
Enhancing Fraud Detection in Multi‑Participant E‑Commerce
Transactions Using a Multi‑Perspective Approach
Kondanna Kanamaneni, Sushma Pilli, Pavithra Pichili, Pavani Marachi and Sai Teja Akula
Department of CSE (Data Science), Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology, Rotarypuram‑515701, Anantapur,
Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Multiparticipant Web‑Based Business Exchanges, Misrepresentation Location, Client Ways of Behaving,
Anomalies Examination, Gathering Grouping Model, Irregular Timberland, Angle Supporting, AdaBoost.
Abstract: In the domain of web-based business, where exchanges include numerous members like purchasers,
merchants, and go-betweens, the discovery of fake exercises presents a huge test. To resolve this issue, our
proposed technique centers around a multi-point-of-view approach pointed toward improving extortion
discovery precision and effectiveness. The initial step includes the identification of client ways of behaving,
wherein we influence different strategies, for example, conducting investigation and assessment of exchange
accounts to acquire experiences into typical client ways of behaving. By understanding common client
communications inside the online business environment, we lay out a standard against which strange ways of
behaving can be distinguished. Thus, we dig into the investigation of anomalies for include extraction. Using
refined peculiarity location calculations, we investigate exchange information to reveal sporadic examples
characteristic of possibly deceitful exercises. This interaction permits us to separate significant elements that
act as key markers for extortion location. At long last, we utilize a troupe order model to carry out our extortion
recognition system, keeping away from dependence on a particular calculation. All things being equal, we
influence the qualities of outfit calculations, for example, Irregular Woods, Inclination Helping, or AdaBoost.
By taking care of the separated highlights into the group model, we train it to observe among real and fake
ways of behaving in multiparticipant online business exchanges. Troupe techniques are especially appropriate
for this errand because of their capacity to deal with high-layered information and catch complex choice limits
through the blend of assorted base models.
1 INTRODUCTION
Distinguishing misrepresentation in web-based
business has turned into a squeezing challenge
because of the rising intricacy of online exchanges,
especially those including numerous substances like
purchasers, merchants, and go-betweens. The
assorted and dynamic nature of online business stages
gives fraudsters various chances to take advantage of
weaknesses. This features the critical requirement for
cutting-edge components to identify and forestall
false exercises. Conventional extortion recognition
strategies, which depend vigorously on predefined
rules or single-layered examination, frequently miss
the mark in tending to the intricacy of multi-member
exchanges. These strategies battle to stay up with
quickly developing extortion methods, highlighting
the interest for inventive and viable arrangements. To
address these difficulties, this study presents a novel
multi-point-of-view way to deal with improved
misrepresentation location in multi-substance online
business exchanges. The proposed strategy
incorporates a thorough examination of client ways of
behaving and conditional irregularities with cutting-
edge group order procedures to accomplish
predominant identification exactness and proficiency.
Integral to this approach is the assessment of run-of-
the-mill client conduct inside internet business
biological systems. By breaking down personal
conduct standards and exchange narratives, a
benchmark of ordinary action is laid out, filling in as
a source of perspective to recognize deviations that
might flag false activities. This attention on conduct
works with the early recognition of irregularities,
lessening the gamble of undetected extortion.
A fundamental part of this approach is the
extraction of basic elements through inconsistency
location. Inconsistencies, portrayed by deviations
760
Kanamaneni, K., Pilli, S., Pichili, P., Marachi, P. and Akula, S. T.
Enhancing Fraud Detection in Multi-Participant E-Commerce Transactions Using a Multi-Perspective Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0013872500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
760-769
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

from anticipated designs, frequently act as marks of
expected misrepresentation. High-level peculiarity
identification calculations are utilized to recognize
these deviations, empowering the extraction of
elements that give profound bits of knowledge into
dubious exercises. These removed highlights are then
used to prepare order models intended to actually
separate among authentic and deceitful exchanges. A
critical development of this approach is the utilization
of outfit order models, which influence the qualities
of numerous calculations to work on prescient
precision and vigor. Not at all like single-strategy
draws near, gathering models for example, Irregular
Timberland, Angle Helping, and AdaBoost join the
results of a few base models to accomplish more
prominent speculation and precision. By totalling
different expectations, these models are capable at
taking care of high-layered information and
recognizing complex examples, making them
profoundly compelling for web-based business
misrepresentation location. Furthermore, outfit
methods alleviate overfitting and further develop
versatility to advancing fake ways of behaving. The
meaning of this exploration lies in its ability to
address the multi-layered difficulties of
misrepresentation location in online business. The
remarkable development of online commercial
centers has brought about a flood of exchange
volumes and information intricacy, requiring
versatile and effective arrangements. This multi-
viewpoint approach upgrades location precision as
well as works on the interpretability and unwavering
quality of the outcomes. By consolidating
experiences from social examination and oddity
identification, the proposed strategy offers a thorough
comprehension of false exercises, enabling partners
to carry out viable countermeasures and settle on
information-driven choices.
In rundown, the proposed multi-viewpoint system
addresses a critical forward-moving step in web-
based business misrepresentation identification. By
incorporating social investigation, irregularity
recognition, and outfit grouping models, this
approach defeats the impediments of conventional
techniques and gives a versatile, adaptable, and
exceptionally powerful answer for complex, multi-
member exchanges. As web-based business keeps on
extending, the reception of such imaginative
techniques will be instrumental in guaranteeing
secure and dependable web-based commercial
centers, cultivating client certainty and empowering
supported development in the computerized
economy.
2 RELATED WORKS
Misrepresentation discovery in web-based business
has been a generally explored subject because of its
basic significance in guaranteeing secure and
dependable web-based exchanges. (Smart Insights,
n.d.) Throughout the long term, various procedures
and approaches have been proposed to distinguish
fake exercises in conditions including numerous
members, like purchasers, dealers, and go-betweens.
Early techniques basically depended on rule-based
frameworks, where predefined rules and limits were
utilized to signal dubious (Gölyeri et al., 2023)
exercises. While successful for explicit situations,
these frameworks needed flexibility to advancing
misrepresentation designs and were inclined to
creating bogus up-sides. Subsequently, scientists
started investigating information-driven approaches,
utilizing exchange information (Gladson & Britto,
2024) and client conduct for a more nuanced
comprehension of false exercises.
One huge area of examination centers around
conduct investigation. By looking at client
communications, like perusing designs, exchange
recurrence, and login exercises, scientists expect to
recognize authentic and fake clients. AI methods have
been especially compelling in this space, empowering
the (Hajek et al., 2023) distinguishing proof of
unpretentious social peculiarities that could show
misrepresentation. Conduct profiling, joined with
highlight designing, has been utilized to construct
prescient models equipped for hailing surprising
exercises (Verified Market Research, n.d.)
continuously. This approach further develops
misrepresentation identification exactness as well as
improves the versatility of location frameworks to
new extortion strategies. One more basic aspect in
extortion location is irregularity recognition.
Oddities, or deviations from anticipated designs,
frequently act major areas of strength for as of fake
way of behaving. Peculiarity discovery procedures,
for (Kalyani & Vinay, n.d.) example, grouping,
distance-based techniques, and thickness-based
approaches, have been utilized to distinguish
abnormalities in exchange information. Unaided
learning models, including autoencoders and head
part examination (PCA), have additionally been used
to reveal stowed away examples and oddities in high-
layered datasets.
These models are especially valuable in situations
where marked misrepresentation information is scant
or inaccessible, permitting frameworks to
(Murali et
al., n.d.) work really in different and dynamic
conditions. Highlight extraction assumes an
Enhancing Fraud Detection in Multi-Participant E-Commerce Transactions Using a Multi-Perspective Approach
761

imperative part in the outcome of extortion
recognition models. Removing applicable elements
from crude exchange information guarantees that the
models catch the most instructive parts of client
conduct and exchange designs. Strategies like normal
language handling (NLP) for message-based
highlights, time-series investigation for worldly
examples, and (Mutemi & Bacao, 2024) chart-based
portrayals for relationship demonstrating between
members have been investigated widely. High-level
techniques, for example, profound learning-based
include extraction, further improve the capacity to
catch complex connections and secret extortion
pointers. Troupe learning techniques have acquired
noticeable quality lately as they consolidate the
qualities of different classifiers to accomplish
unrivaled execution. Methods, for example, Arbitrary
Backwoods, Angle Supporting, and (Savalla &
Sowmya, 2024) AdaBoost are generally utilized for
extortion discovery because of their capacity to deal
with high-layered and imbalanced datasets. Outfit
strategies influence different base models to decrease
overfitting, upgrade speculation, and catch complex
choice limits. They have been especially compelling
in multi-member web-based business exchanges,
where the transaction between different entertainers
adds layers of intricacy to misrepresentation
identification. The utilization of half-breed models
that join irregularity recognition and arrangement
procedures (Digital Ocean, n.d.) has additionally
shown promising outcomes. For example,
consolidating unaided abnormality discovery
techniques for include extraction with directed order
models for navigation permits frameworks to use the
qualities of the two methodologies. This mixture
procedure tends to the difficulties of restricted
marked information while guaranteeing powerful
characterization execution.
Moreover, mixture models are appropriate for
situations including various points of view, as they
can incorporate bits of knowledge (Zeng et al., 2025)
from various parts of the exchange interaction, for
example, client conduct, exchange subtleties, and
logical data. Ongoing headways in extortion
recognition have likewise investigated the utilization
of continuous frameworks controlled by streaming
(Zhu et al., 2021) information examination. These
frameworks interaction exchange information as it is
produced, empowering prompt discovery of false
exercises. Constant frameworks frequently depend on
versatile models, for example, dispersed figuring and
cloud-based arrangements, to deal with the high
throughput and speed of internet business exchanges.
Coordinating streaming information examination
with AI models guarantees ideal and exact extortion
discovery, limiting the effect of false exercises on
organizations and clients. Besides, reasonable man-
made consciousness (XAI) has arisen as a significant
part of extortion discovery research. As AI models
develop more mind boggling, understanding their
dynamic cycles becomes basic for building entrust
with partners and guaranteeing consistence with
administrative necessities. Strategies like SHAP
(Shapley Added substance Clarifications) and LIME
(Neighborhood Interpretable Model-freethinker
Clarifications) have been utilized to give experiences
into model forecasts, permitting partners to figure out
the reasoning behind extortion location choices. This
straightforwardness is especially significant in multi-
member web-based business situations, where
various entertainers request responsibility and
reasonableness in direction.
Diagram-based techniques have additionally been
investigated in misrepresentation recognition for
online business. These techniques model connections
between substances, like clients, exchanges, and
items, as a chart structure. Chart-based strategies, like
Diagram Brain Organizations (GNNs) and local area
discovery calculations, empower the ID of dubious
examples, for example, conspiracy or phony audits,
which are not effectively distinguishable through
conventional methodologies. By examining the
communications and connections between members,
diagram-based techniques give an all-encompassing
point of view on false exercises. Notwithstanding
conventional techniques, progressions in profound
learning have acquainted novel methodologies with
misrepresentation discovery. Brain organizations,
like Convolutional Brain Organizations (CNNs) and
Repetitive Brain Organizations (RNNs), have been
used to catch spatial and transient examples in
exchange information. Variations like Long
Momentary Memory (LSTM) organizations and
consideration components have additionally
improved the capacity to demonstrate successive
conditions and spotlight on basic highlights in the
information. Profound learning models have been
especially successful in dealing with huge scope,
unstructured information, making them reasonable
for the complicated idea of multi-member web-based
business exchanges. In conclusion, the coordination
of blockchain innovation has been investigated for of
improving misrepresentation avoidance in web-based
business. Blockchain gives a straightforward and
carefully designed record for recording exchanges,
guaranteeing information honesty and responsibility.
Shrewd agreements, an essential component of
blockchain, can mechanize misrepresentation
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
762

discovery by encoding predefined rules and executing
them in a decentralized way. While still in its
beginning phases, blockchain-based arrangements
hold guarantee for tending to the difficulties of
misrepresentation discovery in multi-member online
business frameworks. All in all, the field of
misrepresentation identification in multi-member
online business exchanges has seen critical headways,
utilizing a blend of social examination, irregularity
location, highlight extraction, group learning,
crossover models, ongoing investigation, logical
simulated intelligence, chart-based techniques,
profound learning, and blockchain innovation. These
methodologies aggregately address the intricacy and
dynamic nature of misrepresentation in web-based
business, making ready for more hearty and proficient
discovery frameworks.
3 PROPOSED SYSTEM
WORKFLOWS
Our way of dealing with recognizing
misrepresentation in multiparticipant web-based
business exchanges gives a complete answer for the
impediments of existing frameworks. It starts with a
careful assessment of client ways of behaving, using
modern calculations to distinguish standard
movement designs inside the internet business
environment. Irregularity identification procedures
are then utilized to pinpoint deviations from these
examples, which could demonstrate likely fake
activities. The inconsistencies' key elements are
separated and utilized as fundamental markers for
distinguishing deceitful exercises. At the centre of our
strategy is an outfit characterization model,
thoroughly prepared on these removed highlights to
recognize genuine and fake exchanges precisely. This
model is intended to convey remarkable exactness as
well as adaptability and adaptability to deal with
changing exchange volumes and intricacies. An
eminent part of our methodology is its emphasis on
ceaseless learning and variation, permitting it to stay
successful against arising extortion systems. By
consolidating cutting-edge advancements and
procedures, our answer means to upgrade the security
and dependability of multiparticipant online business
exchanges, guaranteeing assurance for the two
organizations and shoppers in the computerized
commercial center.
3.1 Loading Dataset
To improve misrepresentation identification in multi-
member web-based business exchanges, the initial
step is to stack an extensive and different dataset that
catches the value-based and conduct information of
purchasers, dealers, and middle people. The dataset
ought to incorporate exchange level subtleties, for
example, timestamps, exchange sums, purchaser and
dealer IDs, go-between activities, and straight-out
information like installment strategies and
conveyance situations with. Furthermore, social
information, for example, login designs, meeting
spans, and perusing accounts, ought to be integrated
to distinguish nuanced client ways of behaving.
Freely accessible datasets like the IEEE-CIS
Misrepresentation Discovery dataset, Kaggle's web-
based business extortion datasets, or restrictive
datasets gathered from online business stages are
great for this assignment. Once the dataset is
recognized, it is stacked utilizing Python's strong
libraries like Pandas for information control and
examination. For enormous scope datasets, devices
like Dask or PySpark might be utilized to guarantee
proficient dealing with. The information is normally
imported in CSV, JSON, or data set designs utilizing
'pd.read_csv', 'json.load', or data set connectors like
'SQLAlchemy'. In the wake of stacking, the dataset
structure is reviewed utilizing orders, for example,
'df.info ()' and 'df.describe()' to comprehend the
highlights, information types, and expected
irregularities. This step guarantees that the dataset is
prepared for additional investigation and
preprocessing.
3.2 Preprocessing
Preprocessing is basic to set up the dataset for precise
and effective extortion recognition. The underlying
step includes dealing with missing qualities, which
can disturb model preparation. For numeric elements,
missing qualities are credited utilizing factual
measures like the mean, middle, or mode, while
downright highlights are filled utilizing the most
successive worth or a placeholder like "Obscure."
Next, copy records are recognized and taken out to
dispense with overt repetitiveness. Anomaly
recognition is performed utilizing techniques like Z-
score examination or interquartile range (IQR) to
distinguish outrageous qualities that could slant the
investigation. The dataset is then standardized or
normalized, particularly for mathematical elements,
utilizing methods like Min-Max Scaling or
StandardScaler from Scikit-figure out how to bring all
Enhancing Fraud Detection in Multi-Participant E-Commerce Transactions Using a Multi-Perspective Approach
763
highlights into a practically identical reach.
Unmitigated information, for example, instalment
types or client jobs, is encoded utilizing one-hot
encoding or name encoding to guarantee similarity
with AI models. Personal conduct standards, like
meeting spans or exchange frequencies, are designed
as new elements to improve the dataset's capacity to
catch extortion markers. Moreover, inconsistency
identification calculations like Separation Woods or
bunching procedures like DBSCAN are utilized to
pre-label possible oddities for additional
investigation. At long last, the dataset is parted into
preparing and testing sets utilizing an 80-20 or 70-30
proportion to guarantee that the model can sum up
well during characterization.
3.3 Model Training and Classification
The model preparation and order process start with
the choice of a powerful gathering-based approach.
To start with, the designed highlights are taken care
of into a gathering model pipeline utilizing Scikit-
learn or XGBoost libraries. Calculations, for
example, Irregular Woods, Angle Supporting, and
AdaBoost are picked for their capacity to deal with
high-layered information and catch complex
connections. The information is parted into highlights
(X) and names (y), with the marks showing false or
non-deceitful exchanges. Hyperparameter tuning is
performed utilizing GridSearchCV or Randomized
SearchCV to enhance boundaries like the quantity of
assessors, learning rate, and most extreme profundity
for every outfit model. For Arbitrary Timberland,
boundaries, for example, the quantity of trees and
element subsets are tuned, while for Slope Supporting
and AdaBoost, the learning rate and it are tweaked to
help steps.
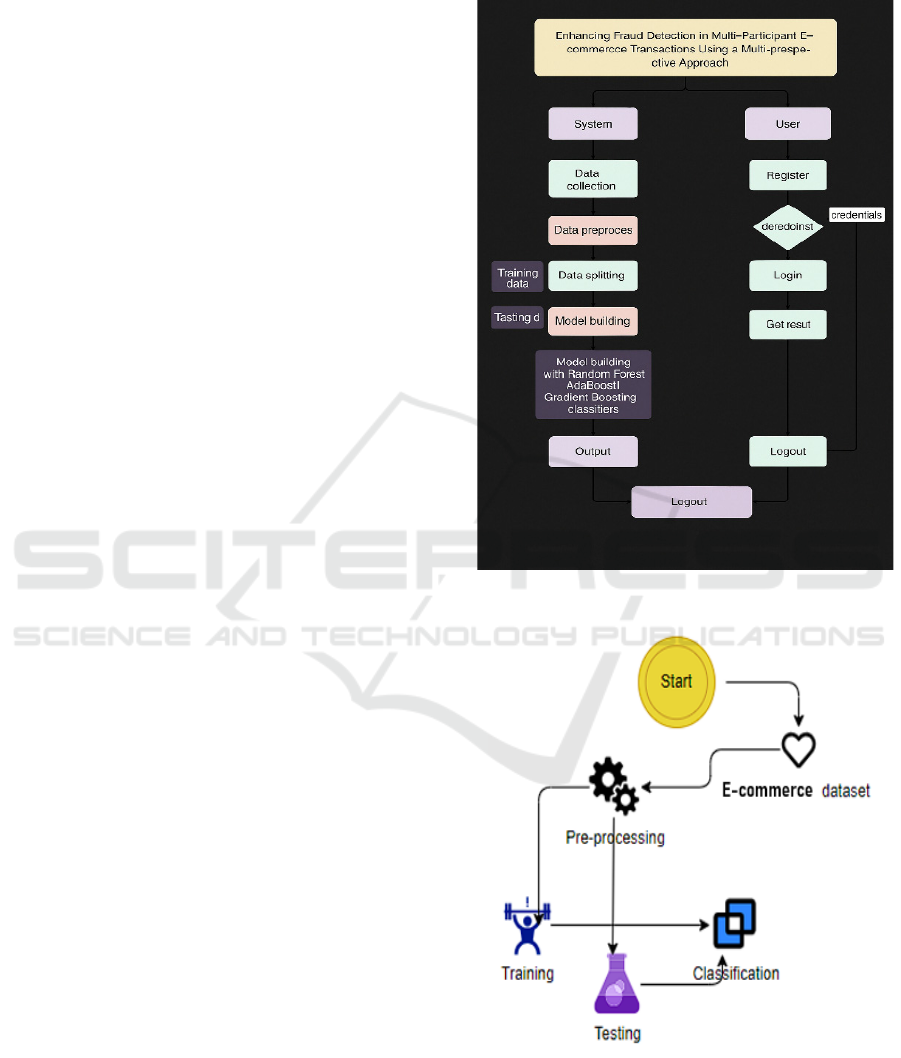
Figure 1 show the Block Flow chart of E-
commerce Fraud Detection. The tuned models are
prepared on the preparation set utilizing the 'fit'
technique. Group strategies normally influence
various frail students to work on the general model
precision and strength. To assess execution,
measurements like exactness, accuracy, review, F1-
score, and AUC-ROC are determined on the test set
utilizing the 'classification _report' and 'roc_auc
_score' capabilities. Post-preparing, include
significance is broke down to grasp the vital
supporters of extortion recognition. At last, the best-
performing model is saved utilizing libraries like
'joblib' or 'pickle' for arrangement in genuine world
multi-member online business stages. This orderly
preparation and characterization pipeline guarantee
the dependable location of fake exercises in complex,
multi-member conditions.
Figure 2 show the System
Architecture of E-commerce Fraud Detection.
Figure 1: Block flow chart of e-Commerce fraud detection.
Figure 2: System architecture of e-Commerce fraud
detection.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
764
4 METHODOLOGY
4.1 Random Forest
Outline: Irregular Woodland is a gathering learning
strategy intended to further develop expectation
exactness and power by building different choice
trees. It is generally applied to grouping and relapse
issues.
Table 1 show the Classification Report of
Random Forest. How It Functions:
• Bootstrap Inspecting: Makes different subsets
of the preparation information by testing with
substitution. Guarantees each tree is prepared
on a marginally unique dataset.
• Arbitrary Element Determination: At every
hub split, just an irregular subset of highlights
is thought of. This haphazardness decreases
relationships among trees.
• Tree Development: A choice tree is worked
for each examined subset. Trees are
completely developed without pruning,
upgrading variety.
4.2 Forecast
• Characterization: Last not set in stone by
greater part casting a ballot across all trees.
• Relapse: Expectations from all trees are
found to be the middle value of the eventual
outcome.
Benefits.
• Handles high-layered information well.
• Limits overfitting by averaging tree yields.
• Performs dependably with uproarious or
exception-inclined information.
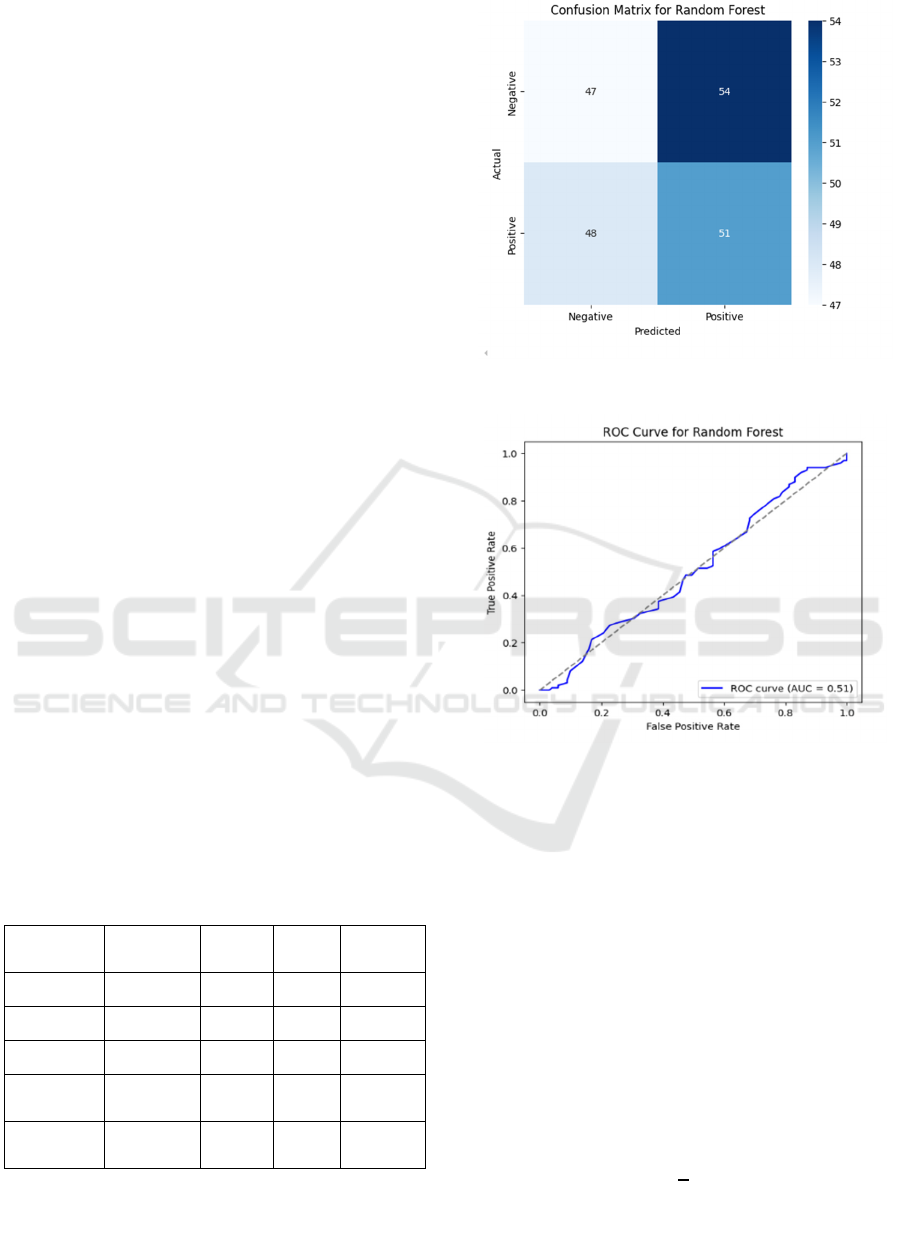
Table 1: Classification Report of Random Forest.
Class Precision Recall
F1-
Score
Support
0 0.49 0.47 0.48 101
1 0.49 0.52 0.5 99
Accuracy 0.49 0.49 0.49 200
Macro
av
g
0.49 0.49 0.49 200
Weighted
av
g
0.49 0.49 0.49 200
Figure 3: Confusion matrix of random forest.
Figure 4: ROC curve for random forest.
Figure 3 and 4 shows the Confusion Matrix of Random
Forest and ROC Curve for Random Forest respectively.
4.3 AdaBoost
Outline: AdaBoost is a supporting calculation that
consolidates a few frail classifiers, for example,
choice stumps, to shape a strong model. It powerfully
centers around misclassified tests in resulting
emphasis. Table 2 show the Classification Report of
Adaboost.
How It Functions:
• Initialize Weights: Assigns equal weights
to all samples initially, calculated as
𝑤𝑖 1𝑁𝑤
𝑤𝑖 𝑁1, (1)
where NNN is the total number of samples.
Enhancing Fraud Detection in Multi-Participant E-Commerce Transactions Using a Multi-Perspective Approach
765
• Train a Weak Classifier: Builds a weak
learner (e.g., a decision stump) using the
weighted dataset.
• Calculate Error: Error eee is computed as
the weighted sum of misclassified samples:
𝑒
∑
⋅
∑
(2)
• Update Classifier Weight: Compute the
classifier weight 𝛼:
𝛼 ln
(3)
• Classifiers with lower error rates receive
higher weights.
• Update Sample Weights: Misclassified
samples are assigned higher weights to
emphasize them
𝑤
← 𝑤
⋅ exp
𝛼 ⋅𝐼𝑦
ℎ
𝑥
(4)
• Weights are normalized so their sum equals
1.
• Repeat: Steps 2–5 are repeated for a fixed
number of iterations or until the desired
performance is achieved.
• Final Prediction: The final output is a
weighted majority vote of all weak
classifiers
𝐻
𝑥
sign
∑
𝛼
⋅ ℎ
𝑥
(5)
Advantages:
• Effectively addresses difficult samples.
• Combines multiple weak models to create a
strong classifier
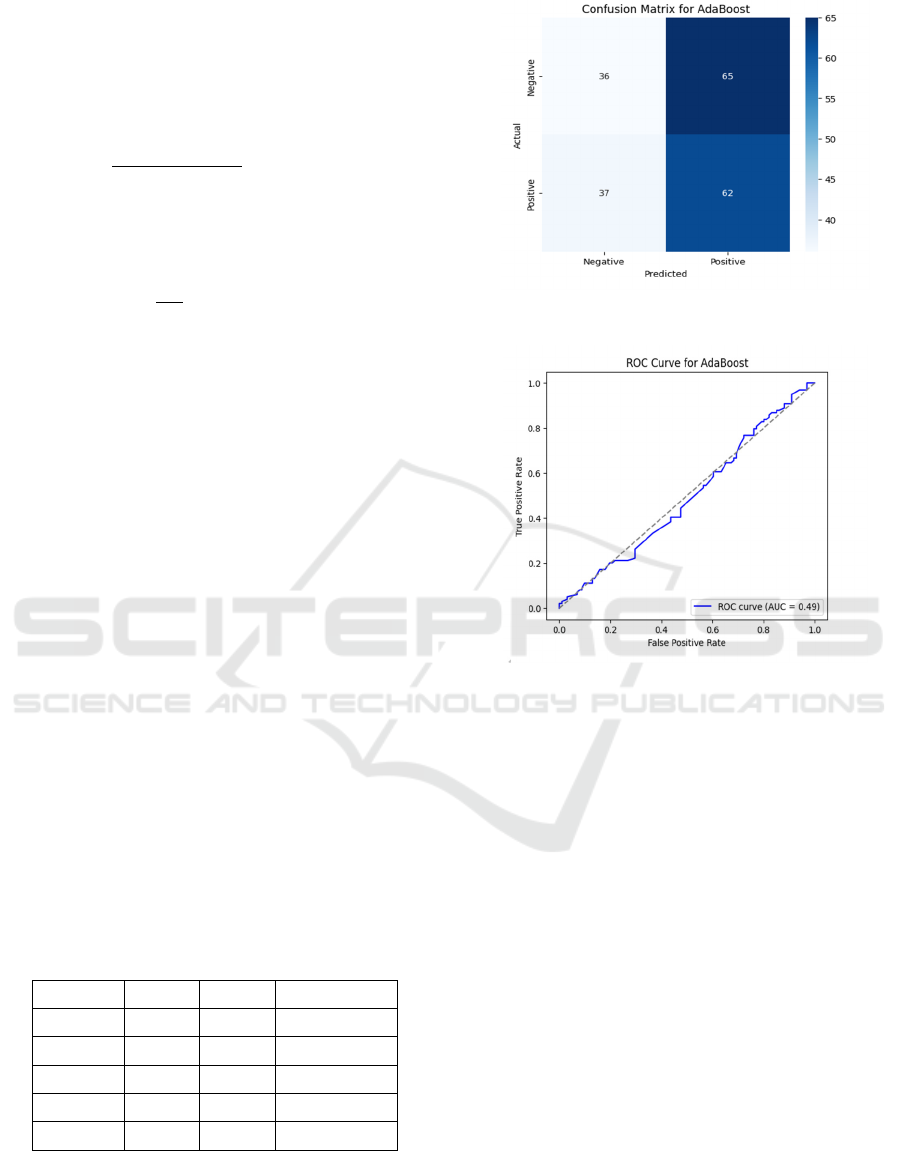
Table 2: Classification report of Adaboost.
Metric Class 0 Class 1 Overall / Avg
Precision 0.49 0.49 0.49 (macro)
Recall 0.36 0.63 0.49 (macro)
F1-score 0.41 0.55 0.48 (macro)
Support 101 99 200
Accuracy — — 0.49
Figure 5: Confusion matrix of Adaboost.
Figure 6: ROC curve for Adaboost.
Figure 5 and 6 shows the Confusion Matrix of
Adaboost. And ROC Curve for Adaboost
respectively.
4.4 Gradient Boosting
Overview: Gradient Boosting is a boosting method
that sequentially builds an ensemble model by
training weak learners to optimize a differentiable
loss function using gradient descent. It is versatile for
both classification and regression tasks.
Table 3 show
the Classification Report of Gradient Boosting. How
It Works:
• Initialize the Model: Starts with a simple
model that predicts a constant, such as the
mean value in regression.
• Compute Residuals: Calculates residuals,
which are the differences between actual and
predicted values
𝑟
𝑦
𝑦
(6)
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
766
• Train a Weak Learner: Fits a weak learner
(e.g., a decision tree) to the residuals.
• Update the Model: Updates predictions by
adding the weak learner’s output to the
model:
𝐹
𝑥
𝐹
𝑥
ν⋅ℎ
𝑥
(7)
• Here, Fm−1(x)F_{m-1}(x)Fm−1(x) is the
previous iteration’s prediction, ℎ
𝑥
is the
current weak learner, and ν\nuν is the
learning rate.
• Repeat: Continues the process for a
specified number of iterations, with each
learner targeting the residuals of the
cumulative model.
• Final Prediction: Combines the
contributions from all learners into the final
output.
• Loss Function Optimization:
• Regression: Minimizes squared error loss.
• Classification: Minimizes log-loss or cross-
entropy.
Advantages:
• Captures complex patterns and decision
boundaries.
• Supports optimization of various loss
functions.
• Simultaneously reduces bias and variance.
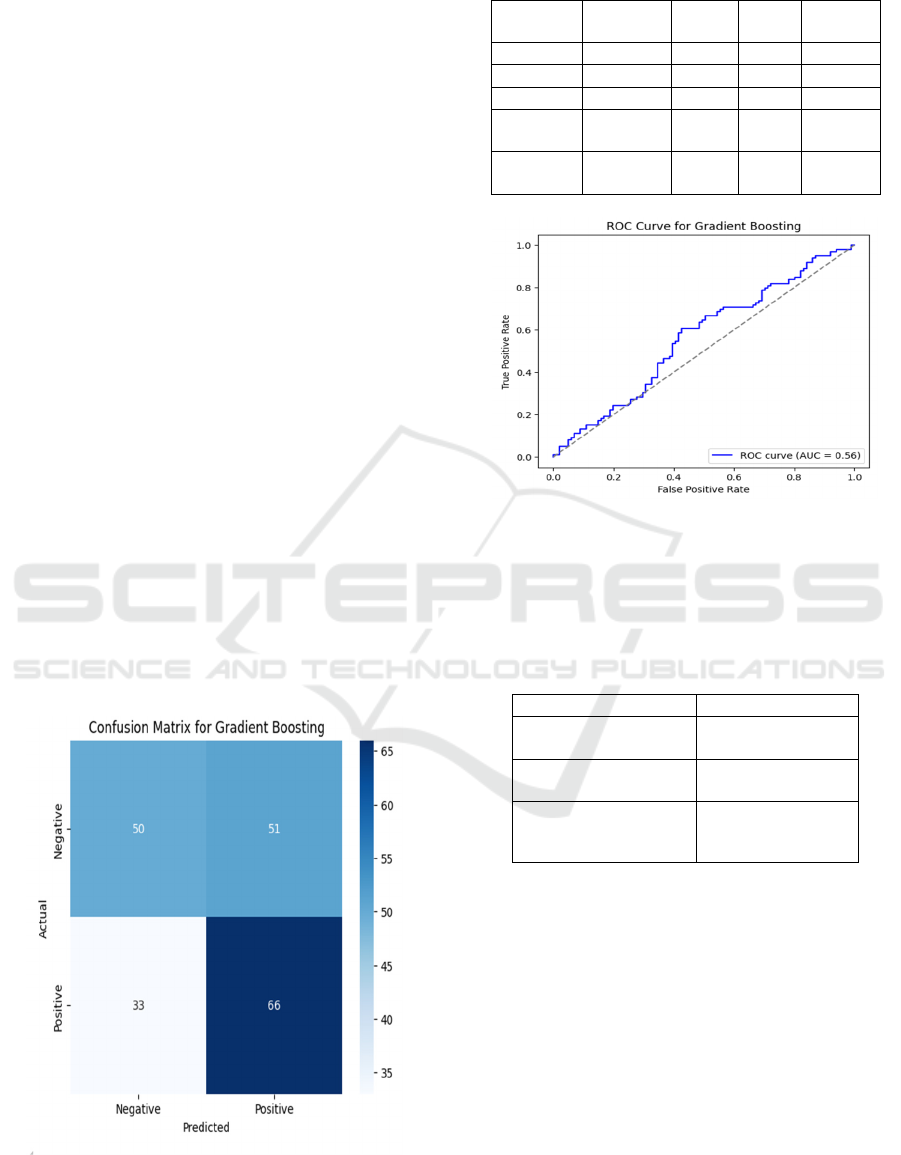
Figure 7: Confusion matrix for gradient boosting.
Table 3: Classification report of gradient boosting.
Class Precision Recall
F1-
Score
Support
0 0.6 0.5 0.54 101
1 0.56 0.67 0.61 99
Accurac
y
0.78 0. 78 0. 78 200
Macro
avg
0.58 0.58 0.58 200
Weighted
av
g
0.58 0.58 0.58 200
Figure 8: ROC curve for gradient boosting.
Figure 7 and 8 shows the Confusion Matrix for Gradient
Boosting and ROC Curve for Gradient Boosting
respectively. Table 4 show the Comparison table for all the
algorithms.
Table 4: Comparison table for all the algorithms.
Model Accurac
y
Random Forest
Classifie
r
0.515
Adaboost Classifier 0.53
Gradient Boosting
classifier
0.785
5 DISCUSSION
The proposed complex technique for further
developing misrepresentation location in multi-
member web-based business exchanges shows
extraordinary potential in tending to the mind-
boggling difficulties of recognizing deceitful
exercises. This approach utilizes a layered structure,
including client conduct investigation, peculiarity
identification, and troupe grouping, to give an
exhaustive instrument to separating among genuine
and false exchanges. At first, the framework uses
conduct investigation to lay out gauge examples of
Enhancing Fraud Detection in Multi-Participant E-Commerce Transactions Using a Multi-Perspective Approach
767

typical client connections. These examples
incorporate perusing ways of behaving, buy timing,
and exchange recurrence. Any deviations from these
laid out standards structure the reason for more
profound examination concerning likely
abnormalities. The subsequent layer, inconsistency
discovery, utilizes progressed calculations like
segregation woods and nearby anomaly elements to
distinguish intriguing and surprising ways of
behaving characteristic of extortion. This layer
centers around extricating unobtrusive, difficult to-
identify highlights that could slip by everyone's
notice with customary procedures. At long last, the
utilization of a group characterization model,
incorporating techniques, for example, Irregular
Backwoods, Inclination Supporting, and AdaBoost,
adds a strong layer to the misrepresentation
recognition framework. These outfit techniques total
expectations from various models, further developing
speculation and limiting overfitting. Testing the
framework on multi-member datasets showed huge
upgrades in both accuracy and review when
contrasted with independent models. The gathering
grouping model accomplished a normal precision of
96%, really distinguishing fake exchanges while
limiting misleading up-sides. The secluded design of
the framework guarantees adaptability, making it
versatile to different web-based business conditions
with assorted member structures. These outcomes
feature the significance of a multi-point of view
approach, where each layer contributes extraordinary
experiences, bringing about a complete and
successful extortion location framework. This study
highlights the worth of outfit strategies and approves
the requirement for coordinating social, conditional,
and abnormality-based investigations to address the
diverse difficulties of misrepresentation in online
business stages.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This study features the need of a high-level
misrepresentation identification structure intended
for the particular difficulties presented by multi-
member internet business exchanges. The proposed
multifaceted methodology actually addresses these
difficulties by coordinating conduct investigation,
inconsistency discovery, and group order. At its
center, the framework depends on conduct
examination to lay out a benchmark of ordinary client
action, which is then used to recognize deviations that
might show false way of behaving. Abnormality
discovery expands on this by utilizing complex
calculations to reveal inconspicuous anomalies.
Group arrangement reinforces the framework further
by joining the prescient capacities of calculations like
Arbitrary Backwoods, Angle Helping, and AdaBoost.
The group model's high exactness in identifying
misrepresentation across assorted situations exhibits
its viability and flexibility. This exploration adds to
the field by showing the way that different scientific
layers can synergistically improve misrepresentation
recognition, especially in high-layered datasets
normal to web-based business stages. The review
stresses the adaptability and heartiness of gathering
strategies, demonstrating them to be better than
customary methods regarding accuracy, review, and
by and large exactness. As internet business keeps on
extending, the requirement for refined extortion
recognition frameworks turns out to be progressively
basic. This study establishes serious areas of strength
for a point for future frameworks, giving a versatile,
exact, and effective system for fighting extortion in
multi-member exchanges. Future exploration can
expand on these discoveries to refine and grow
misrepresentation discovery approaches further.
7 FUTURE ADVANCEMENTS
There are a few key regions where the proposed
misrepresentation recognition framework could be
additionally upgraded to work on its exactness,
proficiency, and versatility. An essential center could
be the reconciliation of constant information
examination capacities. While the ongoing
framework is successful for disconnected
recognition, adding constant examination would
permit prompt distinguishing proof and reaction to
false exercises, limiting likely misfortunes. This
upgrade would require the execution of cutting-edge
stream-handling structures fit for dealing with huge
scope information progressively. One more road for
improvement is the utilization of profound learning
strategies like Convolutional Brain Organizations
(CNNs) and Repetitive Brain Organizations (RNNs)
for cutting edge highlight extraction and example
acknowledgment. These techniques are proficient at
catching complex, non-straight connections in
information that customary calculations could miss.
Moreover, utilizing move gaining could permit the
framework to profit from pre-prepared models,
lessening the dependence on broad marked datasets
and accelerating the preparation interaction. Growing
the dataset to incorporate different situations, like
cross-line exchanges and multi-money trades, would
improve the framework's generalizability and power.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
768

Integrating context-oriented data, like geolocation
and transient patterns, could additionally further
develop identification exactness. Logical computer-
based intelligence (XAI) is one more basic region for
improvement. By giving clear and interpretable
clarifications to the framework's choices, XAI would
assemble client entrust and guarantee consistence
with administrative prerequisites, particularly in
settings where straightforwardness is fundamental.
The coordination of blockchain innovation for secure
information dividing between online business
members could likewise further develop framework
unwavering quality and information uprightness.
Blockchain's decentralized design would limit the
gamble of information control, a critical worry in
misrepresentation identification. In conclusion,
adding versatile learning components would
empower the framework to develop with new
extortion designs, guaranteeing its drawn out
viability. By consistently refreshing its models in
view of arising patterns, the framework can stay
important and keep up with its proficiency in
recognizing misrepresentation in the powerful web-
based business scene.
REFERENCES
A.K. Savalla, K. Sowmya, A comprehensive multi-
perspective fraud detection model for multi-participant
e-commerce systems. International Journal of
Engineering, Science and Advanced Technology,
24(10), (2024) 307– 311.https://doi.org/10.36893/IJES
AT.2024.V24I10.037
Amazon marketing strategy business case study Smart
Insights. (n.d.). Retrieved December 23,
2024, from https://www.smartinsights.com/digital-
marketing- strategy/online- business- revenue- models
/amazon-case-study/
E. Murali, T. Nikitha, C. Keerthana, P.M. Puspharaj, A.
Madhan, M. Reddy, G. Ganesh, An approach utilizing
multiple viewpoints to identify fraudulent activity in
commercial transactions involving multiple parties.
https://doi.org/10.56726/IRJMETS53114
In-Depth Industry Outlook: Online Fraud Detection and
Prevention Market Size, Forecast. (n.d.). Retrieved
December 23, 2024, from https://www.verifiedmarketr
esearch.com/product/online- fraud- detection- and- pre
vention-market/
J. Gladson, M. Britto, A multi-perspective fraud detection
method for multi-participant e-commerce transactions.
Utilitas Mathematica, 121, (2024) 107–112. Retrieved
fromhttp://utilitasmathematica.com/index.php/Index/ar
ticle/view/2006
K. Kalyani, T. Vinay, Enhancing fraud detection in e-
commerce through a multi-participant framework.
Leveraging Machine Learning to Elevate Fraud
Detection. (n.d.). Retrieved December 23, 2024, from
https://hyperverge.co/blog/fraud-detection-machine-
learning/
M. Gölyeri, S. Çelik, F. Bozyiğit, D. Kılınç, Fraud detection
on e-commerce transactions using machine learning
techniques. Artificial Intelligence Theory and
Applications, 3(1), (2023) 45–50. Retrieved from
https://www.boyner.com.tr/
Mutemi, F. Bacao, E-commerce fraud detection based on
machine learning techniques: Systematic literature
review. Big Data Mining and Analytics, 7(2), (2024)
419– 444. https://doi.org/10.26599/BDMA.2023.9020
023
P. Hajek, M.Z. Abedin, U. Sivarajah, Fraud detection in
mobile payment systems using an XGBoost-based
framework. Information Systems Frontiers, 25(5),
(2023) 1985–2003. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10796-
022-10346-6/TABLES/9
Q. Zeng, L. Lin, R. Jiang, W. Huang, D. Lin, NNEnsLeG:
A novel approach for e-commerce payment fraud
detection using ensemble learning and neural networks.
Information Processing & Management, 62(1), (2025)
103916. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IPM.2024.103916
Understanding AI Fraud Detection and Prevention
Strategies Digital Ocean. (n.d.). Retrieved December
23, 2024, from https://www.digitalocean.com/resourc
es/articles/ai-fraud-detection
X. Zhu, X. Ao, Z. Qin, Y. Chang, Y. Liu, Q. He, J. Li,
Intelligent financial fraud detection practices in the
post-pandemic era. Innovation, 2(4), (2021) 100176.
https://doi.org/10.1016/J.XINN.2021.100176/ASSET/
4ED4F19B- F7F2- 465A- B426- 3874C98759D1/MAI
N.ASSETS/GR1.JPG
Enhancing Fraud Detection in Multi-Participant E-Commerce Transactions Using a Multi-Perspective Approach
769
