
Fake Profile Detection on Social Networking Websites Using Machine
Learning
A. Ramesh Babu
1
, Fahimuddin Shaik
2
, K. Devi Sri
3
, M. Keerthi
3
, S. Karuna Sree
3
and K. Nandini
3
1
Department of AI&DS, Annamacharya University, Rajampet, Andhra Pradesh, India
2
Department of ECE, Annamacharya University, Rajampet, Andhra Pradesh, India
3
Department of AI&DS, Annamacharya Institute of Technology and Sciences, Rajampet, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Fake Profile Detection, Machine Learning, Feature Importance, Model Evaluation, Tree Ensembles Social
Media Analysis, Quality Measure, Easy‑to‑Use appbar1, dataload2, algorithm3, comparison4 Interactive
Tool.
Abstract: This project will address the difficult Addressing the issue of detecting fake profiles on social media platforms
to an interactive and engaging approach using and Streamlit based user-friendly application built This new
tool empowers users to seamlessly upload their datasets, preprocess the data, and evaluate a number of support
vector machine learning models, specifically Support Vector Machines (SVM), Random Forest Classifiers,
and Neural Networks. SVMs are well-known as, one class of machine learning tools, used for in this work,
we focus on the aforementioned work which yields expressed structures, examples that behave well in high-
dimensional spaces and also hold resilience to overfitting. Random Forests are recognized for their ability to
manage complex interactions in data through the use of ensemble methods while Neural Networks employ
sophisticated techniques to learn from complex patterns. Random Forest Classifier is one of them that gives
a considerably higher performance compared to other models when it comes to predicting fake profiles.
Random Forests work organizing the predictions from many decisional stumps, improving their capacity of
handling high dimensional data and lifting subtile structures that can be missed by simpler models. This hybrid
class of method has the advantage of being able to use the features of all the participant models, reducing the
likelihood of overfitting while enhancing the model's ability to adapt effectively, making it especially effective
in the diverse and dynamic landscape of social media data, where interactions and patterns can be highly
complex and varied. By combining intuitive design with detailed performance analysis, the application not
only addresses the immediate challenge of fake profile detection but also encourages continuous improvement
and adaptation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Social media has become one of the vents of the
modern digital
world, and is used in many spheres
essential part of our lives, offering space for
networking, broadcasting, and self-presentation. But
since then, the growth of fake profiles and bogus
accounts on these platforms presents serious
challenges. Fake profiles to identity theft, and created
with malicious intent misinformation and security
breaches (
Bontchev, 2020). To combat this business
problem, machine learning has proven to be a very
efficient tool, employing advanced algorithms and
vast databases to detect, analyze patterns and
behaviors that could signal a fake profile (
Feng, Y., &
Li, J, 2022
). Suspicious activities or behaviors that
deviate from normal user behavior are detected using
natural language processing, anomaly detection,
analysis of the network, etc. Example: Machine
learning models trained on large datasets can learn to
differentiate between real and fake accounts based on
data such as profile content, patterns of interaction,
and account age. Such an approach increases
precision while also adapting to changing tactics used
by those who build the fake profiles (
Patel, S. K., &
Kumar, R. 2021
). In summary, enhancing social media
platforms with machine learning enables us to detect
and combat abuses more effectively and create a more
secure and trustworthy online environment for users.
As technology advances, those ones will get even
more sophisticated ways to protect users from being
tricked and create a safer environment for all users on
Babu, A. R., Shaik, F., Sri, K. D., Keerthi, M., Sree, S. K. and Nandini, K.
Fake Profile Detection on Social Networking Websites Using Machine Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013876200004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
21-26
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
21

the internet (Arora, A., & Sharma, P. 2022). The
continuous improvement and adaptation of machine
learning detection methods will allow social media
companies to keep up with the evolving strategies of
those behind fake profiles. By automating the
identification process, these advanced models can
greatly lessen the manual effort and response time
linked to combating fraudulent pursuits. This leads to
a stronger and more authentic online ecosystem,
boosting trust and interaction in digital environments.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
One way of fake profile detection data that has been
a major capitalized on in recent years, as the demand
for interpretable machine learning has been on the
rise prevalence of automated accounts. Cresci et al.
(2017) offered an exhaustive overview of social
spambots describing the different traits and actions
that differentiate them from real users. Their work
emphasizes the need for the latest detection methods
which fit tactics used by such malicious accounts.
Subsequently, Kudugunta and Ferrara (2018)
examined the usage of deep neural networks to bot
detection, demonstrating how powerful these models
can be at capturing Behavioral, leading to more
complex patterns in user behavior, thus improving
detection accuracy. Drawing on these early works,
Wang et al. (2023) was instead about Twitter using
deep learning techniques with great success in
identifying fake profiles. Of all of their research, the
thing that stood out was the specific questions raised
by the data architecture of the platform showing the
power of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) in
detecting micro- indicators of account authenticity. In
the respective study, Yang et al. (2021) is how
spammers’ social networks were studied, creating
a worth of relational data on detection strategy
improvement. There with findings suggesting that
understanding of the connections between it is
important to note that users can greatly increase spam
detection bots. Alghamdi and Shadi (2023) proposed
a new machine learning, but in some cases, hybrid
approaches algorithms with state-of-the-art
techniques, showing better prevention in fake profile
detection. Their study indicates of Health Founding
Professor of Medicine at the University of Eugene,
which incorporates diverse methodologies and can
have higher accuracy and recall rates, giving a
broader solution to the problem. Besel and Co (2022),
again disciplines by profiling and detecting the
malicious employing ensemble accounts on social
media platforms ways to enable detection capabilities
to differ among categories environments. Moreover,
Singh et al. (2023) examined the Fake users on
Instagram: a novel approach for identification and
categorization by using supervised machine learning
techniques. Al Zamal et al. (2022) that wrote on
the application of ML approaches to a variety of
social media platforms offering a broader
detectability approach. The ongoing research
emphasizes the need for ongoing innovation within
detection techniques, because the methods that evil
are constantly changing.
3 DATA COLLECTION AND
PRE-PROCESSING
Developing a model involves data collection and
preprocessing that are the most crucial. Machine
learning models to identify fake profiles. User profile
data, typically collected from social networking
websites in CSV format with fields like
screen_name, verification status, statuses_count,
followers_count and friends_count. This data needs
to be prepared for machine learning. categorical
fields Verified and protected words are encoded to
numpy value using Label Encoder and textual data in
the screen_name field is Thereafter, TF-IDF
Vectorization is then used to process the data and
identify the words and transforms them into
numerical representation. View Image features and
keep the top 5000 key features to balance
information-preserving representation and
computational hardness. These inputted text features
are merged with numerical friends_count and
favourites_count attributes, forming a complete
dataset to train models, the target labels shows
whether a real or fake profile from the status column.
The dataset is divided into three groups the
training dataset, the validation dataset, and the test
dataset stratified train_test_split to maintain the class
balance. SVM, and traditional machine learning
models such as SVM and Random Forest, and a
dense and dropout-based neural network features,
which are the preprocessed features are then sent into
the CNN, in the form of n-dimensional layers. These
models are refined by metrics, like accuracy,
precision, recall, F1 score, and RMSE, which made
a built comprehensive comparison to decide the most
suitable model for detecting fake profiles in a reliable
way.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
22
4 PRINCIPLES AND METHODS
It is known that, in the digital age, marked by the
ubiquity of social networking platforms have become
indispensable in are daily habits the struggle to detect
and fight against fake profiles has never been
pressing. Given the rise of social media, the need for
the authenticity of user profiles is important for
population trust and security. We have a solution at
our project which is working on creating you are a
comprehensive framework developed to identify fake
profiles with better accuracy.
This project merges different data sources would
be more powerful machine learning and deep learning
models, and develop an end-to-end solution for
recognizing fraud profiles.
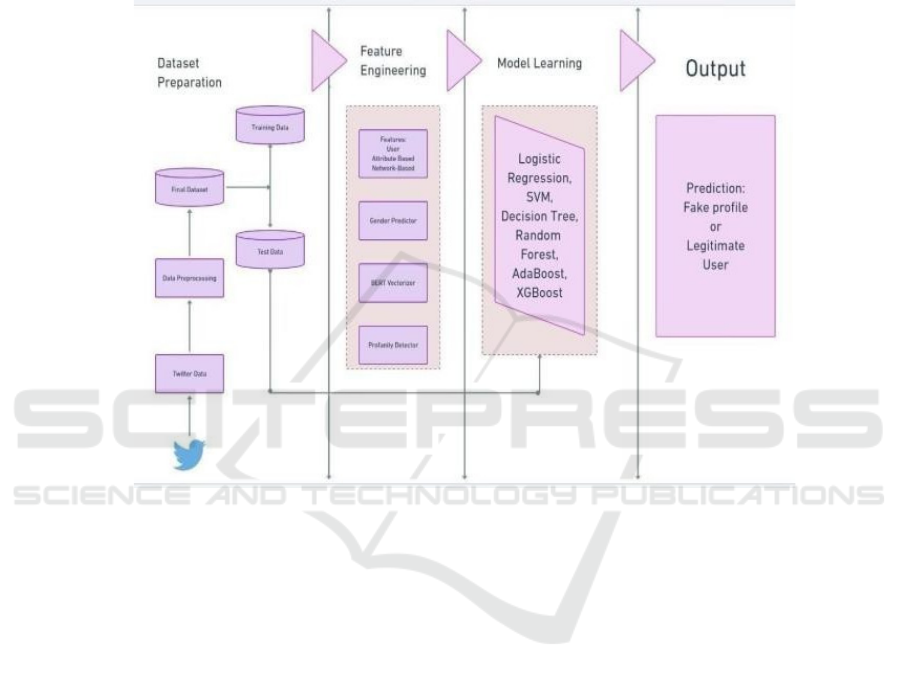
Figure 1: System Architecture Diagram.
From the figure 1 the Data collect the first process
from social networks, concentrating on user profiles
predisposed to be fake. In this early stage, it is vital
to capture the 1410820 and appropriate this includes
screen_name, etc. and is the input to the generated.
Verification status, and other such metrics as the
number of tweets and followers. We cover the 4 types
of Data up to October 2023.structure, quality, and of
the dataset steps. This data is then converted into a
usable format. Categorial features such as verified
and protected statuses are encoded as numeric values
by techniques like Label Encoding.
This transformation ensures that the machine
learning analysis is structured. Textual attributes, like
a user’s screen_name, also contain useful data but
this has to be transformed to numbers a file format
which ML models can process with appropriate
structure. TF the text features are now subjected to
IDF Vectorization, converting them into a matrix of
features based on the frequency and importance of
words across the dataset. This technique captures the
subtleties textual content for those models to leverage
this data to predict fake profiles. After preparing the
data, we split the data stratified into training,
validation, and testing subsets. To retain the global
characteristic in each subset, sampling classes of the
target with their distribution. The training dataset is
used to train the model, and the validation set is used
for fine-tuning and the testing set measures the final
because performance is stable over time, you can get
an accurate evaluation of the model's effectiveness.
Then different machine learning models, including
classical algorithms like SVM, Random Forest to be
the elite model trained and evaluated by various
metrics. Moreover, neural networks are used for
detecting and learn more complex relationships
within the data. These the different types of networks,
including deep networks and dropout layers to avoid
overfitting, learn more complex relationships than
simpler models and what the networks statistically
hate most: By training the networks through back
propagation, they become more predictive.
Fake Profile Detection on Social Networking Websites Using Machine Learning
23
5 RESULTS
In this research, we assessed how well different
machine learning models perform in identifying fake
profiles on social networks, focusing on Random
Forest, SVM, and Neural Networks.
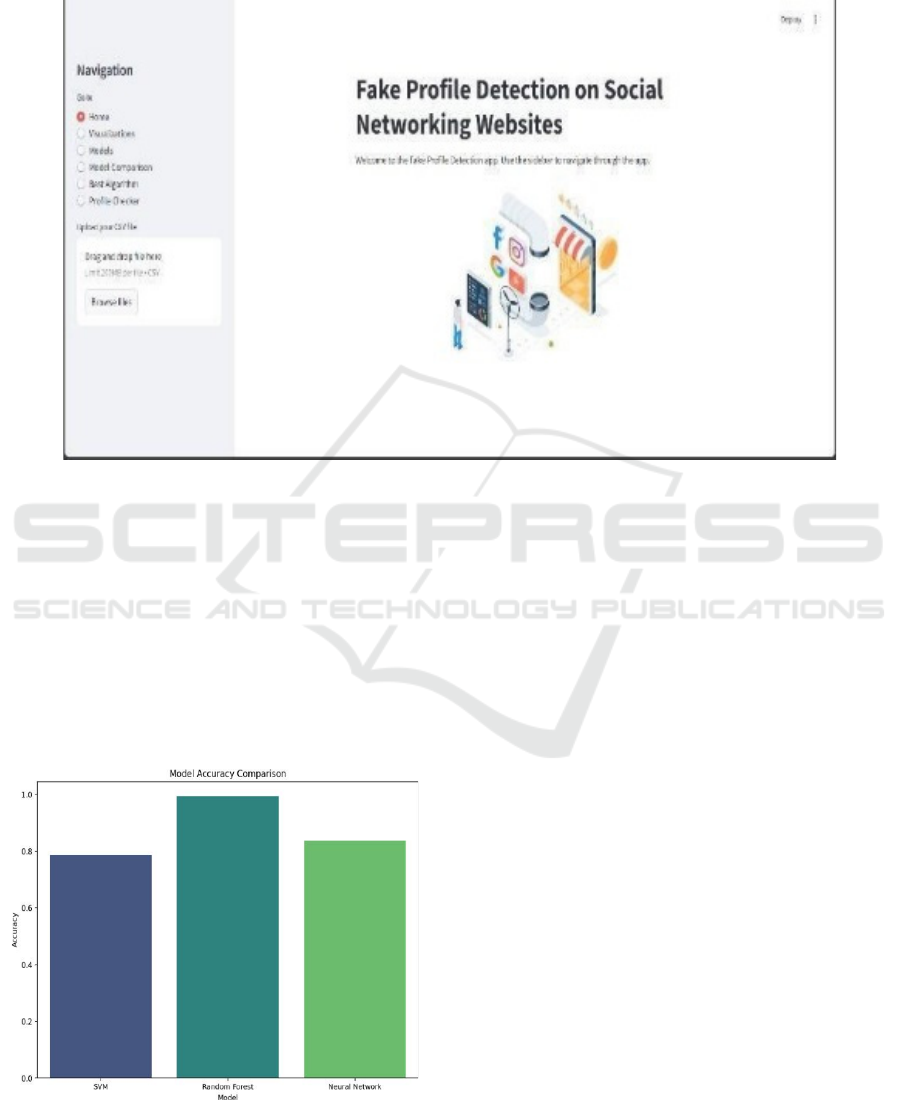
Figure 2: User Interface (Home Page).
The above figure 2 displays the user interface of
the "Fake Profile Detection" app. It includes a side bar
with options like Home, Visualizations, Models,
Model Comparison, and Profile Checker. Users can
upload CSV files, making it easy to interact with their
data. The interface is user-friendly and visually
engaging from the figure 3 the Random Forest model
demonstrated exceptional results, achieving an
impressive 99% accuracy, which highlights its ability
to correctly classify almost all fake profiles in the
dataset.
Figure 3: Accuracy Comparison.
SVM followed with an accuracy of 90%,
performing well but slightly behind Random Forest
due to the complexities of separating the classes in the
feature space. The Neural Network achieved an
accuracy of 89%, showing it can still handle the task
competently, although its performance may have
been influenced by factors such as the network
architecture and data quality.
Beyond accuracy, we assessed the models with
spelling, prediction and RMSE (Root Mean Squared
Error) to allow for a more complete comparison.
Random Forest reaches a near perfect accuracy
99.47%, followed by at 91.54% for the Neural Net
and at 85.30%. Recall, which measures the ability to
Predicted fake profile correct=Random Forest the
Neural Network and led with 99.47%, while Neural
Network and SVM had recall of 89.89% and
79.72%. The F1 score, which reflects a trade-off
between precision and recall, reinforced Random
Forest shoulder with its near-perfect score of
99.47%, with 89.85% for Neural Network and
77.96% for SVM. RMSE was also used to evaluate
the models, which Random Forest had the least error
(RMSE of Its AUC was 0.0729, implying highly
accurate predictions. On the show the worst
performance among the classification models for the
given multiclass dataset, having accuracy in the range
of 44% to 54% (the rest fall on the upper side)
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
24
(Human-AI Model, 2023)-different metrics reported
can result in a difference of 25% in performance had
higher RMSE of 0.1613 and 0.3170, respectively.
Overall, Random Forest beats both SVM and Neural
Networks reliable model to detect fake profiles with
detail this task. Finds followings are as follows.
Performance of the model:
A
ccuracy =
()
(
FP)
(1)
Precision=
()
(2)
Recall =
()
(3)
F1Score =
()
()
(4)
𝑅𝑀𝑆𝐸 =
∑
(
)
(5)
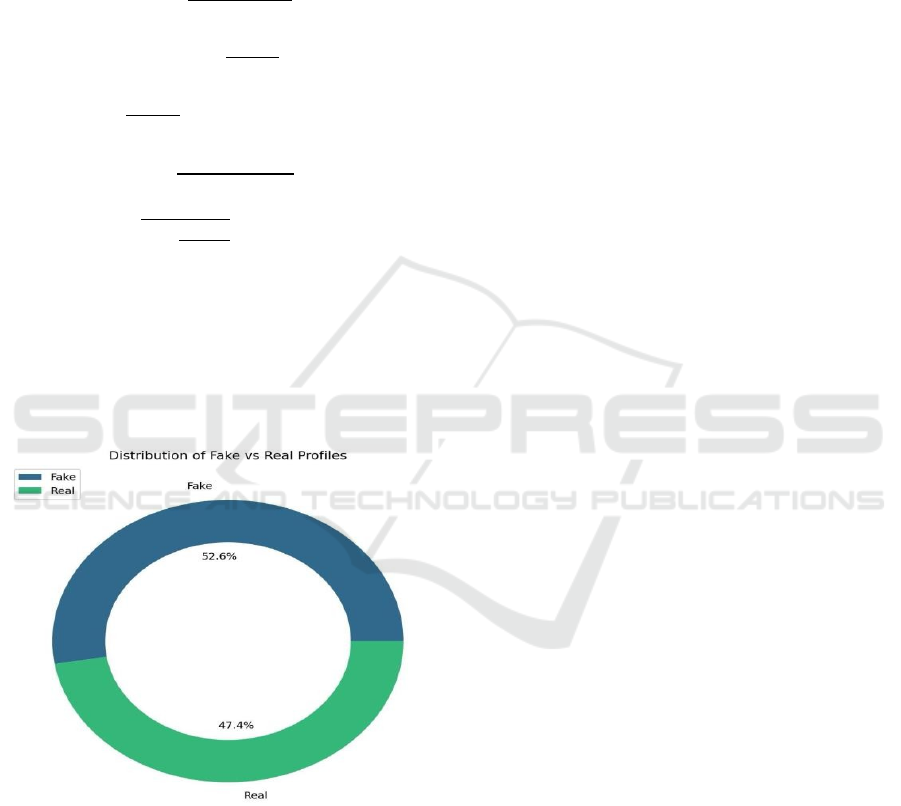
Above figure 4 is a donut chart showing the
proportion of fake and authentic profiles. It reveals
that 52.6% of 47.4% are real and 52.6% the profiles
are fake. The inner section of the chart clearly shows
the percentage for each of them, improving
interpretability, quick visual comparison of the two
groups.
Figure 4: Distribution of Fake Vs. Real Profiles.
6 CONCLUSIONS
To summarize in summary, the use of different
machine learning models, including Random Forest,
SVM and Neural Networks has noted as having good
potential for detecting fake profiles social media
across platforms. By employing sophisticated
traditional methods combined with modern methods,
we are able to successfully improve the precision and
dependability of classification. The use of complete
Streamlit application permitted a real Based on 1D
data, these embeddings can be conditioned on time
interaction with model performance metrics and data
showcasing, in these visualizations, how effective
these approaches. The results underscored the
importance of machine learning in the maintenance
of online platform, providing a strong instrument for
shielding users against fraudulous actions and a
better secure Digital world
.
7 FUTURE SCOPE
In the future, open up plenty more opportunities for
even better detection systems for fake profiles. As
deceptive tactics Deep learning evolves, ashes and
possibly ashes, and ashes. Optimizing existing
algorithms, will be critical to staying ahead of
emerging threats. Enhancing real-time detection new
capabilities, broader datasets, and adding new
inclusion of features like network-based analysis or
behavioral patterns could greatly increase detection
accuracy. Additionally, broadened access to these
tools for users via more Intuitive interfaces and
harnessing advancements in AI will to assure that
social media platforms can continue to be secure,
trustworthy and user- friendly going forward.
REFERENCES
Alghamdi, A. M., &Shadi, M. A. (2023). A Novel
Approach to Fake Profile Detection Using Hybrid
Machine Learning Methods. IEEE Access.
AlZamal, F., Liu,W.,& Wang,D.(2022).Detecting Fake
Profiles on Social Media Platforms Using Machine
Learning. Journal of Applied Computing.
Arora, A., & Sharma, P. (2022). "Profile Classification in
Online Social Networks Using Machine Learning
Techniques." Journal of King Saud University -
Computer and Information Sciences.
Besel, C., & Co, L. (2022). Profiling and Detecting
Malicious Accounts on Social Media Platforms.
Computational Social Systems Journal.
Bontchev, V. (2020). "Towards a Better Understanding of
Fake Accounts on Social Media." Proceedings of
the2020 IEEE/ACM International Conference on
Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining.
Cresci, S., Pietro, R. D., Petrocchi, M., Spognardi, A., &
Tesconi, M. (2017). The Paradigm-Shift of Social
Spambots: Evidence, Theories, and Tools for the Arms
Fake Profile Detection on Social Networking Websites Using Machine Learning
25

Race. Proceedings of the 26th International World
Wide Web Conference (WWW '17).
Feng, Y., & Li, J. (2022). "Fake User Detection Based on
Multi-Feature Fusion and Machine Learning." Journal
of Computer Networks and Communications.
Kudugunta, S., & Ferrara, E. (2018). Deep Neural
Networks for Bot Detection. Proceedings of the 2018
IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in
Social Networks Analysis and Mining.
Li, W., & Yu, S. (2021). "Machine Learning Techniques for
Detecting Fake Users in Online Social Networks."
Computer Applications in Engineering Education.
Patel, S. K., & Kumar, R. (2021). "A Comprehensive
Review on Fake Profile Detection Techniques in Social
Media." International Journal of Computer
Applications.
Rao, S., & Kaur, R. (2023). "An Efficient Approach for
Fake Account Detection in Social Media Using
Ensemble Learning." International Journal of Comp-
uter Applications.
Singh, V., Tolasaria, N., Patel, M. A., & Bartwal, S. (2023).
Classification of Instagram Fake Users Using
Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms. arXiv.
Wang, B., Zhang, J., & Zhu, X. (2023). Fake Profile
Detection on Twitter Using Deep Learning. IEEE
Transactions on Computational Social Systems.
Yang, C., Harkreader, R., Zhang, J., Shin, S., & Gu, G.
(2021). Analyzing Spammers' Social Networks for
Detection of Social Spam Bots. Proceedings of the 21st
International World Wide Web Conference.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
26
