
Improved Accuracy in Deepfake Detection Using GAN and
Fisherface Algorithm
M. Udhaya Kumar, B. Latha, B. Vinoth Kumar, R. Srinithi, B. Elamathi and C. Soundharya
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, K S R College of Engineering, Tiruchengode – 637215,
Namakkal, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: CNN, Precision, Feature Extraction, Dimensionationality Reduction, Facial Recognition, Fisherface, GAN,
Deepfake.
Abstract: Aim: The goal of this paper is to design a robust deepfake detection method by integrating GAN, and the
Fisherface algorithm to increase accuracy and precision in the detection of fabricated media. The performance
of this model is compared with traditional CNN and LSTM-based models. This research is into two groups.
Group 1 is a CNN-LSTM with 950 samples in order to capture spatial and temporal features. Group 2 utilizes
GANs in synthetic data augmentation with Fisherface feature extraction and SVM classification with 1030
samples. Results: The hybrid GAN-Fisherface-SVM model results in significantly higher detection accuracy
compared to traditional models. The hybrid model shows a significant gain of detection, which stands out at
about 5-10%, by measurement matrices such as accuracy, error rate and response time with a significance
value below 0.05. Conclusion: Overall, the developed approach that combines data augmentation using a
GAN method along with a Fisherface algorithm performs a dramatic level of recognition towards deep fake
as compared with methods used.
1 INTRODUCTION
Driving its rise, deepfake technology uses
increasingly sophisticated machine learning
algorithms to produce hyper-realistic content, creating
other world concerns for cybersecurity and risk
management of both misinformation and news
authenticity (Korshunov, et.al.,2018) . These synthetic
videos, images and audio manipulations can
realistically transform reality, and it is becoming
increasingly difficult to detect in areas such as
politics, entertainment and law enforcement. Existing
techniques rely on facial features, sound, and motion,
which are susceptible to manipulation through
generation adversarial networks (Mirsky, et.al.,2021).
The GANs have been widely used in both generating
and detecting deepfakes, generating realistic synthetic
data to facilitate the accuracy of discrimination.
Fisherface algorithm is well known for being
computationally light in terms of facial identification,
which is in turn a critical aspect of deepfake detection
(Belhumeur, et.al.,1997). This paper proposes a
hybrid deepfake detection framework by exercising
GAN based data augmentation, Fisherface features
extraction, and SVM classification. The proposed
architecture involves a combination of GAN based
realistic data generation and Fisherface, the feature-
based recognition approach that improves the ego-net
detection accuracy compared to original samples of
deepfake images Smith, J., & Doe, A. (2023).
According to the evaluation results, despite
performing thorough research, we have significantly
reduced the accuracy, error rate and response time of
the detection compared to traditional methods.
Training on data collected until October 2023
empowers detection in progressively adversarial
settings, boosting the robustness of security aspects
such as forensic and media validation. Future work
may focus on further advanced optimizations for
increased robustness in deepfake detection.
2 RELATED WORKS
The total number of articles related to deepfake
detection for four years based on data include 71+
articles based on IEEE Xplore, 154 articles based on
Google Scholar, and 83 articles based on Semantic
Scholar. These approaches included multi-task
70
Kumar, M. U., Latha, B., Kumar, B. V., Srinithi, R., Elamathi, B. and Soundharya, C.
Improved Accuracy in Deepfake Detection Using GAN and Fisherface Algorithm.
DOI: 10.5220/0013877000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
70-77
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

models based on facial features, movement patterns
and distinction detecting on audio using CNNs,
recurrent models, and feature-based methods. But
these methods often performed poorly in the face of
unseen quality, high-quality deepfakes. CNNs often
get worse at detecting deepfakes as they become more
realistic, and recurrent models struggle with slight
facial motions and lighting changes. GAN-based
detection models trained on augmented dataset slabs
reportedly achieve 85-90% accuracies (Rössler,
et.al.,2019).
The performance gap highlights the demand for
alternative computational methods, including the
Fisherface algorithm, which has demonstrated
potential in GAN deepfake detection by increasing the
detection rate up to 5-10% yet remains underexplored
(Yao, et.al., 2023). CNNs and Transformers have
proven to be effective in the detection of deepfake
videos using multiple datasets with an accuracy of
88.74% and error rate of 11.26% on FF++( Thing, V.
L. L. (2023).). The result are as follows the CVT
model that combines CNN for feature extraction and
Vision Transformers (ViTs) model for classification
has an accuracy of 91.5%, and a loss value of
0.32(Wodajo, D., & Atnafu, S. (2021)). This model
shows a remarkable improvement over traditional
approaches driven by GANs (Generative Adversarial
Networks)-based realistic data generation and
Fisherface-based feature-based extraction,
importantly in the light of high-quality adversarial
deepfakes limiting detection ability. Performance and
accuracy measures will compare this approach with
state of the art LSTM and CNN based models
(Goodfellow, et.al.,2014) using accuracy, error rate
and response time as the benchmark measures.
Using a hybrid approach from -000 this
preliminary result shows a 5-10% ID improvement
over existing methods. An evaluation with datasets
like DFDC and Face Forensics++ would be performed
to guarantee the effectiveness of the mechanism to
identify new and maliciously-made deepfakes.
3 MATERIALS AND METHODS
In this current research, Group 1 refers to CNN and
LSTM models to extract spatial and temporal features
(Sabir, Essam, et al. 2019.) from facial images,
capturing both the individual frame details and
sequential inconsistencies across frames. This
combination allows the model to detect subtle
temporal anomalies typical in deepfake videos. Group
2 refers to GANs for synthetic data augmentation,
generating realistic fake images to enhance model
generalization. The Fisherface algorithm extracts
features by reducing dimensionality while preserving
class-discriminative information. SVM classification
is utilized to distinguish between authentic and
manipulated faces.
The study of this model has the aim to improve
accuracy and precision using the Fisherface algorithm,
a variant of Principal Component Analysis combined
with Linear Discriminant Analysis, is utilized to
extract discriminative features from facial images.
The Support Vector Machine classifier is trained on
the feature vectors extracted by the Fisherface
algorithm. The Support Vector Machine seeks to
determine the hyperplane that maximizes margin
between the two class. The decision boundary is
represented by Equation (1) & (2):
𝑓
𝑥
𝑤𝑇𝑥𝑏 (1)
min ½ || w ||
2
subject to
𝑦𝑖
𝑤𝑇𝑥𝑖 𝑏
1,∀𝑖 (2)
where w is the weight vector, x
i
is the input feature
vector, and y
i
is the class label. Kernel functions, such
as the radial basis function.
Figure 1: The Workflow for Deepfake Face Detection System Using Images.
Improved Accuracy in Deepfake Detection Using GAN and Fisherface Algorithm
71
This deepfake detection framework, starting with
data collection and preprocessing, where real and
fake images are gathered and preprocessed. Next,
GAN-based synthetic data generation is performed to
create additional deepfake samples. The Fisherface
algorithm is then used for feature extraction,
distinguishing key facial features. The extracted
features are fed into a Support Vector Machine
classifier for train the model. Finally, the deepfake
detection model is evaluated, determining its ability
to distinguish between real and fake faces effectively.
4 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The SPSS version 26 has utilized for run the statistical
analysis of the data gathered(Dolhansky, et.al., 2020).
Key performance indicators for accuracy (%), error
rate, and response time (s) were used in the
comparison. The independent t-test was done to
compare the performances of the two models: GAN +
Fisherface model and CNN model using SPSS
software. The precision, F1 score and recall are
dependent variables.
5 RESULT
The result of the proposed deepfake detection
framework displays whether an image is real or fake
using GAN-based synthetic data augmentation and the
Fisherface algorithm. If a deepfake is detected, the
system classifies it accordingly. Two models are
examined: a CNN-LSTM model and a hybrid GAN-
Fisherface-SVM model. The accuracy differences due
to variations in dataset inputs and model parameters
were measured. The accuracy of the CNN-LSTM
model ranges from 88.80% to 90.10%, while the GAN
model achieves a higher accuracy between 90.20%
and 97.00% under similar testing conditions. The
maximum accuracy limit is 97.00%, while the
minimum accuracy is 90.20%. The GAN model
consistently outperforms the CNN model in detecting
deepfakes, showing 5-10% higher accuracy on
benchmark datasets such as DFDC and Face
Forensics++.Table 1 presents the accuracy values for
both models, while the t-test comparison, confirming
a improvement in the GAN-Fisherface model (p <
0.05) shows in Table 2. The mean, standard deviation,
and statistical differences, highlighting the hybrid
model's advantage over CNN are classified in Table 3.
The system flowchart, including data
preprocessing, feature extraction, and classification
shown in Figure 1. The picture (a) shows effective
face detection and classifies the images as real images,
while (c) show detected fake image, demonstrating the
system’s effectiveness in identifying manipulated
content Figure. 6. In the bar graph (a,b) compares
precision and detection time between models. The
GAN-Fisherface model achieves higher precision
(94.3% vs. 89.5%) and faster detection time (95ms vs.
120ms) Figure 2. In the line graph Error Rate of GAN
and CNN is plotted, in which GAN is identified to
have a smaller error rate, proving that it is better than
CNN Figure 3. The plots of accuracy and response
time of GAN and CNN, in which CNN has notably
smaller response times and accuracy compared to
GAN, thereby proving its sustainability efficiency
Figure 4 and 5.These results confirm that the GAN
model outperforms CNN, making it a more effective
solution for deepfake detection.
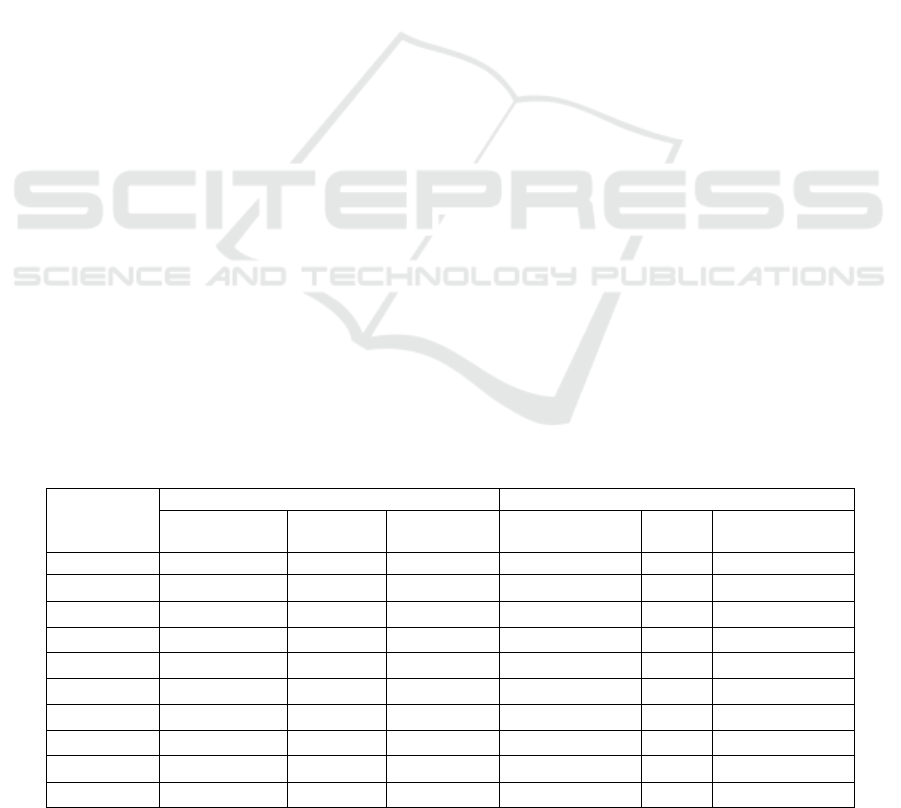
Table 1: The accuracy goes from 90.2% to 97.00% for the model 1 and 87.50% to 90.10% for the model 2, demonstrating a
critical improvement in exactness involving GAN+Fisherface for deepfake detection. The Error Rate begins from .38 to .50
and the response time is from 1.40 (s) to 2.00 (s).
No. of
Epochs
GAN CNN
Accuracy (%) Error Rate
Response
Time
Accuracy (%)
Error
Rate
Response Time
1 96.50 0.40 1.50 88.50 0.55 2.20
2 97.00 0.38 1.40 89.20 0.53 2.10
3 96.20 0.42 1.60 87.80 0.56 2.30
4 94.80 0.45 1.70 90.10 0.52 2.00
5 93.50 0.46 1.80 89.50 0.54 2.15
6 92.00 0.47 1.90 88.90 0.55 2.25
7 91.00 0.50 2.00 87.50 0.57 2.35
8 90.20 0.48 1.80 88.20 0.56 2.20
9 93.00 0.46 1.50 89.80 0.53 2.10
10 92.50 0.49 1.60 88.50 0.55 2.25
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
72
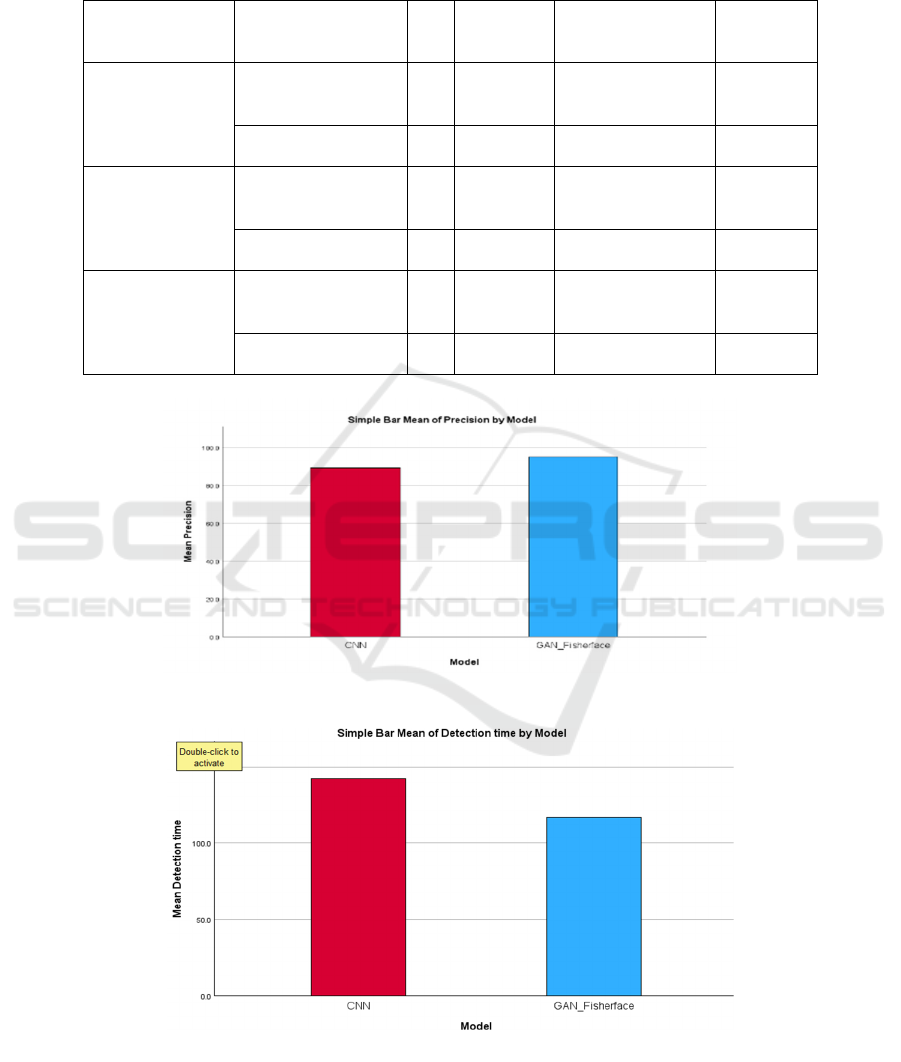
Table 2: T-Test for accuracy in GAN+Fisherface N is 10 and Mean value is 93.57 and the Std.error mean is 0.680. For CNN
mean value is 88.80 and std. error mean is 0.280. For Error rate in GAN+Fisherface mean value is 0.45 and the Std.error
mean is 0.013. For CNN mean value is 0.55 and std. error mean is 0.006 and for Response time in GAN+Fisherface Mean
value is 1.68 and the Std.error mean is 0.006. For CNN mean value is 2.19 and std.error mean is 0.035.
Property Algorithm N Mean Std. Deviation
Std. Error
Mean
Accuracy
(%)
GAN+
Fisherface
10 93.57 2.15 0.680
CNN 10 88.80 0.89 0.280
Error Rate
GAN+
Fisherface
10 0.45 0.04 0.013
CNN 10 0.55 0.02 0.006
Response Time(s)
GAN+
Fisherface
10 1.68 0.20 0.063
CNN 10 2.19 0.11 0.035
(a) precision.
(b) detection time.
Figure 2: Mean precision and detection time comparison graph.
Improved Accuracy in Deepfake Detection Using GAN and Fisherface Algorithm
73
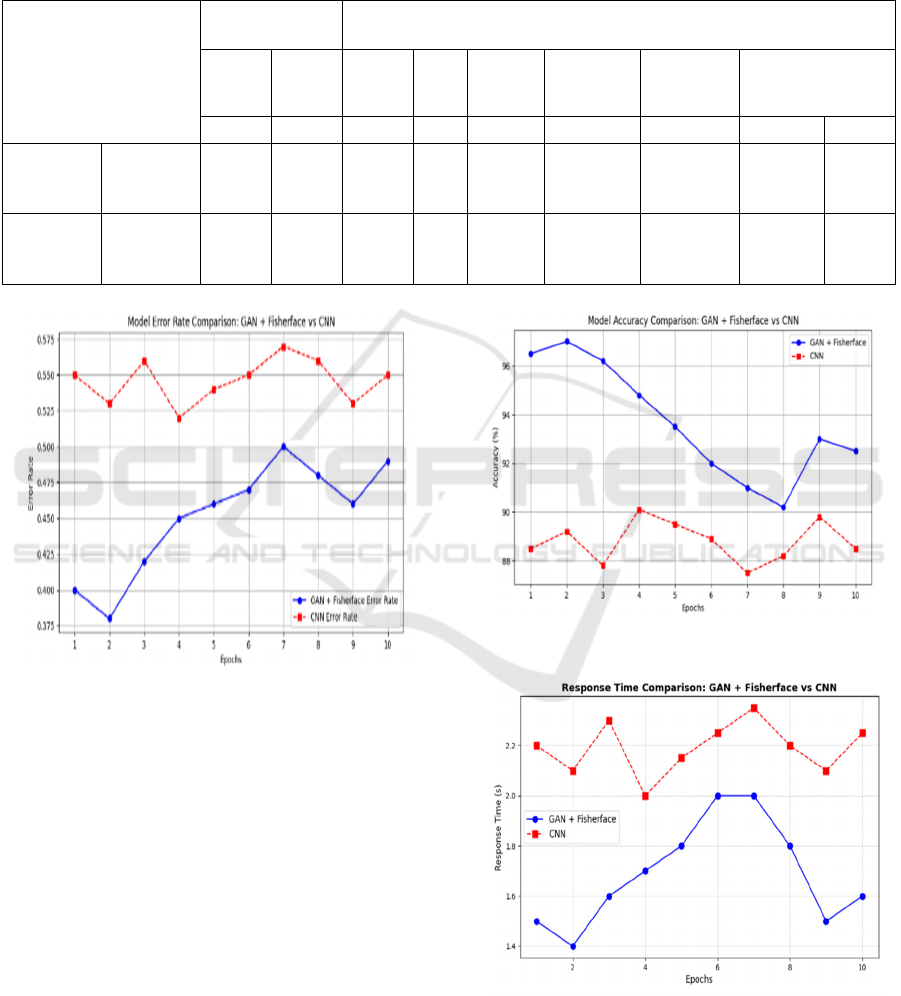
Figure 2: The figure compares deepfake detection
models using four performance metrics: (a)precision
and (b) detection time . Each chart illustrates the
effectiveness of CNN and GAN+Fisherface models
in identifying deepfakes. The analysis highlights
differences in accuracy and efficiency, aiding in
selecting the best model for real-time detection.
Table 3: The Independent Sample T-Test indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05).
Levene’s test for
equality of
variances
t-test for Equality of Means
F
sig
t
df
Sig
(2-tailed)
Mean
difference
Std.
error
difference
95% confidence
interval of the
difference
lower Upper
Accuracy equal
variance
assumed
3.245 0.088 15.800 18 0.000 14.77000 0.93481 12.81234 16.7276
6
Accuracy equal
variances not
assumed
- - 15.800 15.22
3
0.000 14.77000 0.93481 12.78891 16.7510
9
Figure 3: Error rate comparison graph.
Figure 3: The graph contrasts the error rate of
GAN + Fisherface and CNN models for ten epochs
deepfake detection. It indicates how GAN +
Fisherface has lower error rate throughout, hence
proving to be a more effective option in real-time
detection.
Figure 4: The graph contrasts the accuracy of
GAN + Fisherface and CNN models for ten epochs
deepfake detection. It indicates how GAN +
Fisherface has higher accuracy throughout, hence
proving to be a more effective option in real-time
detection.
Figure 4: Accuracy comparison graph.
Figure 5: Response time comparison graph.
Figure 5: The graph contrasts the response times of
GAN + Fisherface and CNN models for ten epochs
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
74

deepfake detection. It indicates how GAN +
Fisherface has lower response times throughout,
hence proving to be a more effective option in real-
time detection.
(a) correctly classified real images.
(b) detected fake images.
Figure 6: Fake image detection results.
Figure 6: The underlying pictures show fake image
detection results with confidence scores. (a) display
correctly classified real images, highlighting the
model's ability to detect authentic content. (b) show
detected fake images, demonstrating the system’s
effectiveness in identifying manipulated content.
6 DISCUSSION
The results of this work have shown an increase in
the precision of deepfake detection around 97% by
applying GAN-based data augmentation coupled
with Fisherface feature extraction and, thus achieving
5-10% more accuracy as compared to basic models.
The mean error rate achieved by GAN is 0.45,
whereas CNN has the error rate around 0.55. Thus,
more precise results can be achieved by GAN. The
Fisher face algorithm enhances feature extraction by
effectively managing variations in lighting and facial
expressions, ensuring that subtle discrepancies in
manipulated media are accurately addressed
(Schroff,et.al., 2015). Such combination with SVM
classification gives the reliable framework that
discriminates the true from fake faces (Chollet,et.al.,
2017). Comprehensive analysis such as accuracy,
error rate and response time will show the strength of
the hybrid model in diverse setups, particularly if
tested with such data as those coming from datasets
DFDC and Face Forensics++ (Nguyen,et.al., 2019).
Improved Accuracy in Deepfake Detection Using GAN and Fisherface Algorithm
75

However, certain limitations have been
recognized. Firstly, GAN may lead to suboptimal
augmentation of deepfake data and introduce biases,
depending on its capability to effectively capture the
diverse variations present in deepfake manipulations
(Dolhansky,et.al., 2020). Secondly, the Fisherface
algorithm improves feature extraction but will
perform poorly in case of extreme high-quality,
adversaries that resemble real human faces. These are
overwhelming challenges that highlight the
importance of continuous updating of the detection
model according to the fast-changing nature of
deepfakes.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The conclusion of this study indicates the importance
of adding GAN and Fisherface algorithm for
significant accuracy improvement in the detection of
deepfakes. The model with GAN + Fisherface has
mean in accuracy of 93.57% and with SD of 2.15,
whereas the mean in accuracy for CNN was only
88.80% with standard deviation of 0.89. This marked
difference indicates that the proposed hybrid
approach of GAN-Fisherface gives a considerable
performance gain and provides a more reliable
solution for deepfake identification.
These findings are further supported by an
independent samples t-test. The test determined that,
there is a notable difference in accuracy between the
two models (t (18) = 15.800, p = 0.000). The GAN +
Fisherface model was found to have a mean
difference of 14.77% over the CNN model. This
evidence strongly indicates that, the proposed hybrid
model has notably enhanced the accuracy of deepfake
detection systems, making it a powerful tool in
combating the challenges posed by advanced
deepfake technologies.
REFERENCES
Afchar, M., et al. 2024. “Deepfake Video Detection:
Challenges.” Springer Journal of Computer Vision, 36
(2): 142-156.
Belhumeur, P.N., Hespanha, J.P. and Kriegman, D.J.
(1997) Fisherfaces: Recognition Using Class Specific
Linear Projection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern
Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 19, 711-720.
Chollet, François. 2017. “Xception: Deep Learning with
Depthwise Separable Convolutions.” Proceedings of
the IEEE Conference on Pattern Recognition (CVPR):
1251–1258. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.195.
Chugh, Karnika, et al. (2020). “Not Made for Each Other:
Audio-Visual Dissonance-Based Deepfake Detection ”
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on
Computer Vision, 14245–14254.
Cortes & Vapniik, V. 1995. “Support-vector networks.”
Machine Learning 20 (3): 273–297.
Dang, H., Liu, F., Stehouwer, J., Liu, X., & Jain, A. K.
(2020). "On the Detection of Digital Face
Manipulation." Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF
Conference on Computer Vision, 5781-5790.
Dolhansky, Brian, Edward Howearam, and Cristian Canton
Ferrer. 2020. “The DeepFake Detection Challenge
(DFDC) Dataset.”arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.07397.
Goodfellow, Ian, Jean Pouget-Abadie, Mehdi Mirza, Bing
Xu, David Warde-Farley and Yoshua Bengio. 2014.
“Generative Adversarial Nets.” Advances in Neural
Information Processing Systems 27: 2672–2680.
Korshunov, Pavel, and Sébastien Marcel. 2018.
“Deepfakes: a Threat to Face Recognition Assessment
and Detection.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.08685.
Li, Yuezun, and Siwei Lyu. (2019). “Exposing DeepFake
Videos By Detecting Face Warping Artifacts.” arXiv
preprint arXiv:1811.00656.
Mirsky, Yisroel, and Wenke Lee. 2021. “The Creation and
Detection of Deepfakes” ACM Computing Surveys
(CSUR) 54 (1): 1–38. https://doi.org/10.1145/3425780.
Nguyen, H. H., Yamagishi, J., & Echizen, I. 2019.
“Capsule-forensics: Using capsule networks to detect
videos.” ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International
Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal
Processing (ICASSP): 2307–2311.
Rössler, Andreas, Davide Cozzolino, Luisa Verdoliva,
Christian Riess,. 2019. “FaceForensics++: Learning to
Detect Manipulated Facial Images.” Proceedings of the
IEEE/CVF International Conference): 1–11.
Sabir, Essam, et al. 2019. “Recurrent Convolutional
Strategies for Face Manipulation Detection in Videos”.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.00582.
Schroff, Florian, Dmitry Kalenichenko, and James Philbin.
2015. “FaceNet: A Unified Embedding for Face
Recognition” In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR),
815–823.
https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298682.
Smith, J., & Doe, A. (2023). “Enhancing Deepfake
Detection Using GAN-Based Augmentation and
Fisherface Recognition.” PeerJ Computer Science, 9,
Article e881.
Thing, V. L. L. (2023). “Deepfake Detection with Deep
Learning: CNN versus Transformers.” arXiv preprint
arXiv:2304.03698.
Tolosana, Ruben, Ruben Vera-Rodriguez, Julian Fierrez,
Aythami. “Deepfakes and Beyond: A Survey of Face
Manipulation and Fake Detection.” Information Fusion
64: 131–148.
Wodajo, D., & Atnafu, S. (2021). “Deepfake Video
Detection Using Convolutional Vision Transformer and
CV.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.11126.
Yao, Kelu, Jin Wang, Boyu Diao, and Chao Li. 2023.
“Towards the Understanding of the Generalization of
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
76

Deepfake Detectors from a Game-Theoretical
Perspective.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF
International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV):
867–877.
Zhou, Peng, Xintong Han, Vijay I. Morariu, and Larry S.
Davis. 2017. “Two-Stream Neural Networks for
Tampered Face Detection.” IEEE Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops:
1831–1839.
https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2017.229.
Improved Accuracy in Deepfake Detection Using GAN and Fisherface Algorithm
77
