
Analysis of Real Time Road Surface and Acoustic Data Processing for
Minimizing the Accident Rate Using Feed Forward Neural Network
Eswaramoorthi R., Velliangiri A., Devaviknesh S., Haribaskar S., Naveen S. and Prasanth D.
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, K.S.R. College of Engineering, Tiruchengode, Namakkal,
Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Feature Selection, Feature Engineering, Classification, Machine Learning, Ensemble Learning, Anamoly
Detection.
Abstract: Simplified road condition monitoring is essential to maintaining road safety and maximizing transportation
efficiency in smart cities. Effective road surface detection has been significantly improved by the use of
artificial intelligence (AI). Issues with asphalt pavement are the main concern of both developed and emerging
countries for the efficient functioning of everyday commutes. The identification of potholes, which are
dangerous to cars and people and can result in an accident, has been the subject of several research. In order
to identify potholes on edge devices, this study aims to explore the possibilities of deep learning models and
use three outstanding deep learning models. This article proposes a low-cost technology for detecting the
surface qualities of road pavement in real-time. The time-frequency domain processing of the inertial signals
given by on-car sensors is done in order to get information about the condition of the road surface. The
effectiveness of the suggested approach in determining the kind and existence of distress is demonstrated by
the high categorization rates. Following data collection from the road surfaces, machine learning methods like
Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) are used for analysis. The outcomes show how well the suggested approach
can distinguish between various road conditions. These findings showed that the MLP had a higher accuracy
of 98.98% when evaluating road conditions. In order to give safe transportation services in smart cities, the
study offers important insights into the creation of a more effective and dependable road condition monitoring
system.
1 INTRODUCTION
A pothole, one of the types of asphalt pavement
failures that occur due to water in the supporting soil
structure and traffic over the used area. First, when
the underlying soil structure is hydrated and water is
added, the supporting soil softens. Traffic wears and
breaks up the poorly-supported wearing pavement in
the affected area. It causes the asphalt and dust
particles underneath to come out and sink, leaving an
empty area in the road due to continuous driving
activity.
Figure 1: A deep pothole.
1.1 Formation of Pothole
Pothole primer A public administrator’s guide to an
understanding and handling of the pothole problem,
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (Eaton et al.), says it
takes two conditions to make a pothole: water and
traffic. Water weakens the soil under the pavement,
or the pressure of traffic applies stresses to the
pavement that make it crack. Potholes do not form
overnight, but rather start as a sign of fatigue within
the surface of the road. Pavement that breaks up in
this way between fatigue cracks is finally released in
the form of a pothole when progressive fatigue leaves
it unvoiced by adjacent surface stresses, and it is
plucked or driven out of the surface by ongoing tire
stresses. In areas that experience freeze and thaw, this
type of freeze and thaw can damage a pavement and
leave openings for water to enter. The process, made
more acute than ever this year by spring thaw which
saturates and weakens the supporting soil happens
208
R., E., A., V., S., D., S., H., S., N. and D., P.
Analysis of Real Time Road Surface and Acoustic Data Processing for Minimizing the Accident Rate Using Feed Forward Neural Network.
DOI: 10.5220/0013880200004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
208-213
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

when the upper parts of a pavement’s soil structure
cannot melt past lower, still-frozen layers. Though
they rarely exceed a few inches in depth, potholes
can stretch out to several feet in width. If large enough
as shown in figure 2 and figure 3, they are likely to
cause damage to tires, wheels and even car
suspensions. On-road implications. This can lead
directly to serious traffic accidents especially on
freeways with high speeds.
Figure 2: Condition of roads with potholes.
Figure 3: Road surface defects.
As illustrated in the figure, pavement distresses
for asphalt sections are primarily divided into eight
categories, as per the Texas Department of
Transportation's (TxDOT) Pavement Management
Information System Rater's Manual: rutting,
patching, block, alligator, longitudinal and transverse
cracking, ravelling, and potholes. Regular road
surface monitoring and maintenance is crucial since
it may extend a road's lifespan from 15 to over 30
years. The goal of this project is to create a road
classification system that can evaluate the
infrastructure in real time. The creation of novel
artificial intelligence methods that can learn on their
own from acoustic data obtained through an
integrated system is the main goal of this article. The
algorithm is implemented on an electronic board that
is fixed to a car's rim flange. It is connected to a
microphone that is placed within the tire hollow and
has components for transmitting Low Energy (LE)
data with web monitoring that is based on the Internet
of Things.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
Moazzam et al. (2013) may provide a pavement
distress detection technique that mainly focuses on
detecting and analyzing potholes and cracks
generated due to road damage. The study addresses
the essential issue of accurately predicting the volume
of filler material required to repair a pothole to avoid
any shortages and wastage. The idea is to extract road
surface depth images from a Concrete and Asphalt
roadway using an inexpensive Kinect sensor. These
photographs are rendered in a way to generate meshes
that facilitate the identification of potholes.
S.S. Rode et al. Pot-hole avoidance system for
vehicles. (2009) propose a unique architecture for a
pothole detection and warning system which is Wi-
Fi based. As Wi-Fi-enabled cars drive through the
area covered by the access points, they will receive
the data broadcasted by the access points along the
roadway. Additionally, acknowledgments responses
may be transmitted by front-end nodes (cars) to the
access points where they are dispatched to the back-
end servers.
H. Youquan et al. proposed a method of efficient
detection of the 3D sectional area of pavement
potholes. (2011). The optical imaging principle of
three-dimensional projection transformation is
adopted to take pictures of the cross-section of
potholes during detection. It involves a variety of
digital image processing techniques like error
analysis and compensation, image preprocessing,
binarization, thinning, and 3D reconstruction. These
experiment observations indicate that this method
outperforms traditional methods in many aspects and
enhances pothole detecting accuracy and
performance.
Different from the more common investigation on
crack detection in pavement distress (J. Lin et al.
(2010) focus on the less studied area of pothole
identification. The paper proposed a pothole detection
method which uses histogram to extract the textural
features that refers to a region of an image. A non-
linear support vector machine (SVM) is then used to
classify if the specified target region is indeed a
pothole. Based on experimental data, the proposed
algorithm offers an effective approach for detecting
potholes on pavements, attaining a significantly high
identification rate.
A DNN model for identifying the speaker was
presented by F. Ye et al. (2021). Published in the
Analysis of Real Time Road Surface and Acoustic Data Processing for Minimizing the Accident Rate Using Feed Forward Neural Network
209

journal of Applied Sciences, these researchers
outlined a strategy to effectively and efficiently
increase the accuracy of speaker identification
systems using deep learning methods**. By using
speech characteristics to identify specific speakers,
the model offers a reliable solution for use cases such
as voice-activated systems and security.
Experimental findings demonstrate that the model
achieves good recognition performance for tasks like
speaker identification.
3 EXISTING SYSTEM
The current pothole-maintenance system has a black-
box camera-based pothole detector. The pothole-
detection system uses the camera to gather pothole
information, including size, position, and appearance.
The pothole-maintenance server utilizes the gathered
data for intelligent pothole maintenance, which is
kept in the pothole database. Based on our prior
pothole database system, we created new software for
the pothole-maintenance server, as seen in Figure 1
on the right. A variety of information about potholes
is provided by this software, including video clips,
images, regions, road authorities, road number,
driving direction, lane number, road type, latitude,
longitude, collectors, date of collection, pavement
type, location, shape, size, and comments. With the
help of the gathered GPS data, the pothole's position
is displayed on a digital map. As a result, viewers can
observe the pothole distribution with ease.
Additionally, pothole maintenance expenses in the
chosen region are precisely estimated by the program.
In this manner, the program makes it simple and
precise for transportation officials to create road-
maintenance rules and strategies. Then, potholes can
be intelligently fixed using a pothole-maintenance
system, like our intelligent asphalt repair systems, and
pothole data can be shared with other users and
services through Open API and external connections.
Pothole-maintenance system (Figure 1). Insofar as the
current approach for detecting potholes only employs
one black-box camera. It is possible to swiftly collect
data over a large region and construct a variety of
survey vehicles for pothole identification at a
reasonable cost. Actually, because current pothole-
maintenance methods do not offer reliable pothole
information, the Korean government is unable to
budget for yearly road repair expenses with any
degree of accuracy. This initiative aims to identify
and track road conditions and raise awareness of
anomalies on the road, which is likely to occur in
nations like India.
4 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The goal of this project is to create a road
classification system that can evaluate the
infrastructure in real time. The creation of novel
artificial intelligence methods that can learn on their
own from visual and inertial data obtained through an
integrated system is the main goal of this research.
The algorithm is implemented on an electronic board
that is positioned on the dashboard or onboard unit of
a car. It is connected to a camera and sensors that are
placed within the suspension cavity and has WiFi or
Internet of Things data transmission components.
Three stages of the system's evaluation were
conducted. First, the two CNNs were trained, and
their outputs were compared. After that, the model
with the best performance was chosen and quantified.
Additionally, as a last comparison, the model
accuracy for both the quantized and floating-point
models was computed. Finally, the classifier was
included into the embedded firmware, and an
Arduino NANO board was used to evaluate its
operation. To evaluate the application's performance
on actual hardware, it was then installed on the
specially made board. The development of a new
dataset comprising the inertial data resulting from the
contact between the wheel and road surfaces is a
significant proposal of this project. The data
collection was created in part through data
augmentation and mostly through many measurement
efforts.
5 PROPOSED DESCRIPTION
One really interesting and valuable project to detect
road quality is to build a road surface analyser with
Arduino Nano, MPU6050 accelerometer, HC-SR04
ultrasonic sensor, and limit switch. Below is step-by-
step instructions to implement this system:
The aim of this project is to check road condition
based on surface roughness, potholes and bumps. The
limit switch can also serve to discern specific trigger
events (for example, did the wheel hit something, or
when the system is moving), while the accelerometer
will pick up vibration and bumps of the ground, and
the ultrasonic could be used to measure the distance
to the road surface.
• Inertial sensors: not least accelerometers form
the foundation
of the cheapest road surface
estimation systems. This project aims to
develop a road classification system that can
assess the infrastructure
in real time.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
210

• New low-cost AI based on on-device and GPS
based on real
time location and identification
of problem areas based on MEMS signals
• AI embedded
architectures consider
constraints that an Internet of Things (IoT)
device must operate within memory and
embedded systems execution limits.
5.1 Data Processing
1. Accelerometer Data: To identify sudden
changes that point to bumps, potholes, or
uneven spots, use the accelerometer data,
particularly along the Z-axis.
2. Ultrasonic Distance: Track variations in
distance, which might reveal imperfections
in the road surface.
3. Limit Switch: To initiate particular actions,
such as recording data only when the system
is in motion or a wheel strikes an
obstruction, use the limit switch.
5.2 Data Analysis
As the machine moves across various road surfaces,
gather and record data over time. Examine trends in
ultrasonic and accelerometer data to identify
particular kinds of anomalies in the road. For a more
sophisticated system, think about wirelessly sending
data for distant monitoring and analysis as well as
recording it on a PC for surface study.
5.3 Fine-Tuning and Calibration
Adapt thresholds to the driving conditions and the
accelerometer's sensitivity. To concentrate on more
important occurrences that probably point to poor
road condition, filter away little vibrations.
6 HARDWARE
6.1 Power Supplies
An apparatus or system that provides electrical or
other forms of energy to an output load or collection
of loads is called a power supply (sometimes referred
to as a power supply unit or PSU). Electrical energy
sources are most frequently referred to by this phrase,
followed by mechanical ones and, seldom, others.
When working with digital circuits, this circuit's tiny
+5V power supply is helpful. Any supermarket or
electronics store will sell small, low-cost wall
transformers with changeable output voltage.
Although such transformers are readily accessible,
they often have extremely poor voltage regulation,
which limits their usefulness for digital circuit
experimenters until a better regulation can be found.
The solution to the issue is the circuit that follows.
6.2 Transformer
A transformer is an apparatus that transfers electrical
energy between two (or more) circuits through
inductively coupled wires. The changing current in
main circuit creates a changing magnetic field, which
also induces an alternating voltage in secondary
circuit. Current can be flowed in the transformer
which allows energy to transfer from one circuit to
another or a load applied to the secondary circuit.
One factor (n) which is (or rather should be) equal to
the number of wires turns in each of them, here is
employed to dilute the secondary induced voltage
(VS) from the primary VP: Therefore, a transformer
can step up an alternating voltage if NS > NP or step
it down if NS < NP by selection of number of turns
carefully. A key application of transformers is
lowering the current before transmitting electrical
energy over long distances through wires. Due to
their resistance, the vast majority of wires dissipate
electrical energy as a function of the square of the
amount of current passing through them.
Transformers enable long-distance electricity
transmission, where electrical power is converted to
a high-voltage, and therefore low-current, state for
transmission and then back again. As a result,
transformers have spread through the electrical
supply industry covertly implanting the general
concept of generating far away from demand. By the
time it finally reaches the user, nearly all of the
electrical power in the World has passed through a
series of transformers. Some enormous units are
capable of transmitting 99.75 percent of their input
power to their output, making transformers some of
the most efficient electrical “machines.”
Transformers vary in size from tiny coupling
transformers tucked inside backstage microphones to
giant gigavolt-ampere rated pieces of gear used to
connect sections of national power grids. There are
many different designs for various functions, both
home and industry, but they all operate on the same
basic principles:
Analysis of Real Time Road Surface and Acoustic Data Processing for Minimizing the Accident Rate Using Feed Forward Neural Network
211
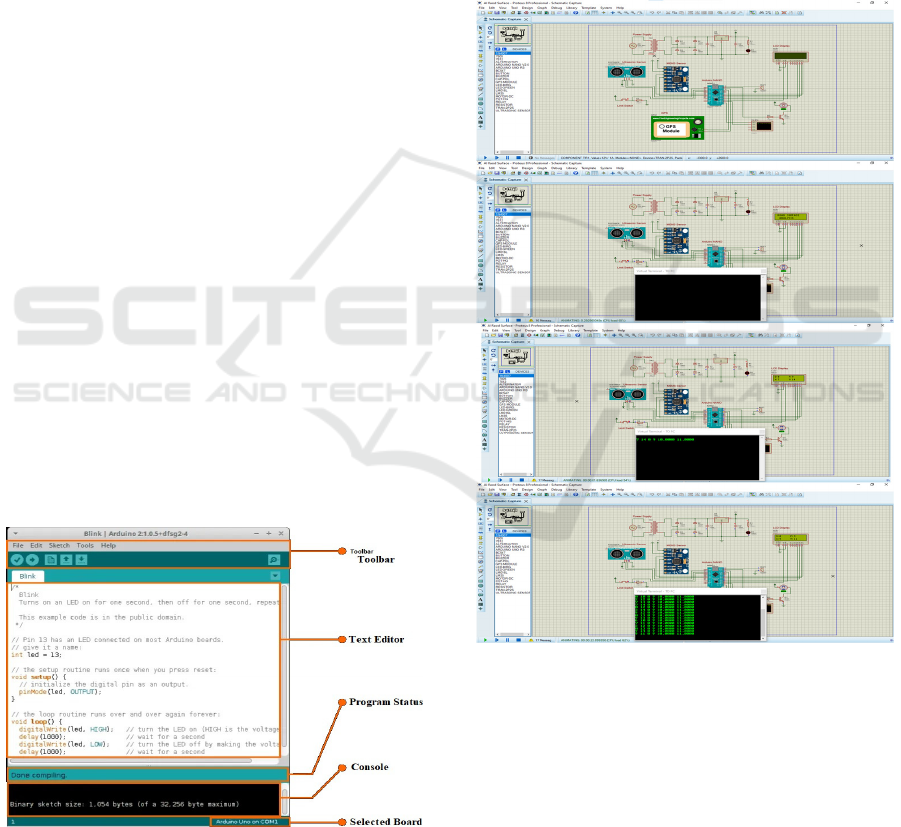
7 SOFTWARE
7.1 Arduino
Arduino is an open-source electronics platform based
on simple software and hardware. Arduino boards
receive an input, the light on a sensor, a finger over a
button, a tweet, and they create an output in the form
of blinking an LED, activating a motor and posting
something online. The microcontroller of your board
can be commanded to perform some actions by
feeding instructions you may refer to as a Program.
This is done using the Arduino software (IDE) shown
in figure 4, which is built on Processing, and the
Arduino programming language, which is built on
Wiring. Whether for more simple everyday items or
more complex scientific devices, Arduino is still the
brain behind millions of projects every year. This
open-source platform has borne from it a global hive
of makers (students, hobbyists, artists, programmers
and professionals) sharing knowledge creating an
insane reservoir of useful information well suited for
beginners and experts alike. Arduino was invented as
a simple prototyping tool in the Ivrea Interaction
Design Institute so students without any electronics
or programming background could prototype quickly.
The moment that the Arduino board became widely
adopted, it began to be evolved to tackle new needs
and challenges, from basic 8-bit boards to choices for
wearables to those for embedded environments to 3D
printing and Internet of Things/IoT applications. All
Arduino boards are fully open-source, so you can
solder them together yourself and then modify
according to your requirements. The program is
public and continually builds through donations
from people all over the world.
Figure 4: Arduino IDE.
7.2 Arduino Software
The Arduino Integrated Development Environment
(IDE), also known as the Arduino Software, includes
a text editor for writing code, a message box, a text
terminal, a toolbar with buttons for commonly used
tasks, and several menus. It connects to the Arduino
hardware to upload programs and interact with the
hardware.
8 RESULT
Figure 5: Real-time road hazard detection and risk mapping
system.
Predicted Risk Level: "High Risk" (based on data
from a road segment exhibiting uneven auditory
signals and potholes that may indicate tire sliding).
Notice: "Warning: Hazardous Road conditions
detected, slow down immediately."
The report on accuracy states, "Model accuracy: 92%,
Precision: 89%, Recall: 91%."
Visual Representation: Figure 5 shows the city map
with areas coloured according to the neural network's
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
212

rating (green for safe, yellow for intermediate risk,
and red for high danger).
9 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, we have introduced an AI-based real-
time road surface monitoring application. The
program is intended to be used on a microcontroller
board that has a microphone installed to record noises
within a tire's cavity. According to preliminary test
findings, the gadget can identify the asphalt's quality
on the test set with 91% accuracy. This illustrates how
well the suggested Tiny architecture works for this
use case and how the Mel-inspired spectrogram can
be used as an input to identify the condition of the
road. The suggested strategy makes use of cutting-
edge methods. Actually, the implementation of AI
systems on embedded systems is a state-of-the-art
technology that is the subject of a lot of ongoing
study.
REFERENCES
"Deep neural network model for speaker identification,"
written by F. Ye and colleagues, Appl. Sci., vol. 11, no.
11, p. 5172, 2021.
"Pothole recognition based on texture measures and support
vector machine," by J. Lin et al., in Proceedings of the
IEEE International Conference on Pictures, 2010, pp.
3653-3656.
"Three-dimensional pavement pothole detection based on
optical imaging principle," IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp.
Syst., vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 291-301, June 2011. H.
Youquan et associates.
"Wi-Fi-based architecture for pothole detection and
warning system," by S. S. Rode et al., in Proceedings of
the IEEE International Conference on Networking,
Sensing, and Control, 2009, pp. 672-677
The article "Pavement Distress Detection and Analysis for
Pothole Repair," by I. Moazzam and colleagues, was
published in 2013.
Analysis of Real Time Road Surface and Acoustic Data Processing for Minimizing the Accident Rate Using Feed Forward Neural Network
213
