
QR Code‑Based Smart Food Ordering and Payment System
K. Lokeshnath, P. S. Yasaswini, M. Nandhini, A. Sujith, B. Siva Manikanta and M. Narendra
Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology, Rotarypuram Village, B K
Samudram Mandal, Anantapuramu, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Add Food Info, Add Tables, Scan QR Code, Choose Food for Order, Waiting List, Payment, AES Encryption,
Secure Payment.
Abstract: On the other hand, food ordering through contactless services has impacted the life of a customer more
positively in that they no longer need to visit a restaurant or food outlet to place an order. Everything is done
from wherever they may be- home or office-to hasten the transactions. This online application allows
customers to explore menus, customize their orders, and make payments. While arriving at the premises,
customers can scan a unique restaurant QR code to check table availability. In case a table is available, it will
get pop-up reserved; in case a table is not available, the customer is put in the waiting list. As soon as the table
is confirmed, one can select food, and that order is processed securely. The food ordering system has delivered
a better part of security and convenience within the QR code-based encryption system. Customers' food orders
are encrypted using AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) to ensure the encryption of data privacy and
security to be sent to the restaurant manager. These encrypted orders and secure QR codes are used for
payment. The customer makes payment without coming into physical contact with another person. So, this
totally provides a smooth, efficient, and most secure experience with fewer human contacts to ensure
convenience.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, an increase in contactless food orders
has greatly changed how customers interact with
restaurants. Thanks to modern web-based platforms,
customers can now place orders and carry out
transactions swiftly and easily from the convenience
of their smartphones or computers. The changeover
to contactless technology is thus enhancing customer
experience and helping restaurants reach new hygiene
standards and operational requirements, especially
after the COVID-19 pandemic. These platforms offer
a seamless and user-friendly interface that allows
customers to view restaurant menus at their own
leisure. There is no need for a physical menu, as
patrons can browse through an extensive selection of
their options right from their devices. This
availability of the menus greatly enhances the whole
dining experience by saving time for guests and
restaurant staff alike. It also helps lessen the
operational costs of printing physical menus, thus
contributing towards a more sustainable practice. The
process starts with QR codes; this has become a staple
in numerous restaurants. By simply scanning the QR
code using their smartphones, customers will
instantly gain access to the restaurant's online
ordering system. Because QR codes allow for the
minimum physical interaction with wait staff, they
also help maintain the safety of dining by minimizing
contact. After scanning, the system checks the
availability of the table; if a table is free, it gets
reserved for the customer right away. Still, if the
restaurant has no available tables for them, the
customer will go on a waiting list, minimizing the
inconvenience of waiting in line or approaching the
hostess. If the table is reserved successfully,
customers get to customize their orders as per
preference. They can add extra toppings, change spice
levels, request specific sides, or specify dietary
restrictions. This high degree of personalization
offered by the platform means the individual tastes
and dietary needs of each customer can be catered to
without the possible incidental oversight of into
lerances or allergens. Patrons can also find detailed
information about their dishes, including nutritional
facts and lists of their ingredients, thus fostering
transparency and trust with the restaurant's offerings.
Other features that enhance customer experience
Lokeshnath, K., Yasaswini, P. S., Nandhini, M., Sujith, A., Manikanta, B. S. and Narendra, M.
QR Code-Based Smart Food Ordering and Payment System.
DOI: 10.5220/0013879500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
169-179
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
169

include the ability to track the customer's order status
in real-time, from preparation in the kitchen to
delivery at the table. Customers also can rate the meal
or provide feedback directly through the system-a
veritable goldmine of information for restaurants on
how to improve. To complete the experience,
customers can also pay through the platform in a
secured manner. The total is calculated by the system
automatically based on the selected items, eliminating
any confusion or error. Payment methods can include
traditional ones, like credit cards, or newer and safer
options like digital wallets.
1.1 Objective of the Study
The project intents to make things easier for their
customers by bringing in an online platform that
allows browsing for menus, placing orders, and
making payments, thus limiting unnecessary physical
interaction between the customer and restaurant staff.
It increases operational efficiency by providing a
faster means to order and allowing staff to concentrate
on preparing food and serving customers. It ensures
cleanliness and safety through contactless QR code
ordering for safer dining. It provides customization of
orders, table reservations in real-time, and secure
payments. The project also works with data collection
for better insights into customers, hence reducing
reliance on physical supplies and providing for an
integrated loyalty program to benefit repeat business.
Finally, real-time order tracking and customer
surveys serve to better the overall dining experience.
1.2 Area of Investigation
The entire project revolves around various
investigation areas directing seeding towards an
effort for developing contact-less food ordering
systems. Some investigations include QR code-based
reservation against tables, menu-display, and
payment mechanism-all for a better customer journey
experience; the other revolves round an interface-
focused development of a user-friendly web-based
program to support such dimensional services in
menu viewing, food ordering, and secure payments,
which can run across multiple devices. Further
insights concern real-time table reservation and
waiting list management systems, which may also
add to customer convenience. Payment security is a
subject of investigation for the project-that involves
encrypted QR code payment-for all possible secure
transactions and confidentiality. Other parameters
investigated include user experience (UX) and
interface design in terms of overall usability
improvement in order customization and navigation.
Along with all this, the study also examines how the
efficiency of restaurants can be increased in terms of
easing processes like order-taking and payments-
increased productivity of staff in return. Data
analytics will be studied for customer insight in
preference and ordering habits to improve services
and marketing systems. Reducing physical menu and
receipt circulation is the other area of investigation in
terms of the possible environmental impact and
sustainable development-what paper-based material
would be saved. Integrated customer feedback
mechanisms will be in place to serve the purpose of
collecting insights for further systematic
improvement of the system and overall experience at
the dining table. Finally, the project investigates how
the system can adhere to health and safety standards,
minimizing physical contact and ensuring a safe
environment where both customers and restaurant
staff can feel secure. The sum of all these spaces aims
at creating a contactless food ordering system that is
both secure and efficient as well as customer friendly.
1.3 Problem Statement
In the old-style ordering in restaurants, people have to
queue up for long stretches, there would be
interaction with waiters when ordering food, and the
physical menus are not less prone to inefficiency or
error. Besides, in-person transactions also pose health
and safety risks, considering recent health concerns
across the globe, and there is no accommodation in
current. restaurant systems for fast, secure, and
personalized ordering experiences. Furthermore,
integration between ordering, reservation, and
payment processes lacks, thereby complicating the
experience both for customers and the restaurant staff.
This project seeks to counter these things by making
a contactless food ordering system integrated with
QR code technology for menu browsing, order
customization, table reservation, and payment,
creating a more operationally efficient and customer-
satisfying environment while safe and less physical
contact involved. In-dining food ordering depends on
queuing for many hours, ordering through a waiter,
and using menus, all of which can be inefficient and
highly error prone. In-person transactions can serve a
health and safety risk, especially considering recent
health issues on the global front. Existing restaurant
systems have nothing to do with fast, secure, and
personalized orders. It makes finding a solution even
more difficult because there is no integration between
the ordering process, reservation of the table, and
payment system. This project will provide a solution
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
170

into these issues by developing a contactless food
ordering integrated with QR code options. Menu
browsing ordering customization reserpvation of
tables and secure payment would increase operational
efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, safety, and
minimize physical contact. Food ordering in
restaurants has a lot to do with standing in queues for
hours, ordering via a waiter, or perusing the menu,
which is quite inefficient and highly error-prone.
Health and safety risks, especially on the global
health scale, are possible with in-person transactions.
There is nothing about fast, secure, and personalized
ordering in the existing restaurant systems. Moreover,
there is no integration between the ordering process,
reservation of the table, and payment system; this
makes the whole experience even more complicated
for both customers and restaurant staff. This project
would counter these things through the development
of a contactless food ordering integrated with QR
code options for menu browsing, ordering
customization, table reservation, and secure payment
which would then create an operationally efficient
and customer-satisfying environment while safe and
less physical contact is involved.
2 RELATED WORK
Contactless Food Ordering System: This study
emphasizes the benefits of QR code-based ordering
systems in reducing physical contact, streamlining the
ordering process, and enhancing customer
satisfaction. (S. Sunanda and Y. Mownika. (2024)).
Bytes to Bites: Investigating QR Code Menu Use
Behavior and Green Satisfaction: This research
explores user behavior towards QR code menus and
their impact on customer satisfaction, highlighting the
importance of user-friendly interfaces and efficient
design. (D. M. Ashrafi et., al. 2025) QR Based Food
Ordering System: The paper analyzes how QR code-
based systems streamline order management, reduce
wait times, minimize errors, and optimize resource
allocation in restaurants. (S. Sunanda and Y.
Mownika, 2025)
Customer acceptance of QR menu ordering
systems in luxury restaurants: This study is concerned
with understanding customer acceptance of QR
ordering menu systems in luxury restaurants by
examining user perception and behavioral intention.(
A. A. Alalwan, et al. 2017) Smart Enhancements to
QR-based Restaurant Dine-in System and Sales
Analysis: The paper identifies the automation process
of traditional paper-based menu ordering to a digital
and well-formed ordering system through QR codes
that will enhance good operational efficiency and
improve the customer experience. (R. Singh et., al.
2022) Customer perception about contactless menu in
restaurants: The interface perceived by customers is
examined, analyzing the benefits of contactless
menus such as easy navigation, enhancement of
customer service, and reduction of costs for
restaurants. There were several factors that were
selected to determine customer satisfaction
concerning drinking from the floor to the ankle while
almost every single person in the house watched, on
their phone or TV, pretending not to see.( Shahril et
al. 2024) QR Code Based Food Ordering System:
This research addresses the challenges of traditional
food ordering methods and proposes a QR code-based
system to enhance ordering accuracy and efficiency.
(V. Venkata Ramanjaneyulu et al.) Application of QR
Code for enchancing the satisfaction of customers:
The focus of the investigation is the application in the
food industry which may lead to greater satisfaction
with the end-particular revelations on technological
adoption and end-user’s engagement. QR Code-
Based Mobile Payment System for Restaurants: A
Literature Review: This review examines the
implementation and adoption of QR code-based
mobile payment systems in restaurants, focusing on
user acceptance and security concerns.( Sunanda, S.,
and Mownika, Y. (2024)) Improving the Customer
Experience Through QR Code Ordering Food: This
review refers to empirical research literature available
on QR code-based food ordering systems and
customer experience, with an element of use as well
as satisfaction levels.( Sunanda, S., and Mownika, Y.
(2024)). The pandemic slowed down but many
restaurants can operate in full capacity, which
becomes a challenge concerning staff. In this paper, a
food ordering system proposed is QR code-based.
The system automates the order-taking and billing
process. Every customer scans the QR code to access
the menu and place orders, while the system
automatically generates bills; thus, reducing the
possibility of human error. The admin interface is
accessible to restaurant owners so they can update the
menu, manage orders, and gain insights into the
business through data visualization. Machine learning
is included to forecast demand and provide better
insight for decision-making. (C.-C. Wong et al.2023).
The increasing coffee consumption in Indonesia has
caused the growth of coffee shops, including in
Bekasi. With the aim to improve customer
satisfaction, a mobile web-based ordering app for
food and beverages was developed, which uses QR
and RFID technology. The app allows customers to
order food and drinks and pay without going to the
QR Code-Based Smart Food Ordering and Payment System
171

cashier, shortening the waiting time and avoiding
food delivery mistakes. The development employed
the Kanban method, with testing involving 20
respondents who found that 65% said the ordering
process was faster and accessible, while 35% thought
it was easy to use. Subsequently, User Acceptance
Testing demonstrated that 91.4% of the functionality
was performed, making the whole process more
efficient and userfriendly. (F.A. Hidayat et al. 2024)
With the academic performance of students, higher
institutions have several dimensions, including
physical attendance in classes. Nevertheless, for the
greatest part, registration for student attendance is still
being done manually, which contributes to its
cumbersome nature and consumption of time,
especially in large courses. Most of the universities
have been managing the manual attendance for years
and still do. In contrast to the manual attendance
systems, the smart attendance system provided in this
paper was proposed and realized in order to pave way
for prospective uses of QR code as an attendance
management system that tracks and records student
attendance in lectures and exercises for all related
courses. (M. Anusha et al. 2025) The issue of food
safety has always existed, tracing back to ancient
times. In this respect, the traditional agri-food
systems do not have any systems for tracking the
produce in the event of foodborne outbreaks. This
issue can be addressed with blockchain-based
systems, but current methodologies are not easily
accessible or verifiable using mobile
devicesFoodSQRBlock, a framework targeting the
blockchain digitization of food production data, is
discussed in this paper. Through QR codes,
consumers and producers can trace and verify such
data. The paper discusses appraising the large-scale
integration of FoodSQRBlock in the cloud and
addresses how the feasibility of this framework meets
the requirements of scalability and experimental
evaluation. (Dey et al. 2021) As shopping centers are
becoming gigantic and sprawling, shoppers are found
to be really getting afflicted. A new system is
propounded which will aim to improve the shopping
experience by bringing to resolve issues regarding
standing in long queues, carrying hefty items, as well
as limited information storage as with the traditional
systems. Using QR code technology, this mobile-
based system eases the shopping activities with fast
payments, more navigable facilities, and effective
customer data mining. The products will generate QR
codes and a python program will keep scanning these
codes and creating bills based on what is purchased.
Applied Artificial Intelligence and Computing
International Conference in 2022. (K. Kaarthik et al.
2022) It enables the customer to place an order online
along with payment processing with the help of
contactless ordering, which has simply changed the
interaction between customers and restaurants.
Customers can explore menus of choice, place orders,
and pay without breaking a sweat via these online
applications. By scanning the restaurant's QR code,
customers may reserve tables, which will
automatically reserve if that specific table is
available. If occupied, it adds the customer to a Wait
List. After selecting the required food, customers can
make secure payments depending on food items
ordered. The order will be served directly to the
customer. Contactless food ordering has made a
convenience revolution and makes the dining
experience so much easier for all. (R. K. Goli, 2023)
Nevertheless, the restaurant business in developing
countries has been confronted by challenges due to
inefficiencies in order handling, resource
management, and food quality. Hence, this paper
proposes what is believed to be the best solution, i.e.
an IoT-based automated order-handling system, into
which has been incorporated many improvements in
the dining experience. The system enhances
operational efficiency apart from ensuring validity in
food orders and privacy for customers. Through
advanced technology adoption, it offers a sustainable
solution towards improving satisfaction and
profitable operation in restaurants, especially in
developing countries. Moreover, the paper reveals the
economic and operational advantages that accrue
from such implementation. (A. Sultana et al. 2024)
With the tracking and billing of orders done manually,
it becomes very difficult to manage a large dining
crowd in a restaurant. The computerized menu
ordering system, proposed here, is all about
improving the internal processes of the restaurants,
lightening the load of staff, and increasing customer
satisfaction. Now, showing the menu, ordering,
updating, and confirming orders becomes possible
with this system, making it reliable, easy to maintain,
and faster. At the same time, it will handle multiple
orders coming into the system efficiently, thus solving
a majority of the problems faced by traditional
restaurants. (S. Deivanayagi et al. 2024) This paper
intelligent centralized IoT billing system such as
RFID technology for automatic tracking of product
location and billing in malls. To take a shopping
assistant, a mobile application that is developed in
Java and Python will assist customers to find
products. The ESP8266 Wi-Fi act as a medium for
transmitting billing information to the cloud. Every
product gets RFID tagged, and the product data is
stored in EEPROM. The living calculates the total of
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
172
purchases by cloud database accessing. The system
has been designed in such a way that it would
eliminate searching for products and waiting in long
queues in malls or supermarkets. This paper presents
a contactless food ordering system that utilizes
holograms to minimize the risk of virus transmission
in restaurants. Based on the light source wavelength
distribution, the hologram-based menu ordering
system operates in both virtual and physical
environments, thus minimizing direct contact points
and creating a consequence of reduced virus
spreading. Furthermore, the paper analyzes the
features of various operational modes, which will
serve as a very important reference for researchers
working on operations and management in food
supply chains. (R. Vinifa et al. 2024)
3 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed system for contactless food ordering is
a web-based platform designed for easy meal
ordering. Through the platform, Customers can study
the menu, choose items they want to send in, get to
know the menu better in order to enrich it according
to their choice, and pay for the stuff they want. Also
incorporated is a QR code system whereby customers
can scan a restaurant's QR code. Scanning an
appropriate QR code will redirect the customer to
detailed information about the restaurant, such as
available tables and the full food menu. If a table is
free, it is automatically reserved for that customer; if
not, the customer will be placed on a waiting list. This
ordering process greatly streamlines and enhances the
customer experience while minimizing the physical
interaction between customers and staff.
3.1 Overview of Our Work
The project objective aims to create a contactless food
ordering mechanism, enhancing the experience of
dining using a web-based and QR-coded technology.
Customers explore restaurant menus, choose food
items, customize orders based on their preference,
and pay for them securely through their smartphones
or other devices. When it comes to entering the
premises, customers are able to scan a restaurant QR
code, which will be able to display the details of the
restaurant, including the information about the
available tables and a full menu. When there's an
available table, it will reserve for the customer
automatically. If there's none, the customer will be put
in a waiting list. Once a table confirms the
availability, customers can proceed and place their
orders, which can be electronically settled. The
primary features of the system include the
management of the reservation of tables, updates on
the food availability in real-time, customization of the
orders, and secure payment through encrypted QR
codes. The vision is to provide seamless, more
straightforward, efficient, and safe dining by
minimizing physical contacts of the customers with
their attendants. Not only does this illustrate better
operational efficiency in restaurants, but also
maximizes the personalized experience of the
customers, which means improved quality as far as
the potential level of service comes from, hence
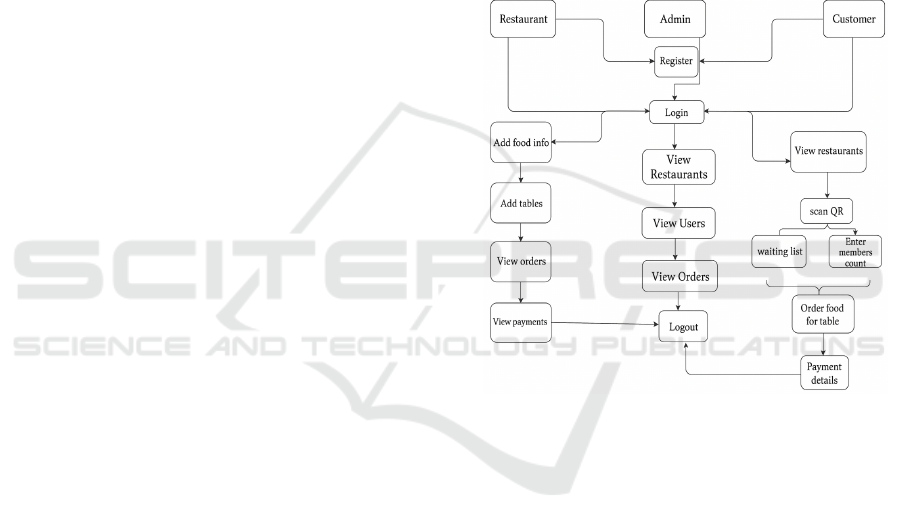
maximized customer satisfaction. Figure 1 shows the
Project Flow.
Figure 1: Project Flow.
Restaurant
• Registration: For registration, the restaurant must
provide their initial, last email, password, and
anaesthesiology, also must have a restaurant
name.
• Login: Restaurant will Login using Email,
Password.
• Add Food Info: Restaurant will add dishes and its
price in Add Food info (Dish name, price).
• Add Table’s: Restaurant will add dishes and
count of members for table in Add Tables
(Members count, Tables count).
• View Order’s: Restaurant will view the all Table
orders.
• View Payments: Restaurant will view the all
Table orders.
• Logout: Finally, Logout.
Customer:
QR Code-Based Smart Food Ordering and Payment System
173
• Registration: Customer will register with details
like First Name, Last Name, Email, password,
confirm password.
• Login: Login with details (Email, Password)
• View Restaurants: Customer view all the
restaurants by selecting the restaurant qr code
will be displayed, user has to scan the QR code
• Enter Members: After that Input field will be
displayed. In that customer has to give members
count then table will be reserved randomly.
• Waiting List: Incase table is not available that
request will be added in waiting list and he can
order food for the table. When it comes to his
time that table will be registered for the next
person
• Food Order: Customer can order the food for that
table.
• Payment: Customer will pay the bill for the
ordered food by giving his card details Logout:
Finally, logout.
4 METHODOLOGY
Advanced Encryption Standard:
AES stands for "Advanced Encryption Standard," and
it is a symmetric encryption algorithm. This is the
encryption standard selected by the U.S. government,
and there is a near-universal consensus that AES is
one of the very most secure of all the encryption
methods. AES works on data in blocks of fixed size
(128 bits), and this process uses key lengths of 128,
192, or 256 bits depending on the level of security
required. AES is a running series of rapid
encrypt/decrypt processes based on a pre-place
number of rounds depending on the size.
• 128-bit key: 10 rounds of encryption
• 192-bit key: 12 rounds of encryption
• 256-bit key: 14 rounds of encryption
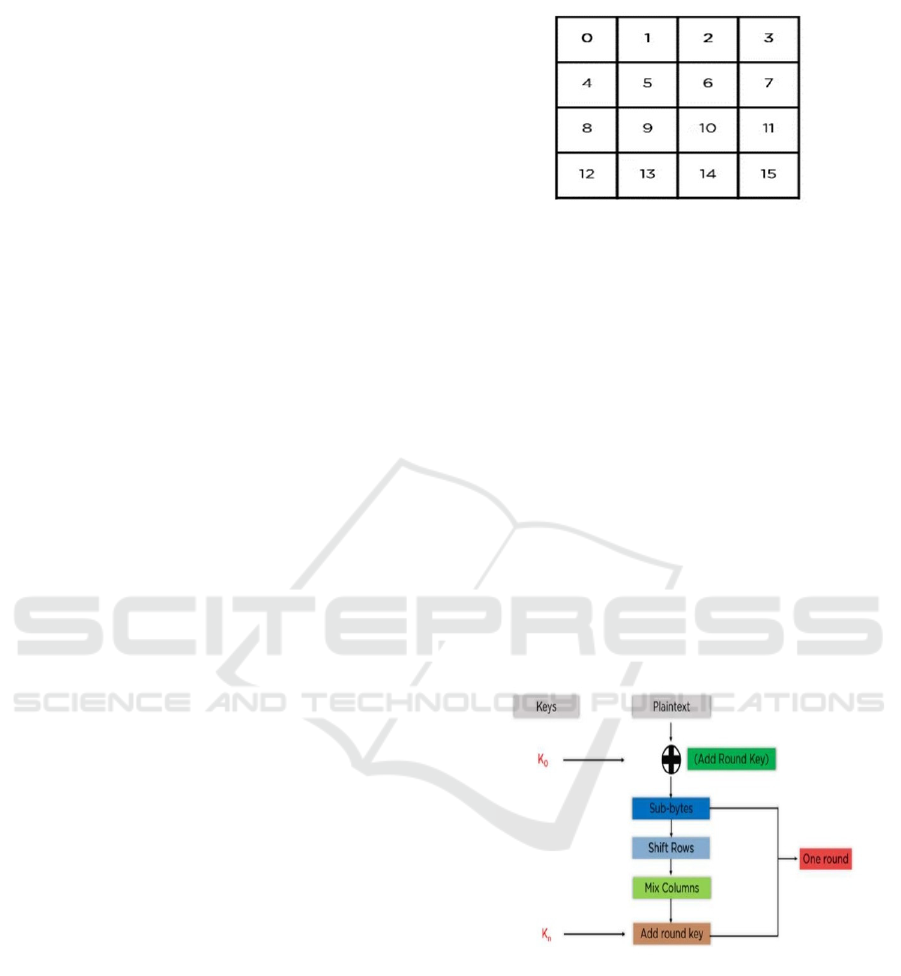
AES functions by executing data encryption through
a series of steps, each of which entails the
manipulation of a 4x4 matrix representing an
individual data block. Within this matrix, each cell
contains one byte of data. Considering that a block
comprises 16 bytes, the matrix comprehensively
encapsulates the entirety of the block's data. Figure 2
shows the Indexing of a 4x4 Grid.
Figure 2: Indexing of a 4X4 Grid.
The state array, Figure 3 illustrated in the
accompanying diagram, plays a pivotal role in the
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) algorithm. In
addition to that, the primary key will be expanded into
a total of (n + 1Plant ont ves towards AES encryption,
which is specifying their number n for the rounds in
the encryption. For instance, in case of using 128 bits
Key and for 16 rounds then maximum of 11 keys will
be generated (i.e. 10+1,). AES Encryption Stages
consist of processes like Sub Bytes, Shift Rows, Mix
Columns, and finally Apply Add Round Key. iteration
state appropriate for the number of rounds. The
aforementioned discussed steps change the input
plaintext into ciphertext using the keys generated
from them. This article briefly introduces the
constituents of the AES algorithm as well as the steps
through which it processes encryption.
Figure 3: Simplified Block Diagram of One Round of the
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
This Figure 4 necessarily follows an orderly set of
operations for each block and then combines them
into the address for one ultimate ciphertext. Stages
would follow in the order: Adding a round key: This
amounts to a XOR operation on the block data in the
stated array and the first generated key (K0). This is
followed by feeding the output state array to the next
operation.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
174
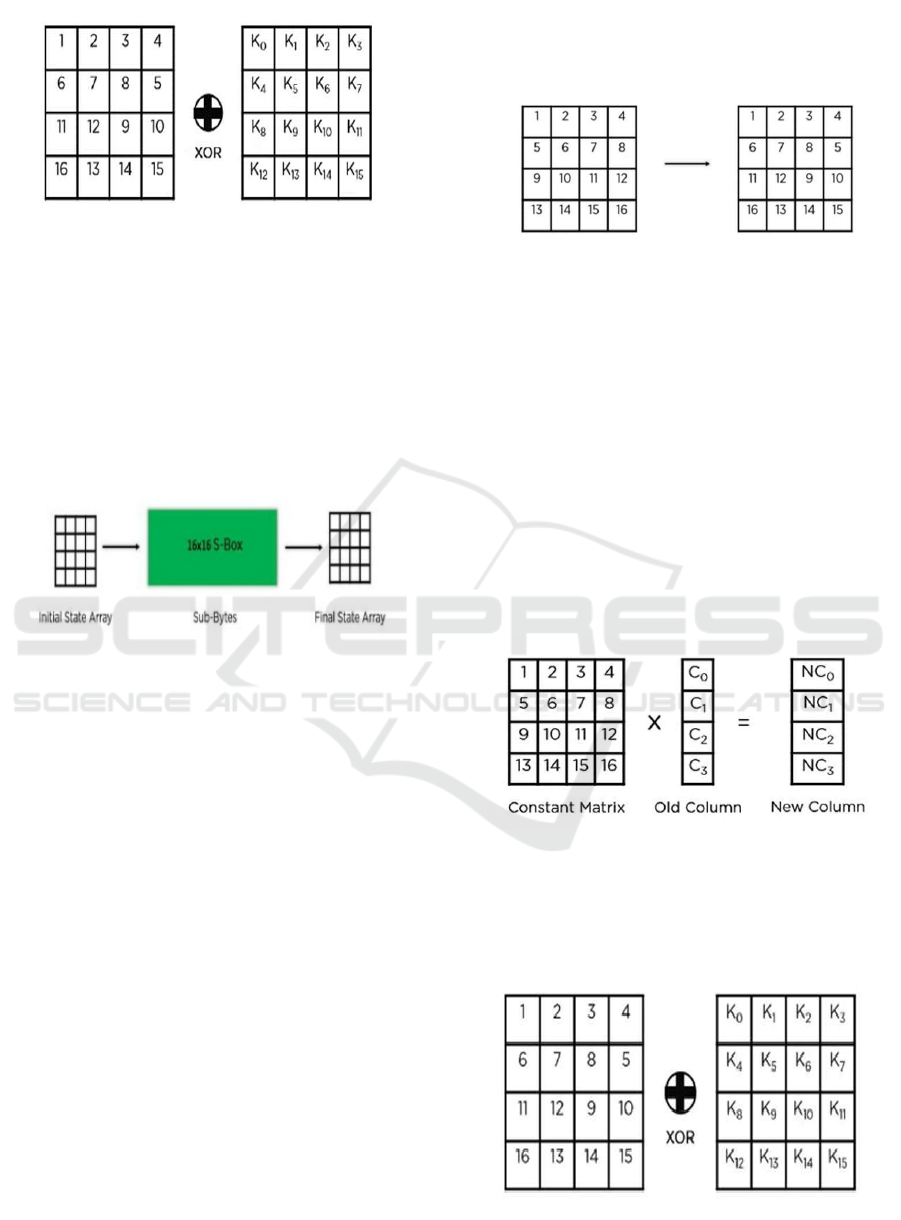
Figure 4: Example of the Add Round Key Operation in
AES.
State-by-state State-substitution on each byte
indicates the process whereby a substitution is applied
to each byte in the state array with every byte being
changed to 2 segments indicating rows and columns
in hex format, replaced by new values from an S-Box-
by-picture or contesting state array.
Illustration of the
SubBytes Transformation in AES Shown in the
Figure 5.
Figure 5: Illustration of the Sub Bytes Transformation in
AES.
Shift Rows is an operation of data modification
entailing the interchange of row elements. It usually
leaves the first row intact and shifts the elements of
the other rows left by a certain number of places. For
example, in a four-row matrix, the two-row elements
can shift an amount of one point on the left. The three-
row elements could shift an amount of two points on
the left. Likewise, the elements in the last row can
shift by three left points. This kind of operation is an
integral part of the security enhancement and ease of
distribution of several encryption methodologies,
including the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
Shift Rows is really an operation pertaining to
data manipulation in which they can interchange row
elements. Normally, it keeps the first-row static and
moves other's components in subsequent rows after a
certain number of places to the left. For example,
elements present in row two of four-row matrix would
be shifted one place to the left; while those present in
the third row would displace two positions left.
Likewise, the final row's elements could shift three
positions to the left. Such an operation, important for
security improvement and ease of distribution in
several encryption methods including the advanced
encryption standard (AES), is the basis of some
encryption methods. Figure 6 Shows the Example of
the ShiftRows Transformation in AES.
Figure 6: Example of the ShiftRows Transformation in
AES.
The mixing columns stage is correspondence in the
AES encryption method. This stage multiplies all the
columns in the state array by a fixed matrix to create
an entirely new column for the next state array. This
process continues for all the columns of the state array
into state arrays for the next step. This is to be
underscored as it is performed in all rounds of
encryption, except in the last round.
From the Figure 7 SubBytes operation followed
by ShiftRows, and MixColumns of the data of the
first round, the round key is then added. The round
function's state array is XORed with the
roundspecific key. If the state array is from the last
round, it will produce the ciphertext of the block.
Figure 7: Illustration of the MixColumns Transformation in
AES.
Otherwise, it serves as the new input state array for
the subsequent round. Detailed View of the
AddRoundKey Operation Shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8: Detailed View of the AddRoundKey Operation.
QR Code-Based Smart Food Ordering and Payment System
175

The extracted State array must be passed on as input
to the subsequent round, observing the similar
operating of the same as heretofore discussed. Here is
what you should do for that:
Round Key Addition:
Figure 9 shows the Numerical Example of the
AddRoundKey Operation in AES.
Figure 9: Numerical Example of the AddRoundKey
Operation in AES.
Sub-Bytes: To obtain a whole new state array, the
elements are passed through a 16x16 S-Box. Resulting
State Array After A Round of AES Operations Shown in the
Figure 10.
Figure 10: Resulting State Array After a Round of AES
Operations.
Shift Rows:
The process of the Numerical Example of the
ShiftRows Transformation, using specific
hexadecimal values, is demonstrated in Figure 11.
Figure 11: Numerical Example of the ShiftRows
Transformation.
Mix Columns:
Figure 12 provides a numerical example illustrating
the MixColumns transformation.
Figure 12: Numerical Example of the MixColumns
Transformation.
Add Round Key:
Figure 13 provides a numerical example of the
AddRoundKey operation specifically for the first
round of the process.
Figure 13: Numerical Example of the AddRoundKey
Operation for Round 1.
The past round-final ciphertext is now that state array.
For this round, this state array serves as input to round
number two. Repeat steps one through ten until round
10 is achieved; at that point, you'll have the final
cipher text, subject to length of the key. Figure 14
illustrates the final state of the data after undergoing
10 rounds of the AES algorithm, along with the
resulting ciphertext output.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
176

Figure 14: Final State Array and Ciphertext Output After
10 Rounds of AES.
The architecture for cloud data access, along with
a visual representation of a possible security threat, is
outlined in Figure 15.
Figure 15: Cloud Data Access and Potential Attack
Scenario.
4.1 Working
The contactless food ordering system operates by
initiating the view of the restaurant order portal with
a unique QR code scanned by customers found on
their tables or at the entrance. Information regarding
the restaurant, such as its location, opening hours, and
promotions is displayed on the platform along with a
menu available for browsing by customers. Once
within the menu, customers customize their orders by
selecting food items while indicating preferences
such as toppings or spice levels and nutrition details.
The system checks table availability, reserving tables
for customers if available; otherwise, customers are
placed on the waiting list.
Once the table is confirmed, then from this
juncture onwards, they make payment through
secured payment methods available on the platform
like credit cards or mobile wireless wallets. The
transactions protect the customer's payment
information through encryption of data, which further
adds to the security of transactions by AES
(Advanced Encryption Standard). After the payment,
the restaurant staff receives the order for preparation
and real-time status updates for customers on their
orders via the platform, with food delivery to the
reserved table as soon as it is ready. In addition, after
the meal, customers have the opportunity to rate the
service and provide feedback through the system,
which the restaurant can review for service
improvement. Overall, the convenience of the system
reduces contact for the comfort of the customers in
terms of payments with security and, in fact, a
pleasant experience from order to payment.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The implementation of the contactless food ordering
system has brought forth remarkable improvements
in customer experience, as well as the overall
restaurant's operations. The contactless system
embedded QR code technology into table reservation,
menu browsing, and secure payment processing,
providing a smooth and efficient experience to
customers. Customers could simply scan the QR code
fixed in the restaurant to view the menu, check the
real-time availability of tables, and order with ease.
This eliminated not only the need for the physical
menu but also the time during which the customers
were made to wait for the waiters to come and take
their orders. Thus, wait times were considerably
reduced, and customer satisfaction was enhanced.
The real-time feature for table reservation could enter
customers into the system from which the tables are
assigned automatically if available or put on the
waiting list should the restaurant be fully booked.
This implied that long queues for seating
arrangements and misleading table availability were
avoided. The very customizable ordering process has
thus been of paramount benefit to customers, giving
them a greater say in their meal selection to suit their
own dietary needs and tastes. In the context of
security, the payment AES encryption was quite
effective in ensuring that sensitive financial
information remained uncompromised. Customers
felt comfortable and secure using the platform for
their payments because they were assured that no one
could trace their transaction details as these were all
QR Code-Based Smart Food Ordering and Payment System
177

encrypted and kept private. The payment interface of
the system was user-friendly, thus further enhancing
customer experience by allowing customers an easy
and efficient way to make the transaction without
facing direct interaction with the waiters. There was
also an improvement in the restaurant staff's
operational efficiency. Eliminating manual order-
taking allowed staff to work more on food preparation
and customer service, thus increasing service speed
and decreasing human error. Additionally, customer
preferences and ordering trends were captured as rich
data by the platform, granting the restaurant insight
into popular menu items and customer behaviors,
thereby helping to reorient marketing and improve the
entire dining experience. However, challenges arose,
mainly with keeping the QR code system running on
different devices, especially with regard to
availability and maintenance. Some customers faced
small challenges accessing the platform mainly due to
compatibility issues of their devices or limited
internet connectivity. Continuous updates and
troubleshooting protocols have been put in place to
solve these issues and keep the system operational. In
addition, quite a few customers have had initial
difficulties using the platform, indicating that instead
of an improvement in UI design and guidance; greater
attention may also need to be channeled towards
usability. Consequently, it can be drawn that, through
enhanced security, convenience, and operational
utility, the contactless food ordering system has
dramatically improved the dining experience.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
Conclusively, the contactless food ordering system
has successfully altered the conventional dining
experience by taking advantage of modern
technology to help enhance client satisfaction and
operational efficiency. Customers can easily access
restaurant services with little physical interaction
thanks to QR codes for table reservations, menu
viewing, and secure payments. The use of AES to
encrypt transactions ensures that the customers feel
confident about the personal and payment data safety.
It has real-time table reservation and waiting list
management functions to Ensure Simplification of
The Whole Process by Cutting Down on Waiting
Time and Improving the Entire Dining Experience.
This system has also enabled restaurants to
compile valuable customer data that informs business
decisions for improving services catered to customer
preferences. In sum, it provides a seamless and secure
solution for customers and restaurant personnel alike,
thereby ushering in a new standard for the restaurant
industry.
For future development, there are other
enhancements to be added to further improve the
system. Making it multi-language will accommodate
a diverse clientele, thus widening the platform's
accessibility to an even larger international audience.
Loyalty and reward offerings would generate repeat
customers by offering discounts, free items, or
exclusive deals in accordance with their order history.
Such personalized recommendations suggested items
that genuinely improve the dining experience, truly
based on something the customer is likely to enjoy.
The program could allow ordering for takeaway or
delivery through popular food delivery services. This
would result in a more advanced analytics dashboard
that could give restaurant owners greater insight into
understanding customer behavior while managing
operational issues such as popular items and peak
bachelor evening dining. Truly, a voice ordering
feature should be considered for a more convenient
and hassle-free experience, especially for impaired
customers. It would also help increase restaurant
visibility if social media sharing options were
integrated. AI chatbots could steer customers through
the menu and questions. Adding these enhancements
would make the contactless ordering system much
friendlier for users and increase the efficiency and
versatility of operational dynamics for the restaurants.
REFERENCES
"Menu Ordering Application using QR Code with User
Experience Analysis" F.A. Hidayat, T. Rubianto,
Nurkhasanah, I.P. Saputro, V.E. Ticoalu, and T.
Prasandy//2024 9th International Conference on
Business and Industrial Research, ICBIR, 01-05, May
2024.doi:10.1109/ICBIR61386.2024.10875903.
"PDF": The Study of Customer Perception on Contactless
Menus at Restaurant- Mar. 14, 2025 [Online].
Available:https://www.researchgate.net/publication/37
2322401_The_Study_of_Customer_Perce
ption_on_Contactless_Menus_at_Restaurant
"QR Code Based Smart Trolley Using Mobile."
EBSCOhost. Accessed March 14, 2025. [Online].
Available:https://openurl.ebsco.com/EPDB%3Agcd%
3A13%3A8358461/detailv2?sid=ebsco%3
Aplink%3Ascholar&id=ebsco%3Agcd%3A16060502
5&crl=c&link_origin=scholar. go ogle.com
A. Sultana, M. M. Billah, M. M. Ahmed, R. S. Aftab, M.
Kaosar, and M. S. Uddin, “Applications of IOT-enabled
smart model: A model for enhancing food service
operation in developing countries,” Journal of Applied
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
178

Engineering and Technological Science (JAETS), vol.
5,no2,pp.11231141,Jun.2024,doi:10.37385/JAETS.V5
I2.4937.
D. M. Ashrafi, A. Iskender, and T. Shahid, "Bytes to bites:
Investigating QR code menuuse behavior and green
satisfaction in the restaurant-scapes through a hybrid
PLS-SEM and machine learning approach," Journal of
Foodservice Business Research, pp. 1-47, Feb. 2025,
doi:10.1080/15378020.2025.2466873.
FoodSQRBlock: Digitizing the Food Production and
Supply Chain with Blockchain and QR Code in the
Cloud: Dey, S., Saha, S., Singh, A. K., and McDonald-
Maier, K. in Sustainability 2021:13:3486, March 2021,
vol. 13:6:3486; doi: 10.3390/SU13063486.
How to cite: Shahril, Z., Den, N. S. A. R., Bahari, N. A. S.
S., & Asnawi, N. I. M. (2024) Customer Satisfaction in
Using Digital QR Code Menu Ordering in Restaurant.
Journal of Tourism, Hospitality & Culinary Arts, 16(1):
820-831.
K. Kaarthik, T. Manibharathi, and D. Rakshith, QR Code
based Shopping System, in Proceedings - International
Conference on Applied Artificial Intelligence and
Computing, ICAAIC 2022, 1005-1010, 2022,
doi:10.1109/ICAAIC53929.2022.9792915.
QR Food Ordering System with Data Analytics by C.-C.
Wong, L.-Y. Chong, S.-C. Chong, and C.-Y. Law is
published in the Journal of Informatics and Web
Engineering, vol. 2, issue 2, pp. 249-272, in September
2023. doi:10.33093/JIWE.2023.2.2.18.
R. K. Goli declared that contactless food-ordering systems
are "interlinked," electronic these projects, and
dissertations, published in August 2023 and accessed
onMarch14,2025.Onlinelink:https://scholarworks.lib.c
susb.edu/etd/1771
R. Vinifa, N. Vishnu Prasad, A. Santhosh, and M.
Amarnath, "Contact-less Food ordering System in
Restaurants using hologram," Proceedings of the 2024
10th International Conference on Communication and
Signal Processing, ICCSP 2024, pp. 444-447, 2024,
doi: 10.1109/ICCSP60870.2024.10544019.
R. Singh, R. Sonje, S. Salkar, and A. Jadhav "Smart QR-
Based Restaurant Dine-In System with a Sales Report",
doi:10.1051/itmconf/20224403014.
S. Deivanayagi, K.T. Sundari, A. Kerutheka, G.M.
Kokilavani and S. Sowmiya, "Smart Menu Ordering
System," 4th International Conference on Power,
Energy, Control and Transmission Systems:
Harnessing Power and Energy for an Affordable
Electrification of
India,ICPECTS2024,2024,doi:10.1109/ICPECTS6221
0.2024.10780283
S. Sunanda and Y. Mownika. (2024). QR Based Food
Ordering System. International Journal of Research in
Engineering, IT and Social Sciences 14:1210-1227.
Accessed March 14, 2025. http://indusedu.org.
S. Sunanda and Y. Mownika, "QR Based Food Ordering
System 1," International Journal of Research in
Engineering, IT and Social Sciences, vol. 14, pp. 1210-
1227, 2024, Accessed: Mar. 14, 2025. [Online]. Source:
httphttp://indusedu.org.
Sunanda, S. and Y. Mownika. 2024. QR Based Food
Ordering System 1. International Journal of Research in
Engineering, IT and Social Sciences. 14, pp. 1210-
1227. Retrieved: March 14, 2025. [Online]. Available
at: http://indusedu.org.
Sunanda, S., and Mownika, Y. (2024). "QR Based Food
Ordering System 1." International Journal of Research
in Engineering, IT and Social Sciences, 14, 1210-1227.
Accessed: Mar. 14, 2025. [Online]. Available:
http://indusedu.org.
That is, Factors influencing adoption of mobile banking by
Jordanian bank customers: Extending UTAUT2 with
trust, In the International Journal of Information
Management, vol.37, no.3, pp.99-110, June 2017, doi:
10.1016/J.IJINFOMGT.2017.01.002, by A. A.
Alalwan, Y. K. Dwivedi, and N. P. Rana.
The paper entitled "QR Based Food Ordering System" was
published by M. ANUSHA, P. V. RAO, R.
PURUSHOTHAM, and T. P. SINGH in the
International Journal of Information Technology and
Computer Engineering, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 95-102, Dec.
2023,Accessedon:Mar.14,2025.[Online].Available:htt
ps://ijitce.org/index.php/ijitce/article/view/393
V. Venkata Ramanjaneyulu, P. Anish Kumar, B. Deepak,
and M. Lavanya, "QR CODE BASED FOOD
ORDERING SYSTEM," n.d.
QR Code-Based Smart Food Ordering and Payment System
179
