
XAI‑Powered Hybrid Model for Real‑Time Financial Fraud
Detection
P. Devika, G. Mathu Kumar, P. Nagul Kumar and S. Naveen Prabhu
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Nandha Engineering College, Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Fraud Detection, Explainable AI, Hybrid Model, SHAP, XGBoost, Random Forest, Financial Security,
Real‑Time Detection.
Abstract: With the rising complexity of false exercises, the discovery of extortion in money related trades has gotten to
be a major challenge. Conventional machine learning models frequently act as dark boxes, making it greatly
troublesome to clarify the choices they make. To address this, this extension proposes a cross breed extortion
location that combines Irregular Timberland and XGBoost models with XAI procedures such as SHAP to
encourage the creation of logical AI touchy to the thinking behind extortion expectations. The framework is
prepared on a Kaggle dataset of budgetary exchanges, with a Java backend and HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
frontend. The cross-breed show utilizes weighted averaging to coordinate both calculations, making extortion
location strong and dependable. In terms of the XAI viewpoint, the system gives human-readable
clarifications, such as highlighting bizarre exchange sums, login irregularities, and suspicious geographic
designs. This system addresses a few real-time challenges related to extortion location, explainability, and ill-
disposed strength, eventually displaying a clean and palatable arrangement for the budgetary division to
improve their extortion avoidance procedures. The proposed system guarantees that any yields given are in
full compliance with straightforwardness, operational guidelines, and administrative rules, reestablishing
certainty in AI's capacity to identify budgetary wrongdoings.
1 INTRODUCTION
As digital transactions have become more prevalent
financial fraud has also tightened and increased the
scope of its risk factors to both businesses and
consumers conventional systems to detect fraud that
exist mostly use rule-based methods or machine
learning models that are good but operate as black
boxes allowing little insight into why a transaction is
considered fraudulent the inability to see into the
systems means it is usually hard for the banks to
justify their choices and comply with regulations or
improve on fraud detection models to address this gap
we propose a hybrid fraud detection system that
combines the best predictive power of random forest
and xgboost with explainable ai xai techniques such
as shap shapley additive explanations while this
allows for more accurate fraud detection each
prediction will come with an explanation that
improves trust and interpretability the system is
developed on an actual kaggle dataset that features
financial transactions making it real-world applicable
the backend is developed with flask while the
frontend features user-friendly tools for fraud
analysis built with html css and javascript the hybrid
model integrates both algorithms through weighted
averaging to maximize detection efficiency shap-
based explanations provide analysts with insights into
key fraud indicators such as atypical transaction
amounts login anomalies or suspicious geographic
patterns this paper elaborates on how we implement
our hybrid fraud detection system its performance in
comparison to traditional models and the rationale of
the incorporation of explainability in fraud detection
our method underpins the very foundations of
transparency disallowing the slithering in of mistrust
and extensive legislation but enhancing trust in ai-
based decision-making bestowing much value on
financial security.
2 RELATED WORKS
S. R. Banu, et al., 2024; E. Ileberi and Y. Sun., 2024;
X. Zhao., et al., 2024 Blackmail disclosure in
budgetary trades has been broadly inspected, with
214
Devika, P., Kumar, G. M., Kumar, P. N. and Prabhu, S. N.
XAI-Powered Hybrid Model for Real-Time Financial Fraud Detection.
DOI: 10.5220/0013880300004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
214-218
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
diverse approaches leveraging machine learning,
significant learning, and graph-based procedures.
Agomuo, et al., 2025, Afterward, consider chart
neural frameworks (GNNs) for blackmail revelation,
leveraging the interconnected nature of budgetary
trades to recognize suspicious plans and irregularities.
T. Awosika, et al., 2024.; R. Kapale, et al., 2024;
R.
Gangavarapu, et al., 2024; While compelling, these
approaches go up against challenges in real-time
dealing with and explainability. D. Jahnavi., et al.,
2024; Al-Maari and M. Abdulnabi, et al., 2023;
A.Behura and M. Srinivas., 2022. Hybrid machine
learning models, such as gathering methodologies
utilizing self-assertive timberland, incline boosting,
and stacking, have moved forward exactness but as
often as possible require straightforwardness. Ill-
disposed ambushes pose another challenge, as
fraudsters control trade plans to dodge disclosure,
driving to the headway of ill-disposed planning and
energetic significant learning models that come at tall
computational costs. Sensible AI (XAI) methods like
SHAP and LIME have been displayed to supply
interpretability in blackmail revelation models,
advancing acceptance and regulatory compliance C.
Kotrachai, et al., 2023 be that as it may their
integration with high-performance blackmail area
models remains complex. Besides, real-time
blackmail area systems require millisecond-level
response times, actuating ask almost into memory-
efficient models, chart compression methodologies,
and dispersed computing courses of action X. Zhao,
et al., 2024 in show disdain toward the reality that
altering speed with interpretability remains a
challenge. Our proposed system builds on these
existing approaches by coordinating a half breed
machine learning utilizing arbitrary woodland and
XGBoost, alongside SHAP-based explainability,
ensuring both tall area exactness and direct decision-
making for financial blackmail expectation.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Data Collection and Preprocessing
The dataset used for this study was taken from the
Kaggle platform and contained financial transactions,
labeled for five types of fraud. In preprocessing,
missing values were imputed, numeric features were
scaled, categorical features were encoded, and
outliers were detected and dealt with. Further basic
feature engineering was applied to uncover useful
patterns in transactions, including users' spending
behaviors, transaction frequencies, and transaction
location anomalies.
3.2 Hybrid Model Development
We implemented a mix of Random Forest (RF) and
XGBoost (XGB) models to detect fraud. Each model
is trained independently, and then their respective
predictions are integrated through weighted
averaging to achieve greater detection accuracy and
performance.
3.2.1 Random Forest
Random forest is an ensemble learning approach
whenever various kinds of classifiers are used, which
in this case are decision trees that enable better
prediction accuracy.
3.2.2 XGBoost (XGB)
XGBoost is an efficient gradient boosting algorithm
that extends the predictive capabilities of weak
learners by optimization.
3.2.3 Hybrid Model Approach
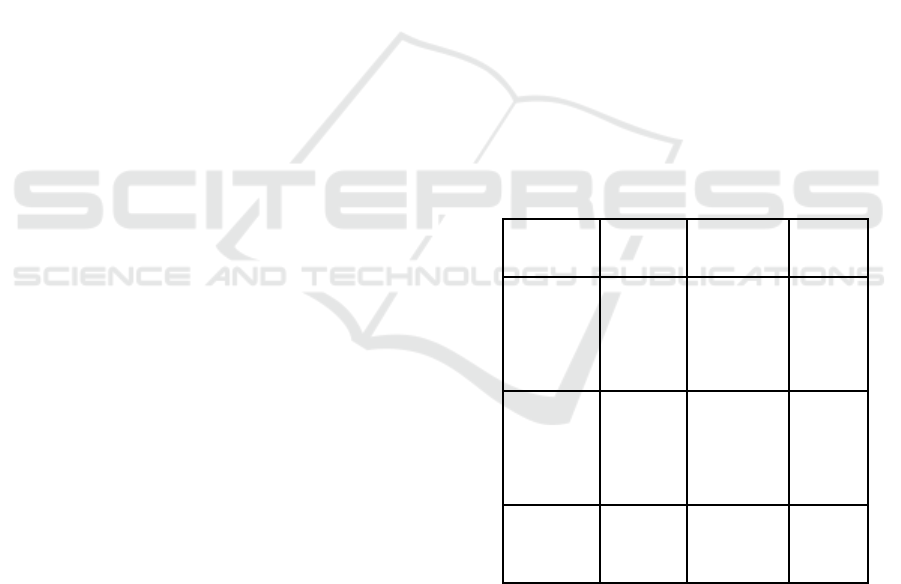
Table 1: Comparative Analysis of Algorithm.
Algorithm Type Strength
Weaknes
s
Random
Forest
Ensemble
(Bagging)
Handles
outliers
well,
reduces
overfitting
Slower
for large
datasets
XGBoost
Ensemble
(Boosting
)
High
accuracy,
handles
missing data
Sensitive
to
hyperpar
ameter
tuning
Hybrid (RF
+ XGB)
Combined
Model
Increased
accuracy,
robustness
Computa
tionally
intensive
Table 1 represents the Hybrid model combines the
strengths of Random Forest (RF) and XGBoost to
improve accuracy and robustness. This combination
works well as it leverages the diverse strengths of
both models. Random Forest is more stable and
handles outliers effectively, whereas XGBoost
provides high predictive accuracy and better handling
of missing data.
XAI-Powered Hybrid Model for Real-Time Financial Fraud Detection
215
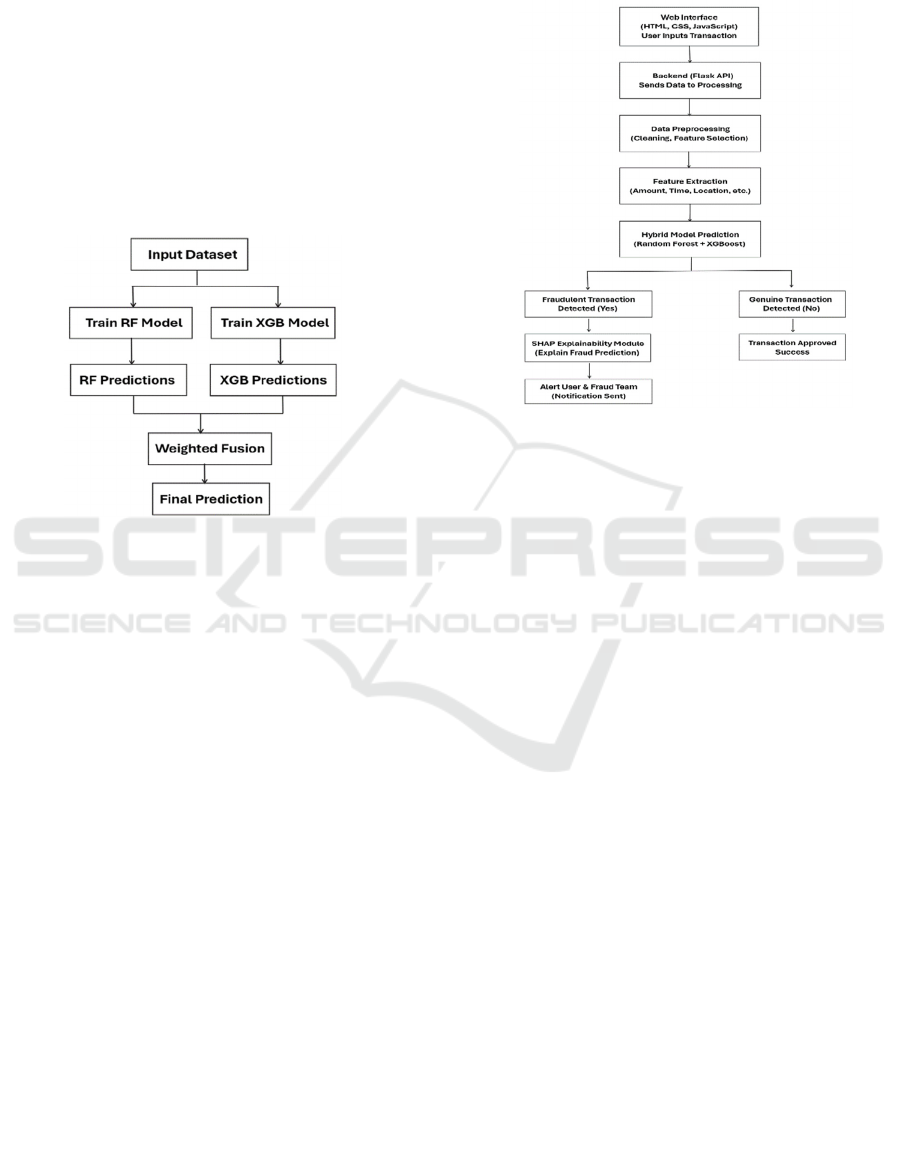
To get the final prediction in the Hybrid model, we
combine the individual predictions from the RF and
XGBoost models.
The formula used is:
Final_Prediction w1 RF_Prediction w2
XGB_Prediction (1)
w1 and w2 represent weights that adjust
according to the performance of the models.
RF_Prediction and XGB_Prediction are the
individual model predictions (either class
probabilities or predicted outcomes).
Figure 1: Hybrid Algorithm.
Figure 1 shows the hybrid algorithm. Therefore,
the output probabilities are multiplied by a final
probability score that renders a final decision upon
external criteria, perhaps fraud detection here.
3.3 Explainability Using SHAP
SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations) offers a
meaningful interpretation and explanation of fraud
detection decisions allowing those affected by the
decision to reasonably perceive them. The SHAP
factors would probably explain which features were
most influential in establishing the log-odds
associated with this transaction being classified as
fraud by feature importance scores awarded to such
or any features under consideration therefore this
offers insight into the rationale and judgement of the
model.
3.4 System Architecture
Victor., et al., 2023, In theory both less and less
practiced in one way a managed deployment of the
model on a Flask backend coupled with an
aggregation number of apis for interactive front-end
and transactions fraud alerts and model prediction
explanations. HTML CSS and JavaScript were used
with deployment through SHAP. Figure 2 shows the
system flow diagram.
Figure 2: System Flow Diagram.
3.5 Model Evaluation and
Optimization
Execution measurements incorporate exactness,
accuracy, review, F1-score, and AUC-ROC.
Hyperparameter tuning with GridSearchCV
optimizes demonstrate performance. Comparative
examination of standalone and half-breed models
guarantees the finest extortion location approach.
3.6 Deployment and Real-Time
Monitoring
The model is deployed as a web-based application
using Flask. Users can input transaction data in real-
time, and fraud risks are flagged with
explanations.Future improvements include real-time
streaming for fraud detection with minimal latency.
4 RESULT
The exploratory comes about to illustrate the
adequacy of the proposed crossover extortion
location framework utilizing arbitrary timberland and
XGBoost in conjunction with SHAP for
explainability. The framework was tried on a kaggle
money related exchanges dataset and the comes about
highlight both tall precision and interpretability
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
216
4.1 System Performance
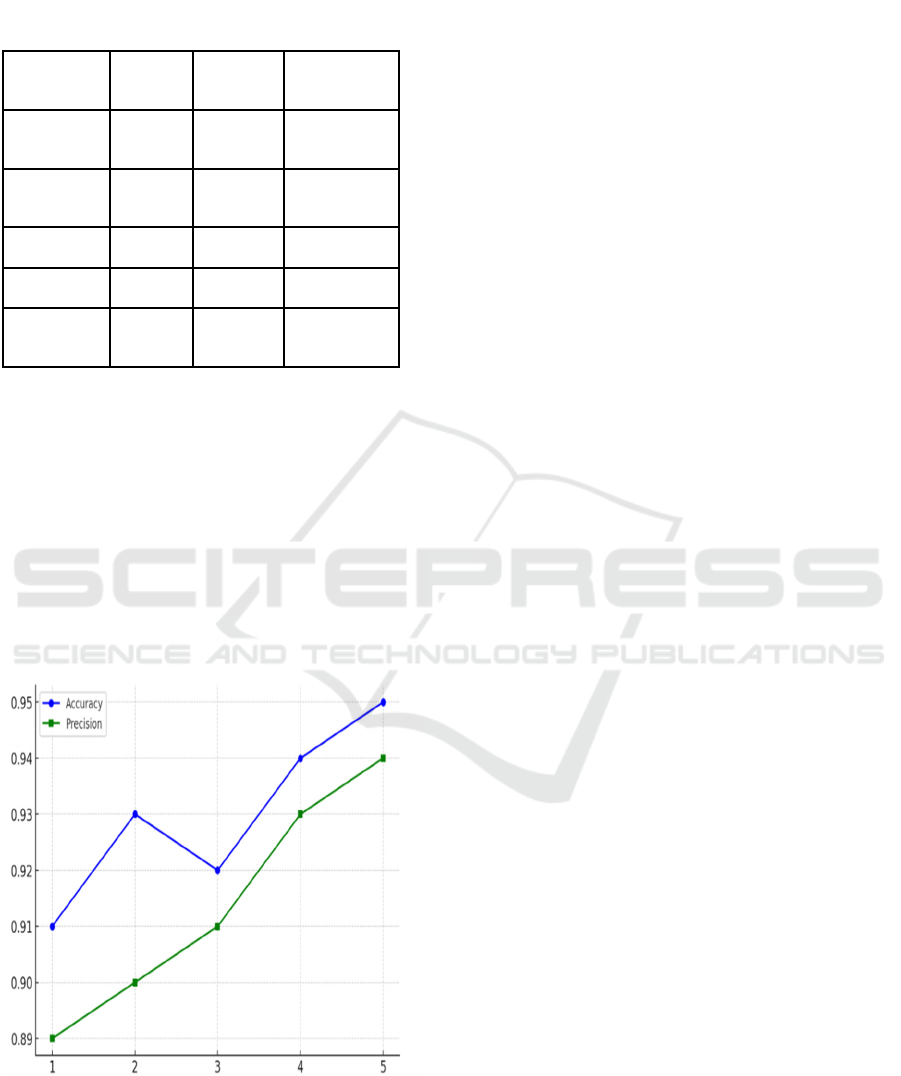
Table 2: Comparative Analysis of Algorithm.
The Hybrid System accomplished the most
noteworthy execution over all measurements. It
combined Arbitrary Forest's capacity to handle
information inconstancy with XGBoost's angle
boosting method for design acknowledgment. The
97.1curacy and 0.989 AUC-ROC score highlight its
adequacy in recognizing false exchanges. Higher
review (97.4%) guaranteed negligible untrue
negatives, pivotal for extortion location. Weighted
forecasts from both models boosted accuracy to
96.8% . Table 2 represents the Comparative Analysis
of Algorithm.
Figure 3: Performance Curve.
Figure 3 a performance curve showing the
accuracy and precision of the hybrid fraud detection
model over multiple trials or datasets.
4.2 SHAP Explainability Results
SHAP explainability highlights beat contributing
highlights for extortion discovery exchange sum tall
compared to client history exchange area abnormal
geographic regions gadget sort unused or
unrecognized gadgets and time of exchange odd
hours beside fizzled login endeavors different
disappointments some time recently the exchange.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This extends presents a half breed extortion location
framework that coordinates arbitrary woodland and
XGBoost for progressed precision and vigor by
leveraging reasonable AI XAI methods such as SHAP
the framework not as it identifies false exchanges but
moreover gives straightforward avocations for its
choices. The frontend web interface guarantees user-
friendly interaction whereas the flask-based backend
effectively exchanges information and forecasts. Our
demonstration effectively distinguishes false
exercises based on different budgetary exchange
designs improving belief and interpretability in ai-
driven extortion discovery.
6 FUTURE WORK
Real-time Extortion Discovery: Executing
spilling information preparation utilizing
Apache Kafka or Start Spilling for moment
extortion discovery.
Deep Learning Integration: Investigating
LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) or
Transformer models to move forward
extortion discovery on successive exchange
of information.
Multi-Factor Verification (MFA):
Improving security by coordination
biometric verification (unique finger
impression, facial acknowledgment) for
high-risk exchanges.
User Behavior Investigation: Executing
inconsistency discovery methods based on
chronicled client behavior for personalized
extortion location.
Automated Detailing Framework:
Creating a computerized extortion report
Metric
Random
Fores
t
XGBoost
Hybrid Model
(Combined)
Accuracy
(%)
95.2 96.4 97.1
Precision
(%)
94.8 96.0 96.8
Recall (%) 95.5 96.6 97.4
F1-Score (%) 95.1 96.3 97.1
AUC-ROC
Score
0.972 0.983 0.989
XAI-Powered Hybrid Model for Real-Time Financial Fraud Detection
217

generator to help monetary examiners in
decision-making
REFERENCES
A.-A. Al-Maari and M. Abdulnabi, "Credit Card Fraud
Transaction Detection Using a Hybrid Machine
Learning Model," 2023 IEEE 21st Student Conference
on Research and Development (SCOReD), Kuala
Lumpur, Malaysia, 2023, pp. 119-123, doi:
10.1109/SCOReD60679.2023.10563915.
A.Behura and M. Srinivas, "Credit Card Fraud Detection
Using Hybrid Learning," 2022 13th International
Conference on Computing Communication and
Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kharagpur,
India, 2022, pp. 1-7, doi:
10.1109/ICCCNT54827.2022.9984518.
C. Kotrachai, P. Chanruangrat, T. Thaipisutikul, W.
Kusakunniran, W. -C. Hsu and Y. -C. Sun,
"Explainable AI supported Evaluation and Comparison
on Credit Card Fraud Detection Models," 2023 7th
International Conference on Information Technology
(InCIT), Chiang Rai, Thailand, 2023, pp. 86-91, doi:
10.1109/InCIT60207.2023.10413100.
D. Jahnavi, M. A, S. Pulata, S. Sami, B. Vakamullu and B.
Mohan G, "Robust Hybrid Machine Learning Model
for Financial Fraud Detection in Credit Card
Transactions," 2024 2nd International Conference on
Intelligent Data Communication Technologies and
Internet of Things (IDCIoT), Bengaluru, India, 2024,
pp. 680-686, doi:
10.1109/IDCIoT59759.2024.10467340.
E. Ileberi and Y. Sun, "A Hybrid Deep Learning Ensemble
Model for Credit Card Fraud Detection," in IEEE
Access, vol. 12, pp. 175829-175838, 2024, doi:
10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3502542.
O. C. Agomuo, A. K. Uzoma, Z. Khan, A. I. Otuomasirichi
and J. H. Muzamal, "Transparent AI for Adaptive Fraud
Detection," 2025 19th International Conference on
Ubiquitous Information Management and
Communication (IMCOM), Bangkok, Thailand, 2025,
pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/IMCOM64595.2025.10857433.
R. Gangavarapu, H. Daiya, G. Puri and S. Narlawar,
"Enhancing Fraud Detection in Payment Systems Using
Explainable AI and Deep Learning Techniques," 2024
Sixth International Conference on Intelligent
Computing in Data Sciences (ICDS), Marrakech,
Morocco, 2024, pp. 1-7, doi:
10.1109/ICDS62089.2024.10756502.
R. Kapale, P. Deshpande, S. Shukla, S. Kediya, Y. Pethe
and S. Metre, "Explainable AI for Fraud Detection:
Enhancing Transparency and Trust in Financial
Decision-Making," 2024 2nd DMIHER International
Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare,
Education and Industry (IDICAIEI), Wardha, India,
2024, pp. 1-6, doi:
10.1109/IDICAIEI61867.2024.10842874.
S. R. Banu, T. N. Gongada, K. Santosh, H. Chowdhary, R.
Sabareesh and S. Muthuperumal, "Financial Fraud
Detection Using Hybrid Convolutional and Recurrent
Neural Networks: An Analysis of Unstructured Data in
Banking," 2024 10th International Conference on
Communication and Signal Processing
(ICCSP),Melmaruvathur, India, 2024, pp. 1027-1031,
doi: 10.1109/ICCSP60870.2024.10543545.
S. Y, N. Victor, G. Srivastava and T. R. Gadekallu, "A
Hybrid Federated Learning Model for Insurance Fraud
Detection," 2023 IEEE International Conference on
Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Rome,
Italy, 2023, pp. 1516-1522, doi:
10.1109/ICCWorkshops57953.2023.10283682.
T. Awosika, R. M. Shukla and B. Pranggono,
"Transparency and Privacy: The Role of Explainable AI
and Federated Learning in Financial Fraud Detection,"
in IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 64551-64560, 2024, doi:
10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3394528.
X. Zhao, Q. Zhang and C. Zhang, "Enhancing Transaction
Fraud Detection with a Hybrid Machine Learning
Model," 2024 IEEE 4th International Conference on
Electronic Technology, Communication and
Information (ICETCI), Changchun, China, 2024, pp.
427-432, doi: 10.1109/ICETCI61221.2024.10594463.
Y. Shinde, A. S. Chadha and A. Shitole, "Detecting
Fraudulent Transactions using Hybrid Fusion
Techniques," 2021 3rd International Conference on
Electrical, Control and Instrumentation Engineering
(ICECIE), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2021, pp. 1-10,
doi: 10.1109/ICECIE52348.2021.9664719.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
218
