
AI‑Powered Fake Review Detection for College Admission Using
BERT and DeBERT
Savitha P., Christopher R., Dinesh M. and Jeevabharathi A.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Nandha Engineering College, Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Fake Review Detection, AI System, College Admissions, NLP, Machine Learning, BERT, DeBERTa, XLNet,
Sentiment Analysis, Review Classification, Web Plugin, Real‑Time Analysis, Supervised Learning,
Reputation Management, Decision‑Making Support.
Abstract: Online audits plays a crucial role in influencing college admission decisions. However, the presence of fake
reviews, whether excessively positive or misleading negative can distort perceptions and misleading
prospective students. This model proposes an AI-powered fake audit discovery framework outlined
particularly for college affirmation audits. The framework leverages Common Dialect Preparing (NLP)
procedures and directed learning models to distinguish beguiling substances. A web plugin is created to
analyze surveys in real-time, with the dataset collected from different college audit stages and preprocessed
utilizing methods like stop word expulsion, lemmatization, and estimation investigation. Progressed models
counting BERT, DeBERTa, and XLNet are prepared to classify surveys as either honest to goodness or fake,
with DeBERT a conveying the most noteworthy exactness. This framework progresses straight forwardness
within the college choice preparation, enabling students and guardians to form educated choices based on
bonafide surveys, whereas too helping educate in keeping up their notoriety by sifting out deceiving or false
surveys.
1 INTRODUCTION
The expanding dependence on online surveys plays a
significant part in forming students' choices with
respect to college affirmations. In any case, fake
reviews whether too positive or misleadingly
negative can make mutilated discernments and delude
candidates. Conventional strategies for recognizing
fake audits are regularly moderate, error-prone, and
not adaptable (Rayana, S., & Akoglu, L. 2015). With
the developing request for dependable surveys,
computerized arrangements for fake audit locations
are getting to be basic. Machine learning models,
especially those utilizing Normal Dialect Preparing
(NLP), are a capable apparatus for distinguishing fake
surveys by analyzing phonetic designs and opinion
(Asaad, W. H et al., 2023). In this venture, we utilize
NLP methods, such as BERT, DeBERTa, and XLNet,
to classify surveys from different college survey
stages (Liu, M., & Poesio, M. 2023). The extension is
executed as a full- stack web application utilizing
Streamlit, permitting real-time survey examination.
The proposed framework consolidates Reasonable AI
(XAI) to supply clients with straightforward and
interpretable approaches, making a difference
between understudies and guardians making educated
choices. By centering on exactness, interpretability,
and client involvement, this extends points to upgrade
the college determination handle, guaranteeing that
clients can distinguish true surveys and maintain a
strategic distance from deluding data (Wu et al.,
2020).
2 RELATED WORKS
Dummy audit, to this end, has been a crucial question
of scope, with a focus on normal ml and NLP
(Custom Dialect Preparing) strategies (Muhawesh, R
et al., 2021). Traditional models (for example,
Gullible Bayes, Back Vector Machines (SVM) and
Arbitrary Timberlands), have been related to fake
survey areas, with some achievements in
distinguishing misleading substances (Asaad, W. H et
al., 2023). Wang et al. (2020) researched about how
assumption investigation utilizing SVM and ML
models can help in classifying fake audits.
Nonetheless, such techniques often struggle with real
244
P., S., R., C., M., D. and A., J.
AI-Powered Fake Review Detection for College Admission Using BERT and DeBERT.
DOI: 10.5220/0013880800004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
244-248
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
time analysis and processing of large datasets
efficiently (Ren et al., 2016). These last few years
have witnessed a surge of transformer-based models
like BERT, DeBERTa, XLNet which have
significantly improved fake audit detection (Liu, M.,
& Poesio, M. 2023). These models make them
sensible for fetch up comprehension tasks, despite the
fact that they exceed desires in comprehending at the
scene and associations in the substance. Such ideas as
those of Kundu et al. (2021) it shows that these
models outshine traditional methods such as SVM
and logistic regression in identifying fake reviews
with greater accuracy (Wang, B., & Kuan, K. K. Y.
2022).
We advance execution through BERT
(Bidirectional Encoder Representations from
Transformers) and DeBERTa (Decoding-enhanced
BERT) by recognizing the subtleties of dialect and
sentence structures (Liu, M., & Poesio, M. 2023).
XLNet overcomes them by better managing context
in text. Transformer models have been particularly
fascinating to process for tasks that require deep
content comprehension, such as determining whether
audits are genuine or fraud (He, S., Hollenbeck, B.,
Proserpio, D., & Thies,A. 2022). This work expands
on these advances using BERT, DeBERTa, and
XLNet to classify college confirmations surveys, with
an application utilizing Streamlit to provide students
with real-time predictions to help them make
educated decisions (He, S., Hollenbeck, B.,
Proserpio, D., & Tosyali, A. 2022).
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Data Collection and Pre-Planning
For this consideration, we utilized datasets sourced
from trusted online review stages, tallying college
overview websites, understudy social occasions, and
social media dialogs (Li, H et al., 2015). The dataset
comprises printed overviews in conjunction with
metadata such as timestamps, commentator
information, and assessments. Each review segment
talks to a supposition around a college, containing
critical properties that offer help recognizing fake or
misdirecting reviews (Muhawesh et al., 2021).
Additionally, the dataset includes sentiment scores
and linguistic patterns that help in detecting biased or
spam reviews.
The metadata also captures reviewer engagement
levels, such as the number of reviews posted and
interaction history, which aids in credibility
assessment. Furthermore, natural language
processing
(NLP)
techniques
are
employed
to
analyze contextual cues and detect inconsistencies
within the reviews.
3.2 Data Preprocessing
To guarantee information quality and move forward
show execution, the taking after preprocessing steps
were connected:
• Handling Missing Data: Lost values within the
dataset were recognized and ascribed utilizing
procedures like supplanting lost values with the
mode or cruel (for numerical metadata) (Ren et
al., 2016).
• Text Cleaning: The content surveys
experienced preprocessing steps, counting:
• Changing over content to lowercase for
consistency (He, S., Hollenbeck, B., Proserpio,
D., & Thies,A. 2022).
• Evacuating extraordinary characters, stop words,
and intemperate accentuation (Wu et al., 2020).
• Tokenization and stemming/lemmatization to
normalize words (Liu, M., & Poesio, M. 2023).
• Feature Scaling: Numerical metadata
highlights (such as audit length, word check,
and time-based qualities) were normalized to
make strides show joining (Rayana, S., &
Akoglu, L. 2015).
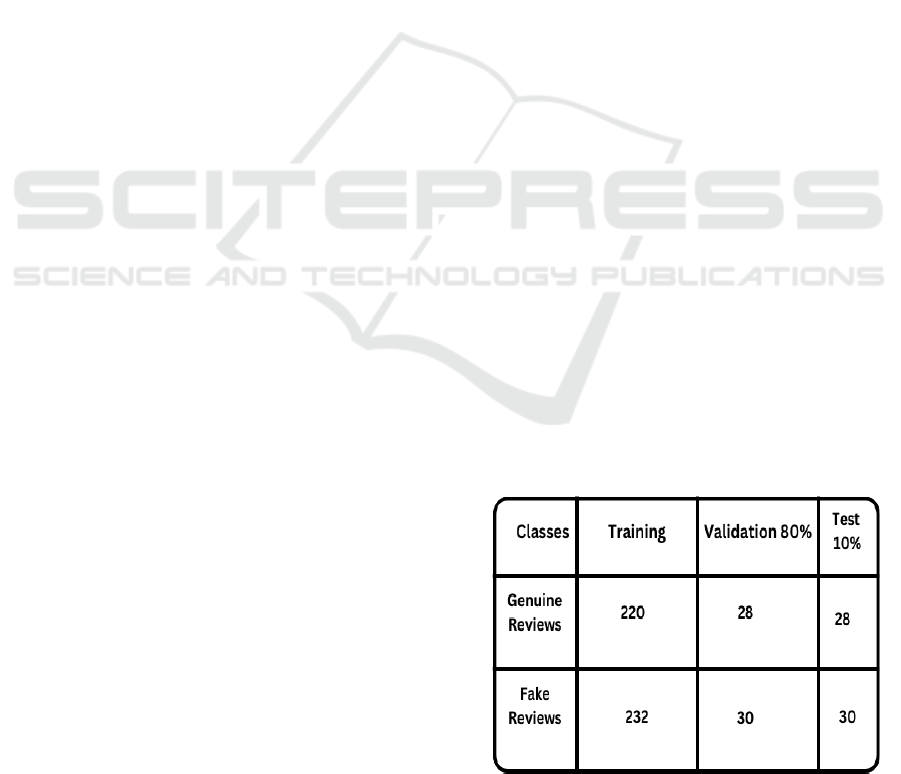
3.3 Data Split
The data file was separated within coordinating,
invigorate, and test groups within an 80-10-10 degree
to guarantee an adjusted representation (11. He,
S., Hollenbeck et al., 2022).
Figure 1 shows the
Dataset Split for Fake Review Detection.
Figure 1: Dataset Split for Fake Review Detection.
AI-Powered Fake Review Detection for College Admission Using BERT and DeBERT
245
3.4 Feature Extraction and Selection
Highlight extraction and assurance play an imperative
portion in recognizing fake and veritable reviews.
The key highlights were chosen based on space data
and quantifiable examination, emphasizing qualities
that earnestly relate with overview validity (Wang,
B., & Kuan, K. K. Y. 2022). Additionally, machine
learning algorithms are employed to classify reviews
by analyzing linguistic patterns and reviewer
behavior (Rayana, S., & Akoglu, L. 2015).
3.5 Feature Engineering
Linguistic Features: Conclusion score (limit and
subjectivity), (Li, H et al., 2015) Lucidness and
substance complexity (e.g., Flesch Scrutinizing Ease
score) Overview length and word repeat scattering.
Metadata-Based Features: Commentator validity
(account age, survey recurrence, etc.) (He, S.,
Hollenbeck et al., 2022) Review posting designs (e.g.,
sudden spikes in comparative reviews) Rating makes
irregularity (e.g., excessively positive/negative audits
with negating content).
3.6 Machine Learning Algorithms
A rule-based approach was to begin with to set up and
arrange criteria for recognizing fake reviews in
college declarations (Muhawesh et al., 2021). This
included recognizing common phonetic plans,
estimation peculiarities, and emphasized expressions
that are as regularly as conceivable found in boggling
reviews (Asaad et al., 2023) Following this, we
orchestrated progressed transformer-based models to
create a solid classification system (Li, H et al., 2015).
We endeavored with models tallying BERT
(Bidirectional Encoder Representations from
Transformers) and DeBERTa (Decoding-enhanced
BERT with Unraveled Thought) (Wu et al., 2020).
These models were chosen for their ampleness in
analyzing printed data, capturing apropos affiliations,
and understanding essential tongue collections that
restricted legitimate to goodness to goodness and fake
overviews (Rayana, S., & Akoglu, L. 2015).
3.7 Model Evaluation
The prepared models were then evaluated on the test
set to quantify the effectiveness of the application to
wiederlect against fake surveys in college admissions
(He, S., Hollenbeck et al., 2022). Assessment and
other measurements including precision, F1 score,
exactness, review, and Region Beneath the Bend
(AUC) can be used to evaluate the model’s prescient
execution and unwavering quality (Liu, M., &
Poesio, M. 2023). DeBERTa showed the finest
performance among various approaches through
contrast stop and was chosen as the best fine-tuned
model (Wang et al., 2022). We chose the
demonstration with the most commendable
evaluation scores to incorporate into the framework
last, giving dependable identification of deluding
audits at the same time bringing down the wrong
positive and false negative rate (He, S., Hollenbeck et
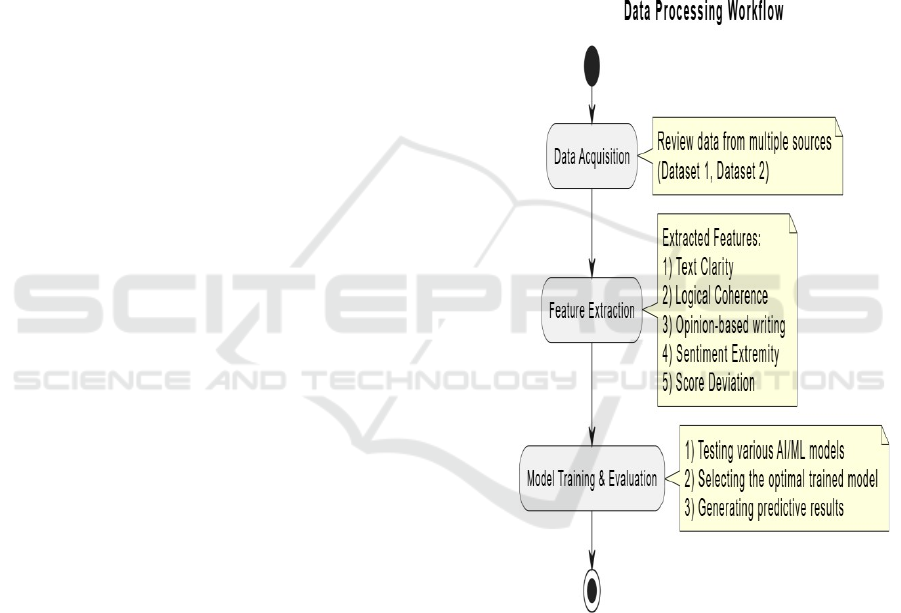
al., 2022) Figure 2 shows the Data Processing
Workflow.
Figure 2: Data Processing Workflow.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS OF
AI: POWERED FAKE REVIEW
DETECTION FOR COLLEGE
ADMISSION USING BERT,
DEBERT ALGORITHMS
Evaluation metrics used show that the BERT and
DeBERTa models are able to label and classify fake
audits successfully in the context of college
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
246
admissions (Wu et al., 2020). Some of these models
use NLP (Normal Dialect Preparing) approaches to
analyze audit genuineness which shows high
precision and robustness (He, S., Hollenbeck et al.,
2022). The evaluation of the tests points out that the
models achieved high accuracy and recall scores Liu,
M., & Poesio, M. 2023), ensuring low false positive
and frame classified (Muhawesh et al., 2021).
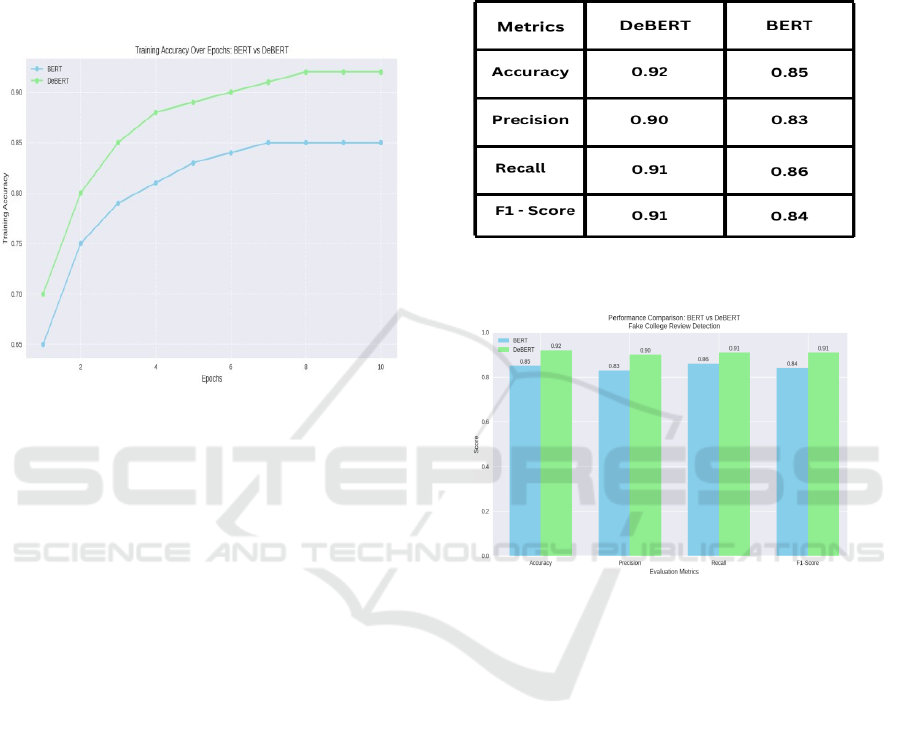
Figure 3: Training Accuracy Curve.
The exploratory aims to post some light on the
performance comparison between BERT and
DeBERTa models in the detection of fake college
reviews. The models were evaluated using essential
execution estimates, numbering exactness, accuracy,
review, and F1-score. Figure 1 lists the setups on
which DeBERTa outperforms BERT on all metrics
(Rayana, S., & Akoglu, L. 2015), (Ren, Y., Ji, D., &
Ren, Y. 2016).
Figure 3 shows the Training Accuracy
Curve.
Accuracy: DeBERTa accomplished a precision of
0.92, outperforming BERT's 0.85, demonstrating
made strides by and large classification execution.
Precision: DeBERTa got an exactness score of 0.90,
compared to BERT's 0.83, illustrating its capacity to
decrease wrong positives viably.
Recall: DeBERTa beat BERT with an accuracy of
0.91 vs. 0.86, which demonstrated that DeBERTa
was better than BERT at capturing fake audits.
F1-Score: The DeBERTa062 achieves an F1-score
of 0.91 against BERT 0.84, ensuring a balanced
precise and recall trade-off.
This is done according to confirm that DeBERTa
could be a more successful portrayal for phony audit
area, giving improved exactness and better
generalization. Its predominant review and F1-
score make it more dependable for recognizing false
audits whereas keeping up exactness (Rayana, S., &
Akoglu, L. 2015).
Figure 4 shows the Performance
Comparison: DeBERT and BERT Algorithms. Figure
5 shows the Performance Comparison BERT vs
DeBERT Fake College Review Detection.
Figure 4: Performance Comparison: Debert and Bert
Algorithms.
Figure 5: Performance Comparison BERT vs DeBERT
Fake College Review Detection.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The AI-powered Fake Survey Location framework
for college confirmations gives an imaginative
arrangement to the developing concern of false audits
within the instructive segment. By utilizing cutting-
edge advances such as Common Dialect Preparing
(NLP) and Machine Learning (ML), the framework is
competent at precisely analyzing and classifying
surveys in real-time, guaranteeing the keenness of
online audits. Built as a web application utilizing
Streamlit, the framework presents a user- friendly
interface, making it simple for both specialized and
non-technical clients to get to and navigate.The center
usefulness of the framework incorporates
recognizing fake surveys
based on different
etymological designs, irregularities, and suspicious
behaviors found within the content. Because it works
AI-Powered Fake Review Detection for College Admission Using BERT and DeBERT
247

in real-time, it can swiftly hail audits that are likely to
be false, empowering teach to provoke activity. This
arrangement can be easily integrated into college
affirmation stages, progressing the
straightforwardness of the audit preparation and
empowering understudies to form more educated
choices based on true input.
6 FUTURE WORK
Within the future, the framework will be extended to
cover an assortment of segments, counting e-
commerce, neighborliness, and healthcare, permitting
it to distinguish fake surveys past college
confirmations. This will help in progress and
straightforwardness over different stages where client
input plays a basic role. To enhance the system's
precision, we'll center on refining the machine
learning calculations and investigating progressed
NLP procedures. This will empower the framework
to better recognize unobtrusive false designs and
adjust to advancing strategies utilized by fake
reviewers. Additionally, the framework will be
upgraded to analyze numerous dialects for fake
audits, broadening its worldwide appropriateness. We
too arrange to coordinate a confirmed audit database
and present real-time location, permitting the
framework to hail fake audits instantly upon
accommodation, guaranteeing the judgment of survey
stages.
REFERENCES
Alshehri, A. H. (2023). "An Online Fake Review Detection
Approach Using Famous Machine Learning
Algorithms." Computers, Materials & Continua, 78(2),
2767-2786.
Asaad, W. H., Allami, R., & Ali, Y. H. (2023)."Fake
Review Detection Using Machine Learning. "Revued'
Intelligence Artificielle, 37(5), 1159-1166.
He, S., Hollenbeck, B., Proserpio, D., & Thies,A. (2022).
"Detecting Fake-Review Buyers Using Network
Structure." Proceedings of the National AcademyofSci
ences,119(47), e2211932119. (CVPR), 2017, pp. 7263–
7271.
He, S., Hollenbeck, B., Proserpio, D., & Tosyali, A. (2022).
"Detecting Fake-Review Buyers Using Network
Structure." Proceedings of the National Academy of
Sciences, 119(47), e2211932119. DOI:
10.1073/pnas.2211932119.
Li, H., Chen, Z., Mukherjee, A., Liu, B., & Shao, J. (2015).
"Analyzing and Detecting Opinion Spam on a Large-
Scale Dataset via Temporal and Spatial Patterns."
Proceedings of the Ninth International AAAI
Conference on Web and Social Media, pp. 634–637.
Liu, M., & Poesio, M. (2023). "Data Augmentation for Fake
Reviews Detection." Proceedings of Recent Advances
in Natural Language Processing, pp. 673–680.
DOI:10.26615/978-954-452-092-2_073.
Muhawesh, R., Xu, S., Tran, S. N., & Maqsood, S. (2021).
"Fake Reviews Detection: ASurvey." arXiv preprint
arXiv:2104. 08521.Engineering Access, 8(2), 192-197.
Rayana, S., & Akoglu, L. (2015). "Collective Opinion
Spam Detection: Bridging Review Networks and
Metadata." Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD
International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and
Data Mining, pp. 985– 994. DOI: 10.1145/2783258.27
83370
Ren, Y., Ji, D., & Ren, Y. (2016). "Detecting Online
Review Spam: A Linguistic Feature Engineering
Approach." Applied Intelligence, 45(3), 868–882. DOI:
10.1007/s10489-016-0794-5
Wang, B., & Kuan, K. K. Y. (2022)."Understanding the
Message and Formulation of Fake Online Reviews: A
Language-production Model Perspective. "Frontiers in
Artificial Intelligence.:2207.02696, 2022.
Wani, M. A., ElAffendi, M., & Shakil, K. A. (2024). "AI-
Generated Spam Review Detection Framework with
Deep Learning Algorithms and Natural Language
Processing. "Computers, 13(10), 264.vol.7, p.1419,
Oct.2016.DOI:10.3389/fpls.2016.01419.
Wu, Y., Ngai, E. W., Wu, P., & Wu, C. (2020)."Fake Online
Reviews: Literature Review, Synthesis, and Directions
for Future Research." Knowledge and Information
Systems, 62(6), 2133–2170.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
248
