
Smart Sensors and Deep Learning for Recognizing Rehabilitation
Exercises
Parumanchala Bhaskar, Siddi Anitha, Siddannagari Susmitha, Katthigalla Sushma Chandrika,
Netla Harshita and Thapeta Anuradha
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Santhiram Engineering College, Nandyal, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Smart Sensors, Graph Neural Networks, Rehabilitation Monitoring, Exercise Evaluation, Motion Analysis,
Deep Learning, Patient Recovery, Remote Healthcare, Wearable Technology.
Abstract: Rehabilitation can be quite a sensitive subject, needing to monitor it closely, especially for those recovering
from drug addiction and individuals who are undergoing physical therapy. The importance of rehabilitation
in basic terms is that structured rehabilitation exercises are the most essential and play a significant role in
physical and mental wellbeing by recovering strength, mobility and stability. In this paper, we propose a
method to identify and assess rehabilitation exercises based on the usage of smart sensors and Graph Neural
Network (GNN). They capture both spatial and temporal relationship in the movement data, thus improving
the accuracy of classifying exercises. Step Two: Utilizing wearable smart sensors to collect information about
the patient's movements and physiological parameters, and a GNN model to analyse the raw data and provide
feedback for teaching patients about their health status. This leads to high-confidence tracking, few errors, no
need for manual marking, and also allows for remote patient monitoring, which improves the overall
efficiency of rehabilitation. This not only stays relevant to drug-addicted individuals in control of their lives,
but it also keeps them engaged and on track to do this effectively with excellent rehabilitation programs during
their recoveries and patients with any kind of therapy-requiring care.
1 INTRODUCTION
Rehabilitation is one of the most important necessary
aspects that individuals need after suffering from
injuries, disabilities, or addiction. These are guided
exercises, designed to restore mobility, strength and
coordination. Rehabilitation traditionally has to be
supervised in-person by physiotherapists, who make
sure patients are doing their exercises correctly. This
approach, however, comes with challenges, including
high costs, accessibility problems, and a lack of
continuous observation.
The rapid development of smart sensors and deep
learning has enabled automated rehabilitation
tracking. Wearable devices have the potential to
enable continuous assessment of body movements,
physiological data recording, and exercise pattern
detection. These systems are real time and enable
patients to correct their mistakes immediately
leading to increase in therapy adherence.
Those who break this a refreshing way to relax and
get rid of stress, for example they have physical
exercises, metadative and others to recover the mental
health and body of them. Smart sensors can monitor
movements, heart rate and stress levels, assisting
professionals in assessing a patient’s progress. Deep
learning models could analyse this data for indicators
of improvement or relapses. These technologies give
tailored feedback, getting the patients to continue
with their procedure. Furthermore, remote
monitoring enables healthcare professionals to
support patients remotely, making rehabilitation more
accessible and effective.
1.1 Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) in
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation Monitoring with Graph Neural
Networks (GNNs) A state-of-the-art deep learning
approach the connected graph modeling body
movements helps in accurate motion analysis and
precise classification of exercises. GNNs improve the
efficacy of rehabilitation by analyzing spatial and
temporal relationships in movement data. 3)
Bhaskar, P., Anitha, S., Susmitha, S., Chandrika, K. S., Harshita, N. and Anuradha, T.
Smart Sensors and Deep Learning for Recognizing Rehabilitation Exercises.
DOI: 10.5220/0013878300004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
111-115
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
111

Personalized Rehabilitation: The system adjusts
exercises according to patient progress, meaning an
optimized treatment plan is proposed, based on the
report of individual patient needs. In addition, the
system acts as an enhanced feedback system that
detects movement errors and allows for instantaneous
correction, which optimises the efficacy of exercise
while minimizing the risk of improper performance.
GNNs, with their complex architecture, improve the
scalability of the system as it is able to analyse no. of
rehabilitation exercises without the need of extensive
retraining for different conditions. Finally, this
system encourages better patient engagement by
providing interactive support and motivation to
foster adherence to rehabilitation programs over time.
GNN-based rehabilitation monitoring Toward these
advancements, a more efficient, accessible, and data-
driven rehabilitation process is ensured.
1.2 IMUs (Inertial Measurement Units)
And IMUs (Inertial Measurement Units) little
sensors that keep collect data about body motion via
acceleration, rotation, and direction. In rehabilitation
they assist in monitoring exercises without
cumbersome kit. IMUs, in conjunction with Graph
Neural Networks (GNNs), can better analyse
movements as it is able to capture different aspects of
the human skeleton. GNN GNN Link body parts to
data to assess exercise quality, abnormal motions, and
stress reactions. In addiction recovery, this
technology aids in tracking behaviors such as
stretching and breathing exercises, predicting risk for
relapse and providing immediate feedback.
Additionally, this allows for remote monitoring,
making rehabilitation more accessible and effective.
1.3 Heart Rate and GSR Sensors
These measure your heartbeat speed or sweat (GSR
or Galvanic Skin Response sensors) and stress or
relaxation. They monitor physical effort, and
emotional state, in rehabilitation.
The sensor data is processed in an ingenious
manner leveraging Graph Neural Networks (GNNs).
Each of the sensors are nodes, and GNNs link them
up to identify patterns between heart rate, stress levels
and movement. This is useful to recognizing signs of
anxiety, fatigue or risks of relapsing in addiction
recovery. Besides, GNN-based systems ensure the
rehabilitation process much more precise and
effective via real-time feedback and remoting of
control.
1.4 EEG Sensors
The patient wears EEG (electroencephalography)
sensors that pick up on electrical signals coming
from the scalp 2. And they track focus, stress and
emotional states, making them valuable in
rehabilitation and addiction recovery.
GNNs use a smart way to process the EEG data.
Among these techniques, we can highlight: Graph
neural networks: this step involves the transformation
of the brain into a network of nodes (each region of
the brain), where GNNs interlink these nodes,
allowing to learn patterns (a common characteristic
between these regions) that connect to an activity in
the brain. This aids in identifying stress, cravings or
improvement during addiction treatment. Finally,
GNN-based EEG systems foster rehabilitation
through personalization and effectiveness, thanks to
real-time insights and remote control.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
The document explores how smart sensors and deep
learning improve rehabilitation by enabling better
exercise tracking and evaluation. Traditional rehab
requires supervision from doctors or physiotherapists,
which can be costly and not always accessible. Many
patients perform exercises at home, but without
proper monitoring, they may do them incorrectly or
lose motivation, leading to slower recovery and less
effective rehabilitation.
Indeed, the Smart Sensor-based Rehabilitation
Exercise Recognition (SSRER) system tackles the
aforementioned problem by monitoring body
movements through the use of wearable sensors,
thereby utilizing deep learning to analyze exercises.
These sensors consist of IMUs, which track your
movement, heart rate sensors to check your heart
health, GSR sensors that identify the skin changes
associated with stress, and EEG sensors that record
your brain activity, including emotional states.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) is the core
of the system for movement recognition, whereas
Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs) can make data
more accurate, and Dynamic Convolutional Neural
Networks (D-CNNs) can accommodate differences in
speed and posture. Such technologies can offer real-
time feedback, monitor patients remotely, and
measure rehabilitation accurately, allowing recovery
to be more accessible, effective and tailor-made for
patients including those stuck at home.
Smart Sensor Based Rehabilitation System
Challenges Data synchronization is a challenge since
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
112
patients do the exercises at varying paces, making it
hard to align. Stimulus data with noise may produce
errors in the recognition of movements, and
variations of the same exercise will reduce accuracy.
The system is computationally intensive, preventing
real-time inference on low-power devices. Sensor
placement is not trivial; if sensors are misaligned,
results will differ. There are also new concerns
around health data being collected, and their clinical
effect needs to be validated their real-world
effectiveness will only be established once deployed.
Fixing these issues will improve system reliability
and patient outcomes.
3 PROPOSED SYSTEM
Table 1: Advantages of the Proposed Gnn-Based Rehabilitation
System Compared to Existing Systems.
Feature
Existing
Systems
Proposed GNN-
Based System
Movement
Tracking
Uses basic
motion
sensors, may
lack accuracy
Uses IMUs with
GNNs for precise
movement
recognition
Exercise
Classification
Limited to
predefined
movements
GNNs analyse
spatial and
temporal
movement
patterns,
improving
recognition
Personalization
Generic
exercise
plans, less
adaptive
Adjusts
rehabilitation
plans based on
patient progress
Error Detection
Requires
manual
supervision
Detects incorrect
movements
automatically and
provides real-
time corrections
Feedback
System
Delayed or
requires
clinical visits
Instant feedback,
improving
exercise
effectiveness
Stress & Mental
State
Monitoring
Rarely
included
Uses EEG and
GSR sensors to
track stress,
fatigue, and
emotional state
Overall
Effectiveness
Requires
frequent
supervision,
less adaptive
More accurate,
adaptive, and
cost-effective,
reducing recovery
time
The rehabilitation system proposed in this paper uses
the cutting-edge model of Graph Neural Networks
(GNNs) and includes sensor | graph} of IMUs, Heart-
rate (HR), GSR, and EEG. IMUs (Inertial
Measurement Units) track body movements to keep
posture and motion algorithms calculation straight.
For instance, if heart rate sensors measure physical
effort, gsr sensors detect stress by measuring the
sweat used by a user. Electroencephalogram (EEG)
sensors measure brain wave activity to Help measure
focus and emotions.
GNNs connect sensor data, treating each sensor
as nodes and examining the links that bind them. This
allows for accurate tracking of movements,
personalized adjustments to rehabilitation exercises,
and instant feedback on performance. The system
identifies motion errors, predicts future risk of stress
or relapse, and provides real-time corrective feedback
to maximize the efficiency of movement.
Rehabilitation becomes more accessible, interactive
and efficient as patients receive continuous support
through remote monitoring and adaptive exercise
plans. This is a smart and scalable solution that
delivers better recovery outcomes for everything
from physical therapy to addiction recovery.
The advantages of our system when compare to
existing system shown in above table 1.
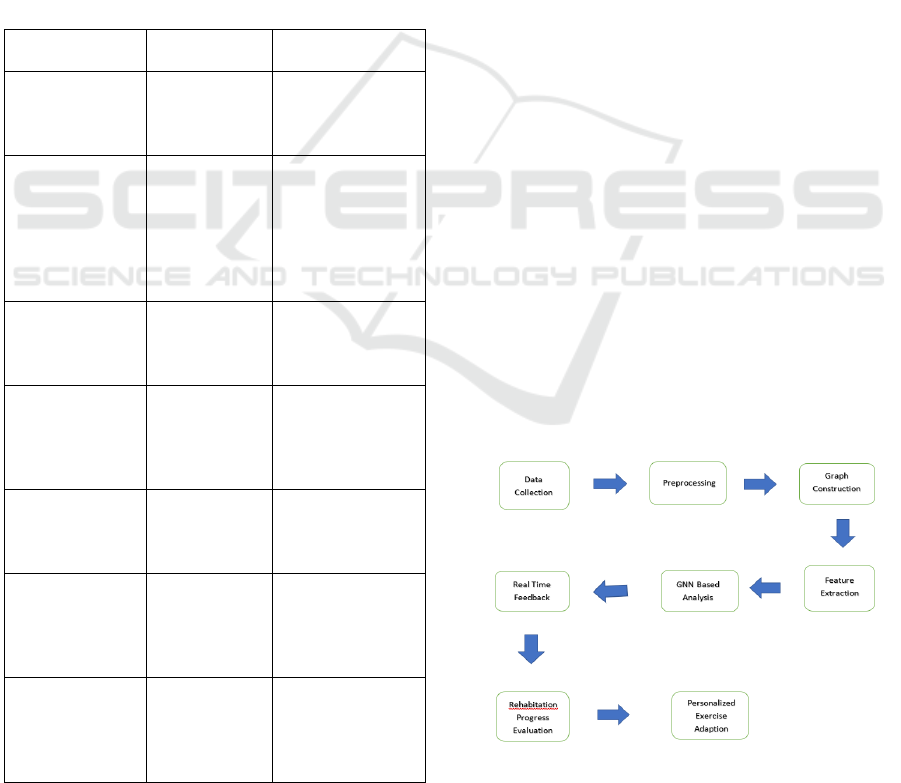
4 MODULES
To implement the proposed approach using smart
sensors and Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) for
rehabilitation exercise recognition and evaluation,
figure 1 shows the System Architecture. The system
can be divided into the following key modules:
Figure 1: System Architecture.
Smart Sensors and Deep Learning for Recognizing Rehabilitation Exercises
113
4.1 Data Acquisition Module
• Wearable Smart Sensors: Analyse motion
and physiological data (e.g., accelerometers,
gyroscopes, EMG sensors, heart rate
monitors).
• Data Preprocessing: It includes noise
filtering, signal normalising, and extracting
features from raw sensor data.
4.2 Feature Extraction and
Representation Module
• Spatial and Temporal Data Processing:
Analyse motion patterns and body
physiology trends.
• Graph Construction: Model the body
movements as a graph in which nodes
represent sensor positions (e.g., joints) and
edges capture the spatial relationship.
4.3 Graph Neural Network (GNN)
Model Module
• Graph-Based Learning Use GNNs (e.g.
Graph Convolutional, Graph Attention
Networks) to analyze movement.
• Exercise Classification: Supervised or semi-
supervised learning to identify and classify
rehabilitation exercises.
4.4 Real-Time Feedback and
Recommendation Module
• Performance Evaluation: Compare patient
movements with standard exercise patterns.
• Personalized Feedback System: Provide
corrective guidance and suggestions based
on deviations.
• Adaptive Recommendations: Adjust
rehabilitation plans based on patient
progress.
4.5 Remote Monitoring and Patient
Engagement Module
• Cloud-Based Data Storage: Securely store
patient data for longitudinal tracking.
• Telemedicine Integration: Enable remote
monitoring and interaction with therapists.
• Gamification & Motivation: Implement
interactive rehabilitation exercises to
enhance engagement.
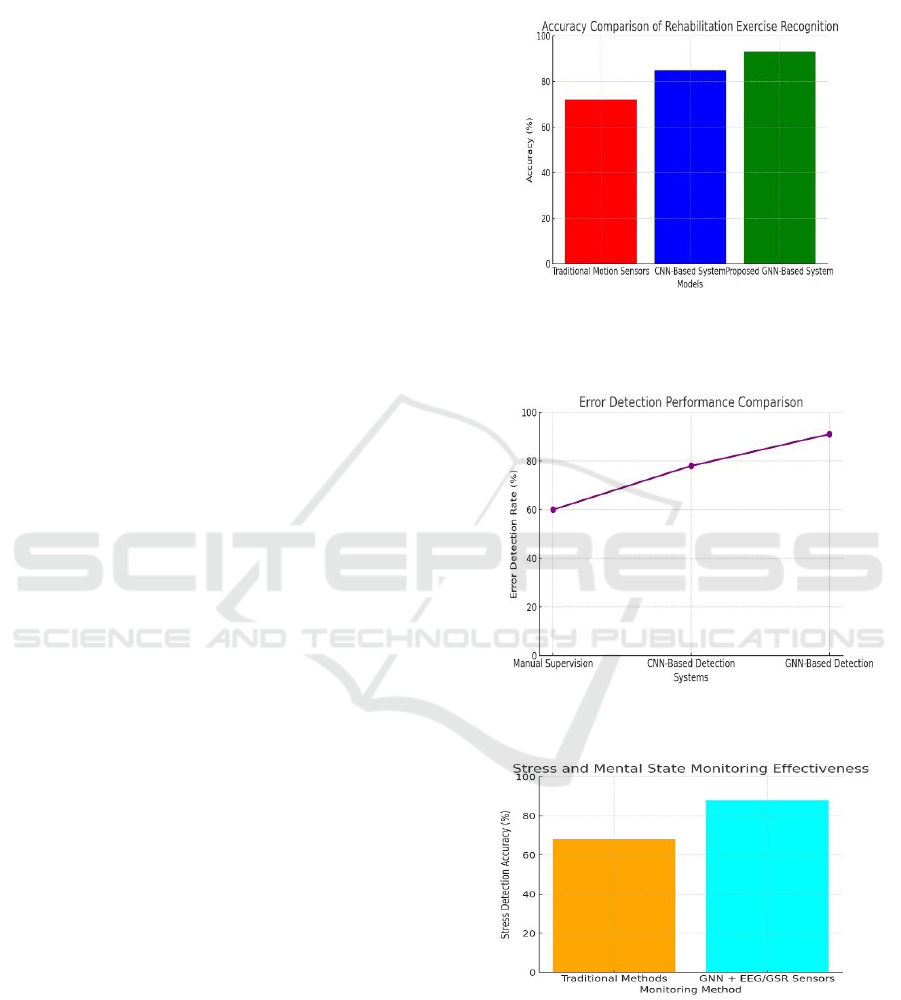
Figure 2 show the Model Accuracy Comparison for
Rehabilitation Exercise Recognition Systems.
Expected Output:
Figure 2: Model Accuracy Comparison for Rehabilitation
Exercise Recognition Systems.
Figure 3: Error Detection Rate Comparison.
Figure 4: Stress Monitoring Accuracy Comparison.
Figure 3 and 4 shows the Error Detection Rate
Comparison and Stress Monitoring Accuracy
Comparison respectively.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
114

5 CONCLUSIONS
It details a reforming framework with the help of keen
indicators and Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to
screen and investigate activities for the individuals
who are recovering from wounds or drug habit.
Wearable sensors track body movements, heart rate,
stress and brain activity. GNNs able to process this
data on the fly to generate immediate feedback and
customized workout routines. The system includes
data collection, analysis in big data analytics, and
remote monitoring, which improves accuracy and
reduces errors, making rehabilitation more effective
and accessible. It provides improved movement
tracking, stress monitoring, and automated feedback
in comparison to traditional methods. Despite issues
on the level of data matching and sensor accuracy, the
ultimate benefit of the system is that people recover
better due to improved organization and efficiency of
the rehabilitation process.
REFERENCES
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi, and G. Vijaya Bhaskar. "A priori
vs Genetic algorithms for Identifying Frequent Item
Sets." International journal of Innovative Research
&Development 3.6 (2014): 249-254.
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi. "Machine Learning Based
Predictive Model for Data Fusion Based Intruder Alert
System." journal of algebraic statistics 13.2 (2022):
2477-2483
Chaitanya, V. Lakshmi, et al. "Identification of traffic sign
boards and voice assistance system for driving.” AIP
Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028. No. 1. AIP
Publishing, 2024
Devi, M. Sharmila, et al. "Machine Learning Based
Classification and Clustering Analysis of Efficiency of
Exercise Against Covid-19 Infection." Journal of
Algebraic Statistics 13.3 (2022): 112-117.
Devi, M. Sharmila, et al. "Extracting and Analyzing
Features in Natural Language Processing for Deep
Learning with English Language." Journal of Research
Publication and Reviews 4.4 (2023): 497-502.
Mahammad, Farooq Sunar, Karthik Balasubramanian, and
T. Sudhakar Babu. "Comprehensive research on video
imaging techniques." All Open Access, Bronze (2019).
Mahammad, Farooq Sunar, and Y Madhu Viswanatham.
"Performance analysis of data compression algorithms
for heterogeneous architecture through parallel
approach." The Journal of supercomputing 76.4 (2020):
2275-2288.
Mahammad, Farooq Sunar, et al. "Key distribution scheme
for preventing key reinstallation attack in wireless
networks." AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028.
No. 1. AIP Publishing, 2024.
Mandalapu, Sharmila Devi, et al. "Rainfall prediction using
machine learning." AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol.
3028. No. 1. AIP Publishing, 2024.
Mr. M. Amareswara Kumar, effective feature engineering
technique for heart Disease prediction with machine
learning” in International Journal of Engineering &
Science Research, Volume 14, Issue 2, April-2024 with
ISSN 2277-2685.
Paradesi Subba Rao,”Detecting malicious Twitter bots
using machine learning” AIP Conf. Proc. 3028, 020073
(2024),https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0212693
Paradesi Subba Rao,"Morphed Image Detection using
Structural Similarity Index Measure”M6 Volume 48
Issue 4 (December 2024)
,https://powertechjournaI.com
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al. "Machine Learning Based
Predictive Model for Closed Loop Air Filtering
System." Journal of Algebraic Statistics 13.3 (2022):
416-423.
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al. "Incorporating Deep Learning
Techniques to Estimate the Damage of Cars During the
Accidents" AIP Conference Proceedings. Vol. 3028.
No. 1. AIP Publishing, 2024.
Parumanchala Bhaskar, et al “Cloud Computing Network
in Remote Sensing-Based Climate Detection Using
Machine Learning Algorithms” remote sensing in earth
systems sciences(springer).
Suman, Jami Venkata, et al. "Leveraging natural language
processing in conversational AI agents to improve
healthcare security." Conversational Artificial
Intelligence (2024): 699-711.
Sunar, Mahammad Farooq, and V. Madhu Viswanatham.
"A fast approach to encrypt and decrypt of video
streams for secure channel transmission." World
Review of Science, Technology and Sustainable
Development 14.1 (2018): 11-28.
Smart Sensors and Deep Learning for Recognizing Rehabilitation Exercises
115
