
Automated Code Review Assistant
Sadish Sendil Murugaraj, Rama Krishna Vardhan Taddi, Jagan Allu and Pallavi Rapolu
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Vel Tech Rangarajan Dr. Sagunthala R&D Institute of Science and
Technology, Avadi, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Automated Code, Artificial Intelligence, Data Privacy.
Abstract: Automated code review is playing an important role in modern software development and the combination of
artificial intelligence is making it more and more important. This project employs artificial intelligence and
machine learning to scan for bugs, vulnerabilities and adherence to ethical norms. It will deliver automated
feedback on things like the algorithmic underpinning, availability to minorities and data privacy, evaluating
whether the software harmonizes with the tenets of equity and inclusion. The designed system will be multi-
language to use in the different programming environment. It will also be fully embedded within the CI/CD
pipelines to offer feedback as early as possible during the development cycle. By integrating a human rights-
based methodology into the code review process, the Tool helps to ensure that software products are also
compliant with ethical standards, thus, striving for transparency and accountability in technology
development. Closing the gap between social justice and technology, the importance of this project lies in
building sustainable and inclusive digital building blocks.
1 INTRODUCTION
The release of an Automated Code Review Assistant
for human-rights-based projects is a monumental step
towards combining ethics with technical excellence
for the future of our software development.
Automated code review tools employ machine
learning and artificial intelligence to scan the source
code for errors, weaknesses, and any deviations from
established criteria. The same goes with Human
Rights where such tools can be customized to
contribute to the alignment of software systems with
core ethical principles, protection of sensitive data,
and even promotion of equitable participation and
inclusion. These tools can save time and minimize
human error by ensuring best practices through
automated code review.
Human rights work often includes handling
sensitive information, so security and privacy are of
utmost importance. As an example, an automated
code review assistant can do static and dynamic code
analysis to find vulnerabilities like those which could
lead to data integrity issues or exposing individuals to
harm. In other words, it can review algorithms for
potential biases or discriminatory practices, allowing
the software to meet ethical standards. For example,
the tool can apply accessibility guidelines to make
sure that marginalized communities are included, in
keeping with global human rights standards.
Furthermore, the assistant may seamlessly
integrate into the current improvement workflows, in
addition to into CI/CD pipelines, giving actual time
feedback on a number of degrees throughout the
coding course of. This allows builders to address
problems before the improvement of lifecycle,
reducing costs and improving significant software
quality. The device can also generate specific
opinions that highlight ethical concerns, safety
hazards and practical recommendations for
remediation. The assistant integrates one's talents into
the upgrade route, promoting transparency and
responsibility in generation creation.
In conclusion, the automatic code study assistant
that we have designed for human rights obligations is
based on technical acting with ethical training. It
guarantees that no longer is the shape of software
program structures satisfactory assembly beneficial
necessities but additionally maintaining thoughts of
equity, safety, and inclusivity. Combining technology
and social justice, it empowers builders to construct
solutions that make an optimistic contribution to
society and adhere to international human rights
criteria.
Murugaraj, S. S., Taddi, R. K. V., Allu, J. and Rapolu, P.
Automated Code Review Assistant.
DOI: 10.5220/0013880000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
195-201
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
195

2 RELATED WORKS
There has been a big deal of interest in automated
code evaluation assistants in latest-day years,
indicating a want for greater green software program
great guarantee practices. This phase of essays
applied works that learn the improvement,
implementation, and impact of these out in world
contexts.
As a result, automated code evaluation has
developed into a vital software for software program
application development to assist the demanding and
tedious technique of analyzing the supply code for
high quality and integrity. The other team adopts a
machine learning and tool watching ammend of AI
in order to research code, find thickening issues, and
provides feedback to builders. The automation of
advantageous elements of code assessment allows
builders to be targeted on extra complicated duties,
improving conventional overall performance and
productivity.
Recently, there has been work done on more
advanced techniques to automatically evaluate code
in a variety of ways. For example, researchers have
used software dependency graphs as decoration for
the reading of code shape records. It corresponds to
translating code into graph sequences the usage of
algorithms like PDG2Seq that permits fashions to
understand code superb judgment greater efficiently.
Models like these can set up statements in natural
language and advise code adjustments enhancing
development performance via giving builders greater
intuitive remarks. We also explored the application
of deep reading (DL) techniques with the goal of
automating finer-grained code quality assessment
tasks, decreasing dependence on guide reviews and
improving consistency.
In order to automate code, evaluate procedures in
recent years, machines learning strategies have
become increasingly used. Machine studying
methods for example, can streamline and improve
critiques by deciphering software program structures.
Additionally, massive language fashions (LLMs)
have proven encouraging effects in industry
functions, aiding in bug localization and enriching
code fine awareness. These models can research
explicitly and generate higher-pleasant opinions
makes them treasured gear in software program
improvement Moreover Candle et al. This tar portrait
paves the walk for lender improvements, should be
people-posed, focused, and balanced, to objurgate
entrenched impediments on directed approaches of
automating metamorphic tribute duties in
improvement, automatic code test measures were
added precisely into software program improvement
workflows to decorate overall performance, and
nice. For instance, the CORE (Code Review Tool)
tool automates examine suggestions for code
modifications to iterate better performance networks
primarily based totally on modifications code and
their respective critiques. But while automatic
equipment offers a few advantages, they're now not
an alternative to human judgment. Research
highlight the value of combining automated tools
with human intervention to ensure quality code.
As computerized code assessment maintains to
conform, future research should recognition on
improving the accuracy and reliability of those
equipment. This might also involve integrating extra
state-of-the-art tool studying models and leveraging
large datasets to enhance model performance shows
in Table 1. Additionally, information a way to
efficaciously stability automated gear with human
oversight may be crucial for maximizing the
blessings of automatic code examine. By advancing
in those regions, computerized code evaluation can
play an increasing number of crucial roles in
enhancing software program application development
techniques, making sure better-nice code and faster
development cycles.
3 METHODOLOGY
The proposed approach for growing an Automated
Code Review Assistant tailor-made to human rights-
targeted software program application software
program initiatives con- sists of a multi-section
technique to make certain ethical compliance,
accessibility, and safety. The tool will combine static
and dynamic code evaluation techniques to come
upon vulnerabilities, insects, and moral problems
inside the supply code. Machines getting to know
algorithms can be employed to find out types of
functionality bias, privateness violations, or
discriminatory practices embedded in the code.
Additionally, predefined rule gadgets aligned with
international human rights necessities will guide the
automatic study method.
The assistant can be included into CI/CD
pipelines to provide actual-time feedback
subsequently of development, making sure non-stop
monitoring and development. It will help multi-
language programming environments and use natural
language processing (NLP) strategies to analyze
comments and documentation for inclusiveness and
readability. To beautify usability, the assistant will
generate specific critiques highlighting problems,
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
196
their human rights implications, and actionable hints
for remediation.
This approach emphasizes collaboration through
way of permitting developers to engage with the tool
via customer- remarkable interfaces in Integrated
Development Environments (IDEs). Furthermore, it
will embody feedback loops to refine its normal
regular overall performance based on consumer input
and evolving human rights guidelines. By embedding
one’s abilities, the mission targets to create a robust
tool that not nice complements code nice but
moreover guarantees that software program
development aligns with moral and human rights
standards.
1. Data Collection
2. Study Design
3. Static Code Analysis
4. Natural Language Processing (NLP) Models
A. Automated code review data collection
B. Study Design
The proposed approach for developing an automatic
code overview assistant leverages a scientific method
to integrate synthetic intelligence (AI) into the code
study machine. This approach is designed to
beautify code pleasant, reduce take a look at time,
and help builders in maintaining excessive coding
necessities. The following outlines the vital element
components of the proposed technique:
Table 1: Dataset Description.
Categor
y
Data Point Description
Code Quality
Metrics
Code Analysis Depth
Measures how thoroughly the static analysis code is being
used.
Number of Defects
Foun
d
Tracks the number of issues reported including bugs, logic
errors, style violations.
Chan
g
e Failure Rate Percenta
g
e of code chan
g
es leadin
g
to errors
p
ost-mer
g
e.
Code Duplication Identifies redundant or duplicate code blocks.
Review Efficienc
y
Review Time Time taken from submission to feedback or a
pp
roval.
Pull Request Size Analyzes size of pull request in lines of code.
Throu
g
h
p
ut Number of reviews com
p
leted over a
p
eriod.
Reviewer Loa
d
Number of open pull requests assigned per reviewer.
Workflow
Integration
Integration with
CI/CD
Compatibility with CI/CD pipeline.
Version Control
System
Compatibility with tools like GitHub, GitLab, and
Bitbucket.
Customization Customizable Rules
Ability to define and enforce team-specific coding
standards.
1. System Integration: Development of IDE
Extension: Create an extension for well-known
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) which
includes Visual Studio Code (VS Code). This
extension will permit developers to provoke code
reviews right away interior their coding surroundings.
2. Code Snippet Capture: Implement functionality to
seize code snippets or complete files that want
examine, sending them to a backend server for
processing.
3. Backend Processing: Server Architecture: Set up a
backend server the usage of cloud offerings (e.G.,
AWS EC2), so as to contend with requests from the
IDE extension.
API Communication: Establish verbal exchange
protocols among the IDE extension and the backend
server the usage of RESTful APIs. This lets in for
green records transfer and processing. (e.G., Chat-
GPT, Gemini API) for reading the captured code. The
models will check out the code for functionality
insects, style improvements, and safety
vulnerabilities.
4. AI Model Analysis: Utilization of Generative
AI Models: Leverage modern generative AI
models.
5. Feedback Generation: The AI model will generate
action- able remarks based totally at the assessment,
alongside tips for exquisite practices and vital
corrections.
Feedback Display: User Interface Design: Design an
intuitive customer interface in the IDE extension
that offers comments in a clean and actionable
format.
Interactive Feedback Mechanism: Enable builders to
interact with the comments, permitting them to take
Automated Code Review Assistant
197
delivery of or adjust recommended adjustments right
away inside their coding surroundings.
6. Continuous Learning and Improvement: Data Col-
lection for Model Training: Collect records from
consumer interactions and comments on the AI-
generated pointers to continuously decorate the
version’s accuracy and relevance.
Integration with Historical Data: Incorporate ancient
code evaluate facts to beautify the AI’s functionality
to provide context-aware suggestions tailor-made to
specific coding styles and assignment necessities.
7. Evaluation and Testing: Pilot Testing with Users:
Conduct pilot trying out with real customers in each
open-supply project and business settings to assess
the effectiveness of the device. Performance Metrics:
Measure overall performance primarily based on
metrics along with reduction in review time, accuracy
of hints, user delight, and improvement in code
exceptional.
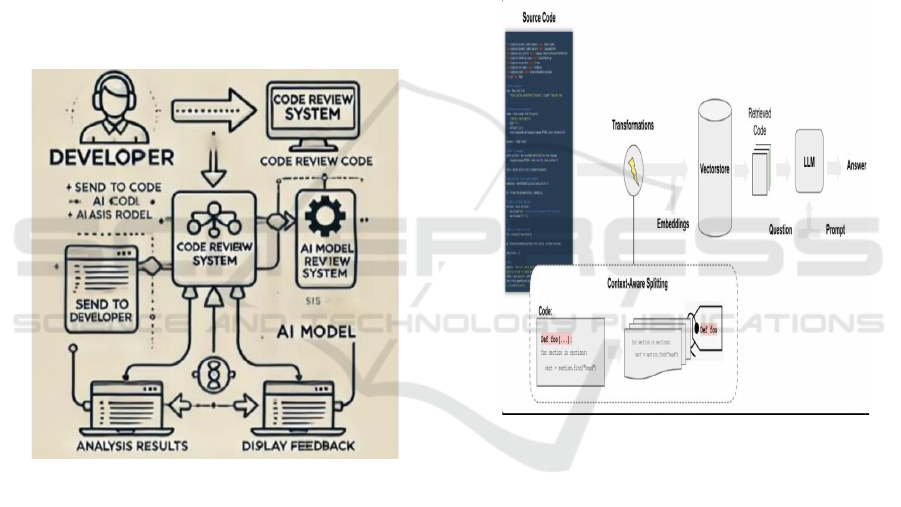
Figure 1: Overview of Proposed Methodology.
C. Static Code Analysis
Static code evaluation is a pivotal issue of automatic
code assessment, supplying a systematic technique to
analyzing source code without execution. This
technique includes the usage of computerized gadgets
to scrutinize the codebase for functionality issues,
which consist of coding requirements violations,
safety vulnerabilities, and logical mistakes. By
integrating static code evaluation into the
improvement workflow, groups can pick out and deal
with problems early inside the improvement cycle,
thereby reducing the time and fee associated with
debugging and safety. This approach is specifically
useful in ensuring code best, safety, and
maintainability, as it enables placed into effect
particular requirements and practices, discover
vulnerabilities which include SQL injection and
buffer overflows, and beautify average software
reliability.
Moreover, static code evaluation aligns with the
“shift left” locating out motion, which emphasizes
integrating finding out and evaluation tools earlier
inside the software program improvement lifecycle to
trap problems in advance than they come to be full-
size issues. By leveraging static code assessment,
developers can build higher-extremely good
software applications, restrict technical debt, and
beautify improvement performance, in the long run
contributing to faster and further reliable software
program releases.
D. Detection Using langchaing
Figure 2: Lang Chain Architecture.
Figure 1 shows the proposed technique for
computerized code assessment entails an entire
approach to enhancing code exceptional and standard
universal performance through the strategic use of
automated machines and software programs. This
approach starts off evolved with the mixture of static
code assessment system, which check supply code for
compliance with predefined hints and notable
practices, figuring out issues together with coding big
violations, protection vulnerabilities, and ordinary
common overall performance bottlenecks. These
systems are carried out via scanning the codebase to
come across capability issues, supplying builders with
actionable remarks to rectify identified troubles right
away. The lang chain architecture is shown in Figure
2.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
198

A key difficulty of this tool is the use of automated
code assessment suites, which provide more superior
abilities than conventional linters. Tools like
SonarQube and Code Climate assist more than one
programming language and can be covered into non-
prevent integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD)
pipelines, imparting close to actual-time feedback to
builders. This integration permits the early detection
of bugs and vulnerabilities, ensuring that code is
dependable and solid in advance than it reaches
manufacturing.
To maximize the blessings of automatic code
evaluation, the proposed technique emphasizes the
importance of blending automated machine with
human oversight. While computerized tools excel at
identifying habitual problems, human reviewers are
vital for addressing complex accurate judgment
mistakes and ensuring that code aligns with venture-
unique necessities and commercial company right
judgment. By balancing automation with human
judgment, improvement organizations can leverage
the strengths of each strategy to decorate code
notably, reduce manual assessment efforts, and
accelerate the improvement cycle.
Furthermore, this device advocates for the
adoption of Agile improvement methodologies, in
which automatic code examine performs a important
characteristic in facilitating faster and extra green
iterations. By automating code reviews, businesses
can align with Agile necessities of handing over
exceptional software application software program in
shorter cycles, promoting collaboration and remarks
amongst corporation humans. This approach not
satisfactory improves code first-class however
moreover fosters a lifestyle of non- prevent
improvement internal development companies.
Overall, the proposed methodology for automatic
code evaluation gives a based framework for
enhancing software improvement processes with the
aid of leveraging generation to streamline code
evaluation, improve high-quality, and decrease
development time. By integrating automatic gear into
the development workflow and balancing them with
human oversight, teams can make certain that their
software meets the very best requirements of first-
class and reliability.
The textit F1 Score is the harmonic imply of
Precision and Recall, supplying a unmarried
measure that balances each metric, mainly useful
while the class distribution is imbalanced. The dataset
used for automated code evaluation is a entire series
of code snippets and related metadata, designed to
beautify the education and overall performance of AI
models in identifying code troubles. This dataset is
compiled from several properties, which encompass
network repositories, GitHub public repositories, and
StackOverflow, ensuring a big variety of coding
patterns and actual-global examples are represented.
The information consists of examples of correct code,
compatibility troubles, commonplace average
performance problems, and runtime errors, each
meticulously classified to facilitate powerful version
schooling. Advanced preprocessing strategies which
encompass records augmentation and normalization
are completed to decorate dataset amazing and
variety. For instance, facts augmentation involves
strategies like flipping code snippets and injecting
minor mistakes to simulate real-global coding
situations, even as normalization ensures consistency
in code formats across the dataset.
This approach is not the simplest aid in
schooling. AI models however also afford valuable
insights for builders throughout the overview method,
permitting them to address capability troubles greater
correctly. Additionally, datasets like those supplied
through Tufano et al. Consist of pre- submission code,
reviewer comments, and post-overview code
adjustments, supplying a rich context for expertise the
code evaluation procedure and enhancing version
accuracy.
Finally, the text Mean Average Precision (MAP)
is the average of the Average Precision (AP) across
all classes. The AP for each class is calculated as the
vicinity underneath the precision-do not forget curve,
which is an indispensable of the precision over the
consider values.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
AND DISCUSSION
In us examine on automated code review, we
determined numerous key findings that highlight the
effectiveness and boundaries of these tools.
Automated code evaluation tools were found to
noticeably enhance the rate and performance of the
evaluation method through figuring out easy issues
which include code fashion inconsistencies and trivial
errors.
For example: tools like Code grip and Sonar Cube
proven high accuracy in detecting code smells and
safety vulnerabilities, presenting developers with
actionable remarks to improve code first-class.
However, regardless of these advantages, depending
totally on automatic gear can cause an illusion of
great manipulation, as they will omit complicated
Automated Code Review Assistant
199

logic mistakes or issues associated with code
rationale and person necessities.
Our experiments additionally discovered that deep
learning- based totally based models can be powerful
in automating unique code evaluating tasks. For
example, Deep Review, a version of the usage of deep
multi-example studying, confirmed promising effects
in figuring out capacity issues in open-supply
projects, with upgrades in both F1 score and AUC
metrics. Additionally, massive language fashions
(LLMs) have been used to beautify code review
efficiency by providing natural language feedback
and guidelines for code changes. However, these
models aren’t without barriers, as they are able to
generate false positives and negatives, which require
human intervention to resolve.
The integration of automatic code evaluation
equipment into continuous integration/non-forestall
deployment (CI/CD) pipelines changed into found to
offer close-to-time feedback, allowing builders to
cope with issues right away. This method no longer
best speeds up the improvement cycle but
additionally fosters a culture of excellent guarantee
in the development crew. Furthermore, combining
computerized code evaluations with practices like
pair or mob programming can in addition decorate
code excellently thru ensuring that human oversight
enhances automated checks.
In phrases of practical applications, our
observation discovered that automated code
evaluation equipment can substantially lessen the
time and effort required for manual critiques,
permitting developers to awareness on greater
complicated duties. However, it’s miles essential to
stability automated gear with human judgment to
ensure complete extremely good manipulation.
While automatic gear excels at detecting positive
sorts of troubles, they cann ot replace the nuanced
understanding and information that human reviewers
convey to the method.
Overall, our experimental outcomes underscore
the functionality of automatic code examine
equipment to enhance software improvement
techniques. By leveraging that equipment efficiently
and integrating it with human oversight, developers
can enhance code first-rate, lessen development time,
and decorate popular software reliability. Future
research needs to reputation on refining the ones
system to restriction faux positives and negatives and
to better address complex code problems that require
human understanding. Figure 3 and 4 shows the
comparison with an efficient code review platform.
Figure 3: Comparison with Efficient Code Review Platform
-1.
Figure 4: Comparison with Efficient Code Review Platform
– 2.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In quit, pc-coded code evaluation is a trans-formative
technique in software application software
development, providing several blessings that
embellish each daily performance and best. Through
the use of automatic de-vice, developers are able to
quickly turn into cognizant concerning capacity
issues along with syntax errors, bugs, and protection
weaknesses, to ensure that code meets installed
requirements and astonishing practices. This
automation no longer just saves time with the
valuable resources of manner of lessening the
dependence on guide assessments but additionally
encourages means of lifestyles of uniformity and
cooperation inner betterment corporations. In spite of
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
200

stressful circumstances along with pretend positives
and negatives, incorporating auto- mated code check
tools along traditional guide reviews offer a solid
platform for strengthening desirable code superb. As
software program responsibilities continue to evolve
in complexity and size, embracing computerized code
review methods could be crucial to passing on superb
applications effectively while reducing dangers
related to security loopholes and program- ming bugs.
Finally, the strategic application of computerized
code analysis tool can appreciably speed up the
improvement process, enabling teams to attain
awareness on more complex and advanced additives
of coding, thus improving the depend- ability and
performance of software programs with utility
software systems.
6 FUTURE WORK
Future work in the realm of automated code review is
poised Future paintings in the realm of automatic
code assessment is poised to be trans formative,
pushed with the useful resource of upgrades in
artificial intelligence and massive language fashions
(LLM). One promising area of studies includes the
improvement of self-analyzing LLM models that
might constantly improve via the usage of using
studying comments from builders, adapting their
pointers to better align with institution opportunities
and undertaking-specific requirements.
Further enhancements could probably incorporate
improving accuracy through schooling AI models on
historical code evaluation facts to enhance the AI’s
capability to offer context conscious guidelines tailor-
made to unique coding patterns and mission
requirements. Also, permitting for personalization of
coding requirements to align AI-driven pointers with
mission- unique fantastic practices is probably useful.
REFERENCES
A. Bacchelli and C. BIRD, ‘’Expectations, outcomes, and
challenges of modern code review,” in 2013 35th
International Conference on Software Engineering
(ICSE). IEEE, 2013, pp. 712-721.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSE.2013.6606617
A. JHindle, E.T. Barr, M. Gabel, Z. Su, ane P. Devanbu,
“On the naturalness of software,’’ Communications of
the ACM, Vol. 59, No.5, 2016, pp. 122-131.
https://earlbarr.com/publications/naturalness_cacm.pdf
A. Vaswani, N. Shazeer, N. parmar, J.Uszkoreit, L. Jones
et al., “Attention is all you need,” arXiv: 1706.03762,
2017. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1706.03762
A. M. Alshahrani et al., “Automating Code Review”, IEEE
Conference Publication, 2024https://doi.org/10.1109/I
CSECompanion58688.2023.00053
A. M. Alshahrani et al., “CORE: Automating Review
Recommendation for Code Changes,” IEEE, 2024,
https://doi.org/10.1109/SANER48275.2020.9054794
Czerwonka, M. Greiler, and J. Tilford, ‘’Code reviews do
not find bugs. How the current code review best
practice slows us down,” in IEEE/ACM 37th
International Conference on Software Engineering,
Vol. 2. IEEE, 2015 pp. 27-28 https://dl.acm.org/doi/
10.5555/2819009.2819015
D.S. Mendonca and M. Kalinowski, “An empirical
investigation on the challenges of creating custom static
analysis rules for defect localization,” Software Quality
Journal, 2022, pp. 1-28. https://doi.org/10.37190/e-
Inf250102
F. Huq, M. Hasan, M.M.A. Haque, S. Mahbub, A. Iqbal
et al., “Review4Repair: Code review aided automatic
program repairing’’, Information and Software
Technology, Vol. 143, 2022, p. 106765.
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2010.01544
J. Smith et al., “Towards Automating Code Review
Activities,” arXiv,2021. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2021.02
518.pdf
M. Staron, W. Meding, O. Soder, and M. Back,
“Measurement and impact factors of speed of reviews
and integration in continuous software engineering,’’
Foundations of Computing and Decision Sciences, Vol.
43 No. 4, 2018, pp. 281-303.http://dx.doi.org/10.1515
/fcd s-2018-0015
M. Staron, M. Ochodek, W. Meding, and O. Soder, “Using
machine learning to identify code fragments for manua
review’’, in 46th Euromicro Conference on Software
Engineering and Advanced Applications (SEAA),
IEEE, 2020, pp. 513-516 http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/S
EAA51224.2020.00085
M. Hasan, A. Iqbal, M.R.U. Islam, A. Rahman, and A.
Bosu, “Using a balanced scorecard to identify
opportunities to improve code review effectiveness: An
industrial experience report’’, Empirical Software
Engineering, Vol. 26, No. 6, 2021, pp. 1-34.
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2101.10585
N. Fatima, S. Nazir, and S. CHUPRAT, “Knowledge
sharing, a key sustainable practice is on risk: An insight
from modern code review,” in IEEE 6th International
Conference on Engineering Technologies and Applied
Sciences (ICETAS). IEEE, 2019, PP. 1-6.
http://dx.doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2020.0110160
Umut Cihan, “Automated Code Review in Practice,” arXiv,
Vol. 2412.18531 2024. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv
.2412.18531
Umut Cihan, “Automated Code Review in Practice,” Vol.
2412.18531, 2024. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.241
2.18531
Ying Yin, et al, “Automatic Code Review by Learning the
Structure Information of Code Graph’’, Big Data
Analytics and Intelligent Computation to Advance
Novel Applications, 23(5), 2551. https://doi.org/10.33
90/s23052551
Automated Code Review Assistant
201
