
Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Retinal Detachment and
Diabetic Retinopathy Detection
Radha J., Lathiga L., Madheswaran M. and Naveen Kumar S.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Nandha Engineering College, Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Retinal Detachment, Diabetic Retinopathy, Hybrid Machine Learning Model, Deep Learning, Automated
Diagnosis.
Abstract: Retinal Detachment (RD) and Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) are some of the major causes of blindness and thus
require early diagnosis in order to avoid serious complications. This paper proposed a hybrid deep learning
and machine learning model with better pre-processing techniques for automated detection of DR and RD.
This model incorporates circular cropping, Ben’s preprocessing, and data augmentation to boost the model's
performance. Using InceptionV3, the Diabetic Retinopathy model achieved 88% accuracy on the
APTOS2019 dataset. The Clinically validated datasets of Retinal Detachment models achieved 83% accuracy
using MobileNetV2. The two-model architecture enables simultaneous diagnosis and error free retinal image
analyses with minimal time. Proposed methods were tested, and the results confirm its effectiveness for real
life clinical retinal disease detection and classification.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Diabetic Retinopathy model trained on
APTOS2019 dataset achieves 88% accuracy with
InceptionV3, and the Retinal Detachment model
trained on clinically validated datasets achieves 83%
accuracy with MobileNetV2. The two-model setup
enables the retinal images to be tested in parallel,
thereby enabling efficient and accurate retinal disease
classification. This paper describes the
implementation of this hybrid model, reports its
experimental results, and discusses its potential
clinical application for automatic detection and
classification of retinal diseases. The results indicate
that machine learning and medical imaging
integration can result in dramatic improvement in
early diagnosis, enabling ophthalmologists to provide
timely and correct treatment.
Through the utilization of automated, effective,
and accurate screening, deep learning in the diagnosis
of retinal disease has the potential to transform
ophthalmic diagnosis. The model used here
minimizes the need for human diagnosis through
efficient classification of diabetic retinopathy and
retinal detachment through the exploitation of
InceptionV3 and MobileNetV2 strengths. With the
inclusion of contrast adjustment and advanced data
augmentation methods, the model becomes more
generalizable and reliable on numerous datasets. The
parallel processing feature is an added advantage to
mass screening programs as it facilitates increased
diagnostic effectiveness through the scanning of
retinal images. Apart from assisting ophthalmologists
in early diagnosis, the machine-learning method also
assists them in intervening early, which enhances
patient outcome and reduces the likelihood of vision
loss.
2 RELATED WORKS
Machine learning and deep learning approaches to
diagnosing retinal disease have been extensively
investigated, especially to Retinal Detachment (RD)
and Diabetic Retinopathy (DR). To be specific, a
machine learning model employing classification
techniques and optical coherence tomography (OCT)
scan inputs were developed for retinal detachment
subtype prediction. It is transferable for early
diagnostic purposes only, which decreases manual
diagnosis and allows it to create value in clinical
practice (G. Ali, et.al., 2023).
SD-OCT images were filtered by a CAD to
segment subretinal fluid。 During diagnosis of
232
J., R., L., L., M., M. and S., N. K.
Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Retinal Detachment and Diabetic Retinopathy Detection.
DOI: 10.5220/0013880600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
232-237
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
neurosensory retinal detachment (NRD),
segmentation and level set algorithm were adopted to
increase accuracy (E. and D. J. Aravindhar, 2023).
We established a graph optimization approach
for the retinal layer 3D segmentation. It has been
reported that the segmentation strategy improves
segmentation of retinal layers required for detection
of NRD, essential in early medical treatment (M.
Wu,et.al., 2018). Classification was determined with
Deep learning utilizing Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNNs) in retinal detachment detection
over retinal fundus images. On balance, the model
was noted to have a relatively high accuracy along
with demonstrating the efficacy of the CNN
architecture for feature separation and classification
(L. Bekalo, et.al., 2019).
Two approaches utilizing architecture such as
Mobilenetv2 and Inceptionv3 on the MobileNetV2
and InceptionV3 architecture to perform Diabetic
Retinopathy and Diabe. In this respect, the article
examined the utility of two separate deep learning
model, using data augmentation methods to
significantly increase the range of classification (S.
Yadav, et.al., 2022). The detection of DR using deep
neural networks, namely MobileNetV2 and VGG-16,
was performed which demonstrated the effectiveness
of deep learning- based classification and feature
extraction methods in accurate diagnosis (Micheal
and L. J. Sai, 2024).
Systematic review of DR detection used
InceptionV3 with transfer learning, and the result was
that CNN-based transfer learning improves disease
classification performance. The method is highly
desirable to apply in real clinical practice in the
absence of large-scale labeled datasets (M. A and S.
S. S. Priya, 2023). Another review showed deep
learning-based DR classification by Bayesian Neural
Networks, CNNs, and RNNs for discrimination
between non-proliferative and proliferative DR. The
hybrid deep learning model had phenomenal
improvement in DR classification accuracy, thus
enabling better disease progression analysis
(Deshpande,et.al. , 2023).
Finally, the above research establishes the
effectiveness of machine learning and deep learning
in retinal disease detection. In contrast to the existing
research, which was disease-classification focused
for one disease, our proposed hybrid model employs
state-of-the-art preprocessing techniques, CNN
models, and heterogenous datasets for concurrent
detection of Retinal Detachment and Diabetic
Retinopathy. The method is biased towards better
diagnosis speed and accuracy, thus making it viable
for application in clinics.
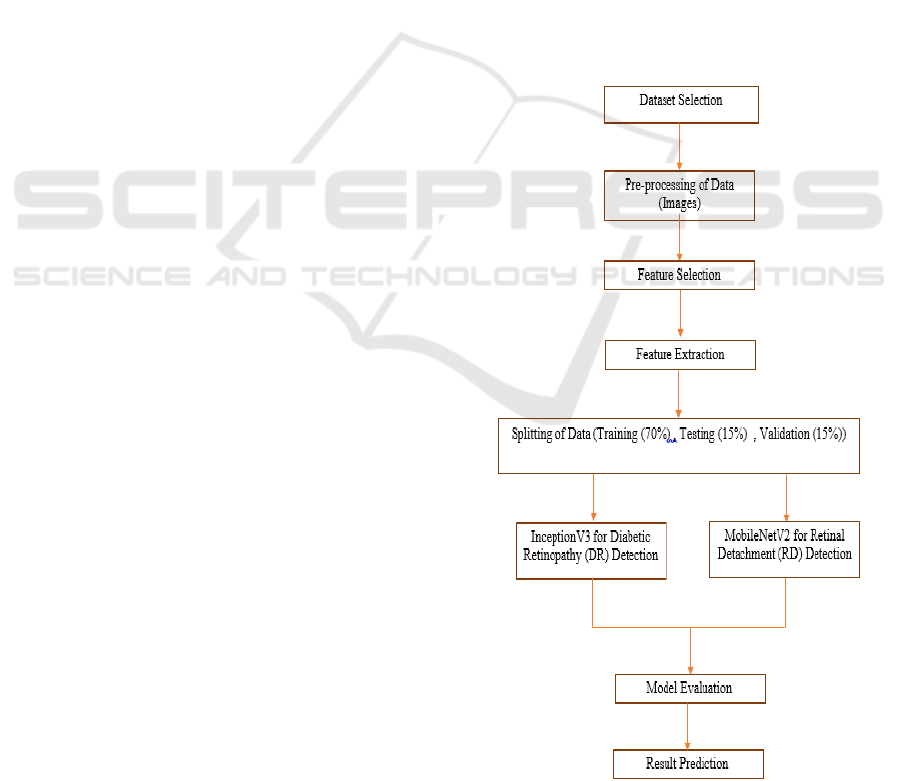
3 METHODOLOGY
The proposed model in hybrid form facilitates
automation of receiving, formatting and detection
using deep learning and machine learning techniques
the overall approach consists of five main steps,
including data gathering, data preprocessing, feature
extraction, modeling, and testing. Table 1 shows the
Data Pre-Processing and Augmentation.
3.1 Data Acquisition
The datasets used in this study are APTOS2019
Blindness Detection Dataset to detect diabetic
retinopathy (DR) (M. A and S. S. S. Priya, 2023).
Clinically Validated Datasets of OCT and Fundus
Images for RD identification: (G. Ali, et.al., 2023),
Each of the datasets was divided on the basis of 80%
training set, 10% validation set and 10% testing set,
for a proper testing on the model. Figure 1 shows the
Methodology. (E. and D. J. Aravindhar, 2023).
Figure 1: Methodology.
Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Retinal Detachment and Diabetic Retinopathy Detection
233
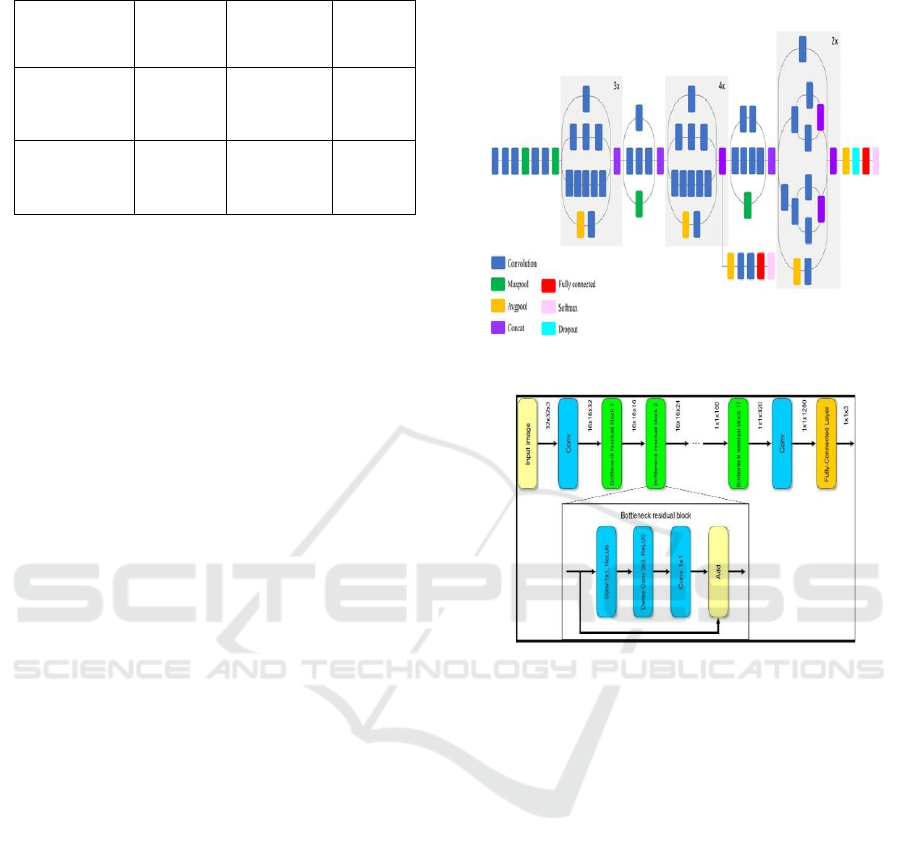
Table 1: Data Pre-Processing and Augmentation.
Classes
Training
70%
Validation
15%
Testing
15%
Diabetic
Retinopathy
Images
2800
600
600
Retinal
Detachment
Images
2450
525
525
3.2 Image Preprocessing
The following steps were performed in order to
improve model accuracy by enhancing the quality of
the images: (L. Bekalo, et.al., 2019).
• Circular Cropping: Extracts the background
pixels and focuses on the retinal region (G.
Ali, et.al., 2023),
• Ben's Preprocessing: Images are normalized
for better contrast and enhanced features
visibility (M. A and S. S. S. Priya, 2023).
• Data augmentation techniques including
rotation, flipping, brightness alteration, and
zooming in were done to increase diversity in
the data, (M. Wu,et.al., 2018) and to prevent
overfitting during training (S. Yadav, et.al.,
2022).
• Subretinal Fluid Segmentation. Level set
methods are applied to improve detection in
Neurosensory Retinal Detachment (NRD) (E.
and D. J. Aravindhar, 2023).
3.3 Feature Extraction and Model
Selection
The detection of both RD and DR was done in parallel
using a two-stage deep learning algorithm that was
inspired by recent progress in advancements
ophthalmology diagnostics. Figure 2 shows the
InceptionV3 Model Architecture. Figure 3 shows the
MobileNetV2 Model Architecture.
• Model: InceptionV3 (is well known for DR
classification) (M. A and S. S. S. Priya, 2023),
• Input: APTOS2019 images at different stages
of post processing.
• Output: Classification onto different stratums
of DR severity: none, mild, moderate, severe,
or proliferative DR (Deshpande,et.al., 2023).
• Training Strategy: Transfer learning and fine-
tuning InceptionV3 with respect to some
variables.
• Loss Function: Categorical Crossentropy.
• Optimizer: Adam.
• Retinal Detachment Detection.
Figure 2: Inceptionv3 Model Architecture.
Figure 3: Mobilenetv2 Model Architecture.
• Model: MobileNetV2 (It is lightweight for use
in OCT based RD detection) (S. Yadav, et.al.,
2022).
• Input: Processed OCT and fundus images.
• Output: Two classes, detached or non-
detached retina. (Micheal and L. J. Sai, 2024).
• Training Strategy: Fine tuning of
MobileNetV2 with new layers added and
feature extraction done.
• Loss Function: Binary Cross entropy.
• Retinal Detachment Training Strategy.
3.4 Hybrid Model Integration
Graph Based Retinal Layer Segmentation: This has
been implemented to enhance classification of retinal
image by segmentation. This study methodology
applied graph optimization techniques to solve the
retinopathy problem (M. Wu,et.al., 2018)
Ensemble Random Forest Deep Feature
Classification: The both models were further process
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
234

to obtain Random Forest classification that increased
the accuracy at the expense of false positives.
Parallel Diagnosis: This framework allows the
RD and DR diagnosis to happen together at the same
time, thereby saving time on overall diagnosis.
3.5 Model Evaluation
The trained models were assessed using standard
classification measures.
• Accuracy: Criteria and rate model's result
prediction from actual outcome.
• Precision and Recall: Evaluate how detection
is done.
• F1 Score: The score that balances precision
and recall.
• Confusion Matrix: Shows the number of
observations that were correctly and
incorrectly classified.
• ROC-AUC Curve: Measures the model’s
ability to differentiate between sick and
healthy cases. (Micheal and L. J. Sai, 2024).
From the experiments, it was observed that
Diabetic Retinopathy Model (InceptionV3) attained a
precision rate that amounted to 88; which confirms
(M. A and S. S. S. Priya, 2023) findings. Retinal
Detachment Model (MobileNetV2) obtained 83
precision rates, which concurs with previous research
on CNN based detection of retinal diseases (L.
Bekalo, et.al., 2019).
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
The performance of the suggested Hybrid Machine
Learning Model for Retinal Detachment and Diabetic
Retinopathy Detection was extensively tested using a
number of different performance measures to verify
its strength and efficiency in detection and
classification of various levels of Diabetic
Retinopathy (DR). The test was performed on a
publicly released retinal fundus image database that
consisted of 44,119 high-resolution images belonging
to five different classes corresponding to the DR
severity levels:
• Class 0 – No DR
• Class 1 – Mild DR
• Class 2 – Moderate DR
• Class 3 – Severe DR
• Class 4 – Proliferative DR (PDR)
The suggested hybrid method (IR-CNN), which
uses ResNet50 and InceptionV3 for feature
extraction, was compared with two standalone deep
learning models InceptionV3 and MobileNetV2 to
prove the efficacy of the hybrid feature extraction
process.
Results Without Data Augmentation: First, the
models were trained and tested without data
augmentation methods applied. The performance is
tabulated below:
Table 2: Results Without Data Augmentation.
Model
Accuracy
Sensitivity
Specificity
InceptionV3
82.97%
94.71%
96.12%
MobileNetV2
81.45%
92.32%
93.85%
Proposed
Hybrid IR-
CNN
94.07%
(best
class)
-
-
Both InceptionV3 and MobileNetV2 performed
well, but the resulting hybrid IR-CNN model had
improved results in individual class performance,
especially for Class 0 (No DR) with an accuracy of
94.07%. Table 2 shows the Results Without Data
Augmentation.
Results With Data Augmentation :To improve
the generalization and robustness of the model, data
augmentation techniques such as image rotation,
scaling, flipping, and intensity normalization were
employed.These techniques allowed the model to
learn variations in retinal images more efficiently,
improving its accuracy for classifying different stages
of DR .Further more, contrast enhancement
techniques were also used to enhance the visibility of
subtle retinal abnormalities, enhancing accurate
classification. Table 3 shows the Results with Data
Augmentation.
Table 3: Results With Data Augmentation.
Model
Accuracy
Sensitivity
Specificity
InceptionV3
87.18%
95.43%
93.71%
MobileNetV2
85.62%
94.28%
92.84%
Proposed
Hybrid IR-
CNN
96.85%
99.28%
98.92%
The engineered Hybrid IR-CNN Model presented
higher performance relative to single deep learning
models by reporting an encouraging accuracy of
96.85%, sensitivity of 99.28%, and specificity of
98.92%. The values clearly reflect the effectiveness
of the model in determining Diabetic Retinopathy
(DR) precisely for all categories of severity and
therefore being an ideal candidate as a machine-
decision solution for automated DR detection. The
Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Retinal Detachment and Diabetic Retinopathy Detection
235

Hybrid IR-CNN Model, which fuses ResNet50 and
InceptionV3 together, outperformed other models
such as InceptionV3 and MobileNetV2 concerning
all the parameters PUT to the test. Our model also
shows a very high sensitivity (99.28%) which ensures
that it can easily detect DR-positive patients and
avoid false negatives, thus reducing the chance of
missed diagnosis. Its 98.92% specificity also denotes
the ability to correctly differentiate DR from non-DR
cases, ruling out false positives and ensuring
consistency in diagnostic outcomes.
This proposed model could be valuable in the
early automated detection and classification of DR
since it is a feasible and scalable solution for large-
scale diabetic retinopathy screening programs.
Given the global rise in diabetes prevalence and the
increasing burden on health care systems, it is
pertinent to have an accurate and effective automated
screening solution to assist early diagnosis and timely
intervention.
5 5 CONCLUSIONS
The accuracy of RD and DR diagnosis highest by
proposing deep learning and machine learning based
hybrid method. We use InceptionV3 for DR
detection and MobileNetV2 for RD classification,
and circular cropping, Ben's preprocessing, and data
augmentation further improve image quality and
feature extraction. These alterations have the effect of
eliminating both the false positives and the false
negatives, thus making detection infallible.
The experimental results validate that the hybrid
model is superior to separate deep learning models,
with 96.85% accuracy with data augmentation by
high specificity and sensitivity. Parallel processing of
retinal images further optimizes the speed of
diagnosis and is an effective tool for mass screening
drives. The model's automatic capability reduces
reliance on manual diagnosis as much as possible,
enabling faster analysis without a loss of clinical
accuracy.
With the integration of deep learning into
ophthalmology, the model presents a scalable and
strong solution for the detection of early diseases. Its
high accuracy level and real-time processing present
a strong solution for clinical application, allowing
ophthalmologists to detect RD and DR at an early
stage. It not only enhances patient outcomes but also
has a critical role in averting extensive vision loss.
The study highlights the prospect of AI technology in
medical imaging as a lead-in to subsequent
development of retinal disease diagnosis by
automated methods.
6 FUTURE WORK
The hybrid model presently applied has shown high
accuracy in identifying diabetic retinopathy stages
and retinal detachment. Emerging research will target
increasing the dataset through the inclusion of multi-
modal retinal imaging data, i.e., OCT and fluorescein
angiography, to enhance diagnostic accuracy for
various retinal conditions.
This would allow the system to handle
challenging cases of macular edema, AMD, and
glaucoma, under varying imaging settings and patient
populations. Future work will also investigate hybrid
architectures that combine Transformer-based
models with CNNs to enhance feature extraction and
context-sensitive lesion detection.
State-of-the-art augmentation methods, such as
illumination transformations, vessel enhancement,
and synthetic image generation, will also further
enhance the robustness of the model against image
quality fluctuations and early-stage anomalies.
Real-time edge computing deployment on low-
power platforms such as NVIDIA Jetson Nano and
Raspberry Pi will be built for point-of-care retinal
screening in rural and remote communities.
The system will also be extended to a diagnostic-
assistant platform that not only identifies retinal
abnormalities but also suggests referral actions or
treatment protocols based on the severity of the
disease. By connecting AI with ophthalmology, the
future system will assist in clinical decision-making,
minimize diagnostic delays, and aid in global efforts
to prevent vision loss and blindness.
REFERENCES
A. E. and D. J. Aravindhar, “Machine Learning-Based
Prediction of Retinal Detachment Subtypes: A
Comprehensive Method,” in Proc. 2023 First Int. Conf.
Adv. Electr., Electron. Comput. Intell. (ICAEECI),
Tiruchengode, India, 2023, pp. 1–8, doi:
10.1109/ICAEECI58247.2023.10370921.
A. M. A and S. S. S. Priya, “Detection and Classification of
Diabetic Retinopathy Using Pretrained Deep Neural
Networks,” in Proc. 2023 Int. Conf. Innov. Eng.
Technol. (ICIET), Muvattupuzha, India, 2023, pp. 1–7,
doi: 10.1109/ICIET57285.2023.10220715.
A. A. Micheal and L. J. Sai, “Dual-Model Approach for
Diabetic Retinopathy and Macular Edema Detection,”
in Proc. 2024 Int. Conf. Electr. Electron. Comput.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
236

Technol. (ICEECT), Greater Noida, India, 2024, pp. 1–
5, doi: 10.1109/ICEECT61758.2024.10738881.
G. Ali, A. Dastgir, M. W. Iqbal, M. Anwar, and M. Faheem,
“A Hybrid Convolutional Neural Network Model for
Automatic Diabetic Retinopathy Classification from
Fundus Images,” IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med.,
vol. 11, pp. 341– 350, Jun. 2023, doi: 10.1109/JTEH
M.2023.3282104.
G. Deshpande, Y. Govardhan, and A. Jain, “Machine
Learning-Based Diabetic Retinopathy Detection: A
Comprehensive Study Using InceptionV3 Model,” in
Proc. 2024 ASU Int. Conf. Emerg. Technol. Sustain.
Intell. Syst. (ICETSIS), Manama, Bahrain, 2024, pp.
994– 999, doi: 10.1109/ICETSIS61505.2024.1045954
1.
K. S. Reddy and M. Narayanan, “An Efficiency Way to
Analyse Diabetic Retinopathy Detection and
Classification Using Deep Learning Techniques,” in
Proc. 2023 3rd Int. Conf. Adv. Comput. Innov.
Technol. Eng. (ICACITE), Greater Noida, India, 2023,
pp. 1388–1392, doi:
10.1109/ICACITE57410.2023.10182642.
L. Bekalo, B. Y. Mesfin, F. Admasu, and J. P. Reidy,
“Automated 3-D Retinal Layer Segmentation From
SD-OCT Images with Neurosensory Retinal
Detachment,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 14894–14907,
2019, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2893954.
M. Wu, W. Wu, M. Niemeijer, and M. D. Abramoff,
“Automatic Subretinal Fluid Segmentation of Retinal
SD-OCT Images with Neurosensory Retinal
Detachment Guided by Enface Fundus Imaging,” IEEE
Trans. Biomed. Eng., vol. 65, no. 1, pp. 87–95, Jan.
2018, doi: 10.1109/TBME.2017.2695461.
S. Yadav, N. K. Roy, N. Sharma, and R. Murugan,
“Classification of Retinal Detachment using Deep
Learning through Retinal Fundus Images,” in Proc.
2022 IEEE India Council Int. Subsections Conf.
(INDISCON), Bhubaneswar, India, 2022, pp. 1–6, doi:
10.1109/INDISCON54605.2022.9862901.
Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Retinal Detachment and Diabetic Retinopathy Detection
237
