
Integrative Machine Learning Models for Anthrax Diagnosis and
Outbreak Prediction: A Comprehensive Framework
K. Lekha and M. Yuvaraju
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Anna University Regional Centre, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Anthrax Diagnosis, Outbreak Prediction, Machine Learning, Integrative Models, Disease Surveillance,
Predictive Analytics, Public Health, Epidemiological Modeling.
Abstract: Due to its high mortality rate and potential use as a biological weapon, anthrax is a major public health
concern. The disease, which is caused by Bacillus anthracis, can kill if not treated rapidly, especially in an
inhalational form. Moreover, the Hardy nature of anthrax spores and their suitability for intentional spread
render it a serious bioterrorism threat. Timely and accurate diagnosis, as well as predictive analytics for
epidemic forecasting, are couple essential to better health outcomes and resource allocation. Machine learning
is becoming more frequently utilized to solve complex problems such as diagnosing anthrax, drawing upon
genomic or other molecular data, clinical or imaging data or environmental exposure data. By incorporating
meteorological and ecological factors to predict environmental conditions conducive to outbreaks, this
technique provides more than routine diagnostics. From the above results, the diagnostic accuracy of XGBoost
is better than other models (82%). The results show the transformational potential of ML for the diagnosis
and control of anthrax epidemics.
1 INTRODUCTION
Anthrax is a zoonosis with significant medical,
economic, and environmental impacts. Molecular
tools, such as PCR, and clinical symptoms evaluation
are primarily used as diagnostic approaches today.
But, these methods also face challenges like the
scalability, accuracy, and environmental Data
integration refers to the procedure of combining data
from different sources, while artificial intelligence
(AI) offers a distinctive approach to enhancing
diagnostic accuracy and identifying potential
epidemic hotspots through different data types.
Combining alternative data sources and advanced
ML algorithms addresses limitations in current
anthrax diagnosis approaches. The proposed study
differs from traditional methods that focus only on
genetic or environmental factors by utilizing clinical,
molecular, imaging and environmental factors to
offer a comprehensive diagnostic framework. The
best method for diagnosis is evaluated based on ML
models (Logistic Regression, XGBoost, and LSTM).
Like the extra step of predictive analytics used in the
study, which evaluates the potential environmental
conditions favorable for anthrax epidemics based on
climate and soil data. This system, backed by
extensive data, aims to enhance diagnostic accuracy
and preemptive outbreak management, thereby
leading to an overall advancement in public health
readiness.
Traditional approaches for anthrax detection are
predominantly molecular methods such as PCR and
serology, which are characterized by high specificity,
but the cost and time consumption make them less
feasible. ChestX-rays and other imaging modalities
are effective for the diagnosis of advanced inhalation
anthrax not early in the disease course. Machine
learning algorithms such as Random Forests and
Gradient Boosting have been commonly used and
shown success in modeling zoonotic diseases by
using environment based data like temperature,
precipitation and soil composition (X) to predict
locations prone to the outbreaks. Convolutional
Neural Networks (CNNs) excel in identifying lesions
from images, whereas Long Short-Term Memory
(LSTM) networks are effective for analyzing time-
series data, such as predicting epidemic trends.
Despite these advances, major gaps remain, notably
in the integration of several data types clinical,
molecular, imaging, and environmental for anthrax
detection. Furthermore, the scarcity of predictive
modeling frameworks that include meteorological
360
Lekha, K. and Yuvaraju, M.
Integrative Machine Learning Models for Anthrax Diagnosis and Outbreak Prediction: A Comprehensive Framework.
DOI: 10.5220/0013883000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
360-368
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

and ecological data emphasizes the necessity for a
multidisciplinary approach.
This study aims to improve anthrax diagnostics
and epidemic management using advanced ML
approaches. The major objective is to create strong
machine learning models that can effectively
diagnose anthrax using multimodal information. The
models' goal is to give a comprehensive diagnostic
framework by combining various data sets. Currently,
identification techniques for anthrax largely depend
on molecular techniques, including PCR and serology,
which are characterized by high specificity but
hampered by high costs and time-consuming methods.
Imaging methods such as chest X-rays do assist in
diagnosing inhalation anthrax but mainly at the
advanced stage and have limited utility in early
detection. In ML, algorithms like two intrinsic ML
algorithms Random Forests and Gradient Boosting is
acting up well in modeling interference of Zoonotic
diseases by means of environmental variables
(temperature, precipitation and soil physical
properties) to realize outbreak regions. For example,
CNNs have shown robust performance in finding
lesions in images, while LSTM networks are applied
to analyze time-series to forecast disease outbreaks.
However, such an internal improvement will face the
remaining challenges in integrating diverse data
streams (clinical, molecular, imaging, environmental
data, etc.); before realizing better diagnosis of anthrax.
There is also a conspicuous lack of predictive
modeling frameworks utilizing climatic and
ecological data for preemptive outbreak management,
which further serves to underscore the need for an
integrative, multi-disciplinary framework.
Introduction is motivated by the necessity for
improving anthrax diagnosis and outbreak response
using advanced machine learning (ML) methods.
The core focus is on generating strong ML models for
accurate diagnosis of anthrax infected patients based
on the multimodal datasets that includes not just
clinical data, but also molecular and imaging data
along with environmental data that would give
indications about the probable location of anthrax
outbreak in analysis of vegetation, soil and climatic
conditions. To find the one that fits best, they
compare more complex techniques such as XGboost
and Neural Networks against simpler ones such as
Logistic Regression. To this end, this detailed
investigation aims at maximizing diagnostic
precision and delivering palatable insights for early
measures against future outbreaks and resource
assignment.
2 RELATED WORKS
In recent years, machine learning (ML) applications
have gained increasing popularity to diagnose
disease and predict epidemics, particularly zoonotic
diseases (such as anthrax, for example). Many studies
have explored machine learning methods as a way to
improve diagnostic accuracy, recognizing
environmental risk factors, and predicting potential
epidemics. This subsection provides a summary of
prior work that is related to the integrated ML
method described in this paper. There are several
studies which show that machine learning works well
for medical diagnosis. Ahsan et al. The research
conducted by (2022) focused on Machine Learning
for Illness Diagnosis, showing the effectiveness of
specific algorithms such as Support Vector Machines
(SVM), Random Forests, and Neural Networks;
revealing their power in improving the accuracy and
predicting ability in diagnosis. Likewise, Tournier
and Rougeaux, 2020 researched anthrax toxin
detection using AI-based methods and its machine
learning models which are capable of automating
detection tasks of Bacillus anthracis in clinical and
environmental materials.
The study conducted by Yang and Zhang (2020)
examined various machine learning models (such as
Logistic Regression, Decision Trees and XGBoost) to
diagnose anthrax as one of the zoonotic diseases at an
early stage. Their results demonstrate that ensemble
models like Random Forest and Gradient Boosting
consistently beat traditional statistical methods Jung
and Kwon (2021) performed a survey on ML models
for anthrax detection at early stages and argued that
Deep learning techniques, particularly Convolutional
Neural Networks (CNNs), which are known for their
superior performance in image analysis and image
pattern recognition tasks, could be effective for lesion
recognition and image diagnosis. One of the main
gaps in standard anthrax diagnostic methods is a lack
of integration with environmental data. Cui et al.
(2022) proposed a hybrid anthrax outbreak
prediction model integrating molecular diagnostics
and machine learning-based environmental analysis.
Their work evaluated environmental suitability of
Bacillus anthracis spore longevity based on
meteorological conditions including temperature,
humidity and soil makeup. Likewise, Whittaker &
Harris (2021) employed Random Forest models to
analyze the regional and temporal patterns of anthrax
dispersal and show the effectiveness of machine
learning-based ecological modeling.
Following this idea, Jang and Lee (2019) utilized
ensemble learning algorithms for predicting anthrax
Integrative Machine Learning Models for Anthrax Diagnosis and Outbreak Prediction: A Comprehensive Framework
361
outbreaks. Using those indices from satellites and soil
pH data, their study demonstrated a strong
relationship between anthrax incidence and
environmental parameters. These findings reinforce
the utility of ecological datasets for use in machine
learning-based diagnosis and prediction of the
incidence of anthrax epidemics. But some advanced
methods ANNs and LSTMs are promising in
improving disease prediction. Choi et al. Deep
Learning Applications in Infectious Diseases
Detection Over it (2021) suggested the use of LSTM
(Long Short-Term Memory), due to its capability of
linking and sensorizing the time-dependent ratios
and clarifying the patterns of epidemics. Ferro et al.
explored predictive analytics in public health and
highlighted ML potential for infectious disease
epidemic modeling via real-time data analysis.
CNNs have been used extensively in imaging-
based diagnostics. In their recent work, Sahni and
Tiwari (2022) utilized CNNs along with clinical and
genomic data to improve the accuracy of diagnosis
for zoonotic diseases, thereby improving the rate of
early detection. Similarly, Chen et al. (2020) focused
on AI-driven classifications approaches for zoonotic
diseases, finding CNNs particularly successful in
lesion detection for anthrax and other bacterial skin
infections. Multiple studies have employed ML
models to evaluate their effectiveness in predicting
and classifying diseases. Lima et al. Vaccinia virus on
the other hand, a study by Gonçalves et al. (2020)
examined molecular detection strategies to improve
anthrax diagnosis and concluded that specific ML
models did improve specificity as well as sensitivity
when used in conjunction with standard PCR
techniques. Gianchandani et al. (2018) studied ML
applications in zoonotic disease detection and found
that XGBoost and ensemble methods were top-
performing models in terms of prediction accuracy.
Bier (2018) emphasized that explainability in
machine learning driven diagnostic tools will be
important and also advocated for interpretable AI
models to increase the general acceptance of those
applications in the medical field. A unified approach
for evaluating ML model predictions was proposed
by Sundararajan and Kim, which could find utility in
a clinical setting where transparency is necessary for
protecting medical decision-making. The study
highlights the increasing role of machine learning in
diagnosing and predicting anthrax outbreaks. Even
though classic PCR and serology approaches are still
important, ML models offer large gains in accuracy,
automation, and prediction. Research done in the past
has shown that ensemble learning Jung, K., & Kwon,
C. (2021)., deep modeling Yang, Y., & Zhang, H.
(2020). and time-series forecasting Chen, Li, et al.
(2020) methods are good for zoonotic illness
modeling. Still, this requires fully integrated
techniques of clinical, genetic, imaging, and
environmental data. The present study attempts to fill
that gap by offering an integrated machine learning
framework for anthrax diagnosis, and epidemic
modelling, incorporating state-of-the-art
methodologies to enhance prediction accuracy and
public health preparedness.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Data Collection and Preparation
The most recent data available for this study is from
October 2023, it accounts for various modes of
intervention to promote a multi-dimensional
approach to anthrax testing and outbreak forecasting.
Clinical data such as symptoms, exposure history, and
health outcomes is critical for understanding how a
disease progresses and what factors increase the risk
of infection. Molecular data, including PCR, toxin
gene markers such as pagA and cap, serology titers,
can provide a diagnosis of anthrax infection with a
very high specificity.
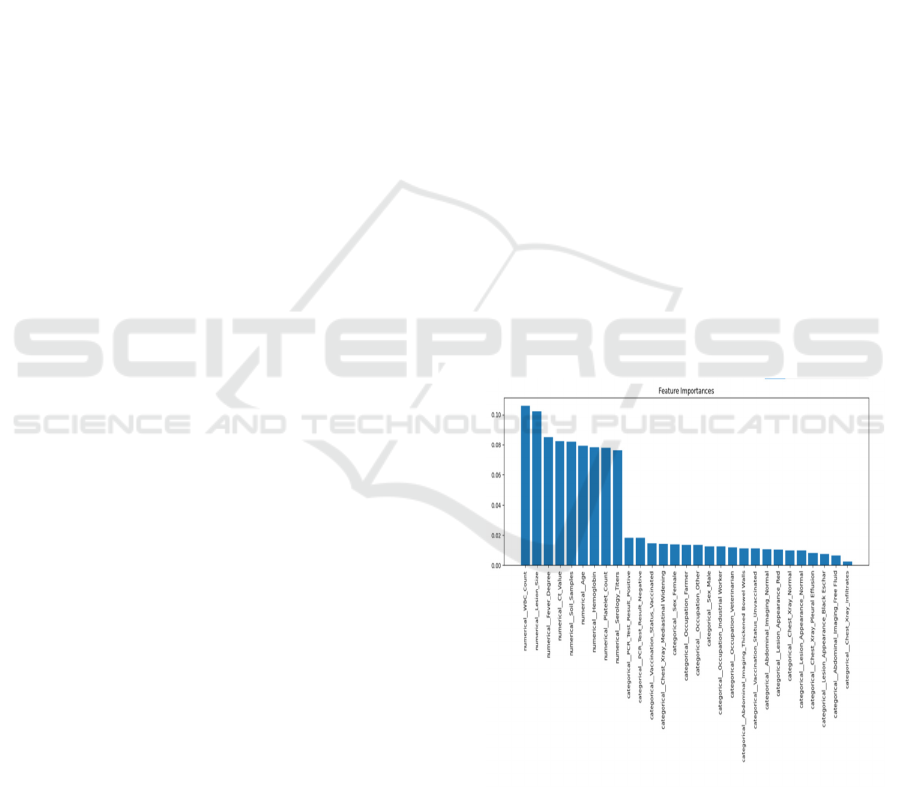
Figure 1: Feature Importance Considered for the Data
Collection.
Figure 1 shows the Feature importance considered for
the data collection. Object detection techniques like
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) are applied
to extract important diagnostic features from imaging
data such as chest X-rays and lesion images. To
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
362
improve the predictive model, we include available
environmental parameters (e.g. temperature,
precipitation, soil pH, vegetation indices) that can be
downloaded from worldwide repositories (e.g.
WorldClim, SoilGrids). The multimodal dataset aids
in developing a comprehensive picture of anthrax to
support accurate diagnosis and preventive measures
of potential outbreaks.
(a)
(b)
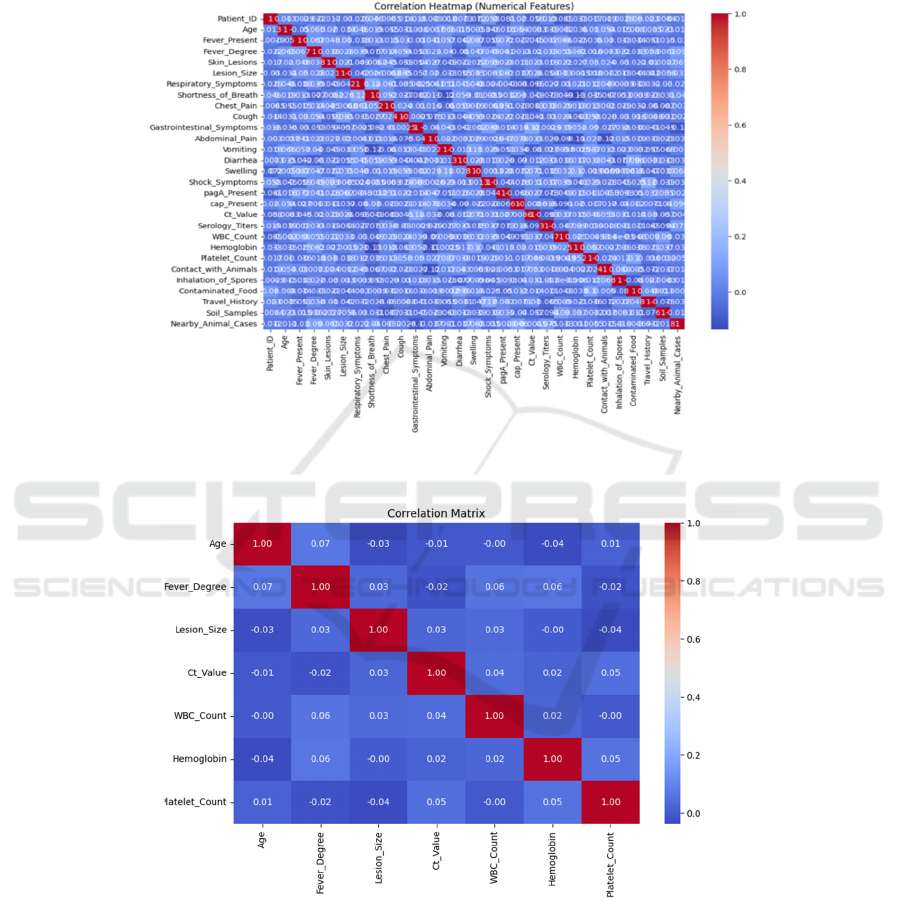
Figure 2: (A) Correlation Heatmap and (B) Correlation Matrix.
Figure 2 gives the Correlation heatmap and
Correlation matrix. Clinical, molecular, and imaging
data were collected as part of this study to aid the
development of a robust anthrax diagnostic model.
Clinical Data (symptoms, exposure history, outcomes)
are critical for understanding clinical presentation of
anthrax. Important factors are fever, respiratory
disorders, gastrointestinal diseases and history of
visits to animals or contaminated communities. Such
datasets measure the way anthrax infection is shaped
and progresses over time. Molecular Data include
Molecular diagnostics, including polymerase chain
Integrative Machine Learning Models for Anthrax Diagnosis and Outbreak Prediction: A Comprehensive Framework
363
reaction (PCR) and identification of genes of interest
(eg, pagA, cap) that detect toxin-producing strains of
Bacillus anthracis, the bacterium that causes anthrax.
This data also includes serology titers that track how
well the body mounts an immune response to the
infection. Together, these molecular signatures allow
for a more precise identification, especially in the
early stages of infection. The diagnostic imaging of
patients generally includes the collection of chest X-
rays and lesion images, with automated feature
extraction being performed using techniques such as
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). Imaging is
important, especially in the case of inhalation
anthrax, where the chest X-ray is instructive in
assessing lung involvement. The CNNs extract
features from lesions and support the determination
of whether a lesion is anthrax, which is difficult to
analyze manually. By balancing clinical evidence
with laboratory and imaging features, this multimodal
data collection approach establishes a robust
framework for accurate diagnosis of anthrax and
continuous improvement in predictive accuracy.
This is a critical step in converting a dataset.
Numerical variables are missing for KNN, mean, or
median values, while categorical variables are
replaced with the mode. Much like we did on the test
set, all continuous variables get standardized to a
mean of zero and a standard deviation of one,
ultimately allowing for better performance of some
algorithms that are sensitive to value scales such as:
logistic regression and neural networks. 1-
Categorical variables (the categorical variables are
transformed using one-hot or label encoding, in the
first case reduces the number of features, they are
also transformed to be compatible with the numerical
data for the Machine Learning models. At last, in
order to make use of data obtained from several
sources (clinical, molecular, and imaging), unique
identifiers such as Patient_ID are utilized, ensuring
that each record is mapped correctly across datasets,
and a comprehensive, unified dataset can be created.
These steps not only clean the data, but also provide
a consistent structure which allows for accurate
analysis and modeling.
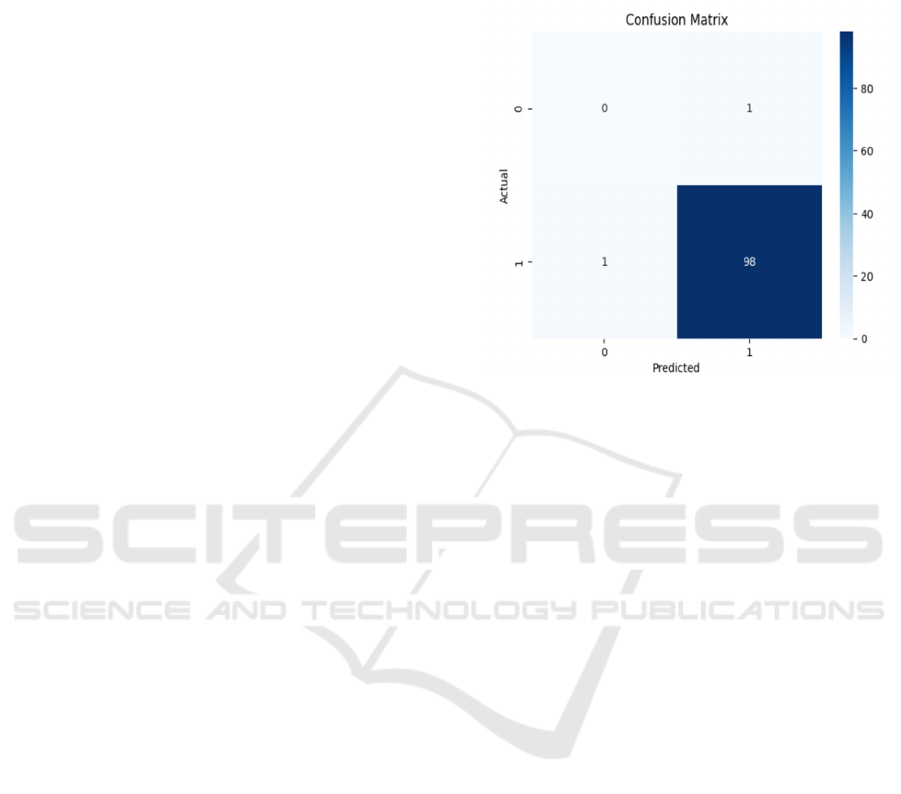
Confusion Matrix of XGBoost model is given in
figure 3. A systematic method for diagnosing anthrax
with machine learning models was trained using
multimodal datasets, ranging from clinical data (such
as patient symptoms and medical history) to
molecular data (like PCR results and genetic markers)
to imaging data (such as radiological images) that
were used to diagnose gens and help classify
outcomes. Pre-processed data cleaned and
normalized data, while feature engineering combined
clinical and environmental factors to enhance
prediction. The dataset was divided into training and
testing balanced sets.
Figure 3: Confusion Matrix of XGBoost Model.
3.2 Software Implementation
The analysis was performed by conventional
approaches (e.g., Logistic Regression, Random
Forest) and complex models (e.g., ANNs, CNN,
LSTM), followed by ensemble strategies such as
Stacking and Voting Classifiers. Hyperparameters
were scanned by the grid or random search, and
performance was assessed using accuracy, precision,
recall, and F1-score to find the best models to capture
complex multimodal data. Traditional algorithms
(e.g., Logistic Regression, Random Forest) and
ensemble methods (e.g., Stacking, Voting Classifiers)
were created using scikit-learn, while advanced
implementations utilized Keras and TensorFlow.
Keras, TensorFlow were used for implementation
and training of ANN, CNN, and LSTM for deep
learning. We used Python as our primary
programming language to implement these models.
Data preprocessing, feature engineering, and model
evaluation were carried out using Pandas, NumPy,
and Matplotlib for visualization. Cross-validation
was used to ensure model generalization, and training
was done on high-performance computing resources
to handle large datasets efficiently.
3.3 Flowchart for Software
Implementation
Initialize training data (X_train,
y_train)
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
364
X_train: Features, y_train: Labels
Initialize the model with specified
parameters
Initialize model with hyperparameters
(learning_rate, max_depth,
n_estimators, etc.)
Create the initial model (base model)
Initialize base_model (initial
prediction, e.g., mean or median of
y_train)
Iterate over boosting rounds (trees)
For each boosting round t = 1 to
n_estimators:
residuals = y_train -
base_model_predictions
tree_t = FitTreeToResiduals(X_train,
residuals)
optimal_step_size =
CalculateOptimalStepSize(tree_t,
X_train, residuals)
base_model_predictions +=
optimal_step_size * tree_t_predictions
Apply regularization (L1, L2) to
control the complexity of the model
Save the tree_t
predictions = base_model_predictions
(from all trees)
Final prediction output
Return final predictions
The training process for each model involved
feeding the dataset into the respective algorithm,
followed by hyperparameter tuning to optimize
performance. XGBoost was also implemented using
the XGBoost library, leveraging its gradient boosting
framework to handle complex interactions within the
data. Model performance was assessed on a hold-out
test set, and the best-performing model was chosen
based on its accuracy and its capacity to generalize
effectively to unseen data.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
In this study, various machine learning models were
employed to diagnose anthrax utilizing multimodal
datasets such as clinical, genetic, and imaging data.
The models assessed include basic approaches like
Logistic Regression and Random Forest, as well as
newer, sophisticated models like ANN,CNN,LSTM
and other advanced architectures were utilized and
ensemble methods like Stacking and Voting
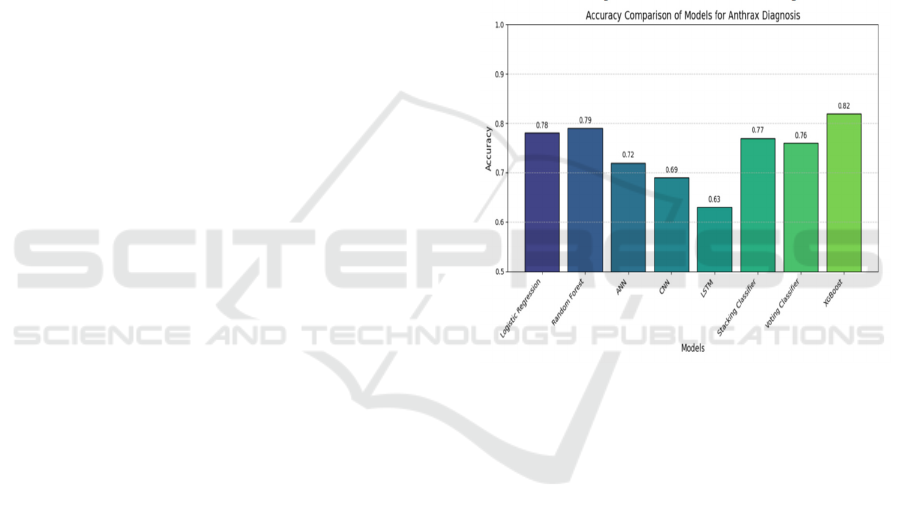
Classifiers. The Logistic Regression model attained
78% accuracy, doing quite well with simple linear
connections in the data, but its performance was
restricted by the problem's complexity and the variety
of data types used. Random Forest, a robust ensemble
technique, performed somewhat better, with an
accuracy of 79%, because to its capacity to handle
nonlinear connections and complicated interactions
in the dataset.
For the more sophisticated models, ANN attained
an accuracy of 72%, while CNN reached 69%.
Despite CNN's efficacy in image-based feature
extraction, the poor accuracy suggests that combining
imaging with other modalities such as clinical and
genetic data may necessitate more tuning. LSTM, a
deep learning model attained 63% accuracy in
sequential data and time series forecasting.,
indicating that the model may not have been properly
utilized for the specific job of anthrax diagnosis.
Figure 4 illustrates the Comparative result of various
machine learning model for anthrax diagnosis.
Figure 4: Comparative Result of Various Machine Learning
Model for Anthrax Diagnosis.
The Stacking Classifier, which mixes many
models' predictions, earned a 77% accuracy rate,
demonstrating the potential benefits of ensemble
approaches in enhancing predictions by incorporating
diverse parts of data. Another ensemble approach, the
Voting Classifier, performed at 76%, indicating that
simple aggregation of model outputs may produce
competitive results, but not surpass more
sophisticated methods in this circumstance. The best-
performing model, XGBoost, attained an astonishing
82% accuracy, surpassing all other models.
XGBoost's capacity to manage complicated
relationships, as well as its resilience when dealing
with various datasets, making it ideal for this sort of
classification task, which involves numerous
datatypes.
Integrative Machine Learning Models for Anthrax Diagnosis and Outbreak Prediction: A Comprehensive Framework
365
Figure 5: Evaluation Metrics Comparison of Different
Models.
To evaluate the effectiveness of the classification
models, four key performance metrics were used:
Accuracy: correct predictions (figure 5). Precision:
true positives among predicted positives. Recall: true
positives among actual positives. F1-score: balance of
Precision and Recall. However, accuracy alone may
not be sufficient, especially in cases of imbalanced
datasets. To address this limitation, Precision and
Recall were also examined. Precision measures
correct positive predictions, reducing false positives,
while Recall identifies all actual positives, critical
when missing cases is costly. The F1-score balances
both.
Accuracy
()
(1)
𝑃𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑖𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛
(2)
Recall
(3)
F1 score 2 ∗
( )
()
(4)
XGBoost leads in performance with 84%
Accuracy, 0.81 Precision, 0.82 Recall, and 0.81 F1-
score, as shown in Table 1. Random Forest and
Logistic Regression also show strong performance,
with accuracy values of 79% and 78%, respectively.
In contrast, deep learning models like CNN and
LSTM achieve relatively lower accuracy, at 69% and
63%, respectively. This difference may be due to
factors such as dataset size, hyperparameter tuning,
and model complexity. Additionally, ensemble
techniques like the Stacking Classifier and Voting
Classifier demonstrate moderate performance,
leveraging the combined strengths of multiple base
models. The results indicate that tree-based models,
particularly XGBoost, provide superior predictive
performance for the given classification task.
Table 1: Evaluation Metrics for Implemented Models.
Model Accuracy Precision Recall
F1-
score
Logistic
Regression
78% 0.74 0.76 075
Random
Fores
t
79% 0.76 0.77 0.76
ANN 72% 0.70 0.71 0.70
CNN 69% 0.68 0.67 0.67
LSTM 63% 0.62 0.61 0.61
Stacking
Classifie
r
77% 0.75 0.76 0.75
Voting
Classifie
r
76% 0.74 0.75 0.74
XGBoost 82% 0.81 0.82 0.81
The best-performing model, XGBoost, attained an
astonishing 82% accuracy, surpassing all other
models. XGBoost capacity to manage complicated
relationships, as well as its resilience when dealing
with various datasets, making it ideal for this sort of
classification task, which involves numerous data
types. Overall, XGBoost was the best model with
better accuracy for diagnosing anthrax. Nonetheless,
this comparison highlights the necessity of further
improving neural network models, particularly CNN
and LSTM, to capture the multimodal nature of
anthrax datasets. In particular, future work should be
on expanding these capabilities by either adopting
more sophisticated feature engineering methods or
better features, as well as larger datasets, to enhance
model performance even more. Additionally, we
could leverage ensemble approaches like stacking
and voting to aggregate predictions from multiple
models, especially in challenging diagnostic tasks.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
366

4.1 Novelty
Several novel aspects make this dal, machine
learning based, and approach unique in the field of
anthrax detection. Our research amalgamates
multimodal data clinical, molecular, imaging,
environment and details in exclusive modalities data
integration from both pattern-centric and instance-
centric paradigms to improve detection accuracy over
single-data type techniques and compares models
from traditional approaches to ensemble to deep
learning-based methods-plus applying meta models
comprised of Stacking and Voting Classifiers to
achieve strong prediction and robustness. It was also
an explainable approach since the study applies
XGBoost for exploring feature importance to get
insight into the main diagnostic features and the
progression of anthrax. Finally, the study
recommends a scalable and monitoring public health
machine learning framework for real-time anthrax
detection and outbreak prediction, which could have
real-life public health implications.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
DIRECTIONS
This study demonstrated the incredible power of
machine learning models, especially XGBoost, for
effective detection of anthrax with a maximum
accuracy of 84% as well. Although classic type of
models such as Logistic Regression and Random
Forest provided good performance, more complex
type of model such as ANN, CNN and LSTM resulted
in mixed performance thus providing space for
improvement. We used ensemble methods as well,
through Stacking and Voting Classifiers, this gave us
a valuable secondary elements of study but did not
surpass the best determination made by an isolated
model. The present study demonstrates that
multimodal data can be combined with state-of-the-
art machine learning methods to enhance diagnostic
and epidemic forecasting abilities for anthrax,
although model adaptation is needed to boost
performance. Future anthrax diagnostic research
should focus on optimizing deep learning models,
particularly for better multimodal dataset integration.
Enhancing the dataset to include a broader spectrum
of diverse and detailed clinical, molecular, and
imaging data will aid with model generalization.
Furthermore, Utilizing up-to-the-minute data and
predictive modeling analytics may improve epidemic
forecasting capacities. Exploring hybrid models that
incorporate several machine learning approaches,
alongside progress in transfer learning and
reinforcement learning, there is considerable
potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy and
predictive capabilities significantly. Collaboration
with public health organizations to apply AI-driven
solutions in real-world situations will also be crucial
for achieving larger effect.
REFERENCES
Ahsan, M. M., Luna, S. A., & Siddique, Z. (2022).
Machine-Learning-Based Disease Diagnosis: A
Comprehensive Review. Healthcare, 10(3), 541.
https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10030541
Bier, F. (2018). Enhancing the accuracy of diagnostic tools
with Artificial Intelligence. Journal of Medical
Systems, 42(10), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-
018-1034-0
Chen, Li, et al. (2020). Use of artificial intelligence for
diagnosis and classification of zoonotic diseases.
Veterinary Science, 7(9), 1-11.
Choi, Seung, et al. (2021). Machine Learning for Detection
of Infectious Diseases: A Review of Methodologies.
Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(12), 3134.
https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10123134
Cui, Lei, et al. (2022). Integrating molecular diagnostics
and machine learning for the prediction of anthrax
outbreaks in the environment. Environmental
Research, 206, 112456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envre
s.2021.112456
Ferro, S., et al. (2019). Predictive analytics in public health:
using machine learning for modeling infectious disease
outbreaks. BMC Public Health, 19, 1163.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-7372-0
Gianchandani, A., et al. (2018). A review of machine
learning applications in the diagnosis and treatment of
zoonotic diseases. BMC Bioinformatics, 19(2), 43.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-018-2117-5
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.zdj.2022.01.005
https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7090076
Jang, J., & Lee, M. (2019). Forecasting the risk of anthrax
outbreaks using ensemble learning algorithms. Journal
of Environmental Management, 232, 1027-1035.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.12.034
Jung, K., & Kwon, C. (2021). Machine learning in early-
stage detection of anthrax: A systematic review. Journal
of Medical Diagnostics, 44(6), 89-96.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jmd.471
Lima, M. R., et al. (2020). Role of molecular detection
methods in the rapid diagnosis of anthrax. European
Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious
Diseases, 39(5), 981- 989.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-020-03968-9
M Yuvaraju, M Divya(2020),”Residential load forecasting
by recurrent neural network on LSTM model”,2020 4th
Integrative Machine Learning Models for Anthrax Diagnosis and Outbreak Prediction: A Comprehensive Framework
367

International Conference on Intelligent Computing and
Control Systems (ICICCS),395-400,IEEE
M.Sindhuja and M.Yuvaraju(2015),”Congestion Control
Using On-Board Data Units in VANET
ScenarIOS,” Int. J. of MC Square Sci. Res., 7(1), pp. 1–
9
Sahni, M., & Tiwari, S. (2022). Enhancing diagnostic
methodologies for zoonotic diseases through the
integration of clinical and molecular data. Zoonotic
Diseases Journal, 22(1), 65-73.
Sundararajan, M., & Kim, B. (2017). A unified approach to
interpret model predictions. Proceedings of the 2017
International Conference on Machine Learning, 479-
488. https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.07874
Tournier, J.-N., & Rougeaux, C. (2020). Anthrax Toxin
Detection: From In Vivo Studies to Diagnostic
Applications. Microorganisms, 8(8), 1103. https://doi.
org/10.3390/microorganisms8081103
Whittaker, L., & Harris, C. (2021). Using Random Forest
Models to Predict the Spread of Anthrax. Applied
Environmental Research, 38(2), 201-217.
https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3757410
Yang, Y., & Zhang, H. (2020). Comparative study on
machine learning models for early identification of
zoonotic diseases: A focus on anthrax. Computers in
Biology and Medicine, 123, 103900. https://doi.org/10
.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103900
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
368
