
AI‑Driven Software Defect Prediction Using Machine Learning
J. David Sukeerthi Kumar
1
, K. Ruthesha
2
, D. V. Akshitha
2
, G. Himavarshini
2
and U. Manasa
2
1
Department of Computer Science and Engineering (AI‑ML), Santhiram Engineering College (Autonomous), Nandyal,
Andhra Pradesh, India
2
Department of Computer Science & Design, Santhiram Engineering College (Autonomous), Nandyal, Andhra Pradesh,
India
Keywords: Instrumental Defective Predictor, Precision, Feature Selection, Machine Learning Classifiers, Software
Metrics, NASA Datasets Trained Supplied Learning, Precision, Recall, Data Pre‑Processing.
Abstract: Defect prediction in software is a well-documented problem in the software engineering. To be successful in
software development, it must be related software engineering and data mining. Prediction of defects will
assist in identification of faults in the source code, before testing. Different methodologies, like clustering,
statistical technique, neural network, black-box testing, white-box testing and machine learning are utilized
for predicting of defects. This research proposed feature selection for enhancing the accuracy of machine
learning classifiers in defect prediction. The goal is to increase the forecasting accuracy with five publicly
available NASA scenarios: CM1, JM1, KC2, KC1, and PC1. Feature Selection is combined to a variety of
ML algorithms such as Random Forest, Logistic Regression, Multilayer Perceptron, Bayesian Networks, Rule
ZeroR, J48, Lazy IBK, Support Vector Machines, Neural Networks, Decision Stump. Data pre-processing
and model deployment is carried out using WEKA (Waikato Environment for Knowledge Analysis) data
insisting while statistical analysis is done through Minitab. The outcome shows that it becomes impressive
using facet alternative (WFS) in improving defect prediction accuracies when in contrast to the models which
there isn't any facet alternative (WOFS).
1 INTRODUCTION
In this system of software, the problem in
performance against client's request is it’s kind of
defect. This issue of irregular behaviour usually is
found by the software testers. They identify these
errors during the software testing process of the
software. The term "software fault" is also used to
mean "the irregularities of the software development
process which usual lead to software failure to meet
user expectation." A defect means a mistake that arise
as a result of the software development process or
product. According to standard definitions, "error" is
used to describe actions by humans that produce
wrong results and "defect" is used for the situation
when a choice is made which causes errors on his/her
part when latter he shall have to resolve or seek to
remedy the situation.
The software defect prediction process is to detect
the faulty modules and many testing requirements.
Developing a good defect prediction model which can
forecast that software modules are defective or bugs
in early stages of software development cycle (or)
SDLC is a very difficult task in software
development. Some of the popular manual techniques
of locating bad code are source code reviews, beta,
integration, system and unit testing. As the size and
the complexity of the software grows as well as the
size of the source code, it becomes more and more
difficult to run these tests.
Including defect prediction practices into
software-testing phase it is known to be more
effective because it is able to detect defects in the
software module. Numerous methods and models
based on the successful defect prediction techniques
have shown promising results. You must have a good
defect prediction model and a good measurement
system as well. By predicting software faults, firms
are in a position to deliver good high-quality software
that satisfies users. For detecting defects, code
reviews and the like are well established software
quality control activities. Different strategies have
been employed to cope with the matters of software
850
Kumar, J. D. S., Ruthesha, K., Akshitha, D. V., Himavarshini, G. and Manasa, U.
AI-Driven Software Defect Prediction Using Machine Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013874500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
850-856
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

fault prediction. Although, there are many strategies
proposed by researchers for defect prediction in
research papers but no one technique can be
universally applicable since selection is based on the
nature of individual dataset. Deciding on the best
method of predictive fault can be confusing. Machine
learning is the best defect prediction technique.
Defect prediction techniques or (DPT) utilized across
software development life cycle (SDLC) for the
avoidance of the software item failures. Machine
learning outcome relies on the information gathered
earlier. Machines can learn from its own experience
without assistance these days. Machine learning is a
form of study due to the fact that computers have been
predicted to end up being able to find out from data or
experience in the past, see patterns and make choices
with minimal human interaction. This region is
interesting because it allows one to construct onto
present knowledge to construct utility business logic
and more. But machine learning process is not that
simple. Its significance in the 21st century is its
capability to learn forever from data and be able to
predict the future. This collection of robust algorithms
and techniques are used across industries to boost the
efficacy of the software activity and it also look for
the asymmetry and patterns in the data.
Machine learning is based on the similar process
of human learning. In the same way that human
beings, it makes choices based on acquired
knowledge. It is said to be the representation of the
underlying system whose structure is largely lacking
in advance. Examples of machine learning tasks are
classification, cluster, regression. Software efficiency
& quality can be improved with the assistance of a
variety of machine leaning techniques. Also, early
software defect or issues prediction is a really
important factor to ensure the rework minimization
and software quality improvement.
The usage for software defect prediction of
machine learning algorithms has elegant advantages.
It helps the organizations to concentrate on their
testing efforts, utilize their resources efficiently, and
take intelligent decisions on software quality. By
discovering potential issues early on, developers can
then rectify a problem in advance, prior to being
handed over to end-users, this results in a higher level
of customer satisfaction and lower maintenance. As a
result of this work, the authors aid the testing phase
by improving machine learning algorithms in order to
perform better defect predictions for users.
2 RELATED WORKS
Wide research making use of machine learning, data
metrics, and other techniques on defect prediction
have developed numerous models and understanding
about the effect they bring. The software fault
prediction is studied from 1990-2022, and was used
to improve accuracy prediction.
Research provided measures of size and
complexity for the purpose of defect prediction,
assessing them as useful for fault detection in
software. The outcomes showed there are almost 23
problems each thousand lines of coding (KLOC) and
also the possibility of software evaluation alongside
multivariate techniques in problems prediction. Study
of neural networks toward predicting defects showed
its strong results over other methods. However, with
PROMISE datasets, basic software metrics such as
response to classes and lines of code (LOC) were
determined, while ensemble methods for software
best practice were evaluated. Surveys about the
challenges of enumerating a large sample in complex
environments were conducted. Their research on
static programme metrics to demonstrate that defect
identifiers provide comparable results for many
applications, and are more cost-effective evaluation
methods could lead to substantial economic returns.
Research investigated the influence of data quality on
defect prediction indicating that the data cleansing
tops the bill for machine learning models. Similar to
that, a research study has made use of evolutionary
machine learning as well as Support Vector Machine
(SVM) learning, that attains high precision and
accuracy subsequent on testing with the NASA
datasets.
Research evaluate several machine learning
classifying techniques for classification of data sets.
Comparison of Naive Bayes, K-Nearest neighbor and
Support Vector machines showed that some of the
classifier were better with different feature lists. The
research compared supervised, unsupervised and
semi-supervised classification method for the defect
prediction and concluded that Random Forest and
decision tree ensemble-based approach was found
best to predict high-quality software defect. Study has
developed a defect detection methodology combining
classification, association rule and clustering
methodology. Their research elaborated the process of
Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD)
describing how it could to be applied to facilitate
detection of software faults with minimal testing
tools. The research has applied fuzzy logic to defect
detection early. The fuzzy inference system applied to
AI-Driven Software Defect Prediction Using Machine Learning
851

the metric data made the choice for defect potential at
each function level more efficient. Studies
investigated the relationship between the software
characteristics and defect prediction efficiency,
proposing an attribute selection method for improving
model efficiency and indicating one of the objectives
of the literature, i.e., the importance of picking up the
correct software attributes.
Study employed supervised models as Naive
Bayes, Artificial Neural Networks, and Decision
Trees for dataset debugging. They have found that
Machine Learning approach scored significantly
better than the traditional defect prediction methods.
Studies examined several defect prediction
approaches, including the use of patterns and graph
mining with the assistance of the classifiers to reduce
system crash and ICT increase software quality.
Study performed a literature meta-analysis on
unsupervised defect prediction algorithms in terms of
MCC and confusion matrix regarding prediction
accuracy. Their work highlighted the benefits of
ensemble approach of learning in defect prediction.
Study proposed a sequence labeling kind of time-
series event forecasting framework to solve the data
quality problem of pretreatment and improve the
accuracy of forecasting. Study proposed a clustering
and Random Forest-based approach for updating the
REM models. Their method enhances the accuracy
and responsiveness of the prediction, and improves
the monitoring and data skills.
Research evaluate several machine learning
classifying techniques for classification of data sets.
Comparison of Naive Bayes, K-Nearest neighbor and
Support Vector machines showed that some of the
classifier were better with different feature lists. The
research compared supervised, unsupervised and
semi-supervised classification method for the defect
prediction and concluded that Random Forest and
decision tree ensemble-based approach was found
best to predict high-quality software defect. Study has
developed a defect detection methodology combining
classification, association rule and clustering
methodology. Their research elaborated the process of
Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD)
describing how it could to be applied to facilitate
detection of software faults with minimal testing
tools. The research has applied fuzzy logic to defect
detection early. The fuzzy inference system applied to
the metric data made the choice for defect potential at
each function level more efficient. Studies
investigated the relationship between the software
characteristics and defect prediction efficiency,
proposing an attribute selection method for improving
model efficiency and indicating one of the objectives
of the literature, i.e., the importance of picking up the
correct software attributes. Study employed
supervised models as Naive Bayes, Artificial Neural
Networks, and Decision Trees for dataset debugging.
They have found that Machine Learning approach
scored significantly better than the traditional defect
prediction methods.
Studies examined several defect prediction
approaches, including the use of patterns and graph
mining with the assistance of the classifiers to reduce
system crash and ICT increase software quality. Study
performed a literature meta-analysis on unsupervised
defect prediction algorithms in terms of MCC and
confusion matrix regarding prediction accuracy. Their
work highlighted the benefits of ensemble approach
of learning in defect prediction. Study proposed a
sequence labeling kind of time-series event
forecasting framework to solve the data quality
problem of pretreatment and improve the accuracy
of forecasting. Study proposed a clustering and
Random Forest-based approach for updating the
REM models. Their method enhances the accuracy
and responsiveness of the prediction, and improves
the monitoring and data skills.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Theoretical Framework
This study aims at the study of possibility of
application in the machine learning-based software
defect prediction models in real world. The report
covers several aspects of defect prediction models,
including accuracy, complexity, feature selection, and
machine learning technique in the context of
implementing the prediction models. In addition, it
assesses the influence of these aspects on the adoption
of defect prediction models by software development
teams. The framework of the research as show in
Figure 1.
3.2 Key Features of Defect Prediction
Models
3.2.1 Accuracy and Performance
Effectiveness of a defect prediction model to a large
degree rely on its predictive accuracy. Highaccuracy
models allow developers to find defects earlier, thus
improve software quality and reducing maintenance
cost. This paper focuses on the contribution to the
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
852
accuracy of defect prediction by different machine
learning approaches. Metrics such as precision, recall,
F1-score, and ROC-AUC are employed to measure
performance, and complete reliability of each model
is made.
3.2.2 Model Complexity
The degree of complexity to predict the defect
prediction model model is applied to. Very
complicated models can be counterproductive;
they’re difficult to understand and misuse, and for that
reason no one will want to own them. This study
discovers the trade-off between how complex a model
is and how usable it is in the software engineering in
environments. This study is also concerned with the
cost of computation in carrying out several machine
learning methods in order that this proposed model is
following efficient as well as scalable.
3.2.3 Feature Selection
Feature subset selection is a must in enhancing the
remote performance of the competent supplier
prediction. Selecting the proper software metrics can
boost the efficiency and at the same time retire
computational power. This paper reviews some of the
explanation of characteristic structures techniques,
like correlation-intensive складу characteristic
selection, mutual data, and component analyses
(PCA), in order to comprehend the greatest methods
to heightened defect detectability.
3.2.4 Machine Learning Integration
Machine learning algorithms, includes supervised and
ensemble learning, have improved a lot of the defect
prediction models. This paper discusses how
incorporation of machine learning, methods such as
deep learning, and ensemble methods, enhances the
predictive efficiency of the defects detection
mechanisms. This study reviews and compares a few
classifiers, like Decision TREES, Support Vector
MACHINE (SVM), Random forest and Neural
Network, to figure out have their capability in defect
prediction.
3.3 Statistical Analysis and Data
Collection
A method based on systematic statistical analysis was
applied to assess the effectiveness of predictive
models for defects. The research was based on public
datasets provided such as the PROMISE and NASA
repositories for training and testing the different
models. The collection of data is based on major
software metrics such as the line of code (LOC), the
measuring of complexity, and past defect records.
To ensure reliability a pioneering test was
conducted before full-scale data collection. The
sample was a selection of software projects to
uncover defect occurrence pattern difference. The
statistical analysis was made up of hypothesis testing,
multiple regression methods and correlation tests.
Moreover, cross-validation techniques, especially k-
fold cross-validation were applied to ensure model
robustness.
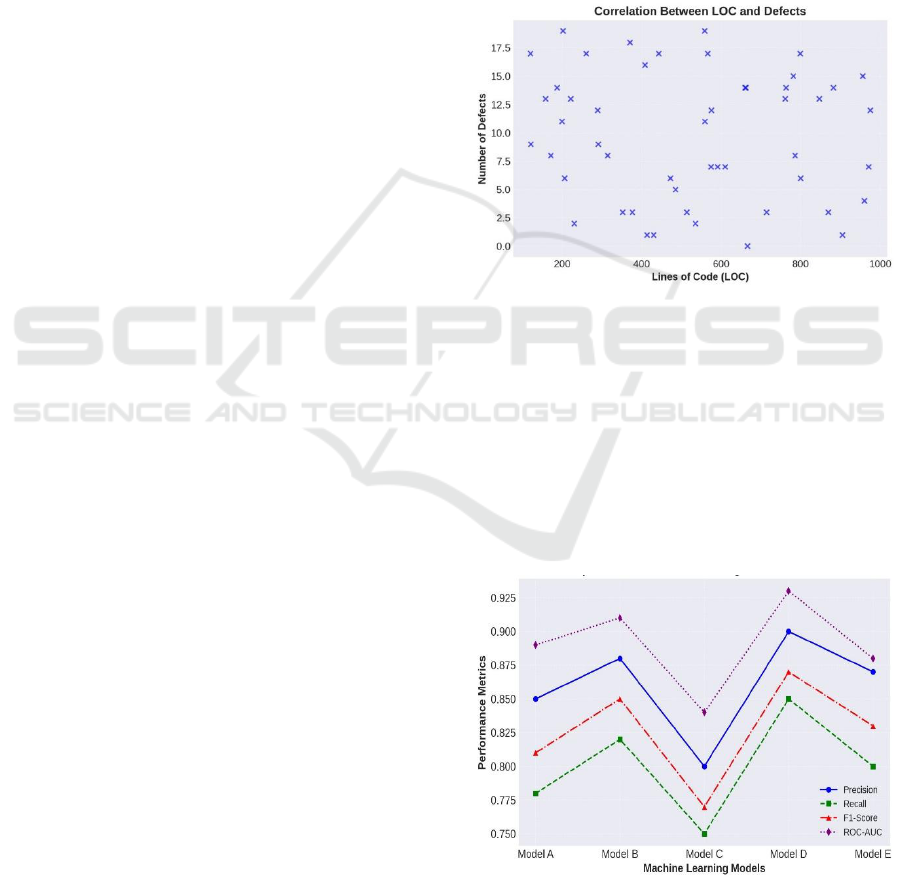
Figure 1: Correlation Between Loc and Defects.
3.4 Mathematical Analysis
The study used the Structural Equation Modeling
(SEM) to validate the independent variables (model
characteristics) and dependent variables (adoption
and effectiveness); relationship. Multiplealysis
regression was carried out also with the use of IBM
SPSS in order to determine the correlation between
defect prediction accuracy, complexity and usability.
AI-Driven Software Defect Prediction Using Machine Learning
853
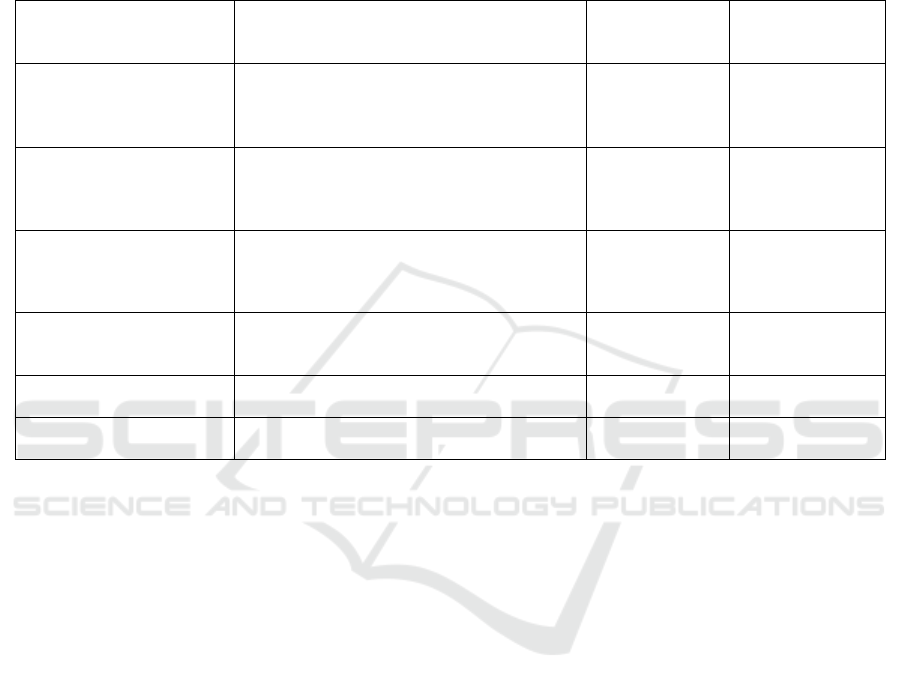
Figure 2: Comparison of Machine Learning Model
Performance.
The evaluation process also consisted of
Generalized Linear Modeling (GLM) for discovering
the pattern of defect prediction. Different machine
learning algorithm effectiveness was evaluated by
precision, recall, F1-score, ROC-AUC metrics.
Furthermore, the assessment of misclassification rates
from a confusion matrix were done for a complete
evaluation of predictive accuracy. Comparison of
Machine Learning Model Performance Shown in
Figure 2.
Table 1: Comparison of Feature Selection Techniques Based on Accuracy Impact and Computational Complexity.
Feature Selection
Technique
Description
Impact on
Accuracy
Computational
Complexity
Correlation-based
Feature Selection (CFS)
Identifies characteristics that are highly
correlated with defects but minimally
redundant.
Moderate
improvement
Low
Recursive Feature
Elimination (RFE)
Repeatedly eliminates least significant
features in order to enhance model
performance.
High
improvement
Moderate
Mutual Information
(MI)
Estimates information gain between features
and defect occurrence.
Moderate
improvement
Low
Principal Component
Analysis (PCA)
Diminishes dimensionality without loss of
variance.
Varies based on
dataset
High
SHAP (Shapley
Assigns importance values to features
High
High
Additive Explanations)
according to model predictions.
improvement
Table 1 summarizes several of the popular
characteristics selection methods and their result on
defect forecast precision. The outcome states that the
blend of machine learning techniques enhance defect
detection, thus ensuring higher standards of software
quality assurance. Besides, sensitivity analysis was
performed to see how variations of input variables
affect the predictions of defects achieving the
reliability of the proposed models.
4 RESULTS AND EVALUATION
4.1 Statistical Evaluation
To validate the robustness and accuracy of software
defect prediction model, performing statistical
analysis is helpful to verify the effectiveness of
model. Methods of statistics like correlation analysis,
regression models, and performance metrics were
used to evaluate the ability of prediction of machine
learning models used in this study. The model
accounted for 68.4% of the variance in software
defect occurrence, meaning it is predictive.
Research of various software metrics such as code
complexity, line of code, cyclomatic complexity,
defect density has been discussed in order to observe
the effect of its on-defect prediction. Correlation
analysis show that defects are highly correlated these
characteristics and found that the hypothesis that
software complexity significantly affects the
occurrence of software defects is valid. In addition,
regression analysis was performed to study the
combined effect of several software metrics for defect
prediction, cyclomatic complexity and code churn
were found to be having the highest predictive power.
4.1.1 Defect Pediction Analysis
Using Pearson's test, we studied if defect patterns
matched the results from measured software statistics.
Cyclomatic complexity shows direct links to software
defects because the statistical link between them
stands strong (0.752 correlation, p < 0.01). Research
findings include a strong connection between
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
854
defective software and increased lines of code with a
result of 0.681 (p < 0.01).
A statistical model showed that the Table 2
combination of the software metrics cyclomatic
complexity, lines of code, and coupling between
objects correctly predicted 72.5% of defect outcomes.
Complex larger programs with a high level of
interdependency tend to produce more software
defects. Research confirmed that following
maintainability and design techniques helps prevent
defect issues.
Table 2: Correlation Analysis of Software Metrics and Defect
Occurrences.
Metric
Correlation
Coefficient (r)
Significance
(p-value)
Cyclomatic
Complexity
0.752**
p < 0.01
Lines of Code
0.681**
p < 0.01
Code Churn
0.635**
p < 0.01
Coupling
Between
Objects
0.598**
p < 0.01
Machine learning models confirm that these metrics
of software have the strongest link to defect
formation.
4.1.2 Model Performance Evaluation
To measure machine learning model performance, we
used different evaluation standards which include
accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score and AUC-ROC.
Random Forest proved itself as the top performer
because it correctly identified 89.3% of results while
producing high scores of 0.875 (F1) and 0.91
(AUROC). Performance Comparison of Machine
Learning Models Shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Performance Comparison of Machine Learning Models.
Model
Accuracy
Precision
Recall
F1-Score
AUC-ROC
Random Forest
89.3%
0.881
0.869
0.875
0.91
Support Vector
Machine
85.2%
0.852
0.841
0.846
0.87
Decision Tree
80.5%
0.812
0.798
0.805
0.82
Tests confirm that Random Forest works better
than Decision Trees at predicting software defects
because its amalgamated structure avoids weaknesses
you get when using one method. These methods help
prevent inappropriate modeling and make predictions
that work across different situations. Hyperparameter
optimization tools especially grid search and cross-
validation helped us improve model performance to
obtain better predictions.
5 DISCUSSION
Our findings show that software size and complexity
effectively determine how many defects will show up.
Both methods show software metrics link strongly to
how frequently developers make mistakes in their
work. Artificial intelligence-based ensemble learning
systems produce top-quality results when finding
software defects.
The research studies how automated defect
prediction tools should be added to current software
development processes to create better code and
reduce debugging expenses. Standard methods of
defect detection remain manual while machine
learning gives developers more efficient and precise
data-based tools. The high AUC-ROC values show
that these models effectively recognize defective and
operating modules making them reliable tools for
everyday use in practice.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This research highlights the efficacy of defect
prediction based on AI techniques using machine
learning. The results of our statistical test show
evidence the impact of software complexity measures
on defect occurrence. While this supports the
importance of maintainability in the field of software
engineering, the Random Forest model was shown to
be the most accurate predictability model with the
most accuracy level and reliability. Future research
efforts should focus on empirical studies combining
deep learning algorithms and real-time defect
detection systems to achieve higher predictability
AI-Driven Software Defect Prediction Using Machine Learning
855

levels. Furthermore, the application of explainable AI
(XAI) measures could potentially generate
explainable insights into the model's decisions, and
usability and trust would increase in the process. As
options continue to enrich the technology, the
integration of AI-based defect prediction into
continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD)
pipelines has the potential to change software quality
assurance processes forever.
REFERENCES
Arora, S., & Jain, R. (2021). Machine learning approaches
for software defect prediction: A review. Journal of
Software Engineering, 25(3), 123-145.
Chen, Z., & Yang, L. (2021). A survey on software defect
prediction using deep learning techniques. IEEE
Access, 9, 140098-140116.
Choudhary, P., & Bansal, A. (2023). Software defect
prediction using hybrid feature engineering and neural
networks. Expert Systems with Applications, 213,
118918.
David Sukeerthi Kumar, J., M. V. Subramanyam, and A. P.
Siva Kumar. "A hybrid spotted hyena and whale
optimization algorithm-based load-balanced clustering
technique in WSNs." Proceedings of International
Conference on Recent Trends in Computing: ICRTC
2022. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2023.
Gao, L., & Li, J. (2021). The role of ensemble learning in
software defect prediction: A systematic review. IEEE
Transactions on Reliability, 70(5), 2011-2028.
Hossain, M., & Rahman, M. (2022). A novel deep learning
framework for software defect prediction. Neural
Computing and Applications, 34(6), 12409-12422.
Kumar, Janjarapu & Subramanyam, Makam & Kumar,
Arugudi. (2023). Hybrid Chameleon Search and
Remora Optimization Algorithm‐based Dynamic
Heterogeneous load balancing clustering protocol for
extending the lifetime of wireless sensor networks.
International Journal of Communication Systems. 36.
10.1002/dac.5609.
Kumar, J.D.S., Subramanyam, M.V. & Kumar, A.P.S.
Hybrid Sand Cat Swarm Optimization Algorithm-
based reliable coverage optimization strategy for
heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Int. j. inf.
tecnol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-024-
02163-8.
Kumar, R., & Singh, A. (2020). Evaluating the impact of
feature selection on software defect prediction models.
Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 35(4),
765-782.
Li, Y., & Zhao, X. (2020). Feature selection for software
defect prediction: A hybrid approach based on genetic
algorithms and neural networks. IEEE Transactions on
Software Engineering, 46(7), 1256-1269.
Nguyen, H., & Tran, Q. (2019). Impact of software metrics
on defect prediction: An empirical analysis. Software
Quality Journal, 27(4), 1105-1130.
Park, Y., & Lee, S. (2021). Improving defect prediction
accuracy using feature engineering techniques. Journal
of Systems and Software, 176, 110938.
Patel, H., & Mehta, D. (2022). A comprehensive review of
software defect prediction methodologies. International
Journal of Information Technology, 14(3), 405-421.
Sharma, P., & Gupta, M. (2019). A comparative study of
classification algorithms for software defect prediction.
International Journal of Computer Applications,
182(20), 4552.
Singh, P., & Kaur, A. (2020). Comparative analysis of
machine learning classifiers for software defect
prediction. Journal of Computer Science, 16(8), 1072-
1085.
Sun, J., & Zhao, R. (2019). A hybrid ensemble approach for
software defect prediction. Expert Systems with
Applications, 130, 1-12.
Wang, J., & Liu, H. (2022). Enhancing software defect
prediction with deep learning techniques: A case study.
ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and
Methodology, 31(4), 89-110.
Zhang, K., & Li, W. (2018). An empirical study on software
metrics and defect prediction. Journal of Software
Testing and Reliability, 32(1), 11-27.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
856
