
QR Code‑Based Attendance System Using Deep Learning
P. Jacob Vijaya Kumar
1
, Patan Madarvali
2
, Basapuram Mahesh
2
, Jammana Govardhan Reddy
2
,
Chakali Mahidhar
2
and Dwaram Satish Reddy
2
1
Department of Computer Science and AI/ML, Santhiram Engineering College, Nandyal‑518501, Andhra Pradesh, India
2
Department of Computer Science and Design, Santhiram Engineering College, Nandyal‑518501, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: QR Code, Attendance System, Deep Learning, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Image Processing,
Automation.
Abstract: Integrating QR code generation with deep gaining knowledge of has revolutionized attendance control
structures. This paper offers a complicated QR code-based attendance machine augmented with deep
mastering strategies to enhance accuracy, scalability, and efficiency. The gadget leverages QR codes for
speedy, contactless statistics retrieval, even as deep mastering models address challenges along with QR code
deformation, terrible lights conditions, and real-time processing. The CNNs are used to detect the QR code
and improve accuracy, even under suboptimal conditions. In addition, a user -friendly interface ensures
spontaneous operations for both administrators and participants.
1 INTRODUCTION
Traditional attendance systems face demanding
situations, including manual errors, time inefficiency,
and scalability barriers. QR code-primarily based
systems provide a contactless, fast, and automatic
opportunity. However, conventional QR scanners
battle with distortions, low lights, or partial
obstructions. By integrating deep studying, this
gadget enhances robustness, ensuring reliable
performance in various situations.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 QR Codes for Taking Attendance
QR codes are those square barcodes you scan with
your phone. They're popular for attendance because
they're:
• Simple to use
• Quick to process
• Able to hold lots of information
But basic QR attendance systems have some
problems:
• People can cheat by creating fake QR codes
• They struggle with large groups
• They don't work well in poor lighting or when
the code is at an odd angle
That's where AI comes in to help solve these issues.
2.2 How AI Improves These System
Researchers are using advanced AI techniques to
make QR attendance systems better:
• Better QR Code Reading: AI models like YOLO
can find and read QR codes quickly, even in bad
lighting or when the code is distorted.
• Catching Cheaters: AI can spot fake QR codes
by finding tiny details that humans might miss.
• Double-Checking Identity: Some systems pair
QR codes with facial recognition - you scan the
code, then the system checks your face to make
sure it's you.
2.3 Recent Breakthroughs
• One research team created a system that uses
both QR codes and facial recognition, making
it much harder to cheat.
Kumar, P. J. V., Madarvali, P., Mahesh, B., Reddy, J. G., Mahidhar, C. and Reddy, D. S.
QR Code-Based Attendance System Using Deep Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013883300004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
383-388
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
383

• Another team developed a super-fast QR code
detector that works well even when people are
moving around.
• A third group built an AI system that can spot
tampered QR codes by examining unusual
patterns in the pixels.
2.4 Current Challenges and What's
next
Despite this progress, some hurdles remain:
• Processing Power: AI requires serious
computing power, which can be a problem for
real-time applications.
• Training Data: Teaching AI to recognize all
possible QR code variations requires lots of
example data.
• Connected Devices: Future systems might
connect QR attendance with smart devices for
seamless tracking.
2.5 Researchers Are now Working on
• Creating lighter AI models that don't need as
much computing power
• Developing methods that protect privacy
while improving security
• Combining QR codes with fingerprints or
voice recognition for extra security.
3 EXISTING SYSTEMS
3.1 Old-School QR Code Attendance
Problems
• People can cheat by using fake QR codes
• Doesn't work well in poor lighting or weird
angles
• Just scanning a code doesn't prove it's you
3.2 QR Systems with Brain QR Codes
that Recognize Your Face
How it works: Scan your QR code, and then the
system checks your face to make sure it's you.
Cool features:
• Uses smart computer vision to match your face
with your stored photo
• Much harder to cheat the system
Drawbacks:
• Needs powerful computers to work quickly
• Struggles in dark rooms
3.3 Super-Fast QR Code Spotting How
It Works
Uses a smart technology called YOLO that can find
and read QR codes instantly, even when they're
moving.
Cool features:
• Can spot and process many QR codes at once
• Works well even in challenging conditions
Drawbacks:
• Needs a gaming-level graphics card to run
smoothly
• Still has trouble with badly damaged QR codes
3.4 Fake QR Code Detective
How it works: The system learns to spot tiny
differences between real and fake QR codes that
humans can't see.
Cool features:
• Catches people trying to use fake codes
• Makes the whole system more trustworthy
Drawbacks:
• Needs to study thousands of fake and real codes
to learn the difference
• Uses lots of computing power
3.5 Connected Smart Attendance
How it works: Combines QR codes with internet-
connected devices and AI to track attendance in real
time.
Cool features:
• Attendance data gets stored in the cloud
instantly
• Can show patterns like who's usually late or
which days have poor attendance
Drawbacks:
• Needs a good internet connection
• Costs more to set up initially
3.6 Triple-Check Security
How it works: After scanning your QR code, you
also need to verify your fingerprint or voice.
Cool features:
• Extremely secure nearly impossible to cheat
• Perfect for high-security places
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
384
Drawbacks:
• Requires extra hardware like fingerprint
scanners
• More complicated and expensive
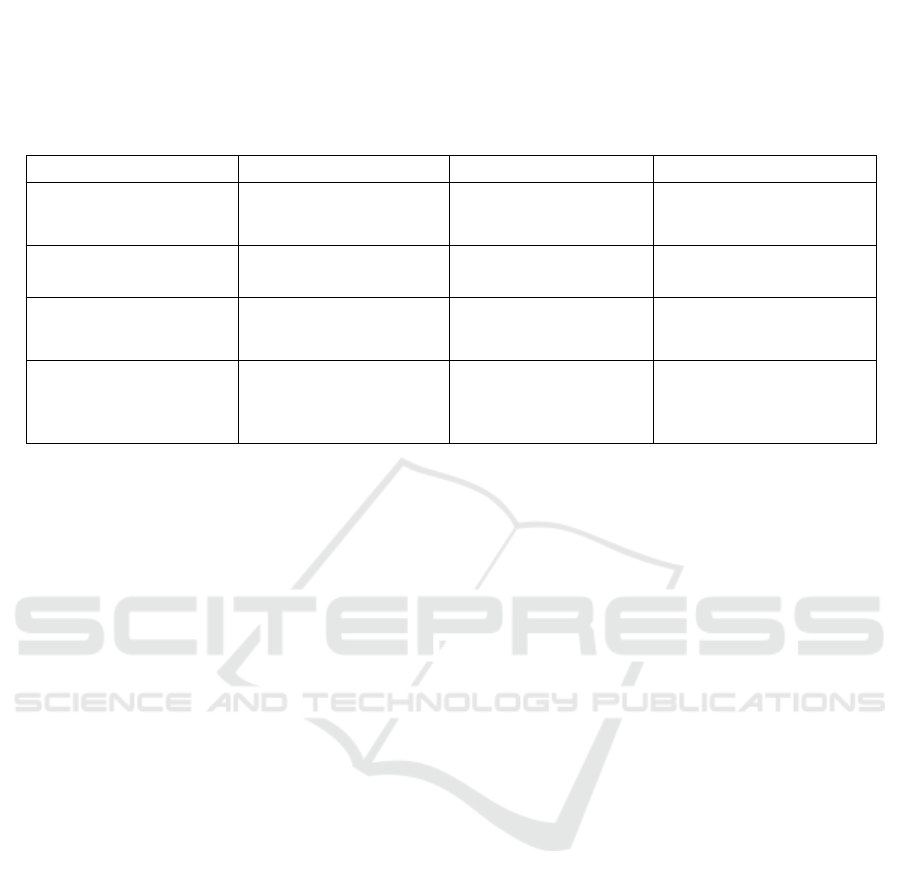
• TopComparison of Existing Systems
(Table 1)
Table 1: Comparison of Existing Systems.
System Key Features Advantages Limitations
Hybrid QR Code + Face
Recognition
Combines QR code
scanning with face
reco
g
nition.
High accuracy, robust
against spoofing.
Computationally intensive,
performance degrades in
p
oor li
g
htin
g
.
Tampered QR Code
Detection
Detects fake QR codes
using deep learning.
Enhances security, and
high accuracy.
Requires large dataset,
computationally intensive.
IoT-Integrated System
Combines QR codes with
IoT for real-time data
p
rocessing.
Scalable, provides real-
time analytics.
Requires stable internet,
high setup cost.
Multi-Factor
Authentication
Adds biometric
authentication (e.g.,
fingerprint, voice) to QR
code scanning.
Highly secure, and
suitable for high-security
environments.
Requires additional
hardware, increased
complexity, and cost.
4 METHODOLOGY
4.1 Problem Definition
To accomplish the objectives outlined in advance, a
dependent step-through-step method has been
implemented.
The methodology is defined as follows:
Develop a QR Code Generator Android
Application: Create an Android app that generates
QR codes the usage of student-specific records
including roll wide variety and scholar ID.
Develop an Attendance Management Android
Application: Build an Android app capable of
scanning QR codes to file attendance for precise
topics and routinely generate attendance sheets based
at the accumulated statistics.
4.2 Software Requirements
• Development Tools: Android Studio (for
cellular app improvement)
• Python (for deep mastering version education
and backend processing)
• MS Excel
4.3 Hardware Requirements
Android Smartphone.
4.4 Inputs / Outputs
• Inputs: QR codes, and Bar codes
• Outputs: Excel sheets
Database usage
MYSQL Database
4.5 Use Case
The machine involves more than one actors, each
with precise roles and functionalities. These actors
and their interactions inside the QR code-primarily
based attendance machine are defined underneath:
• Student:
o Generates a personalized QR code using the
Android app, which incorporates their specific
identification details which include roll wide variety
and student ID.
o Presents the QR code for scanning throughout
attendance recording.
• Teacher/Administrator:
o Uses the Android app to scan student QR codes
during class or events.
o Manages attendance records for specific subjects
or sessions.
o Generates and reviews attendance sheets
automatically created by the system.
QR Code-Based Attendance System Using Deep Learning
385
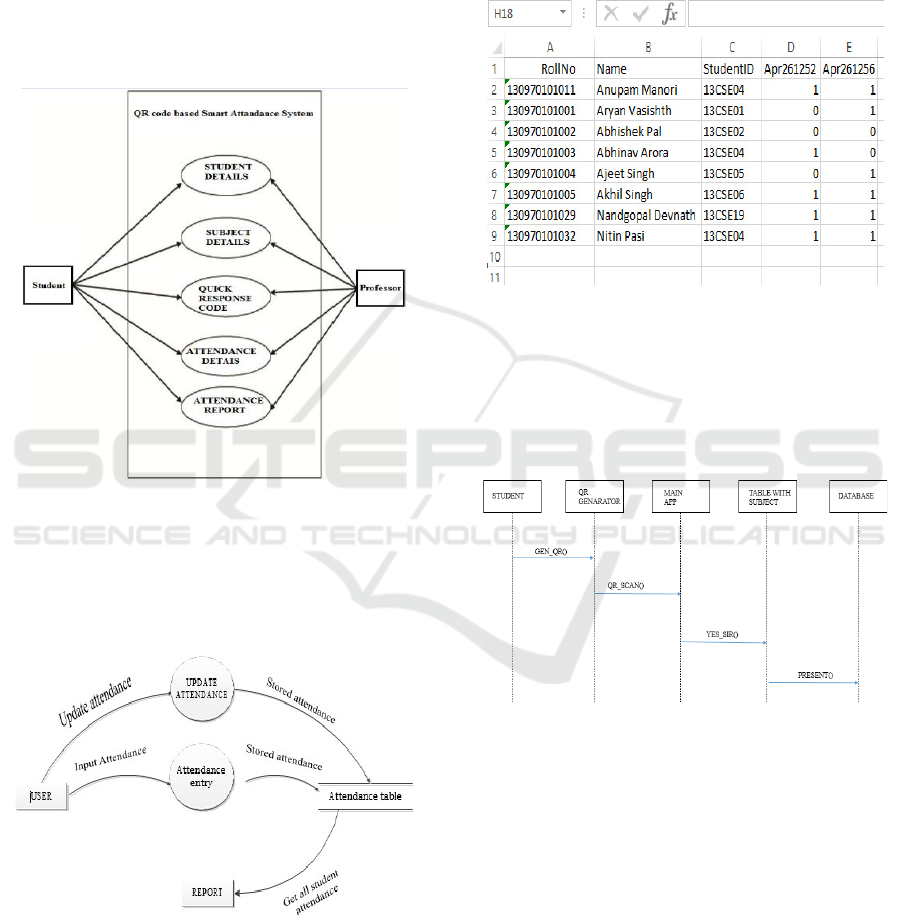
• System:
o Validates scanned QR codes to ensure accuracy
and prevent duplication.
o Stores attendance data securely in a database.
o Generates real-time attendance reports for
teachers or administrators.
This use case (figure 1) highlights the seamless
interaction between students, teachers, and the system,
ensuring an efficient and reliable attendance tracking
process.
Figure 1: Use Case Diagram.
4.6 Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
The data flow diagram (DFD) of the system is
illustrated in Figure 2:
Figure 2: DFD.
4.7 Database
The scholar attendance database is managed by the
use of SQLite. It shops the subsequent facts:
• Subject name and code.
• Student name and ID.
• Attendance repute (present/absent).
The database desk structure for a specific issue is
shown underneath in figure 3:
Figure 3: The Database Table Schema for Individual
Subject Records.
4.8 Sequence Diagram
The system's operational workflow is depicted in the
sequence diagram (figure 4):
Figure 4: Sequence Diagram.
The sequence diagram demonstrates the step-by-step
interaction between the student, professor, and the
system, including:
• Student QR code generation and
presentation.
• The professor scanned the QR code and
recorded attendance.
• System validation and storage of attendance
data.
• Generation of attendance reports.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
386
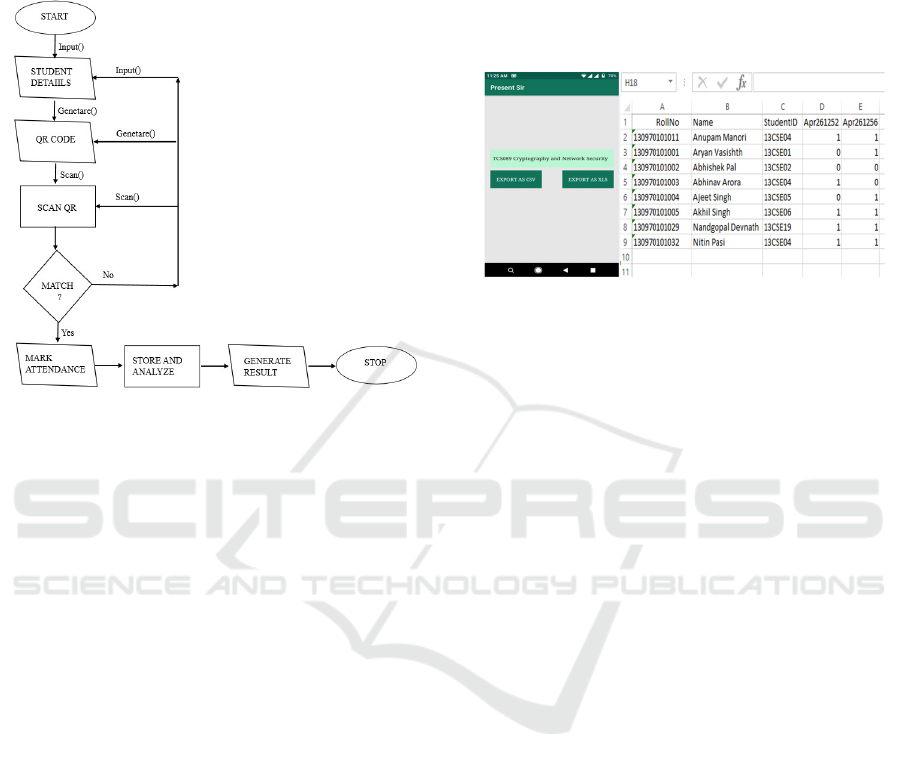
4.9 Flowchart
The flowchart of the QR Code-Based Attendance
System is shown in figure 5:
Figure 5: Flowchart of the Application System.
5 EXECUTION AND OUTCOMES
5.1 Model Evaluation
We tested a range of deep learning architectures:
• Model-1: CNN (Our proposed framework for
capturing temporal characteristics).
• Model-2: LSTM (Captures long-range
dependencies in price fluctuations).
• Model-3: GRU (Gated Recurrent Units for
efficient sequence analysis).
• Model-4: Random Forest (Baseline machine
learning approach for reference).
• Model-5: ARIA (Classic model for time-series
forecasting).
5.2 Export the Attendance to
CSV/EXCLS Files
• To export the overall attendance sheet in CSV
or XLS format, the trainer or administrator need
to pick out the relevant problem code. The
device then compiles the attendance records and
generates a file in which:
• 0 represents an absent status.
• 1 represents a present status.
Below is a screenshot (figure 6) of the generated CSV
file, showcasing the attendance records in a structured
and easily accessible format.
This feature allows for efficient record-keeping and
analysis of attendance data, making it convenient for
teachers and administrators to manage and review
attendance trends.
Figure 6: Export the Attendance to CSV/EXCLS Files.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The advanced gadget offered in this paper has been
efficiently designed and examined, demonstrating its
functionality to analyze and export pupil attendance
reputation correctly. Attendance tracking structures
play a crucial position in our daily lives, and among
numerous code-scanning technologies, the QR Code-
Based Attendance System will be the most correct
and reliable. In this task document, we have delivered
the idea of the Attendance Monitoring System and
highlighted its numerous advantages. By leveraging
QR code generation, this machine provides an
efficient and green answer for storing attendance
records digitally on smartphones, doing away with
the want for paper-based strategies. This not only
enhances accuracy however additionally contributes
to sustainability and comfort, making it an ideal
desire for modern-day educational and professional
environments.
7 FUTURE EXTENT
Our next paintings will focus on giving pupils access
to notes and ignored elegant issues. Complete control
over instructors with safer and more reliable
substitutes. Lastly, we conclude that this attendance
tracking system will solve the problem of actual
worldwide attendance if it is combined with a facial
recognition device.
QR Code-Based Attendance System Using Deep Learning
387

REFERENCES
Brownlee, J. (2020). "Deep Learning for Time Series
Forecasting: Predict the Future with MLPs, CNNs, and
LSTMs in Python." Machine Learning Mastery.
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi. "Machine Learning Based Predicti
ve Model for Data Fusion Based Intruder Alert
System." journal of algebraic statistics 13.2 (2022):
2477-2483
Devi, M. Sharmila, et al. "Extracting and Analyzing
Features in Natural Language Processing for Deep
Learning with English Language." Journal of Research
Publication and Reviews 4.4 (2023): 497-502.
FAO. (2021). "The State of Agricultural Commodity Mark
ets: Trends and Challenges in Price Volatility." FAO
Publications.
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). (2023). "Global
Information and Early Warning System (GIEWS) on
Food and Agriculture." FAO Publications.
Li, H., et al. (2021). "A Comparative Analysis of Machine
Learning and Deep Learning Techniques for Time-
Series Forecasting in Agricultural Markets." IEEE
Transactions on AI, 29(4), 320-333.
Mishra, D., & Singh, P. (2020). "A Survey of Machine
Learning Methods for Predicting Crop Prices." Interna
tional Journal of Data Science, 12(2), 112-125.
Mr.M.Amareswara Kumar, “Baby care warning system
based on IoT and GSM to prevent leaving a child in a
parked car” in International Conference on Emerging
Trends in Electronics and Communication Engineering
- 2023, API Proceedings July-2024
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al. "Machine Learning Based
Predictive Model for Closed Loop Air Filtering
System." Journal of Algebraic Statistics 13.3 (2022):
416-423.
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al. "Incorporating Deep Learning
Techniques to Estimate the Damage of Cars During the
Accidents" AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028.
No. 1. AIP Publishing, 2024.
Patel, A., & Kumar, R. (2022). "Utilizing Deep Learning
for Predicting Agricultural Prices." Journal of AI
Research in Agriculture, 18(3), 45-57.
Sharma, R., & Gupta, K. (2023). "Agricultural Market
Forecasting Using Hybrid CNN- LSTM Models." Co
mputational Intelligence in Agriculture, 30(4), 201-
218.
World Bank. (2022). "Commodity Markets Outlook: The
Impact of Climate Change on Agricultural Prices."
World Bank Group.
Zhang, X., et al. (2019). "Models for Price Prediction in
Agricultural Markets Using Neural Networks." Applied
AI Review, 27(1), 98-115.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
388
