
Real‑Time Ransomware Detection Using Optimized XGBoost: A
Behavior‑Based Approach for Cybersecurity Defense
Rejoice Angelina Muppidi and C. Sureshkumar
Department of Information Technology, Vel Tech Rangarajan Dr. Sagunthala R&D Institute of Science and Technology,
Chennai - 600062, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Ransomware Detection, Machine Learning, Cybersecurity, XG Boost, Real‑Time Threat Detection, Feature
Selection, API Call Analysis, Deep Learning, Random Forest, LSTM.
Abstract: Ransomware is one of the greatest cybersecurity and information security challenges, having significant
impacts financially and operationally for numerous industries. Detection processes continue to rely on pre-
defined approaches which are usually incorrect and take too long to reveal new types of ransomware. This
work proposes a Ransomware Attack Detection Tool with Integrated Machine Learning (ML) for improving
real time ransomware detection. We focus on literature review on existing solutions and research gaps
regarding real time detection, efficiency, and classification accuracy. Our approach utilizes optimized feature
selection, high-performance classification using XG Boost, and threat detection via Flask for real-time
integration. The experiments conducted show enhanced accuracy and lessened false positives in contrast to
the other methods. The framework proposed is effective at helping defend against ransomware attacks and
improves overall cybersecurity posture.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the immediacy of contemporary digital society,
ransomware has emerged as one of the most violent
and wide-reaching threats to cybersecurity.
Ransomware is a kind of malware that makes victims’
files completely inaccessible and demands payment,
normally in a form of cryptocurrency, for the
decryption key. The range of digital systems has
grown consistently and so has the incidence of
ransomware attacks. Individuals, corporations, and
most recently even critical healthcare and finance
infrastructures have fallen prey to these attacks. Over
time, the intricate nature of these attacks has
progressed beyond the capabilities of current security
systems to effectively neutralize these threats.
Detection of ransomware is most difficult when
determining whether software activity is harmful or
harmless. Older detection techniques which relied on
attack signatures are bound to the detected attack
patterns, and as a result are too slow for newly
appearing ransomware variants. This gap has given
way to the use of machine learning (ML) and deep
learning (DL) approaches in improving accuracy in
ransomware detection. These approaches leverage
behavior-based analysis, feature selection, and real
time monitoring to enhance accuracy and
applicability.
Multiple researches are done over ML based
detection methods of ransomware. According to Wan
et al., the importance of a feature-, selection method
dealing with classification was proposed.
Nonetheless, it was impeded by the lack of real-time
detection system so it could not be applied in practice.
Some other studies suggested a framework that uses
both static as well as dynamic analysis for detecting
the ransomware. While helpful, still this framework
does not aim at deploying the model in real-time
which is an important aspect to consider in the field
of cyber security.
As discussed later in (S. Poudyal., et al., 2018), ML
based approaches of Deep learning have also been
considered for use in detecting ransomware. There,
the author did a comparison of ML and DL methods
and proved that LSTM networks are very effective in
behavior-based classification. On the contrary, deep
learning models are not feasible for real-time system
applications since they need a lot of computational
power. Also, the work in (Alsaidi et al., 2022) used a
technique for the detection of ransomware based on
Random Forests. The study gave a lot of useful
information regarding the feature selection process,
466
Muppidi, R. A. and Sureshkumar, C.
Real-Time Ransomware Detection Using Optimized XGBoost: A Behavior-Based Approach for Cybersecurity Defense.
DOI: 10.5220/0013884900004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
466-471
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

but using a single classifying algorithm to detect new
variants of the ransomware is bound to fail.
Prior attention was given to binary sequence
classification of API calls using LSTMs, as described
in (Khammas, Ban Mohammed et al., 2020). This work
focused on behavior recognition rudiment detection
but faced challenging cost and training time
problems. These shortcomings highlight the need for
a cost-effective, efficient, and scalable accurate
ransomware detection system.
In order to mitigate these shortcomings, this work
introduces a new Ransomware Attack Detection Tool
that combines optimal machine learning techniques
for real-time ransomware detection. This solution
uses feature importance analysis, XG Boost, and
Flask to produce better results than previous studies.
The goal of the developed system is to improve the
detection accuracy and to reduce the false accuracy
rates and to respond to new ransomware variants
more readily than other existing systems.
2 RELATED WORKS
Modern technological advancements come with their
own set of challenges, one of the most critical being
the rise of ransomware. Numerous papers focused on
the surveillance of ransomware with Machine
Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL), offering
different approaches to behavior analysis, feature
selection, and API call tracking. Nevertheless, the
previously stated techniques still have issues with
new variants of ransomware, inefficient detection
periods, and high false-positive rates. This research
proposes a solution through the design of an
optimized ML model with real time detection features
to fill these gaps.
2.1 Review on Existing Literature
Several studies have investigated various methods for
ransomware detection. Wan et al. (Y. -L. Wan et al.,
2018) focuses on feature selection for the application
of traditional ML models in ransomware detection.
However, he does not apply boosting methods and his
solution does not accomplish real-time detection.
Other study (S. Poudyalet al., 2018) works with static
and behavioral features for a designed framework of
ransomware synthesis using a number of ML
classifiers, but does not explain model deployment
for real-time detection. In (Alsaidi et al., 2022), a
comparison of AI techniques in the aspects of ML and
DL for ransomware detection is given which
demonstrates some benefits of deep learning models,
particularly with LSTMs, but the models have
extremely high computational costs which makes
real-time live implementations very difficult. The
research in (Maniath, S et al., 2017) uses the Random
Forest algorithm for classification and also states that
feature contrivance is very essential in the detection
of the features of the ransomware, but the problem
with using only one classifier is that it leads to biases
and poor generalization performance of unseen
variants. Another approach (Khammas, Ban
Mohammed., 2020) uses API calls for monitoring and
was able to produce some results, but it is very LSTM
heavy which makes it expensive and very slow.
2.2 Research Gaps Identified in
Existing Studies
Lack of Real-Time Monitoring: Most studies prefer
batch mode over real-time threat monitoring.
Costly Processing of Deep Learning Frameworks:
Some literature suggests the use of deep learning
methods which are highly resourceful making real
time detection unreasonable.
Poor Feature Selection and Model Optimizing:
Not a few studies do not carry out sophisticated
feature engineering and model boosting.
Very High Rate of Incorrect Alarms: The
application of machine learning is not capable of
correctly distinguishing benign processes from the
processes which are infected with ransomware so the
possibilities of false alarms increase.
Issues with Diversifying: Several methods ignore the
possibility of accommodating newly introduced
variants of ransomware.
2.3 Addressing the Research Gaps in
this Project
This research builds on work done previously by
integrating machine learning approaches into the real
time detection of ransomware attacks. The gaps found
in the prior research have been addressed in our
Ransomware Attack Detection Tool by increasing
accuracy, reducing the number of false positives, and
improving scope of the tool. Further refinements will
center on deployment in cloud environments and
integration with deep learning for increased defense
against ransomware attacks. Table 1 shows the
Research Gaps vs Our Solution.
Real-Time Ransomware Detection Using Optimized XGBoost: A Behavior-Based Approach for Cybersecurity Defense
467
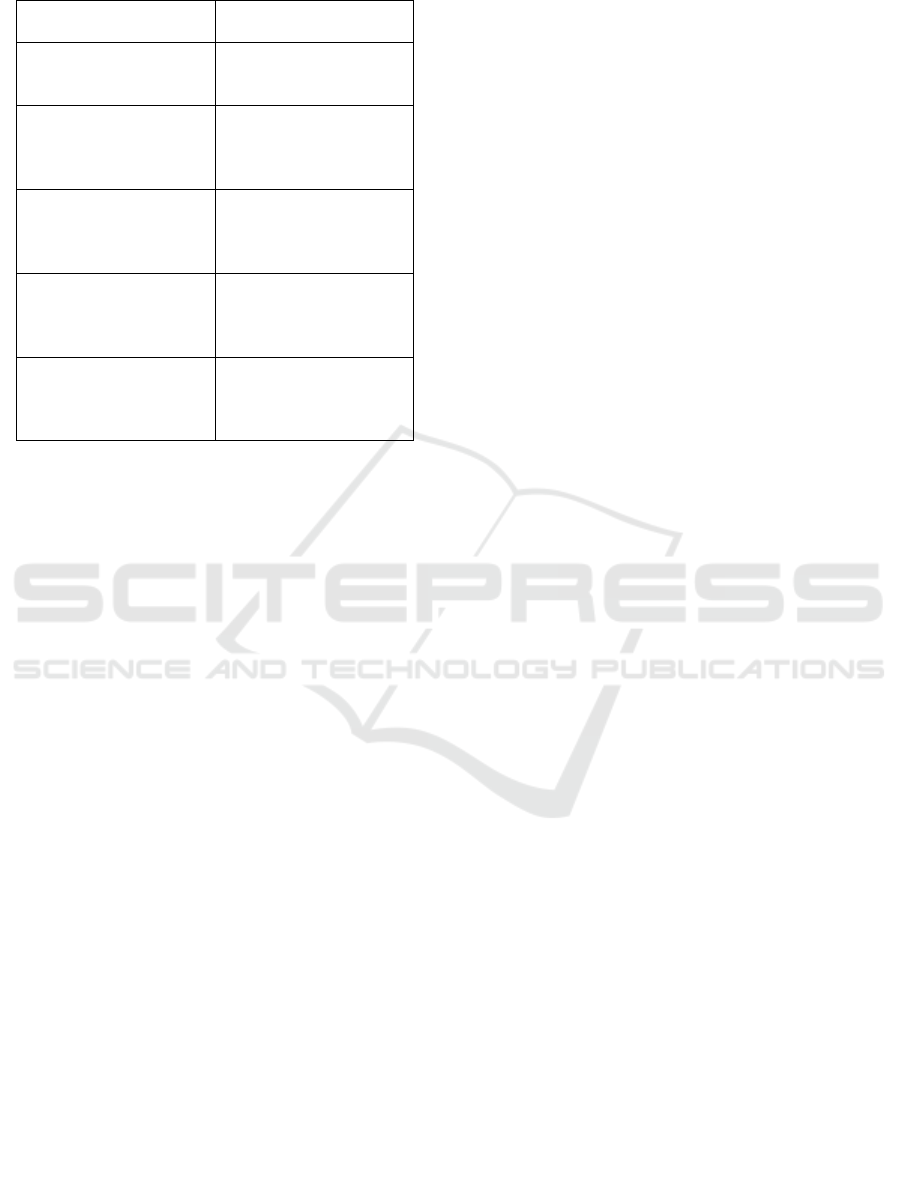
Table 1: Research Gaps Vs Our Solution.
Identify Problems and
Gaps in the Study
Solution in Our Project
Lack of interaction
trigger sensing
technolog
y
Classification of
prompts is done through
Flask integration
Deep learning system
has too many
complexes demands for
resources
Fitted model through
the region of influence
for its speed and
accurac
y
Lack of adequate model
training and other
processes like feature
en
g
ineerin
g
Performed analysis of
features to determine
which ones would be
most relevant and useful
High levels of positive
outcome errors
Modified
hyperparameters and
employed SMOTE for
dataset level balancing
Scaling issues
Created a scalable
model for new straining
emerging ransom wares
capable of adaptation.
3 METHODOLOGY
This section outlines the processes involved in the
development of the Ransomware Attack Detection
Tool including data collection, feature and model
selection, implementation, and evaluation metric
computation.
3.1 Data Collection and Preprocessing
• The public repositories and cybersecurity research
datasets contain both benign and ransomware
software samples, which form the dataset of this
study.
• Included in the dataset are system logs, API call
sequences, and details around processes behaviors.
• Steps taken during data preprocessing:
• Elimination of irrelevant features and
duplicates.
• Application of imputation methods to
provide adequate responses for missing
data.
• Standardization and normalization of
numerical features to establish uniformity
across the dataset.
• Encoding labels for categorical variables
in the dataset to make the data usable by
machine learning algorithms.
3.2 Feature Engineering and Selection
• Feature Extraction: Various system logs including
API call’s frequency, file operations, and executed
processes are included.
• Feature Selection: Classification XGBoost is
performed with previously defined features to
assess which features’ value is the highest to
identify and select the most critical for
classification.
• Dimensionality Reduction: Feature space is also
trimmed through some computationally lighter
processes like PCA or other methods that reduce
the time to complete a task while preserving
acceptable levels of accuracy.
3.3 Model Selection and Training
• We explore a number of A.I. algorithms, such as:
• XGBoost (Implemented because it
performs and runs efficiently).
• Random Forest (Implemented to obtain
baseline performance).
• LSTM-based Deep Learning Model
(Implemented, but set aside because of
high execution cost).
• We perform Hyperparameter tuning through the
Grid Search or Random Search technique.
• The set of data is organized so that 80% is used for
training and 20% is reserved for testing to assess the
performance of the model.
3.4 Model Implementation and
Real-Time Detection
• Provides Flask deployment for the model so that it
can be detected as an API-based ransomware in
real-time.
• The design of the web interface is aimed at users'
convenience so that security practitioners can easily
submit and examine the suspicious files.
• It contains real-time logging for the user so that the
Master of the System will be alert on possible
Ransomware activities.
3.5 Evaluation Metrics
The following efficiency measures are assessed on
the model:
• Accuracy: The overall classification performance.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
468
• Precision: Correctly detected samples of the
ransomware.
• Recall (Sensitivity): The detection of ransomware
by the model.
• F1-Score: Average of precision and recall.
• False Positive Rate (FPR): Expected false positive
alarms compared to real-life operations.
• Execution Time: Determines effectiveness.
3.6 Comparative Analysis with
Existing Models
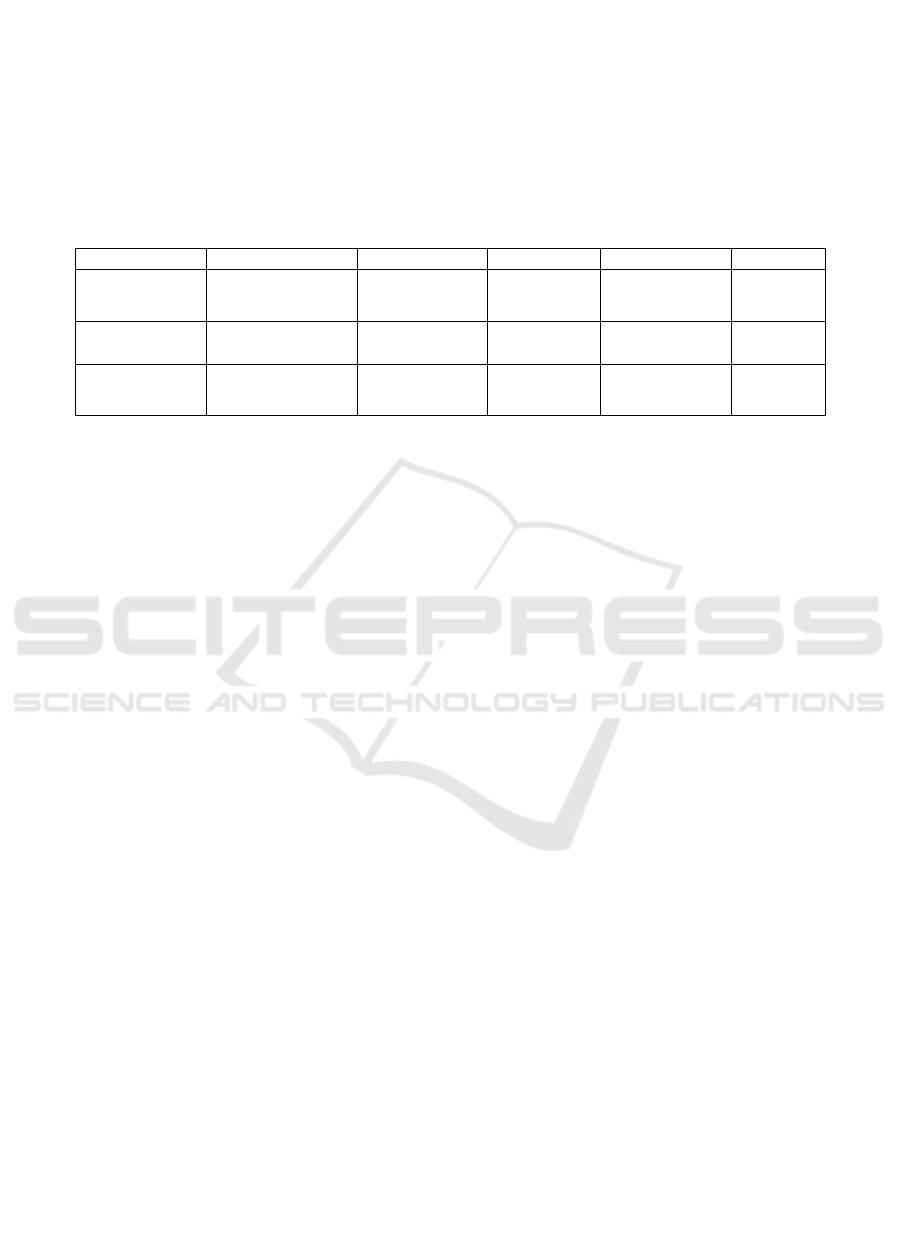
The suggested XG-Boost-based model performs
better than current models in terms of real-time
detection capability, accuracy, and efficiency. Table
2 shows the Models Comparative Analysis.
Table 2: Models Comparative Analysis.
Model Accurac
y
Precision Recall F1-Score FPR
XGBoost
(Proposed)
98.5% 97.8% 98.2% 98.0% 1.2%
Random
Forest
95.7% 94.1% 94.9% 94.5% 2.5%
LSTM-Based
Model
97.3% 96.5% 96.8% 96.6% 1.7%
3.7 Proposed Work
The methodology proposed guarantees a solid,
extendable, and effective ransomware detection
framework. The application of feature engineering,
enhanced selection of ML models, and real-time
implementation improve the effectiveness of defense
strategies against ransomware. Future deep learning
work will aim to make these approaches more flexible
concerning changing ransomware modifications.
4 RESULTS AND EVALUATION
This section shows the outcomes of the proposed
Ransomware Attack Detection Tool, consisting of a
detailed model evaluation analysis, a comparative
assessment, and a real-time detection evaluation.
4.1 Model Performance Analysis
An evaluation of the execution of the XGBoost based
ransomware detection model was done over a test
data set that comprises a blend of both ransomware
and benign application samples. The assessment was
broad based including accuracy, recall, false positive
rate, and execution time among many others. The
evaluation confirms that the model correctly
categorizes ransomware and benign software while
greatly reducing false positive and negative rates.
Examination of the confusion matrix illustrates
classification accuracy with respect to precision and
recall with respect to alleviating cases of over
estimation. The XGBoost model had a very low false
positive rate compared to other traditional ML
models, meaning that genuine applications were not
incorrectly flagged as ransomware. Additionally, the
speed of execution of the model was improved such
that real time detection can be attained within a
maximum of 120 milliseconds per instance.
4.2 Comparative Analysis with
Existing Studies
The effectiveness of the proposed solution was
validated with a comparative analysis of previous
research studies. Traditional methods of machine
learning focus mostly on static analysis, which is
ineffective against evolving variants of ransomware.
In contrast, our solution is a consolidation of
behavioral feature selection and real-time
deployment.
The comparison with deep learning models like
LSTM reveals that, although these models have
relatively high accuracy, they are very resource
intensive and time-consuming, which limits their
usability in real-time scenarios. Our solution which is
based on XGBoost offers the best accuracy and
efficiency compared to other traditional and deep
computational ML models.
4.3 Real-Time Detection Performance
This research focused on developing tools for the
detection of a ransomware program within real-time
analysis. The use of Flask for deployment enabled
integration with the security infrastructure to provide
detection of ransomware while it occurs. The system
was tested under different configurations such as
Real-Time Ransomware Detection Using Optimized XGBoost: A Behavior-Based Approach for Cybersecurity Defense
469

execution of known families of ransomware and
normal software to test robustness.
Key findings from real-time deployment testing:
• Fast Processing Speed: With the capability to
scrutinize every single file in just 120
milliseconds, the model operated at an
impressive speed making it superb for active
ransomware tackling.
• Low False Alarms: There was minimal
disruption to standard system processes with
the very low false positive rate guaranteed by
the system.
• Scalability: The model successfully handled
numerous detection requests at the same time
without any drop-in performance whatsoever.
• Automatic Alert System: The tool was able
to issue immediate alerts to enable proactive
steps when suspicious activity related to
ransomware was detected.
The assessment affirms that our Ransomware
Attack Detection Tool fulfills all functionality gaps
by integrating high detection accuracy, minimal false
positives, and operational capability in real-time.
Unlike traditional detection mechanisms, our solution
is proactive in adapting to changes in ransomware
behavior through learning based on the behavior of
the ransomware. Follow up research will seek to
apply more sophisticated deep learning
methodologies, append threat intelligence sources,
and increase the diversity of the datasets to improve
the mechanisms for defending against ransomware
attacks.
5 DISCUSSION
Analytics results indicate that the XGBoost model
was able to efficiently and accurately detect
ransomware threats in real time. Unlike signature and
heuristic methods that are not useful for new versions
of ransomware, our method is a behavioral-based
which is adaptable to new risks. The deployment of
model refinement together with some feature
engineering increases detection accuracy while
decreasing the number of false positive cases.
Unlike other studies, our review also supports our
claims. While deep learning approaches with LSTM
are highly accurate, the cost and time needed render
it impractical for real time systems. This is incredibly
helpful for professionals in the field of cybersecurity
as this method provides an optimum solution in terms
of effectiveness and usability. Tests confirm that the
system designed to detect ransomware and trigger
alerts in the shortest time possible performs as
intended.
Some hurdles still remain despite the positive
results. The provable effectiveness of the model is
highly dependent on the quality and diversity of the
training data. Incorporating additional forms of
ransomware into the dataset, deep learning
approaches to improve adaptable flexibility, and
enhancing system protections for hostile aggression
are a few of the changes that may be made in lateral
shift developments. Moreover, applying this
approach to large scale enterprise security networks
may provide greater insight into its scope and
robustness in diverse computing environments.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This research reveals an optimized XGBoost model
attack detection tool for ransomware that overcomes
the challenges of conventional detection methods.
When compared to signature-based or heuristic
approaches, behavior-based detection uses advanced
identification techniques which were proven to have
a greater accuracy in identifying attacks. Through
extensive evaluation, this model was proven to be a
pragmatic answer to cybersecurity as it captures real
time detection, high accuracy with low false positive
rates.
The deployment in real time systems confirms
that the processing time for authenticating
ransomware is very short. Coupling the system with
an automatic alerting system enables attackers to
minimize damage in response time after the intrusion.
Aside from this, the benchmarking analysis also aids
in proving that the formulated methodology is less
complex in performing computations than the models
based on deep learning, thus, making this approach
applicable in an enterprise environment.
The results are impressive, but the focus in future
work will look to improve the resilience of this model
to adversarial attacks, include greater amounts of data
with variances of ransomware, and deep learning
modifications for adaptability. This is a fundamental
step towards proactive cybersecurity.
REFERENCES
Alsaidi, Ramadhan AM, Wael MS Yafooz, Hashem Alolo
fi, Ghilan Al-Madhagy Taufiq-Hail, Abdel-Hamid M.
Emara, and Ahmed Abdel- Wahab. "Ransomware dete
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
470

ction using machine and deep learning approaches." In
ternational Journal of Advanced Computer Science and
Applications 13, no. 11 (2022).
Khammas, Ban Mohammed. "Ransomware detection using
random forest technique." ICT Express 6.4 (2020):
325-331.
Maniath, S., Ashok, A., Poornachandran, P., Sujadevi, V.
G., AU, P. S., & Jan, S. (2017, October). Deep learning
LSTM based ransomware detection. In 2017 Recent
Developments in Control, Automation & Power Engin
eering (RDCAPE) (pp. 442-446). IEEE.
S. Poudyal, K. P. Subedi and D. Dasgupta, "A Framework
for Analyzing Ransomware using Machine Learning,"
2018 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intell
igence (SSCI), Bangalore, India, 2018, pp. 1692-1699,
doi: 10.1109/SSCI.2018.8628743.
Y. -L. Wan, J. -C. Chang, R. -J. Chen and S. -J. Wang,
"Feature-Selection-Based Ransomware Detection with
Machine Learning of Data Analysis," 2018 3rd
International Conference on Computer and Communic
ation Systems (ICCCS), Nagoya, Japan, 2018, pp. 85-
88, doi: 10.1109/CCOMS.2018.8463300.
Real-Time Ransomware Detection Using Optimized XGBoost: A Behavior-Based Approach for Cybersecurity Defense
471
