
Advanced Phishing Detection System: Integrating Deep Learning
Machine Learning and Transformers for Real‑Time Protection
P. Phanindra Kumar Reddy
1
, S. Fahimuddin
2
, D. Hameed
1
, D. Allipeera
1
,
V. Rajkumar
1
and P. Harshavardhan
1
1
Department of AI&DS, Annamacharya University, Rajampet, Andhra Pradesh, India
2
Department of ECE, Annamacharya University, Rajampet, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: AI Models, Feature Extraction, Flask Interface, Machine Learning, Phishing Detection, Real‑Time Analysis,
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA), Web Security.
Abstract: This research article proposes an Advanced Phishing Detection System that integrates advanced feature
extraction, exploratory data analysis (EDA), and various machine learning models to enable real-time
detection of phishing threats. Online data is being processed to extract key features and then extensive EDA
is being done to identify patterns from which phishing activity can be deduced. We perform the detection of
phishing websites using techniques like Decision Tree, Random Forest, Multilayers perceptrons (MLP),
XGBoost, Autoencoder Neural Network, Support Vector Machines (SVM) - 6 well known AI models. In the
experimental results, it was observed that Multilayer perceptron was right behind XGBoost with training
accuracy of 0.858 and testing accuracy of 0.863 against maximum accuracy of XGBoost where it achieved
training accuracy of 0.866 and testing accuracy of 0.864. Though least accurate, Autoencoder Neural Network
and SVM give their corresponding results as complement, whereas Random forest and decision tree models
outperforms them all. Using Flask, an easy-to-use interface is developed so that a real-world application can
be easily done, to get instant insight and feedback regarding a potential phishing site.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the greatest threats to cybersecurity in today’s
digital age is phishing, where users are deceived into
giving away sensitive information such as account
passwords and banking credentials (Hubbard et al.,
2023). These attacks are used to e xploit
vulnerabilities in internet communications systems,
either by masquerading as trusted corporations or
issuing fraudulent emails or webpages. One advanced
phishing detection system, machine learning (ML)
and artificial intelligence (AI) approaches, learns the
patterns or behavior of the detector that indicates a
detector attack (Abouzakhar et al., 2002). Using
several AI models allows these systems to improve
the precision and effectiveness of phishing detection,
providing preventive defense against constantly
changing threats.
Phishing attacks are
a huge issue for society over
multiple dimensions of cost, thousands of dollars lost,
personal information compromised annually. Recent
data shows that one of its most frequent and deadly
cyberthreats continues to be phishing, which affects
individuals and businesses alike. Intelligent phishing
detection systems can significantly reduce these risks
by labeling phishing attempts in time and with high
precision. Such protection not only protects financial
loss and personal information but also helps to ensure
a safer online ecosystem in general Next-Generation
Detection Mechanisms These solutions adopt next
gen detection mechanisms to help restore public
confidence in online platforms and build a sustainable
cyberdefense.
This is the finalisation of a wide literature review
to inhibit phishing that merges exploratory data
analysis, feature extraction and machine learning
approaches. Different models such as decision trees,
random forests, MLP, XG-Boost, Autoencoder
Neural Networking, and Support Vector Machines
(SVM) are can be found being applied to e xa mine
the performance of AI models in detecting phish
activities. A comparative analysis of the algorithms'
performance is given based on how successfully they
distinguish phishing websites from non-phishing
ones. The practical application of this work is made
Reddy, P. P. K., Fahimuddin, S., Hameed, D., Allipeera, D., Rajkumar, V. and Harshavardhan, P.
Advanced Phishing Detection System: Integrating Deep Learning Machine Learning and Transformers for Real-Time Protection.
DOI: 10.5220/0013875800004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 2, pages 5-10
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
5

easier by the development of a Flask-based user
interface (Petre et al., 2019) that enables the real-time
detection of phishing websites.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
The majority of previous phishing detection research
has gone toward creating and improving systems to
detect phishing attempts using different approaches.
Heuristic techniques and rule-based systems, which
employed established rules to identify phishing based
on recognized patterns and signatures (Moghimi.,
2016), were the mainstays of early attempts.
Shahrivari et al. proposed the internet has made it
possible for hackers to trick victims through social
engineering and spoof websites, a practice known as
phishing (Shahrivari et al., 2020). Because machine
learning and these assaults have similar traits,
machine learning is an effective way to identify them.
In order to anticipate phishing websites, this research
exa mines the outcomes of many machine learning
techniques. Rashid et al. provides an effective
machine learning-based phishing detection method
that uses just 22.5% of novel functionality to correctly
identify 95.66% of phishing and suitable websites.
When the method (Rashid, 2020) is combined with a
support vector machine classifier, it performs well
when tested against common phishing datasets from
the University of California, Irvine collection.
Gandotra et al. e xa mines feature selection
techniques (Gandotra et al., 2021) for phishing
website detection and finds that, despite the time -
consuming aspect of creating a large number of
features, random forest reduces model building time
without sacrificing accuracy. Nimeh et al. using a
data set of 2889 authentic and phishing emails, this
study exa mines machine learning methods (Abu-
Nimeh., 2007) for phishing email prediction. 43
characteristics are used for classifier train ing and
testing. Sahingoz et al. proposed the transition from
traditional retail to electronic commerce has been
facilitated by the Internet's e xplosive e xpansion
(Sahingoz, Ozgur Koray, et al, 2019). Phishing tactics
are employed by cybercriminals to trick victims and
get confidential data. The complexity of authorized
websites is a result of attack mechanisms based on
semantics. Based on the features of NLP (natural
language processing) and seven categorization
techniques, this study offers a real-time anti-phishing
solution. A novel method for identifying phishing
attempts (Boddapati, Mohan Sai Dinesh, et al., 2023)
is presented by Jain et al., which looks at hyperlinks
in websites' HTML source code. It utilizes twelve
different types of hyperlink-specific attributes as well
as machine learning techniques. Because it is
customer-side, language-independent and scores
above 98.4% accuracy on the logistic regression
classifier the technique is an extremely efficient
method to identify phishing websites.
3 DATA COLLECTION &
PREPROCESSING
The effectiveness of a phishing detection mechanism
is significantly impacted by the caliber and
comprehensiveness of its training and assessment
data. In order to ensure the accuracy and robustness
of the detection models, preprocessing and data
collection are crucial procedures in this work. The
methods used to gather information and the initial
processing techniques used to prepare the data for
analysis are covered in this part. Data collection
involves acquiring a diverse range of cases from both
trustworthy and malicious sources in order to
adequately train the models. Datasets for phishing
detection (Alazaidah, R., et al., 2024) usually contain
characteristics that are taken from URLs, content on
websites, and metadata. This was an effort that
leveraged several resources, including collaborative
data sharing sites, publicly available phishing
datasets, and scraping tools, to build a comprehensive
dataset. Appendix (click for a larger view): Figure 1
(the collection, Figure 1) consists of URLs labeled as
genuine or phishing, along with relevant metadata
such as page layout, content features, and domain
registration data.
One of the most important steps in the process is
feature extraction, converting unstructured data into
an input format for training a model. In order to
produce
a
feature-rich
dataset, features
are
taken
from both phishing and trustworthy websites. To
generate a feature-rich dataset, features are extracted
from both phishing and legitimate websites. Such
aspects involve filters, such as information (e.g.,
domain age, SSL certificate status), URL features
(e.g., length, presence of special characters), and
HTML content features (e.g., presence of a login
form, iframes).
This helps the algorithm identify and extract such
attributes to pull out important indications of phishing
activity. Exp loratory data analysis aims to
understand the relations, patterns, and distribution of
the dataset. EDA helps us to identify important
features that aid in identifying phishing attacks and
also
uncovers any potential biases or inconsistencies
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
6
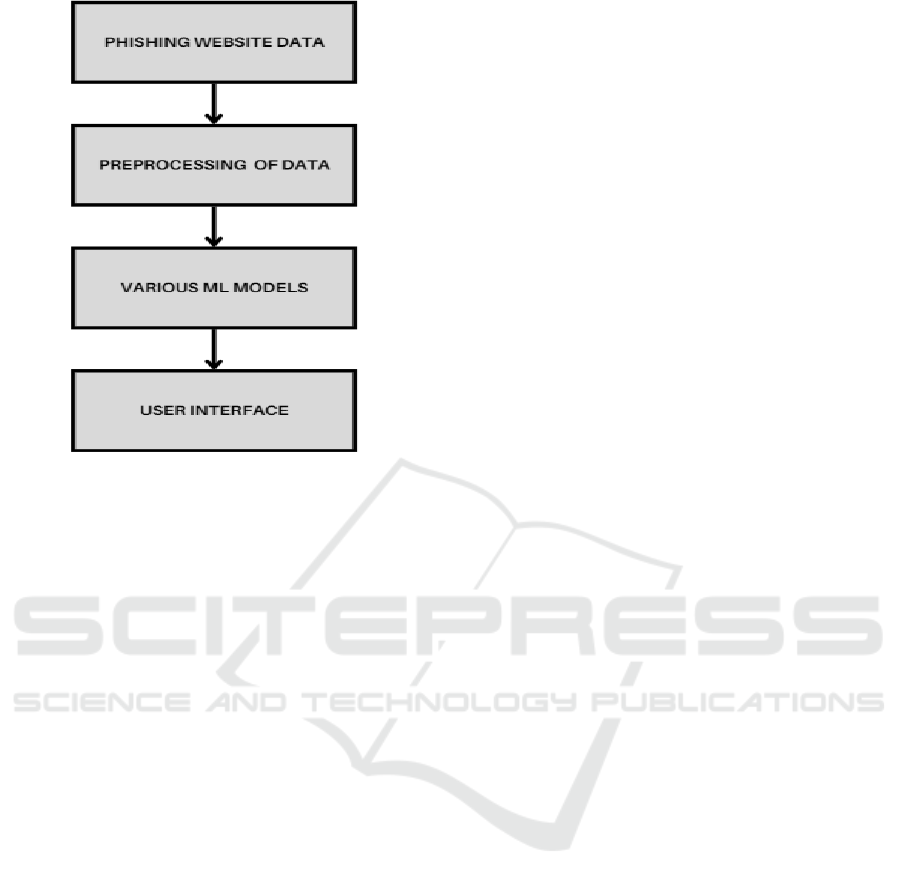
Figure 1: Architecture of System.
in our provided data. You can use statistical
summaries, correlation analysis, visualizations
(scatter plots, histograms, etc.) to get the overview of
the dataset.
Data cleaning (handling missing values and
errors, removing duplicates, correcting
inconsistencies) is an essential preprocessing step. In
this research, the dataset is properly cleaned to ensure
the dependability and quality of data. Duplicate
entries are dropped to avoid results being biased, and
missing values are dropped or imputed based on how
they affect the analysis. This resolves differences in
labels or data formats that would result in inconsistent
dataset. Data normalization is used to ensure that
features are on a same scale. This is very important
for machine learning algorithms, because they are
affected by the magnitudes of features. We use
methods such as z-score normalization, min-max
scaling, etc., to normalize characteristics into a
common range, or distribution.
4 PRINCIPLES AND METHODS
The effectiveness and accuracy of our phishing
detection system are driven by the concepts and
methods that it uses. Multiple ML techniques and AI
models are employed to achieve the central goal of
the system, which is to rapidly detect and suppress
phishing attacks. In this chapter, the concepts behind
the design and realization of the detection system are
explained. The computerised system that is trained to
detect phishing websites relies on mathematical
model which works on various machine learning
technology which enables them to learn from the data
fed into them and make predictions accordingly. The
constructed systems must be trained for machine
learning techniques so that they can find patterns and
relationships in the dataset. By training on past data
from both phishing and legitimate websites,
the
algorithm
learns to identify unique features and
behaviour associated with phishing attacks.
The extraction and selection of features are
critical processes for efficient phishing detection.
Feature Extraction: This refers to finding and
measuring relevant attributes from raw data, such as
the length of the URL, presence of special characters,
HTML content structures, domain information, etc.
This step transforms unstructured data into a
machine-readable format. Feature selection further
enhances this process by selecting the most crucial
features that enhance the model's predictive ability.
Feature selection improves efficiency and accuracy,
and techniques like feature priority ranking,
correlation analysis, and dimensionality reduction
(Principal Component Analysis, etc.) are commonly
employed to ensure the model better concentrates on
the most important characteristics. Detection enabler:
improves detection potential with a variety of
machine learning models Each model plays to its
strengths with different approaches to predictions and
classification. Decision trees, on the other hand, are
more interpretable in the sense that rules can be used
to describe relationships in terms of feature values
and decisions; Random Forests are the hashing of
many decision trees, combined in a way to provide
accuracy and robustness.
4.1 EDA
After collecting the data, the first thing we do before
using any machine learning models is exploratory
data analysis (EDA) which is the process of
inspecting and understanding the dataset. EDA is
about using the visual and statistical techniques to
uncover patterns, anomalies, test hypothesis and
verify assumptions. This initial study helps make
informed decisions about feature selection, data
processing, and model construction. This is an in-
depth overview of the major steps in the EDA
process. The first step here is to gather and collate
data from multiple sources, and this is done as part of
the EDA process. This is hinted at collection of
URLs, content of sites and their metadata for Phishing
detection system. Data can be acquired by using data-
sharing services, web scraping, or public databases.
Advanced Phishing Detection System: Integrating Deep Learning Machine Learning and Transformers for Real-Time Protection
7
Integrating data from multiple sources into one
common set while maintaining the format of the
dataset is called integration. This is an important step
because it provides an overall view of the data that
sets the stage for additional analysis.
One of the most powerful techniques in EDA is
data visualization, which involves putting the data in
a graphical representation to show correlations,
patterns, and trends. They are used as bar charts
comparing categorical data, as box plots to find
outliers, scatter plots to analyze feature correlations,
histograms to plot distributions of numerical values,
etc. Visualizations are also easier to interpret
compared to statistics summaries, enabling analysis
of complex data and identification of outliers or
trends. Correlation Analysis examines the
relationships between different features to study
possible dependencies or correlations. Pearson
correlation coefficients measure the e xtent and
direction of linear correlations between numerical
data. You can use contingency tables or chi-square
tests to check relationships for categorical data. This
is easily done once we know the correlation between
features and their duplicates can be removed by
choosing the dominant ones while forming the model.
4.2 Machine Learning Models
The Decision Tree approach is a classification
method that uses a tree-like graph to represent choices
and possible outcomes. Each node in the structure
represents a feature each branch indicates an option
rule, and each leaf node represents an outcome. The
model iteratively generates branches by segmenting
the data based on the feature that provides the best
separation so breaking the data into several
categories. The phishing detection system's Decision
Tree achieved 81.0% training accuracy and 82.6%
testing accuracy. The Decision Tree is easy to
understand and picture, but if it is not properly pruned
it may overfit. Random Forest is an ensemble learning
technique that generates the average forecast
(regression) or way to identify the classes (grouping)
for each individual decision tree constructed during
training. The model performs better because it
reduces variance and avoids overfitting by averaging
many trees. The phishing detection system's Random
Forest model obtained training accuracy of 81.4%
and testing accuracy of 83.4%. The Random Forest
approach is well known for its robustness and ability
to handle large highly dimensional datasets.
One or more hidden layers exist behind the input
and output layers of a type of neural network known
as a multilayer perceptron (MLP). MLPs are very
helpful in capturing non-linear connections. In the
phishing detecting system the MLP model achieved
testing accuracy of 86.3% and training accuracy of
85.8%. Although MLPs are known for their
versatility and capacity to replicate intricate patterns,
exact hyperparameter modification could be required.
The enhanced gradient boosting method known as
Extreme gradient booster or XG-Boost combines the
predictions of multiple weak models typically
decision trees to create a powerful predictive model.
To improve performance and efficiency it makes use
of strategies including regularizing, processing in
parallel and tree pruning. The XG-Boost model
within the phishing detection tool has the highest
accuracy scoring 86.6% during training and 86.4%
during testing. For many machine learning
applications XG-Boost is a popular choice due to its
excellent performance and scalability.
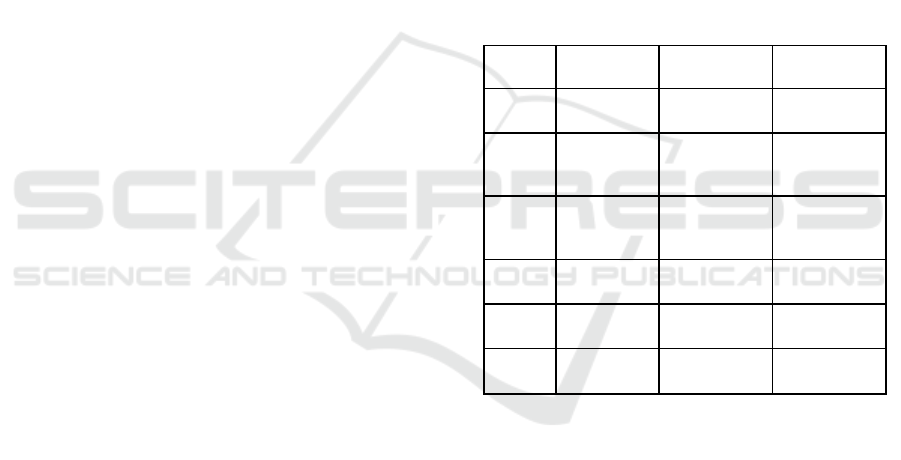
Table 1: Accuracies of Various Models.
Index ML Model Train
Accurac
y
Test
Accurac
y
3 XGBoost 0.866 0.864
2
Multilayer
Perceptrons
0.858 0.863
1
Random
Forest
0.814 0.834
0 Decision Tree 0.81 0.826
4 AutoEncoder 0.819 0.818
5 SVM 0.798 0.818
Table 1 Shows the Accuracies of Various Models.
Testing and training accuracy for the Auto Encoding
in the phishing system of detection were 81.8% and
81.9%, respectively. Although autoencoders can be
helpful in identifying outliers and abnormalities they
may require e xtensive fine- tuning. A type of
supervised learning method known as Support Vector
Machines (SVM) is applied to classification and
regression problems. In order to find the best, the
hyperplane for categorizing the data SVM maximizes
the difference between the classes. SVMs can handle
both nonlinear and linear classifications now that
kernel functions have been added. Details about SVM
based phishing detection system showed 79.8%
training accuracy and 81.8% testing accuracy. SVMs
with an appropriate kernel are known to generalize
well and perform effectively in high-dimensional
environments.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
8

5 RESULTS
The results of the phishing detection system indicate
the ability of various machine learning models to
identify phishing attacks. Each model’s effectiveness
in predicting URLs as either phishing or legitimate
was evaluated using metrics like training and testing
accuracy. The models performed differently; the
margins of accuracy were closest for
the MLP and XG Boost models. While Autoencod-
ers and SVM had much lower accuracy, Decision
Trees and Random Forests also behaved quite well
here. These results highlight the strengths and
weaknesses of each model and point to how suited
they all are to real-world phishing detection. Decision
Tree Model achieved Training accuracy of 81.0% and
Testing accuracy of 82.6%. The performance of
the
Random Forest model is exce llent, with testing and
training accuracy up to 83.4% and 81.4%,
respectively. With accuracy of 86.3% testing and
85.8% training Multilayer perceptrons (MLP)
predicted well. To be better with multiple relative
conditions through its neural network structure, the
MLP may catch the trend and non-linear relations in
the data. That's because it can mimic complicated
phishing events, and adapt to virtually any data
distribution. The phishing detection system is tightly
integrated with the Flask-based user interface,
providing a seamless experience for the users. The
Flask application is responsible for entering URLs
directly into a web form and starting the backend
operations for phishing detection. Once the user
inputs
a URL, Flask takes over the feature extraction
Figure 2: User Interface.
and data preperation before it sends the cleaned data
to trained machine learning models. Then, the system
immediately analyzes the URL and returns a
classification result that indicates whether the URL is
authentic or phishing. This integration enhances
users' ability to quickly detect and avoid phishing
threats by providing timely and actionable feedback.
User Interface Shown in Figure 2.
As illustrated in Figures 3 and 4, real-time
detection results demonstrate the model’s
effectiveness under varying conditions.
Figure 3: Real Time Detection.
Figure 4: Real Time Detection.
Flask project Real-time latest results and good fuse
on Load are the major features. It is also easy and smooth
for users to check the URLs through a simple user
interface without any knowledge of complex details of
the models. Practical developments are displayed in the
actual application of speed and accuracy of obtaining
predictions making it useful only when detecting
phishing attempts in real-time. Based on the power of
Flask the solution interconnects the user to a user-
Advanced Phishing Detection System: Integrating Deep Learning Machine Learning and Transformers for Real-Time Protection
9

friendly environment which promotes overall digital
security and promotes proactive cyber-security actions.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The development of this study, the developed phishing
detection system that uses real-time user
interface on different browser and advanced machine
learning algorithms will be a big step forward in
preventing and detection of online attacks. Their details
can be found in the Full Model section of the document:
Decision Trees, Random Forests, Multilayer perceptrons
(MLP), XG-Boost, Autoencoders
and
Support
Vector
Machines (SVM). The best apparatuses are XG-Boost
and MLP, according to the results and this is consistent
with their capacity to
manage numerous complex and
advanced phishing patterns.
REFERENCES
Abouzakhar, Nasser S., and Gordon A. Manson. "An
intelligent approach to prevent distributed systems
attacks." Information management & computer security
10.5 (2002): 203-209.
Abu-Nimeh, Saeed, et al. "A comparison of machine
learning techniques for phishing detection."
Proceedings of the anti-phishing working groups 2nd
annual eCrime researchers’ summit. 2007.
Alazaidah, R., et al. "Website phishing detection using
machine learning techniques." Journal of Statistics
Applications & Probability 13.1 (2024): 119-129.
Boddapati, Mohan Sai Dinesh, et al. "Creating a Protected
Virtual Learning Space: A Comprehensive Strategy for
Security and User Experience in Online Education."
International Conference on Cognitive Computing and
Cyber Physical Systems. Cham: Springer Nature
Switzerland, 2023.
Committee on Patient Safety, and Health Information
Gandotra, Ekta, and Deepak Gupta. "An efficient approach
for phishing detection using machine learning."
Multimedia security: algorithm development, analysis
and applications (2021): 239-253.
Hubbard, Douglas W., and Richard Seiersen. How to
measure anything in cybersecurity risk. John Wiley &
Sons, 2023.
Moghimi, Mahmood, and Ali Yazdian Varjani. “New rule-
based method for phishing detection.” Expert systems
with applications 53 (2016): 231-242.
Petre, Bogdan. Improving the Performance of a
Performance Monitor. The case of the Flask Monitoring
Dashboard. Diss. 2019.
phishing detection from URLs." Expert Systems with
Applications 117 (2019): 345-357.
Rashid, Junaid, et al. " Machine learning technique for
phishing detection." first international conference of
smart systems and emerging technologies
(SMARTTECH). IEEE, 2020.
Sahingoz, Ozgur Koray, et al. "Machine learning based
Shahrivari, Vahid, Mohammad Mahdi Darabi, and
Mohammad Izadi “Machine learning techniques for
phishing detection.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.11116
(2020).
Technology. "Health IT and patient safety: building safer
systems for better care." (2012).
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
10
