
Synthesizing Human Expert Opinion to Assess News towards News
Authenticity
S. Sangeetha
1
, S. Padmapriya
2
, J. Sudha
2
, R. Sudha
2
, A. Vivekanandhan
2
and R. Valampuranayaki
3
1
Department of IT, E.G.S. Pillay Engineering College, Nagapattinam, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of CSE, A.V.C College of Engineering, Mannampandal, Tamil Nadu, India
3
Department of IT, A.V.C College of Engineering, Mannampandal, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Media Manipulation, Fake News Impact, Socio‑Political Influence News Authenticity, Information
Verification, Internet News Challenges.
Abstract: Socio-Political impact on news dissemination, the media is flooded with News with biased headlines to
generate a substantial profit and sometimes due to some socio-political influence it becomes grey area and is
widely use to influence it. As a result, there are several issues that have come to the forefront. such as the
socio-political impact of news propagation, the declining independence of news media, and a straightforward
news assessment system have become increasingly relevant issues due to the rising use of internet news.
Political polarization, motivated reasoning, and social media algorithms are the cause of fake news. Fake
news, no matter the extent of impact, is definitely damaging. The essence is that the news, we read or receive,
shall have good sources and the information shared in the news shall be authentic. This study tries to find and
verify the fake news. The Natural Language Processing (NLP) model is trained iteratively using the
incremental data to achieve the desired output before being utilized for fake news detection.
1 INTRODUCTION
News media in modern news media, as a top for
public, are the basis for of information access and
discussion. But between the grand mission of
enlightening the masses, a darker undercurrent of
news fake news, sensationalism, and This reporting,
often referred to as agenda driven or policy driven
reporting, has emerged as a real threat to the integrity
of public discourse and democratic processes. So,
what I really want to do here is to investigate the
complex entanglement of issues at play in the ever-
evolving media with a particular emphasis on the
pernicious impact of biased headlines, money-driven
editorial choices, and socio-political pressures on
journalistic standards.
Located at the heart of this debate is the problem
of fake news, a misleading trend exacerbated in the
digital age, when information spreads quickly and
widely. Driven by political motives, profit or raw
opportunism, the purveyors of fake news-savvy
hoaxes take advantage of the failings of online
platforms, fostering narratives that substitute reality
with divisive fare that erodes confidence in traditional
institutions. Set against this context, fears about the
erosion of press freedoms, the proliferation of echo
chambers fuelled by social media algorithms and the
unleashing of disinformation as a weapon of political
warfare, have reignited calls to action and re-enter
discourse with urgency.
2 RELATED WORK
In (M. A. Al Mumin et al. 2019)- Detecting fake news
using a Machine Learning Approach is a more
detailed machine learning approach which is focused
on detecting the Fake news in online media. In this
paper, the authors introduce a new approach for
accurately detecting and classifying fake news
articles based on the framework of natural language
processing, social network analysis, and supervised
learning algorithms. This framework extracts textual
features from news articles (including linguistic
patterns, sentiment analysis, and credibility
indicators) and integrates them with social network
features (such as source reputation and dissemination
patterns) to improve classification performance. As
Sangeetha, S., Padmapriya, S., Sudha, J., Sudha, R., Vivekanandhan, A. and Valampuranayaki, R.
Synthesizing Human Expert Opinion to Assess News towards News Authenticity.
DOI: 10.5220/0013876100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages
17-20
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
17

the authors show, their approach performs this
detection task on a large dataset with a number of
actual news articles, and they achieve promising
accuracy and efficiency results. In this study, we
propose an integrated framework comprising a
combination of state-of-the-art machine learning
algorithms and model-friendly linguistic and social
network features to detect and differentiate between
the genuine news and its false counterparts.
For example, in (B. Uddin et al. 2021) - Spread of
Misinformation is the authors use a large dataset of
articles and social media shares to analyse whether
patterns exist in the dissemination of
misinformation. They also find that misinformation
spreads more rapidly and reaches a larger audience
than does fact, in part because misinformation is
new, emotionally compelling, and fits the social
network structure. University of California, Berkeley
Fake News Spread: The Role of Social Media
Misinformation has become a standard term in this
paper due to the mechanisms in fake news spread. By
examining thousands of news articles and millions of
social media shares, the authors pinpoint factors and
patterns that contribute to the virality of
misinformation. As a foundational source, this study
shall improve the understanding of the dissemination
of fake news which shall pave the way to future
research in detection and prevention of
misinformation.
Reference (S. Nath and S. Ray 2022)- Automation
Detection of Fake News. The authors discuss
previous methodologies such as content-based
analysis, social network analysis, and machine
learning algorithms, comparing their pros and cons. It
discusses the challenges in fake news detection,
including dataset bias, algorithmic bias, and
adversarial attacks and provides directions for future
work. This paper presents them with detailed
information on advanced approaches to combat fake
news as well as the foundation for both researchers
and practitioners in the area. It provides a detailed
overview of automated Methods for detecting and
analyzing misinformation, thus serving as an
important reference to researchers and practitioners
in the area of misinformation detection. A systematic
literature review of existing methods is made,
emphasizing their pros, cons, and applicability in a
given context.
Media Literacy Intervention for Misinformation
in reference (M. Kowsher et al. 2021) - The authors
discuss various educational programs, initiatives and
interventions that attempted to foster critical thinking
skills, media competence. and the traditions of
individual and group responsible information
consumption. They isolate common attributes
associated with successful media literacy programs,
including interactive instructional approaches,
customized course content, and techniques for
fostering community involvement. (M. A. Al Mumin
et al. 2019) This review comes with
recommendations and describes effective strategies
to combat misinformation, which could be used by
educators, media organizations and policy-makers.
Drawing from a study of a dozen media literacy
programs, the authors outline key elements that
increase the likelihood of successful media literacy
campaigns and recommend data-supported strategies
for creating effective programs. The review provides
a field guide for how to correctly respond to the
dangers of misinformation and the importance of
critical thinking skills and responsible information
consumption habits in the digital age.
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
These authors explore educational programs or
initiatives or interventions that promote critical
thinking skills and digital literacy, and habits of
responsible information consumption for individuals
and communities. They analyze the main elements
that underscore just how successful media literacy
interventions are, including interactive learning
styles, context-specific programs, and community-
facing initiatives. The review highlights important
takeaways on how to effectively combat
misinformation and provides actionable
recommendations for educators, policymakers and
media organizations. Through systematic review of
academic literature associated with a diverse array of
educational programs and initiatives, these authors
illuminate important elements that promote the
efficacy of media literacy interventions and provide
concrete recommendations for developing 588
evidence-based interventions. It's an invaluable guide
in navigating the challenges posed by
misinformation and on how to promote critical
thinking and responsible information consumption in
the digital age.
Google Cloud computer for News Authentication
Application consists of modules of News
Authentication Cloud server client creation Reverse
news classification Publish Authenticated news
Cloud Server Creation – During cloud server
creation authorization the module authenticates to the
selected cloud provider using secure credentials,
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
18
establishing a trustworthy connection for the next
operations. You are read well new server instances as
instance type so or geographical zone.
Moreover, it also supports features such as
automatic scaling, where the users can easily adjust
server capacity in real-time based on demand
patterns. It also features strong error handling to
elegantly handle exceptions and minimize operation
disruption. In addition, the module provides
comprehensive feedback on the creation of servers,
providing information on real-time status updates and
resource allotment.
02 data monitoring — In this module the data
posted as news will be monitored. As well as News
extracted from general data. A high priority media
monitoring is done across most spreading media. A
monitoring news module utilizes contextual
embeddings to calculate the authenticity of news
articles. Integrating with news outlets, it constantly
fetches articles for review. It utilizes advanced natural
language processing techniques to generate
contextual embeddings for each article that capture
fine-grained semantic information. These
embeddings are then processed through a pre-trained
model that is built on real news articles, allowing the
module to verify authenticity through the calculation
of similarity scores.
Module 1: News Classification — Extracted
news will be classified in this module. Sensitive and
non-sensitive news are classified thus Non sensitive
news gets published. The Classification Module: A
module that employs machine learning algorithms to
classify news articles in various categories, separating
authentic articles from potentially misleading ones
based on the output generated by the module titled
"Enhancing News Authenticity Assessment with
Contextual Embeddings." The classification module
consisted of threshold-based classification to the
Determine authenticity category of article, upon
receiving contextual embeddings and authenticity
scores from the above module.
Articles that score above an authenticity threshold
are classified as authentic, for which the algorithm
has a high certainty, vis-a-vis the reliability and
accuracy of facts in the article. On the other hand,
any article that scores lower than the threshold is
labeled as potentially harmful, requiring additional
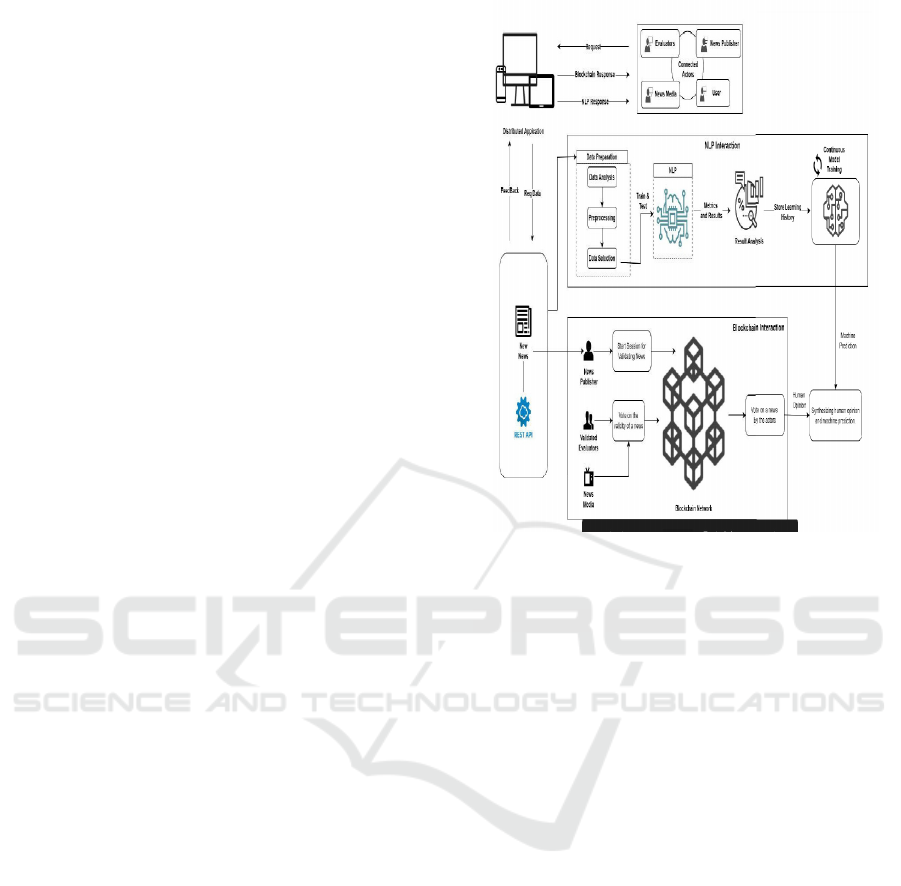
examination or confirmation. Figure 1 shows the
Blockchain and NLP-Based Framework for News
Validation and Opinion Synthesis.
Figure 1: Blockchain and NLP-Based Framework for News
Validation and Opinion Synthesis.
Publish Authenticated News: Secure news
authentication. This module sends the Sensitive news
for authentication. After integrity check it will be
supervised learning. News will be published by
authentication. The Publish Authenticated News
module acts as a forum for publishing authenticated
news articles, designed to promote the distribution of
accurate and checked information to the general
population. It works together with the authentication
and classification modules to ensure news articles are
genuine before being published.
When an article is submitted by a journalist or
contributor, the module conducts a full authenticity
assessment using contextual embeddings and
classification algorithms. Articles that surpass this
threshold of authenticity are considered
authenticated and eligible for publication.
The module provides a user-friendly content
management interface where editors can validate,
enrich with context or metadata, and set publish times
for authenticated articles. It also enables collaborative
editing and approval workflows to maintain editorial
integrity. In addition, the module connects with
social media and news aggregation channels,
enabling the dissemination of validated pieces to 【ɑ
】 larger audience. It uses HTTPS to ensure that the
data when published is protected from interception
Synthesizing Human Expert Opinion to Assess News towards News Authenticity
19

and malicious attacks. If the authenticity score of an
article is greater than a preset threshold, it is
categorized as authentic, thereby establishing a
relatively high certainty that the article is reliable and
factually appropriate. On the other hand, articles with
scores lower than the threshold are designated
potentially misleading and require further inspection
or verification.
4 CONCLUSIONS
A marvel of contemporary media: a delicate
balancing act, ever so close to being toppled by
unforeseen consequences applied nationally. The
proliferation of skewed journalism, motivated by
finance and socio-political agendas, has resulted in
widespread distortion, and added a layer of fog to
news reporting. Issues of socio-political impact,
shrinking freedom of the news terrorism and the
necessity for a basic news evaluation process have
appeared regarding the increasing sulfide of internet
news. There are several factors that encourage fake
news, such as political polarization, motivated
reasoning, and social media algorithms, all of which
play a role in how fake news spreads, and this is not
without consequences. Then the news we read
should come from real-world sources and contain
truthful information. This study heats up the hastst
game of identifying and verifying which news
authenticity in order to tackle the critical challenge of
countering the influence of fake news on public
perception towards general topics and human societal
conversations.
REFERENCES
A. Riaz and F. Zaman, ‘‘Working under the ‘sword of
damocles’: Experiences of journalists in a hybrid
regime,’’ in Masks of Authoritarianism. Singapore:
Springer, 2022, pp. 37–55, doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-
43149_3. management, analysis and future prospects.6
,54(2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s405370190217.
A. Riaz and F. Zaman, ‘‘Working under the ‘sword of
damocles’: Experiences of journalists in a hybrid
regime,’’ in Masks of Authoritarianism, A. E. Ruud and
M. Hasan, Eds. Singapore: Palgrave Macmillan, doi:
10.1007/978-981-16-4314-9_3.
B. Uddin, N. Reza, M. S. Islam, H. Ahsan, and M. R. Amin,
‘‘Fighting against fake news during pandemic era: Does
providing related news help student internet users to
detect COVID-19 misinformation?’’ in Proc. 13th
ACM Web Sci. Conf., Jun. 2021, pp. 178–186, doi:
10.1145/ 3447535.3462508.
K. A. Ahmed, ‘‘In bangladesh: Direct control of media
trumps fake news,’’ J. Asian Stud., vol. 77, no. 4, pp.
909–922, Nov. 2018.
M. A. Al Mumin, M. H. Seddiqui, M. Z. Iqbal, and M. J.
Islam, ‘‘Neural machine translation for low-resource
EnglishBangla,’’ J. Comput. Sci., vol. 11, no. 11, pp.
1627–1637, 2019.
M. H. Alkawaz and S. A. Khan, ‘‘Use of fake news and
social media by main stream news channels of India,’’
in Proc. 16th IEEE Int. Colloq. Signal
Process.Appl. (CSPA), Feb. 2020, pp. 9397, doi:10.11
09/CSPA48992.2020.9068673.
M. Kowsher, M. J. Uddin, A. Tahabilder, M. R. Amin, M.
F. Shahriar, and M. S. I. Sobuj, ‘‘BanglaLM: Data
mining-based Bangla corpus for language model
research,’’ in Proc. 3rd Int. Conf. Inventive Res.
Comput. Appl. (ICIRCA), Sep. 2021, pp. 1435–1438.
Q. Shishir, ‘‘Reports misleadingly claim Saudi Arabia
plans to remove Islamic oath from national flag,’’ Tech.
Rep., Feb. 2022.
R. Bayes and J. N. Druckman, ‘‘Motivated reasoning and
climate change,’’ Current Opinion Behav. Sci., vol. 42,
pp. 27–35, Dec. 2021.
S. Nath and S. Ray, ‘‘Political campaigning in west
bengal: Violence, professionalisation, and communalis
ation,’’ South Asian Hist. Culture, vol. 13, no. 3,
pp. 305320, Jul. 2022, doi: 10.1080/19472498.2022.20
75208.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
20
