
Early Recognition System for Adverse Drug Effects Using NLP
Model
Narmadha R. P., Balaselsiya J., Keerthana B. and Rakiniya K.
Department of Artificial Intelligence and Data Science, KIT‑Kalaignarkarunanidhi Institute of Technology, Coimbatore,
Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Drug Identification, Adverse Effects, Natural Language Processing, Toxicity Detection, User Feedback,
Medication Management.
Abstract: This work focuses on creating an intelligent system for improving medication therapy management in
patients, with correct identification of drugs and encouragement of safer medication use. The system works
by having the patient enter a computer screen, under which it takes a picture of a drug tablet and identifies it
through sophisticated image processing algorithms that examine the shape, colour, and distinctive markings
of the tablet. After being successfully identified, the system searches a wide drug database for retrieving
essential information such as the drug's indications, chemical structure, potential side effects,
contraindications, and the potential interaction with other medications. Besides identification of drugs, the
system further employs Natural Language Processing (NLP) in order to review medical reports and patient
histories contained in the system. This centre assists in identifying abnormal patterns or repeated signs of
drug-related toxicity and allows for early intervention to avoid harmful health complications. For convenience
in use by people of all lifestyles, the system gives feedback in the form of verbal response, breaking down
complex medical jargon into easy comprehension. By combining image processing, database management,
and NLP, this system provides an end-to-end solution to medication management with the goal of minimizing
the risks involved in off-label drug use and enhancing patient safety.
1 INTRODUCTION
Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) and drug-induced
toxicity are key threats to the safety of patients and
rank high on the list of healthcare challenges. In spite
of strict clinical trials and regulatory processes,
unexpected adverse effects tend to emerge only after
the drugs are in wide use. Traditional detection
systems, e.g., post-marketing surveillance and
voluntary reporting, are usually slow and passive,
leading to delayed interventions. This project sets out
to adopt an innovative strategy that utilizes Natural
Language Processing (NLP) in processing
unstructured medical data like clinical notes,
electronic health records, and patient feedback in the
detection of ADRs at an early stage. Combining
state-of-the-art machine learning with a voice-
enabled assistant, the system not only flags potential
adverse reactions but also supplies real-time, easy-to-
comprehend feedback to clinicians for better
decision-making and more safe medication use.
2 LITERATURE STUDY
State-of-the-art transformer models like BERT have
shown excellent performance in identifying adverse
drug reactions (ADRs) from clinical texts. Such
models are very efficient at learning intricate
language patterns and medical terminology and can
be used to analyse unstructured data such as patient
records and clinical notes.(Siyun Yang &Supratik
Kar 2023).
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) have been used
with great success on patient reviews and electronic
health records (EHRs). The combined method
improves detection accuracy, although it is
associated with challenges such as high
computational requirements and risks of overfitting,
necessitating careful optimization of the
model.(Francisca Udegbe, et, al 2024).
The drug pills can be classified accurately by
using image recognition methods, and detection of
medicines is easy with high accuracy. With the help
P., N. R., J., B., B., K. and K., R.
Early Recognition System for Adverse Drug Effects Using NLP Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0013878100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
105-110
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
105

of Natural Language Processing (NLP) in toxicity
evaluation, the method is such that the end-to-end
system can deal with visual as well as text inputs,
which are suitable with the aim of early ADR
detection.(D. Mohanapriya, et, al, 2024).
Knowledge graph-based systems can associate
drug entities with their possible adverse effects and
increase detection rates. The systems give a
structured view of drug-drug interactions, side
effects, and related biomedical concepts, which
improves the interpretability of models and decision-
making accuracy.(Anu Amorim, et, al, 2024)
Machine learning algorithms are superior to rule-
based systems in detecting ADR, especially detecting
latent patterns in clinical text. Rule-based systems are
more interpretable, reflecting the accuracy-
explainability trade-off, an important consideration
in healthcare applications.(Xinxin Qi, et, al, 2024).
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks are
appropriate for clinical narrative mining since they
can understand long-range dependencies in medical
vocabulary. These models are particularly good at
identifying rare ADRs that cannot be easily identified
by simpler algorithms.(Beichang Liu, et, al, 2023).
End-to-end NLP workflows that combine named
entity recognition (NER) and sentiment analysis
make it possible for real-time monitoring of adverse
drug events. These systems can provide real-time,
actionable insights to healthcare professionals,
averting possible harm to patients.(Alexander
Tropsha, et, al 2023).
Combining image and text data through multi-
modal learning enhances ADR detection. Learning
image embeddings and text features jointly improves
model accuracy, serving as a strong solution for drug
toxicity and adverse reaction identification from
different data sources.(OladapoOyebode& Rita Orji
2023).
Pre-trained biomedical NLP models can be
transferred to ADR detection, allowing models to
generalize well to novel drugs with small amounts of
training data. This approach solves the problem of
limited data and accelerates the creation of reliable
ADR monitoring systems.(Jianxiang Wei, 2023)
NLP-powered voice-based systems can query
medical databases and provide real-time data about
drug safety to healthcare professionals. Natural
language queries enhance user interaction and make
decision-making easier, as it is easy to assess
potential drug risks through natural
language inputs(Lalitkumar Vora, et, al, 2023).
3 FINDINGS FROM THE
LITERATURE SURVEY
High Computational Cost and Complexity: Deep
learning algorithms, though capable, are
computationally intensive to train and implement.
Processing high amounts of unstructured medical
data, including patient reviews and clinical notes, is
time-consuming. Model architecture optimization or
cloud computing can be utilized to balance accuracy
with efficiency and make real-time ADR detection
more practical.
Sufficient Database Integration Requirement;
Combination of NLP models with trustworthy drug
databases, such as DrugBank, significantly enhances
ADR detection accuracy. A linked database offers the
system new drug profiles, established side effects,
and toxicity data that enable the model to provide
timely and accurate information. The combination
increases the usability of the model in real-world
applications by providing health professionals with
complete and updated information on drug safety.
4 DISADVANTAGES OF
CURRENT ALGORITHM
Limited Interpretability: Complex models are
"black boxes," whereby it is difficult for healthcare
workers to understand and have faith in the
predictions of the system.
Overfitting on Small Datasets: Models tend to have
difficulties with infrequent ADR events, memorizing
noise rather than informative patterns, which
constrains generalizability to novel data.
High Computational Complexity: Deep learning
models consume enormous computational resources
and time, thus rendering real-time ADR detection
challenging without specialized hardware.
Failure to Accommodate New or Unusual Drugs:
Algorithms are weak in the scenario of recently
released or rarely prescribed medications, especially
without continuous learning or updated databases.
Conclusion of Findings: Conclusion of the
Literature Survey early detection of drug adverse
reactions, the results indicate that approximately 50%
of the studies employ machine learning and deep
learning models in the detection of ADRs with non-
homogeneous accuracy between 50% and
90%despite being effective, the models are plagued
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
106
with drawbacks like high computational complexity,
overfitting, and lack of interpretability. The system
under development circumvents these by blending
models like Logistic Regression, Decision Trees, and
CNN with an NLP voice assistant. This method
increases precision, raises patient safety, and
facilitates quicker, better-qualified decision-making
for practitioners.
5 EXISTING SYSTEM
Currently used ADR detection and drug-induced
toxicity detection systems heavily rely on machine
learning and artificial intelligence approaches.
Decision Trees, Support Vector Machines (SVM), k-
Nearest Neighbors (KNN), and ensemble models like
Random Forests are among the widely utilized
algorithms for structured medical data
analysis.Image processing models are also used to
detect drugs by analysing visual attributes such as
shape, colour, and imprint.
5.1 Performance and Limitations
Current algorithms demonstrate accuracy between
50% and 90%, they come with significant limitations
that impact their reliability and effectiveness.
Computational Costs: High-performance models,
such as transformers and convolutional networks, are
computationally intensive, which can restrict
deployment in real-world applications.
Lack of Real-Time Feedback: The majority of
systems work with past data, and hence it is difficult
to provide instant notifications to the medical
professionals in case of critical cases.
Data Imbalance Issues:ADRs are relatively rare,
resulting in class imbalances making it difficult for
models to recognize less common but
dangerous side effects.
6 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The system to be proposed identifies the drawbacks
of current adverse drug reaction (ADR) detection
techniques and endleavors to overcome them by
combining Natural Language Processing (NLP),
machine learning, and voice-based technology. This
system increases the ability of early detection,
enhances the interaction with the user, and offers
real-time information to medical practitioners.
NLP-Driven Text Analysis: The system utilizes
sophisticated NLP models to process unstructured
medical information, including clinical notes,
electronic health records (EHRs), and patient
reviews. This enables the detection of latent patterns
and linguistic signals that suggest possible ADRs or
drug-induced toxicity.
Machine Learning Algorithms: Logistic
Regression, Decision Trees, Random Forest, SVM,
and deep models such as CNNs and LSTMs are
utilized to increase the detection rate. Models are
trained to identify drugs, classify the toxicity level,
and forecast side effects.
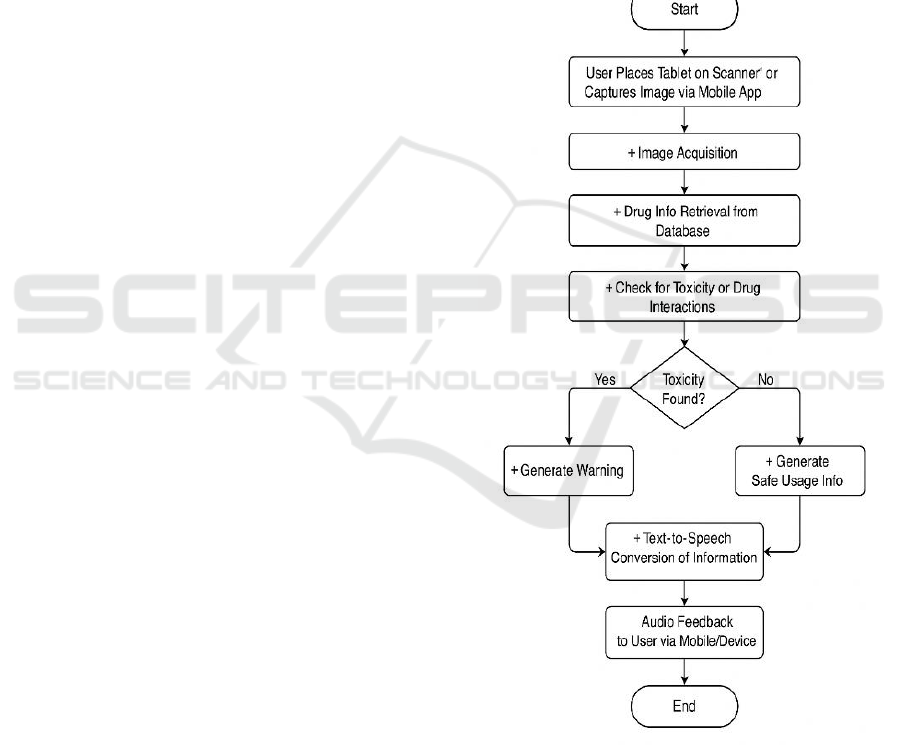
Figure 1: Drug Toxicity Detection Flow.
Image Processing for Drug Identification: The
system has an identification module that is drug
image processing based. The users are able to scan a
drug tablet, and the system reads the image and
identifies the drug type and matches it to a database
Early Recognition System for Adverse Drug Effects Using NLP Model
107
for further analysis.
Voice-Enabled Assistant: To facilitate better
access, the system comes equipped with a voice
assistant based on NLP. The medical professionals
can pose questions to the system in natural language,
e.g., querying about possible side effects or recent
ADR reports. The assistant offers voice answers,
offering instant and convenient access to
information.
Database Integration: The system interfaces with
drug databases (such as DrugBank) to fetch current
drug profiles, established side effects, and toxicity
data. The model is thus ensured to operate using the
most recent pharmaceutical data for increased
accuracy and reliability. Figure 1 shows the drug
toxicity detection flow.
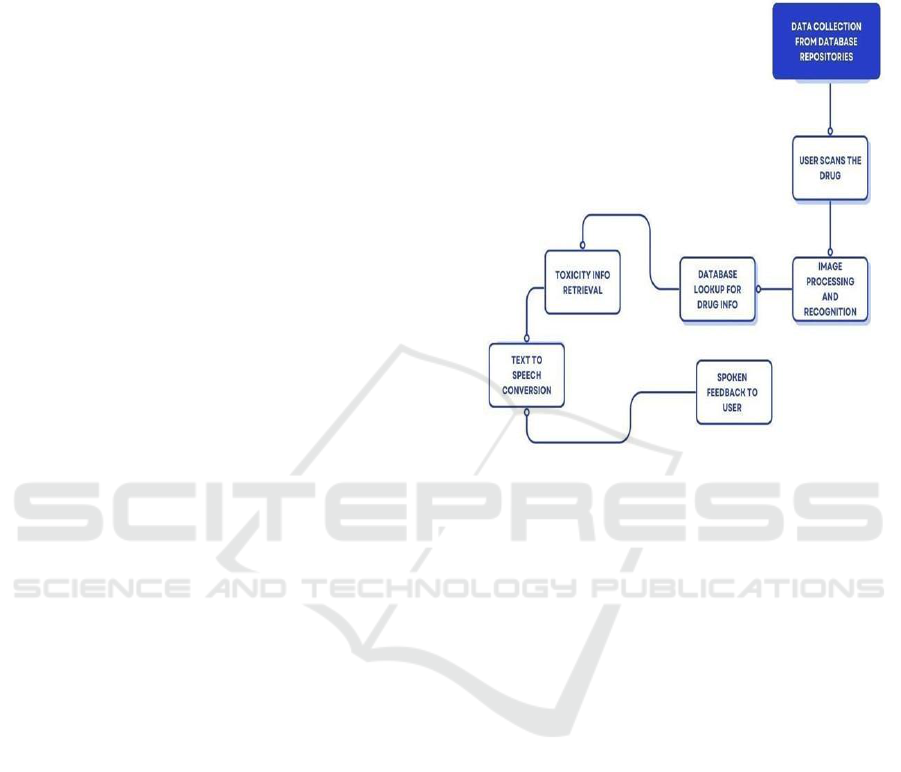
7 WORK FLOW DIAGRAMS
The proposed system process is intended to simplify
the identification of drug-induced toxicity and
adverse drug reactions (ADRs) using image
processing, machine learning, and Natural Language
Processing (NLP). Below is an overview of the step-
by-step process of the system (figure 2):
Drug Image Input: The system begins by the user
either scanning or uploading an image of a drug tablet
using a camera or mobile device. Image data is
obtained and preprocessed with libraries such as
OpenCV for quality improvement and accurate drug
identification.
Drug Identification via Image Processing: The
preprocessed image is input into a Convolutional
Neural Network (CNN) to identify the drug by its
shape, color, and imprint. The drug name identified
is taken and forwarded to the next level for further
processing.
Query to the Drug Database: The discovered drug
is compared with an extensive drug database (e.g.,
DrugBank). Relevant information, including drug
composition, usage, potential side effects, and known
ADRs, is retrieved.
Text Data Analysis with NLP: Unstructured
medical data, such as clinical notes, EHRs, and
patient reviews, is processed using NLP models (like
BERT or BioBERT). The NLP model scans for
adverse effect mentions, linguistic patterns, and
correlations between drug names and toxicity reports.
Machine Learning-Based ADR Prediction: The
extracted text is then fed into machine learning
models (such as Random Forest, SVM, LSTM) to
foresee potential ADR risks. The model gives a risk
score or prediction of whether the drug is associated
with any side effects.
Figure 2: Drug Identification and Feedback System
Workflow.
Voice-Enabled Feedback: It has a voice assistant
that reads out the results in sound feedback.
Physicians or consumers can ask questions like
"What are the side effects of this drug?" and receive
instant, natural language responses.
8 EXPECTED OUTCOMES
The proposed system is expected to significantly
enhance drug safety surveillance using the
application of image processing, Natural Language
Processing (NLP), and machine learning for on-time
detection of drug-induced toxicity and adverse drug
reactions (ADRs). By integrating a combination of
different technologies, the system will provide rich,
real-time data to health professionals, allowing them
to make decisions and prevent patient harm.
Accurate Drug Identification: The module for
processing images will reliably identify drug pills
with high accuracy and minimize chances of
medication mistakes (figure 3).
Early Detection of ADRs: Adverse reactions
detection via NLP will effectively spot issues from
patient testimonials, clinician notes, and electronic
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
108
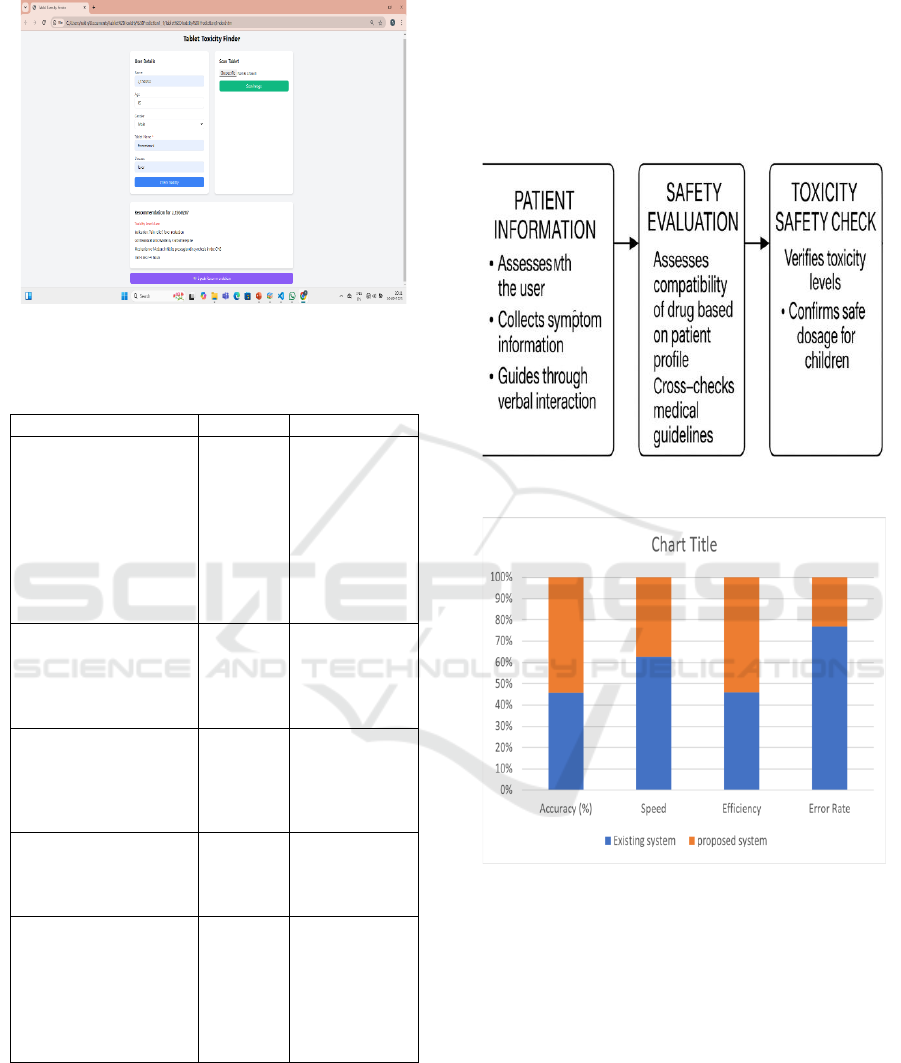
patient data, ensuring intervention at the early stage.
Figure 3: Tablet Toxicity Finder – User Interface
Dashboard.
Table 1: Ml Algorithms: Accuracy & Use Cases.
Algorithm/Technology
Accuracy
Advantages
CNN (Convolutional
Neural Networks)
90%
CNNs are
good at
processing
sophisticated
images and
can learn
automatically
sophisticated
features.
KNN (K-Nearest
Neighbors)
90%
KNN is easy
to use and
works well
with small
datasets.
Logistic Regression,
Naïve Bayes, Random
Forest, Decision Tree,
Support Vector
Machine
>95%
Prediction of
toxicity
Linear Regression,
Random Forest
>92%
Recommended
Dosage and
Usage
Guidelines
ANN (Artificial
Neural Network)
90%
Versatile
ANNs can
efficiently
manage
almost any
audio-related
task.
High Accuracy Predictions: Medications will be
determined based on risk profiles with high accuracy
rates of predicting potential ADRs and toxic levels by
drug models.
The voice assistant: The voice assistant will provide
immediate verbal feedback to healthcare providers,
whereas the system delivers real-time warnings for
high-risk medications to allow timely
clinical intervention. Table 1 shows the ML
Algorithms: Accuracy & Use Cases.Figure 4 shows
the Voice-Driven Drug Safety Interface. Figure 5
shows the performance comparison between existing
and proposed systems.
Figure 4: Voice-Driven Drug Safety Interface.
Figure 5: Performance Comparison Between Existing and
Proposed Systems.
9 CONCLUSIONS
The system of early detection of ADRs and drug-
induced toxicity proposed in this work integrates
image processing, NLP, and machine learning to
improve patient safety and assist clinical decision-
making. With automated drug identification, medical
text analysis, and real-time feedback via a voice
assistant, the system presents an active method for
monitoring drug safety. This approach overcomes the
Early Recognition System for Adverse Drug Effects Using NLP Model
109

shortcomings of the conventional methods,
minimizes medication-related harm risk, and works
towards safer and more effective healthcare
practices.
REFERENCES
Alexander Tropsha, OlexandeIsayev, Gisbert Schneider &
Artem Cherkasov (2023) – This research highlights
how deep learning and QSAR modeling are changing
drug discovery, making the process smarter and more
precise. Found in the Journal of Discovery.
Anu Amorim, Luiz Piochi, Ana Gaspar, Antonio Preto,
Nicia Ferreira & Irina Moreira (2024) – A glimpse of
how computational models can anticipate drug toxicity
at an early stage in the development process, making
drugs safer even before they reach patients. It is in the
Journal of Chemical Research in Toxicology.
Beichang Liu, Guoqing Cai, Jili Qian, Tiambo Song &
Quan Zhang (2023) – A team of scientists developed a
machine learning-based system for the identification of
drugs more accurately and efficiently. Published in the
International Journal of Computer Science and
Information Technology.
D. Mohanapriya, Jyothi Chepur, Deepali Hirolikar, K.
Sundareswari, Kiran Pokkuluri& R. Subbulakshmi
(2024) – This research centers on the application of
machine learning to classify patient drug reviews and
identify adverse drug reactions. Published in the
Journal of Measurement Sensors.
Francisca Udegbe, OgochukwuEbulue, Charles
Ebulue&ChukwunonsoEkesiobi (2024) – A dive into
using machine learning in drug discovery, its
advantages, and the challenges to researchers. Featured
in the Journal of Computer Science & IT Research.
Jianxiang Wei, Tianling Hu, Jimin Dai, Ziren Wang, Pu
Han &Weidong Huang (2023) – This article discusses
how AI is able to identify mentions of adverse drug
reactions from text through the use of deep learning and
NLP methods.
Lalitkumar Vora, Amol Gholap, Keshava Jetha, Raghu
Thakur, Hetvi Solanki & Vivek Chavda (2023) –
Review of the new advancements in drug research, i.e.,
how AI is making drug side effects more identifiable
and understandable. Published in the Journal of
Pharmaceutics.
OladapoOyebode& Rita Orji (2023) – A fascinating study
on how AI and natural language processing (NLP) can
analyze patient reviews on social media to detect
possible drug reactions. It is in the Journal of Health
Informatics.
Siyun Yang &Supratik Kar (2023) – This article explores
how AI and machine learning can be used to detect
adverse drug reactions and toxicity at an early stage,
leading to improved patient safety. It is in the Journal
of Artificial Intelligence Chemistry.
Xinxin Qi, Yuanchun Zhao, Zhuang Qi, Siyn Hou &Jiajia
Chen (2024) – This article discusses the application of
machine learning to drug discovery and encompasses
its potential, practical applications, and some of the
challenges that researchers must face. It is in Journal of
Moleculars.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
110
