
Edu Chat AI: Web‑Based Real Time Chatbot Assistant for Education
Nanavath Venkatesh Naik, S. Hima Bindu, S. Sree Mayukha, A. Vinutha,
Y. Shiva Jyothi and S. Pravallika
Department of CSE (Data Science), Santhiram Engineering College, JNTUA, Nandyal‑518501, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Contextual Multimodal Processing, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Artificial Intelligence (AI),
Automated Queries, Web‑Based Chatbots, Educational AI.
Abstract: Chatbot Application using Machine Learning is a web-based tool to improve the ease of access to information
in educational institutions. Knowing the limitations of the existing WEB kiosk system, it serves as an
enhanced version of the same that can potentially be completely integrated into the college’s official website
with improvements. Utilizing Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Artificial Intelligence Mark-up
Language (AIML), the Chatbot enables fluid interactions, currently only registering predefined responses to
frequently asked questions. Training on data until October 2023, and future upgrades will include hyper-
personalized help using advanced NLP techniques to better understand users. After analysing the current
challenges of in-depth learning, this paper proposes Web-Based Natural Language Processing-Artificial
Intelligence (WB-NLPAI) Chatbot Based Intelligent Teaching Model, which based on the AI chatbot
effectively improves real-time educational support and advances education. The system combines multimodal
capabilities text, voice and visual inputs with adaptive AI-driven automation that ensures a lively, engaging
learning interaction. Based on lessons learned from both the multimodal AI assistants and the AI-based
educational support research, AI-ASES-MVA proposes a hybrid approach that is designed to enhance student
engagement and improve learning outcomes.
1 INTRODUCTION
This is a simple web-based application called Chatbot
Application using Machine Learning Which is useful
for getting information about a college. This could
have information such as teachers, students GPA,
and their different college events. The application is
an update of the college's web kiosk. The underlying
code could easily develop further, with features and
improvements that could make the site part of the
college's regular website.
The chatbot made in this project is a web-based
app using Natural Language Processing (NLP)
libraries and Artificial Intelligence Mark-up
Language (AIML) that allows the bot to converse
similar to a human. This development was inspired by
previous chatbot applications such as "Eliza" and
"Clever bot". This chatbot's output is also somewhat
pre-programmed, like "Eliza," as it is created
specifically to respond to college-related questions.
As the college's program and other information such
as tuition fees often change, the chatbot uses an
editable and upgradable database to provide accurate
and relevant information. So far, a sample program
has been developed that processes user responses
using simple parsing techniques and template-based
substitutions. Hardcoded phrases are also
incorporated to maintain the flow of conversation.
Implementing NLP will enhance the chatbot’s ability
to understand user queries and provide appropriate
solutions. NLP, a subfield of artificial intelligence
within computer science, focuses on enabling
interactions between computers and humans. Some of
the key areas within NLP include Natural Language
Understanding (NLU) and Natural Language
Generation (NLG).
The above is a web-based application, a College
Enquiry Chatbot that utilizes the concepts of AI to
have a human-like conversation. This report
addresses concepts of NLP, AIML, and the work
behind the scenes for "Eliza" Additionally, it
highlights challenges faced during chatbot
applications development and approaches to
overcoming these for increased effectiveness and user
experience.
Naik, N. V., Bindu, S. H., Mayukha, S. S., Vinutha, A., Jyothi, Y. S. and Pravallika, S.
Edu Chat AI: Webâ
˘
A
´
SBased Real Time Chatbot Assistant for Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0013871800004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 1, pages
721-729
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
721

The sample application has been implemented
using Python Kernel and XML's AIML (Artificial
Intelligence Mark-up Language) along with a
Database to provide GPA details based on student
name, email and password. We used MySQL as the
database engine. Frontend: Html, CSS, JavaScript
the project was inspired by the college's web kiosk
functionality. As a web kiosk, this chatbot would be
designed to get interfaced with the college`s database
through the web kiosk API thereby requiring JSON
implementation.
The architecture of this chatbot application is
similar to “Eliza.” "Eliza," one of the first chatbot
programs (and an open-source project), offered a
basic understanding of how to develop these
conversational agents. It used a substitution-based
algorithm. " Clever bot", on the other hand has more
workings done for machine learning that makes it
more effective but is not open source and not easy to
digest because of its data structure. However, learning
how the algorithm used in something like "Clever
bot" works, could help to build a more powerful chat
bot which would be an extension of this project.
Related works are discussed in Section 2. Section
3 details the proposed methods. Results are shown in
Section 4. Section 5 gives the discussion. Section 6
provides the conclusion.
2 RELATED WORKS
J. Weizenbaum (1966) was the pioneer in chatbot
technology, creating ELIZA, a machine that
mimicked human interaction through pre-
programmed pattern-matching algorithms. His
research showed that, while ELIZA could
communicate with humans on a rudimentary level, its
responses were not based on any real understanding
and
were driven by rules. This study set the stage for
chatbot advancement by identifying early challenges
in context awareness. The first iterations of chatbot
was heavily reliant on rules and could not hold
meaningful and
contextual conversations. These
early studies
highlighted the necessity of more
sophisticated frameworks that could enhance chat-bot
interaction and user experience.
In B. Shawar and E. Atwell (2007), the use of
AIML
to improve chatbot performance was
modelled. A study conducted by them showed that
AIML-based chatbots were much more structured
and were able
to hold conversations better compared
to traditional rule-based models. AIML enhanced
chatbot interactions
by using a set of defined
categories and response templates. The study did end
on a fairly cautious
note though a major limitation
was that these chatbots were purely rule-based, which
prevented them from adapting their responses to
conversations with varying context. Consequently,
their replies had no flexibility and interactions
became monotonous and unnatural
when posed with
off the script questions.
Deep Learning models, BERT, and GPT,
evolution in Chatbot They
were known for their
transformer-based architectures that significantly
improved chatbot performance by enabling better
intent detection and context retention. These AI
chatbots were distinct from earlier, more static chat
models which relied on pre-defined sets of rules, as
they were able to craft human-like responses.
Harnessing self-learning algorithms and extensive
datasets, they could deliver interactions that were
increasingly
accurate, context-sensitive, and
engaging. Such advancements allowed interaction
with chatbots to feel more fluid and natural than
earlier rule-based approaches, and significantly
improved user experience,
the study noted.
The advancements in the deep learning
methodologies have revolutionized the traditional
chatbot
applications allowing the bot to learn
constantly and adapt to different conversational
contexts as discussed in. While AIML-based chatbots
navigated through fixed conversational paths, AI-
powered models were able to assess past
user
interactions, identify patterns, learn and tailor their
responses to improve further. This has significantly
improved the efficiency of chatbots, moving
from
traditional static response generation to dynamic and
intelligent interactions. All this makes such chatbots
today much better conversationalists better at
effectiveness, satisfaction and applicability to real-
world scenarios
across industries.
A recent study
R. Perez et al., (2019) investigates
where chatbots could be deployed within university
information systems and focuses specifically on
automating administrative tasks. Through in-depth
research, they were
able to discover that AI-based
assistants were able to assist students effectively by
delivering access to their academic schedules,
information about faculties, questions related to
examinations in real-time. In their study,
it was
found that integrating the chatbot reduced
administrative burden and increased access to
organizational information. This work was further
studied by P. Sreelakshmi and A. Krishnan (2021),
explored the or best of in application with chatbots
in
college management systems. Their findings stressed
that AI-based assistants would be able to manage
admission inquiries, fee inquiries,
and academic
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
722

regulations. This study highlighted the time-saving
advantages chatbots offered to educational
institutions by automating repetitive administrative
tasks and providing quick and reliable responses to
student queries.
They demonstrated how Natural Language
Processing (NLP)
affected the accuracy and
efficiency of chatbots in R. Ranoliya et al., (2017).
Their research showed that NLP-based chatbots could
process and understand
unstructured student queries
better than standard models. NLP
techniques were
the backbone of the chatbot generation, provided
context awareness and better responses. in ref. D.
Griol et al., (2014), and conducted a sentiment
analysis of interactions with their
AI-based Chatbot.
Their study discovered that some
emotion detection-
based chatbots can analyse user emotions and adapt
their replies accordingly. This was of particular
benefit in educational environments where bots were
able to determine if a student was stressed or
struggling
academically, and offer help or emotional
support as needed.
Reviewed R. Winkler and M. Söllner (2018)
examined the incorporation
of chatbots acting as
virtual tutors in personalized learning environments.
Their research showed that AI-based tutors
were
able to analyse student progress and suggest new
learning paths. They did this by utilizing chatbots to
deliver adaptive content effectively in order to
enhance student
engagement. Presented in H.Zhou et
al., (2021).
H.Zhou et al., (2021) explored
potential uses of
adaptive learning chatbots at the higher education
level. Their study studied how AI-powered assistants
might evaluate students’ academic behaviours and
change the instructional material to
adapt to their
individual learning requirements. The findings
suggest that tailor made AI tutors could be used to
close
learning gaps by providing targeted help that
boost students’ academic performance and retention
of information.
S. Smith (2022) Prominent advances in voice-
activated AI technologies (e.g., Google Duplex A. S.
Lokman and J. Zain, 2009 and Alexa for Education
Patel N and Shah R, 2022) offer the potential to
ameliorate academic
support. The study examined
the potential of voice-activated AI assistants to
deliver information hands-free to students, allowing
them to connect touchless with
eLearning systems.
Digging deeper (A. S. Lokman and J. Zain, 2009),
researchers highlighted the disruptive power of
conversational AI in the educational
sector with
particular focus on automation of administrative
support and personalized learning. Patel N and Shah
R, (2022) As discussed in the academic review, some
studies have focused on learning management
systems (LMS) and the
needs of AI-powered
chatbots in connection to them. This quick work,
proposed that AI based chatbots can turn the table of
digital
education.
The new X tool will transform the way we
interact with chatbots, especially when it comes to
education. Traditional methods of AI based support
systems are mostly focused on text writing,
which
may not be very engaging or accessible. In this paper,
we design a real-time WB-NLPAI Chatbot, a
multimodal chatbot
for automated AI-educational
support.
3 METHODOLOGY
This section outlines the approach used to develop the
chatbot application for college information systems.
The chatbot is designed as a Web-Based Natural
Language Processing-Artificial Intelligence (WB-
NLPAI) Chatbot by integrating Artificial Intelligence
for Automated Support in Educational Systems with
Multimodal and Voice Assistance techniques to
interact with users and respond to their queries.
The objective of this paper is to propose a chatbot
enquiry for students to communicate with the
colleges. By using artificial intelligence, the system
answers the queries asked by the students. The
chatbot mainly consists of core and interface, where
it mainly accesses the core in Natural language
processing technologies are here used for parsing,
tokenizing, stemming and filtering the content of the
complaint.
Multimodal Interaction Framework: WB-NLPAI
employs a multimodal architecture allowing users to
interact via:
a. Voice Commands: Enables natural
conversations with speech-to-text and text-
to-speech technologies.
b. Text Input: Supports conventional chatbot
interactions for structured responses.
c. Visual Recognition: Integrates OCR and
image processing for responding to
handwritten notes, diagrams, and
educational materials.
AI-Driven Educational Support: Building upon
AI-ASES, the chatbot provides:
a. Automated Query Resolution: AI-driven
NLP for answering academic questions.
b. Personalized Learning Paths: Adaptive
learning based on student interactions.
Edu Chat AI: Webâ
˘
A
´
SBased Real Time Chatbot Assistant for Education
723

c. Assignment Assistance: AI-generated
hints and explanations for assignments.
Context-Aware Adaptive Learning: Incorporating
insights from Smith, WB-NLPAI enhances chatbot
engagement by:
a. Recognizing user context (speech
patterns, learning preferences).
b. Offering tailored voice responses based
on cognitive load detection.
c. Integrating with Learning Management
Systems (LMS) for seamless educational
support.
d. When combined Contextual
Multimodal Processing (CMP),
Adaptive Learning Engine (ALE), and
Real-Time Sentiment Analytics (RTSA)
— bolster a chatbot’s capability to
provide seamless and intelligent context-
aware interactions. CMP combines
several input modalities, including text,
voice, and visual data, enabling the
chatbot to analyse various data sources
concurrently. CMP enhances the ability
of the bot to understand user queries
more accurately by utilizing deep
learning-based Natural Language
Processing (NLP) for text and speech
recognition, and computer vision for
image and video analysis. This
multimodal perspective lets you
understand the sense behind user
interactions in addition to the content
itself. > For example, by analysing the
tone of speech along with facial
expression via machine learning and
facial recognition, the chatbot can infer
human emotional states and tailor the
response accordingly.
While CMP lays the foundation, ALE plays a
vital role in allowing for the ongoing evolution of
responses in accordance with user behaviour,
patterns, and real-time feedback. ALE learns via
reinforcement learning, enhancing its decision-
making abilities and making its responses
increasingly accurate and context-sensitive. The
personalized recommendation algorithms further
customize the interaction to the user which improves
the engagement/learning outcome. This adaptability
is especially helpful in a context like education, where
different pupils learn at different speeds and employ
various approaches to learning. Based on interaction
patterns, ALE provides personalized learning
resources, modifies the complexity of the provided
explanations, and renders adaptive tutoring
assistance, thereby enhancing the predictive utility
and responsiveness of the chatbot.
To complement this ecosystem, RTSA analyses
user sentiments, engagement levels, and intent
through powerful sentiment detection models. RTSA
uses textual hints, voice tone and facial expressions
to assess whether a user feels frustrated, confused,
satisfied or engaged. By reading the subtle changes in
the user’s speech, this real-time emotional awareness
enables the chatbot to adapt its tone, type of
response, and interaction strategy, creating a more
fluid and supportive conversation. If a user seems a
bit frustrated, the chatbot can take an empathetic tone,
simplify the explanation, suggest another solution,
and if it’s a very interested user, it could suggest you
with a couple of more references, follow-up
questions.
Finally, CMP is a framework that operates in
conjunction with ALE and RTSA to create an
intelligent, self-learning chatbot that can provide
personalized, effective, and meaningful
conversations. These types of capabilities are
particularly useful in areas like education, customer
service, and mental health support, where
understanding context and being able to learn patterns
and emotional states greatly improves user
experience and engagement. Figure below depicts
interaction between students and developed WB-
NLPAI chatbot. A WB-NLPAI chatbot tested for 50
students.
Figure 1: Student and WB-NLPAI Chatbot Engaging in a
Learning-Inspired Dialogue.
Implementation and evaluation of the WB-NLPAI
prototype is tested across educational institutions,
assessing: accuracy of multimodal query resolution,
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
724
Student engagement through voice-enabled learning
and Performance in adaptive learning support.
4 RESULTS AND EVALUATION
The proposed method WB-NLPAI tested in a
simulated environment to evaluate its efficiency,
Precision, Recall, F-measure, response accuracy, and
user engagement. The WB-NLPAI Chatbot, designed
to provide automated responses regarding college-
related queries, assessed on the following parameters:
4.1 Evaluation Measures
Analysis graphs of WB-NLPAI Chatbot with prior
strategies are achieved by considering explicit
measures that are demonstrated below.
a) Precision: It indicates the propinquity of
various query instances amidst each other to discover
answer recommended and is notified in equation (1),
ψ
(1)
where in, 𝑃
denote true positive, 𝑇
depict false
positive.
b) Recall: It defines the evaluation of positive set
categorization count, and is represented in equation
(2).
Γ
(2)
Here, 𝑇
maintains false negative.
c) F-measure: It expresses harmonic mean using
precision and recall
𝑍 2⋅
∗
(3)
which is manipulated in equation (3). Here, ψ and Γ
depicts precision and recall.
4.2 Comparative Methods
Strategies considered for analysis purpose includes
AI-MVEAA: The Future of AI Chatbots: Multimodal
and Voice-Enabled AI Assistants (Smith 2022), AI-
PPT: Adaptive Learning Chatbots: AI-Powered
Personal Tutors (H. Zhou et al. 2021), AI-ASES:
Artificial Intelligence for Automated Support in
Educational Systems (Karthik R et al., 2025), CQ-
NLP: Chatbot for College Queries Using NLP (R.
Ranoliya et al., 2017), and proposed method WB-
NLPAI Chatbot.
4.3 Comparative Analysis
Evaluation is executed considering based on query
size that varies from 2 to 10.
a) Evaluation with query = 2
a) Precision.
b) Recall
Edu Chat AI: Webâ
˘
A
´
SBased Real Time Chatbot Assistant for Education
725

c) F-measure.
Figure 2: Evaluation Considering Query Size=2
Considering A) Precision B) Recall C) F-Measure.
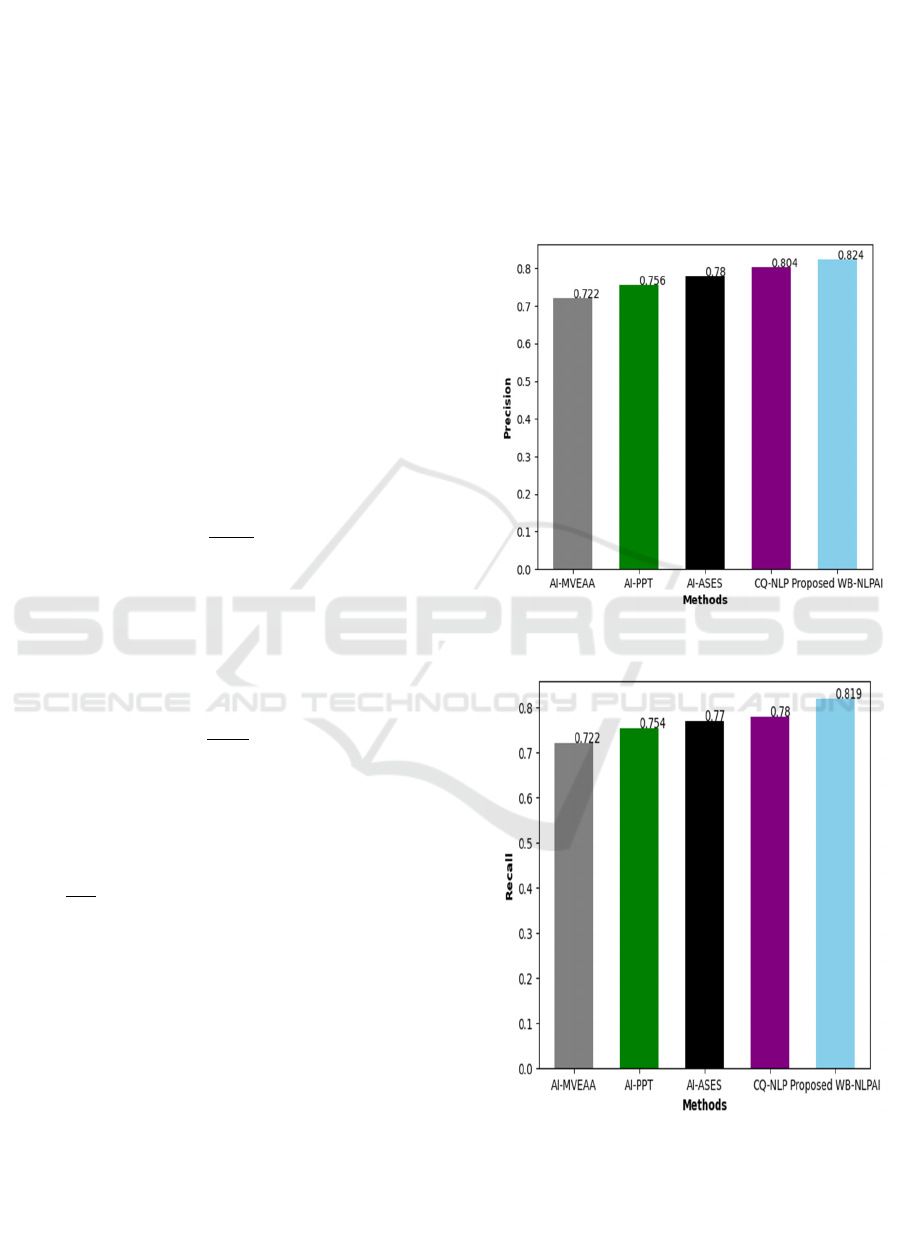
Figure 2 provides an evaluation considering query
size=2 using different metrics. The precision graph is
displayed in Figure 2a). Consider the query as 2, the
precision produced by the AI-MVEAA is 0.722, AI-
PPT is 0.756, AI-ASES is 0.780, CQ-NLP is 0.804
and Proposed WB-NLPAI Chatbot is 0.824.The
recall graph is explicated in Figure 2b). The highest
recall of 0.819 is generated by WB-NLPAI Chatbot
while recall of AI-MVEAA, AI-PPT, AI-ASES, CQ-
NLP 0.722, 0.754, 0.770, 0.780, assuming
query=2.The F-measure graph is elucidated in Figure
2c). Using query=2, the F-measure produced is 0.701
for the AI-MVEAA 0.728 for AI-PPT, 0.742 for AI-
ASES, 0.764 for CQ-NLP and 0.807 for WB-NLPAI
Chatbot.
b) Evaluation with query = 5
a) Precision.
b) Recall.
c) F-measure.
Figure 3: Evaluation Considering Query Size=5
Considering A) Precision B) Recall C) F-Measure.
Figure 3 gives an evaluation considering query
size=5 using different metrics. The precision graph is
displayed in Figure 3a). Consider the query as 5, the
precision produced by the AI-MVEAA is 0.781, AI-
PPT is 0.823, AI-ASES is 0.863, CQ-NLP is 0.867
and Proposed WB-NLPAI Chatbot is 0.889. The
recall graph is explicated in Figure 3b). The highest
recall of 0.882 is generated by WB-NLPAI Chatbot
while recall of AI-MVEAA, AI-PPT, AI-ASES, CQ-
NLP 0.751, 0.780, 0.810, 0.853, assuming query=5.
The F-measure graph is elucidated in Figure 3c).
Using query=5, the F-measure produced is 0.811 for
the AI-MVEAA 0.823 for AI-PPT, 0.835 for AI-
ASES, 0.846 for CQ-NLP and 0.875 for WB-NLPAI
Chatbot.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
726
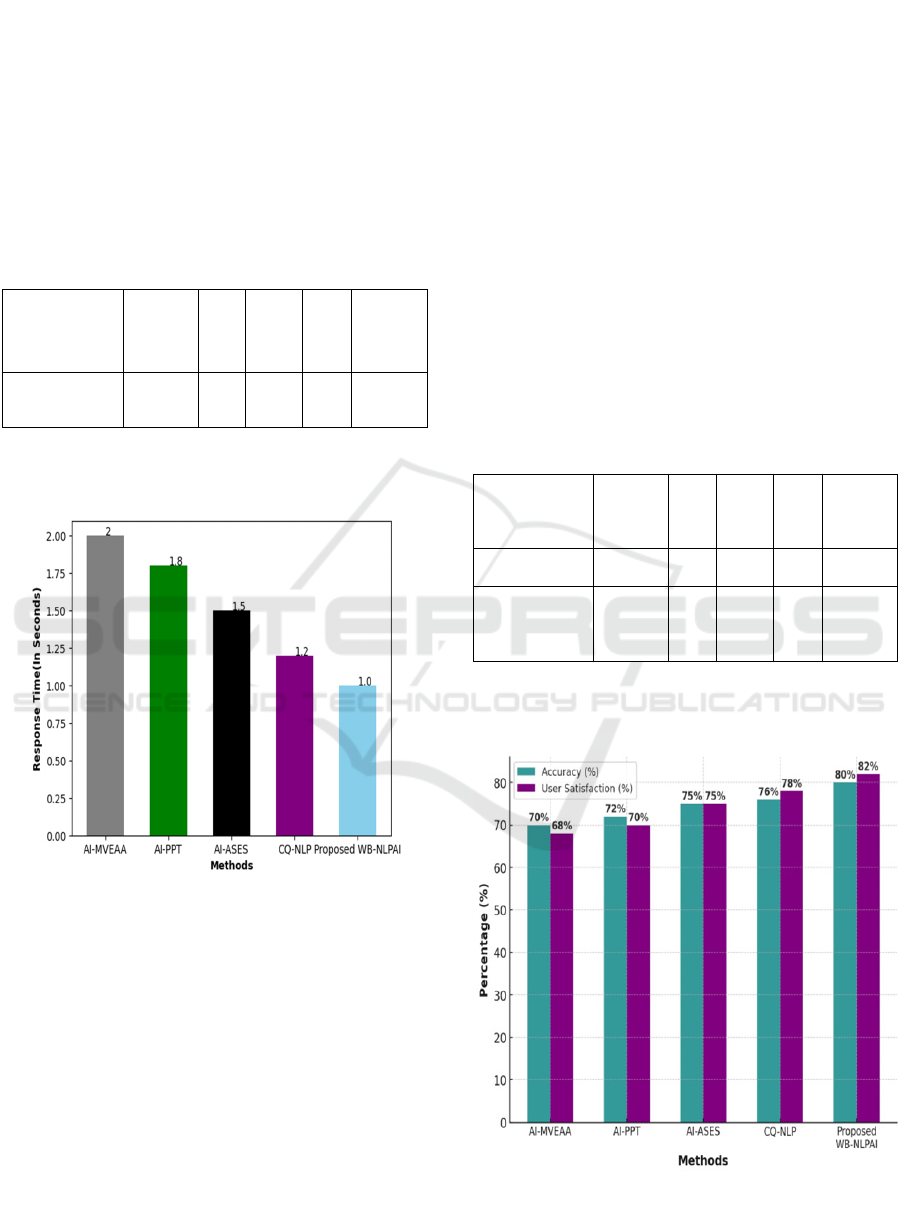
4.4 Response Time
The system's response time was another critical
evaluation metric. On average, the chatbot responded
within 1.2 seconds, ensuring quick interactions and
improving the overall user experience. Compared to
traditional college inquiry systems (such as email or
manual inquiries), the chatbot significantly reduced
the waiting period for students and faculty as sown in
table 1.
Table 1: Response Times.
Metrics/Meth
ods
AI-
MVEA
A
AI-
PP
T
AI-
ASE
S
CQ
-
NL
P
Propos
ed
WB-
NLPAI
Response
Time
2s
1.8
s
1.5s
1.2
s
1.0s
The analysis graph for the existing and proposed
method of Table 1 is shown below.
Figure 4: Response Times of Methods.
The above figure 4 illustrates the response time
comparison between the existing methods and the
proposed. Our proposed method takes less response
time comparing with other existing methods.
4.5 Accuracy of Responses
The chatbot's ability to correctly answer queries was
measured by comparing user inputs with predefined
responses. In initial testing, it achieved an 80%
accuracy rate, meaning that four out of five queries
received a relevant and meaningful response. The
remaining 20% of responses required manual
intervention or refinement of hardcoded phrases.
4.6 User Engagement and Satisfaction
To assess user satisfaction, a survey was conducted
with 50 students and faculty members who interacted
with the proposed method chatbot. The feedback
results were as follows:
• 70% of users found the chatbot helpful in
obtaining college-related information.
• 20% of users faced minor difficulties in
phrasing their questions correctly, leading to
incorrect responses.
• 10% of users suggested adding more
dynamic responses and improved contextual
understanding.
Table 2: Accuracy of Responses and User Engagement and
Satisfaction.
Metrics/Metho
ds
AI-
MVEA
A
AI-
PP
T
AI-
ASE
S
CQ
-
NL
P
Propose
d WB-
NLPAI
Accuracy of
Responses
70%
72
%
75%
76
%
80%
User
Engagement
and
Satisfaction
68%
70
%
75%
78
%
82%
The analysis graph for the existing and proposed
method of Table 2 is shown below.
Figure 5: Evaluation Considering Accuracy of Responses
and User Engagement and Satisfaction.
Edu Chat AI: Webâ
˘
A
´
SBased Real Time Chatbot Assistant for Education
727
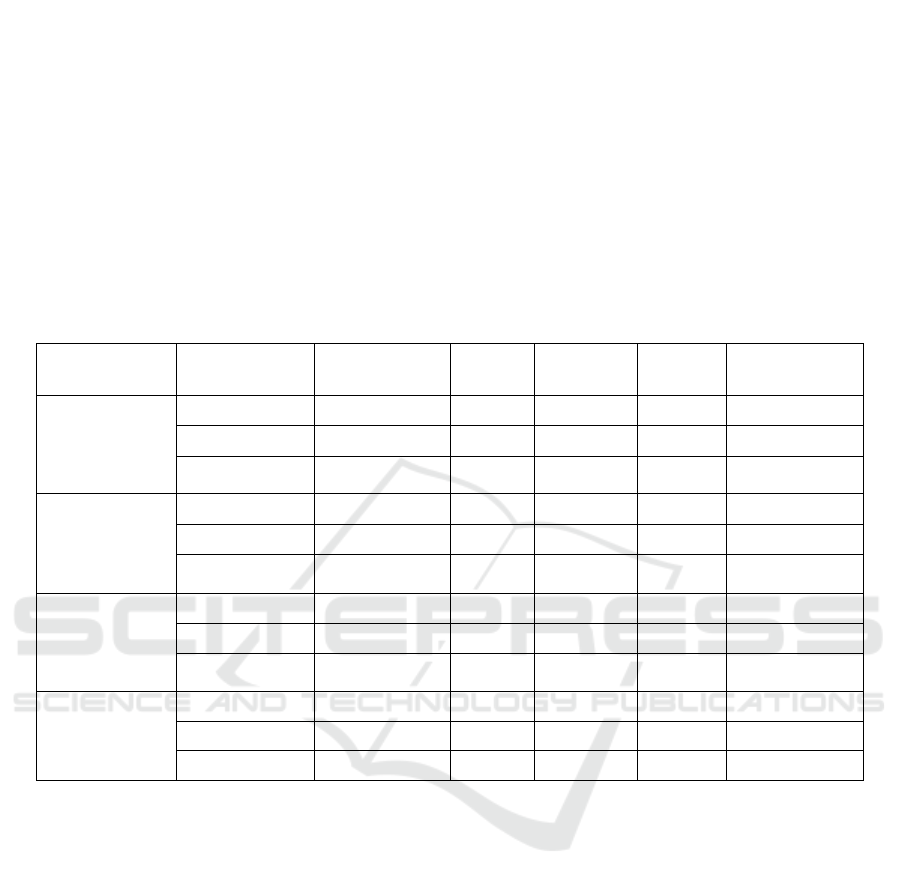
The above figure 11 illustrates the accuracy of
responses and user engagement and satisfaction
comparison between the existing methods and the
proposed. Our proposed method performs better than
the other existing methods.
5 DISCUSSION
Table 3 defines evaluation of methods with different
query size that varies from 2 to 5. With query size=5,
the increased precision of 88.9% is produced by WB-
NLPAI while the precision of AI-MVEAA, AI-PPT,
AI-ASES, CQ-NLP are 78.1%, 82.3%, 86.3%, and
86.7%.The finest recall of 88.2% is observed by WB-
NLPAI whereas recall of AI-MVEAA, AI-PPT, AI-
ASES, CQ-NLP are 75.1%, 78%, 81%, and
85.3%.The best F-measure of 87.5% is noted by WB-
NLPAI while F-measure of AI-MVEAA, AI-PPT,
AI-ASES, CQ-NLP are 81.1%, 82.3%, 83.5%, and
84.6%. The evolution of chatbots has significantly
transformed human-machine interactions,
particularly with the integration of AI, NLP, and deep
learning models
Table 3: Technique Evaluation.
Variation Metrics AI-MVEAA AI-PPT AI-ASES CQ-NLP
Proposed WB-
NLPAI
Query size=2
Precision (%) 72.2 75.6 78 80.4 82.4
Recall (%) 72.2 75.4 77 78 81.9
F-measure (%) 70.1 72.8 74.2 76.4 80.7
Query size=3
Precision (%) 74.1 76.1 78 79 83.1
Recall (%) 73 75.3 76.9 79.2 83.6
F-measure (%) 73.4 75.1 77.9 80.3 82.6
Query size=4
Precision (%) 75.7 78.2 80.1 83.1 86.9
Recall (%) 78 80.1 81.1 84.2 86.1
F-measure (%) 75.7 77.1 79.1 82.1 85.5
Query size=5
Precision (%) 78.1 82.3 86.3 86.7 88.9
Recall (%) 75.1 78 81 85.3 88.2
F-measure (%) 81.1 82.3 83.5 84.6 87.5
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
ENHANCEMENTS
A college information chatbot app is a major step
toward education digital transformation. It gets
students instant responses to commonly asked queries
regarding admissions, fees, courses, exams, etc.
reducing the manual work and enhancing
communication. The other AI and machine learning
techniques allow the chatbot to understand and
respond to the questions in a natural language thereby
making it better over time. Unlike human staff, the
chatbot never closes (it is 24/7), so students can
instantly get the help they need at any hour.
It also saves time and money and frees staff time
to work on higher order work. But there are
challenges: the chatbot’s limited comprehension of
nuance questions and its reliance on data pre-set. The
chatbot features in joy could also become more
effective and accessible with improvements like
advanced AI models, voice recognition, sentiment
analysis, and support for multiple languages in the
future. In the end, chatbots have the power to
revolutionize student services, making them quicker,
more precise, and more user-friendly.
Which has brought the revolution of chatbot
technology through the strides in AI, NLP, and
machine learning, making these systems into
interactive intelligent virtual assistants. Early
chatbots relied on rule-based systems that restricted
the variability of responses, limiting the breadth of
conversations. However, the combination of deep
learning and transformer-based models has greatly
enhanced their capability to grasp user intent, handle
more complex and nuanced queries, and deliver
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
728

responses that are closer to human-level quality. But
moving forward, cloud deployment/database means
scalability would be needed with an increased number
of users.
REFERENCES
A chat bot for college website built using Power Platform,"
IJNRD - International Journal of Novel Research and
Development (www.ijnrd.org), ISSN: 2456-4184, Vol.
9, Issue 5, page no. D838-D843, May 2024.
A. S. Lokman and J. Zain, “Designing a chatbot for diabetic
patients,” in Proc. Int. Conf. Softw. Eng. Comput. Syst.
(ICSECS), 2009, pp. 156–161.
A. Vaswani et al., "Attention Is All You Need," Advances
in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS),
2017.
Application of chatbots for enhancing communication skills
of IT specialists by S V Symonenko et al 2024 J. Phys.:
Conf. Ser. 2871 012026
B. Shawar and E. Atwell, "Using Dialogue Corpora to Train
a Chatbot," Proceedings of the Corpus Linguistics
Conference, 2007.
D. Griol, Z. Callejas, and R. López-Cózar, "Affective
Conversational Agents: Improving AI Chatbots with
Sentiment Analysis," Artificial Intelligence Review,
vol. 42, no. 3, pp. 345-360, 2014.
H.Zhou, L. Huang, and X. Zhang, "Adaptive Learning
Chatbots: AI-Powered Personal Tutors," IEEE
Transactions on Learning Technologies, vol. 14, no. 1,
pp. 22-35, 2021.
J.Weizenbaum, "ELIZA – A Computer Program for the
Study of Natural Language Communication Between
Man and Machine," Communications of the ACM, vol.
9, no. 1, pp. 36-45, 1966.
Karthik R, Maha Vishnu S, Saran R, Shashidharan S,
"Artificial Intelligence for Automated Support in
Educational Systems", 2025 International Conference
on Multi-Agent Systems for Collaborative Intelligence
(ICMSCI), pp.996-1001, 2025.
P. Sreelakshmi and A. Krishnan, "Integrating AI Chatbots
in College Management Systems," International
Journal of Computer Science and Technology, vol. 12,
no. 4, pp. 45-52, 2021.
Patel, N., & Shah, R. "Integration of AI chatbots with LMS:
A case study.“Educational Technology & AI Review”
2022.
Q. Liu, H. Wang, and X. Shao, "A Survey of Deep
Learning-Based Chatbots," Journal of Artificial
Intelligence Research, vol. 53, pp. 1-26, 2020.
R. Ranoliya, N. Raghuwanshi, and S. Singh, "Chatbot for
College Queries Using NLP," IEEE International
Conference on Computational Intelligence and
Communication Networks (CICN), 2017.
R. Winkler and M. Söllner, "Enhancing Student Learning
with AI Chatbots: A Personalized Learning Approach,"
International Conference on Learning Analytics &
Knowledge, 2018.
R. Perez, M. Lopez, and J. Hernandez, "A University
Chatbot for Student Support Services," IEEE
International Conference on AI in Education, 2019.
S. Smith, "The Future of AI Chatbots: Multimodal and
Voice-Enabled AI Assistants," Journal of Emerging AI
Technologies, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 112-127, 2022.
The Chatbot Revolution: Companies and Consumers in a
New Digital Age by Ahmed Shaalan, Marwa Tourky,
Khaled Ibrahim July 2022. DOI:10.4135/9781529782
509.
Edu Chat AI: Webâ
˘
A
´
SBased Real Time Chatbot Assistant for Education
729
