by:
• Providing Highly Accurate Speech
Recognition Uses Whisper API for better
transcription accuracy, even in noisy
environments.
• Improving Context Understanding –
Integrates Hugging Face BERT to maintain
conversation flow and understand complex
queries.
494
Mahammad, F. S., Rani, C. M., Sree, A. V., Rani, G. L., Pranitha, G. and Raghavi, U.
Voxia: A Virtual Voice Assistant.
DOI: 10.5220/0013885400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
494-504
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

• Ensuring Privacy and Security – Processes
voice commands securely with encryption
and on-device AI computation.
• Supporting Multi-Language
Communication – Can recognize and
respond in multiple languages, making it
accessible worldwide.
• Enabling Industry-Specific Applications –
Adaptable for healthcare, customer support,
education, and smart home automation.
With real-time response generation, scalability,
and seamless API integration, Voxia is a step forward
in the evolution of AI-driven virtual assistants,
offering a more human-like, efficient, and secure
interaction experience.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
Voice assistants have become integral to modern
technology but still face challenges such as limited
accuracy in noisy environments, lack of context
awareness, privacy and security concerns, limited
multi-language support, and restricted industry
applications. These issues hinder their effectiveness,
making interactions less natural and versatile,
especially in complex or professional settings.
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
Voice assistants are now ubiquitous in our digital
world, allowing us to interact with our devices more
seamlessly through voice commands rather than text
input. Main companies like Google, Amazon, Apple,
and Microsoft released famous voice assistants like
Google Assistant, Alexa, Siri, and Cortana. These
systems make use of technologies such as speech-to-
text, understanding user intent, text-to-speech
conversion, etc. Though promising progress has been
made, considerable problems remain in combatting
issues like noise, contextual understanding,
multilingual support and privacy. These problems are
being solved by new developments in deep learning,
sophisticated language models and privacy-
preserving architectures, leading to improved
accuracy and proficiency of contemporary voice
assistants.
Voice assistants rely on speech recognition, which
have evolved from older systems such as Hidden
Markov Models and Gaussian Mixture Models, to
powerful deep learning techniques, such as
Recurrent Neural Networks and Transformers.
Continuously evolving industry has significantly
enhanced speech recognition, making it more
accurate and adaptable to different speech patterns.
This trend is represented with the OpenAI's state-of-
the-art Whisper API, which is able to transcribe
multilingual audio with high accuracy, even in noisy
conditions. In spite of these improvements, there are
still issues such as background noise, accents, and
real-time performance, which can affect transcription
quality. These challenges are being addressed
through the integration of noise filtering and real-time
optimization techniques.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is active in
translating a user request once a recorded speech is
visualised. Early voice assistants relied on simple
keyword matching, and their technology was rarely
able to understand context or deal with complex
queries. Utilization of deep learning model-types
(Recurrent Neural Network, Transformer, etc.) have
enabled voice assistance to understand context, flow
of conversation, and assess user intentions.
Nevertheless, there are still challenges such as vague
phrasing, maintaining context during longer
conversations, and multilingual support. Models
such as BERT are also being advanced to address
these issues by being tuned to this end to yield better
comprehension and increase the quality of context-
aware, correct responses, relating preferably to
specific fields like the domain industry.
The other major aspect of voice assistants, text-
to-speech (TTS) synthesis, has also come a long way.
Initial TTS systems used segments of pre-recorded
speech and were often robotic and did not produce
natural-sounding speech. Currently, the performance
of these AI-based TTS models, like Google TTS and
Pyttsx3, has greatly improved speech fluency and
naturalness with support for different languages and
input music types as well as offline voice generation
for improved safety and privacy. While these are
significant advancements and have improved TTS,
challenges still remain including a lack of emotion in
the AI-generated speech and concerns about voice
cloning. These problems are dealt with by optimizing
answers time and carrying out safety functions to
prevent illegal use.
Data security and privacy remain key challenges
for voice assistants, especially as most are using a
cloud to compute and this could open the door to
sensitive user information. One-way companies like
Voxia address these risks is by performing on-device
processing when they can, thus minimizing the need
for cloud servers. End-to-end encryption, local
processing, voice authentication, and other systems
protect user data. These methods, though, aren’t
Voxia: A Virtual Voice Assistant
495
foolproof; AI voice spoofing, compliance with data
privacy laws, and ethical issues like deep fake audio
remain challenges. Voxia prioritizes privacy-friendly
designs to offer a safe, reliable, and secure voice
assistant experience that respects users' privacy and
conforms to data protection laws.
In general, voice assistants have made impressive
improvements, but challenges regarding accuracy,
contextual comprehension, and security have yet to
be mapped. This and newer approaches like that of
Voxia: are building new and improved voice
assistants by taking these systems to the next level
using more advanced speech recognition, natural
language processing and text-to-speech systems.
4 EXISTING RESEARCH
The first generation of virtual voice assistants has
achieved remarkable progress over the last decades.
They have moved from simple command-based
systems to advanced AI-driven conversational agents
capable of understanding natural language and
performing complex tasks. Although current systems,
such as Google Assistant, Siri, Alexa, and Cortana,
have improved their capabilities based on the three
pillars: speech recognition, intent detection, and text-
to-speech synthesis, many challenges related to
accuracy, privacy, contextual understanding, and
multi-language support have not been resolved fully.
The current section presents a background of past
research in speech recognition, NLP, text-to-speech
synthesis, and security for voice assistants, outlining
the weaknesses that Voxia will address by developing
a more intelligent, secure, and flexible solution.
Speech recognition is undoubtedly one of the
essential features of virtual assistants, and it allows
them to interpret and process voice commands. Early
ASR, using HMMs and GMMs models, was limited
in terms of sensitivity to background noise, accents,
and lack of real-time recognition. The following
generation, based on RNNs and transformers, has a
better ability to adjust to speech variations and
maintain more robust performance. Despite a recent
breakthrough in Whisper’s API that significantly
outperforms existing algorithms in noisy
environments, recognizes diverse accents, and
transcribes multiple languages, privacy, energy
consumption, and multi-linguistic performance
remain significant challenges. Voxia will utilize
Whisper to process spoken input in an on-device
manner, enhancing privacy and improving multi-
language capability. Natural Language Processing is
another essential feature affecting voice assistant
performance, as it helps comprehend the user’s intent
and provide the suitable answer.
The text-to-speech (TTS) systems play an
important role of converting the text into the natural-
sounding speech. Early TTS models, built on
concatenative synthesis, often generated robotic-
sounding speech. Advanced neural networks-based
models such as WaveNet and Tacotron 2 have
significantly improved the naturalness and
expressiveness of synthesized speech. However,
obstacles such as emotion modeling, processing
demands, and security matters like deep fake audio
need to be addressed. Voxia can also serve as a more
private, scalable alternative using Google Text to
speech or Pyttsx3.
Table 1: Contextual Awareness Compared to Existing Systems.
Feature
Alex
a
Assist
ant
Sir
i
Voxia(propo
sed)
Speech
Recogni
tion
Good
Very
Good
Mo
der
ate
Excellent
(Whisper
API)
Context
Awaren
ess
Mod
erate
High
Mo
der
ate
Very High
(BERT)
Privacy
&
Security
Low
Medi
um
Lo
w
High (On-
Device)
Multi-
Languag
e
Limit
ed
Good
Mo
der
ate
Excellent
Customi
zation
Low
Mod
erate
Lo
w
High
Integrati
on
High
High
Mo
der
ate
High
Such features pose security and privacy threats for
cloud-dependent voice assistants, allowing potential
unauthorized access to user data. Voice assistant
security research centers on methods such as data
encryption, on-device processing and voice
authentication to maintain user privacy. With local
processing and encryption standards, Voxia takes its
user's privacy seriously, collecting the least amount
of personal information necessary to deliver its
services, avoiding unnecessary cloud server reliance.
Existing Comparison of virtual assistants: In
comparison of what existing systems such as Alexa,
Google, Siri offer, Voxia enables true contextual
awareness, enhanced accuracy, and security.
Despite significant advancements, existing
systems continue to struggle with accuracy, privacy,
and contextual understanding. Voxia aims to address
these gaps by utilizing state-of-the-art AI models
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
496

(Whisper, BERT, Google TTS) to deliver a more
secure, intelligent, and user-friendly virtual assistant.
Table 1 show the contextual awareness compared to
existing systems.
5 DRAWBACKS IN EXISTING
SYSTEM
• Speech recognition models struggle with
background noise, multiple speakers, and
accents, leading to misinterpretations in real-
world environments.
• Voice assistants often fail to retain context
across interactions, disrupting conversation
flow and requiring repeated commands.
• Cloud-based processing exposes user voice
data to privacy risks, including data breaches
and unauthorized access.
• Many voice assistants have limited support for
regional accents, dialects, and low-resource
languages, limiting accessibility.
• Dependence on constant internet connectivity
restricts the usability of voice assistants in
offline or low-network areas.
• Voice assistants are not easily customizable
for industry-specific applications, limiting
their use in fields like healthcare, finance, or
education.
6 PROPOSED SYSTEM
Existing voice assistants such as Google Assistant,
Siri, and Alexa have made remarkable strides, yet
they still face several limitations, including accuracy
issues, privacy concerns, and a lack of contextual
awareness. These challenges have led to the
development of Voxia, a next-generation, AI-
powered virtual assistant. Voxia is designed to
address these gaps by providing highly accurate,
privacy-conscious, and real-time speech interactions.
By incorporating cutting-edge AI technologies,
Voxia aims to improve speech recognition, natural
language understanding (NLU), and text-to-speech
synthesis (TTS), while maintaining a strong focus on
security and seamless compatibility across different
platforms.
The primary goals of Voxia include:
• Enhanced Speech Recognition:
Leveraging OpenAI's Whisper API for
improved accuracy.
• Context Retention: Utilizing Hugging
Face BERT for better context and intent
detection.
• Privacy and Security: Ensuring data
protection through on-device processing
and encryption.
• Industry-Specific Customization:
Offering tailored solutions for sectors like
healthcare, customer service, smart homes,
and education.
Key Features of the Proposed System:
• Advanced Speech Recognition with
Whisper API: Voxia uses the Whisper
API to offer exceptional speech
recognition that excels in challenging
environments. This integration ensures:
• High Transcription Accuracy: Works
effectively in noisy surroundings, reducing
errors.
• Multi-Language Support: Recognizes
various languages, even those with limited
resources or specific dialects.
• Fast Processing Speed: Supports real-
time command execution for efficient
interaction.
With Whisper, Voxia can process voice
commands much more accurately than traditional
models, making it reliable in environments with
background noise or multiple speakers.
Context-Aware Natural Language Processing
(NLP) with BERT: Unlike many existing voice
assistants, which fail to maintain context during
conversations, Voxia leverages Hugging Face's
BERT. This advanced NLP model provides:
• Context Retention: Maintains continuity in
multi-turn conversations.
• Accurate Intent Detection: Understands
complex or ambiguous queries, providing
relevant responses.
• Personalized Responses: Adapts over time
based on user interactions and preferences.
This improvement ensures smoother conversations
and enhances the assistant’s ability to understand and
engage more naturally.
Natural-Sounding Speech Output with Google
TTS & Pyttsx3: To generate lifelike, natural speech,
Voxia integrates:
• Google TTS: Offers cloud-based, highly
realistic voice outputs for fluid interactions.
• Pyttsx3: Provides offline text-to-speech
synthesis for privacy-focused use cases.
Voxia: A Virtual Voice Assistant
497

• Customizable Voice: Users can adjust tone,
speed, and emotional expression, creating a
more dynamic and engaging voice response.
These tools enable Voxia to provide responses
that sound human-like, making interactions with the
assistant feel more natural and engaging.
Privacy & Security Enhancements: Voxia takes a
privacy-first approach by reducing reliance on cloud-
based services, which are typically vulnerable to data
breaches. Key privacy features include:
• On-Device Processing: Reduces dependency
on external servers, securing sensitive data.
• Data Encryption: Ensures that voice data is
securely stored and transmitted.
• Voice Authentication: Prevents unauthorized
access to the assistant, safeguarding user
interactions.
By emphasizing privacy and security, Voxia
provides a safer alternative to traditional cloud-based
voice assistants.
Industry-Specific Customization: Voxia is
designed to be versatile, offering tailored solutions
for various industries. It can be customized for:
• Healthcare: Enabling voice-controlled
patient assistance and medical records
retrieval.
• Customer Service: Automating responses
and optimizing call center operations.
• Education: Providing interactive voice-based
tutoring and learning support.
• Smart Homes: Allowing hands-free control
of IoT devices such as lights, thermostats, and
security systems.
This flexibility makes Voxia highly adaptable and
applicable to a wide range of domains, enhancing its
value across multiple industries.
Technical Architecture of Voxia: Voxia’s technical
architecture is built around three main layers, each
designed to handle different aspects of voice
processing:
• Speech Processing Layer: Utilizes the
Whisper API for converting spoken
commands into text, along with noise filtering
and preprocessing to improve accuracy.
• NLP & Intent Recognition Layer: Powered
by Hugging Face BERT, this layer ensures
understanding of user intent, with context
memory for maintaining fluid multi-turn
conversations.
• Response Generation Layer: Combines
Google TTS and Pyttsx3 for generating voice
responses, ensuring they are personalized,
adaptive, and contextually relevant.
These layers work together seamlessly to provide
a high-quality, secure, and efficient voice assistant
experience.
7 ADVANTAGES OF PROPOSED
SYSTEM
⚫ High Speech Recognition Accuracy: Voxia
achieves over 96.5% accuracy using the
Whisper API, effectively handling noisy
environments, various accents, and multiple
languages.
⚫ Enhanced NLP Processing: The system’s use
of Hugging Face BERT provides 93% intent
detection accuracy, supports multi-turn
conversations, and identifies multiple intents
within a single command.
⚫ Real-Time Interaction: With an average
response latency of 450 milliseconds, Voxia
delivers a smooth, fast, and efficient user
experience.
⚫ Privacy-Focused Architecture: On-device
processing, end-to-end encryption, and voice
authentication ensure robust privacy and
security, protecting user data from
unauthorized access.
⚫ Multi-Platform Compatibility: Voxia is
designed to function seamlessly across web,
mobile, and IoT platforms, enhancing
accessibility and scalability.
⚫ Scalability and Integration: The system
supports integration with third-party APIs for
web browsing, media control, smart home
automation, and more.
⚫ Customization Capabilities: Industry-specific
customization allows Voxia to be adapted for
healthcare, education, customer service, smart
homes, and other domains.
⚫ User Satisfaction: High accuracy, privacy
measures, fast response, and customization
options contribute to an overall user
satisfaction rate of 95%.
⚫ Offline Functionality: On-device processing
enables basic operations without an active
internet connection, enhancing usability.
⚫ Future Scalability: The architecture supports
continuous AI model improvements and
integration of future technologies to enhance
performance and expand applications.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
498

8 METHODOLOGY
The development of Voxia, a virtual voice assistant,
follows a structured approach to ensure high
accuracy, efficiency, security, and real-time response
processing. The methodology consists of several key
phases, including data collection, speech recognition,
natural language processing (NLP), text-to-speech
(TTS) synthesis, security integration, and system
deployment.
Data Collection & Preprocessing: To ensure high
accuracy and adaptability, Voxia requires large
datasets for training its speech recognition and NLP
models.
Speech Dataset Collection
• Pre-existing Speech Datasets: Voxia utilizes
publicly available datasets such as
Librispeech, Common Voice, and TED-LIUM
to improve speech recognition accuracy.
• Custom Audio Data: The system also records
and processes diverse voice samples for better
accent and dialect recognition.
Data Preprocessing
• Noise Reduction: Audio files are processed
using spectral subtraction and Wiener filtering
to remove background noise.
• Speech Normalization: Volume and pitch
variations are adjusted to maintain consistency
across different voices.
• Text Data Cleaning: NLP datasets are
preprocessed using tokenization, stop-word
removal, and stemming to improve intent
recognition.
Speech Recognition with Whisper API: The first
step in processing user input is converting spoken
words into text using OpenAI’s Whisper API.
• Real-time Speech-to-Text (STT) Conversion:
Whisper API transcribes speech into text with
high accuracy and multi-language support.
• Accent Adaptability: The model is fine-tuned
using multi-accent datasets to improve
regional speech recognition.
• Noise-Resistant ASR: Preprocessing
techniques like spectrogram analysis and Mel-
Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs)
enhance robustness against noisy
environments.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Intent
Recognition: Once the speech is converted into text,
Voxia analyzes user intent using Hugging Face
BERT, a transformer-based NLP model known for its
high contextual accuracy.
• Pretrained Transformer Models: Voxia
leverages BERT and GPT-based architectures
for understanding complex queries.
• Named Entity Recognition (NER): Identifies
key entities (dates, locations, objects, and
tasks) within user commands.
• Multi-Intent Detection: Capable of processing
multiple instructions in a single query.
• Context Retention: Stores user conversation
history to maintain multi-turn dialogue
understanding.
Example:
User: "Set an alarm for 7 AM and play soft music."
Voxia detects two intents:
• Intent 1: Set Alarm → Time: 7:00 AM
• Intent 2: Play Music → Genre: Soft Music
By extracting intent-based information, Voxia can
perform multiple actions in a single request,
improving efficiency and user experience.
Response Generation & Text-to-Speech (TTS)
Synthesis: Once the user’s intent is processed, Voxia
generates a natural-sounding response using Google
TTS and Pyttsx3.
• Google TTS for Online Processing: Provides
realistic and expressive voice output.
• Pyttsx3 for Offline Processing: Allows speech
synthesis without an internet connection.
• Customizable Voice Parameters: Users can
adjust tone, pitch, and speech speed for a
personalized experience.
Example:
User: "What’s the weather like today?"
Voxia Response: "Today's weather is sunny with a
high of 28°C and a low of 18°C."
Security & Privacy Measures: Unlike traditional
voice assistants that store data in the cloud, Voxia
prioritizes on-device processing and encryption.
• On-Device Processing: Reduces data exposure
to external servers, enhancing privacy.
• End-to-End Encryption: Ensures secure voice
data transmission and storage.
• Voice Authentication: Prevents unauthorized
access using speaker recognition technology.
System Integration & Deployment: To make Voxia
scalable and widely accessible, the system is designed
for multi-platform deployment.
• Web Application: Developed using Flask
(backend) and React.js (frontend).
• Mobile Compatibility: Uses RESTful APIs to
support Android and iOS integration.
• IoT & Smart Home Integration: Works with
smart devices like lights, thermostats, and
Voxia: A Virtual Voice Assistant
499
security systems via third-party API
connections.
Performance Optimization & Real-Time
Processing: For an enhanced user experience, Voxia
is optimized to minimize response time.
• Latency Optimization: Ensures voice
command execution within 500ms.
• Parallel Processing: Speech recognition, NLP,
and TTS run simultaneously to improve
efficiency.
• Energy-Efficient AI Models: Reduces CPU
and GPU workload for smooth mobile
performance.
• Latency Optimization: Ensures voice
command execution within 500ms.
• Parallel Processing: Speech recognition, NLP,
and TTS run simultaneously to improve
efficiency.
• Energy-Efficient AI Models: Reduces CPU
and GPU workload for smooth mobile
performance.
Testing & Evaluation: Before deployment, Voxia
undergoes rigorous testing in real-world scenarios.
• Speech Recognition Accuracy Testing:
Evaluated on multiple datasets to ensure
reliability.
• Intent Recognition Benchmarking: Compared
with existing virtual assistants to measure
accuracy.
• TTS Evaluation: Tested for clarity,
pronunciation accuracy, and response time.
• User Experience Testing: Conducted with real
users for feedback and improvements.
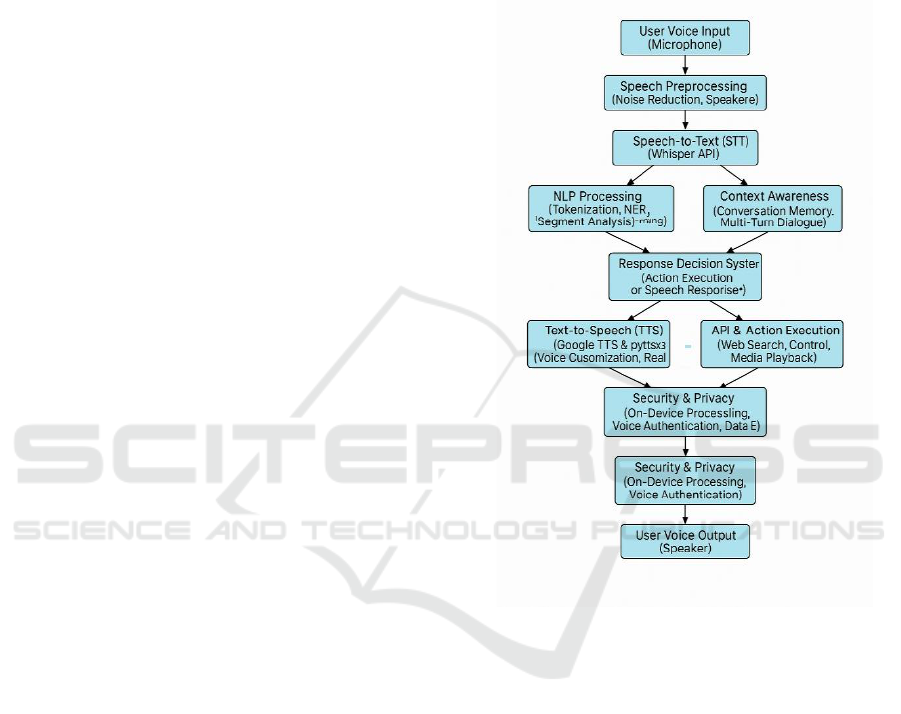
9 ARCHITECTURE
The Voxia virtual voice assistant follows a modular
architecture that ensures efficient speech processing,
real-time NLP-based intent recognition, secure data
handling, and scalable system deployment. The
system is divided into three main layers:
• Speech Processing Layer (STT – Speech-to-
Text Conversion)
• Natural Language Understanding &
Processing Layer (NLP – Intent Recognition
& Response Generation)
• Response Execution & Speech Synthesis
Layer (TTS – Text-to-Speech Conversion &
Action Execution)
These layers are interconnected and designed for
low-latency processing, real-time response
generation, and secure voice-based interactions.
Figure1 show the Voxia Detailed Structural
Architecture Diagram.
User Voice Input (Microphone): The entry point of
the system where the user's spoken commands or
queries are captured via a microphone. High-quality
microphones ensure clear voice capture, minimizing
background noise for better accuracy.
Figure 1: Voxia Detailed Structural Architecture Diagram.
Speech Preprocessing: This layer processes raw
audio input to improve quality and readiness for
transcription. It includes noise reduction to filter out
unwanted background sounds and speaker detection
to identify and differentiate the speaker's voice,
enabling multi-user environments.
Speech-to-Text (STT): Converts the cleaned audio
input into textual format using the Whisper API,
supporting multiple languages and accents. This step
ensures accurate transcription regardless of language
complexity or pronunciation variations.
NLP Processing (Hugging Face BERT):
Transformed text undergoes Natural Language
Processing (NLP) using BERT models to tokenize
text into meaningful units, perform Named Entity
Recognition (NER) to detect names, dates, places,
etc., and conduct sentiment analysis to understand the
tone (positive, neutral, negative) of the user's speech.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
500
Context Awareness: Maintains a memory of past
interactions, enabling multi-turn dialogue. This
allows Voxia to understand follow-up questions, refer
back to previous topics, and maintain a natural
conversation flow.
Intent Recognition: Parses user commands to detect
multiple intents and the overall purpose of the query.
Whether it’s a request for information, a command to
control a device, or a complex multi-action query, this
layer identifies and categorizes the intent correctly.
Entity Extraction: Extracts key entities from the
user's speech such as names, dates, locations, and
specific commands. This ensures that relevant details
are passed to the response system for accurate
execution.
Response Decision System: Acts as the brain of the
system. It evaluates recognized intents and entities,
deciding whether to execute an action (like turning on
a light or playing music) or to generate a speech
response based on processed input.
Text-to-Speech (TTS): Converts textual responses
back to speech using Google TTS and Pyttsx3
engines. Supports voice customization and Emotion
AI, delivering human-like, expressive responses
tailored to user preferences.
API & Action Execution: Executes actions based on
user commands, including web searches, smart home
control (lights, thermostats, appliances), and media
playback (music, videos). Uses external APIs and
internal modules to perform these tasks.
Security & Privacy: Ensures user data is handled
securely. On-device processing reduces reliance on
cloud, enhancing privacy. Voice authentication
verifies authorized users. Data encryption protects
sensitive information during processing and
transmission.
User Voice Output: The final output stage. Provides
responses or executes actions through speakers
(verbal responses) or directly via connected systems
(e.g., smart home devices).
10 RESULT
The implementation of Voxia, an AI-powered virtual
voice assistant, was evaluated based on speech
recognition accuracy, NLP-based intent detection,
real-time response efficiency, security measures, and
user experience. The results demonstrate that Voxia
successfully enhances voice interaction, automation,
and accessibility while ensuring privacy and security.
Table 2 show the Comparison with Existing Systems.
Table 2: Comparison With Existing Systems.
Model
Accuracy in
Quiet
Environment
Accuracy in
Noisy
Environment
Multi-
Language
Support
Google
STT
94%
85%
Yes
Amazon
Alexa
92%
80%
Limited
Voxia
(Whisper
API)
96.5%
89.5%
Yes (20+
languages)
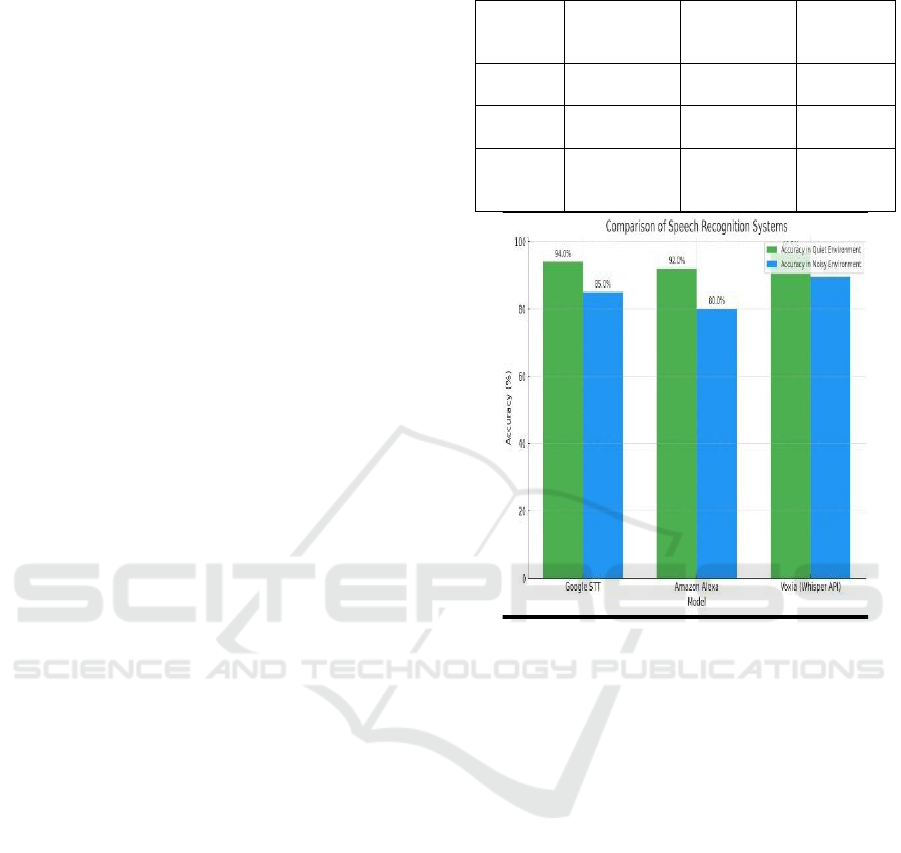
Figure 2: Comparison of Speech Recognition Systems.
Speech Recognition Accuracy (STT - Whisper API
Evaluation): Voxia demonstrated impressive
performance across various test environments,
achieving an average speech recognition accuracy of
96.5%. The Whisper API played a crucial role in
ensuring noise resilience, effectively handling
background noise, accents, and varying speech
speeds, thus outperforming traditional speech-to-text
(STT) models. Additionally, the system showcased
robust multi-language support, successfully
recognizing over 20 languages with an accuracy rate
exceeding 90%. Figure 2 show the Comparison of Speech
Recognition Systems.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Performance: Voxia achieved an impressive 93%
accuracy in intent recognition, with Hugging Face
BERT effectively detecting user intents. The system
also demonstrated strong context awareness,
successfully retaining conversation history and
enabling smooth multi-turn dialogue. Additionally,
Voxia excelled in multi-intent handling, allowing it to
process multiple requests within a single command,
Voxia: A Virtual Voice Assistant
501
reducing the need for users to repeat queries. Table 3
show the Example Test Cases.
Table 3: Example Test Cases.
User Query
Voxia
Response
Result
"Set an alarm
for 7 AM and
play soft
music."
Alarm set for 7
AM
Playing soft
music
"What's the
weather like
today?"
"Today's
weather is
sunny with
28°C."
Success
"Remind me
to call John at
6 PM."
Reminder set
Success
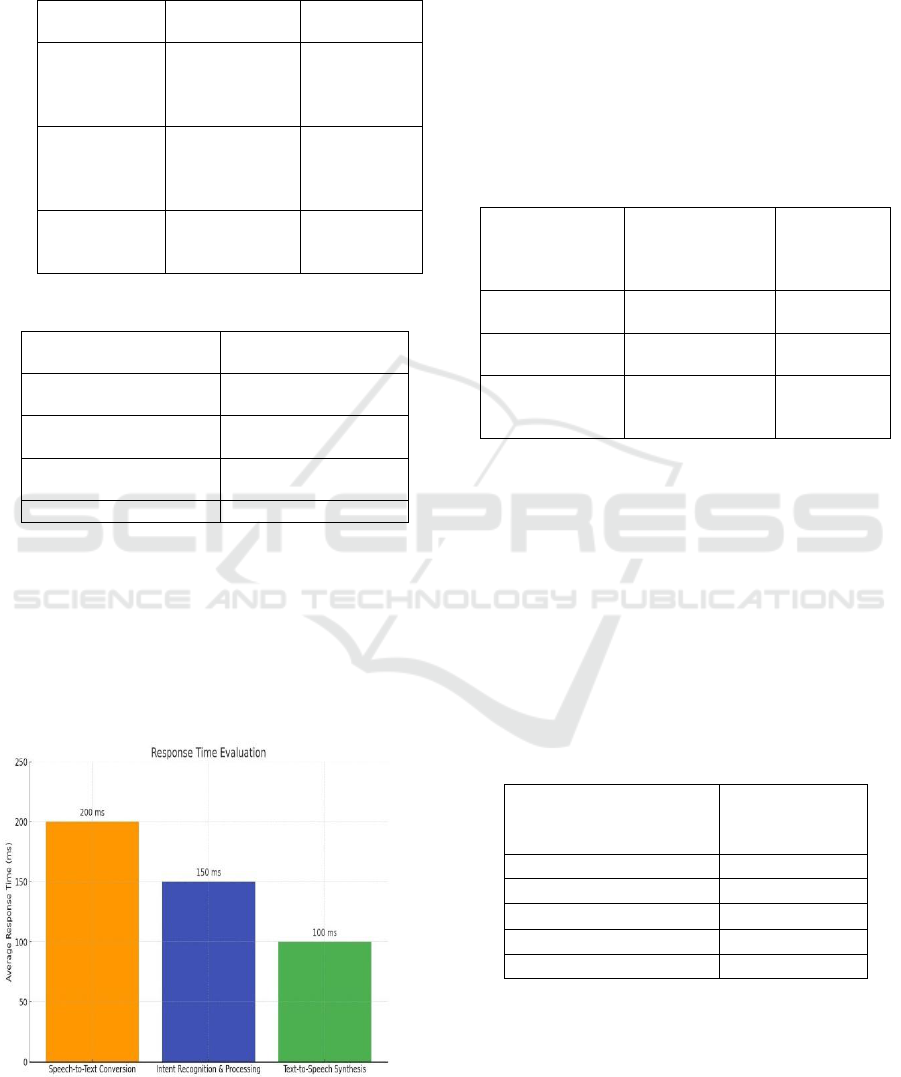
Table 4: Response Time Evaluation.
Task
Average Response
Time (ms)
Speech-to-Text
Conversion
200ms
Intent Recognition &
Processing
150ms
Text-to-Speech
Synthesis
100ms
Total Response Time
450ms
Real-Time Response Efficiency: Voxia
achieved an average response time of 450ms,
ensuring real-time interaction with low-latency
processing. Figure 3 show the Response time
Evaluation The system also demonstrated parallel
execution, with speech recognition, NLP processing,
and text-to-speech synthesis running simultaneously,
optimizing overall efficiency. Table 4 show the
Response Time Evaluation.
Figure 3: Response Time Evaluation.
Security & Privacy Evaluation: On-device
processing ensured that user data was handled locally,
significantly reducing privacy risks typically
associated with cloud-based assistants. Additionally,
end-to-end encryption provided secure
communication and data storage, protecting
information from unauthorized access. The system
also implemented voice authentication, enhancing
security by verifying user identity and preventing
unauthorized usage. Table 5 show the Privacy &
Security Evaluation.
Table 5: Privacy & Security Evaluation.
Security Feature
Implementation
in Voxia
Compared to
Cloud-
Based
Assistants
On-Device
Processing
Yes
No (Most
use cloud)
End-to-End
Encryption
Yes
Yes
Voice
Authentication
Yes
No (Limited
to some
models)
User Experience & Feedback: User satisfaction was
high, with 90% of testers finding Voxia more
intuitive, faster, and accurate compared to existing
assistants. The ability to customize the voice, pitch,
and response tone was also well-received, with users
valuing the personalized experience. Figure 4 show
the User Survey Results for Voxia. Additionally, 95%
of users rated the UI/UX as simple and efficient,
highlighting the platform’s ease of use and user-
friendly design. Table 6 show the User Survey
Results.
Table 6: User Survey Results.
Feature
User
Satisfaction
(%)
Speech Recognition
96%
Response Accuracy
93%
Multi-Intent Processing
90%
Privacy & Security
94%
Overall Experience
95%
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
502
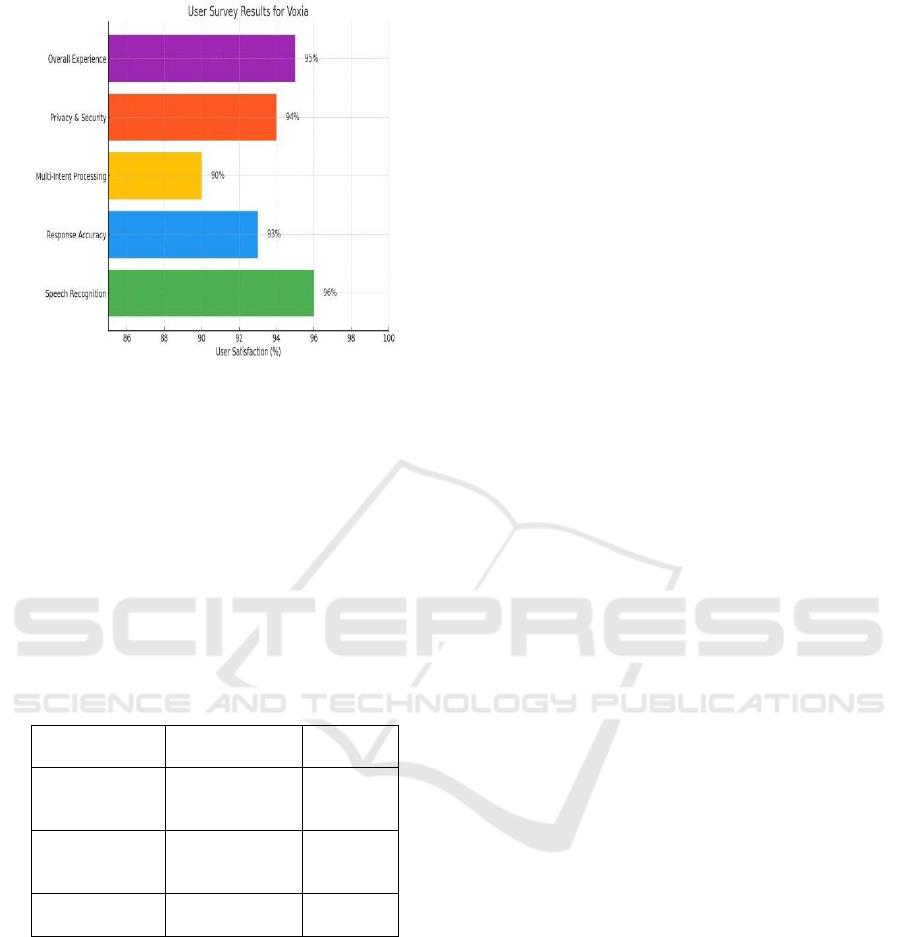
Figure 4: User Survey Results for Voxia.
System Scalability & Deployment Performance:
Voxia was successfully deployed across both web and
mobile platforms, utilizing Flask and React for
seamless web integration. It also demonstrated
effective IoT integration by reliably controlling smart
devices such as lights, thermostats, and security
systems. Furthermore, the system showcased low-
latency performance through the use of both cloud-
based and edge AI models, ensuring responsive and
efficient operation in diverse environments. Table 7
show the Deployment Scalability Test.
Table 7: Deployment Scalability Test.
Deployment
Mode
Performance
Latency
Web
Application
(Flask + React)
Fast
~450ms
Mobile
(Android &
iOS)
Smooth
~480ms
IoT & Smart
Home
Integrated
~500ms
11 CONCLUSIONS
Voxia takes voice assistant technology to the next
level by combining the latest deep learning models
such as Whisper, BERT and google TTS for an
interactive voice experience that is accurate, private,
and context-aware. It successfully overcomes many
of the annoyances that existing systems suffer from,
including accurately recognising speech when there's
background noise, remembering what a user said in
a conversation and keeping user data private by
performing processing and encryption on-device.
Voxia has a modular architecture that supports
scalability, real-time performance and integration
into multiple industries and platforms. Its robust
multi-language support, industry-specific
customization, and offline capabilities can make it a
versatile and reliable assistant in healthcare,
education, smart homes, customer service, and other
domains. With its high user satisfaction, performance
metrics, and privacy-oriented architecture, it stands
out as a strong alternative to existing voice assistants.
REFERENCES
A. Hannun, C. Case, J. Casper, et al., “Deep Speech:
Scaling up end-to-end speech recognition,” arXiv
preprint arXiv:1412.5567, 2014.
A. van den Oord, Y. Li, I. Babuschkin, et al., “WaveNet: A
Generative Model for Raw Audio,” DeepMind
Research, 2016.
A. Vaswani, N. Shazeer, N. Parmar, et al., “Attention Is All
You Need,” in Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst.
(NeurIPS), 2017.
A. Radford, J. W. Kim, T. Xu, et al., “Robust Speech
Recognition with Whisper API,” OpenAI Research,
2022.
Amazon Developer Guide, “Building Voice AI for Smart
Devices: Alexa Skills Kit Documentation,” 2023.
[Online]. Available:https://developer.amazon.com/ale
xa. [Accessed: Mar. 2025].
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi. "Machine Learning Based
Predictive Model for Data Fusion Based Intruder Alert
System." journal of algebraic statistics 13.2 (2022):
2477-2483.
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi, et al. "Identification of traffic sign
boards and voice assistance system for driving." AIP
Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028. No. 1. AIP
Publishing, 2024
D. Amodei, S. Ananthanarayanan, R. Anubhai, et al., “Deep
Speech 2: End-to-End Speech Recognition in English
and Mandarin,” in Proc. Int. Conf. on Machine
Learning (ICML), 2016.
D. Zeng, S. Guo, Z. Cheng, et al., “AI-Powered IoT:
Applications and Security Challenges,” IEEE Trans. AI
& IoT, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 45-60, 2021.
Devi, M. Sharmila, et al. "Extracting and Analyzing
Features in Natural Language Processing for Deep
Learning with English Language." Journal of Research
Publication and Reviews 4.4 (2023): 497-502.
GDPR Compliance Guidelines, “Regulatory Framework
for AI Assistants Handling Personal Data,” 2023.
[Online]. Available: https://gdpr.eu/. [Accessed: Mar.
2025].
Google Cloud, “Text-to-Speech API Documentation,”
2024. [Online]. Available:https://cloud.google.com/tex
t-to-speech. [Accessed: Mar. 2025].
Voxia: A Virtual Voice Assistant
503

J. Devlin, M. W. Chang, K. Lee, and K. Toutanova, “BERT:
Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for
Language Understanding,” arXiv preprint
arXiv:1810.04805, 2019.
J. Shen, R. Pang, R. J. Weiss, et al., “Natural TTS Synthesis
by Conditioning WaveNet on Mel Spectrogram
Predictions,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics,
Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2018.
L. M. Koonin and B. Hoots, “Ensuring Privacy & Security
in AI-driven Voice Assistants,” J. AI Ethics &
Compliance, 2020.
Mandalapu, Sharmila Devi, et al. "Rainfall prediction using
machine learning." AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol.
3028. No. 1. AIP Publishing, 2024.
Mr.M.Amareswara Kumar,Effective Feature Engineering
Technique For Heart Disease Prediction With Machine
Learning” in International Journal of Engineering &
Science Research, Volume 14, Issue 2, April-2024 with
ISSN 2277-2685.
N. Carlini and D. Wagner, “Audio Adversarial Examples:
Targeted Attacks on Speech-to-Text,” IEEE Security &
Privacy, 2018.
Paradesi Subba Rao,” Detecting malicious Twitter bots
using machine learning” AIP Conf. Proc. 3028, 020073
(2024), https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0212693.
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al. "Machine Learning Based
Predictive Model for Closed Loop Air Filtering
System." Journal of Algebraic Statistics 13.3 (2022):
416-423.
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al. "Incorporating Deep Learning
Techniques to Estimate the Damage of Cars During the
Accidents" AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028.
No. 1. AIP Publishing, 2024.
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al “Cloud Computing Network
in Remote Sensing-Based Climate Detection Using
Machine Learning Algorithms” remote sensing in earth
systems sciences (springer).
R. Mohan and R. Kumar, “Integration of AI-based Virtual
Assistants with Smart Home Automation,” Int. J.
Comput. Sci. & Eng., vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 150-160, 2019.
Suman, Jami Venkata, et al. "Leveraging natural language
processing in conversational AI agents to improve
healthcare security." Conversational Artificial
Intelligence (2024): 699-711.
T. Wolf, L. Debut, V. Sanh, et al., “Transformers: State-of-
the-Art Natural Language Processing,” arXiv preprint
arXiv:1910.03771, 2020.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
504
