
Spiritual Leadership and Organizational Performance: A
PRISMA-Based Systematic Review and Future Research
Directions
Pushkar Dubey and Alpana Sharma
Department of management, Pandit Sundarlal Sharma (Open) University Chhattisgarh, Bilaspur, Chhattisgarh, India.
Keywords: Spiritual Leadership Organizational Performance, Systematic Review. Prisma, Workplace Success,
Employee Well-being, AI-based bibliometric analysis.
Abstract: The research follows a clear methodology using PRISMA rules to study what makes employees successful in
their workplace. This study is an AI-based bibliometric analysis and a systematic study. The research objective
is to examine how spiritual leadership affects job satisfaction, employee engagement, job performance also
employee well-being. In this study, the researcher used 524 publications and reviewed company performance
it has been observed that Spiritual leadership has excellent working conditions through employee engagement
and ethical decision support that produce optimized organizational excellence. The research shows that
organizations should use spiritual leadership to improve their workplace performance and leadership style. It
also gives new ideas for research related to management and helps in future studies on this topic.
1 INTRODUCTION
Spiritual leadership enables organizations to learn
many important aspects of leadership approaches,
Organization, workplace culture construction, and
employee welfare dimensions. Spiritual leadership
extends conventional approaches by combining
employee growth with shared moral values
because it draws from integrity alongside
compassion and vigorous purpose. The leadership
model creates a workplace environment where
employees can build connections based on
different goals and meet workplace objectives
while being treated with respect and work
motivation. The method now stands recognized
because it produces Motivated and satisfied
employees who help organizations advance. The
review follows PRISMA criteria to evaluate
spiritual leadership development and describes its
impact on organizational growth. The study
evaluates academic work about how spiritual
leadership impacts employee satisfaction together
with job engagement job performance and work-
related well-being to determine its present-day
organizational value. The principles of spiritual
leadership in modern times carry similar concepts
from ancient Bhagavad Gita wisdom because they
focus on compassionate work ethical responsibility
and spiritual fulfillment. When organizational
practices adopt these principles, they develop into
workplaces that prioritize employee personal and
professional growth. The study adopted PRISMA
criteria to analyze how spiritual leadership affects
employee well-being job satisfaction employee
engagement and job performance. High-level
investigations show that spiritual leadership
creates beneficial workplace environments that
lead to better organizational sustainability and
growth.
1.1 Objectives and significance of the
study
The research goal uses PRISMA guidelines and
AI-based bibliometric evaluation to perform a
thorough survey of modern organizational studies
on spiritual leadership. The research finds how
spiritual leadership affects both the psychological
state of employees and their job contentment, as
well as their satisfaction with work and dedication.
This research evaluates the effects of spiritual
leadership on ethical choices and both workplace
environment and organizational operational
outcomes. The study finds its importance through
Dubey, P. and Sharma, A.
Spiritual Leadership and Organizational Performance: A PRISMA-Based Systematic Review and Future Research Directions.
DOI: 10.5220/0013884400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
443-448
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
443

scientific analyses of how spiritual leadership
based on ancient teachings including the Bhagavad
Gita techniques applies to present-day business
leadership. The study combines the data from
various research databases to explain that
leadership principles which include selflessness
purposeful and meaningful work and ethical
responsibility enhance leadership performance
motivate team members and build organizational
growth.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The review of publications conducts analytical
research on the different ways that spiritual leadership
impacts organizations through their work progress
and performance results. This study analyzed 464 key
studies to illustrate spiritual leadership principles to
be used for practice in different organizational
contexts involving both leadership methodologies
and employee wellness work engagement job
performance and employee satisfaction. Many
research studies provided important insights
regarding the effects of spiritual leadership on
management areas as well as organizational
performance and employee well-being. The paper
clearly shows how spiritual leadership improves work
performance and employee engagement while
boosting job satisfaction and positions it as a crucial
factor for employee well-being and Employee
engagement (
Islam, A., et al. 2024)
. The research
analyzes turnover intention reduction and work-life
quality advancement through spiritual leadership
while demonstrating how spiritual well-being
inclusion produces desirable individual and
organizational outcomes (
Li, W., et al. 2023)
.
Modern organizational leadership insights benefit
strongly from the development of measurement tools
that examine how spiritual leadership affects
workplace performance (
Karim et al. 2022)
. New
research Demonstrates how spiritual leadership
generates positive organizational results by helping
organizations develop culture and maintain
operational stability when analyzing working
conditions and operational success (
Hunsaker, W. D.
(2022)
. The study shows that spiritual leadership
along with meaning creation in organizations creates
both positive job and life satisfaction and
performance effects (
Pio, R. J. (2022)).
The research
confirms spiritual leadership enhances lower burnout
and stronger employee endurance through its
accomplishment of better emotional exhaustion
results (
Astakoni et al. 2022)
. Professional advisor
encourages incorporating spiritual leadership
principles within leadership research methods to
create improved organizational frameworks that
focus on top-level ethical decisions
Pio, R. J. (2022)
.
This paper shows how spiritual leadership creates
ethical behavior while creating trust through spiritual
value execution which raises organizational
commitment
Göçen, A., & Şen, S. (2021).
Research
findings attest to the positive relationship between
spiritual leadership and employee job satisfaction, job
performance, and employee engagement while it
improves their work-life quality and prevents
turnover
Gunawan, I., & Adha, M. A. (2021).
The
examination studies how spiritual leadership
elements in higher education institutions affect both
faculties and student achievements (
Yang et al.
2021)
. The paper examines ethical management cases
and stress management methods that produce
performance improvements from spiritual leadership
implementations
Anser et al. 2021)
. Scientific
investigations demonstrate that spiritual leadership
techniques should be included in modern
management to create honesty and participation while
promoting ethical conduct (
Supriyanto et al. 2020)
.
The research shows that leadership that supports
spiritual integration helps develop long-lasting
positive organizational cultures that link personal
values to institutional values
Oh, J., & Wang, J.
(2020)
. Spiritual leaders actively improve teamwork
and increase workplace cooperation inside their
organizational structures
Pio, R. J. (2020)
. Several
studies prove that spiritual leadership creates higher
job satisfaction, and good performance because
employees under such a leadership context achieve
enhanced workplace purpose alongside superior work
satisfaction
Karadag et al.2020
. The research
confirms that spiritual leadership functions as a stress
reduction tool that helps employees develop better
well-being methods, to gain job performance and also
helps in employee engagement while minimizing
professional stress elements
Fry, L. W., &
Nisiewicz, M. S. (2020).
The findings confirm that
spiritual leadership in organization and management
produces desirable performance benefits that
combine financial advantages with improved
operational results and innovative solutions
Samul, J.
(2019).
The observed findings reveal spiritual
leadership facilitates organizations to pursue ethical
decisions together with responsible CSR actions
directed toward society and the environment (
Wang
et al. 2019
. Spiritual leadership in organizations
affects creativity and innovation while leaders build
innovative settings through customer value
incorporation alongside innovative thoughts
Pio, R.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
444
J., & Tampi, J. R. E. (2018)
. Organizations gain
increased strength from spiritual leadership according
to the review because spiritual leaders use positive
thinking to direct employees toward a meaningful
approach during crises (
Jabeen, N et al. 2017)
. The
concept of spiritual leadership improves employee
commitment while improving retention because
workers feel stronger associations with leaders and
also work effectively to achieve organizational goals
Fry, L. W., et al, 2017
. Spiritual leadership practices
increase employee engagement, and job performance,
job satisfaction through their effect on building
community connections and staff member
belongingness according to research findings
Fry, L
et al. 2011
. The paper explores how spiritual leaders
encourage communication to resolve workplace
conflicts thus improving teamwork
Chen et al. 2013
.
Additionally, it investigates spiritual leadership
impacts on corporate ethics through role modeling
and ethical leadership guidance for organizations
Fry,
L et al. 2010.
Workers blossom in their personal and
professional lives through spiritual leadership which
enhances their work-life balance according to
research
Sweeney et al. 2012
. The paper explores
spiritual leadership's effects on cultural evolution by
analyzing how leaders integrate spiritual approaches
to create moral work environments that draw
attention to staff welfare and enduring business
success while encouraging united teams and
continuing performance
Kaya, A. (2015)
. The
review demonstrates that spiritual leadership located
within transformational leadership helps
organizations improve their performance through
employee commitment, job satisfaction, and
employee engagement also trust creation, and
innovative solutions
Latham, J. R. (2014).
Spiritual
leadership promotes goal coordination between
employees and their organizations which gives
leaders directions to develop goal-oriented
innovation within the workplace
Fry, L et al. 2010.
3 METHODOLOGY
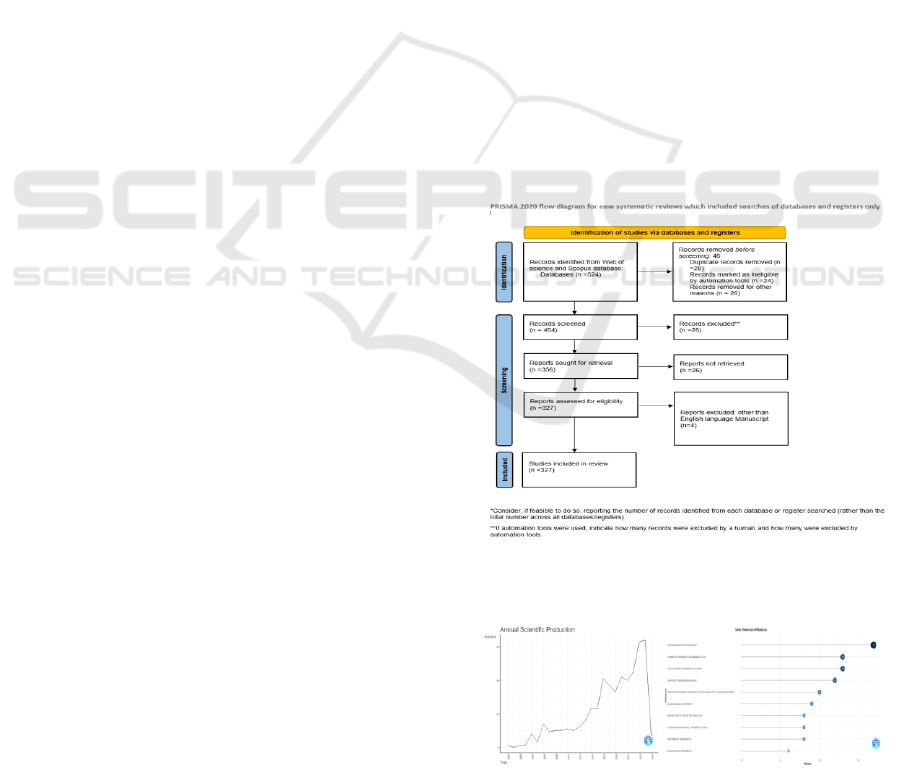
Using the PRISMA 2020 guidelines, the systematic
review of literature on "Spiritual Leadership and
Organization Performance" in the Web of Science
and Scopus database forms the basis of this analysis
(Figure 1). A three-phase method was followed to
find and evaluate the most accurate and legitimate
items. The first phase of record identification was
done using a generic Web of Science and Scopus
Database search turning up 524 records. The second
step screening took place. 46 records were
disqualified before 2010. Fourteen records were
eliminated since they were from non-article sources.
Of 464 documents, 24 were chosen for detailed
textual analysis. In the last stage, three 22 confirmed
valid records were added for examination for the
whole research. Between 2010 and 2025, the data set
was gathered using the literature database Web of
Sciences and Scopus using the keywords "Spiritual
leadership" and "Organizational Performance". The
hunt turned up 26 papers from 24 separate sources.
Still, the yearly growth rate comes out to be 8.45%.
Calculated at an average of 18.69 citations per
document, the citation count for the documents comes
to 689 references. Furthermore, suggestive of a great
degree of cooperation is the pattern of document
authorship. With 137 dedicated researchers, every
document has an average of 2.49 co-authors.
Furthermore, the figure of 21.76% for international
cooperation indicates that the topic is of general
global importance. Thus, over the 15 years, the
subjects "Spiritual Leadership" and "Organizational
Performance" have generated great academic interest
and curiosity; different authors cut across document-
type published publications. This accumulated data
was subjected to bibliometric analysis using the
biblioshiny technique using the R Studio program.
Figure 1: PRISMA technique for inclusion of research
articles.
Figure 2: Annual scientific production and most relevant
affiliations.
Spiritual Leadership and Organizational Performance: A PRISMA-Based Systematic Review and Future Research Directions
445

The Difference may reflect changing levels of
interest in the subject under study. Figure 2
illustrates the annual changes in the number of
articles published on the keywords "Spiritual
Leadership" and "Organizational Performance."
This area of scientific research does not show a
consistent growth trend. Factors influencing these
variations could include changes in government
funding policies or growing trends in management
theory that divert focus to new areas of interest.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Analyzing the associations contributing to the
literature offers a valuable understanding of the
global research landscape on "Spiritual Leadership"
and "Organizational Performance." Figure 2
highlights the institutions actively publishing in this
domain. According to the figure, Colorado State
University leads with seventeen articles,
demonstrating a strong research focus in this area.
COMSATS University Islamabad (CUI) and Texas
A&M University System follow, each contributing
thirteen articles. Other institutions, such as
Universitas Negeri Malang and Vietnam National
University Ho Chi Minh City (VNUHCM) System,
have each contributed thirteen and twelve articles
respectively. Notably, Indian institutions do not
appear among the leading contributors in this dataset,
suggesting that while spiritual leadership is deeply
rooted in Indian philosophy, its academic exploration
of organizational performance has not been as notably
represented in recent international research
publications. This absence may reflect differing
research priorities, financial frameworks, or
publication trends across regions.
Figure 3. Presents statistics and a map illustrating
the geographic distribution of scientific output on
"Spiritual Leadership" and "Organizational
Performance." The USA is the primary contributor
with an impressive 3,913 publications, followed by
China and Canada with 1,411 and 620 publications,
respectively. Consequently, these nations
demonstrated considerable interest in this field of
study. The results from other nations, such as
Australia, Thailand, Indonesia, and the United
Kingdom, are negligible. Multiple reasons may
elucidate this particular allocation. These factors may
stem from cultural influences, scholarly pursuits in
leading nations, or a financial framework. The notion
of Spiritual Leadership is fundamentally entrenched
in American institutional and leadership scholarship.
The United States demonstrates the highest
publishing rate, reflecting its robust academic and
research emphasis on the integration of spirituality
with management and organizational success.
Figure 3: Country scientific production and most cited
countries.
The aforementioned information Figure 3 and the
accompanying chart illustrate the total citations and
average article citations from nations that have
contributed to the literature on Spiritual Leadership
and Organizational Performance. The United States
possesses the highest citation count (TCs) among the
countries in the chart, with 3913. The average citation
count per item is notably high at 3,913, indicating that
each piece from the USA is significantly cited. China,
Canada, and Australia exhibit modest citations,
whereas Thailand's publications demonstrate an
extraordinarily high citation rate of 88.20. Indonesian
articles exhibit a notable average citation of 6.40,
indicating a relatively low quantity of published
works.
Figure 4: Word cloud.
The word cloud presented in Figure 4 highlights
the frequency of key terms connected with the
literature on Spiritual Leadership and Organizational
Performance. As anticipated, the term "Spiritual
Leadership" appears most frequently, emphasizing its
key role in the research theme. Other renowned terms,
such as "workplace spirituality," "transformational
leadership," "performance," "job satisfaction," and
"employee engagement," indicate a broad and
interconnected investigation of the subject. These
keywords reflect the different perspectives
researchers have adopted in studying the relationship
between spiritual leadership and organizational
effectiveness. This research shows how modern
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
446

organizations and management can adopt spiritual
leadership principles as an important part of their
organizational and management systems. Spiritual
leadership changes ethical leadership environments
and enhances employee connection as well as Job
satisfaction which leads to organizational
performance improvements. The integration sticks to
the present focus on ethical business management and
workplace spirituality as it provides modern answers
to workplace challenges including stress reduction
ethical decisions and employee retention. The
research findings from this study generate new
opportunities for spiritual business ethics
examination and expand the feasible use of leadership
and management techniques.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Research shows how leadership techniques create a
direct connection with vital workplace results that
include workplace spirituality along with
transformational leadership which generates better
performance stronger job satisfaction and improved
employee engagement. Many studies show how
spiritual leadership functions as a vital mechanism to
create ethical leadership together with improved
employee welfare and organizational cultural
development. Leadership approaches that focus on
the spiritual aspects of the organization provide direct
positive effects because they generate highly engaged
workforces alongside satisfied employees. Spiritual
leadership coordinates transformational leadership
approaches so it generates workplace spiritual
dimensions which enhances employee motivation
according to the research review. While providing
major findings to the research still requires further
research that will analyze spiritual leadership effects
on organization sustainability and industry-wide
cultural performance. Organizations can grow moral
leadership and improve employee commitment by
connecting present management practices with
spiritual ethics to achieve uninterrupted business
success.
REFERENCES
Islam, A., Zawawi, N. F. M., & Wahab, S. A. (2024).
Rethinking survival, renewal, and growth strategies
of SMEs in Bangladesh: the role of spiritual
leadership in a crisis. PSU Research Review, 8(1),
19-40.
Li, W., Abdalla, A. A., Mohammad, T., Khassawneh, O.,
& Parveen, M. (2023). Towards examining the link
between green HRM practices and employee green
in-role behavior: spiritual leadership as a moderator.
Psychology Research and Behavior Management,
383-396.
Karim, A., Bakhtiar, A., Sahrodi, J., & Chang, P. H.
(2022). Spiritual leadership behaviors in religious
workplace: the case of pesantren. International
Journal of Leadership in Education, 1-29.
Hunsaker, W. D. (2022). Spiritual leadership and
employee innovation. Current Psychology, 41(8),
5048-5057.
Pio, R. J. (2022). The mediation effect of quality of work
and job satisfaction in the relationship between
spiritual leadership and employee performance.
International Journal of Law and Management,
64(1), 1-17.
Astakoni, I. M. P., Sariani, N. L. P., Yulistiyono, A.,
Sutaguna, I. N. T., & Utami, N. M. S. (2022).
Spiritual Leadership, Workplace Spirituality and
Organizational Commitment; Individual Spirituality
as Moderating Variable. ITALIENISCH, 12(2), 620-
631.
Pio, R. J. (2022). The mediation effect of quality of work
and job satisfaction in the relationship between
spiritual leadership and employee performance.
International Journal of Law and Management,
64(1), 1-17.
Göçen, A., & Şen, S. (2021). Spiritual leadership and
organizational citizenship behavior: A meta-
analysis. SAGE Open, 11(3), 21582440211040777.
Gunawan, I., & Adha, M. A. (2021). The effect of instr
uctional, transformational, and spiritual leadership
on elementary school teachers’ performance and
students’ achievements. Cakrawala Pendidikan, 40(
1), 17-31.
Yang, J., Chang, M., Chen, Z., Zhou, L., & Zhang, J.
(2021). The chain mediation effect of spiritual leade
rship on employees' innovative behavior. Leadership
& Organization Development Journal, 42(1), 114-
129.
Anser, M. K., Shafique, S., Usman, M., Akhtar, N., &
Ali, M. (2021). Spiritual leadership and organizatio
nal citizenship behavior for the environment: an
intervening and interactional analysis. Journal of
Environmental Planning and Management, 64(8),
1496-1514.
Supriyanto, A., Ekowati, V., & Maghfuroh, U. (2020).
Do organizational citizenship behavior and work
satisfaction mediate the relationship between spiritu
al leadership and employee performance? Managem
ent Science Letters, 10(5), 1107-1114.
Oh, J., & Wang, J. (2020). Spiritual leadership: Current
status and Agenda for future research and practice.
Journal of Management, Spirituality & Religion,
17(3), 223-248.
Pio, R. J. (2020). The relationship between spiritual
leadership and quality of work life and ethical
behavior, and its implication for increasing organiza
Spiritual Leadership and Organizational Performance: A PRISMA-Based Systematic Review and Future Research Directions
447

tional citizenship behavior. Journal of Management
Development, 39(3), 293-305.
Karadağ, M., Altınay Aksal, F., Altınay Gazi, Z., &
Dağli, G. (2020). Effect size of spiritual leadership:
In the process of school culture and academic succe
ss. Sage Open, 10(1), 2158244020914638.
Fry, L. W., & Nisiewicz, M. S. (2020). Maximizing the
triple bottom line through spiritual leadership. Stanf
ord University Press.
Samul, J. (2019). Spiritual leadership: Meaning in the
sustainable workplace. Sustainability, 12(1), 267.
Wang, M., Guo, T., Ni, Y., Shang, S., & Tang, Z. (2019).
The effect of spiritual leadership on employee effect
iveness: An intrinsic motivation perspective. Fronti
ers in Psychology, 9, 2627.
Pio, R. J., & Tampi, J. R. E. (2018). The influence of
spiritual leadership on quality of work life, job
satisfaction, and organizational citizenship behavior.
International Journal of Law and Management,
60(2), 757-767.
Jabeen, N., Irfan, S., & Salman, Y. (2017). Spiritual
leadership in organizational context: A research gap
in South Asia. South Asian Studies, 32(01), 205-218.
Fry, L. W., Latham, J. R., Clinebell, S. K., & Krahnke,
K. (2017). Spiritual leadership as a model for perfor
mance excellence: a study of Baldrige award recipie
nt. Journal of Management, Spirituality & Religion,
14(1), 22-47.
Fry, L. W., Latham, J. R., Clinebell, S. K., & Krahnke,
K. (2017). Spiritual leadership as a model for
performance excellence: a study of Baldrige award
recipients. Journal of Management, Spirituality &
Religion, 14(1), 22-47.
Fry, L. W., & Walumbwa, F. O. (2011). RETRACTED:
Impact of spiritual leadership on unit performance.
Chen, C. Y., & Li, C. I. (2013). Assessing the spiritual
leadership effectiveness: The contribution of
follower's self-concept and preliminary tests for the
moderation of culture and managerial position. The
Leadership Quarterly, 24(1), 240-255.
Choudhary, A. I., Akhtar, S. A., & Zaheer, A. (2013).
Impact of transformational and servant leadership on
organizational performance: A comparative analysis.
Journal of Business Ethics, 116, 433-440.
Fry, L. W., Matherly, L. L., & Ouimet, J. (2010). The
spiritual leadership balanced scorecard business
model: The case of the Cordon Bleu‐ Tomasso Corp
oration. Journal of Management, Spirituality & Reli
gion, 7(4), 283-314.
Sweeney, P. J., & Fry, L. W. (2012). Character develop
ment through spiritual leadership. Consulting Psych
ology journal: practice and research, 64(2), 89.
Kaya, A. (2015). The Relationship between Spiritual
Leadership and Organizational Citizenship Behavio
rs: A Research on School Principals' Behaviors.
Educational Sciences: Theory and Practice, 15(3),
597-606.
Latham, J. R. (2014). Leadership for quality and innova
tion: Challenges, theories, and a framework for
future research. Quality Management Journal, 21(1),
11-15.
Chen, C. Y., & Yang, C. F. (2012). The impact of
spiritual leadership on organizational citizenship
behavior: A multi- sample analysis. Journal of Busi
ness Ethics, 105, 107-114.
Fry, L. W., Matherly, L. L., & Ouimet, J. (2010). The
spiritual leadership balanced scorecard business mo
del: The case of the Cordon Bleu‐ Tomasso Corpora
tion. Journal of Management, Spirituality & Religio
n, 7(4), 283-314.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
448
