
Efficient Server Management Architecture Based on Cloud Edge
Integration with Advanced Security Enhancements
D. Prasanna, S. Parasuraman, S. R. Magesh, S. Narayana Badri and G. Ragul
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Mahendra Engineering College, Namakkal, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Server Management, Cloud Edge Integration, Security Enhancement, Cloud Security, AEICS, Cloud
Manufacturing, CMS.
Abstract: This research examines the transition from completely automated to fully data-assisted process control in
production systems. The process is optimized in current concepts through data analysis using a decision
support system after manufacturing is finished. Prescriptive automation endeavors to regulate the process
independently and beforehand by employing a prescriptive analytics methodology. The development of
information technology architecture is a critical component of the overall concept. By conducting expert
interviews and reviewing recent literature, it is feasible to ascertain the components of IT architecture that are
necessary for prescriptive automation. These requirements, which are solution components, are in opposition
to the purpose of a modular architectural concept. Reference architecture is established by analyzing the
requirements and, as a result, the components of the solution that are necessary, provided that the data
processing resources are available. The processing components of this architecture are built upon a
combination of cloud and peripheral computing. This study concentrates on the latest hazards to privacy, data
security, and real-time processing in the cloud manufacturing environment. The objective of the investigation
is to establish a scalable security framework that can ensure secure data transmission, safeguard sensitive
information, and facilitate secure access control in dynamic and distributed manufacturing environments by
capitalizing on the synergy between cloud and edge technologies. This study introduces a novel technique,
Advanced Edge Integrated Cloud Security (AEICS), and employs it to evaluate the efficacy of the proposed
scheme by cross-validating it with the current approach, Cloud Manufacturing System (CMS). The research
will also assess the potential benefits of this integrated security architecture in enhancing the reliability,
efficiency, and resilience of cloud manufacturing systems, as well as provide best practices for its deployment
and implementation. The results section contains a comprehensive demonstration of the efficacy of the
proposed scheme in detail.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Internet has grown exponentially in size and
complexity over the past few decades Zhanyang Xu,
et al. 2020. Nearly half of the world's population has
internet access by year's end 2014. The growth of the
internet, however, exacerbates the network security
vulnerabilities. The security of the Internet of Things
(IoT) will be a top priority since it will encompass all
objects and devices that may connect to the internet.
Threats to human safety can arise from many sources,
from basic home sensors to advanced medical
devices, automobiles, aircraft, and even nuclear
power plants. In 2013, the number of breaches
increased by 62% from 2012. Vijay M., 2024; P.
Velmurugadass, et al., 2021.; Ahmed M Alwakeel,
2021, The Internet edge is where typical security
controls such as firewalls, along with intrusion
detection and prevention systems are deployed. SDN
supports the enforcement of policies dynamically;
fine-grained traffic filtering, and rapid response to
security incidents. This introduces an IoT security
solution based on SDN architectures. The first key
aspect of the proposed security system was to
construct and protect the wireless and wired network
infrastructure. The second was to explore the
possibility of extending the proposed architecture to
support access control systems for Ad-Hoc networks
and network objects (sensors, tablets, smart-phones,
etc.). Then, Chapter 4 describes a proposed network
access control system called PANATIKI based on
Internet of Things devices. Abhay Verma, et al.,
770
Prasanna, D., Parasuraman, S., Magesh, S. R., Badri, S. N. and Ragul, G.
Efficient Server Management Architecture Based on Cloud Edge Integration with Advanced Security Enhancements.
DOI: 10.5220/0013872600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
770-778
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

2021; Dulana Rupanetti, et al., 2024, Software
Defined Networks (SDN) is a novel technology
concept for networking that arose from recent
advancements in computer networking. The SDN
controller is a centralized piece of software that
controls the way the network operates as a whole.
With SDN, there is a natural consolidation of network
intelligence and a decoupling of the control and data
planes.
In response to packets or proactively via rules, the
controller has the capacity to add, edit, or remove
flow entries. Also, SDN allows for dynamic policy
enactment, fine-grained traffic filtering, and rapid
response to security events. An SDN architecture-
based Internet of Things security paradigm is present.
In summary, the reported research was successful
towards delivery of the first goal of the proposed
security model, which is to design and secure a
wireless and wired network infrastructure. M. Yasir
Mehmood, et al., 2021, The next step would be to
expand the proposed model to include Ad-Hoc
networks and network object, like sensors, tablets,
smartphones, etc. An inventive method to cloud
manufacturing has taken shape, incorporating the
tenets of “Internet of everything, intelligent leading,
digital/analog driving, shared services, cross-border
integration and universal innovation.” This
methodology also changes how services are provided
in cloud and IoT environments, developing a wider
range of possibilities. With the introduction of new
sensing units, perception technologies, and internet of
things (IoT) infrastructure, intelligent manufacturing
resources, capabilities, and products are being linked
to new networks. Odugu Rama Devi, et al., 2022;
Bhagwati Sharan, et al., 2022; Akhil Pandey, et al.,
2023, These networks include private networks,
sensor networks, software-defined networks, global
positioning systems (GPS), remote sensing, radar,
and quick response (QR) codes. As a result, the
network perimeter of the new cloud manufacturing
system is become more and more open and diffuse.
Existing security architectures rely on information
security technologies to safeguard modern cloud
manufacturing systems, and they are not adequate.
2 RELATED WORKS
Edge computing and security problems in cloud
networks are very widespread now. Sina Ahmadi,
2024 This study concentrates on investigating such
problems and formulating the ideal answers. In this
sense, a thorough literature review has been done.
According to the results, edge computing is connected
to various difficulties like privacy issues, security
breaches, expensive expenses, low efficiency, etc.
Thus, appropriate security policies must be put in
place if we are to solve these problems. Emerging
developments such machine learning, encryption,
artificial intelligence, real-time monitoring, etc. assist
to reduce security concerns by means of technology.
Moreover, via cloud computing they may create a safe
and secure future. It was found that new technologies
and approaches readily allow one to cover the security
consequences of edge computing.
The fast-growing Internet of Things environment
makes solutions for effective data processing and
analysis much sought after. The topic of this paper
is the possible Internet of Things (IoT) usage of hybrid
architectures, cloud computing, and edge computing.
Using extensive search and analysis of industry
publications, conference proceedings, and peer-
reviewed articles, the technique highlighted current
advancements in computing technology for the
Internet of Things (IoT). Although cloud computing
offers more scalability and flexibility, the results
reveal that edge computing excels in reducing latency
and enhancing data privacy by localized processing.
Fog and mist computing is two hybrid systems
aggregating the best aspects of cloud and edge
computing. For Internet of Things (IoT)
deployments, these hybrid systems enhance
bandwidth consumption and provide low-latency,
privacy-sensitive applications. For situations needing
low-latency processing and excellent bandwidth
control, hybrid architectures are found very
successful. These methods satisfy the limitations of
both edge and cloud computing for IoT as they offer a
balanced method of data analysis and resource
management. They also exhibit a tremendous
progressive progress.
Shalin Parikh, et al., 2019, New computing
paradigm known as cloud computing entered the
scene with the arrival of IoT/5G and the data
warehousing and processing now mostly use cloud
computing as their platform. Data storage into the
cloud does, however, provide a unique set of security
issues and problems. Moreover, as every device
creates more data; the traditional cloud computing
paradigm cannot manage problems like excessive
latency, bandwidth limitation, and resource
restriction. New computational paradigms such as
edge and fog computing are being proposed to solve
the issues of the former at the device itself or close by.
Both of these approaches offer compute decisions and
memory storage very adjacent to the device. No
system is flawless notwithstanding their benefits.
Efficient Server Management Architecture Based on Cloud Edge Integration with Advanced Security Enhancements
771

Muktar Yahuza, et al., 2020, One interesting
concept that improves the capacity of cloud
computing is edge computing. Maintaining the
provision of computer services depends on keeping
the surroundings free from security and privacy
violations. Privacy and security concerns make most
people not consider the edge computing environment
as a coherent paradigm. While many have examined
privacy and security concerns with edge computing,
not everyone has considered the necessary criteria. A
system's ability and functions to eliminate specific
security and privacy concerns are reflected in its
security and privacy requirements. This study aims
to help researchers in the future identify promising
research areas by taking a close look at the privacy and
security requirements of the edge computing and the
many technology approaches used to mitigate these
risks. This literature review covers a wide range of
subjects, including: (1) a taxonomy of edge network
attacks and the related technological trend that
mitigates these attacks; (2) a classification of edge
computing security and privacy requirements; (3)
state-of-the-art techniques that combat these threats;
(4) metrics for measuring the effectiveness of these
techniques; (5) potential avenues for future research in
this area; and, finally, research opportunities.
Elahe Fazeldehkordi, et al., 2022, The Internet of
Things (IoT) is a creative idea with enormous uses that
have crept into our daily existence. IoT and linked
devices are fast increasing in count. Problems with
service availability, security, privacy, bandwidth,
network resources, data transmission costs, long
transmission times leading to increased power
consumption of IoT devices, and latency are among
the many issues that develop when transferring the
matching enormous quantities of data produced by
these devices to the cloud. By bringing data
processing and storage closer to end users and IoT
devices, edge computing (EC) avoids these issues.
Edge computing and related computing paradigms are
defined in depth in the outset of the article, along with
their advantages and disadvantages. After that, we
provide possible solutions and countermeasures after
going into detailed on the primary security and privacy
breaches inside the scope of EC-based IoT.
Following this, we provide an EC-based architecture
that is secure for use in Internet of Things applications.
We also provide an edge computing application
scenario for the Internet of Things and compare it to
cloud computing, weighing the pros and cons of each
technology. Concerns regarding the security and
privacy of Internet of Things devices based on EC
have been addressed.
3 METHODOLOGY
Cloud servers often employ security features such as
encryption, access control mechanisms, and
conventional firewalls to safeguard sensitive data
while it is stored and processed on these servers. But
as cloud manufacturing gets more complicated and
dispersed, these systems’ latency and scalability
issues become increasingly notable. The integration
of cloud and edge security is becoming increasingly
important in order to deal with any threats as they
arise. An integrated architecture that smoothly
integrates edge and cloud security is still missing
from many of these systems' security measures.
Security issues, including hacking and illegal access,
become increasingly critical as the system grows in
size. Because of their proximity to the data source,
edge devices require extra safeguards to avoid
security holes in real-time functionality. The demands
of cloud manufacturing systems are always changing,
therefore it's possible that conventional security
methods won't be enough. The necessity for a more
cohesive security architecture that incorporates
elements of both cloud and edge security is, therefore,
growing in importance. Some of the limitations such
as, edge registration has several drawbacks. One
drawback is it requires more local equipment
components. Another is, as more and more "smart"
devices enter edge servers and IoT devices with
powerful built-in PCs, there are fresh opportunities
for mischief makers to bargain for these devices.
Lastly, it would also increase costs because it would
require a more complicated PC with more training
resources.
Cloud and edge security measures will be
integrated to offer low latency for monitoring and
detecting threats in real-time. The solution will use
new encryption technology to prevent unauthorized
access to data traveling from edge devices to the
cloud. Local data processing and filtering on the edge
devices will improve data and cyber breach
prevention before contacting the cloud. We will build
a consolidated platform to monitor and manage
security in both environments. Authentication and
access control will be strengthened with multi-factor
authentication (MFA) and role-based access controls
to ensure that sensitive production data will only be
accessed by authorized users. The cloud and edge
infrastructure will be outfitted with intrusion
detection and prevention systems (IDPS) for
improved detection and prevention of cyber threats.
The strategy will improve our ability to protect
against the latest threats by automatically adjusting
security practices through AI and ML. All of these
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
772
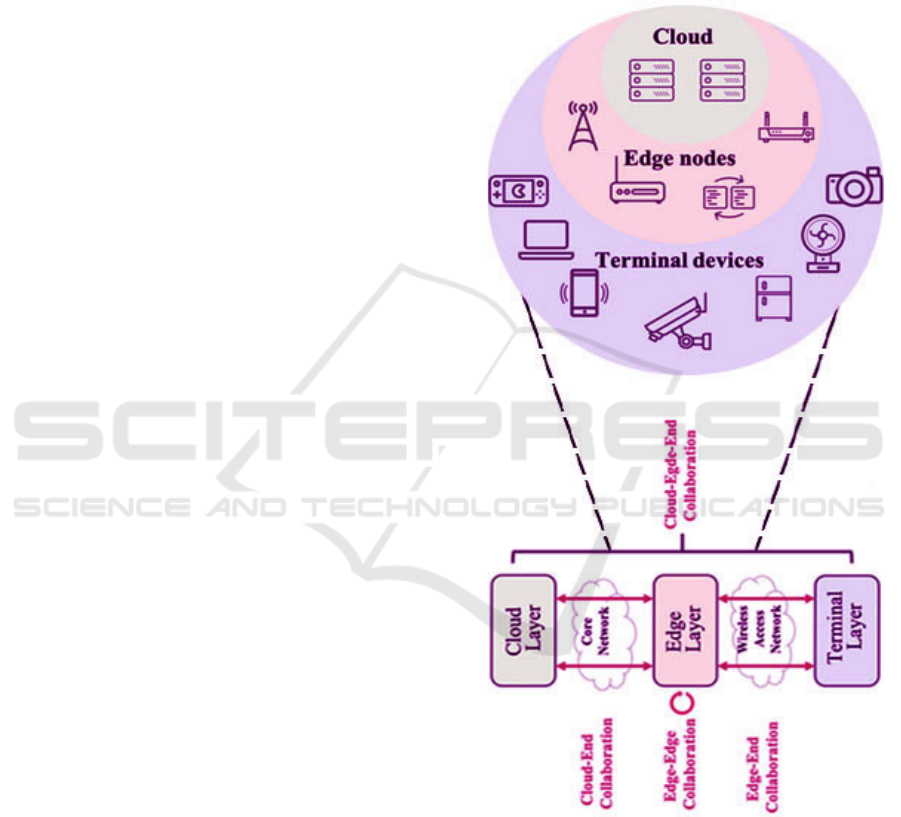
integrated strategies provide an improved, secured,
scalable, and efficient approach to security in a cloud
manufacturing environment. By enhancing the
efficiency of conventional security system design, the
suggested approach known as Advanced Edge
Integrated Cloud Security (AEICS) outperforms the
current one, Cloud Manufacturing System (CMS).
Below are the characteristics of the proposed
architectural design:
• Implementing security measures in both cloud
and edge settings in a distributed manner.
• Cloud and edge node threat detection and
response in real-time.
• The cloud and edge devices' security rules are
seamlessly integrated.
• Secure architecture that can scale to
accommodate various cloud manufacturing
systems.
• Encryption of data and safe transfer of data
from edge devices to the cloud.
• Multi-factor authentication used for managing
identities and access.
At present, there is a set logic in place for
controlling production facilities, and this logic
considers dependencies and correlations using data
that is mainly out of date. With the advent of
digitalization, new avenues have opened up for the
improvement of decision making using complete and
current data. Research on predictive analytics for
production control mostly focuses on broad needs and
difficulties with specific components (like data
processing) or technology (like cloud computing).
Data analysis and optimization, in the form of a
decision support system, occurs after production,
although process data extraction is typically
contemplated. There must still be a human decision-
maker and manual executor for this auxiliary system
to work. It is easy to use for managing devices,
configuring access controls to the devices, and
developing cloud and edge layer security protocols.
The Internet of Things (IOT), which includes sensors
and connected equipment, sends encrypted data to
Cloud and Edge nodes. The design incorporates
authentication protocols to ensure the system cannot
be accessed by unauthorized people and devices. The
data around security is provided by the solutions that
monitor assets in real-time, allowing the quick
identification of vulnerabilities or attacks. Edge
devices are meant to process data at the device, which
improves responsiveness and minimizes latency of
critical security operations. The system is flexible to
support different industrial environments due to the
ability to work with numerous input types and
protocols. Data logs and event histories are collected
for additional discernment into event processing to
ensure security compliance. Finally, input design
purposes adaptive mechanisms in response to the
continuously changing threat landscape to ensure
continual protection to the extent new threats are
introduced. The following figure 1 shows the
architecture diagram and the following figure 2 shows
the system design.
Figure 1: Architecture Diagram.
Alerts in relation to a security incident is sent to
administrators or security personnel in real-time,
enabling immediate verification and action. It will also
generate odes of full and complete security reports
featuring details relating to cloud or edge system
performance, vulnerabilities, and potential threats.
The reports also come with visual dashboards that
capture risk changes in the security posture, trends,
Efficient Server Management Architecture Based on Cloud Edge Integration with Advanced Security Enhancements
773
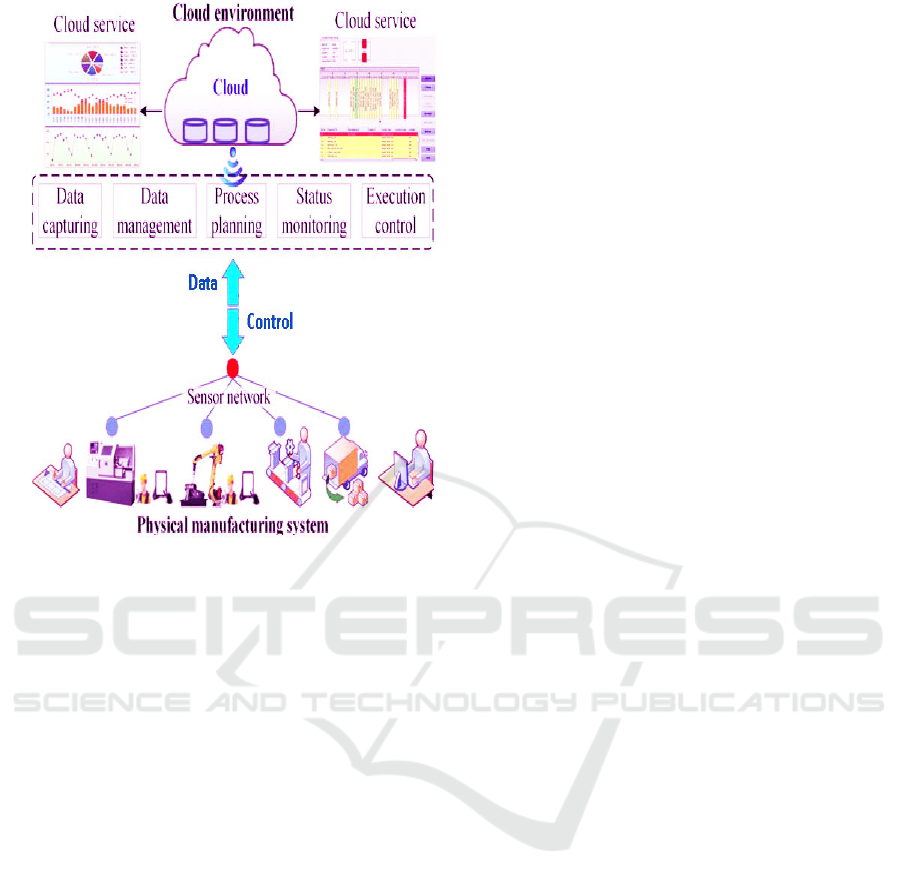
Figure 2: System Design.
and highlight events. The architecture is able to
generate role-specific outputs, allowing multiple
stakeholders to receive information according to their
user role. All activities and security events are logged
in a secured data logger to provide full audit and
compliance. As well, the output is structured to
integrate with third-party security monitoring and
incident management services easily. Security actions
evolve continuously, based on processed output and
feedback from edge devices. The last step in
proactively mitigating future security breaches is the
analysis of output and actionable recommendations
based on the analysis provided by the system once
completed, given that it remains fed on data until
October 2023.
In the micro-services architecture, data encryption,
authentication, threat detection, and other components
work as stand-alone parts and can be scaled with
demand. You are extracting information that is used
by the initializer to make programmatic decisions --
the code is executing multiple protocols, including
TLS/SSL, and the encrypted incoming payload will
help transfer data between the cloud and edge layers
securely. In addition, robust identity management
solutions use token-based authentication protocols
for authentication and access control. Moreover, the
system also utilizes various technologies like Web-
Socket for the real-time monitoring of edge devices,
and for the continuous upload of their data to the
Cloud. You will process incoming data using rule-
based systems for procedural anomaly detection
according to the parameters and machine learning
models for threat detection. Load balancing, fault
tolerance, etc. provide high availability. Also, there is
an API layer to avoid interoperability issues using
which code has been created for multiple IoT devices
and industrial machines. It's the development
lifecycle with continuous security patching and
updating as the ultimate line of defence to keep the
system up to snuff against the latest vulnerabilities.
During the Dataset Design process, you document
not only the design of the business process, but the
relevant tables and fields of a dataset. Read the topic
to get an idea about helpful dataset is the backbone of
policy and procedural governance so you can
understand it state of the migration to be. The Edge
Integrated Cloud Security (AEICS) is a highly
advanced solution that secures the cloud by providing
cutting-edge encryption and access control
mechanisms. It employs multi-factor authentication
(MFA) to provide an extra layer of security and
employs role-based access controls (RBAC) to restrict
who has access to what content for users connecting
to the cloud. Continuous monitoring systems can
monitor for anomalous data access patterns, which can
help detect both benign activity as well as malicious
action, in real-time. This module provides protection
against the external attack as it concerns cloud-native
security protection devices (such as firewalls and
intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDPS)). It will
have encryption of cloud-based data, both in transit
and at rest for end-to-end security. In this module, we
include protection measures for data loss in case of an
incident, such as backup and disaster recovery
strategies. Policies undergo frequent reviews to stay
ahead of emerging cloud security threats. Compliance
with Laws is Maintained Cloud security is aligned
with compliance standards and ensures compliance
with the law and other regulations.
Edge Security aims to protect the sensors,
machines, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices at the
periphery of the manufacturing environment. Each
device is protected by encrypted communication
channels and secure authentication mechanisms,
meaning no data can be intercepted in transit to the
cloud. For device level cyber-attacks, localized
security measures like threat detection and prevention
system can assist in preventing these types of attacks.
This module also includes firmware integrity checks,
which help prevent edge devices from being infected
with malware or from downloading unauthorized
software updates. Real-time monitoring can rapidly
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
774
detect any vulnerabilities or breaches at the edge. opt
for lightweight security protocols for optimal device
performance and less waiting time. Further down the
line, minimize your cloud dependency by letting edge
devices run independently with local security controls.
They are updated and patched regularly to ensure that
the edge devices are protected from continuously
changing threats. This module protects the privacy,
authenticity, and secrecy of cloud manufacturing
system data. It applies strong encryption mechanisms
to the data in transit and at rest to avoid unauthorised
access to important production data. The module also
includes measures for data security, such as
tokenization and data anonymization at the individual
level.
Data access is tightly controlled with the
mechanism of access control and constant monitoring
and auditing of data activity for leakage, illegal
access, etc. We periodically review and enhance our
policies to align with privacy legislation such as
GDPR, CCPA, etc. Data Retention Policies: These
policies are introduced to automatically delete old data
while retaining data that's of utmost necessity. Secure
data exchange protocols should exist between cloud
and edge devices to ensure sensitive data doesn't end
up in the wrong hands. This will also seamlessly
ensure ethical and transparent data processing through
user consent management. The purpose of testing is
to discover mistakes. This approach works because
the purpose of testing is to discover vulnerabilities in
a product or service, including all that exist. Software
testing is the process of stroking a software system to
ensure it meets users’ expectations and criteria without
failing in an undesired way. It is a method to verify
operations of components, subassemblies, assemblies
and the end product.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The paper proposed a cloud edge-based service
architecture called Advanced Edge Integrated Cloud
Security (AEICS), that is intended for service
orchestration in practical contexts and the proposed
design enhances service delivery and efficiency by
leveraging the benefits of cloud and edge computing.
The utilization of edge computing architectures in the
development of corporate management systems has
garnered research interest. These investigations
investigate the practicality, objectives, user
requirements, and functional architecture of these
systems. By employing peripheral computing, these
systems aim to reduce latency and enhance data
processing efficiency, thereby generating more
responsive corporate management solutions. Another
area of interest is the deployment of deep learning
within cloud-edge collaborative architectures, as this
approach addresses critical technologies, challenges,
and applications, thereby influencing future research
directions. Federated learning improves privacy and
security by enabling decentralized data processing
through the utilization of distributed systems. Secure
Access Service Edge (SASE) is a cloud service that
combines comprehensive security features with the
capabilities of a wide area network (WAN). SASE
systems intend to reduce complexity, enhance
performance, increase cost efficiency, and provide
universal access by consolidating security and
networking functions at the periphery. Cloud and
peripheral computing introduce numerous security
concerns, including data intrusions, privacy
violations, and access control infractions. In order to
address these concerns, it is necessary to implement
robust security policies that are specifically designed
to address the unique requirements of edge computing
systems. The study collectively underscores the
importance of the developments and factors that must
be considered when developing server management
systems, which include enhanced security features
that integrate cloud and periphery computing. Figure
3 illustrates the data security evaluation outcome of
the proposed scheme, AEICS, which is cross-
validated with the conventional approach, CMS, to
assess the data security of the proposed scheme. Table
1 is a descriptive representation of the
aforementioned.
Table 1: Analysis of Data Security.
Data Size (bps) CMS (%) AEICS (%)
500 85.13 97.57
1000 84.14 97.53
1500 82.49 97.46
2000 83.54 97.51
2500 85.56 97.47
3000 82.47 97.39
3500 84.52 98.66
4000 85.26 97.42
4500 84.45 98.54
5000 83.37 97.39
5500 83.12 98.16
The proposed scheme, AEICS, is cross-validated
with the conventional approach, CMS, to assess the
privacy of cloud servers. The privacy evaluation
outcome is illustrated in Figure 4. Table 2 is a
descriptive representation of the same.
Efficient Server Management Architecture Based on Cloud Edge Integration with Advanced Security Enhancements
775
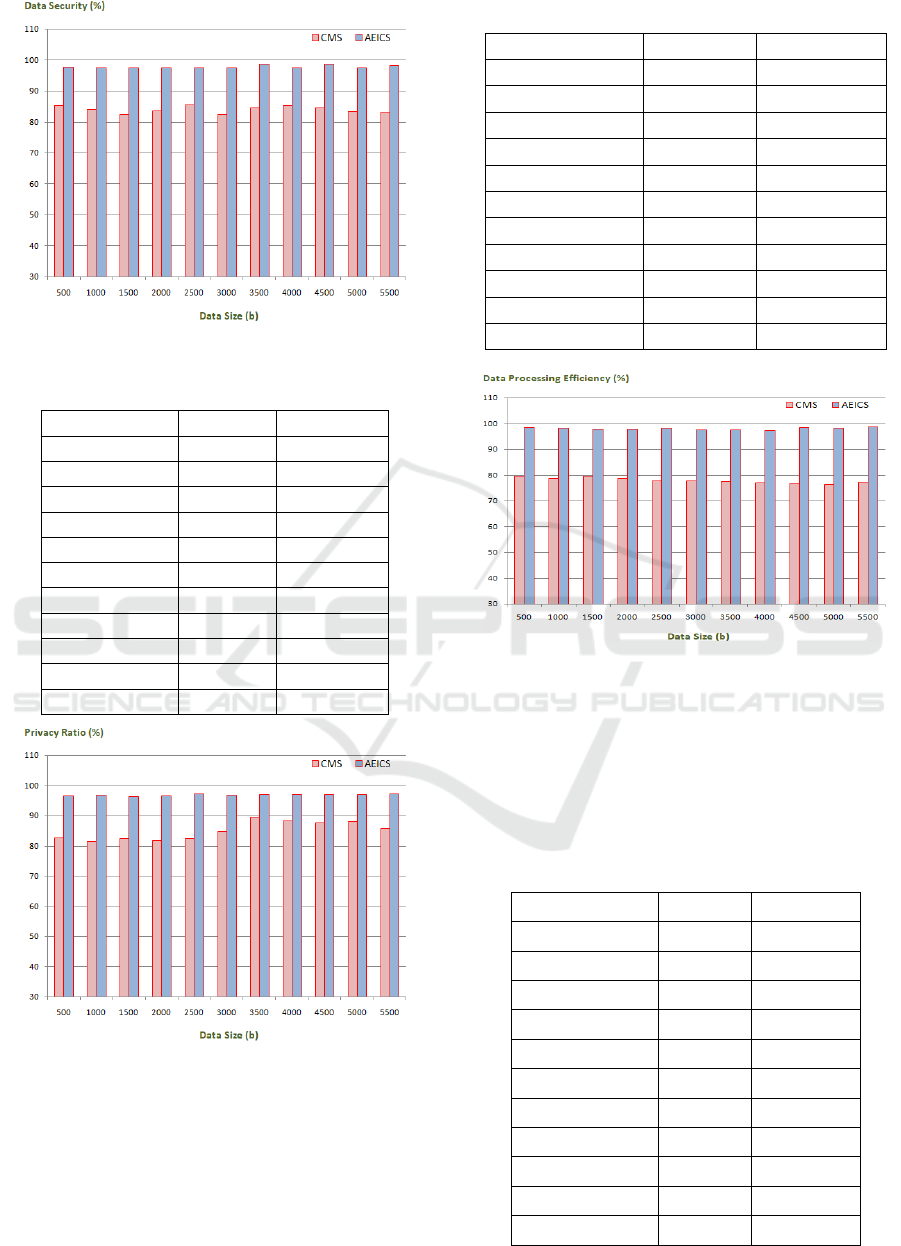
Figure 3: Data Security.
Table 2: Analysis of Privacy Between Aeics and Cms.
Data Size (bps) CMS (%) AEICS (%)
500 82.64 96.52
1000 81.56 96.71
1500 82.37 96.34
2000 81.66 96.51
2500 82.39 97.09
3000 84.69 96.72
3500 89.52 96.88
4000 88.31 96.95
4500 87.56 97.01
5000 88.09 97.08
5500 85.63 97.14
Figure 4: Privacy Ratio Analysis.
The data processing efficiency evaluation result of
the proposed scheme, AEICS, is shown in Figure 5.
This figure represents a cross-validation of the
proposed scheme with its conventional counterpart,
CMS, in order to evaluate its data processing
efficiency. Table 3 Shows the Analysis of Data
Processing Efficiency.
Table 3: Analysis of Data Processing Efficiency.
Data Size (bps) CMS (%) AEICS (%)
500 79.46 98.39
1000 78.52 98.14
1500 79.59 97.63
2000 78.71 97.79
2500 77.64 98.09
3000 77.75 97.45
3500 77.40 97.45
4000 77.06 97.31
4500 76.71 98.41
5000 76.37 98.12
5500 77.12 98.73
Figure 5: Data Processing Efficiency.
The processing time test result of the proposed
scheme based on AEICS is illustrated in the following
figure, Figure 6. A cross-validation is employed on
this scheme against conventional scheme (CMS) to
check the processing time. The next table 4 presents
a descriptive summary for the same.
Table 4: Data Processing Time Efficiency.
Data Size (bps) CMS (s) AEICS (s)
500 6 1
1000 8 1
1500 11 1
2000 12 2
2500 12 4
3000 13 4
3500 15 4
4000 16 8
4500 17 9
5000 17 9
5500 18 11
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
776
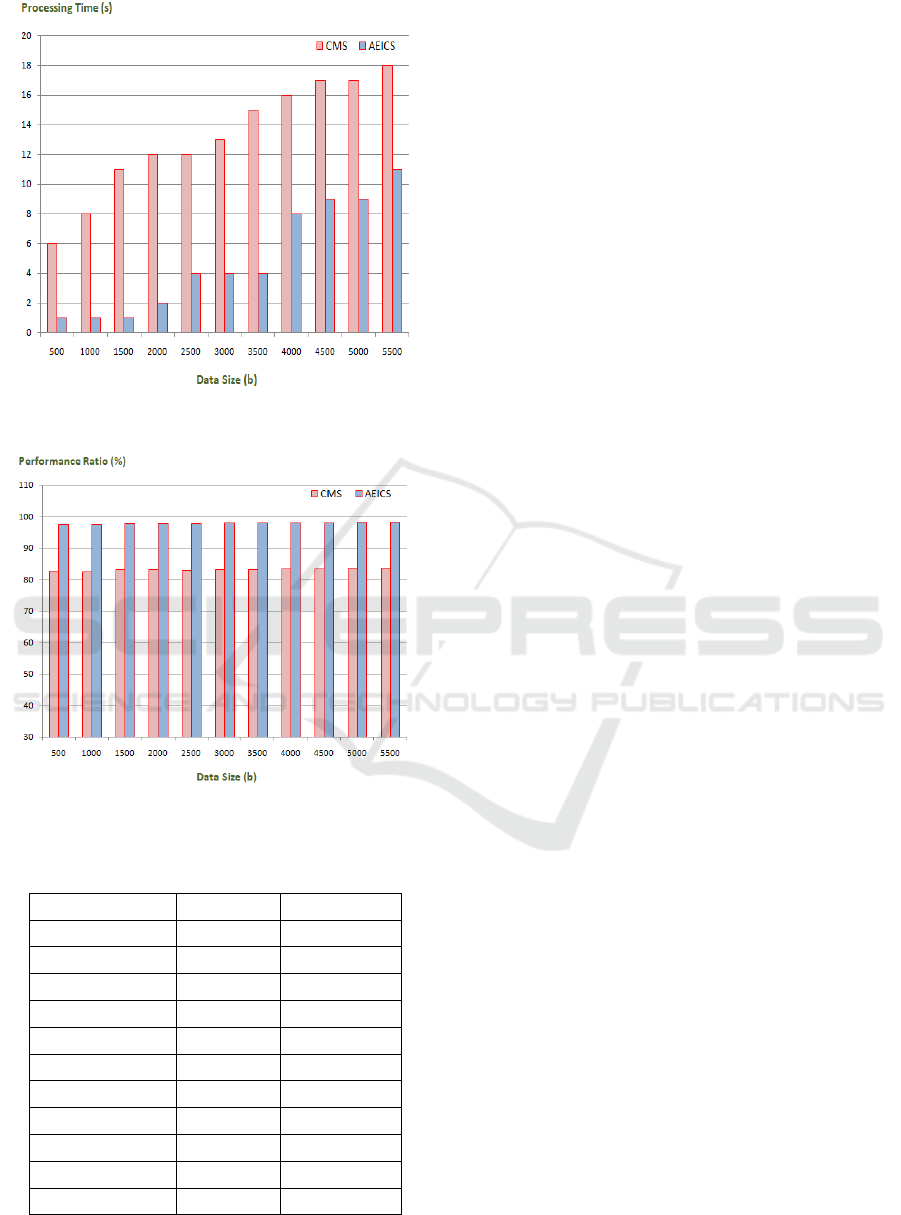
Figure 6: Processing Time Efficiency.
Figure 7: Performance Ratio Evaluation.
Table 5: Comparison of Performance Ratio Between Aeics and
Cms.
Data Size (bps) CMS (%) AEICS (%)
500 82.56 97.54
1000 82.47 97.47
1500 83.09 97.63
2000 83.14 97.69
2500 82.76 97.74
3000 83.07 97.80
3500 83.20 97.86
4000 83.29 97.92
4500 83.39 97.99
5000 83.49 98.05
5500 83.59 98.11
We have shown the performance ratio evaluation
result of the proposed scheme AEICS, in the above
figure, Figure 7. The ratio of performance is
measured by applying this scheme where it is cross-
validated with the conventional approach CMS. The
same is descriptively represented in Table 5 above.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
SCOPE
This research discusses advanced network topologies
with distributed controllers that secure their basis on
software-defines networking (SDN). Also, this
research has a significance in the field of Internet of
Things (IoT) and Ad-Hoc networks. We first
presented a much-needed new design called AEICS,
that is based on balance among a variety of software-
defined network controllers. Second, we proposed a
scalable design supporting multiple SDN domains
There can be various controllers per domain, and
networks can be associated with a domain whether or
not the domain has infrastructure. This is where edge
controllers come in: Controllers that specialize in
allowing data to pass between domains. If a failure
occurs, these edge controllers need to enter a new
distributed interaction to ensure each domain's
independence. We designed an architecture that
utilizes the grid of security concept at each controller,
to protect the full network from attacks. In future
work, we will explore more closely the characteristics
of the extended SDN-Domain, including the possible
applications of other security technologies in the SDN
domain, in addition to the exploration of other
security technologies. We would also like to do more
extensive testing at a bigger scale to fine-tune the
architecture in line with the enhanced AI based
architectural framework. Our team will build and
conduct terrestrial trials to this architecture.
In the forthcoming work, we will develop further
into the features of the expanded SDN domain,
analyze the potential applications of other security
methods within the SDN framework, and investigate
other security methods. In order to enhance our
system design, we plan to conduct additional testing
on a larger scale and leverage the AI based
architectural framework to a greater extent.
REFERENCES
Abhay Verma, et al., "Comparative Study of Cloud
Computing and Edge Computing: Three Level
Efficient Server Management Architecture Based on Cloud Edge Integration with Advanced Security Enhancements
777

Architecture Models and Security Challenges",
International Journal of Distributed and Cloud
Computing, 2021.
Ahmed M Alwakeel, "An Overview of Fog Computing and
Edge Computing Security and Privacy Issues", Sensors,
doi: 10.3390/s21248226, 2021.
Akhil Pandey, et al., "Security and Privacy Issues in Cloud,
Fog and Edge Computing", Proceedings of the
International Conference on Innovative Computing &
Communication, 2023.
Bhagwati Sharan, et al., "A Review on Edge-Computing:
Challenges in Security and Privacy", International
Conference on Applied Artificial Intelligence and
Computing, 2022.
Dulana Rupanetti, et al., "Combining Edge Computing-
Assisted Internet of Things Security with Artificial
Intelligence: Applications, Challenges, and
Opportunities", Appl. Sci., 2024.
Elahe Fazeldehkordi, et al., "A Survey of Security
Architectures for Edge Computing-Based IoT", IoT,
2022.
Francesco Cosimo Andriulo, et al., "Edge Computing and
Cloud Computing for Internet of Things: A Review",
Informatics, 2024.
M. Yasir Mehmood, et al., "Edge Computing for IoT-
Enabled Smart Grid", Security and Communication
Networks, 2021.
Muktar Yahuza, et al., "Systematic Review on Security and
Privacy Requirements in Edge Computing: State of the
Art and Future Research Opportunities", IEEE Access,
2020.
Odugu Rama Devi, et al., "The Future Development
Direction of Cloud-Associated Edge-Computing
Security in the Era of 5G as Edge Intelligence",
Scientific Programming, 2022.
P. Velmurugadass, et al., "The Cloud based Edge
Computing with IoT Infrastructure and Security",
International Conference on Computational
Performance Evaluation, 2021.
Shalin Parikh, et al., "Security and Privacy Issues in Cloud,
Fog and Edge Computing", Procedia Computer
Science, 2019.
Sina Ahmadi, "Security Implications of Edge Computing in
Cloud Networks", Journal of Computer and
Communications, 2024.
Vijay M. Rakhade, "SECURITY CHALLENGES IN
EDGE COMPUTING", International Journal of
Futuristic Innovation in Arts, Humanities and
Management, 2024.
Zhanyang Xu, et al., "Artificial Intelligence for Securing
IoT Services in Edge Computing: A Survey", Security
and Communication Networks, 2020.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
778
