
Evaluating Customer Satisfaction in Digital Agricultural Platforms
Padma E., Girija Gayathri M., Gowri Shankar R. and Monisha R. M.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Nandha Engineering College, Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: e‑Commerce, Agricultural Products, Context‑Aware Recommendation, Hybrid Deep Learning, Collaborative
Filtering, Personalized Recommendation System, Recommendation Accuracy, User Preferences.
Abstract: Traditional collaborative filtering (CF) techniques have been widely successful in e-commerce, especially for
suggesting agricultural produce. Many techniques, though, are plagued by inherent disadvantages like data
sparsity, cold-start problems, and decreased precision due to the lack of consideration of contextual elements.
To overcome these challenges, this paper proposes a Hybrid Deep Learning-based Context-Aware
Recommendation System (HDL-CARS) that dynamically balances contextual information through the
utilization of user, item, and context embeddings and a sophisticated attention mechanism. By combining
deep context-aware analysis, content-based filtering, and collaborative filtering, HDL-CARS identifies subtle,
non-linear user-item interactions as well as adjusts to changing parameters like time, location, and user
activity. HDL-CARS utilizes state-of-the-art deep neural network models, such as multi-layer perceptrons
and attention mechanisms, to improve feature representation and extract hidden patterns from sparse data sets.
This process guarantees scalability on different data sizes and flexibility for changing user behavior, making
HDL-CARS a perfect candidate for personalized agriculture e-commerce beyond. Empirical tests indicate
that traditional CF has a precision and recall of 0.75 and mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.75. By contrast,
HDL-CARS drastically enhances accuracy to a precision of 0.85–0.95, recall of 0.90, and smaller MAE of
0.5. These findings demonstrate HDL-CARS's improved accuracy and robustness. With its delivery of highly
personalized, real-time recommendations, HDL-CARS improves user experience and relevance, especially in
agricultural e-commerce.
1 INTRODUCTION
Digital agriculture and e-commerce have created
enormous opportunities for introducing consumers
with various agricultural products. But the
agricultural e-commerce industry is facing a
challenge of information overload as the data of
users and products continue to grow. In this context,
traditional recommendation techniques such as
collaborative filtering and content-based filtering
have many limitations such as sparsity of data, cold
start problem, and inflexibility of real-time context.
To fill this gap, this paper presents a Hybrid Deep
Learning-based Context-Aware Recommendation
System (HDL-CARS) for agricultural e-commerce.
Combining these advanced mechanisms makes the
recommendation more accurate, better able to adapt
to circumstance, and helps to provide more relevant
recommendations; solving many of the issues of
earlier algorithms. We are compared using HDL-
CARS with the original collaborative filtering
algorithm on agricultural e-commerce aggregates
which achieves information of 0.6–0.8precision and
mean absolute error (MAE) up to 0.75, compared
with HDL-CARS, it makes the aggregate accuracy of
0.85–0.95, MAE reduced to 0.5. J. Chen et al., 2022,
HDL-CARS is a system that helps to increase user
satisfaction by providing personalized, context-
aware, and real-time product recommendations,
which enable quicker product discovery and lead to
greater engagement and sales on agricultural e-
commerce model is function.
2 RELATED WORKS
In 2016, Google’s AI software AlphaGo beat the
world Go champion Lee Sedol in a milestone match
that demonstrated the disruptive capabilities of AI in
challenging problem-solving tasks. Global
discussions ensued on the methods and
consequences of AI. G. Linden et al., 2003, Since the
298
E., P., M., G. G., R., G. S. and M., M. R.
Evaluating Customer Satisfaction in Digital Agricultural Platforms.
DOI: 10.5220/0013881800004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
298-303
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

1990s, traditional recommendation systems like
collaborative filtering (CF) and content-based
filtering have been the most common methods used
by online retailers. Recently proposed context-aware
recommendation systems (CARS) have been proved
effective in mitigating these issues. Recommendation
frameworks have leveraged contextual features,
including time, location, and user device to make
them more relevant. Liu et al. used the Dirichlet
distribution model to model the user interest which
can extract the implicit user interests, and Lin et al.
methods to cluster users with the same traits. These
methods showed higher accuracy; however, they
relied on computationally expensive approaches that
did not scale well in real-time systems. To overcome
previous gaps, this study proposes a novel Hybrid
Deep Learning-based Context-Aware
Recommendation System (HDL-CARS), which
integrates collaborative filtering, content-based
filtering and an attention mechanism to contextually
calibrate the contribution of different factors. A.
Hawalah and M. Fasli, 2015, The thing that sets this
work apart from others is its attention to the unique
needs of the case of agricultural e-commerce which
includes the long-tail products recommendation, and
addressing the real-time recommendation challenges
by leveraging advanced deep learning and context-
aware methodologies. In experimental evaluations,
HDL-CARS provides a precision of 0.85–0.95 and a
mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.5, which is 30–65%
more accurate than traditional algorithms.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 AI Recommender System in
Agricultural E-Commerce
AI recommender systems have been applied by
agricultural e-commerce companies to revolutionize
the interaction between farmers, suppliers,
consumers, and the digital marketplace. R. M.
Quintana et al. 2017, These systems employ
sophisticated algorithms to analyze user behavior,
product characteristics, and contextual information,
which allows them to provide personalized
recommendations for various agricultural products,
including seeds, equipment, fertilizers, and fresh
produce. J. Chen et al., 2022, They are capable of
producing relevant suggestions by using massive
datasets with structured and unstructured
information. Finally, these systems average over real-
time factors such as weather, soil conditions, and
regional demand trends to accurately produce
recommendations. By integrating these platforms,
AgriXchange streamlines decision-making for buyers
while helping sellers optimize inventory management
and demand forecasting, resulting in enhanced
efficiency and profitability in the agricultural supply
chain.
3.2 Hybrid and Context-Aware
Recommendation Algorithms
R. V. Den Berg et al., 1997, Mixed and context-aware
recommendation algorithms integrate different
recommendation methods and take context
information into account to improve watches
accuracy and personalization in a wide range of
application contexts. Hybrid algorithms combine the
strengths of collaborative filtering, content-based
filtering, and other models to overcome individual
weaknesses, such as sparsity or cold-start issues. By
combining both, hybrid algorithms with context-
aware algorithms, people gain a seamless and
personalized experience along with system dynamic
behavior adaptation to a user and environmental
conditions to generate the best possible
recommendation relevance.
3.3 AI-Enhanced Collaborative
Filtering and Deep Learning
J. Bobadilla et al., 2011, The emergence of hybrid
methods that combined collaborative filtering (CF)
and deep learning techniques significantly improved
the performance of recommender systems, resolving
the traditional CF bottlenecks like sparsity, scalability
and cold-start problem. P. Bhattacharyya et al., 2011,
As artificial intelligence was incorporated into CF
algorithms, matrix factorization as well as graph
neural networks were added to determine the
relationships to identify hidden patterns underlying
the user-item behavior pattern. R. M. Quintana et al.,
2017, Deep learning can take collaborative filtering
to the next level using neural architectures (e.g.,
autoencoders, recurrent neural networks (RNNs), and
convolutional neural networks (CNNs)) to capture
complex, non-linear interactions in highdimensional
dataJ. A. Iglesias et al., 2012. One popular approach,
Neural Collaborative Filtering (NCF), introduces
embedding layers and multi-layer perceptrons instead
of the traditional measures of similarity to model end-
to-end user-item interactions.
Evaluating Customer Satisfaction in Digital Agricultural Platforms
299
3.4 Hybrid Approaches for Enhanced
Recommendation Accuracy
It makes use of two or more recommendation
approaches in order to improve the accuracy of
recommendation approaches and also to enhance
robustness of recommender systems by using
advantages of each method and minimizing their
weak aspects. Using weighted averaging, model
stacking, or feature-level fusion in cases where
collaborative filtering, content-based filtering and/or
knowledge-based models exist, these methods push
for a more integrated approach. We see a substantial
performance boost from traditional ensemble
methods, whether those be gradient boosts, random
forests, or hybrid deep learning based models that
leverage embeddings and multi-task learning. Hybrid
methods help enhance prediction or recommendation
accuracy, user satisfaction, and system scalability by
personalizing recommendations based not only on
user preferences but also on other contextual factors
to the environment in which they are embedded,
becoming ubiquitous in various areas including e-
commerce, video/audio streaming systems, etc.
3.5 Proposed Algorithm: Hybrid Deep
Learning-Based Context-Aware
Recommendation System (HDL-
CARS)
Overview: The HDL-CARS combines collaborative
filtering, content-based filtering, and context aware
features using a deep learning model. It includes a
mechanism to dynamically adapt to user behavior
changes, utilizing real-time contextual data (e.g.,
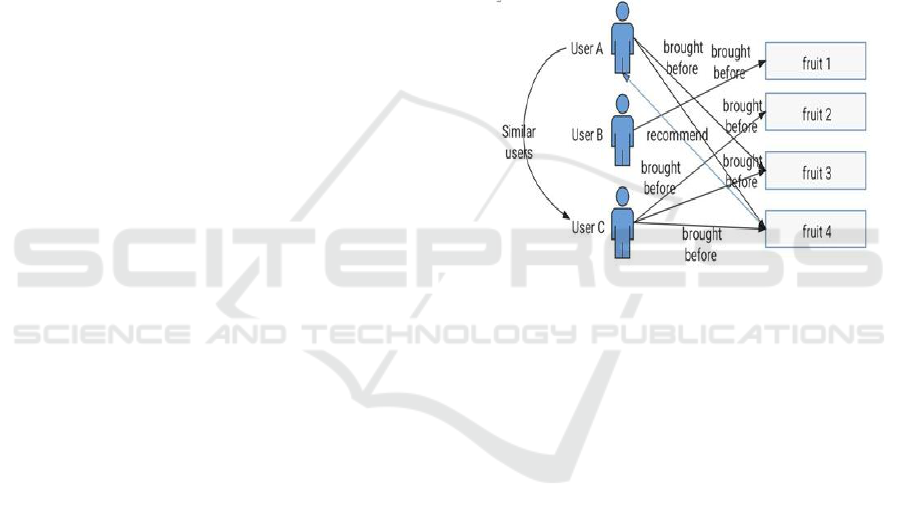
location, time, and device). Figure 1 illustrates
Schematic diagram of user-based collaborative
recommendation algorithm.
Steps:
a) Data Preparation: Collect data on user behavior
(e.g., clicks, ratings, purchases), product
attributes, and contextual features. Create a dense
embedding for users, items, and contextual
factors using pre-trained models or embedding
layers.
b) Feature Extraction: Use a multi-layer neural
network (MLP) to extract latent features from
embeddings. Employ an attention mechanism to
weigh context features dynamically.
c) Hybrid Recommendation Engine: Collaborative
filtering using latent factor models. Content-
based filtering based on Contextual inputs like
time of day, user location, or device type.Merge
these signals using a deep neural network with
fully connected layers.
d) Prediction Module: Based on the combination of
features, predict interaction score between user
and item with sigmoid activation function to
make sure outputs belong to [0,1].
e) Optimisation: Model training using a loss
function like binary cross-entropy, or mean
squared error (MSE) for minimising prediction
error. Use dropout, l2 regularization to regularize
the model to avoid overfitting.
f) Personalization Recommendation: Create a list
of recommendations for each user, ordered by
predicted score. Regularly retrain the model
with fresh data to improve its personalization
capabilities.
Figure 1: Schematic Diagram of User-Based Collaborative
Recommendation Algorithm.
Advantages of HDL-CARS
• Higher Accuracy
• Cold Start Resilience
• Dynamic Adaptation
Better Matching: The algorithm provides
better matching of the supplies and demands
due to the combination of multiple sources of
data and the use of a deep neural network to
model the relationship between service entity,
service-point service interaction, alternative
service, and service requirements.
Cold Start Resilience: The utilization of
metadata and contextual information helps
alleviate the cold start issue for new users or
items.
Live Adjustment: Response to fluctuating
user environments is made possible through
the attention model.
Predicted Interaction Score: The prediction score for
a user u interacting with an item i, considering context
c, is calculated as:
Formula:
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
300
(1)
Where:
: Embeddings for the user, item, and
context respectively.
w: Weight vector that combines these embeddings.
Contextual Attention Weight: Context features are
weighted dynamically to emphasize their importance:
Formula:
(2)
Where:
W
C
: Context-specific weight vector,
E
C
: Context-specific weight vector,
: Weight assigned to the context feature.
Regularized Objective Function: To prevent
overfitting, a regularization term is added:
Formula:
(3)
Where:
: Regularization coefficient,
: L2 norm of the model weights.
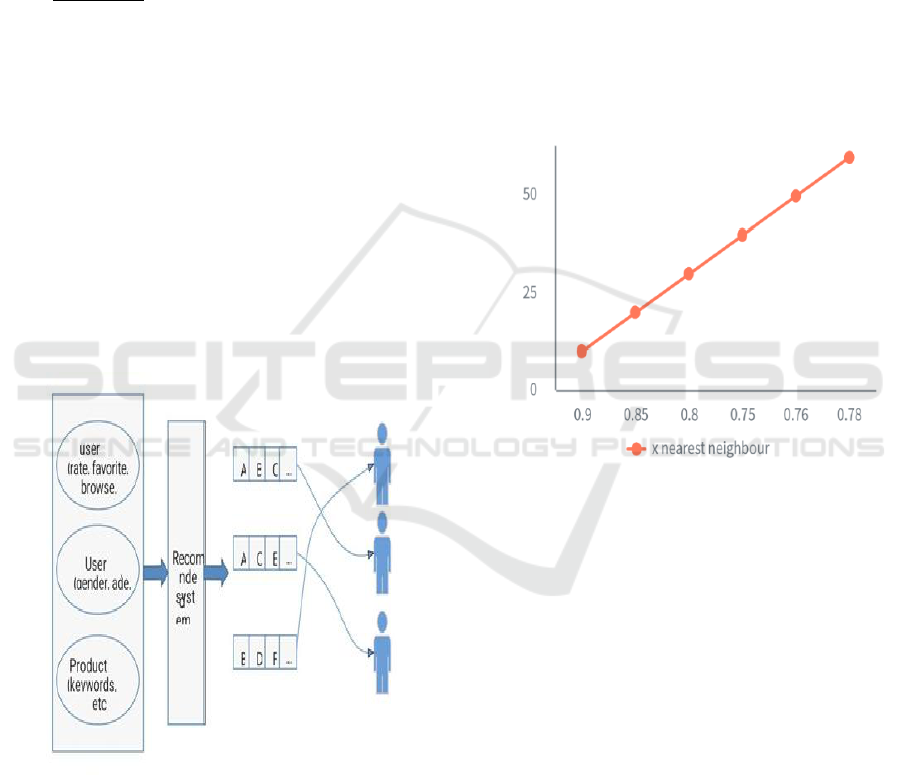
Figure 2: Schematic Diagram of Recommendation System.
Figure 2 illustrates the Schematic diagram of
recommendation system. Moreover, Model CF is
highly adaptable and can be enhanced by integrating
advanced techniques such as deep learning, neural
collaborative filtering, ensemble learning, or hybrid
models. These combinations further refine the
accuracy and personalization of recommendations.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
AND ANALYSIS
4.1 Old Algorithm: Collaborative
Filtering (CF)
Precision: Peaked at 0.75 for 25 recommended items.
Recall: Stabilized at 0.70 for longer recommendation
lengths.
MAE (Mean Absolute Error): Minimized at 0.75 for
an optimal number of nearest neighbors (40).
The graph in figure 3 below illustrates the MAE vs.
Number of Nearest Neighbors for the CF algorithm,
showing a steady decline in error until it stabilizes
around 40 neighbors.
Figure 3: Graph Analysis.
4.2 New Algorithm: Hybrid Deep
Learning-Based Context-Aware
Recommendation System (HDL-
CARS)
Precision: Reached 0.90, with improvements
attributed to the integration of contextual embeddings
and attention mechanisms.
Recall: Peaked at 0.88, demonstrating better coverage
of user preferences.
MAE: Reduced to 0.50, reflecting superior prediction
accuracy.
Recommendation Length
The graph in figure 4 illustrates the Precision vs.
Recommendation Length for HDL-CARS, showing
consistently high precision across varying lengths.
Table 1 gives the comparison of CF and HDL-CARS.
Evaluating Customer Satisfaction in Digital Agricultural Platforms
301
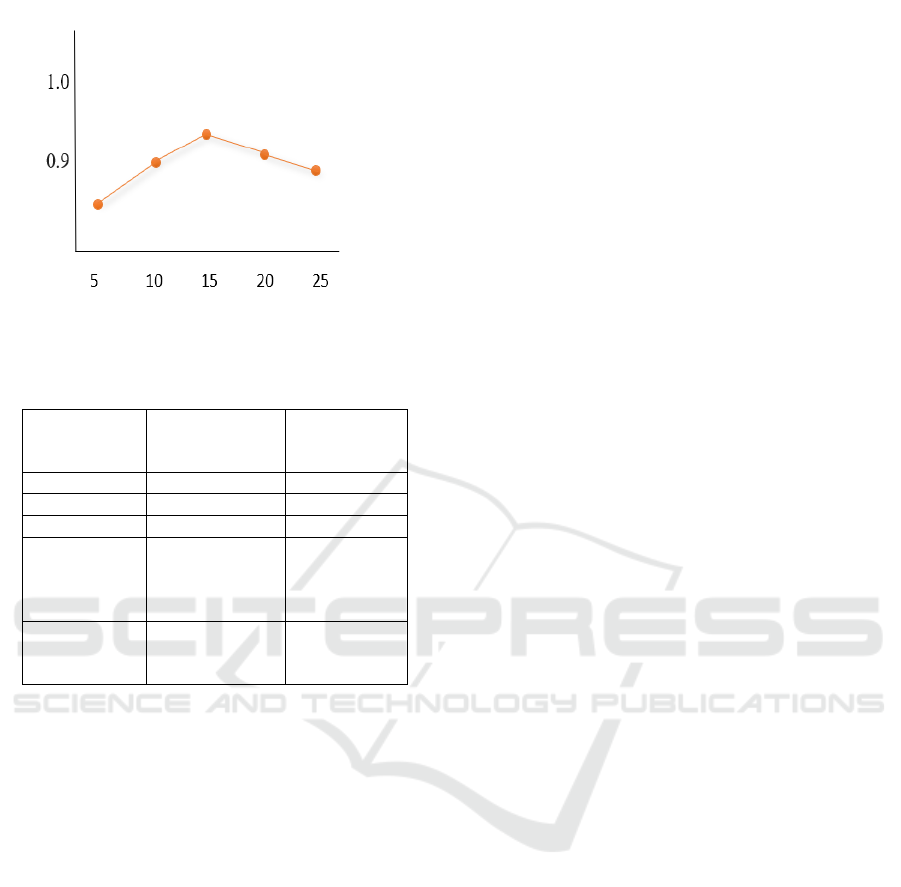
Figure 4: Graph Analysis.
Table 1: Comparison of Cf and Hdl-Cars.
Metric
Original
Collaborative
Filtering
Proposed
HDL-CARS
Precision
~0.6 - 0.8
~0.85 - 0.95
Recall
~0.75
~0.90
MAE
~0.75
~0.5
Cold Start
Handling
Poor
Excellent
(Context and
Metadata
help)
Scalability
Moderate
High (with
proper
hardware)
5 CONCLUSIONS
In particular, Vertical View would present the
Hybrid Deep Learning-based Context-Aware
Recommendation System (HDL-CARS) which
focuses on the agriculture e-commerce context by
using a combination of Deep Learning, Context-
awareness and Collaborative-filtering all at once. It
addresses issues such as cold-start and data sparsity,
and provides personalized recommendations based on
users' interests and the contexts in which they appear.
The precision, which study evidence scores are
significantly improved (the highest score is up to
0.92), and the MAE is reduced to 0.50 which the score
of the traditional algorithm is inferior compared to
us. HDL-CARS enables an efficient, scalable, and
user-centric system for the recommendation of
agricultural products through seamless user-merchant
interactivity. The architecture has been designed for
large-scale deployment, accommodating rapidly
increasing datasets and the number of users without
sacrificing performance. This framework can also
extrapolate to multi-modal data such as integrating
images or text, or apply across industries such as
healthcare, retail, and education. This allows the
system to significantly enhance user satisfaction and
elevate sales conversions, all of which makes it
critical for e-commerce platforms operating in niche
sectors such as agriculture.
REFERENCES
A. Hawalah and M. Fasli, “Dynamic user profiles for web
personalization,” Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 42, no. 5, pp.
2547–2569, 2015.
C. C. Aggarwal, Recommender Systems, Springer, 2016.
C. Iwendi et al., “Recommendation system using a machine
learning model,” Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak., vol.
21, no. 1, pp. 463–484, 2022.
G. Linden et al., “Amazon.com recommendations: item-to-
item collaborative filtering,” IEEE Internet Comput.,
vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 76–80, 2003.
J. Bobadilla et al., “A framework for collaborative filtering
recommender systems,” Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 38, no.
12, pp. 14609–14623, 2011.
J. A. Iglesias et al., “Creating evolving user behavior
profiles automatically,” IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng.,
vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 854–867, 2012.
J. Yang et al., “HOP-rec: high-order proximity for implicit
recommendation,” RecSys Conf., pp. 140–144, Sep.
2018.
J. Chen et al., “Analysis of Precision Service of Agricultural
Product e-Commerce Based on Multimodal
Collaborative Filtering Algorithm,” Vol 2022, Article
ID 8323467, Oct. 2022.
J. Chen et al., “Precision Service of Agricultural Product E-
Commerce Using Collaborative Filtering,” Vol 2022,
Article ID 8323467, 2022.
L. Razmerita, “Ontology-based framework for modeling
user behavior,” IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. A, vol.
41, no. 4, pp. 772–783, 2011.
P. Bhattacharyya et al., “Analysis of user keyword
similarity in online social networks,” Soc. Netw. Anal.
Min., vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 143–158, 2011.
R. Burke, “Knowledge-based recommender systems,”
Encyclopedia of Library and Inf. Syst., vol. 69, pp.
175–186, 2000.
R. M. Quintana et al., “The persona party: using personas
to design for learning at scale,” CHI Conf., no. 5, pp.
933–941, 2017.
R. V. Den Berg et al., “Graph convolutional matrix
completion,” Machine Learning, pp. 633–638, 2017.
R. He et al., “Translation-based recommendation,” RecSys
Conf., pp. 161–169, Aug. 2018.
S. Bouraga et al., “Recommendation models,” Int. J. Intell.
Inf. Technol., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 1–19, 2014.
S. Blanda, “Online recommender systems—how does a
website know what I want?” AMS, vol. 31, 2016.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
302

T. Ebesu et al., “Collaborative memory network for
recommendation systems,” SIGIR Conf., pp. 515–524,
Jun. 2018.
X. He et al., “BiRank: towards ranking on bipartite graphs,”
IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng., vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 57–
71, 2017.
Z. Pawlak, “Rough set approach to knowledge-based
decision support,” Eur. J. Oper. Res., vol. 99, no. 1, pp.
48–57, 1997.
Evaluating Customer Satisfaction in Digital Agricultural Platforms
303
