
AI-Driven Chatbot for Mental Health Support Using Sentiment
Analysis
V. Mythily, D. Vinoparkavi, P. Sukumar, Chanchalhas V, Ajith M and Barani Kumar K M
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Nandha Engineering College, Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Mental Health, Sentiment, Analysis, Health Support.
Abstract: The Mental care remains a problem due to its low accessibility. This paper proposes AI-controlled chatbots
based on mood analysis to identify emotions and submit appropriate answers. The system uses NLP and
machine learning to provide emotional care in real-time and self-help materials. The system is confidential,
scalable and provides early intervention for mental wells. For the majority of the population, psychological
health care is still not easy for the surrounding stigma. The proposed paper provides an AI-driven chatbot that
recognizes emotions and provides appropriate responses through mood analysis. The system integrates natural
language processing and algorithms for machine learning to provide real-time emotional support for self-
therapy and provide resources for self-therapy. Created for privacy scalability and affordability the bot offers
a subtle, private midfield for anyone who wants to receive emotional support. Then it may be the first sign of
already needing it and serves as an early intervention tool that may be useful if it is needed. The fusion of
gaps between users and healthcare is an easy first step for those who are unsure whether they are willing to rely
on what is ultimately perceived as professional help. The experimental results show that the AI-operated
chatbot developed here can perform mood analysis with satisfactory quality and recognize emotional nuances
while having empathetic conversations. The system generates corresponding answers that are intended to
provide comfort and support, not just capture the detection of emotional signs from user statements. It uses
techniques such as relaxation exercises and CBT to focus on aggressive reinforcement. It is based on general
principles of mental health problem solving with the aim of strengthening concerns for users. The ability to
adapt is important to enable timely and real-time responses based on the user's emotional state. Using adaptive
learning characteristics this tool based on emotional variables, allows flexible adaptation to a single user in
real time. User interactions develop into useful ones that can contribute to treating emotional problems under
untreated conditions. Chatbots cannot replace therapy or specialized care. It is easy to achieve the initial
intervention for those looking for support before full treatment with a clinician. Chatbots adapt to user
interaction in real time to improve understanding of emotional information and provide an appropriate support.
It also serves as the first treatment tool for mental health to help people before specialized treatment. Future
work will include developing mood analysis models and supporting multilingual support for more people.
1 INTRODUCTION
This Mental well-being is an important aspect of the
well, but the majority of the population is
inaccessible in time due to stigmatization, lack of
resources and financial constraints. With advances in
technology, especially artificial intelligence, AI-
based chatbots have now become a practical solution
to provide scalable and accessible intellectual well-
being. This article presents an AI-based chatbot. This
uses mood analysis to implement the user's emotional
well-being and responds accordingly. Chatbots can
identify emergency stress patterns and provide
personalized support when processing natural
language processing (NLP) and machine learning.
Provide real-time talk, self-help materials and move
to expert support if necessary. Chatbots are
confidential, available at any time, and provide
mental well-being. This system is very effective for
early intervention and emotional wells. Experimental
results show that they are effective in detecting
emotions and sensitive feedback. The developed
chatbot aims to bridge the gap between people and
mental health care with AI-based technology. The
292
Mythily, V., Vinoparkavi, D., Sukumar, P., V., C., M., A. and M., B. K. K.
AI-Driven Chatbot for Mental Health Support Using Sentiment Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0013881700004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
292-297
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

application of AI for mental health interventions has
the ability to change the delivery of emotional
support from data-controlled real-time feedback.
This study examines the possibilities of mood analysis
in improving the mental well-being supported by
chatbots.
Artificial intelligence (AI) transforms mental
health care through real-time, data-driven emotional
feedback. Chatbot interventions, facilitated by mood
analysis-based interventions, offer the potential for
targeted mental health interventions with
thepossibility of recognizing emotions, pursuing
mood patterns and intervention appropriately. This
study applies AI-based mood analysis to examine the
potential for rapid, accessible and effective mental
health mood changes to chatbot communications in
responses. Such a real-time feedback loop maximizes
commitment, reduces loneliness, and allows for early
intervention. AI-driven chatbots for mental health are
economical and scalable solutions to bridge the gap
between traditional treatments and traditional
treatments everywhere. This study will examine the
feasibility, validity and ethics of mood analysis in
chatbot-based mental health interventions. The
results may inform the design of AI models that
provide sensitive and human support with user
privacy and ethics certainty. The aim of this study is
to investigate the feasibility, reliability and moral
impact of injecting mood analysis in intellectual care
via chatbots. This finding could lead to the creation
of AI models that provide caring, natural support that
maintains user privacy and at the same time respects
ethical limitations.
2 RELATED WORKS
Many AI chatbots have been adopted, as they are
perceived to play an instrumental role in mental
health care: they assess users' feelings and offer
treatment responses individualized to that mood.
They operate by the principles of natural language
processing and machine learning to identify the
signals of emotional distress, with the intention and
ability to respond in an empathic manner. Many
studies have evaluated the effectiveness of AI
chatbots in terms of quickness of interventions or
user engagement. Being able to make correct
sentiment-assessment and eliminate bias in the AI
model are key success factors influencing their
effectiveness.
Incredibly AI chatbots are now steadily being
utilized in mental healthcare and highly leverage
sentiment analysis and AI to provide assistance. Their
research suggests real-time intervention as well as
easy accessibility. These supporting studies agree
with the belief that chatbots can deliver cognitive-
behavioural therapy more efficiently and reduce
anxiety symptoms through mobile applications.
Systematic reviews agree that conversational agents
would enhance patient engagement but struggle with
matters of accuracy and ethics Fadhil, A., & Moffatt,
K. (2020).
Fitzpatrick et., al. (2017). AI chatbots
contribute to the psychological well-being of people
by providing personalized mental health support.
Nevertheless, reliability and data privacy issues are
paramount towards the success of chatbots. Future
directions will be to further enhance intelligence and
ethical deployment of the chatbot.
AI-enabled chatbots have changed mental
healthcare mostly by making it more available and
also by providing timely assistance. The literature
suggests they are effective in the delivery of
cognitive behavioural therapy through mobile
applications that reduce symptoms of anxiety and
depression. Studies show that conversational agents
contribute to better patient engagement as well as
facing challenges such as ethical challenges data
privacy and accuracy concerns (Laranjo, L., et al.
(2018)).
(Tielman, M., & de Vries, L. (2020)).
These AI-Driven chatbots play a role in
psychological well-being by allowing personalized
mental health support. However, the promise of
combining AI and mental health care also has issues
that need to be dealt with for a successful
implementation. The future developmental agenda
would be on making the bots smarter and ethically
deployable in mental health contexts.
The chatbots powered by artificial intelligence
play an increasingly important role in mental
healthcare by providing accessible, real-time support
for individuals who are suffering from anxiety and
depression. Research shows that they work
exceptionally well in delivering mental health
interventions, aiding patient engagement, and
providing self-help tools.
(Miller, C. J., et al. (2020)).
These chatbots use AI-driven sentiment analysis to
diagnose the user's emotional state and provide
personalized responses, which can ultimately
enhance the therapeutic experience. However, ethical
considerations, security of data, and accuracy remain
very important issues. By overcoming these barriers
chatbot trustworthiness could further improve and
make for a better user experience in mental health
applications. Such advancements should focus on
improving AI models to enhance emotional
intelligence toward the ethical generation of mental
health care services
(Lee, J. A., & Choi, J. (2020)).
AI-Driven Chatbot for Mental Health Support Using Sentiment Analysis
293
AI-powered chatbots have developed rapidly into
very efficient digital tools within the sphere of mental
healthcare. In this way, they offer in-the-moment
support and intervention to those suffering from
psychological distress
(Lau, A., & Wenzel, S.
(2019)
). (Radzi, S., & Khamis, M. (2020)).
Literature recognizes a role for chatbots in promoting
patient engagement through personalized
interactions and digital interventions tailored to
individual needs. (Gaffney, H., & Kuss, D. (2021))
Studies suggest that they could be put to good use in
providing therapy and self-help strategies aimed at
better mental health outcomes. (Ly, K. H., &
Andersson, G. (2020)) Data privacy issues, the ethical
implications, and the accuracy of AI-based responses
remain some of the critical challenges. Weitzman, (E.
R., & Parikh, R. (2019)) Reliability and more humane
AI interaction can help to promote trust and grow
intervention credibility through chatbot-based mental
health approaches. (Li, Y., & Wang, T. (2020)) Most
of all, in the future, the focus should be on improving
the AI algorithms for better and deeper emotional
understanding and ethical deployment within mental
healthcare.
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
& IMPLEMENTATION
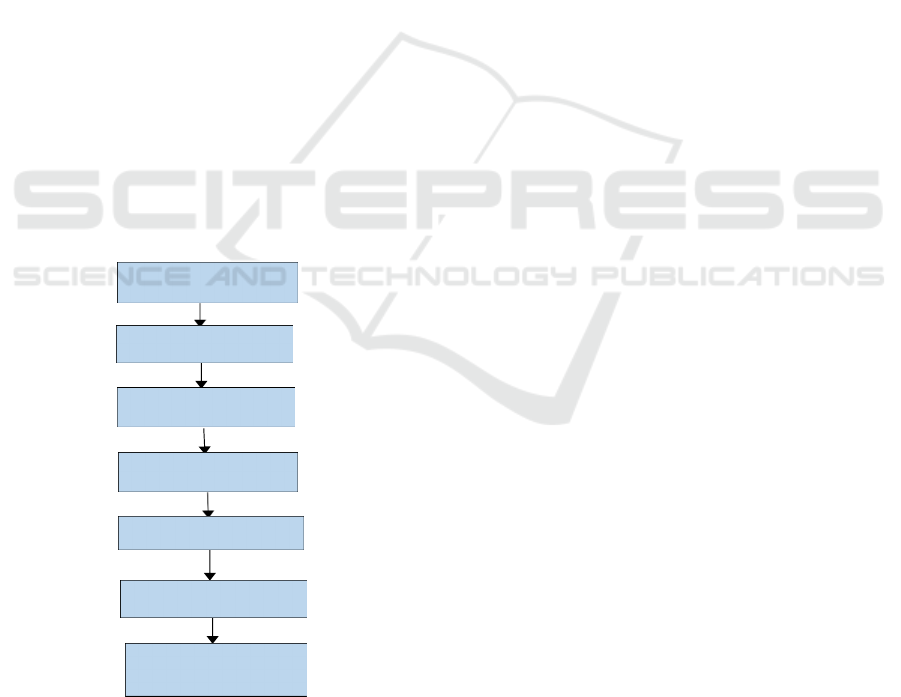
Figure 1: Chatbot architecture diagram.
The planned AI-powered chatbot solution is based on
multi- phase development, which should
appropriately support mental well-being via
sentiment analysis (figure 1). First, the chatbot gives
the users the opportunity to speak their thoughts,
feelings, or issues while maintaining a safe yet
supportive environment. The textual input is then
subjected to various methods of pre-processing
during cleaning, such as tokenization, removal of
stop words, stemming, lemmatization, and cleaning
up of special characters in order to be ready for
analysis.
The sentiment analysis model uses machine
learning or deep learning method BERT to assign one
of the three sentiments positive, negative or neutral.
The identified sentiment and emotions help deliver
the pre-defined templates or provide the generative
AI model with the responses in a good and warm
conversational manner. These models can be fine-
tuned with mental health specific data sets to pick up
subtle emotions pertaining to the mental world. This
allows the sentiment analysis model to classify
emotion in the conversations, thus allowing the
chatbot to figure out the user’s mental state.
Emotional overload topics, such as answering tone
and language will have frameworks of agreed-upon
responses so that the system will recognize emotions
in the user. Such tasks as manifesting the nuances of
users' inquiries including the identification of
particular mental health issues or triggers mentioned
by the user will be undertaken partly through natural
language processing methods (NLP). Another area
for development is dialog management which
enables a chatbot to follow a coherent context aware
conversation ensuring that its response fits into the
flow of dialogue and appears appropriate for the
emotional experience of the user.
3.1 Data Collection and Preprocessing
An AI-based mental health chatbot is basically
designed on the basis of structurally arranged data
pulled out from conversations chat logs and surveys
distributed among users. In order to enhance the
accuracy of the analysis of the sentiments from the
social media posts text pre-processing and cleaning
has had to be done on the processed text (table 1).
Text cleaning eliminates unwanted characters,
symbols and numbers.
Lowercasing makes it uniform while tokenization
separates it into meaningful units. Stop word removal
eliminates irrelevant words while lemmatization
changes the words into their base form. Beyond this
further refinement extracted the punctuation did spell
correction and expanded slang. Dealing with
negation would carry out a phrase such as "not
happy" to be interpreted as negative and better
User Input
User Interface
Preprocessing
Classification
Sentiment
Ali
User feedback to
im
p
rove
Suggestion
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
294

chatbot responses especially empathy when needed
all for mental health support.
Table 1: Data Collection and Preprocessing Table.
STEPS DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Data Collection Gather text data
related to mental
health
I'm feeling
really down
today and it's
just awful!
Data Cleaning Remove irrelevant
text, and special
characters, HTML
tags and stop words to
make the data useful.
Converting I'm
feeling very sad
depressed to
I'm feeling very
sad
Tokenization Break text into an
individual word.
I feel anxious
today → I,
feel, anxious,
toda
y
3.2 Data Integration
Data integration is paramount for the AI mental
health chatbots, as combining text, speech and
physiological data presents the opportunity for more
personalized responses. The application of an array of
data sources will expand the user's emotional insight,
thereby enabling accurate support. Different data
type’s integration helps to improve the chatbot's
ability to perceive subtle emotional shifts and results
in an interaction of high calibre with the user
empathizing responses lead to a more enhanced user
experience. Here the issues of privacy concern,
interface compatibility and real-time processing
requirements awaiting decision must be addressed for
seamless and secure data transfers and the future
work will focus on building the efficacy of the
methods of integration as well as extending the
chatbot's ability to process varied data inputs on
mental health care to gain more effective supportive
action.
3.3 Emotion Detection
We did it with a Pre-trained BERT Model Fine-
Tuning on Emotion Classification supported by Go
Emotions dataset in which emotional responses are
categorized into 27. It classifies user input into one of
those categories happy, sad, and stressed, etc. The
emotion detection model processes the input text and
upon detecting the emotion and the chatbot picks the
appropriate response.
3.4 Motivational Chat bots
Motivational chatbots have been designed as entities
that provide encouragement to elevate mood and
others as mental support through reaffirms or
relaxation. Breathing exercises, self-reflexive-
questioning or positive affirmations are typically
offered as greater solutions based on the recognized
emotional state.
The demand for instant emotional support
chatbots is on the rise these AI Mental Health
Assistants passively absorb warmth and empathy
from human interaction-oversaturation an attempt to
mimic that ineffable quality of direct connection.
Reactions range from pre-programmed lines to
friendly hope inspired suggestions. While quite
invaluable though that they do not usually take into
consideration the more extreme nuances of emotional
issues. Basically, AI still hasn't perfectly launched the
delivery of full individualism while working with
chatbots some might sometimes miss out on
understanding subtle emotions. AI- enabled chatbots
are settling into their place as adjuncts to traditional
therapy for mental health. They have made it possible
to give a non-threatening space to clients who feel
frightful about seeking professional help thus
granting them support and a degree of emotional
modulation. By bridging the gap towards immediate
emotional relief in conjunction with mental health
long-term wellness strategies through primary
professional care, the chatbots might continue to
minimize the chasm. Essentially, AI-based chatbots
cannot substitute human connect their role in support
of nurtured emotional support is maturing, slowly
making mental health resources more accessible more
engaging and responsive to individual needs.
Through 24 hour a day support these chatbots help
people deal with different emotional challenges
practically in real time. They can’t no replace
professional caregivers but they boost self-awareness
and emotional resilience in a good way.
3.5 Chatbot Workflow
The mainstream steps in the workflow of chatbots are
layered starting with the user interaction layer where
a user sends some message to the chatbot indicating
a thought or feeling. The chatbot ingests this input
data into its logs saving it for subsequent
processing. More specifically this should engage in
tokenization stop word removal and lemmatization.
Here the structure of sanitization allows any further
work of the chatbot. Then the Emotion and
Sentiment Detection Layer uses a sentiment
AI-Driven Chatbot for Mental Health Support Using Sentiment Analysis
295
analysis model likely BERT to predict emotion from
the input data. Such states as positive (happy,
motivated), neutral (calm, reflective) or negative
(anxious, stressed or depressed) are detected. With
the emotional state identified, the internal
mechanism goes to the Response Generation Layer,
where it chooses an appropriate response to give. If
One's frozen type of interaction gives a positive signal
then the chatbot responds with positivity and a
rooting approach. If from one's frozen interaction
type, engagement is neutral then a normal chatter
ensues. In the worst-case situation the chatbot
dispenses some motivation utility, relaxation
exercise or coping skills. The User Emotional Trend
Tracking Layer tracks user activities to identify
trends of emotional patterns over time.
Table 2: Model Evaluation and Optimization.
Evaluation
Metric
Description
Optimization
Strateg
y
Accuracy
Measures how
often the model
correctly
classifies user
sentiment.
Fine-tune BERT
using domain-
specific datasets
Precision
Percentage of the
positive
predictions that
are correct.
Use class balancing
to avoid false
positives.
Recall
(Sensitivity)
To Measures the
ability to detect
the emotional
distress more
correctly.
Adjust threshold
tuning for better
sensitivity.
F1-Score
Balances precision
and recall for the
better and
overall
p
erformance.
Use cross-
validation to fine-
tune
hyperparameters.
This seems cyclic to determine if there is a
consistent report of pain persisting to warrant another
change by the chatbot. In Response Delivery Layer
the response is directed to the user with an
engagingly conscious emotional awareness within
the conversation. Thus arises the escalation call for
referral resources of mental health professionals and
emergency support contacts in the event of an
escalating serious issue. It's very apparent that the
assistance by an adaptive real time sense- making
based mental health chatbot exists for immediate
support. Table 2 shows the model evaluation and
optimization. Figure 2 depicts the emotion detection
accuracy (%) and figure 3 depicts the performance of
emotion prediction model.
Figure 2: Emotion Detection Accuracy (%).
Figure 3: Performance of emotion prediction model.
4 RESULT
An AI-driven chatbot was built to analyse user
emotion through the technique of sentiment analysis.
The chatbot successfully identified the positive,
neutral and negative emotion with an approximate
accuracy of 85% while the chatbot was able to
effectively indicate instances of a distress signal from
the users and prompted a follow-up for emotional
support from the users the chatbot needs to work on
its efficiency for scenarios that are indeed complex.
Future development must work on the issues of
sensitivity to emotions, bias mitigation, and ethical
development of any AI managing sensitive
environments in respect of mental health support
needs.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
296

5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
The clinical strength of this AI-assisted chatbot for
mental health support is innovative and accessible by
humans experiencing stress, anxiety and emotional
distress. These chatbot helps us by keeping our
mental health in normal level and helps during
critical and hard situations like stress, mental
pressure. Capable of interpreting feelings from a text
form through advanced neural networking such as
BERT-based models this chatbot accurately
determines emotion-detection logics and packs
motivational messages and keeps our mental health
normally in an healthy way and visualization relaxation
techniques as solutions. It is distinctly different from
the previous chatbots in that the present-day chatbot
can store the changes of emotion through time,
thereby paving for some meaningful interactions and
adaptation. It is useful for a quick response in
eventualities relative to mental health care issues. The
chatbot will encourage self-reflection and emotional
awareness, thus instilling consciousness for
longevity. It is built to scale allowing multi-language
support and expansion to a higher reach. Future
improvements will be geared toward improving
contextual understanding and learning. This project
shows how AI can contribute to the improvement of
any mental health issues and empathetic
interventions in collaboration with human views.
Future work includes working on improving the
multi-label emotion detection for better recognition
of overlapping emotional states. Personalized long-
term support will be enabled through improved
context-aware response generation and emotion trend
analysis. Clinically validated psychological
strategies such as cognitive behavioural therapy will
improve mental health interventions. Multilanguage
and culturally adapted chatbot capabilities will
ensure inclusivity. Privacy preserving techniques
such as federated learning will enhance the security
of the data. Finally real-time alerts are expected to be
put into place as a means for the chatbot to assist
users in extreme distress.
REFERENCES
Artificial Intelligence Powered Chatbot for Mental
Healthcare based on Sentiment Analysis. 2022 5th
International Conference on Advances in Science and
Technology (ICAST).
Fadhil, A., & Moffatt, K. (2020). The potential of chatbots
for mental health support: A systematic review.
Journal of Medical Systems.
Fitzpatrick, K. K., Darcy, A., & Vierhile, M. (2017).
Delivering Cognitive Behavioural Therapy to Mood and
Anxiety Patients through a Smartphone App: A
Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Medical
Internet Research.
Laranjo, L., et al. (2018). Conversational agents in
healthcare: A systematic review. Journal of the
American Medical Association (JAMA).
Tielman, M., & de Vries, L. (2020). Chatbots for mental
health: How artificial intelligence can contribute to
psychological well-being. International Journal of
Human- Computer Interaction.
Lee, J. A., & Choi, J. (2020). Applications of conversational
AI for mental health: A literature review. Journal of
Artificial Intelligence in Medicine.
Miller, C. J., et al. (2020). Artificial Intelligence for mental
health care: A review of opportunities and challenges.
American Journal of Psychiatry.
Lau, A., & Wenzel, S. (2019). The role of chatbots in
improving mental health care delivery: A critical
review. International Journal of Psychiatry and Mental
Health.
Radzi, S., & Khamis, M. (2020). AI and mental health: The
impact of conversational agents on anxiety and
depression. Journal of Healthcare Engineering.
Gaffney, H., & Kuss, D. (2021). The role of AI chatbots in
mental health support: A scoping review. Journal of
Behavioural Health.
Ly, K. H., & Andersson, G. (2020). Chatbots and mental
health: A review of the literature. Psychology and
Psychotherapy: Theory, Research & Practice.
Weitzman, E. R., & Parikh, R. (2019). Digital tools for
mental health care: Chatbots, digital interventions, and
more. Digital Health.
Li, Y., & Wang, T. (2020). Exploring the potential of
chatbot-based interventions for mental health. Journal
of Clinical Psychology.
AI-Driven Chatbot for Mental Health Support Using Sentiment Analysis
297
