
Predictive Analytics and Generative AI for Customer Churn
Prediction and Proactive Retention
Anju Thomas, Tamizh Murugan T., P. Ranjana and Constance Xavier S.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Hindustan University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Machine Learning, Generative AI, Telecom Communication.
Abstract: Churn prediction system is the advanced analytics and machine learning based system which predicts the
customer that might churn from the business. Thus, drawing leverage from information regarding transaction
histories, behavioral patterns, engagement levels and user feedback, the system enables businesses to take
proactive measures to retain consumers, recovering lost revenue, while ensuring the long-term sustainability
of the firm. The key processes such as data preparation, feature engineering, model building and insight
generation. Next step, Generative AI takes this model a step further, making them more accurate and frequent
in predicting potential churners, to nip the issue in the bud.
1 INTRODUCTION
Effective churn prediction models rely on robust data
representations. Thus, the performance of churn
models is enhanced through robust feature selection
techniques and text mining processes. It includes
emphasis in certain features so that only the most
relevant information reaches the model, and the best
of contemporary Natural Language Processing
techniques to bring value-added insights from text-
based inputs. One way to bridge this communication
gap is to have feedback loops and crowdsource
programs to keep your models fresh with
continuously updated data sets and user-generated
content. Models are constantly consumed, modified,
and re-consumed as output, which allows for dynamic
refinement of models.
Feedback loops are an essential part of improving
model performance which helps with updating the
results regularly so that the models can still provide
higher accuracy. Also, generalizability will help
models be accurate for new and unseen data, making
them more robust and applicable to different settings.
Overall, these techniques collectively improve the
performance and reliability of machine learning
models for churn prediction, resulting in more
effective solutions. Churn prediction models are
critically reliant on the quality of the data
representation. Improved feature engineering and
textual data mining processes can significantly
enhance the quality of these representations. This
includes creating features from existing variables,
aggregating data points, and using statistical methods
to make sure that features created are robust and
informative. Unlike general data mining, however,
textual data mining deals with unstructured text data;
it deals with unstructured text data by processing and
analyzing unstructured text data to retrieve
information. These include techniques such as NLP,
sentiment analysis, and topic modeling, which assist
us in transforming the unstructured text data into
structured features that we would feed into the
predictive model. These need to be fine ginned
constantly and continuously to stay accurate while
being able to perform specific tasks. This involves
tons of feedback loops and crowdsourcing working
in symbiosis. The internet made it easier than ever for
customers to compare products and switch between
competitors, resulting in higher churn. Delivering
product quality and personalized experiences is
critical, as product failures are a leading cause for
customer loss. Churn is also driven by dissatisfaction
with customer service and pricing concerns. This ties
to churn rates and the rise of life changes,
subscription models and the lack of data insights. This
becomes especially critical when there are too many
unsatisfied customers — companies looking to
capture the market often spend significantly more on
acquiring new customers relative to retaining
customers already on board, which in turn increases
churn and decreases profitability. The case highlights
128
Thomas, A., T., T. M., Ranjana, P. and S., C. X.
Predictive Analytics and Generative AI for Customer Churn Prediction and Proactive Retention.
DOI: 10.5220/0013878900004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
128-134
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

important aspects for providing customer success
e.g., understanding customer needs, delivering
customer success experience, delivering on customer
service & preventing churn leveraging data analytics
and continuously iterating on product & service.
1.1 Enhancing Churn Prediction
The accuracy of churn prediction models always
depends on an effective representation of data. We
can leverage advanced textual data mining
techniques, optimizing feature engineering to derive
better representations of their data. This helps in
enhancing the efficacy and reliability of the model.
These techniques ensure that the data being fed into
the models is relevant and complete. This allows the
models to better predict client behaviour. The classic
models will help organisations to get insight about
their customers and reduce churn which eventually
boosts revenue and customer retention with the help
of advanced methodologies. Improve Data
Representation: Move towards feature engineering
and textual data mining for better susceptible data.
These include generating interaction terms, time-
based features, and using NLP techniques for
sentiment analysis and topic modeling.
We train this model on data until October 2023.
The role of feedback mechanisms is paramount here,
such as real-time updates and online learning; using
crowdsourcing to gather diverse insights and quickly
collect data.
Performance that gets better: Over time, because of
the feedback cycle, models become steadily better.
Continual learning and up-to-the-minute feedback
keep your model accurate.
Four techniques:- Generalizability: Techniques such
as cross-validation, regularization, and ensemble
methods improve the model's ability to generalize to
new, unseen data, making it more robust and
applicable.
Boosted Efficacy: We harness AutoML for
hyperparameter tuning, robustness testing, leading to
immensely superior effectiveness and reliability of
ML applications. Also, ensuring the interpretability
of the model with tools such as SHAP and LIME is
also critical.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
It evaluates the challenges encountered in this field,
such as data protection issues, the difficulty of
integrating these technologies into existing systems,
and the relatively limited real-world testing. The
results of this work highlight the importance of these
factors for the practical use of generative AI for
consumer analytics: improving predictions and
keeping a pulse with operational needs in consumer
behavior. (Mitra Madanchian et al. 2024)
Hence, this paper is tackling the problem of
improving bank churn detection with advanced
machine learning methods. It employs Random
Forest (RF) and Light Gradient-Boosting Machine
(LGBM) classifiers, combined with the
SMOTETomek method to address class imbalance
apresenting in the dataset. The paper highlights key
challenges, such as the possibility of synthetic noise
hindering the ability of the model to learn and
generalize. Potential need for other machine learning
methods or ensemble of models to achieve better
predictive performance Through this study, we
explored the use of big data analytics, creating a
trusted algorithm that is here to ensure accurate
detection of churn towards making the banking
industry more relevant in the customer retention
perspectives. (Alin-Gabriel Văduva et al. 2024).
These approaches and algorithms were used to
adapt a generative AI-augmented knowledge base
(ChurnKB) to improve feature engineering for
customer churn modeling. It overcomes fundamental
challenges like data dependence and generative AI
difficulties for efficient generalization. The study
underlines the importance of textual data mining,
along with the combination of crowdsourcing to
enhance features and using feedback loops from
classifiers to train the sample. This research aims to
improve customer prediction by incorporating
machine learning classifiers with generative AI
techniques, creating a more accurate and
comprehensive framework to predict customer churn,
which can deeply impact customer retention
strategies across different sectors. (Maryam
Shahabikargar et al. 2024).
This paper serves an interesting research on
customer churn, where the authors developed a
customer churn prediction framework based on
integrating large language model (LLM) embeddings
by the OpenAI Text-embedding-ada-002 model with
a logistic regression classifier. The work emphasizes
the necessity of using techniques after training to
reduce difference between embeddings and
predictive outcome, and highlights scalability of
models on different datasets. In addition, it
discusses major shortcomings such as limited
generalizability of certain embedding techniques and
the incapability of the model to incorporate both
objective and subjective components of churn. The
research seeks to deliver significant information to
Predictive Analytics and Generative AI for Customer Churn Prediction and Proactive Retention
129

extend churn prediction accuracy and improve
programme usage and analysis through scrutinising
such practices as well as their respective limits.
(Meryem Chajia et al. 2024)
The models were evaluated using ACCURACY,
RECALL, F1-SCORE, and PRECISION
performance metrics, and the Random Forest
Classifier obtained an accuracy of 96.12%, which is
higher than that of Decision Trees. The limitations
include reliance on structured data, potential bias, and
the exclusion of advanced deep learning methods.
Data preprocessing, feature selection, and model
evaluation techniques play important roles in
improving churn prediction accuracy, according to
the study. They may guide future exploration of
ensemble learning, deep learning models and cost-
sensitive learning that can further refine our
prediction ability. (Aditi Chaudhary et al. 2023).
This study aims to classify customers in order to
predict churn using machine learning techniques.
The research focuses on imbalanced datasets and
mitigates it with the CTGAN (Conditional Tabular
GAN) and the SMOTE (Synthetic Minority
Oversampling Technique). (HSLR) model is
proposed based on hybrid stacking and logistic
regression (LR) as a meta-classifier, with random
forest (RF), extreme gradient boosting (XGB),
adaptive boosting (ADA), and light gradient
boosting (LGBM) as base classifiers. The
performance is measured with accuracy, precision,
recall, F1-score, MCC and ROC score, where
SMOTE generated data gives better results (94.06%
accuracy). The limitations of these methods might be
the absence of deep-learning techniques, the
potential bias from the synthesis of the datasets, and,
possibly, the requirement for real-time
implementation. Findings indicate the need for
future research to adopt techniques harnessing deep
learning capabilities, real-time churn prediction, and
ethical concerns around AI. (Nomanahmad et al.
2024)
We studied customer churn prediction using
machine learning algorithms primarily Support
Vector Machines (SVM). The study highlights factors
that might predict churn, including service quality,
pricing, customer satisfaction, and influence from
competitors. Data preprocessing, feature selection
and regression methods are carried out further for
customer attrition prediction. The SVM model
samples hyperplanes and maps data to higher-
dimensional spaces using kernel functions, enhancing
accuracy in classification. It suffers from some
limitations, such as being dependent on structured
data, inability to adjust to new data in real time, and
exclusion of deep learning models. Future studies
can leverage upon deep learning, real-time analytics
and more sophisticated feature engineering to
improve churn prediction accuracy. (RajaGopal et al.
2021).
The third paper is entitled "Analysis and Prediction of
Bank User Churn Based on Ensemble Learning
Algorithm," and envisages customer churn prediction
in a bank using the three ensemble algorithms
CatBoost, LightGBM, and Random Forest. On
quarterly user data, the model achieves 90% accuracy
and more than 80% AUC that not only useful in
customer retention but also marketing strategies
refinement for bank. Indeed, as the study indicates,
ensemble learning integrated with the proper return of
data can improve the prediction results, but issues
such as overfitting and data optimization must still be
addressed. (Yihui Deng et al. 2021).
The paper titled "Prediction of Player Churn and
Disengagement Based on User Activity Data of a
Freemium Online Strategy Game" explores
predicting player churn in "The Settlers Online" using
machine learning algorithms like random forests,
decision trees, and neural networks. By analyzing
player activity data and employing methods such as
sliding windows and quartile approaches, the
researchers achieved high accuracy, with AUC values
exceeding 0.99 and prediction accuracies over 97%.
However, the study acknowledges limitations in
generalizing the results to other games and highlights
potential biases and the need for fine-tuning labeling
approaches and feature selection. The findings are
particularly relevant for game developers seeking to
retain players in freemium games.( Karsten
Rothmeier et al. 2020)
The paper "Development of Churn Prediction
Model using XGBoost - Telecommunication Industry
in Sri Lanka" explores customer churn prediction
using machine learning algorithms like Decision
Tree, Logistic Regression, SVM, ANN, Random
Forest, AdaBoost, and XGBoost. Analyzing data
from 10,000 postpaid users, XGBoost achieved the
highest accuracy of 82.90%, improving to 83.13%
after hyperparameter tuning. The study highlights the
effectiveness of ensemble methods but notes the need
for better feature selection and data pre-processing to
address potential overfitting (Prasanth Senthan, et al.
2021).
3 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The system uses supervised machine learning
algorithms, particularly Random Forest, to predict
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
130
customer churn based on historical data, which allows
businesses to implement data-driven retention
strategies. Through detailed visualisations like
correlation heatmaps, distribution plots, and churn
reason breakdowns, the system delivers key insights
into customer behaviour and churn trends. For
additional insights and to assist with our task
classification, we used NLP techniques with the
textual field vectorized (using TF-IDF) and
classification models implemented to extract
appropriate reasons for customers not being happy.
Moreover, transformer-based models are also used
for summarizing customer feedback to create a
concise and actionable summary that helps decision-
makers formulate proactive retention strategies.
Using predictive analytics along with generative AI
we create a smart, powerful, and automated way to
retain customers by improving their engagement and
loyalty.
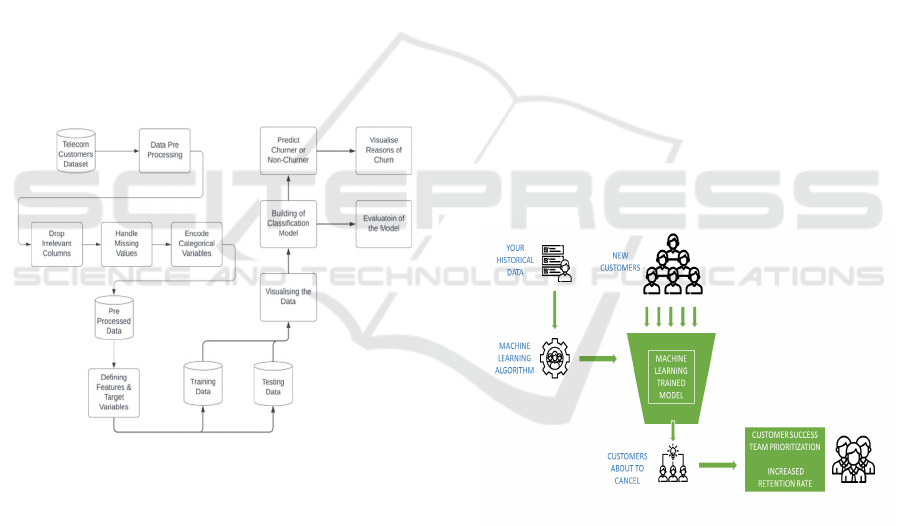
4 ARCHITECTURE DIAGRAMS
Figure 1: Overall Architecture Diagram.
The architecture diagram in figure 1 is for a simple
telecom customer churn prediction workflow. It starts
in data cleaning, such as dropping unnecessary
columns, dealing with missing data and categorical
encoding. Next, segments the data into a training and
testing with target sets and appropriate features. The
training set is analyzed in an exploratory way,
summarizing important rules, and building a strong
classifying model. Before predicting churn
likelihood, the accuracy of the model is validated
with the testing data. Lastly, charting churn triggers
helps formulate actionable steps that organizations
can take to address the issues and retain customers.
5 MODULE DESCRIPTION
Historical Customer Data Loader — this key module
collects and consolidates customer data across
different platforms (transaction histories, CRM
systems, customer interactions, social media
activities, and so on). Its primary goal is to establish
a robust dataset that captures customer interactions,
inclinations, and patterns, serving as the foundation
for predictive analytics and business intelligence.
Data ingested from different sources is the first step:
streams of structured and/or unstructured data from
multiple channels. Data cleansing and preprocessing
follows it, which involves handling missing values,
removing duplicates, and standardizing formats. The
second phase is the integration and transformation of
data: a heterogeneous set of data are integrated into a
single, uniform, structured repository; data is
featured and encoded so that its usability is optimal.
Inspired by that, and a few other various ideas for data
streaming flows, a producing pipeline would look
like this: Raw data comes from a data source (social
media, news articles, or images) It gets processed by
various rules, laws, and filters (here is where key
value-sets are applied, such as Figure ground)The
clean data is dumped into a data lake/store/warehouse
or cloud storage for scalability and quick access.
Figure 2: Workflow of Churn Prediction.
The resulting dataset fuels customer insights, churn
prediction, and personalized marketing strategies,
improving business performance as a whole.
Figure 2
illustrates the workflow of churn prediction.
Data Catalog Pre-processing Module: A system of
systematically converting raw customer data into a
formatted and structured analyzable format for
predictive analytics and AI-driven churn prediction.
First, we load the dataset, in this case using a Telco
Customer Churn dataset as the primary data source.
Predictive Analytics and Generative AI for Customer Churn Prediction and Proactive Retention
131

Processed Irrelevant Columns:Columns like
customerID are removed to reduce unwanted
attributes that do not help in predictive analysis. Data
cleaning: Missing values are an important aspect of
dataset preprocessing, and Total Charges column is
converted into a numeric format and missing data is
imputed using mean to keep the data integrity.
Handling Missing Values:
If x
i
is missing in feature X, replace it with:
𝑥
=
∑
𝑥
(1)
To prepare categorical features for machine learning,
Label Encoding is applied, ensuring compatibility
with numerical models. Example of working of label
encoding is shown in figure 3.
Figure 3: Example of Working of Label Encoding.
Furthermore, feature scaling using StandardScaler is
performed to standardize numerical values, ensuring
balanced model learning.
𝑋𝑠𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑟 =
(2)
Lastly, the data has been split into training and
testing sets for the sake of model testing. The pre-
processing pipeline encompasses crucial steps
including imputation methods for filling missing
values, feature encoding for accommodating
categorical data, scaling transformations, and data
partitioning, ultimately yielding a dataset that is
clean, consistent, and well-suited for accurate and
efficient predictive modelling. With these structured
steps, AI models can perform better at customer churn
prediction, allowing businesses to take proactive
retention measures with greater efficacy.
Churn Risk Scoring Module: a predictive
analytics engine which measures risk of customer
churn by analyzing historical data, consumer
behaviours and engagement patterns. We are
deploying methods like Feature selection, Data pre-
processing and Classification models like Random
Forest and Logistic regression, wherein Train the
module/model with available data.Churn Probability
Score (PC)
Using Logistic Regression:
Ρ(churn = 1|X) =
(
∑
)
(3)
5.1 Machine Learning Models for
Prediction (PM)
5.1.1 Random Forest (RF)
𝑓
(
𝑥
)
=
∑
ℎ
(𝑥) (4)
Following that are data clearance, missing value
filling, encoding of categorical features, feature
scaling and finally train-test dataset splitting. Then it
learns churn behaviour from the past, with the
performance metrics accuracy, precision, recall and
F1-score. In addition, AI based insights and statistical
methods (e.g., correlation analysis, feature
importance, etc.) can help further fine-tune the churn
related risk score. This scoring mechanism allows
businesses to proactively identify high-risk customers
and develop retention plans accordingly accordingly,
which in turn increases customer engagement and
reduces churn rates.
Predictive Analysis Integration: This module uses
machine learning, generative AI and advanced
analytics to forecast customer behavior and automate
retention initiatives. This facilitates customer
retention as it predicts the probability of customers
leaving based on historical behaviour, transaction
trends, and engagement metrics, allowing businesses
to design personalized retention strategies such as
targeted promotions, loyalty rewards, and proactive
customer support. Using deep learning models
(LSTMs, XGBoost, Random forest) and generative
AI, it continuously improves forecasts and adapts
strategies to real-time events. This feedback-loop
process, which is a deep learning technique, ensures
consistent improvement, thus making retention
efforts more accurate than ever. It can give businesses
higher retention, lower acquisition costs and greater
customer lifetime value (CLV).
Mathematical formulation & Algorithm
Random Forest (RF)
Prediction for Regression:
𝑦=
∑
ℎ
(𝑥)
(5)
Prediction for Classification:
𝑦 = 𝑚𝑜𝑑𝑒(
ℎ
(
𝑥
)|
𝑡 = 1,2, … , 𝑇𝑥
) (6)
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
132
Where:
T is the number of decision trees
ht(x) is the prediction from the t-th tree
6 RESULTS
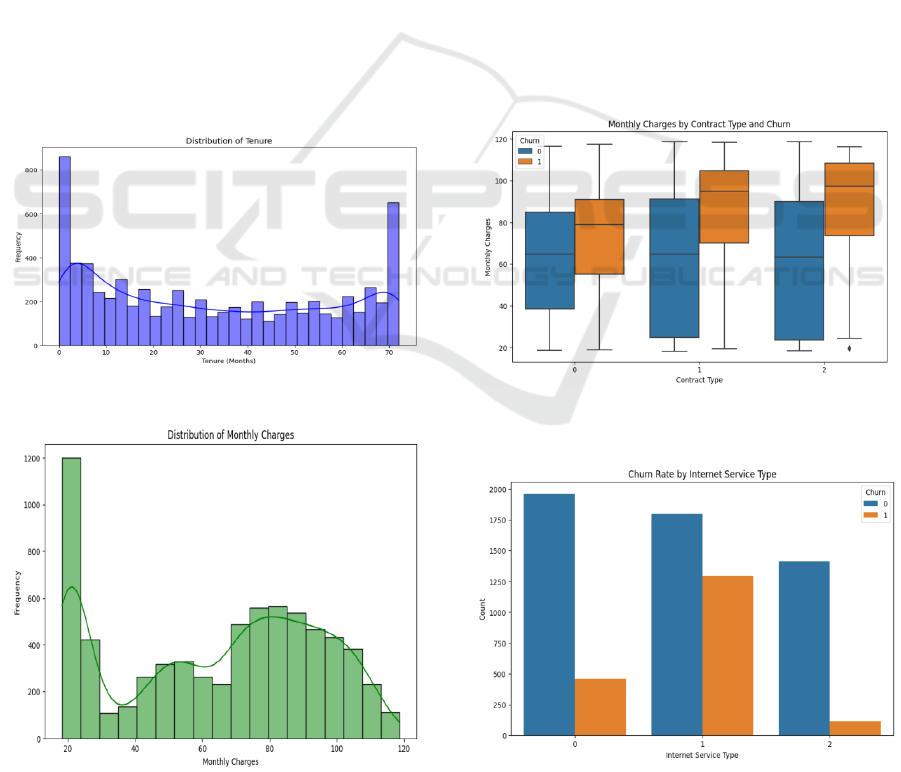
The distributions of Tenure and Monthly Charges are
shown in Figures 4 and 5 and are important
characteristics that provide crucial information about
individual instances in the dataset.
The tenure distribution is multimodal with spikes
at the start (0mo) and the upper end (70+mo). That
implies that many of these customers are either new
to the service, or have remained subscriber for some
time. The tenure distributed across intermediate
periods suggests a spreadin consumer retention.
High frequency at zero months might indicate a rate
of early contract cancellations or a very high rate of
signups. From the distribution of monthly charges,
you can see a right-skewed shape with a significant
count of charges in lower range (around 20) The
distribution slowly tapers off to larger values before
Figure 4: Distributions of Tenure.
Figure 5: Distributions of Monthly Charges.
peaking again, at around 70 to 100. By this, I mean
that, while many customers in the sample are lower-
tier customers of the company (basic plans, lower-
cost services), many customers are premium
consumers (i.e., premium or high-touch plans).
Customers with greater monthly spendings, i.e.,
those with multiple services or premium
subscriptions, occupy the right tail of the distribution.
Data Visualization − Figures 6 and 7 represent the
distributions of Monthly Charges by Contract Types
and Churn Status as well as the visual representation
of Churn Rate segmented by Internet Service Type.
Enhancing visualization of key features of dataset
provides valuable insights about the factors causing
churn behavior.
Churn analysis by contract type and monthly
charges for customers provides critical insights.
Contract Type 0 shows a diverse utilization pattern
or service packages as it has a varying price range
monthly charges. The churned and non-churned
customers are also noticabely different, Churned
customers generally tend to pay higher monthly
charges.
This tendency remains across Contract
Figure 6: Distribution of Monthly Charges by Contract
Type and Churn.
Figure 7: Distribution of Churn Rate by Internet Service
Type.
Predictive Analytics and Generative AI for Customer Churn Prediction and Proactive Retention
133

Types 1 and 2, albeit to a lesser degree. The monthly
charge data is hinting at a potential correlation
involving contract type: higher monthly charges
could lead to a higher churn rate for customers with
contract type 0 — something to consider! Churn Rate
distribution of ISPs this clearly shows that there was
a massive variation in the percentage of customers
who opted not to renew their subscription with an
ISP. Internet Service Type 0 has the most customers
while having a relatively small churn rate. Internet
Service Type 1, on the other hand, shows an
unrealistically high turnover rate, which may suggest
problems with service quality or service price.
Internet Service type 2 with lower customers has a
reasonably low churn rate too. This bimodal
distribution of churn by Internet service type is worth
investigating to understand why Internet Service
Type 1 has a higher level of churn associated with it.
7 CONCLUSIONS
This study introduces a churn prediction method that
combines feature engineering, machine learning
models, and possible deep learning advancements for
improved client retention analysis. The pipeline
consists of data preparation (missing value
imputation, label encoding, and feature scaling) and
model training with Random Forest and Logistic
Regression. The results indicate that the system:
• Outperforms simple models using feature
engineering and ensemble learning.
• Handles categorical and numerical data
efficiently, resulting in reliable predictions
even with skewed datasets.
• Provides interpretability through feature
significance analysis, which assists
organisations in identifying major churn
factors.
8 FUTURE WORK
Our churn prediction framework integrates deep
learning techniques, utilizing neural networks like
LSSTM and Transformer-based models for enhanced
sequential pattern recognition. It incorporates
sentiment analysis by leveraging NLP and the
transformers library to analyze customer feedback,
improving prediction accuracy. To optimize
performance, we implement automated
hyperparameter tuning through Grid Search or
Bayesian Optimization. Furthermore, the model is
deployed as a real-time prediction system using
Streamlit or Flask, enabling interactive and
immediate churn predictions. This comprehensive
approach empowers businesses with advanced
machine learning tools to refine customer retention
strategies, enhance decision-making, and effectively
reduce churn rates.
REFERENCES
Aditi Chaudhary, Ali Rizvi, Navneet Kumar, Ashish Kumar
Mishra, “A Novel Approach for Customer Churn
Prediction in Telecom using Machine Learning
Models”, Research Square, 2023
Alin-Gabriel Văduva, Simona-Vasilica Oprea, Andreea-
Mihaela Niculae, Adela Bâra Anca-Ioana Andreescu,
“Improving Churn Detection in the Banking Sector: A
Machine Learning Approach with Probability
Calibration Techniques”, MDPI, 2024.
Karsten Rothmeier, Nicolas Pflanzl, Joschka A. H¨
Ullmann, Mike Preuss, “Prediction of Player Churn and
Disengagement Based on User Activity Data of a
Freemium Online Strategy Game”, IEEE Transaction
on Games, 2020
Maryam Shahabikargar, Amin Beheshti, Wathiq Mansoor,
Xuyun Zhang, Jin Foo, “Generative AI-enabled
Knowledge Base Fine-tuning: Enhancing Feature
Engineering for Customer Churn”, Research Gate,
2024
Meryem Chajia, El Habib Nfaoui, “Customer Churn
Prediction Approach Based on LLM Embeddings and
Logistic Regression”, MDPI, 2024
Mitra Madanchian, “Generative AI for Consumer Behavior
Prediction: Techniques and Applications”, MDPI,
2024.
Nomanahmad Haitham Nobanee Mazharjaved Awan,
Azlan Mohdzain Ansar Naseem and Amena
Mahmoud, “Customer Personality Analysis for Churn
Prediction Using Hybrid Ensemble Models and Class
Balancing Techniques”, Institute of Electrical and
Electronics Engineers(IEEE) Access, 2024
Prasanth Senthan, RMKT Rathnayaka, Banujan
Kuhaneswaran, BTGS Kumara, “Development of
Churn Prediction Model using XGBoost –
Telecommunication Industry in Sri Lanka”, IEEE
International IoT, Electronics and Mechatronics
Conference (IEMTRONICS), 2021.
RajaGopal Kesiraju VLN P. Deeplakshmi, “Dynamic
Churn Prediction using Machine Learning Algorithms
- Predict your customer through customer behavior”,
International Conference on Computer Communication
& Informatics (ICCCI), 2021
Yihui Deng, Dingzhao Li, Lvqing Yang, Jintao Tang,
Jiangsheng Zhao, “Analysis and prediction of bank user
chum based on ensemble learning algorithm”, IEEE
International Conference on Power Electronics,
Computer Applications (ICPECA), 2021
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
134
