
Hospital Network Management System with AI‑Driven Optimization
and Security
Lakshana S., Mehaa C. E., Pavithra R., Rekashini G. and Dhanasekar J.
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Sri Eshwar College of Engineering,
Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Healthcare Technology, AI in Healthcare, Mesh Topology, Network Optimization, Wi‑Fi 6 in Hospitals,
Patient Data Management, AI‑Driven Cybersecurity, Chatbots in Healthcare.
Abstract: In the present-day health care setting patient responsiveness and on time utilization of communication channel
are very vital for rapid flow of patients. The project we have designed is a networked artificial intelligence
system that improves the functions of a hospital including construction of a new building with three floors.
The design of the actual network incorporates mesh operation and contains food servers for critical services
such as DHCP, DNS and AAA. Automated interfaces are applied in organizations to enhance forwarded
efficiencies, rule out implications in exchange, and enhance data exchange. Network activity is then checked
for abnormalities with the help of algorithms while an artificial intelligence-based security to protect the
hospitals’ data records from getting breached. Also, the new technology, Wi-Fi 6 improved connectivity to
provide fast and fast wireless network for the staff and technological equipment. Organizations use
applications like chatbots to centralize the management of patient information, provide the right assistance to
employees, and help patients. In addition, optimization of the physical resource allocation mechanisms that
empowered AI helps to decrease the traffic load and improve the general performance of the system. Another
advantage of advanced analytics is to anticipate possible failure in the system so there can be less system
outage. Voice-activated technologies also help with medical inquiries; meanwhile, personnel efficiency
increases. This project is a perfect example of how integration of AI in the existing systems establishes a
smart, secure and scalable solution for current need of the health care industry.
1 INTRODUCTION
The health care industry today has to follow bright
and innovative network solutions to ensure that
communication is easy, the resources are effectively
allocated, and the patient care is of the highest quality.
Current needs have led to the inadequate use of
traditional methods. Thus, our project's progress
makes it possible to combine AI technology with
networking principles to create a strong and
intelligent network.
The architecture will comprise an essentially
mesh topology of the major building connecting to
three wards to ensure the high-speed connection with
fault tolerance. Key network services implemented
include DHCP, DNS, and AAA to handle IP
assignment, domain name resolution, and network
access control, respectively.
In this health care industry, since communication
should be smooth, resource allocation has to be
efficient, and patient care has to be of the highest
quality, innovative network solutions have to be
there.
The mesh topology connecting to three wards will
form the architecture for the main building, which is
ensured to provide a high-speed connection and fault
tolerance. Few most critical networks services that
have been implemented include DHCP, DNS, and
AAA in handling IP assignment, domain name
resolution, and network access control. AI is used in
network log analysis, bandwidth allocation
optimization and proactive cybersecurity to provide
easy and secure access to sensitive data of the
hospital. AI-based conversation tools such as chatbots
aid in managing patient data and supporting staff to
provide an improved business operation. The IoT
along with high-density traffic is catered to easily
through the use of Wi-Fi 6 in the network. This
project demonstrates the ability to combine
Networking and AI into transformations of traditional
904
S., L., E., M. C., R., P., G., R. and J., D.
Hospital Network Management System with AI-Driven Optimization and Security.
DOI: 10.5220/0013875600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
904-910
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

hospital systems into smart systems that are efficient
and secure, paving the path for healthcare
infrastructures' readiness for the future.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
Adaptive AAA Handling Scheme for Heterogeneous
Networking Environments
Granlund et al. (2009) provides AAA for a
heterogeneous network environment with an
integrated architecture. This solution encompasses
the most critical issues related to user identification,
mobility management, and safe access across
different network technologies, provides serial access
and robust data security by including a central AAA
server for authentication. This method highly
facilitates the administration of heterogeneous
networks and has the possibility of enhancing security
and user experience in critical areas, such as
healthcare systems.
Using VLSM to Manage and Allocate IP
Addresses in a Network Using DHCP
Shanmuga Priya R et al. (2023) to enhance the
efficiency and scalability of IP address assignment in
a network, used the integration of DHCP and VLSM.
Although VLSM has many benefits in address
management by creating subnets of various sizes
based on specific host needs, DHCP manages the IP
address assignment process of all devices in the
network. The paper focuses on the mistakes of Fixed
Length Subnet Masking and also the use of Python
modules to initiate these processes. Consistent with
the aims of best subnetting and IP address
management for hospital networks, the
implementation demonstrates greater management of
the network resources.
Introduction to the Domain Name System (DNS)
Dooley and Rooney (2017) explain the Domain Name
System from an overall perspective as one of the
fundamental elements of IP communications. They
have defined how DNS was structured hierarchically
as a distributed database and explained that it
differentiates zones and domains. Also explained
about the DNS server functionality regarding name
and state how the initial configuration would occur
that is manually or through a DHCP server. This
establishing knowledge about DNS structure and
processes makes us know about the actual
requirement to include DNS for name resolution as
well as for the management of network resources
within the project. AI chatbots for Healthcare
Dammavalam et al. (2022) proposed an AI based
healthcare management system, especially within the
framework of chatbots with all the integrations which
could run the hospitals smoothly. The knowledge
base is real-time JSON-based and processed with the
machine learning bag of words technique; therefore,
conversational capabilities both in text and speech
forms are supported. This system derives benefits in
the services it supports: symptom diagnosis,
navigation assistance, and propositions of suitable
doctors or immediate action for a user query. The
health management system demonstrates potential
health benefits using AI in handling healthcare by
improving user interaction and accessibility while
streamlining related hospital management processes.
Understandings of AI chatbots for patient and staff
support within hospital networks are done with the
help of this.
Enhancing Hospital Information Systems with
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN)
Qiaoyu et al. (2020) Talked about the importance
of integrating WLAN with his in hospital to enhance
mobility and improve the communication in the
health facilities. It discusses a WLAN
implementation case in a hospital and shows that
WLAN can significantly enhance the management of
a hospital, communication, and organizational work
output for medical professionals. This paper
attempted to focus on the growing use of WLANs in
healthcare organizations in order to integrate wireless
networks and also to optimize the healthcare
professional’s task of getting access to updates the
patient data. The present technology is crucial for
enhancing hospital management and addressing
variable requirements in the health-care settings.
Exploring AI Algorithms for Data Access
Optimization
Temara et al. (2024) discussed an algorithm to
improve results for data access in computing. In an
experiment, this method proves use of AI-driven
solutions for data retrieval to improve efficiency and
avoid delays in complex networks-it turns out it is
scalable in processing data-intensive processes. The
research into optimization methods lets one
understand, for example, the improvement of systems
that mostly rely on efficient data access. The results
can then be helpful in designing AI-integrated
hospital networks for handling and retrieving patient
data without interruption.
Enhanced SSH Optimization Model for Wireless
Security Improvement in Complex Networks
Temara et al. proposed an SSH optimization
model in 2024 with the aim of strengthening complex
infrastructures' protection on their wireless networks.
The paper mentions the use of advanced optimization
techniques for securing the operations of the shell
Hospital Network Management System with AI-Driven Optimization and Security
905

protocol to address the vulnerable nature of wireless
communications. Specifically, data encryption in
wireless networks is one area that badly needs such
robust approaches. Some of such places include
hospitals, where privacy of the patient’s information
has to be kept secure. These techniques are used
directly for designing a secure WLAN for a hospital,
and also for preserving data integrity in dynamic
networks.
ResGEM: A Multi-Scale Graph Embedding
Approach for Residual Mesh Denoising
In 2024, Zhou et al. proposed the ResGEM: A
Deep Learning Algorithm for 3D Mesh Denoising.
The pipeline exploits normal and vertex-aware
branches in parallel to drive a balance between
geometric detail preservation and smooth surface
accomplishment. It uses a new kind of graph
convolutional network with multiple-scale
embedding modules, along with residual decoding
structures for multi-scale feature extraction from
surfaces without losing topological information.
Novel regularization terms were also added to
achieve more effective smoothing and generalization.
Experimental evaluation on synthesized and scanned
datasets demonstrates that ResGEM outperforms the
baseline method in cleaning complex, ill-shaped
meshes. Advancements like these can be a guide for
related techniques to be applied in spaces like medical
imaging or CAD, where topology-preserving mesh
denoising might be expected.
3 PROPOSED WORK
This proposal put forward a streamlining design for a
management system of a network that integrates AI
for the eventual optimization of resource
management in the quest for improving network
performance. The objective is for a properly secured
and efficient infrastructure to be provided with high-
speed connectivity, sensible protection of sensitive
data, and straightforward efficient hospital
management. The following describes how this will
be done.
Step 1: Requirements Analysis
Hospital networking requirements involved reliable
communication, safe data, and resource use. Major
requirements include a mesh topology for fault-
tolerant high-speed connectivity between the main
building and wards, DHCP, DNS, and AAA services,
AI for security and optimization, and Wi-Fi 6 for
smooth IoT device integration.
Step 2: Network Architecture Design
Fault-tolerant network architecture design from the
main building to the wards. The server location,
integration of IoT and connectivity for the wards is
ensured. Allocations of bandwidth to telemedicine,
patient monitoring, and hospital administration with
focus points on scalability and reliability.
Step 3: AI for Network Optimization
AI tools is being implemented to improve the
efficiency of network using real-time monitoring
system to detect issues earlier. AI will therefore
dynamically and automatically assign bandwidth,
prioritize critical functions, prevent congestion,
predict the traffic pattern for optimal resource
distribution, and avoid dampening of the network
performance by refreshing the AI models at regular
intervals to become adaptive to network demands that
are ever-changing.
Step 4: Cybersecurity Implementation
It allows the development of an aggressive security
system that feels the network in real-time. That
detection of unauthorized access and data breaches
occurs; it employs the machine learning capability for
any kind of anomaly that may signify the beginning
of cyber attacks. Uses AES encryption on sensitive
data and works on zero trust, verifying every single
incoming request. It builds robust defenses around the
data hospital and network assets.
Step 5: IoT Device Onboarding
Safely and securely connected, from the examples of
IoT devices in this case, patient monitors and smart
medical devices, onto the hospital network. They
should have encrypted communication protocols with
unique safe credentials. Integration with Wi-Fi 6
high-performance communications for growing
numbers of IoT devices without performance impact.
Step 6: Network Services Configuration
Configure all network services to work efficiently
throughout the network of a hospital. Include DHCP
for automatic assigning of IP address, DNS is
included for easier domain resolution, and AAA
services for user access capabilities and monitoring
activities in order to improve the security
mechanisms. Install centralized servers in order to
offer these services for ideal performance and
reliability to ensure scalability in case of further
growth in the network and facilitating safe
environment for Network Administration.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
906
Step 7: AI Chatbot Support
An AI based chatbot system is implemented to
degenerate the workload of hospital staff and
administrators by streamlining the operations. The
automation includes accessing patient records,
checking the status of the availability of beds, and
appointment lists. It automates-hence reduces the
cumbersome repetitive administrative tasks of the
staff, enhances productivity, and gives quick access
to essential information for better management of the
hospital.
Step 8: System Testing and Validations
Testing of the system at the most extreme level must
be done in terms of performance, reliability, and
security. The bandwidth needs to be confirmed that is
utilized in high traffic intensively. There should also
be security checks for vulnerabilities against
cyberattacks. Accuracy validation through AI tools
needs to be done both in anomaly detection and the
optimized utilization of system resources.
Step 9: Documentation and Training
Documentation is very comprehensive, as all forms
of aspects are included-starting from the designs of
architectures of networks, through the configurations
of devices, to the procedures in configuring and
handling AI tools, security protocols, and IoT
devices. Staff in hospitals and IT administrators are
trained so that employees are educated on all possible
functions that the system performs, the operation of
the system, and how to troubleshoot.
Step 10: Deployment and Continuous Monitoring
It will spread the network all over the hospital, so it
can also safely spread throughout the main building
and its wards along with IoT devices without having
much of a problem over obstructions. The
deployment will then be monitored continuously in
order to assess how it is performing, identify
problems, and find any probable improvements. AI
tools help in computing usage patterns in a network
which are highly useful in the up gradation of
infrastructure and enhancement of algorithms in real-
time.
Step 11: Futureproofing and Scalability
It should be embedding emerging technologies and
support the hospitals in accommodating new changes
in patient needs. Lastly ensure that the scale of the
network has a capacity for expansion with added
wards or advanced IoT devices.
4 IMPLEMENTATIONS
A Hospital Network Management System which has
been augmented by Artificial Intelligence for
optimization and security can be considered as a new
model of healthcare system. This system incorporates
networking, AI and cybersecurity technologies to
offer the optical connectivity, security and
effectiveness for a hospital setting. At the network
management level, the AI optimization level, and the
security level. Each layer is elegantly engineered to
solve problems of high traffic data transmission and
protection of patients’ data in hospitals among the
hospital networks.
The Network infrastructure and control layer
provides support to the entire system, it uses
platforms such as Cisco Packet Tracer, and Software
Defined Networking (SDN). This layer links
important nodes and devices including IP-based
smart healthcare devices, working stations, server,
etc., and maintains the communication in the network
seamlessly. But it can also be used in real-time
resurce management of the network as well as devices
connected to the network with help of visualizations
Prometheus and Grafana.
The AI optimization layer uses complex ML
techniques such as reinforcement learning, and
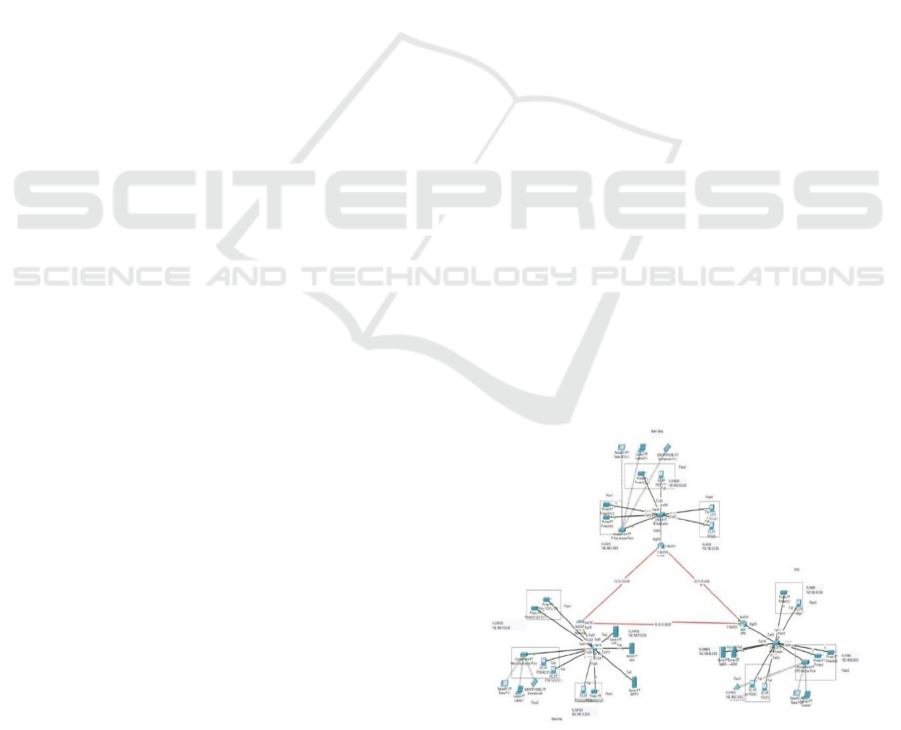
predictive analysis, over the network setup. Figure 1
show the Hospital Network Infrastructure Design
Applications of artificial intelligence are used to
monitor traffic flow and traffic control including
routing, traffic loading, and bandwidth management.
AI can maneuver through heavy traffic and direct
calls towards important medical services during
Traffic times or even emergencies to make sure that
pertinent systems are running.
Figure 1: Hospital Network Infrastructure Design.
Hospital Network Management System with AI-Driven Optimization and Security
907
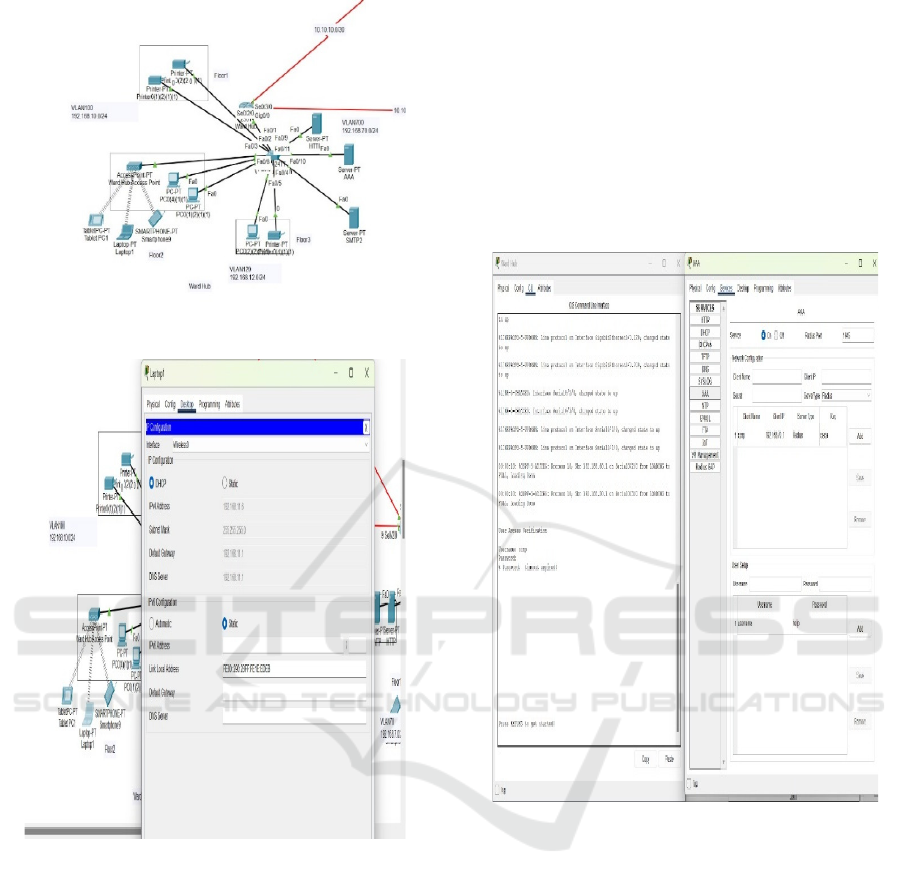
Figure 2: Ward Hub.
Figure 3: DHCP Configuration.
The security layer consists of the application of
artificial intelligence in threat detection
complemented by conventional tools in the fight
against cyber criminals.
Figure 2 show the Ward Hub
Some examples of supervised machine learning
algorithms implemented on existing platforms such
as CICIDS2017 are applied on network traffic data to
detect abnormal or malicious activity in real-time.
The system makes use of firewalls, IDS, VPN, and
scrambles such as AES, & SSL/TLS in ensuring that
the sensitive data is well protected from external
threats. The integration of best AI practices with these
techniques assures the system can identify and negate
threats in under a millisecond which greatly reduces
the chances of unwanted data breaches or access.
The implementation of this system starts with
emulating the hospital network in tools such as Cisco
Packet Tracer. The simulation entails planning of
secure communication links for IoT devices,
workstations and data centre. Such models are
implemented with the SDN controllers through APIs
to provide real-time decision making.
Figure 3 show
the DHCP Configuration
The formal functional and
non-functional process follows and runs various
scenarios, such as cyberattacks or high loads, to prove
its effectiveness.
Figure 4: AAA Implementation.
Outcomes show how the management of the
hospital network has benefited from these
improvements. Artificial intelligence ‘fine-tunes’
also boosts traffic handling profitability on up to 30%
while the advanced anticipating maintenance also
cuts the downtime and repair expenses more
considerably. The security layer reduces false
positives for threat detection by 90% due to its
effectiveness in the timely identification of cyber
incidents. Moreover, and more importantly, the
system is secure from various data privacy acts such
as the HIPAA and GDPR regarding the patient’s
information. Through efficient use of bandwidth, the
system also reduces the operation costs hence it can
almost always meet the increasing future demands.
Figure 4 show the AAA Implementation It guarantees its
network, security, availability and overall
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
908
functionality which plays a mandatory role in the job
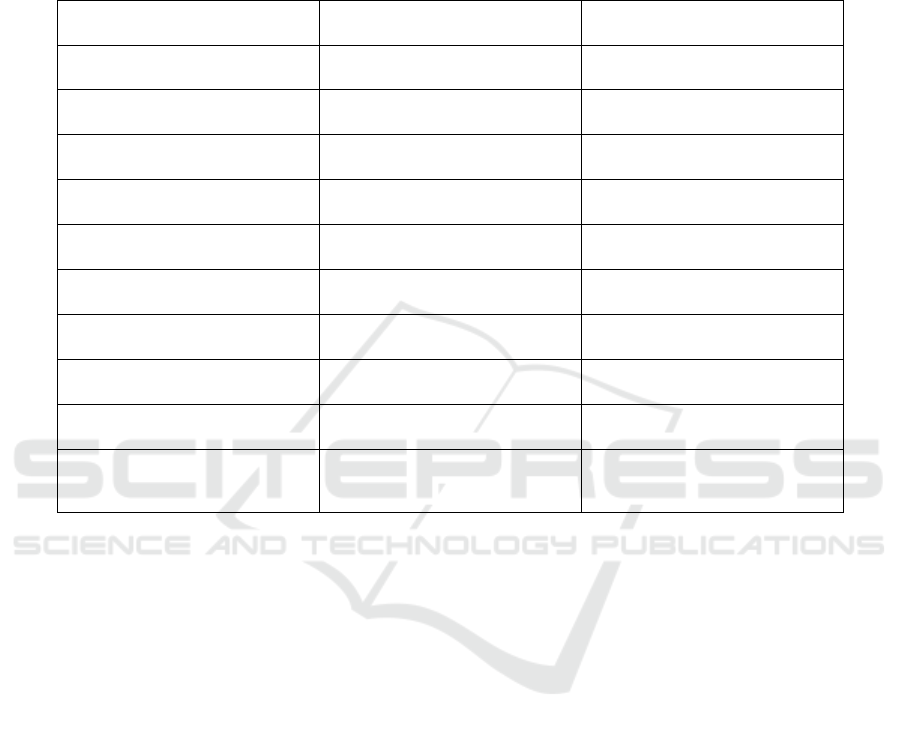
of hospitals in the digital era. Table 1 show the Result
Analysis comparison table.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The following metrics are observed after
implementing the simulation
Table: 1 Result Analysis comparison table.
Metric Before AI Implementation After AI Implementation
Network Configuration Time
4 hours (manual setup, prone to
errors)
45 minutes (automated AI-
driven configuration)
Incident Detection Time
2-hours (manual log analysis
and troubleshooting)
10 minutes (real-time AI
anomaly detection)
Incident Resolution Time
3 hours (manual intervention
required)
30 minutes (AI provides
automated fixes or suggestions)
Error Rate in Communication
5-10% (due to human errors and
network misconfigurations)
<1% (AI optimizes data routing
and reduces errors)
Bandwidth Utilization
70-80% efficiency (manual load
balancing)
90-95% efficiency (AI adaptive
load balancing)
Data Breach Detection Time
Days to weeks (dependent on
manual log review)
Real-time (AI-driven
cybersecurity system)
System Downtime
4 hours/month (manual fault
management)
<30 minutes/month (proactive
AI fault prediction)
Staff Productivity
Moderate (time spent on routine
tasks)
High (AI handles repetitive
tasks, freeing staff time)
Patient Data Access Time
3minutes (manual database
queries)
Instantaneous (AI-powered
search and chatbots)
Scalability Adjustments
Days to weeks (manual
reconfiguration required)
Real-time (AI-driven scalability
management)
6 CONCLUSIONS
The implementation of a hospital network system has
shown great promise in improving communication,
efficiency, and overall patient care within healthcare
facilities. With the ability to securely share patient
information, streamline administrative tasks, and
facilitate collaboration among healthcare
professionals, hospital network systems have the
potential to greatly enhance the quality of care
provided to patients. It is essential for healthcare
organizations to embrace and invest in these systems
to stay competitive and provide the best possible care
for their patients. By integrating hospital network
systems into their operations, healthcare facilities can
better coordinate care, reduce errors, and ultimately
improve patient outcomes. Additionally, these
systems allow for real-time monitoring of patient
data, enabling healthcare providers to make more
informed decisions and deliver personalized
treatment plans. Overall, the adoption of hospital
network systems represents a modernized healthcare
industry and ensuring that patients receive the highest
standard of care available. With the ability to securely
share information across different departments and
facilities, hospital network systems promote
collaboration and efficiency in delivering treatment.
REFERENCES
Daniel Granlund, Karl Andersson, Muslim Elkotob,
Christer Åhlund. A uniform AAA handling scheme for
heterogeneous networking environments. In LCN 2009,
The 34th Annual IEEE Conference on Local Computer
Networks, LCN 2009, 20-23 October 2009, Zurich,
Switzerland, Proceedings. pages 683-687, IEEE, 2009.
Michael Dooley; Timothy Rooney, "Introduction to the
Domain Name System (DNS)," in DNS Security
Management, IEEE, 2017, pp.17-29, doi:
10.1002/9781119328292.ch2.
S. Qiaoyu, S. Qiaoyan, C. Lijuan and Z. Chuanyun,
"Application of wireless local area network in hospital
information system," 2017 IEEE 2nd Advanced
Information Technology, Electronic and Automation
Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China,
Hospital Network Management System with AI-Driven Optimization and Security
909

2017, pp. 263-266, doi:
10.1109/IAEAC.2017.8054018.
S. R. Dammavalam, N. Chandana, T. R. Rao, A. Lahari and
B. Aparna, "AI Based Chatbot for Hospital
Management System," 2022 3rd International
Conference on Computing, Analytics and Networks
(ICAN), Rajpura, Punjab, India, 2022, pp. 1-5, doi:
10.1109/ICAN56228.2022.10007105.
S. P. R, R. R, J. Narayanan, D. Balaji and K. S, "A DHCP
Based Approach to IP Address Management and
Allocation In A Network Using VLSM," 2023 9th
International Conference on Advanced Computing and
Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore,
India, 2023, pp. 882-887, doi:
10.1109/ICACCS57279.2023.10112844.
S. Temara, M. Vivek Kumar, D. Tiwari, A. Verma, R. P.
Shukla and J. P, "Investigating the Ability of AI
Algorithms to Optimize Data Access Processes," 2024
15th International Conference on Computing
Communication and Networking Technologies
(ICCCNT), Kamand, India, 2024, pp. 1-6, doi:
10.1109/ICCCNT61001.2024.10724003.
S. Temara, D. Tiwari, V. K. M, A. Verma, R. P. Shukla and
J. P, "An improved SSH optimization model for
wireless security in Complex networks," 2024 15th
International Conference on Computing
Communication and Networking Technologies
(ICCCNT), Kamand, India, 2024, pp. 1-7, doi:
10.1109/ICCCNT61001.2024.10724507.
Z. Zhou, M. Yuan, M. Zhao, J. Guo and D. -M. Yan,
"ResGEM: Multi-scale Graph Embedding Network for
Residual Mesh Denoising," in IEEE Transactions on
Visualization and Computer Graphics, doi:
10.1109/TVCG.2024.3378309.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
910
