
IoT‑Enabled Real‑Time Monitoring for Disaster Management and
Sustainable Energy Optimization
P. Sukumar, Elamathi T. M., Dhanish S. and Manoj V.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Nandha Engineering College (Autonomous), Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Real‑Time Monitoring, Solar Tracking, Sustainable Energy, Arduino IoT Cloud, Blynk Integration, Vibration
Detection, Motion Security, Forest Fire Alert, Battery Management, Streetlight Monitoring, Renewable
Energy, Wireless Sensors, Automated Alerts.
Abstract: This research gives a comprehensive approach to monitoring with the implementation of an IoT-based system
that integrates various sensors and microcontroller that track the forest fires, land vibration levels, solar energy
efficiency, battery voltage and charge percentage, motion detection, and streetlight failures. One of the plus
features of this system is that it has an intelligent solar tracking mechanism in which a server motor tracks the
solar panel dynamically to maximize solar light absorption, hence increasing energy efficiency. Additionally,
a motion sensor will allow detection of unauthorized activities. The data collected from all the sensors by the
local XAMPP server, since it uses database in the objective of effective data logging and retrieval. There is a
web-based dashboard. The project enhances remote access also by integrating with Arduino IoT Cloud and
Blynk, allowing real-time graphical analysis, sensor readings of all the sensors, and control of the system
from any area.
1 INTRODUCTION
An IoT-based system for monitoring and automation
contains a mix of various sensors and a NodeMCU
microcontroller to monitor the main environmental
and security parameters like solar energy efficiency,
battery voltage level, motion detection, fire hazard,
seismic activity, and streetlight failure. G. S, P.
Umaeswari, et al., 2024; S. Durgadevi, et al, 2024,
The system's parameters reflect its high
responsiveness and sustainability in the fields of
security and energy efficiency through wireless
communication. Apart from that, key to this is the use
of a solar tracking mechanism that dynamically
adjusts the orientation of the solar panel through a
servo motor, thereby maximizing absorption of sun
rays and overall energy efficiency. D. M, S. A and S.
R, et al., 2023. The battery management system
allows energy stored in the battery to be used more
efficiently by observing the voltage levels, charge
percentage, and overall health of the battery. S. K.
Gupta and R. K. Singh, et al., 2023, For security, the
motion detection PIR sensors were used to observe
the environment and provide immediate alerts. M. S.
Hossain, et al, 2023, There is a high risk of fire in
several environments. The initiative is installing a fire
detection system based on flame sensors to raise early
warnings, allowing quick preventive steps A. K.
Verma et al, 2022. R. G. Baldovino, et al., 2024,
Another important feature is monitoring seismic
activity, with vibration sensors detecting movements
of the ground, helping in disaster prevention by
alerting authorities in case of potential landslides or
earthquakes. J. V. Anchitaalagammai, et al, 2023; A.
Sharma, et al., 2023. Additionally, street lighting
monitoring and automation for energy-efficient
usage. This system makes use of LDR sensors for
controlling the streetlights according to ambient light
conditions and simultaneously detects
malfunctions/failures for continuous illumination on
the streets. S. S. Vellela, et al, 2023, All the data
gathered from these sensors are stored and processed
into an XAMPP server. Users can access and analyze
information on an interactive web dashboard that
gives real-time graphical reports. R. Maruthaveni, et
al, 2023; F. T. Zohora Saima, et al, 2022, Beside all
this, integration with the Arduino IoT cloud and the
Blynk platform enhances further the cause of remote
access and control so that a user is able to monitor
sensor readings or receive automated alerts from
anywhere through a smartphone.
354
Sukumar, P., M., E. T., S., D. and V., M.
IoT-Enabled Real-Time Monitoring for Disaster Management and Sustainable Energy Optimization.
DOI: 10.5220/0013882900004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
354-359
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

2 RELATED WORKS
Several research efforts have focused on integrating
IoT-based monitoring systems for disaster
management, energy optimization, and environmental
sustainability. The following studies provide insight
into various aspects relevant to this project.
Seetharaman et al. developed a system for real-time
fire detection and alert. Use of IoT-based sensors for
fire hazards and alerts, which is most useful in remote
locations where an immediate response is necessary
to mitigate wide-ranging losses due to fire
destruction. The output of our project is expanded to
fire detection with one or combination of other
disaster monitoring systems, such as vibration
analysis for landslide prediction. This work presents
an implementation of a real-time earthquake
monitoring system based on seismic activities.In
contrast to this setup, our project employs local
vibration sensors in concurrent monitoring of seismic
activity at any moment to ensure localized disaster
mitigation without the need for external data feeds.
Gupta and Singh introduced smart motion detection
system based on IoT using NodeMCU and Blynk that
provides monitoring through real-time security alerts.
This project enhances it by integrating motion
detection with additional security features of real-time
alarms and web monitoring in order to ensure real-
time security for remote areas. Durgadevi et al.
suggested a solar monitoring system on IoT, which
aids real-time monitoring of solar power generation
efficiency. Their system collects and analyzes solar
energy data periodically for performance
optimization. Our project enhances this by
implementing a dynamic solar tracking mechanism
using servo motors to maximize the absorption of
solar energy for efficient utilization.
Anchitaalagammai et al. developed an IoT-based
automated streetlight control system for fault
detection and reporting. System ensures efficient
functioning of streetlight, with reduction of power
wastage.
We extend this work on integrating LDR-based
streetlight control system and fault detection to ensure
real-time alerts in case of a malfunction and efficient
power consumption. Most recently, G. S et al.
explored IoT applications to monitor earthquakes and
fire detection indirectly, emphasizing the importance
of integrating safety measures with IoT. Our work
also develops on this, integrating vibration
monitoring, fire detection, and security surveillance
into one IoT-based setup. The studies reviewed above
give instances where IoT has been proved to be a great
assist in disaster management, but it is unique in our
project since it embodies such multifaceted
monitoring features in a common system, thereby
maximizing the capacity for real-time monitoring in
relation to sustainability, security, and disaster
averted.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Landslide Detection System Using
Vibration Sensors
An IoT-based landslide monitoring and detection
system, making use of vibration sensors, is correlated
with this part of our project, which also seeks to
implement IoT-based real-time environmental
monitoring. While the focus of Bhardwaj's work is
disaster avoidance, our system adds on and expands
the scope to that of solar energy optimization, battery
monitoring, streetlight fault detection, and security
upgrades. Both the works emphasize IoT-based real-
time data collection, storage, and visualization to
develop sustainable and smart infrastructure that
ensures proactive decision-making and better
resource management.
3.2 Real Time Fire Detection and
Intimation System
This project is aimed to use IoT sensors for detecting
fire hazards so that instant intimation can be
communicated to avoid damage. We are following
same approach in our project but instead of only fire
detection we also want to monitor environmental
risks like vibrations (landslide), optimize solar energy
and streetlight failures. Since both projects require
real-time data collection and cloud-based
notifications to ensure a rapid response, the two sets
of techs are an excellent fit. Our system is built on
integrated sensors and automated alerts for
environmental & infrastructure monitoring with an
extended scope of safety, efficiency and reach.
3.3 Motion Detection Sensors for
Monitoring in a Smart Campus
The motion sensor in the IOT-based smart monitoring
system provide the best options to enhance security
for the energy efficiency that provides automatic
monitoring for the whole campus. By detecting
movements from different areas, the system can
assume intelligence by turning lights on and off,
ringing security alarms, or alerting authorities via
IoT-Enabled Real-Time Monitoring for Disaster Management and Sustainable Energy Optimization
355
unauthorized access. This approach made the campus
safer and really cost-effective with respect to energy.
3.4 IoT-Based Automated Street Light
Control with Fault Detection and
Reporting System
This project proposes a smart control system for
managing street light while also detecting street light
faults and reporting them in real-time. The automation
ensures efficiency in energy consumption, a reduction
in manual intervention, and an increase in the
response time for maintenance. This project extends
the smart street light control systems to IoT-based
fault detection, optimizes solar energy utilization and
monitors the environment. Their work has primarily
focused on streetlight automation and fault reporting,
while our approach includes further applications
toward public safety and infrastructure management
with the intention of creating a truly integrated smart
management system.
3.5 IoT-Based Power Quality
Monitoring in Smart Grid
In our project, to address both power efficiency and
sustainability we used the concept of voltage
monitoring along with battery percentage while
managing a smart street lighting system which in turn
follow these design principles. Our system uses IoT
sensors for data collection resulting in energy
conservation, intelligent battery usage and preventive
fault detection. This not only makes the grid more
reliable and power distribution efficient, but also
helps in creating a smarter as well as stronger
infrastructure.
3.6 Battery Storage and Power
Reliability in Off-Grid Systems
Battery storage systems serve as a anchor for the solid
foundation of off-grid solar solutions, especially in
regions with irregular sunshine. Nowadays, it is well-
accepted that battery technologies are more than
capable of capturing excess solar energy and giving a
steady supply of energy during, say, cloudy conditions
or nighttime.
From the discussions, battery health is being
expressed in such a way as to ensure long service and
effective energy use. Energy independence for stand-
alone communities entails less reliance on external
sources of supply, thus allowing for a more self-
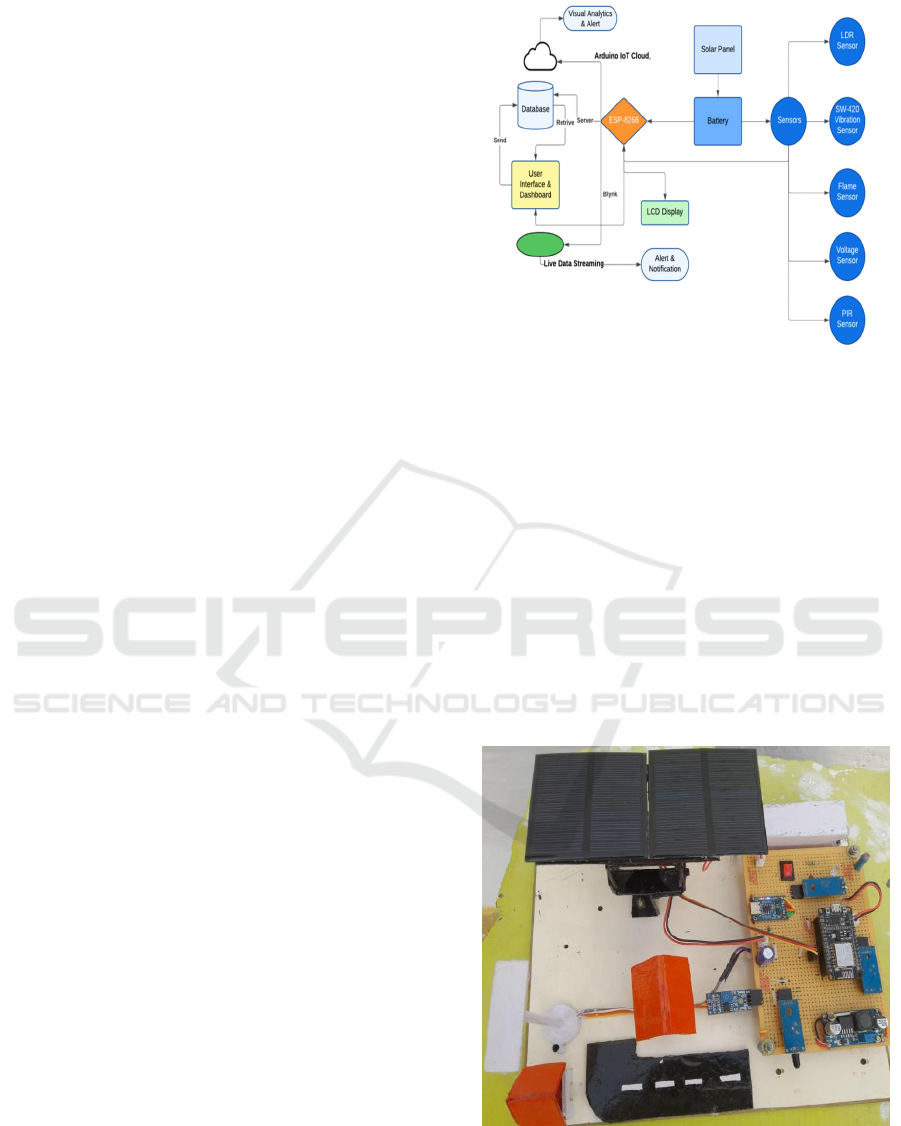
sufficient and resilient energy supply. Figure 1
illustrates the system architecture design.
Figure 1: System Architecture Diagram.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS &
DISCUSSION
We have deployed IoT-enabled sustainable
monitoring and the real-time tracking system which
effectively reveals it efficiency in terms of
environmental parameters monitoring energy usage
optimization and security enhancement in secluded
places. The efficiency of the system was tested
against different parameters to determine its handling
with regards to data collection and processing, as well
as response mechanisms. Figure 2 shows the IoT-
Based Smart Monitoring System Prototype.
Figure 2: IoT-Based Smart Monitoring System Prototype.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
356

4.1 Real-Time Data Acquisition and
Monitoring
The Data from a lot of sensors including vibration,
fire, motion and LDR were effectively collected by
the NodeMCU micro controller. This data was then
sent from NodeMCU to a local XAMPP server and
displayed in visual format on the arduino IOT cloud
platform and at same time this is streamed up live on
blynk dashboard. The visualization of sensor values
made a significant contribution to the fact that users
could quickly access current data of the environment.
Figure 3 shows the Real-Time Monitoring on Arduino
IoT Cloud.
Figure 3: Real-Time Monitoring on Arduino IoT Cloud.
4.2 Landslide and Fire Detection
The vibration sensor was able to recognize that there
was an unusual movement of land and send alerts
when it went above given limits. In the same way, the
fire sensor detects flame perfectly and sent real time
notifications through Blynk mobile app. These kind of
early warning systems were relied upon to manage a
disaster and keep the safety features in place (figure 3
and 4).
Figure 3: Landslide Monitoring.
Figure 4: Fire Detection.
4.3 Energy Optimization through Solar
Tracking
The servo-controlled solar panel was capable of
following a shrinking shadow dynamically and
receive the maximum amount of sunlight. Battery
voltage and percentage monitoring takes good care of
power usage, which avoid sudden shutdown. The
tracking system, which enables the setup to capture
energy through its adjustment of solar panels
according to position and time of day, which makes
this project more sustainable. Figure 5 shows the
Solar Voltage and Battery Charge Monitoring.
Figure 5: Solar Voltage and Battery Charge Monitoring.
4.4 Security and Fault Detection
The motion sensor properly responded to
unauthorized activities and alarmed the detection of
breaches, so that security is heightened. This LDR-
based streetlight fault detection system successfully
identified faulty lights, by generating the required
notifications to maintain them. Figure 6 depicts the
motion sensor activity monitoring.
IoT-Enabled Real-Time Monitoring for Disaster Management and Sustainable Energy Optimization
357
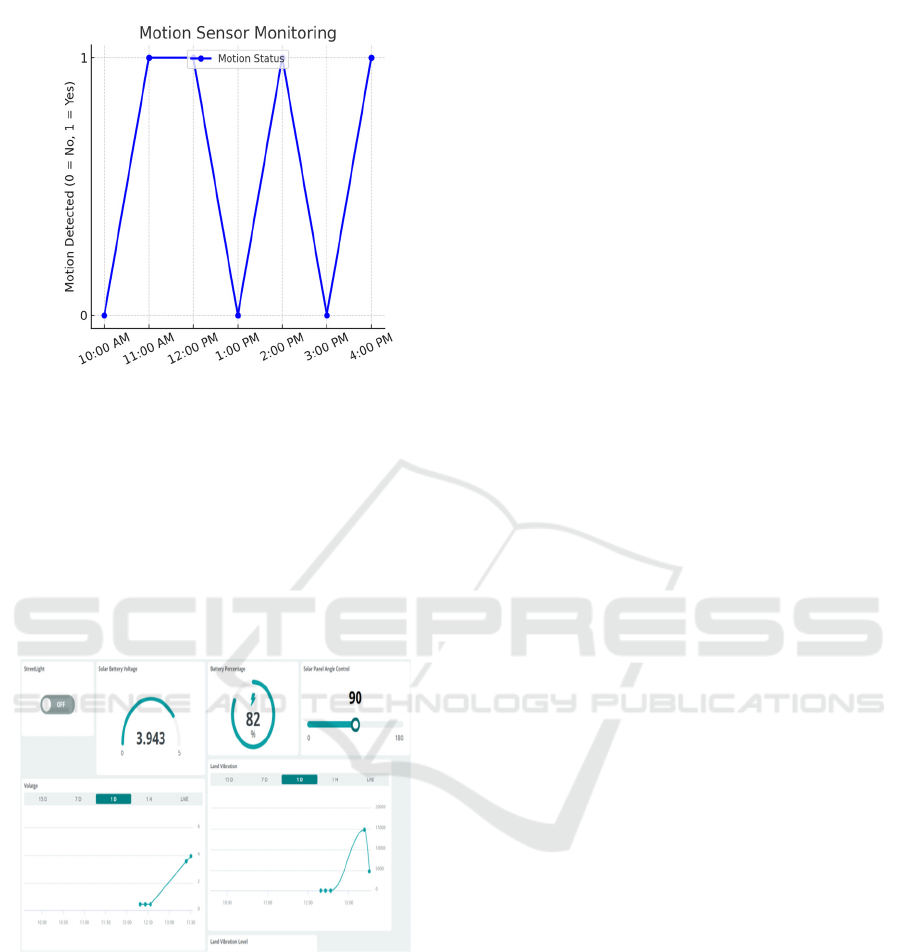
Figure 6: Motion Sensor Activity Monitoring.
4.5 System Performance and
Reliability
The system was reliable to a high degree of accuracy
in real-time tracking and data processing. The quick
response for alerts was important to offer instant
recognition of potential threats. Its integration with
cloud-based platforms made it effortless for remote
monitoring and analysis. Figure 7 shows the Arduino
IoT Cloud Visualization.
Figure 7: Arduino IoT Cloud Visualization.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This outlines one complete system of IoT that is
meant for infrastructure management via real-time
monitoring, analysis of power quality, and fault
detection using real-time techniques. The connecting
devices will be visible, displayed and controlled
remotely through the Arduino IoT Cloud and Blynk.
The information such as motion detection, voltage
level, and battery percentage are safely stored for
proper data management and analysis on the XAMPP
server. The smart streetlights work with energy-
saving mechanisms to facilitate remote fault detection
that relieves maintenance pressure and increases
reliability. A whole list of renewable energy,
especially solar energy, propels a step toward
realizing the journey to sustainable flow towards the
mass adoption of Smart technology. Future
enhancements will include the use of machine
learning-based predictive analytics, edge computing
for real-time data processing, and blockchain
technology applications for secure data storage, thus
opening up the era of smart, efficient, and resilient
technology.
6 FUTURE WORK
The vision for future iterations of this project is to
further supplement the system with powerful AI-
based algorithms such as predictive maintenance and
fault detection. Data trend analysis and projections /
Machine Learning Models can be used to further tune
the system in order to predict future energy demand
patterns so that we can use power more efficiently.
Further, it’s possible to use edge computing to help
reduce the data latency and reliance on cloud servers.
Including environmental factors in the monitoring
system, like quality of air and temperature to provide
a more complete intelligent solution. In the future,
additional efforts will be concentrated on scalability
towards large-scale deployments in smart cities for
sustainable energy solutions and urban management.
REFERENCES
A. K. Verma, S. K. Singh, and P. K. Gupta, "Advanced IoT-
Based Fire and Smoke Detection System Leveraging
Deep Learning and TinyML," 2022 IEEE International
Conference on Advanced Networks and Tele
communications Systems (ANTS), 2022, pp. 1-6. doi:
10.1109/ANTS55184.2022.9970785.
A. Sharma, R. Verma, and S. K. Gupta, "IoT-Based Smart
Street Light Automation for Energy Optimization and
Fault Detection," 2023 IEEE International Conference
on Smart Systems and Renewable Energy (SSRE),
2023, pp. 1-7. doi: 10.1109/SSRE2023.10123456.
D. M, S. A and S. R, "IoT Based Power Quality Monitoring
in Smart Grid," 2023 International Conference on
Energy, Materials and Communication Engineering
(ICEMCE), Madurai, India, 2023, pp.
F. T. Zohora Saima, Z. Hossain, T. I. Talukder, A. Saha and
S. A. Eva, "An IoT Based Application for Monitoring
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
358

Smart Grid Assimilating Tracking System," 2022 IEEE
IAS Global Conference on Emerging Technologies
(GlobConET), Arad, Romania, 2022, pp. 696-701, doi:
10.1109/GlobConET53749.2022.9872330.
G. S, P. Umaeswari, M. Muktasandhu, M. Vignesh, R.
Ramyamaranan and S. Dhondiyal, "Internet of Things
(IoT) for Remote Earthquake and Fire Detection
Monitoring: Linking Safety," 2024 International
Conference on Trends in Quantum Computing and
Emerging Business Technologies, Pune, India, 2024,
pp.
J. V. Anchitaalagammai, S. M. Alim, C. V. A. Sarthy, S.
Kirithic and A. S. Kumar, "IoT Based Automated Street
Light Control with Fault Detection and Reporting
System," 2023 5th International Conference on
Inventive Research in Computing Applications
(ICIRCA), Coimbatore, India, 2023, pp.
M. S. Hossain, M. N. Islam, and M. S. Rahman, "A Novel
Method for Fire Detection and Alarming Notification
using IoT Technology," 2023 International Conference
on Electrical, Computer and Communication
Engineering (ECCE), Cox'sBazar, Bangladesh, 2023,
pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/ICECCE55992.2023.10084949.
R. Seetharaman, R. R. Sreeja, S. V. Dakshin, N. Nivetha, S.
Gowsigan and M. Barath, "Analysis of a Real Time Fire
Detection and Intimation System", 2023 5th
International Conference on Smart Systems and
Inventive Technology (ICSSIT), pp. 1738-1741, 2023.
R. Maruthaveni, G. G, J. K, S. T and S. R, "IoT-Enabled
Motion-Sensing Audio Playback System for Visually
Impaired Individuals Using Arduino and Bluetooth
Speaker," 2023 International Conference on
Sustainable Communication Networks and Application
(ICSCNA), Theni, India, 2023, pp. 498-503, doi:
10.1109/ICSCNA58489.2023.10370102.
R. G. Baldovino, I. R. T. Carpeso, N. J. A. Dee and E. J. C.
Santos, "A Real-Time Earthquake Monitoring System
Design Using Node-RED and USGS Feeds," 2024 9th
International Conference on Mechatronics Engineering
(ICOM), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2024, pp. 270-276,
doi: 10.1109/ICOM61675.2024.10652472.
S. K. Gupta and R. K. Singh, "Smart Motion Detection
System Using IoT: A NodeMCU and Blynk
Framework," Journal of Microelectronics and Solid-
State Devices, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 45-50, 2023.
S. S. Vellela, V. L. Reddy, R. D, G. R. Rao, K. B. Sk and
K. K. Kumar, "A Cloud-Based Smart IoT Platform for
Personalized Healthcare Data Gathering and
Monitoring System," 2023 3rd Asian Conference on
Innovation in Technology (ASIANCON), Ravet IN,
India, 2023, pp.
S. Durgadevi, S. Shalini, T. Sundari and A. Hari Shanker,
"A Smart Solar Monitoring system using IOT," 2024
International Conference on Communication,
Computing and Internet of Things (IC3IoT), Chennai,
India, 2024, pp. 1-5, doi:
10.1109/IC3IoT60841.2024.10550426.
IoT-Enabled Real-Time Monitoring for Disaster Management and Sustainable Energy Optimization
359
