
PDF Malware Detection: Toward Machine Learning Modelling with
Explainability
Venkatesh K.
1
, Gopi Chand K.
2
, Aravind B.
2
, Kantha Raju K.
2
and Madhan Mohan Reddy Y.
2
1
Department of CSE (Data Science), Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology, Anantapuramu, Andhra Pradesh, India
2
Department of CSE (AI & ML), Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology, Anantapuramu, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: PDF Malware Detection, ML, RF, SVM, DNN, Explainability, Cybersecurity, Malicious PDF, Classification
Algorithms, Kaggle Dataset.
Abstract: In the digital age, PDF files are widely used for document sharing, but their popularity also makes them a
target for malware attacks. This project, titled " Detecting Malware in PDFs: Advancing Machine Learning
Models with Interpretability Assessment," aims the goal is to design and assess machine learning models
aimed at identifying malware within PDF files. Utilizing a dataset from Kaggle, which contains labelled
examples of malicious and benign PDFs, various algorithms including RF, C5.0, J48, SVM, AdaBoost, DNN,
GBM, and KNN will be applied. The primary focus is on achieving high detection accuracy while also
providing explainability to gain insight into how the models make decisions. By leveraging machine learning
techniques, this project seeks to enhance cybersecurity measures, offering a robust solution to identify and
mitigate potential threats embedded in PDF documents.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the digitalization era taking the world by storm,
file formats have also evolved, and PDF is one of the
most commonly used formats for documents sharing
because of its portability, compatibility, and security
features. But their wide usage is also why they are a
key target, with cybercriminals usually inserting
malicious content into PDF documents to take
advantage of (many times unpatched) vulnerabilities.
Example: Signature based techniques traditional
methods to detect malware often fail to keep up with
the evolution of cyber threats. (Alam, S, et.al 2015)
This project also strives towards developing
explainable ML-based detection models to detect
malware in PDF files as a solution over this problem.
The dataset used in this study is publicly available
through Kaggle and consists of labeled examples of
benign and malicious PDF documents. (Alshamrani,
S. S. 2022). We will use a range of ML algorithms
such as RF, C5. Here, the competing classifiers are
LDA, RF, NB, MLP, LR, DT, 0, J48, SVM,
AdaBoost, DNN, GBM, and KNN. The objective is
to assess the models' effectiveness based on metrics
like accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score in order
to uncover the top-performing model for malware
detection. (Aslan, O., & Samet, R. 2020).
Furthermore, interpretability methods would be
adopted to elucidate the models' predictions, enabling
the security analyst to gain insights into the reasons
behind labelling a file as malicious or benign. Read
More (Han, K. S., et.al, 2015) This project contributes
to improve cybersecurity with trade-off explainable
and high detection. Explain ability - The findings
yielded from the explain ability analysis will further
enhance the trust and transparency of machine
learning derived malware detection techniques.
(Hossain, G, et,al, 2024)The project aims to provide
organizations and individuals with an effective,
scalable, and interpretable solution for mitigating
PDF-based threats. Objective of Project.
State-of-the-art ML based system for detection of
malware embedded into PDFs. (Islam, R, 2013) This
includes using and studying a few algorithms, for
example, ML algorithms will be utilized, for
example, RF, C5. 0, J48, SVM, AdaBoost, DNN,
GBM, and KNN) to perform classification on the
features extracted in the first stage, in order to
determine whether a PDF is harmful or safe. (Kang,
A. R, et, al2019) Firstly, high detection accuracy
should be achieved, (Komatwar, R, 2021) and the
decision-making process of these models should be
interpretable and transparent. The project aims at a
432
K., V., K., G. C., B., A., K., K. R. and Y., M. M. R.
PDF Malware Detection: Toward Machine Learning Modelling with Explainability.
DOI: 10.5220/0013884200004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
432-437
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

valuable solution for detecting and neutralizing
threats in PDF files, with a dual focus on accuracy and
explain ability. (Komatwar, R, 2021). The project
would also evaluate the performance of these models
with different metrics and integrate the most
promising approaches in a functional system for
online malware detection, all aimed at enhancing
sensitive information protection and a secure digital
environment.
This project focuses on building and evaluating
machine learning models to detect malware in PDF
files. 3.2.1. Classifier (Liu, C, et.al 2021) Different
classification algorithms are applied, namely, ML
algorithms RF, C5 are used in this scope. 0, J48,
SVM, AdaBoost, DNN, GBM, and KNN to the
Kaggle dataset of labelled PDFs. The project focuses
on achieving both high detection accuracy and model
explain ability, enabling users to comprehend the
basis for classifications and improving the model's
usability. (Livathinos, N, et.al 2021) Main project
stages include dataset pre-processing, model training
and evaluation as well as performance comparison by
accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. Ultimately,
this will result in a practical system for real-time
malware detection within PDF documents, which will
aid in strengthening cybersecurity measures and
deliver tangible insight into the reasoning behind the
models' decisions. (Li, Y., 2022). The malware type
and the built integration with present security
framework is outside of the project scope
This makes PDF files an example of a common vector
for malware distribution due to their common use and
support for embedding different forms of content.
However, traditional security systems are often
unable to detect and neutralize threats hidden in PDF
documents due to the growing sophistication of
malware. (Maiorca, D., & Biggio, B. 2019). This
project was developed in response to the high demand
for better detection methods and it specifically uses
machine learning algorithms to classify the PDF files
into harmful or safe. With the difficulty of sifting
through numerous PDF files and the evolving tactics
of malware, automated detection solutions are
critical. (Maiorca, D., & Biggio, B. 2019b) say this
project presents a robust, fast, and explainable ML
Model to help enhance the malware detection
capabilities and improve the overall cybersecurity
defences.
While PDF files are commonly used for
document sharing, the unfortunate fact is that they are
frequently the subject of malware attacks. Identifying
any harmful content in these files is essential to
protecting sensitive data and ensuring cyber safety.
Maiorca, D., Giacinto, G., & Corona, I. (2012).
Traditional methods of detection often fail due to the
sophisticated methods taken by attackers. Title of the
project is - Detecting Malware in PDFs: Towards
Improving Machine Learning Models with
Interpretability Evaluation This challenge is the
primary focus of this project - to apply state-of-the-
art machine learning algorithms on the relevant
dataset of labelled PDFs obtained from Kaggle. (Mao,
Z., et.al 2022) Our aim of providing a more
comprehensive due to not only emphasizing high
detection accuracy but also explain ability of the
models. The increasing use of PDF files for document
sharing has unfortunately made them a prime vector
for malware attacks. Detecting malicious content
within these files is crucial to safeguarding sensitive
information and maintaining cybersecurity (Maiorca,
D., Giacinto, G., & Corona, I. 2012). Traditional
detection methods often fall brief because of the
advanced methods used by attackers. This project,
Detecting Malware in PDFs: Advancing Machine
Learning Models with Interpretability Assessment,
seeks to address this challenge by applying advanced
machine learning algorithms to a dataset of labeled
PDFs from Kaggle. (Mao, Z., et.al 2022). By not only
focusing on high detection accuracy but also on the
explainability of the models, our goal is to offer a
more thorough.
2 RELATED WORKS
Identifying malware in PDF files has become a
crucial aspect of cybersecurity. Muir, N. (2009).
Several research studies have explored different
machine learning techniques to enhance PDF
malware detection. This literature survey is structured
into five subheadings, providing an overview of
existing methodologies and challenges.
PDF Malware takes advantage of vulnerabilities
in PDF viewers as well as embedded scripts to carry
out malicious actions. Among the attack vectors used
are JavaScript-based attacks, embedded files, and
obfuscated code Shijo, P. V., & Salim, A. (2015).
Research has shown that fine-tuning the language
model using edited embeddings works well Laskov et
al. (2011), attackers utilize evasion techniques to
circumvent traditional signature-based detection
methods. Singh, P., Tapaswi, S., & Gupta, S. (2020a).
More recent works have demonstrated that current
PDF malware applies greater use of encoding and
encryption patterns to obfuscate payloads making
them harder to detect. PDF malware detection using
ML models typically uses static and dynamic
features to classify PDFs as malware or benign.
PDF Malware Detection: Toward Machine Learning Modelling with Explainability
433
Classifiers like Random Forest and SVM have been
shown effective at distinguishing malicious PDFs
from benign (Kang, A. R., et. al 2018), (Liu, C, et.al
2021) Static analysis retrieves metadata, object
counts, and JavaScript presence, while dynamic
analysis looks at execution behavior in a sandboxed
environment. Souri, A., & Hosseini, R. (2018).
Feature Feature Engineering Feature selection is a
critical step to increasing model performance. Static
features like JavaScript presence, embedded file
counts, and object types are complemented by
behavioural features such as execution patterns and
API calls. Researchers like Maiorca et al. As
discussed in (2019), in order to improve both
accuracy and explain ability, they used methods such
as Information Gain, which essentially implements
analyzing what features are needed and applying
PCA. Šrndić, N., & Laskov, P. (2016). Incorporating
explain ability is critical to construct trust and
increase adoption in cybersecurity solutions. As
recent studies focused on model interpretation
decisions have used LIME and SHAP methods, they
will be discussed below. As noted by Ribeiro et al.
(2016) showed how LIME can generate
explanations, which are human interpretable, for
classifier predictions. Ucci, D., Aniello, L., &
Baldoni, R. (2019). One paper addresses way to
detect PDF malware which has made great strides,
however, challenges remain. Artificial Intelligence
in Computer Networks tends to become impassable
due to adversarial attacks, gradually improving
evasion techniques, and unequal class distribution.
Wiseman, Y. (2019). Future work will continue to
explore adversarial robustness, real-time detection,
and federated learning approaches.
The field of PDF malware detection has seen
significant advancements with machine learning
models. While various approaches, including
Random Forest, SVM, and deep learning, have shown
promise, ensuring model explainability and
robustness against adversarial attacks remains a
challenge. Zhang, J. (2018). Future work should
focus on improving feature selection, developing
adversarial robust models, and leveraging explainable
AI for cybersecurity applications.
3 METHODOLOGY
One suggested document oculus technique is to use
mulled over machine discovery following to
distinguish PDFs as either malignant or non-
terrifying. Using a large (rather than from all the
labelled examples of both classes of PDF) and
extracting valuable information from PDF
documents involves a myriad, both it will use ML
algorithms such as from RF, C5. Six machine
learning algorithms were utilized: C4. Such
approach allows a comprehensive evaluation of the
performance and effectiveness of the algorithms for
malware detection. One of the main components of
the proposed system is explain ability, which
guarantees the transparency and interpretability of
the decision-making process of the ML models. the
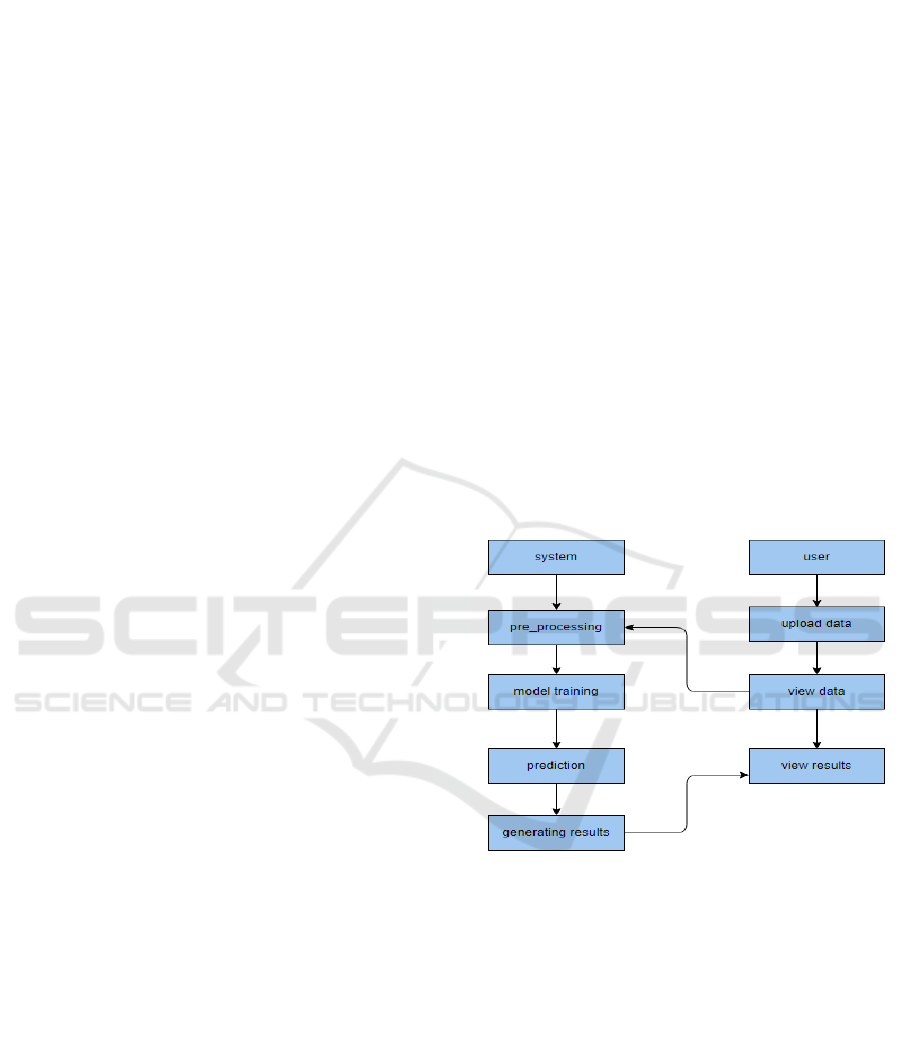
figure 1 shows the Block diagram of the proposed
system.
The system also uses explainable AI techniques to
help users understand the reasoning behind each
classification, improving trust and reliability. It aims
for high detection accuracy while providing insights
into likely threats, which is a great solution for
detecting and addressing malware in PDF files.
Moreover, it will focus on making timely detection
enabling proactive safeguarding of sensitive data and
enhancing cybersecurity efforts.
Figure 1: Block Diagram of the Proposed System.
3.1 Data Collection
In this project, we use a malicious and benign sample
labeled dataset of PDF files from Kaggle. It consists
of static features, taken from the PDFs, including
metadata attributes, JavaScript, object counts, and
embedded file details. The labels denote if a PDF file
is malicious (1) or benign (0) thus allowing for
supervised learning. The dataset is comprehensively
reviewed to provide diversity in malware families,
showing different attack vectors, including JavaScript
based exploits, embedded shellcode, and obfuscation
techniques. Because benign PDFs are likely to far
outweigh malicious PDFs in number, oversampling
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
434

(e.g., SMOTE) or under sampling may be utilized to
balance the dataset.
3.2 Data Preprocessing
Data preprocessing is essential for maintaining
quality and enhancing model performance. Initially,
missing values and redundant features are removed to
eliminate noise. The dataset undergoes feature
engineering, where static properties such as
JavaScript occurrences, embedded objects, and
entropy-based measures are extracted. To enhance
model efficiency, feature scaling (MinMax or
StandardScaler) is applied to normalize numerical
attributes. Additionally, Feature selection methods
such as RFE and Information Gain help in reducing
dimensionality while retaining the most relevant
features. For categorical data, one-hot encoding or
label encoding is used. Given that PDF malware often
exhibits patterns detectable in text-based features,
TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document
Frequency) and n-gram analysis are employed for
textual components.
3.3 Model Training
Several ML models are trained to detect malware in
PDF files. The selected classifiers ML algorithms will
be employed, including RF, C5.0, J48, SVM,
AdaBoost, DNN, GBM, and KNN. The dataset is
divided into training (80%) and testing (20%) sets to
assess the model's generalization. Cross-validation
(5-fold or 10-fold) is employed to prevent overfitting
and optimize hyperparameters. The training process
involves fitting models using optimized
parametersGrid Search or Bayesian Optimization is
used for hyperparameter tuning to maximize
performance. Given the need for interpretability in
cybersecurity applications, explainability methods
like SHAP and LIME) are integrated to assess the
significance of features and the decision-making
process. The final models' performance is assessed
using Metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, F1-
score, and ROC-AUC are used to guarantee a
dependable detection system.
3.4 Evaluation
It should be ensured that these trained machine
learning models can effectively detect malicious
PDFs showing promising result. Metrics including
accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and ROC-AUC
to determine the model’s predictive capabilities. Due
to the potential severe cybersecurity ramifications of
incorrect positives and incorrect negatives, proper
attention is paid to precision and recall to strike a
balance between accurate detection and preventing
misclassifications. Cross-validation techniques (5-
fold or 10-fold) are then used to validate the resilience
of the model and minimize the risk of overfitting
across different segments of the data. Also, confusion
matrices are reviewed to show how correct and
incorrect predictions are distributed together with an
analysis of weaknesses in the different models.
In addition to traditional evaluation techniques,
explainability techniques such as SHAP and LIME
are employed to examine the decision-making of the
model. 1. These techniques help determines which
features whether the presence of JavaScript,
embedded objects, or metadata anomalies contribute
most to classification decisions. The experts'
overview of explainable AI shows the integration of
explainability in the model, which not only ensures
the transparency of the model but also facilitates the
security analyst to understand why a particular PDF
is marked as malicious. Select the model with the
highest evaluation results with good applicability.
3.5 Deployment
Once the architecture is selected we can now deploy
it to a production based cyber security environment to
allow automated PDF malware detection. The
deployment process starts with model optimization,
where model optimization techniques such as
quantization and pruning, are performed to decrease
the computational burden and still maintain detection
accuracy. The trained model is then converted into a
deployable format such as ONNX (for
interoperability), TensorFlow SavedModel, or
serialized Pickle (3. pkl) model (only for scikit-learn
if you are using scikit-learn models).
To provide real-time detection capabilities, the
model is embedded into a cybersecurity pipeline,
where it receives oncoming PDF files as email
attachments, web downloads or from enterprise
document systems. Web-based or even command-
line user interface allowing users to upload/scan files
with a REST API developed using flask or fast API
the system can be deployed in cloud instances such
as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud for successful large
deployment, allowing scaling and remote access.
Moreover, containerization is achieved with the help
of tools like Docker and Kubernetes, providing
seamless integration with security tools, including
SIEM systems.
PDF Malware Detection: Toward Machine Learning Modelling with Explainability
435

4 RESULTS AND EVALUATION
The chart above demonstrates the accuracy
comparison of different ML algorithms, highlighting
the performance differences among the different
models. Highest accuracy achieved by GBM and RF
indicates their ability to solve the problem. Ensemble
models, which use multiple decision trees to produce
resilient, generalized predictions that lower
overfitting and boost performance. AdaBoost also
fared well, ranking just below Gradient Boosting and
Random Forest, which shows the effectiveness of
boosting techniques that take a weak learner and
refine it. We compared the accuracy of various
algorithms; SVM and KNN showed slightly less
accuracy as compared to the rest. SVC carries over
some of its performance on kernel choice and
hyperparameters which can be hard to tunetune.
However, KNN is less accurate for high dimensional
data. Interestingly, DNN has the worst performance
of the classifiers. This could happen due to reasons
such as a lack of training data or an inefficient
network architecture or even not tuning the
hyperparameters enough.
In conclusion, Ensemble models like RF and
GBM perform much better than individual models by
crafting multiple week learners, thereby increasing
the accuracy and generalization. On the other hand,
the lower performance of DNN indicates that either a
more complex architecture or more data is necessary
in order to exploit the full potential of DNN. As
discussed earlier, the choice of a suitable algorithm is
determined by data characteristics, computational
limits, and optimization techniques.
5 DISCUSSION
Speculations in regard to improvements on this
project could be incorporating high-level
explainability methods such as SHAP or LIME to
increase the interpretability of complex models as the
DNN. Furthermore, augmenting the dataset with
diverse and up-to-date PDF samples might enhance
the model's robustness against evolving malware
execution tactics. Real-time threat detection and
automatically updating the models to defend against
new threats would also improve the system’s
effectiveness. Lastly, investigating hybrid models
that merge machine learning with classical rule-based
techniques may provide a more comprehensive
approach to PDF malware detection, thereby
enhancing cybersecurity defenses.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This project helps us to understand how different ML
algorithms can be used to detect malicious content in
PDF files. Using models like Random Forest, SVM,
DNN, etc., this project not only performs well in
terms of detection accuracy but also accentuates
explainability of the models. The methods approach
also addresses the dual crisis of trust in the detection
process, in addition to simplification of the detection
task. The integration of explainability into the
detection models is an important step forward in
cybersecurity, offering a reliable and interpretable
method for protecting against the threat of PDF-
based malware.
REFERENCES
Abu Al-Haija, Q., Odeh, A., & Qattous, H. (2022). PDF
Malware Detection Based on Optimizable Decision
Trees. Electronics 2022, Vol. 11, Page 3142, 11(19),
3142.https://doi.org/10.3390/ELECTRONICS1119314
2
Alam, S., Horspool, R. N., Traore, I., & Sogukpinar, I.
(2015). A framework for metamorphic malware
analysis and real-time detection. Computers and
Security,48,212233.https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COSE.20
14.10.011
Alshamrani, S. S. (2022). Design and Analysis of Machine
Learning Based Technique for Malware Identification
and Classification of Portable Document Format Files.
Security and Communication Networks, 2022(1),
7611741. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7611741
Aslan, O., & Samet, R. (2020). A Comprehensive Review
on Malware Detection Approaches. IEEE Access, 8,
62496271.https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2963
724
Han, K. S., Lim, J. H., Kang, B., & Im, E. G. (2015).
Malware analysis using visualized images and entropy
graphs. International Journal of Information Security,
14(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10207-014-0242-
0
Hossain, G. M. S., Deb, K., Janicke, H., & Sarker, I. H.
(2024). PDF Malware Detection: Toward Machine
Learning Modeling with Explainability Analysis. IEEE
Access,12,1383313859.https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCE
SS.2024.3357620
Islam, R., Tian, R., Batten, L. M., & Versteeg, S. (2013).
Classification of malware based on integrated static and
dynamic features. Journal of Network and Computer
Applications,36(2),646656.https://doi.org/10.1016/J.J
NCA.2012.10.004
Kang, A. R., Jeong, Y. S., Kim, S. L., & Woo, J. (2019).
Malicious PDF detection model against adversarial
attack built from benign PDF containing javascript.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
436

Applied Sciences (Switzerland), 9(22).
https://doi.org/10.3390/APP9224764
Komatwar, R., & Kokare, M. (2021). A Survey on Malware
Detection and Classification. Journal of Applied
Security Research, 16(3), 390–420.
https://doi.org/10.1080/19361610.2020.1796162
Li, Y., Wang, X., Shi, Z., Zhang, R., Xue, J., & Wang, Z.
(2022). Boosting training for PDF malware classifier
via active learning. International Journal of Intelligent
Systems,37(4),28032821.https://doi.org/10.1002/INT.
22451
Liu, C., Lou, C., Yu, M., Yiu, S. M., Chow, K. P., Li, G.,
Jiang, J., & Huang, W. (2021). A novel adversarial
example detection method for malicious PDFs using
multiple mutated classifiers. Forensic Science
International: Digital Investigation, 38.
https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FSIDI.2021.301124
Livathinos, N., Berrospi, C., Lysak, M., Kuropiatnyk, V.,
Nassar, A., Carvalho, A., Dolfi, M., Auer, C., Dinkla,
K., & Staar, P. (2021). Robust PDF Document
Conversion using Recurrent Neural Networks.
Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial
Intelligence,35(17),1513715145.https://doi.org/10.160
9/AAAI.V35I17.17777
Maiorca, D., Giacinto, G., & Corona, I. (2012). A pattern
recognition system for malicious PDF files detection.
Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including
Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and
Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), 7376 LNAI, 510–
524. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31537-4_40
Maiorca, D., & Biggio, B. (2019a). Digital Investigation of
PDF Files: Unveiling Traces of Embedded Malware.
IEEE Security and Privacy, 17(1), 63–71.
https://doi.org/10.1109/MSEC.2018.2875879
Maiorca, D., & Biggio, B. (2019b). Digital Investigation of
PDF Files: Unveiling Traces of Embedded Malware.
IEEE Security and Privacy, 17(1), 63–71.
https://doi.org/10.1109/MSEC.2018.2875879
Mao, Z., Fang, Z., Li, M., & Fan, Y. (2022). EvadeRL:
Evading PDF Malware Classifiers with Deep
Reinforcement Learning. Security and Communication
Networks, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7218800
Muir, N. (2009). Working with Files and Folders.
Windows® 7 Just the StepsTM for Dummies®, 25–35.
https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118257562.CH3
Shijo, P. V., & Salim, A. (2015). Integrated static and
dynamic analysis for malware detection. Procedia
ComputerScience,46,804811.https://doi.org/10.1016/J.
PROCS.2015.02.149
Singh, P., Tapaswi, S., & Gupta, S. (2020a). Malware
Detection in PDF and Office Documents: A survey.
Information Security Journal: A Global Perspective,
29(3),134153.https://doi.org/10.1080/19393555.2020.
1723747
Singh, P., Tapaswi, S., & Gupta, S. (2020b). Malware
Detection in PDF and Office Documents: A survey.
Information Security Journal, 29(3), 134–153.
https://doi.org/10.1080/19393555.2020.1723747
Souri, A., & Hosseini, R. (2018). A state-of-the-art survey
of malware detection approaches using data mining
techniques. Human-Centric Computing and
Information Sciences, 8(1).
https://doi.org/10.1186/S13673-018-0125-X
Šrndić, N., & Laskov, P. (2016). Hidost: a static machine-
learning-based detector of malicious files. Eurasip
Journal on Information Security, 2016(1).
https://doi.org/10.1186/S13635-016-0045-0
Ucci, D., Aniello, L., & Baldoni, R. (2019). Survey of
machine learning techniques for malware analysis.
Computers and Security, 81, 123–147.
https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COSE.2018.11.001
Wiseman, Y. (2019). Efficient Embedded Images in
Portable Document Format (PDF). International
Journal of Advanced Science and Technology, 124,
129–138. https://doi.org/10.33832/IJAST.2019.124.12
Zhang, J. (2018). MLPdf: An Effective Machine Learning
Based Approach for PDF Malware Detection.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1808.06991
PDF Malware Detection: Toward Machine Learning Modelling with Explainability
437
