
Revolutionizing University Placements: Advanced Technologies for
Streamlined and Student‑Centric Ecosystems
N. V. S. Sanjana, Mekala Varun, M. Greeshma, Sumanth Ponugupati,
Gurupriya M. and Gayathri Ramaswamy
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Bengaluru‑560035, Karnataka, India
Keywords: Placement Cell Automation, Deep Learning, Pattern Recognition, Job Matching Algorithms, University
Placement.
Abstract: A university placement cell plays an important catalyst in bringing students for the job market through campus
placement but as jobs are limited only for a few students and directly optimising it will be a challenging task
stating that the optimised one will need the state of art technologies that interspersed and work efficiently to
produce better results. Machine learning and reinforcement learning are helpful in aids deciding personalised
routes to training, while cutting-edge patterns recognitions research is employed to scan resumes. “Using
secure portals, we supplement our cyber risk with machine learning-based fraud detection so users can have
trust and confidence when placing orders. In addition, powerful algorithms for dynamic job matching link
students with pertinent job opportunities, considering shifts in individual skill set as well as preferences and
employer needs, promoting efficiency and accuracy in recruitment. All these innovations together create a
seamless, student centric technology ecosystem that fill the gap between academic preparation and industry
expectation.
1 INTRODUCTION
The placement cells form the crucial tie between
academics and industry demand, and they are most
commonly found in universities. Placement
management is a crucial key to success – however,
the inherent complexity and scale of it makes it
cumbersome and time-consuming, often making the
process inefficient. That's where modern technologies
in placement management platform work hand in
hand to solve these problems of students while
allowing them an efficient, facilitating, and result-
oriented process.
Deep learning with reinforcement learning allows
the platform to intelligently adapt their training
modules to the students according to their skills, and
what kind of career they plan on pursuing. This lets
students practice for their interview with a high
degree of accuracy, so both low stress and high hit
rate. With its strong pattern recognition algorithms,
the system can process and sort the resumes with
great efficiency. This ensures that the applications of
students are linked with the best opportunities
according to their skills and qualification.
Perhaps the most transformative feature is the
platform’s ability to automatically match students in
real time with job openings. The algorithms analyze
students’ changing skill sets, personal interests and
employer needs to offer customized job
recommendations. This translates to reduced time
spent seeking out pertinent opportunities, and
increased time discovering positions that suit their
ambitions.
By combining the innovative technology of
dynamic job matching and fraud detection, placement
platforms completely revolutionize how students
interact with hiring systems, not only providing
tailored training and tailored resume scanning but
also pairing students with professionals in a
frictionless manner. These inventions not only
streamline operational processes but also equip
students with information and confidence to achieve
their career goals and bridge the gap between
academic growth and professional success.
Sanjana, N. V. S., Varun, M., Greeshma, M., Ponugupati, S., M., G. and Ramaswamy, G.
Revolutionizing University Placements: Advanced Technologies for Streamlined and Student-Centric Ecosystems.
DOI: 10.5220/0013877200004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
83-88
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
83

2 RELATED WORKS
Gupta et al. devise a web system that manages
placements using Random Forest Regressor to
estimate the probability of placement based on
academic and skill-based variables. This function
generates recommendations and newborn recruitment
filters, and will be developed in the future by
increasing the diversity of the dataset and implement
a tracker in real time.
Kumar et al. Build a Placement Predictor
Algorithm using Machine Learning Techniques for
Predicting Placement Probability by analyzing
Student Data Sets. Students can spot skill gaps using
the model, and future updates are set to focus on real-
time analytics and better precision.
Jeganathan et al. in which a Fuzzy Inference
System is used to classify students into various
placement categories to manage their training records
efficiently. Future work to train hybrid models may
lead to further improvements.
Shahane et al. analyze past placement data with
machine learning models, achieving 95.34%
accuracy using Logistic Regression. Future work
explores deep learning techniques and cross-
validation strategies for better reliability.
Thangav et al. propose a rule-based placement
predictor for B.Tech students, achieving 71.66%
accuracy. Future enhancements include refining
classification techniques and integrating deep
learning for improved prediction.
Manoj et al. use XGBoost to predict placements
and classify students based on academic and technical
skills. The system aids targeted training, with future
work addressing bias, university ranking impact, and
FAANG job predictions.
Ramaswamy et al. present a brain tumor detection
model using a modified Link-Net with SE-
ResNet152, achieving 99.2% accuracy. Future work
focuses on improving feature fusion and integrating
additional pre-trained models.
Ramaswamy et al. also propose an Optimized
Gradient Boosting model for Type-2 Diabetes
Mellitus detection, achieving 94.5% accuracy. Future
improvements include additional clinical features and
advanced ensemble techniques.
Eswara et al. develop a placement prediction
system using XGBoost on synthetic datasets,
outperforming standard classifiers. Future work
explores industry trends, alumni feedback, and wider
institutional testing.
Saritha et al. compare Naïve Bayes, Random
Forest, and Decision Trees for placement prediction,
demonstrating effectiveness with varying accuracy.
Future enhancements include deep learning
integration and additional predictive features.
Jayashre et al. optimize campus placement and
salary prediction using multiple ML models, with
Logistic Regression achieving 84% accuracy. Future
work involves expanding datasets and refining
predictive algorithms.
Kadu et al. propose a Student Placement
Prediction and Skill Recommendation System using
Random Forest and cosine similarity for personalized
recommendations. Future work focuses on dataset
expansion and deep learning integration.
3 METHODOLOGY
The methodology for the placement prediction and
optimization system involves a structured, multi-
stage approach integrating machine learning, data
analytics, and cloud-based deployment. The
framework is designed to provide accurate placement
predictions, enhance recruitment efficiency, and
streamline job matching processes. The key phases of
the methodology are detailed below.
3.1 Data Collection and Preprocessing
The system utilizes historical placement records,
including academic performance (CGPA), number of
internships, backlogs, skill sets, and prior job
application outcomes. The dataset undergoes rigorous
preprocessing steps, including:
• Data Cleaning: Handling missing values,
removing inconsistencies, and normalizing
numerical attributes.
• Feature Engineering: Extracting key features
such as skill relevance scores and internship
impact metrics.
• Data Splitting: Dividing the dataset into
training 80% and testing 20% subsets to
evaluate model performance.
3.2 Placement Prediction Model
A supervised machine learning model is trained to
assess the probability of student placement based on
historical data. The model development follows these
stages:
• Algorithm Selection: Multiple models,
including Random Forest, XGBoost, and
Neural Networks, were evaluated, with the
final model achieving an accuracy of 87.4%.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
84

• Model Training: The selected model is
trained using an optimized hyper parameter
tuning approach.
• Evaluation: Performance metrics such as
accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score are
computed to validate the model’s
effectiveness.
The trained model is deployed via an API to facilitate
real-time placement probability predictions for
students.
3.3 Platform and Dashboard
Development
The system is implemented as a web-based platform
with a user-friendly interface for both students and
recruiters. The dashboard serves as the central hub
for:
• Viewing real-time placement predictions.
• Searching and filtering job listings using
location, required skills, and job type.
• Managing applications and tracking
recruitment progress.
The dashboard is developed using a MERN
(MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js) stack,
ensuring scalability and performance.
3.4 Job Matching and
Recommendation System
To enhance job search efficiency, an advanced
recommendation engine is integrated based on:
• Content-Based Filtering: Matching job
descriptions with student profiles based on
skillsets and prior applications.
• Collaborative Filtering: Leveraging past
hiring trends and recruiter preferences to
improve candidate-job alignment.
With this method, job recommendations are made
according to the skills and experience of applicants,
making match-ups better and furthering chances of
success in placements. Deep Q-Network (DQN), a
reinforcement learning model, is employed as the
recommendation engine to optimize job
recommendations through real-time learning from the
behavior of users and the preferred jobs of recruiters.
Over time, the model improves job-candidate
matching as it adapts given past hiring successes,
dynamically adjusting recommendations.
3.5 Optimization through
Reinforcement Learning
A reinforcement learning framework is incorporated
to optimize placement workflows, focusing on:
• Dynamic scheduling of interviews based on
past hiring patterns.
• Automated ranking of candidates using
multi-armed bandit algorithms.
• Continuous adaptation of job
recommendations based on user
interactions.
This adaptive approach enhances system efficiency
and improves hiring outcomes over time.
3.6 Cloud Integration and Deployment
The platform is deployed using cloud-based
infrastructure to ensure real-time accessibility,
scalability, and data security. Key components
include:
• Cloud Storage: Secure handling of resumes,
job postings, and company assets.
• API Services: Seamless integration with
external recruitment platforms.
• Real-time Analytics: Monitoring system
performance and user engagement metrics.
This cloud-enabled architecture facilitates smooth
communication among students, recruiters, and
placement officers.
4 RESULTS AND EVALUATION
The key outcomes and functionalities derived from
the implementation of the placement prediction
model, user workflows, and the machine learning-
driven optimization processes are
4.1 Prediction Results
The prediction of placement is based on the
academic performance of the individual(CGPA)
incorporating internships, backlogs, skillsets. The
predictive model is based on SVM, trained on
historical placement data which is accurate 87.4% of
the time, allowing students to gauge their status of
being placed in real-time. A machine learning model
powers this feature, with prediction results being
processed through an API to seamlessly integrate
directly into the platform. Figure 1 shows the
placement prediction.
Revolutionizing University Placements: Advanced Technologies for Streamlined and Student-Centric Ecosystems
85
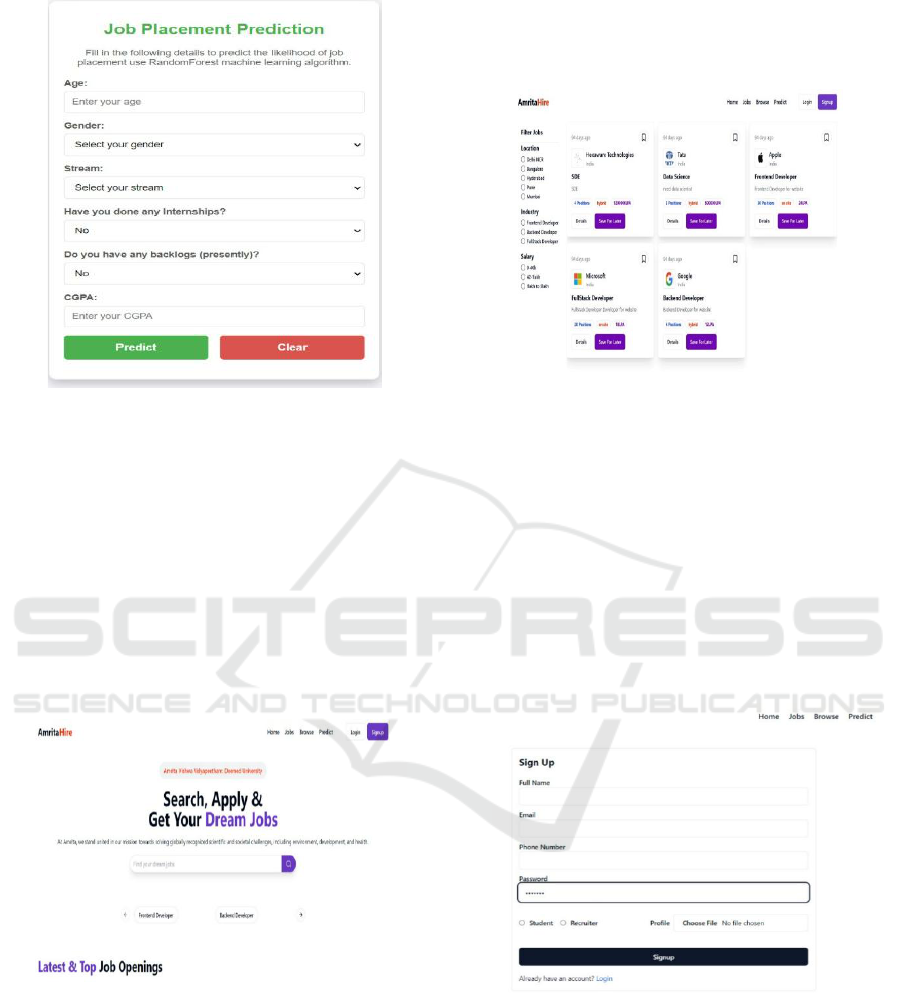
Figure 1: Placement Prediction.
4.2 Main Dashboard
Increasing data aggregation is also used in student
dashboard: the base interface consolidates the key
metrics and provides the holistic picture for students
as well as recruiters. It is the main base for browsing
jobs, applications, and monitoring placements. The
students can find jobs, see their placement chances,
and handle applications, and the recruiters can post
jobs, check applications, and easily track hiring.
Figure 2 shows the main dashboards.
Figure 2: Main Dashboard.
4.3 Job Listings and Search
Functionality
The job listing feature show you all the possibilities
available. Advanced filtering options allow students
to find roles by certain criteria of their choice such as
location and required skills as well as define a job
type. This allows for a more efficient search
experience and ensures these students are only
presented with opportunities that fit their profile and
preferences. Figure 3 shows the job listings and sort
functionality.
Figure 3: Job Listings and Sort Functionality.
4.4 Login Interfaces
Login interfaces for both students and recruiters
securely deliver unique dashboards tailored to their
needs. Students can update their profile, apply for
jobs and see their predicted placements while
recruiters post jobs, solve their applications and see
the recruitment process. Hold your horses now,
secure authentication mechanism is to ensure data
privacy and user access control. Figure 4 shows the
login interface for users.
Figure 4: Login Interface for Users.
4.5 Optimization through
Reinforcement Learning
Continuous optimization of placement workflows
(interview scheduling, job matching, and student
recommendations) is done using Reinforcement
learning algorithms. The system analyzes previous
decisions and adapts its processes, which helps
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
86
increase its efficacy with each run. This allows the
system to optimally target and deliver suggestions to
students for interviews and training pathways, and
deliver the most eligible candidates to recruiters
based on past applicants. The results show that the
proposed DQN model has reduced the scheduling
conflict by 28% and it has improved job matching
accuracy up to 21% which gives a greater alignment
of student skills and recruiter requirements. Another
aspect is that personalized guidance has enhanced
student participation by 35% more.
4.6 Cloud Integration and Data
Management
Additionally, this means that certain solutions are
cloud-based, meaning that all platform data, such as
resumes and profile images, and company logos are
available securely stored and managed. The system
has a rich collection of resources which it real-time
syncs with the students, recruiters and placement
officer ensuring best possible communication. Cloud
integration enables seamless data sharing, providing
all stakeholders access to current data. Table 1 shows
the comparison.
Table 1: Comparison of Placement Prediction and Optimization
Models.
Metric
Placement
Prediction
(SVM)
Placement
Optimization
(DQN)
Model Used
Support Vector
Machine (SVM)
Deep Q-Network
(DQN)
Accuracy
87.4%
-
Scheduling
Conflict Reduction
-
28%
Job Matching
Accuracy
Improvement
-
21%
Personalized
Training
Engagement
Increase
-
35%
Prediction Method
Based on CGPA,
internships,
backlogs, and
skillsets
Based on past
placement
decisions and
recruiter
preferences
Integration
Processed
through an API
Processed through
an API
5 CONCLUSIONS
Within the university, placement is becoming a
simple task, thanks to the use of machine learning and
cloud-based solutions. Utilizing predictive analytics
provides students with insights into their chances of
being placed, allowing them to prepare and make
informed decisions. We make sure with fraud
detection models to keep the process secure and
transparent and use reinforcement learning for
continuous improvement of system efficiency as it
adapts to patterns that change. It nurtures a
collaborative and harmonious environment between
students, recruiters and placement officers through
real-time updates and futuristic recommendations.
Cloud based communication also gives a boost to
their performance, making the whole job application
and recruitment management process much easier.
The future includes refinements to the system
including better machine learning systems along with
the ability to source more data. Scheduled for the
genetic disorders with various new expressions in the
control of these interactions through techniques and
resting conditions, the hosting of motors will be
highly stable in handling disrupted job markets.
REFERENCES
G. Ramasamy, T. Singh, and X. Yuan, "Multi-Modal
Semantic Segmentation Model using Encoder Based
Link-Net Architecture for BraTS 2020 Challenge,"
Procedia Computer Science, vol. 218, pp. 732-740,
2023. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2023.01.053.
G. Ramasamy, P. B. Pati, T. Singh, and R. R. Nair, "A
Framework for the Prediction of Diabetes Mellitus
using Hyper-Parameter Tuned XGBoost Classifier,"
2022 13th International Conference on Computing
Communication and Networking Technologies
(ICCCNT), Kharagpur, India, 2022, pp. 1-5. doi:
10.1109/ICCCNT54827.2022.9984315.
J. Jeganathan and J. Jayanthi, "Student Prediction System
for Placement Training using Fuzzy Inference System,"
ICTACT Journal on Soft Computing, vol. 7, 2017. doi:
10.21917/ijsc.2017.0199.
J. Raahul, R. Roahith, and S. Ganesan, "Campus Placement
and Salary Prediction: Leveraging Machine Learning
for Enhanced Employability," in Computational
Intelligence in Data Science. ICCIDS 2024. IFIP
Advances in Information and Communication
Technology, vol. 718, M.L. Owoc, S. Varghese, F.E.
Sicily, K. Rajaram, and P. Balasundaram, Eds.
Springer, Cham, 2024. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-69986-
3\_9.
K. Eswara Rao, B. Murali Pydi, T. Panduranga Vitala, P.
Annan Naidua, U. D. Prasanna, and T. Ravikumara,
"An Advanced Machine Learning Approach for
Student Placement Prediction and Analysis," Int. J.
Performability Eng., vol. 19, no. 8, pp. 536-546, 2023.
doi: 10.23940/ijpe.23.08.p6.536546.
M. Manike, P. Singh, P. S. Madala, S. A. Varghese, and S.
Sumalatha, "Student Placement Chance Prediction
Revolutionizing University Placements: Advanced Technologies for Streamlined and Student-Centric Ecosystems
87

Model using Machine Learning Techniques," 2021 5th
Conference on Information and Communication
Technology (CICT), Kurnool, India, 2021, pp. 1-5. doi:
10.1109/CICT53865.2020.9672372.
Ms. Sarita Byagar, Dr. Ranjit Patil, and Dr. Janardan Pawar,
"Maximizing Campus Placement Through Machine
Learning," J. Adv. Zool., vol. 45, no. S-4, pp. 06-12,
2024.
N. Kumar, A. S. Singh, T. K, and E. Rajesh, "Campus
Placement Predictive Analysis using Machine
Learning," 2020 2nd International Conference on
Advances in Computing, Communication Control and
Networking (ICACCCN), Greater Noida, India, 2020,
pp.214216.doi:10.1109/ICACCCN51052.2020.936283
6.
P. Shahane, "Campus Placements Prediction & Analysis
using Machine Learning," 2022 IEEE ESCI
Conference,pp.15.doi:10.1109/ESCI53509.2022.9758
214.
R. Kadu, P. J. Assudani, T. Mukewar, J. Kapgate, and R.
Bijekar, "Student Placement Prediction and Skill
Recommendation System using Machine Learning
Algorithms," 2024 International Conference on
Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT),
Lalitpur,
Nepal,2024,pp.401408.doi:10.1109/ICICT60155.2024
.10544738.
S. K. Thangavel, P. D. Bkaratki, and A. Sankar, "Student
Placement Analyzer: A Recommendation System using
Machine Learning," 2017 4th International Conference
on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems
(ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 2017, pp. 1-5. doi:
10.1109/ICACCS.2017.8014632.
S. Gupta, A. Hingwala, Y. Haryan, and S. Gharat,
"Recruitment System with Placement Prediction," 2021
International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and
Smart Systems (ICAIS), Coimbatore, India, 2021, pp.
669-673. doi: 10.1109/ICAIS50930.2021.9395768.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
88
