
A Comparative Study on Tongue Tumor Detection and Classification
Using Neuro Dynamic Ensemble Fusion Classifier
S. Preethi
1
, K. Raju
2
, Rajalakshmi D
3
, P. Venkata Subba Reddy
3
, Shaik Taher
3
and Sannapu Deepak
3
1
Department of Information Technology, E. G. S. Pillay Engineering College, Nagapattinam, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, Rajalakshmi Engineering College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
3
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, R.M.D Engineering College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Image Processing, Deep Learning, Tongue Tumor, Oral Cancer, Neuro Dynamic Ensemble Fusion.
Abstract: Recently, the deep learning technique plays a vital role in health care industries to classify and diagnose any
disease at early stage. By applying deep learning algorithms, the diseases such as heart disease, brain tumor,
lung disorder, and several other deadly diseases has been early diagnosed. This promising technique endlessly
extends its viability in detecting oral cancer. This life threating tumor can forms on any region of the mouth
namely uvula, tonsil, gum, palate and cheeks. As mouth has been the crucial part in our body, because it
performing functions such as eating, sleeping and breathing. Hence, early detection and diagnosing of oral
cancer is mandatory. If it is not treated, this disease endangers the life of humans. Earlier the traditional
convolutional neural networks were used for diagnosing oral cancer. But the advancement of information
technology brings development in neural networks. This study proposes a novel Neuro dynamic ensemble
fusion (NDEF) classifier to enhance the detection of oral cancer at earliest. The proposed model is tested on
the publically accessible oral cancer dataset and comparing its performance with other classifiers including a
hybrid RCNN and ResNet—50, VGG16, and U-Net. This proposed classifier exhibits higher accuracy of
96.27%, precision and recall of 96% and 94%, respectively. The NDEF has obtained promising results and
accurately detected the affected regions as well.
1 INTRODUCTION
The term “cancer” is known as a disease where the
abnormal body cells dissect enormously and damage
the tissues of the whole body. About 200 more types
of cancers have been discovered. The most frequently
occurring cancers take place in the breast, lungs, skin,
stomach, liver and tongue. According to the World
Health Organization (WHO), oral cancer is one of the
most dominant and widely spreading types of cancer
and its mortality rates are also high in several
countries notably in South Asia. Usage of tobacco,
consuming heavy amounts of alcohol, and HPV
infection with some specific genetic factor cause the
tongue tumor in which the cancerous cells dissociate
from the tumor and spread to the other parts of the
body especially inside the mouth, head, neck, in the
areas of lungs and the areas which are close to the
lymph nodes. In India, nearly 52,000 people die of
tongue tumor per year. So, detecting and curing it in
its early stage is mandatory which saves thousands of
people from its threat.
In human life, the Artificial Intelligence (AI)
techniques play a vital role which helping people
being endangered. Deep learning is one among them
that has a significant impact on detecting tongue
tumor. Some of the earliest detection methods for
tongue tumor were, (K. Nakanura et al., 2012) used
Raman Spectroscopy-based system for detecting oral
cancer which is non-invasive and reduses the risk of
discomfort but failed to produce larger number of
datasets and could be more expensive. And then, (S.
Wang et al., 2017) detected tongue tumor with the
help of CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) based
detection with simple architecture along with the
robust feature extraction it couldn’t provide a larger
number of datasets. Following this, (y. zhang et al.,
2018) used Auto encoder-based detection which
provided unsupervised learning but only had limited
features. Additionally, (S.S Iyer et al., 2019) used
880
Preethi, S., Raju, K., D., R., Reddy, P. V. S., Taher, S. and Deepak, S.
A Comparative Study on Tongue Tumor Detection and Classification Using Neuro Dynamic Ensemble Fusion Classifier.
DOI: 10.5220/0013875000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
880-887
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

transfer learning-based detection which is an efficient
training model but it ended up with a limited fine
issue. The above researchers were some of the earliest
detection of tongue tumor using the existing models.
This study let us analyze how to recognize and
classify tongue tumor with proper pre-processing
filtering called Multi Scale Adaptive Filtering by
image resizing, and denoising in addition to some of
the feature extraction processes which is followed by
the specific segmentation called Fractal Texture
Mapping for Neurodegenerative Segmentation
(FTM-NS) technique for depicting the affected areas.
Finally, the process is classified using the
classification model named as Neuro-Dynamic
Ensemble Fusion to detect and eradicate the tumor in
its early stage. This study also serves as a comparative
analysis of existing and proposed tongue tumor
detection techniques for better results.
2 RELATED WORKS
To utilize deep learning for detecting the abnormal
growth of oral tissue (Welikala et al., 2021) applied
an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) for the
automated detection of oral lesions. This study
promotes the early identification of oral lesions which
can significantly reduce treatment costs and even
prevent mortality rates. To classify the image, the
ResNet-101 model was employed achieving an
accuracy of 87.07%. Furthermore, the damaged
tissues in the images were accurately identified with
78.3% of precision. Though the performance in
identifying followed by classifying tongue tumours
using DNN was demonstrated acceptably, several
limitations were also noted, which include limited
data set size inconsistent annotations lack of external
validation restricted evaluation metrics followed by
the absence of comparative analysis with limited
clinical validation. (Nandita et al., 2022) employed
both deep learning and machine learning techniques,
which promote the identification of tongue tumours.
In this study, a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
with 43 deep layers was engaged to predict the data.
This results in detecting CT scan images with high
accuracy which is also effectively stimulating
malignant oral lesions with utmost precision. AI has
become apparent in the diagnosis of several diseases,
including cancer. To identify the tongue lesions,
(Panigrahi et al., 2022) employed histopathological
images. This study assessed 6 widely used algorithms
called Support Vector Machine (SVM), Random
Forest, Neural Network, Simple Bayes, Decision tree
and K- nearest neighbor (KNN) which are the most
relevant methods in classifying oral lessons.
Additionally, the study admitted that the neural
network algorithm achieved its reasonable accuracy
of 90.4% with satisfactory potential in diagnosing the
disease. (Singh et al., 2022) introduced an innovative
intelligent computing framework for deducting
tongue tumours. He evaluated the strategy with the
help of the disease imaging data. This concluded in
revealing the tumor in their early stage. To distinguish
healthy tissue from cancerous tissue (Jeng et al.,
2022) utilised Raman spectroscopy through specific
subsite analysis. This focused on the tongue, gingival
and buccal mucosa. The classification of healthy and
cancerous tissues was successful by employing
Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) followed by
Quadratic Discriminate Analysis in cooperation with
Principle Quality Analysis (PQA). Principally,
Raman's Spectroscopy highlighted the potential in
detecting oral cancer by finding that the proteins,
amino acids and beta carotene served as consequent
biomolecular markers to get rid of cancer. (Sahu et
al., 2023) achieved a sensitivity of 64% and
specificity of 80% with the application of
the Principle Component Liner Discriminate
Analysis Mode which examined the potential of
serum Raman Spectroscopy in diagnosing tongue
tumor. Though they tend to have some limitations,
they lead to optimal performance in spectral data
classification. Despite this, deep learning models
enable automatic feature extraction from raw data to
an end-to-end learning approach. Hence these deep
learning AI models have an optimistic perspective in
improving the accuracy of tumor classification.
3 METHODOLOGY
This section provides a detailed explanation of the
steps followed in proposed technique which includes
dataset collection, pre-processing, segmentation and
classification.
3.1 Dataset Collection
The current study utilizes the oral cancer images
acquired from a publicly available oral cancer data
set. The images of the oral cancer obtained from the
database are in the JPEG format, which is with a
specific resolution of 256 × 256 pixels. The obtained
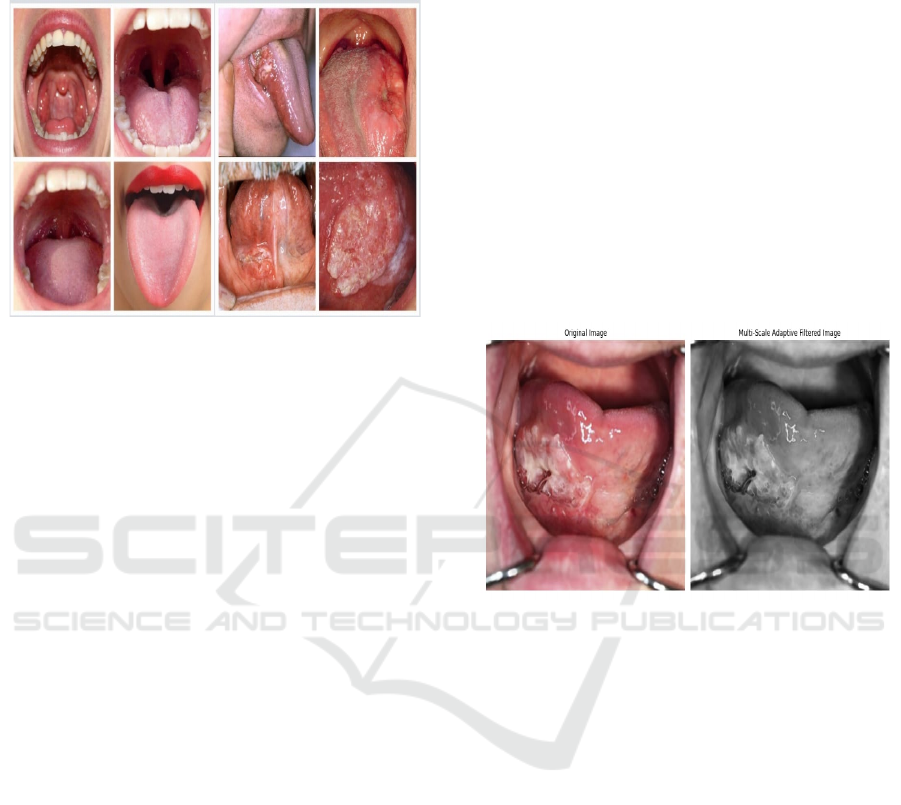
dataset holds the collection of tongue Figure 1 which
are grouped into two categories, namely cancerous
and non-cancerous images. Furthermore, the images
in the dataset comprise 500 sets of oral cancer images
and 450 sets of non-cancer oral images, which are
A Comparative Study on Tongue Tumor Detection and Classification Using Neuro Dynamic Ensemble Fusion Classifier
881
being compiled that can be used for various medical
visualization in the detection and therapeutic
treatment of oral cancer earlier.
Figure 1: Non-cancerous and cancerous tongue.
3.2 Pre-Processing
In this study, the images will be compiled from
classified reports, which offer significant data for
better study. Moreover, the images which are
obtained from the specific source have some
complications which we have to work on like the
quality of the image, and its structure followed by
some denoising process. Though some of the images
are quite clear and well-organized others may be
composed by the presence of noise which makes the
study to be decreased in its accuracy. To overcome
the issue, some of the preprocessing techniques are
essential to enhance the quality of the image,
ultimately promoting the betterment of the proposed
study. For enhancing the image quality effectively,
multi scale adaptive filtering serves as a crucial pre-
processing step in tongue tumor detection.
Denoising: It is very difficult to detect the tongue
tumor accurately from the tissue surrounding the
tumor. It's been more complicated when the image
quality is compromised by noise or even lightning.
This is effectively eradicated with the help of the
multiple scales adaptive efficiently and reducing the
noise by preserving some crucial details, including
the edges of the tumor and contours, therefore making
tumor identification much easier. At first, the noisy
images cannot be detected accurately. So, the
adaptive filter helps in locating the edges of the
images which are composed of noises. Next, the
images which are comprised of noises are
decomposed with the wavelets. Then the edges are
located with the adaptive filters. The edges and the
contours were detected at multiple scales.
Furthermore, the adaptive filters store the details of
the images even after removing the noises. At each
selected scale the process of filtering is applied to the
image. By analysing and adjusting its guidelines
based on the texture, contrast and intensity in that
particular region, the filter is being operated. After the
filtering has been done in multiple scales, the scale
allows the preservation of the edges of small tumours
and the structure of the borders. The processed final
image is then claimed and detailed with enhanced
features making it suitable for further processing.
This Multi-scale adaptive filtering process ensures
the improvement in tumor detection's accuracy, better
edge detection, and adaptability rather to the other
filters. Finally, multi-scale adaptive filtering makes
the tumor detection more reliable by playing a crucial
role in improving image quality.
Figure 2: Original and the filtered image using Multi-scale
adaptive filter.
To remove noise from an image while keeping
important details like edges, a technique called Multi-
scale Adaptive Filtering is used. This method
involves applying filters at different scales to the
image. Each scale reduces noise in a specific way.
This process Figure 2 Shows the Original and the
filtered image using Multi-scale adaptive filter. can
be broken down into mathematical steps to achieve
effective denoising. The general mathematical
equation for the denoising process using Multi-scale
Adaptive filter is given below.
Let I(x,y) be the pixel coordinates of the noisy
image. Initially, the image is decomposed into
Multiple Scales.
Let Is(x,y) represent the image at the s’th scale,
where s =1,2,…, S and S is the number of scales. At
scale s, the adaptive filter Fs is applied to the image
Is(x,y) yielding the filtered image Îs(x,y): Îs (x,y) =
Fs(Is(x,y),σs)
Where σs represent the noise variance that
depends on the scale. The images at different scales
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
882

are then combined to produce the final denoised
output. This is given by, Î (x,y) = ∑Ss=1 ws Îs(x,y)
where ws is the weight assigned to each scale that
depends on factors like the scale or the effectiveness
of the denoising at that scale. Finally, the denoised
image Î (x,y) is used as the input for the detection of
tongue tumor. Hence this ensures the reduction of
noise effectively at multiple scales which allows for
better tongue tumor detection.
3.3 Segmentation
After the Multi-scale adaptive filtering, the enhanced
image is now ready for the tumor
segmentation. Fractal Texture Mapping for
Neurodegenerative Segmentation (FTM-NS) works
by segmenting the texture of the images which consist
tumor. The affected patterns may be fractal which
remains the same across different scales. Hence,
fractal texture mapping helps in segmenting the tumor
of neurodegenerative diseases, which exhibit
complex structures at different scales. It highlights
the irregularities in tissue patterns caused by tumor by
mapping these fractal characteristics. Firstly, it
identifies the affected areas. The affected areas may
have irregular patterns. The fractal method helps in
analyzing the irregularities and detects the changes.
Next, the detected changes of the neurodegenerative
diseases are mapped, which helps in differentiating
the tumorous and the non-tumorous tongue. Finally,
the segmentation process takes place by locating the
affected areas at various scales. Thus, the affected
tissues with complex structures are detected by fractal
geometry, which results in mapping the changes in
the texture for more accurate segmentation in
neurodegenerative diseases. This method enables the
exact segmentation and the reduction of
abnormalities accurately. For a better understanding,
the tumor in a tongue is segmented and the image is
projected below Figure 3.
Figure 3: Segmented tongue using FTM-NS.
3.4 Classification
Neuro-Dynamic Ensemble Fusion (NDEF)
classification is one of the best classifiers for
detecting tongue tumor. It combines various tumor
detecting techniques to classify the tumor in the
tongue with an increased amount of accuracy. It
works by involving the neural networks, where the
information is being processed. These neural
networks can handle the complex patterns which are
in the acquired images. Then the models which
depend on one another are ensembled. Then those
ensemble models work together resulting in
classifying the tumor with accurate prediction.
Finally, the tumor are classified after sorting the data
in the medical images. In brief, this proposed NDEF
combines different neural networks with various
models and fuses the techniques of the models with
the networks to classify the tongue tumor more
accurately. Thus, the Neuro Dynamic Ensemble
Fusion (NDEF) model results in excellent tongue
tumor detection. It outperforms the existing models
like RCNN, ResNet-50, VGG16, and U-Net. NDEF
combines multiple algorithms which increases the
accuracy and robustness. It adapts to complex
patterns and features in medical imaging. This makes
NDEF to be the most effective for tongue tumor
detection. For the earliest detection and diagnosis,
accurate detection of the disease is a must. Several
deep learning models, including RCNN, ResNet-50,
VGG16, and U-Net, are also being used for medical
imaging. Each of the models has its strengths and
weaknesses. This study also compares the
performance of the existing models with the proposed
Neuro Dynamic Ensemble Fusion (NDEF) model for
enhanced tongue tumor detection.
RCNN is mainly used for the detection of objects.
It works by using a CNN to classify every region and
divide the images into regions of interest (RoIs). This
process makes RCNN detect specific regions such as
tumor and the affected areas effectively. Moreover,
RCNN plays a significant role in detecting and
segmenting the tumor within the image. Though it
detects the tumor efficiently it also has some
limitations. One of the major drawbacks is, that the
speed of the image processing is extremely slow
which further processing steps like, feature
extraction, and classification. This also makes the
RCNN perform very slowly in medical diagnostics.
The next major drawback is, that RCNN requires a
larger number of computational resources,
particularly in handling huge medical images. This
can’t be resolved making RCNN work slowly. Hence
in the detection of tongue tumor, RCNN supports
detecting the tumor regions effectively. However, its
slow processing speed limits its work in the earliest
disease diagnostics, as the fastest detection and
diagnosis are very important.
A Comparative Study on Tongue Tumor Detection and Classification Using Neuro Dynamic Ensemble Fusion Classifier
883
ResNet-50 is also a deep learning, convolution
neural network model. It uses residual connections
which makes deeper networks. It is very significant in
detecting even a tumor with minor characteristics
which is very effective in medical image analysis. Its
enhanced architecture helps us to analyze the tumor
which has irregular features and patterns. It has
residual connections which prevent degradation. This
makes it applicable to deeper networks. ResNet-50 is
known for its larger number of datasets making it
beneficial for analyzing medical images. However,
this classifier too has some limitations. As the model
is very large, the highest memory storage is required.
The next major drawback is, that to gain the highest
accuracy in tongue tumor detection; the model has to
be tuned finely along with the labelled data.
VGG16 is also a deep learning-based convolution
neural network. It has enhanced features which are
well known for its simple architecture and peculiar
structure. The model has 16 layers, with 3x3 filters
which can be applied through all the layers along with
small receptive fields. This makes the medical
diagnosis very easy as it classifies the image
accurately which promotes the model to be popular
among the researchers. Furthermore, its unique
structure helps it to understand and implement the
image classification process very easily. The 16
layers in the model allow for projecting even the
complicated details in the image which makes the
tumor detection very easier. Though it works very
efficiently, this too has some limitations. As the
structure is deep, the model requires the highest
amount of memory storage and increases the
computational costs which results in overfitting.
Additionally, the model gives only a limited number
of datasets. However, VGG16 is very useful in
classifying the tongue tumor but the model may not
work very efficiently due to its overfitting property
and limited number of datasets which results in giving
poor quality data.
U-Net is a popular architecture which used as a
deep learning model for semantic segmentation
mainly in medical image analysis. It works with the
help of an encoder-decoder architecture which has
skip connections that help preserve tumor based
information. This feature makes U-Net perform
accurately in segmenting and classifying the images.
It works well not only in classifying the images but
also in segmenting the tumor edges perfectly in the
detection of tongue tumor. U-Net models are trained
by using a minimum number of datasets with limited
data. Moreover, U-Net has also struggled with some
limitations. As it is very good at segmenting the
images, it couldn’t perform well in classifying the
images. As a result, U-Net requires additional
classification steps in the detection of tongue tumor
to make the treatment quick and easier.
Neuro-Dynamic Ensemble Fusion (NDEF)
classification is one of the best classifiers for
detecting tongue tumor. It combines various tumor-
detecting techniques to classify the tumor in the
tongue with an increased amount of accuracy. It
works by combining multiple neural networks to
improve classification accuracy. Based on the
features obtained from the tumor, their learning
patterns and the data that is imported into the image,
the neural networks operate and update the
classification efficiently. It combines various types of
classifiers, which are from different neural networks
to generate a final decision by improving the
robustness. The combination of the classifiers helps
in predicting the image data from different models
which results in producing the accurate classification.
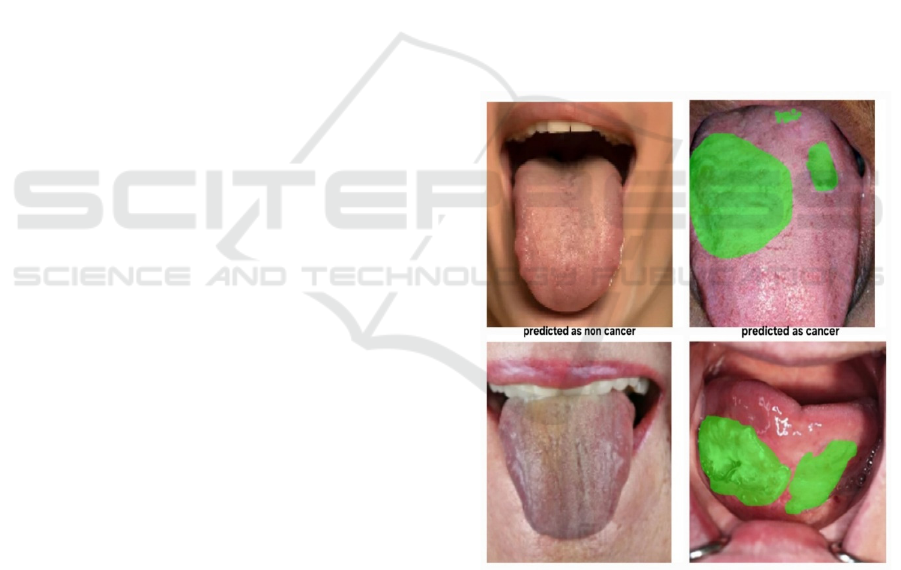
The following Figure 4 grouped below shows the
classification of the tumor in the tongue and the non-
tumorous tongue for more clarification.
Figure 4: Classification result.
4 RESULT & DISCUSSION
The Proposed system was validated using the
publically available data set which contains Images of
the oral cancer with 256 x 256 pixels that can be used
for medical visualization with correct resolution. For
enhancing the image quality, denoising and filtering
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
884
is done by using the Multi-scale Adaptive Filter and
the proper image is obtained which makes it suitable
for the further processing like segmentation. The
tumor affected area is segmented perfectly with the
help of Fractal Texture Mapping Neurodegenerative
Segmentation. It highlights the irregularities in tissue
patterns caused by tumours by mapping these certain
characteristics. Finally, in classification, the existing
models like RCNN, ResNet50, VGG16 and U-Net are
compared with NDEF's classification model and
concluded that the highest accuracy and reliability is
most effective in tongue tumor deduction is acquired
only by using NDEF classification model.
Further the evaluation metrics namely accuracy,
precision-recall, are widely utilised in the field of
image classification to describe the model’s
performance.
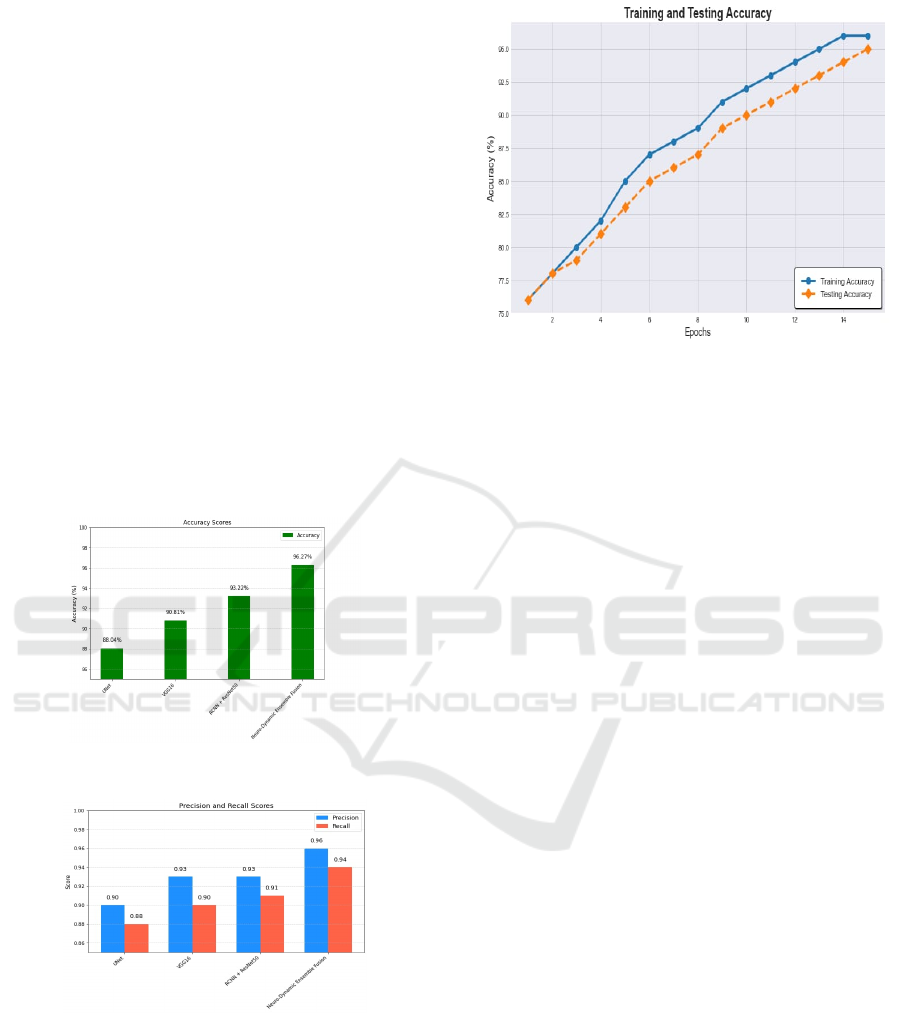
The proposed classifier has achieved the accuracy
of 96.27% more than the other existing models like
RCNN+ResNet50 which have 93.22%, VGG16
which has 90.81% and UNet which has 88.04% of
accuracy which is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5: Accuracy comparison.
Figure 6: Precision-Recall comparison.
Its effectiveness is also been calculated by the
precision and recall scores in which the proposed
model has achieved the highest precision of 0.96 and
recall score of 0.94 than the existing model which are
discussed in the Figure 6. The training and testing
accuracy obtained by the proposed classifier is
depicted in Figure 7.
Figure 7: Validating the Training and Testing accuracy.
Here, the proposed model has the highest training
and testing accuracy of about 96.27%
For the further enhancement of the proposed
study, the works of different authors using the
existing methods are also compared. From the
proposed NDEF technique, it is known that the
technique has overcome all other methods in
detecting the tongue tumor with the highest accuracy
of 96.27%. In (P. Kalaivani, 2022) the technique uses
the Gabor Filter for increasing image quality along
with the K-Means Clustering segmentation for
detecting affected areas which has an accuracy of
94%. Despite, this the technique used in (L. Li et al.,
2022) that employs Gabor, Sobel, and Median Filters,
for pre-processing and Thresholding, K-Means
Clustering, and Watershed Transform methods for
segmentation achieves an accuracy of 93%. In the
techniques (W. Wang et al., 2023) and (J. Heo, 2022)
the image quality is done by using Multi-Resolution
Analysis Filters and Gaussian filter, Median filter,
CLAHE along with the region-based segmentation
and Mask R-CNN& U-Net segmentation models in
depicting the tumor areas resulting in the accuracies
of 82% and 78.6%, respectively. Technique (T.
Thakuria, 2022) achieves the accuracy of 89.47% by
using Gaussian, Median, CLAHE, Wiener, and
Anisotropic Diffusion Filter and by using FCN,
SegNet, and DeepLab segmenting models. Finally,
NDEF has its significant combination of Multi-scale
Adaptive Filter along with FTM-NS segmentation
technique over all other techniques, which results in
the highest position as the most effective method for
tongue tumor detection. Table 1 Shows the
Comparing the other existing technique with the
proposed technique.
A Comparative Study on Tongue Tumor Detection and Classification Using Neuro Dynamic Ensemble Fusion Classifier
885
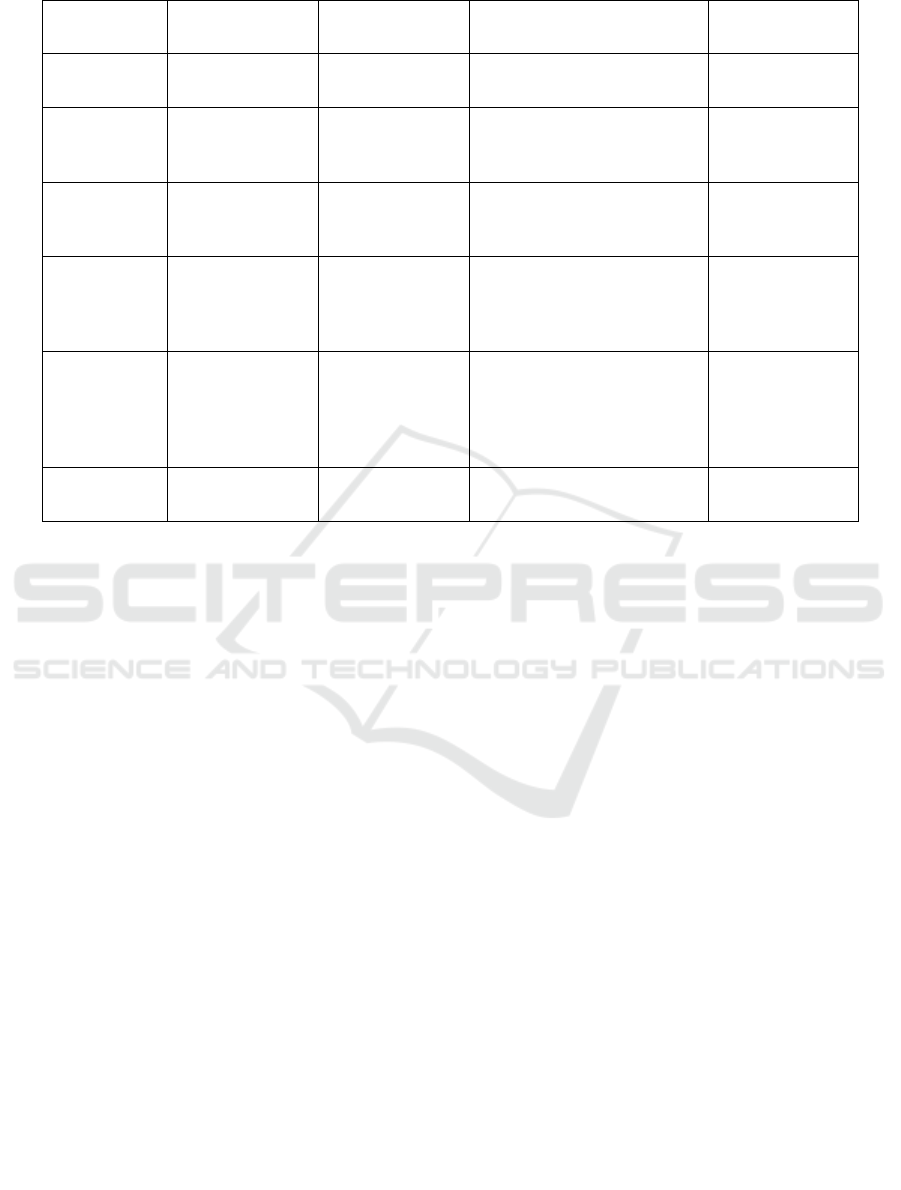
Table 1: Comparing the other existing technique with the proposed technique.
Author
Name
Dataset Filter Segmentation Accuracy
W. Wang et
al.,
Oral cancer
dataset
Multi-Resolution
Analysis Filters
Region based segmentation 82%
P. Kalaivani
Oral
Histopathology
Dataset
Gabor Filter K-Means Clustering 94%
L. Li et al.,
Oral Cancer
Dataset
Gabor, sobel &
median filters
Thresholding,
K-Means clustering &
Watershed transform
93%
J. Heo
TCEED (Tongue
Cancer
Endoscopic
Dataset)
Gaussian filter,
Median filter&
CLAHE
Mask R-CNN& U-Net 78.6%
T. Thakuria
Oral Cancer
Dataset
Gaussian,
Median, CLAHE,
Wiener and
Anisotropic
diffusion filte
r
FCN, SegNet & DeepLab 89.47%
Proposed
NDEF
Oral Cancer
Dataset
Multi-scale
Adaptive Filte
r
FTM-NS 96.27%
5 CONCLUSIONS
The experimental results of the proposed Neuro
Dynamic Ensemble Fusion mechanism have
achieved its maximum accuracy. While comparing
the proposed with the other classification models, the
NDEF approach achieves accurate tumor detection
even at low resolutions. The use of Fractal Texture
Mapping for neurodegenerative segmentation
enhances the exact tumor-affected regions by its
effective segmenting technique and the Multi-scale
Adaptive Filtering helps in eliminating the impurities
in the images including the edges. Thus, the model
helps the information to be preserved on the original
image. The increased prediction level trains the
model to extract the essential features in the feature
extraction technique. As a result, the model achieves
an overall accuracy of 96.27%, which serves as the
perfect replacer of other classification models. The
proposed model's effectiveness is proved by the
evaluation metrics such as precision and recall. In
summary, the proposed model offers efficient and
accurate tongue tumor detection, with a large number
of datasets and decreased detection time. Thus, it
serves as the best alternative approach to any other
models for effective tongue tumor detection.
REFERENCES
K. Nakamura, "Raman spectroscopy for detecting oral
cancer," Diagnostics, vol. 12, no. 12, pp. 2896, 2012.
S. Wang et al., "Detection of tongue tumor using
convolutional neural network (CNN)," Computer
Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, vol. 145, pp.
73-82, 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.04.011.
Y. Zhang et al., "Automatic detection of tongue tumor using
auto encoder and support vector machine," IEEE
Access, vol. 6, pp. 38601-38609, 2018, doi:
10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2854823.
S. S. Iyer et al., "Transfer learning-based tongue tumor
detection using deep neural networks," IEEE Access,
vol. 7, pp. 103941-103953, 2019.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2931953
X. Cai, "Breast cancer diagnosis by convolutional neural
network and advanced thermal exchange optimization
algorithm," Computational Mathematics and Methods
in Medicine, vol. 2021, 2021.
Nanditha, B., Geetha Kiran, A. Sanathkumar, M. P., "Oral
cancer detection using machine learning and deep
learning techniques," International Journal of Current
Research and Review, vol. 14, no. 01, pp. 64, 2022.
S. Panigrahi, B. S. Nanda, and T. Swarnkar, "Comparative
analysis of machine learning algorithms for
histopathological images of oral cancer," in Advances
in Distributed Computing and Machine Learning,
Springer, 2022, pp. 318-327.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
886

A. Singh, A. Sahu, and S. Verma, "Computer intelligence
in detection of malignant or premalignant oral lesions:
The story so far," Computer Intelligence in Oncology,
vol. 1016, pp. 187-200, 2022.
C.I. Faur et al., "Raman spectroscopy in oral cavity and
oropharyngeal cancer: a systematic review," Internati-
onal Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, vol.,
pp., 2022.
"Deep multi-feature fusion residual network for oral
squamous cell carcinoma classification and its
intelligent system using Raman spectroscopy,"
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, vol., pp.,
2023.
W. Wang, Y. Liu, and J. Wu, "Early diagnosis of oral
cancer using a hybrid arrangement of deep belief
network and combined group teaching algorithm,"
Scientific Reports, vol. 13, pp. 22073, 2023.
P. Kalaivani, "Oral cancer detection using deep learning,"
Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, vol. 60, no.
2, pp. 347-362, 2022. doi: 10.1007/s10844-021-00761-
5.
L. Li, C. Pu, J. Tao, L. Zhu, S. Hu, B. Qiao, L. Xing, B.
Wei, C. Shi, P. Chen, and H. Zhang, "Development of
an oral cancer detection system through deep learning,"
Computers in Biology and Medicine, vol.
142, pp. 105512, 2022.
doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105512.
J. Heo, "Deep Learning Model for Tongue Cancer
Diagnosis Using Endoscopic Images," Journal of
Clinical Medicine, vol. 11, no. 11, pp. 3024, 2022. doi:
10.3390/jcm11113024.
T. Thakuria, "Deep learning for early diagnosis of oral
cancer via smartphone and DSLR image analysis: A
systematic review," Journal of Oral Pathology &
Medicine, vol. 51, no. 9, pp. 641-653, 2022. doi:
10.1111/jop.13441.
A Comparative Study on Tongue Tumor Detection and Classification Using Neuro Dynamic Ensemble Fusion Classifier
887
